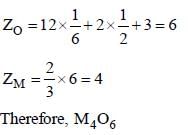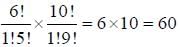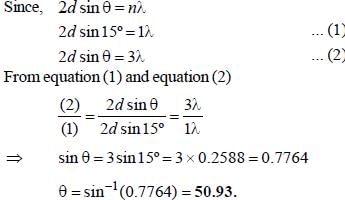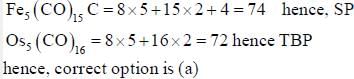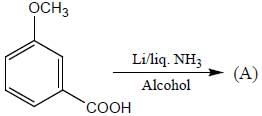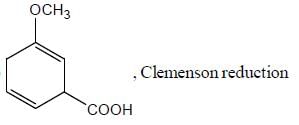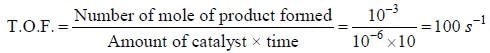All Exams >
GATE Chemistry >
GATE Chemistry Mock Test Series >
All Questions
All questions of Topic wise Tests for GATE Chemistry Exam
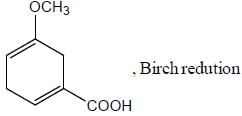
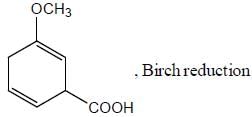
Pickout the incorrect statement- a)
- b)
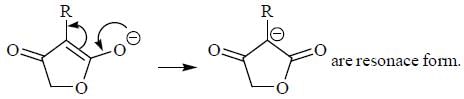
- c)
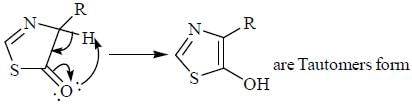
- d)
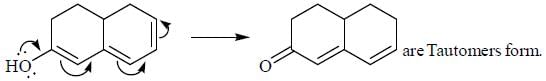
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pickout the incorrect statement
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Situ Verma answered |
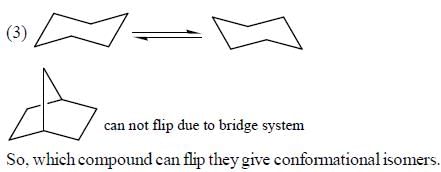
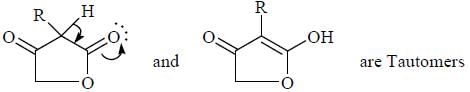
Tautomers represent 2 keto-enol forms in equilibrium.
but here enol form leads to aromatic compound which is highly stable ,so here in option c the the keto form once converted to enol form cant be reverted back.So it is a reaction not 2 isomers
Which of the following expression are CORRECT ?- a)Chemisorption occur at all temperatures.
- b)The magnitude of chemisorption increases with rise in temperature.
- c)The activation energy of desorption is very low in case ofphysisoiption.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following expression are CORRECT ?
a)
Chemisorption occur at all temperatures.
b)
The magnitude of chemisorption increases with rise in temperature.
c)
The activation energy of desorption is very low in case ofphysisoiption.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Sonakshi Singh answered |
D
Calculate the adsorption of a dye on activated carbon at 25°C, where k = 0.025, n = 0.5 and C = 0.04.
Based on the Freundlich isotherm.
Correct answer is between '0.040,0.041'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the adsorption of a dye on activated carbon at 25°C, where k = 0.025, n = 0.5 and C = 0.04.
Based on the Freundlich isotherm.
Based on the Freundlich isotherm.

