All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Business Economics for CA Foundation >
All Questions
All questions of Theory of Production and Cost for CA Foundation Exam
Can you explain the answer of this question below:The average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. _________.
- A:
50
- B:
45
- C:
25
- D:
20
The answer is b.
The average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. _________.
50
45
25
20

|
Dipika Kaur answered |
Given,
Average fixed cost for producing 6 units = Rs. 30
We know that,
Average fixed cost (AFC) = Total fixed cost / Output
Let's assume the total fixed cost to be 'F'.
So,
AFC = F / 6
F = 6 x AFC
Now, we need to find the AFC for producing 4 units of the product.
So,
AFC = F / 4
Substituting the value of F in the above equation, we get
AFC = (6 x AFC) / 4
AFC = (3/2) x AFC
AFC = AFC + (1/2) x AFC
Therefore, the AFC for producing 4 units will be 1/2 of the AFC for producing 6 units.
So,
AFC for producing 4 units = (1/2) x Rs. 30
AFC for producing 4 units = Rs. 15
But we need to find the total fixed cost for producing 4 units.
Total fixed cost = AFC x Output
Total fixed cost = Rs. 15 x 4
Total fixed cost = Rs. 60
Hence, the same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. 45.
Average fixed cost for producing 6 units = Rs. 30
We know that,
Average fixed cost (AFC) = Total fixed cost / Output
Let's assume the total fixed cost to be 'F'.
So,
AFC = F / 6
F = 6 x AFC
Now, we need to find the AFC for producing 4 units of the product.
So,
AFC = F / 4
Substituting the value of F in the above equation, we get
AFC = (6 x AFC) / 4
AFC = (3/2) x AFC
AFC = AFC + (1/2) x AFC
Therefore, the AFC for producing 4 units will be 1/2 of the AFC for producing 6 units.
So,
AFC for producing 4 units = (1/2) x Rs. 30
AFC for producing 4 units = Rs. 15
But we need to find the total fixed cost for producing 4 units.
Total fixed cost = AFC x Output
Total fixed cost = Rs. 15 x 4
Total fixed cost = Rs. 60
Hence, the same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. 45.
Economic cost excludes : - a)Accounting cost + explicit cost
- b)Accounting cost+ implicit cost
- c)Explicit cost + implicit cost
- d)Accounting cost +opportunity cost
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Economic cost excludes :
a)
Accounting cost + explicit cost
b)
Accounting cost+ implicit cost
c)
Explicit cost + implicit cost
d)
Accounting cost +opportunity cost
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
Economic profit can be both positive and negative and is calculated as follows: Total Revenues - (Explicit Costs + Implicit Costs) = Economic Profit. Accounting Profit - Implicit Costs = Economic Profit.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Average Fixed Cost = Rs. 20Quantity Produced = 10 units What will be the Average Fixed Cost of 20th unit?
- A:
Rs. 10
- B:
Rs. 20
- C:
Rs. 5
- D:
None
The answer is a.
Average Fixed Cost = Rs. 20Quantity Produced = 10 units What will be the Average Fixed Cost of 20th unit?
Rs. 10
Rs. 20
Rs. 5
None

|
Samiksha answered |
Well lets solve this step by step... As it is given in the question AFC =Rs 20.. Nd output =20 units so from this we can find out TFC.. TFC=AFC*output =20*10=Rs 200... Now we can easily find out AFC at 20th unit=TFC/output =200/20=Rs 10... Hence AFC at 20th unit is Rs 10
A firm’s total cost is Rs. 200 at 5 units of output and Rs. 220 at 6 units of output. The marginal cost of producing 6th of output will be ______.- a)20
- b)120
- c)220
- d)320
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm’s total cost is Rs. 200 at 5 units of output and Rs. 220 at 6 units of output. The marginal cost of producing 6th of output will be ______.
a)
20
b)
120
c)
220
d)
320