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
Given data
n = 0.5
Kd = 0.025
C = 0.04
Substitute the values in the corresponding equation
q = Kd C(1/n)
q = (0.025) (0.04)(1/0.5)
q = 0.040.
n = 0.5
Kd = 0.025
C = 0.04
Substitute the values in the corresponding equation
q = Kd C(1/n)
q = (0.025) (0.04)(1/0.5)
q = 0.040.
Number of molecule that show fluxional behavior among. CH4,CF4,PCI5,PF5,BrF5,SF6,XeO3 is _________
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of molecule that show fluxional behavior among. CH4,CF4,PCI5,PF5,BrF5,SF6,XeO3 is _________

|
Saikat Ghoshal answered |
Fluxional behavior among molecules
Fluxional behavior refers to the rapid interchange of positions of two or more atoms or groups in a molecule. It is a type of isomerism that occurs due to the low energy barrier between two or more isomeric forms of the molecule. The following is the number of molecules that show fluxional behavior among CH4, CF4, PCI5, PF5, BrF5, SF6, XeO3.
CH4
CH4 is a tetrahedral molecule with four hydrogen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom. It has no possibility of fluxional behavior because all the hydrogen atoms are identical, and there are no other atoms or groups that can interchange their positions.
CF4
CF4 is a tetrahedral molecule with four fluorine atoms bonded to a central carbon atom. It also has no possibility of fluxional behavior because all the fluorine atoms are identical, and there are no other atoms or groups that can interchange their positions.
PCI5
PCI5 is a trigonal bipyramidal molecule with five chlorine atoms bonded to a central phosphorus atom. It shows fluxional behavior because the axial and equatorial positions interchange rapidly due to the low energy barrier. This process is known as pseudorotation.
PF5
PF5 is also a trigonal bipyramidal molecule with five fluorine atoms bonded to a central phosphorus atom. It shows fluxional behavior for the same reason as PCI5.
BrF5
BrF5 is a square pyramidal molecule with five fluorine atoms and one bromine atom bonded to a central bromine atom. It shows fluxional behavior because the axial and equatorial positions interchange rapidly due to the low energy barrier.
SF6
SF6 is an octahedral molecule with six fluorine atoms bonded to a central sulfur atom. It does not show fluxional behavior because all the fluorine atoms are identical, and there are no other atoms or groups that can interchange their positions.
XeO3
XeO3 is a trigonal planar molecule with three oxygen atoms bonded to a central xenon atom. It shows fluxional behavior because the oxygen atoms interchange their positions rapidly due to the low energy barrier. This process is known as Berry pseudorotation.
Conclusion
Out of the given molecules, three molecules show fluxional behavior, namely PCI5, PF5, and XeO3. This behavior is due to the low energy barrier between the isomeric forms of these molecules, which allows them to interchange their positions rapidly.
Fluxional behavior refers to the rapid interchange of positions of two or more atoms or groups in a molecule. It is a type of isomerism that occurs due to the low energy barrier between two or more isomeric forms of the molecule. The following is the number of molecules that show fluxional behavior among CH4, CF4, PCI5, PF5, BrF5, SF6, XeO3.
CH4
CH4 is a tetrahedral molecule with four hydrogen atoms bonded to a central carbon atom. It has no possibility of fluxional behavior because all the hydrogen atoms are identical, and there are no other atoms or groups that can interchange their positions.
CF4
CF4 is a tetrahedral molecule with four fluorine atoms bonded to a central carbon atom. It also has no possibility of fluxional behavior because all the fluorine atoms are identical, and there are no other atoms or groups that can interchange their positions.
PCI5
PCI5 is a trigonal bipyramidal molecule with five chlorine atoms bonded to a central phosphorus atom. It shows fluxional behavior because the axial and equatorial positions interchange rapidly due to the low energy barrier. This process is known as pseudorotation.
PF5
PF5 is also a trigonal bipyramidal molecule with five fluorine atoms bonded to a central phosphorus atom. It shows fluxional behavior for the same reason as PCI5.
BrF5
BrF5 is a square pyramidal molecule with five fluorine atoms and one bromine atom bonded to a central bromine atom. It shows fluxional behavior because the axial and equatorial positions interchange rapidly due to the low energy barrier.
SF6
SF6 is an octahedral molecule with six fluorine atoms bonded to a central sulfur atom. It does not show fluxional behavior because all the fluorine atoms are identical, and there are no other atoms or groups that can interchange their positions.
XeO3
XeO3 is a trigonal planar molecule with three oxygen atoms bonded to a central xenon atom. It shows fluxional behavior because the oxygen atoms interchange their positions rapidly due to the low energy barrier. This process is known as Berry pseudorotation.
Conclusion
Out of the given molecules, three molecules show fluxional behavior, namely PCI5, PF5, and XeO3. This behavior is due to the low energy barrier between the isomeric forms of these molecules, which allows them to interchange their positions rapidly.
From the below compounds I, II, III and IV chiral compound is- a)
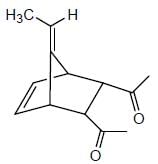
- b)
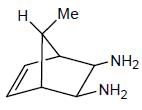
- c)
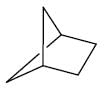
- d)
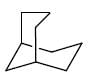
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From the below compounds I, II, III and IV chiral compound is
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Shail Ghoshal answered |
Due to plane of symmetry present in B, C and D. So, they are chiral.
The pH of 10-7 HCI solution is - a)7
- b)6.8
- c)6.4
- d)7.4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The pH of 10-7 HCI solution is
a)
7
b)
6.8
c)
6.4
d)
7.4

|
Sinjini Nair answered |
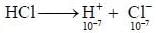
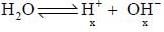
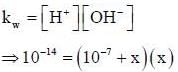
On solving the equation, x = 0.62 x 10-7M
{Negative value of x will be neglected}
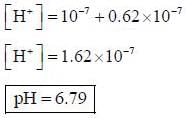
The volume of gases NH3, CO2 and H2 gas adsorbed by 1 gm charcoal at 300 K lie in the order ?- a)CO2 > NH3 > H2
- b)NH3 > CO2 > H2
- c)NH3 > H2 > CO2
- d)H2 > CO2> NH3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The volume of gases NH3, CO2 and H2 gas adsorbed by 1 gm charcoal at 300 K lie in the order ?
a)
CO2 > NH3 > H2
b)
NH3 > CO2 > H2
c)
NH3 > H2 > CO2
d)
H2 > CO2> NH3

|
Soumya Sengupta answered |
More readily soluble and easily liquifiable gases such as NH3/HC1/C12 and SO2, are adsorbed more than H2/N2.
i.e.. adsorption
proportional to intemiolecular interaction,
proportional to molecular mass,
proportional to ease of liquidation,
proportional to 'a’.
proportional to ciitical temperature (Te.
Therefore, order of adsoiption of gases:
SO2 > NH3 > HC1 > CO2, > CH4 > CO > N2 > H2
i.e.. adsorption
proportional to intemiolecular interaction,
proportional to molecular mass,
proportional to ease of liquidation,
proportional to 'a’.
proportional to ciitical temperature (Te.
Therefore, order of adsoiption of gases:
SO2 > NH3 > HC1 > CO2, > CH4 > CO > N2 > H2
The substances which act as iron transport and iron storage respectively are:- a)Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
- b)Hemocyanin and Hemerythrin
- c)Transferrin and Ferritin
- d)Carbonic anhydrase and Carboxy peptidase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The substances which act as iron transport and iron storage respectively are:
a)
Hemoglobin and Myoglobin
b)
Hemocyanin and Hemerythrin
c)
Transferrin and Ferritin
d)
Carbonic anhydrase and Carboxy peptidase

|
Athul Chaudhary answered |
Transferrin and ferrtin are responsible for Fe transport and storage respectively.
For which set of ΔH• and ΔS- will the reaction be spontaneous only at high temperature- a)ΔH = 70 kJ, ΔS = 30J/K
- b)ΔH = 70 kJ, ΔS = -30 J/K
- c)ΔH = - 7 0 kJ, ΔS = - 3 0 J/K
- d)ΔH = 0 kJ. ΔS = -30 J/K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For which set of ΔH• and ΔS- will the reaction be spontaneous only at high temperature
a)
ΔH = 70 kJ, ΔS = 30J/K
b)
ΔH = 70 kJ, ΔS = -30 J/K
c)
ΔH = - 7 0 kJ, ΔS = - 3 0 J/K
d)
ΔH = 0 kJ. ΔS = -30 J/K