|
Bhaskar Sharma answered |
Is a business entity that engages in commercial activities with the aim of earning profits. It can refer to a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or other legal entity that sells goods or services. Firms can operate in various industries, including manufacturing, finance, healthcare, retail, and technology. The primary objective of a firm is to generate revenue and maximize profits for its owners or shareholders. To achieve this, firms may employ various strategies, such as cost-cutting, innovation, marketing, and expansion into new markets or product lines.
What is the total cost of production of 20 units, if fixed cost is Rs. 5,000 and variable cost is Rs. 2/-?
- a)5400
- b)5040
- c)4960
- d)5020
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the total cost of production of 20 units, if fixed cost is Rs. 5,000 and variable cost is Rs. 2/-?
a)
5400
b)
5040
c)
4960
d)
5020

|
Srsps answered |
Cost of Production Calculation
- Fixed Cost = Rs. 5,000
- Variable Cost per unit = Rs. 2
- Number of units = 20
Total Cost of Production
- Total Variable Cost = Variable Cost per unit x Number of units = 2 x 20 = Rs. 40
- Total Cost = Fixed Cost + Total Variable Cost = 5000 + 40 = Rs. 5040
Therefore, the total cost of production of 20 units is Rs. 5040.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Fixed cost is known as _______cost.
- A:
Prime
- B:
Supplementary
- C:
Overhead
- D:
Direct
The answer is c.
Fixed cost is known as _______cost.
Prime
Supplementary
Overhead
Direct

|
Akshay Saini answered |
Fixed costs are expenses that have to be paid by a company, independent of any specific business activities. Fixed cost is known as Overhead cost.
Increasing returns to scale occurs due to: - a)Economies of scale
- b)Specialization
- c)Indivisibility of factors
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Increasing returns to scale occurs due to:
a)
Economies of scale
b)
Specialization
c)
Indivisibility of factors
d)
All of these
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
An increasing returns to scale occurs when the output increases by a larger proportion than the increase in inputs during the production process. For example, if input is increased by 3 times, but output increases by 3.75 times, then the firm or economy has experienced an increasing returns to scale.
What will be the TVC if we produce 2 units?
Units 0 1 2
TC 20 37 50- a)15
- b)05
- c)17
- d)30
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the TVC if we produce 2 units?
Units 0 1 2
TC 20 37 50
Units 0 1 2
TC 20 37 50
a)
15
b)
05
c)
17
d)
30

|
Samiksha answered |
Well as we know TFC=TC at 0 level of output so TFC =20.. Now TVC at 2 units will be... (use formula TC=TVC+TFC) TVC=TC-TFC=50-20=Rs 30...
Suppose the total cost of production of commodity ‘X’ is Rs. 1, 25,000 Out of other cost implicit is Rs. 35,000 and normal profit is Rs. 25,000 what will be the explicit cost of commodity ‘X’?- a)Rs. 60,000
- b)Rs. 65,000
- c)Rs. 90,000
- d)Rs. 80,000
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose the total cost of production of commodity ‘X’ is Rs. 1, 25,000 Out of other cost implicit is Rs. 35,000 and normal profit is Rs. 25,000 what will be the explicit cost of commodity ‘X’?
a)
Rs. 60,000
b)
Rs. 65,000
c)
Rs. 90,000
d)
Rs. 80,000