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
At high temperature, ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Only, ΔH = +ve , ΔS = +ve, T = high
Reaction spontaneous, ΔG = -ve
Only, ΔH = +ve , ΔS = +ve, T = high
Reaction spontaneous, ΔG = -ve
The HOMO in 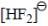 molecule
molecule - a)σ-bonding
- b)σ* - bonding
- c)Non-bonding
- d)π-bonding
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The HOMO in 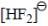 molecule
molecule
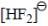 molecule
molecule a)
σ-bonding
b)
σ* - bonding
c)
Non-bonding
d)
π-bonding

|
Shivani Mehta answered |
Molecular orbital diagram of 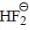
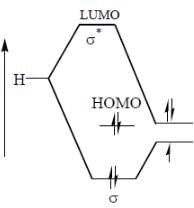
Hence both are gerade.
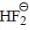

Hence both are gerade.
Which of the following test is used for the detection of aldoses?
- a)Seliwanoff's test
- b)Fehling’s test
- c)Bendict’s test
- d)Bromine water test
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following test is used for the detection of aldoses?
a)
Seliwanoff's test
b)
Fehling’s test
c)
Bendict’s test
d)
Bromine water test
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Seliwanoff's test is a chemical test that distinguishes between aldose and ketose sugars. A mixture of concentrated HCl and resorcinol of 3ml is added to the sugar. Then the solution is boiled for a little time. If it is a ketose sugar like fructose and sucrose is the solution turns cherry red.
The number of spinels having equal number of A2+ and B3+ ions in octahedral and tetrahedral voids are________
NiCr2O4, FeCr2O4, CO3O4, CrFe2O4, AlMg2O4, NiGa2O4
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of spinels having equal number of A2+ and B3+ ions in octahedral and tetrahedral voids are________
NiCr2O4, FeCr2O4, CO3O4, CrFe2O4, AlMg2O4, NiGa2O4
NiCr2O4, FeCr2O4, CO3O4, CrFe2O4, AlMg2O4, NiGa2O4

|
Arnab Pillai answered |
The inverse spinel has the equal number of A2+ and b3+ ions in octahedral voids.
In [Ni(PNP)X]2 [NiX4] complex, the total coordination number of metal ion is______________
(X is a uninegative monodentate ligand)
Correct answer is '12'. Can you explain this answer?
In [Ni(PNP)X]2 [NiX4] complex, the total coordination number of metal ion is______________
(X is a uninegative monodentate ligand)
(X is a uninegative monodentate ligand)

|
Athul Chaudhary answered |
The compound [Ni(PNP)X]2 [NiX4] where PNP (tridentate) =
(C6H5)2PCH2CH2NRCH2CH2P(C6H5)2 the total coordination number of metal ion is 12.
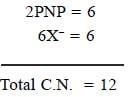
(C6H5)2PCH2CH2NRCH2CH2P(C6H5)2 the total coordination number of metal ion is 12.
If K < Q. where, K = equilibrium constant.
Q = reaction quotient
The reaction move in which direction to achieve equilibrium- a)forward direction
- b)backward direction
- c)already in equilibrium
- d)carnot be predicted
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If K < Q. where, K = equilibrium constant.
Q = reaction quotient
The reaction move in which direction to achieve equilibrium
Q = reaction quotient
The reaction move in which direction to achieve equilibrium
a)
forward direction
b)
backward direction
c)
already in equilibrium
d)
carnot be predicted

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
Application of equilibrium constant
K > Q ⇒ forward direction
K < Q ⇒ backward direction
K = Q ⇒ at equilibrium
K > Q ⇒ forward direction
K < Q ⇒ backward direction
K = Q ⇒ at equilibrium
Nickel forms a gaseous compound of the formula Ni(CO)x. The value of x given that under the same conditions of temperature and pressure methane effuses 3.25 times faster than the compound is _____(answer should be an integer). (Given : Ni = 58.7)
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Nickel forms a gaseous compound of the formula Ni(CO)x. The value of x given that under the same conditions of temperature and pressure methane effuses 3.25 times faster than the compound is _____(answer should be an integer). (Given : Ni = 58.7)