|
Sanjana Khanna answered |
X is given by the function C(x) = 1000 + 2x, where x is the quantity of commodity X produced. The marginal cost of production (MC) is the derivative of the total cost function with respect to x, which is given by MC = dC(x)/dx = 2.
This means that the marginal cost of production of commodity X is constant and equal to 2. This implies that every additional unit of commodity X produced incurs an additional cost of $2. For example, if the company produces 100 units of commodity X, the total cost of production is C(100) = 1000 + 2(100) = $1200. If the company decides to produce one more unit of commodity X, the total cost of production will increase to C(101) = 1000 + 2(101) = $1202, which means that the marginal cost of production for the 101st unit is $2.
Knowing the marginal cost of production is important for businesses because it helps them make decisions about how much to produce. If the price of commodity X is higher than the marginal cost of production, the company can increase its profit by producing more units. However, if the price of commodity X is lower than the marginal cost of production, the company will incur a loss by producing additional units. Therefore, businesses need to find the right balance between the price of their product and the cost of production to maximize their profits.
This means that the marginal cost of production of commodity X is constant and equal to 2. This implies that every additional unit of commodity X produced incurs an additional cost of $2. For example, if the company produces 100 units of commodity X, the total cost of production is C(100) = 1000 + 2(100) = $1200. If the company decides to produce one more unit of commodity X, the total cost of production will increase to C(101) = 1000 + 2(101) = $1202, which means that the marginal cost of production for the 101st unit is $2.
Knowing the marginal cost of production is important for businesses because it helps them make decisions about how much to produce. If the price of commodity X is higher than the marginal cost of production, the company can increase its profit by producing more units. However, if the price of commodity X is lower than the marginal cost of production, the company will incur a loss by producing additional units. Therefore, businesses need to find the right balance between the price of their product and the cost of production to maximize their profits.
The total cost incurred for 10 units is Rs. 400 and 20 units is Rs. 800. Find the marginal cost.
- a)Rs.400
- b)Rs. 40
- c)Rs. 200
- d)Rs. 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The total cost incurred for 10 units is Rs. 400 and 20 units is Rs. 800. Find the marginal cost.
a)
Rs.400
b)
Rs. 40
c)
Rs. 200
d)
Rs. 20

|
Srsps answered |
Calculation of Marginal Cost
- Firstly, calculate the cost per unit for 10 units:
Total cost for 10 units = Rs. 400
Cost per unit for 10 units = Rs. 400 / 10 = Rs. 40
- Next, calculate the cost per unit for 20 units:
Total cost for 20 units = Rs. 800
Cost per unit for 20 units = Rs. 800 / 20 = Rs. 40
- Now, calculate the marginal cost using the formula:
Marginal Cost = Cost for additional units - Cost for initial units
Marginal Cost = Cost for 20 units - Cost for 10 units
Marginal Cost = Rs. 800 - Rs. 400
Marginal Cost = Rs. 400
Therefore, the marginal cost is Rs. 40.
- Firstly, calculate the cost per unit for 10 units:
Total cost for 10 units = Rs. 400
Cost per unit for 10 units = Rs. 400 / 10 = Rs. 40
- Next, calculate the cost per unit for 20 units:
Total cost for 20 units = Rs. 800
Cost per unit for 20 units = Rs. 800 / 20 = Rs. 40
- Now, calculate the marginal cost using the formula:
Marginal Cost = Cost for additional units - Cost for initial units
Marginal Cost = Cost for 20 units - Cost for 10 units
Marginal Cost = Rs. 800 - Rs. 400
Marginal Cost = Rs. 400
Therefore, the marginal cost is Rs. 40.
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 40 at 12 units. What will be the average fixed cost at 8 units:
- a)Rs. 60
- b)Rs. 70
- c)Rs. 90
- d)Rs. 80
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 40 at 12 units. What will be the average fixed cost at 8 units:
a)
Rs. 60
b)
Rs. 70
c)
Rs. 90
d)
Rs. 80

|
Srsps answered |
Calculating Average Fixed Cost at 8 units
- Given that the average fixed cost at 12 units is Rs. 40.
- To find the average fixed cost at 8 units, we can use the concept of fixed costs being spread over a larger or smaller number of units produced.
Calculation
- Let's assume the total fixed cost at 12 units is Rs. 480 (40 * 12).
- To find the average fixed cost at 8 units, we divide the total fixed cost by the new number of units.
- Average fixed cost at 8 units = Total fixed cost / Number of units = Rs. 480 / 8 = Rs. 60.
Therefore, the average fixed cost at 8 units is Rs. 60. So, the correct answer is option A: Rs. 60.
- Given that the average fixed cost at 12 units is Rs. 40.
- To find the average fixed cost at 8 units, we can use the concept of fixed costs being spread over a larger or smaller number of units produced.
Calculation
- Let's assume the total fixed cost at 12 units is Rs. 480 (40 * 12).
- To find the average fixed cost at 8 units, we divide the total fixed cost by the new number of units.
- Average fixed cost at 8 units = Total fixed cost / Number of units = Rs. 480 / 8 = Rs. 60.
Therefore, the average fixed cost at 8 units is Rs. 60. So, the correct answer is option A: Rs. 60.
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 20 at 6 units of output what will it be at 4 units of output?- a)Rs. 60
- b)Rs. 30
- c)Rs. 40
- d)Rs. 20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 20 at 6 units of output what will it be at 4 units of output?
a)
Rs. 60
b)
Rs. 30
c)
Rs. 40
d)
Rs. 20
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Average fixed cost per unit is Rs. 20 when 6 units of product produced.
Total fixed cost = 6 X 20 = Rs. 120.
Therefore fixed cost per unit when production is 4 units = 120/4 = Rs.30
Which of the following is considered production in Economics?- a)Tilling of soil.
- b)Singing a song before friends.
- c)Preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road.
- d)Painting a picture for pleasure.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is considered production in Economics?
a)
Tilling of soil.
b)
Singing a song before friends.
c)
Preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road.
d)
Painting a picture for pleasure.