|
Athul Chaudhary answered |
Solution:
Effusion rate is inversely proportional to the square root of molar mass.
For methane, effusion rate (r) is given as:
r = 1/√(16)
For Ni(CO)x, effusion rate (r') is given as:
r' = 1/√(58.7 + 12 +16x)
The ratio of effusion rates is given as:
r/r' = 3.25
Substituting the values of r, r' and solving for x, we get:
x = 6
Therefore, the value of x for the gaseous compound Ni(CO)x is 6.
Effusion rate is inversely proportional to the square root of molar mass.
For methane, effusion rate (r) is given as:
r = 1/√(16)
For Ni(CO)x, effusion rate (r') is given as:
r' = 1/√(58.7 + 12 +16x)
The ratio of effusion rates is given as:
r/r' = 3.25
Substituting the values of r, r' and solving for x, we get:
x = 6
Therefore, the value of x for the gaseous compound Ni(CO)x is 6.
Vibrations of diatomic molecules are usually modelled by a harmonic potential. If the potential is given by x2 the correct statement is- a)force constant is 2 and force is 2x
- b)force constant is 2 and force is –2x
- c)force constant is –1 and force is 2x
- d)force constant is –1 and force is –2x
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Vibrations of diatomic molecules are usually modelled by a harmonic potential. If the potential is given by x2 the correct statement is
a)
force constant is 2 and force is 2x
b)
force constant is 2 and force is –2x
c)
force constant is –1 and force is 2x
d)
force constant is –1 and force is –2x

|
Maitri Sen answered |
given v = x2
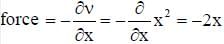
∴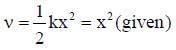
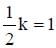
⇒
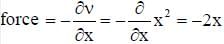
∴
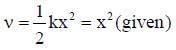
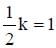
⇒

The infrared spectrum of HCl gas shows an absorption band centred at 2700 cm–1. The zero point energy of HCl molecule under harmonic oscillator approximation is
- a)2.686 × 10–22 J
- b)2.8665 x 10-20J
- c)5.273 × 10–22 J
- d)5.273 × 10–20 J
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The infrared spectrum of HCl gas shows an absorption band centred at 2700 cm–1. The zero point energy of HCl molecule under harmonic oscillator approximation is
a)
2.686 × 10–22 J
b)
2.8665 x 10-20J
c)
5.273 × 10–22 J
d)
5.273 × 10–20 J

|
Rutuja Sengupta answered |
During Nuclear-explosion, one of the product is 90Sr with half-life is 28.1 year. If 1μg od 90Sr was absorbed in the bones of a newly born baby instead of calcium. How much of it will remain after 10 year if it is not lost metabolically? (in unit of μg) (Round off to two decimal places).
Correct answer is between '0.70,0.82'. Can you explain this answer?
During Nuclear-explosion, one of the product is 90Sr with half-life is 28.1 year. If 1μg od 90Sr was absorbed in the bones of a newly born baby instead of calcium. How much of it will remain after 10 year if it is not lost metabolically? (in unit of μg) (Round off to two decimal places).

|
Sinjini Nair answered |

Which is more nucleophilic than the other of the following compounds?
- a)P(X), Q(Y), R(Y), S(Y), T(X), U(Y)
- b)P(X), Q(X), R(X), S(Y), T(Y), U(Y)
- c)P(Y), Q(Y), R(Y), S(X), T(X), U(X)
- d)P(X), Q(X), R(Y), S(Y), T(Y), U(Y)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is more nucleophilic than the other of the following compounds?

a)
P(X), Q(Y), R(Y), S(Y), T(X), U(Y)
b)
P(X), Q(X), R(X), S(Y), T(Y), U(Y)
c)
P(Y), Q(Y), R(Y), S(X), T(X), U(X)
d)
P(X), Q(X), R(Y), S(Y), T(Y), U(Y)

|
Nilotpal Basu answered |
Nucleophilicity increases with the increase in the size of atom in same period and decreases with the increase in electronegativity.
The rotational constant and the fundamental frequency of HBr are respectively, 20cm-1 and 4000cm-1. The corresponding values for DBR approximately are- a)10cm-1 4000cm-1
- b)15 cm-1 2828.8cm-1
- c)10cm-1 2828.8cm-1
- d)20cm-1 2828.8cm-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The rotational constant and the fundamental frequency of HBr are respectively, 20cm-1 and 4000cm-1. The corresponding values for DBR approximately are
a)
10cm-1 4000cm-1
b)
15 cm-1 2828.8cm-1
c)
10cm-1 2828.8cm-1
d)
20cm-1 2828.8cm-1

|
Maitri Sen answered |
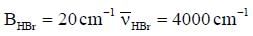
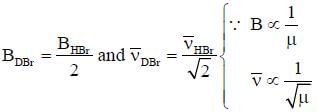
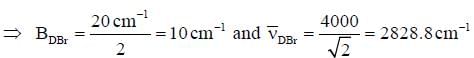
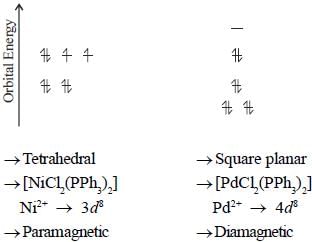
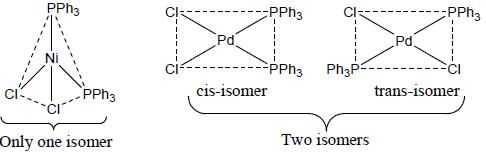
A complex of Ni(ll), [NiCl2(PPh3)2] is paramagnetic, the analogous complex of Palladium (II) is diamagnetic, the number of isomers shown by both complexes respectively are- a)one and two
- b)two and one
- c)one and one
- d)two and two
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A complex of Ni(ll), [NiCl2(PPh3)2] is paramagnetic, the analogous complex of Palladium (II) is diamagnetic, the number of isomers shown by both complexes respectively are
a)
one and two
b)
two and one
c)
one and one
d)
two and two

|
Pragati Sharma answered |
Which type of chromatography process requires that when materials that cannot be readily dissolved in a solvent for chromatography need to be heated or pyrolyzed to a high temperature is- a)TLC
- b)Gas chromatography
- c)HPLC
- d)Pyrolysis can be used for any and all chromatography process
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of chromatography process requires that when materials that cannot be readily dissolved in a solvent for chromatography need to be heated or pyrolyzed to a high temperature is
a)
TLC
b)
Gas chromatography
c)
HPLC
d)
Pyrolysis can be used for any and all chromatography process

|
Hrishikesh Verma answered |
Gas chromatography
Correct option is (b).
Correct option is (b).
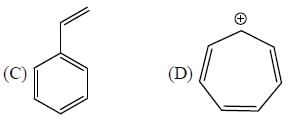
The number of anti-aromatic systems present among the following compounds is/are _____________(Answer should be an integer)


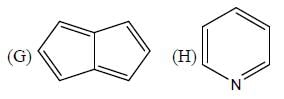
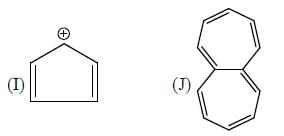 Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct answer is '6'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of anti-aromatic systems present among the following compounds is/are _____________(Answer should be an integer)







|
Niharika Kulkarni answered |
B, E, F, G , J, I are anti-aromatic in nature
What is the sequence of reagents that will accomplish the synthesis of the following aromatic amine from benzene?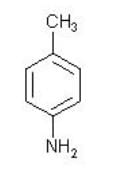
- a)CH3Cl, AlCl3; HNO3, H2SO4; H2
- b)CH3Cl, AlCl3; HNO3, H2SO4; Fe, HCl; NaOH
- c)HNO3, H2SO4; Fe, HCl; NaOH; CH3Cl, AlCl3
- d)HNO3, H2SO4; CH3Cl, AlCl3; Fe, HCl; NaOH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the sequence of reagents that will accomplish the synthesis of the following aromatic amine from benzene?