|
Jatin Mehta answered |
Production in Economics
Production in economics refers to the creation of goods and services using the available resources. It involves combining various factors of production such as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship to produce goods and services that satisfy human wants.
Tilling of Soil
Tilling of soil is considered production in economics because it involves the use of land and labor to produce agricultural products. Farmers use their labor to till the soil and plant crops, which are then harvested and sold in the market. This activity contributes to the economy by providing food for consumption and generating income for the farmers.
Other Options
Singing a song before friends, preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road, and painting a picture for pleasure are not considered production in economics because they do not involve the creation of goods and services for the market. Singing a song before friends is a leisure activity that does not generate income, preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road is a social responsibility, and painting a picture for pleasure is a hobby.
Conclusion
In conclusion, production in economics refers to the creation of goods and services using the available resources. Tilling of soil is considered production in economics because it involves the use of land and labor to produce agricultural products. Other activities such as singing a song before friends, preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road, and painting a picture for pleasure are not considered production in economics.
Production in economics refers to the creation of goods and services using the available resources. It involves combining various factors of production such as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship to produce goods and services that satisfy human wants.
Tilling of Soil
Tilling of soil is considered production in economics because it involves the use of land and labor to produce agricultural products. Farmers use their labor to till the soil and plant crops, which are then harvested and sold in the market. This activity contributes to the economy by providing food for consumption and generating income for the farmers.
Other Options
Singing a song before friends, preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road, and painting a picture for pleasure are not considered production in economics because they do not involve the creation of goods and services for the market. Singing a song before friends is a leisure activity that does not generate income, preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road is a social responsibility, and painting a picture for pleasure is a hobby.
Conclusion
In conclusion, production in economics refers to the creation of goods and services using the available resources. Tilling of soil is considered production in economics because it involves the use of land and labor to produce agricultural products. Other activities such as singing a song before friends, preventing a child from falling into a manhole on the road, and painting a picture for pleasure are not considered production in economics.
Which of the following curves never touch any axis but is downward?- a)Marginal cost curve
- b)Total cost curve
- c)Average fixed cost curve
- d)Average variable cost curve
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following curves never touch any axis but is downward?
a)
Marginal cost curve
b)
Total cost curve
c)
Average fixed cost curve
d)
Average variable cost curve
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Average fixed cost is the total fixed cost divided by the number of units of output produced. Therefore,
AFC = TFC/Q
Where Q represents the number of units of output produced.
Thus average fixed cost is the fixed cost per unit of output.
Average fixed cost curve slopes downward throughout its length. As output increases, the total fixed cost spreads over more and more units and therefore average fixed cost becomes less and less. When output becomes very large, average fixed cost approaches zero.
It is seen that average fixed cost curve continuously falls throughout. Mathematically speaking, average fixed cost curve approaches both axes asymptotically. In other words, AFC curve gets very nearer to but never touches either axis.
Calculate total cost of 4 units:
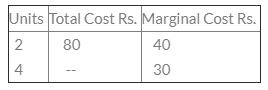
- a)140
- b)120
- c)50
- d)40
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate total cost of 4 units:
a)
140
b)
120
c)
50
d)
40

|
Srsps answered |
Marginal cost = ∆Total cost/∆Output.
At 4 units,
Let the required units be 'x' units at 4 units.