a)
CH3Cl, AlCl3; HNO3, H2SO4; H2
b)
CH3Cl, AlCl3; HNO3, H2SO4; Fe, HCl; NaOH
c)
HNO3, H2SO4; Fe, HCl; NaOH; CH3Cl, AlCl3
d)
HNO3, H2SO4; CH3Cl, AlCl3; Fe, HCl; NaOH

|
Edurev.iitjam answered |
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution of the methyl group with lewis acid leads to toluene. Through nitration, the nitro group is added then the reduction of nitro group leads to the amine.
The distribution coefficient of an organic compound A for benzene and water is 10. The amount of A extracted if 1.0 gm of it dissolved in 100 mL of water is equilibrated in a separatory funnel with 100 mL of benzene is ______ gm. (Round off to two one decimal place)
Correct answer is between '0.8,1.1'. Can you explain this answer?
The distribution coefficient of an organic compound A for benzene and water is 10. The amount of A extracted if 1.0 gm of it dissolved in 100 mL of water is equilibrated in a separatory funnel with 100 mL of benzene is ______ gm. (Round off to two one decimal place)

|
Siddharth Banerjee answered |
Suppose amount of A extracted with 100 mL of benzene = xg. The amount of A left in 100 mL water = 1–xg
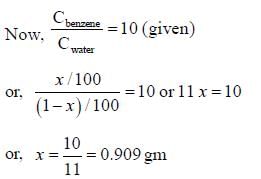
The amount of A extracted with 100 mL of benzene is 0.909 gm.
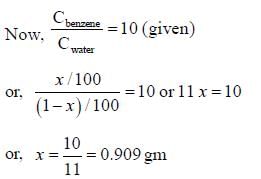
The amount of A extracted with 100 mL of benzene is 0.909 gm.
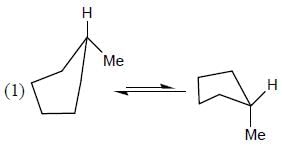
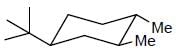
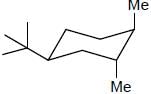
The more stable conformation of the following compound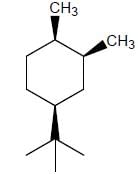
- a)
- b)
- c)
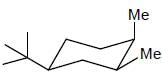
- d)
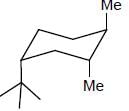
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The more stable conformation of the following compound

a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Tejas Goyal answered |
In the given compound, all substituent in cis position (above the plane). So, all group must be in up side.
Among the following amino acids, how many is/are basic
Val, Arg, His, Cys, Leu, Lys, Met
Correct answer is '3'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following amino acids, how many is/are basic
Val, Arg, His, Cys, Leu, Lys, Met
Val, Arg, His, Cys, Leu, Lys, Met

|
Niti Mukherjee answered |
Arg, His, and Lys are the basic amino acids
The substances containing iron and responsible for oxygen transport are- a)Hemoglobin and ferritin
- b)Hemoglobin and myoglobin
- c)Hemoglobin and hemerythrin
- d)Hemoglobin and transferrin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The substances containing iron and responsible for oxygen transport are
a)
Hemoglobin and ferritin
b)
Hemoglobin and myoglobin
c)
Hemoglobin and hemerythrin
d)
Hemoglobin and transferrin

|
Vandana Gupta answered |
Hemoglobin and hemerythrin contain iron and both are responsible for oxygen transport.
π-boncl length between C-C atoms. f.i and v is calculated by using the empirical formula,
Rμv = 1.52Å - 0.186 Å Pμv
where Pμv= is π - bond order between μ and v C -atom .
According to HM O theory. delocalization energy o f Benzene is 2|β|. Then T-bond length in Benzene is- a)1.53 Å
- b)1.39 Å
- c)1.33 Å
- d)1.23 Å
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
π-boncl length between C-C atoms. f.i and v is calculated by using the empirical formula,
Rμv = 1.52Å - 0.186 Å Pμv
where Pμv= is π - bond order between μ and v C -atom .
According to HM O theory. delocalization energy o f Benzene is 2|β|. Then T-bond length in Benzene is
Rμv = 1.52Å - 0.186 Å Pμv
where Pμv= is π - bond order between μ and v C -atom .
According to HM O theory. delocalization energy o f Benzene is 2|β|. Then T-bond length in Benzene is
a)
1.53 Å
b)
1.39 Å
c)
1.33 Å
d)
1.23 Å

|
Mahi Dasgupta answered |
Since, delocalization energy = 2|β|
So, one extra delocalizedT-bond Benzene.
The total energy of π-bond = 4(According to HMO Theory)
Since, there are 6(C- C ) bond in benzene.
So. each (C-C) bond has 4/6 π-bond = 2/s = 0.66
Now. by using formula,
Rμv = 1.52Å - 0.186 Å x 0.66 = 1.39 Å
So, one extra delocalizedT-bond Benzene.
The total energy of π-bond = 4(According to HMO Theory)
Since, there are 6(C- C ) bond in benzene.
So. each (C-C) bond has 4/6 π-bond = 2/s = 0.66
Now. by using formula,
Rμv = 1.52Å - 0.186 Å x 0.66 = 1.39 Å
The correct statement (s) is/are(I) π Bond energy of ethene is 2α(II) π Bond energy of 1-3-Butadiene is 4.472 β(III) π Bond energy of benzene is 8β(Iv) π Bond energy of benzene is 6β- a)I, II, III and IV
- b)I, II and III
- c)I and II
- d)II and III
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The correct statement (s) is/are
(I) π Bond energy of ethene is 2α
(II) π Bond energy of 1-3-Butadiene is 4.472 β
(III) π Bond energy of benzene is 8β
(Iv) π Bond energy of benzene is 6β
a)
I, II, III and IV
b)
I, II and III
c)
I and II
d)
II and III

|
Rutuja Sengupta answered |
(II) π Bond energy of 1-3-Butadiene is 4.472 β
(III) π Bond energy of benzene is 8β
Half life of Na24 radionuclide is 15h the time in which the activity of a sample of Na24 radionuclide will decrease by 87.5% is- a)40 h
- b)30 h
- c)45 h
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Half life of Na24 radionuclide is 15h the time in which the activity of a sample of Na24 radionuclide will decrease by 87.5% is
a)
40 h
b)
30 h
c)
45 h
d)
1

|
Aryan Gupta answered |
Let the initial activity of sample is 100 u. Then from question the final activity should be 100 – 87.5 = 12.5 u
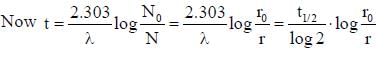
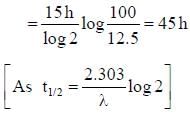
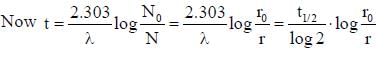
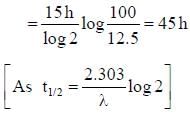
The number of classes in CH4 molecule is/are ________(answer should be an integer).
Correct answer is '5'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of classes in CH4 molecule is/are ________(answer should be an integer).

|
Aryan Gupta answered |
The number of classes in CH4 molecule is 5.
The oxidation state of Ru metal ion in [Ru(Terpy)2)J (PF6)2 is__________
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation state of Ru metal ion in [Ru(Terpy)2)J (PF6)2 is__________

|
Rishabh Mehta answered |
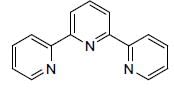
Terpyndine (neutral ligand)
or
Terpy
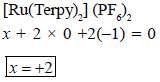
Chapter doubts & questions for Topic wise Tests - GATE Chemistry Mock Test Series 2025 is part of GATE Chemistry exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the GATE Chemistry exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for GATE Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Topic wise Tests - GATE Chemistry Mock Test Series in English & Hindi are available as part of GATE Chemistry exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
GATE Chemistry Mock Test Series
18 docs|37 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily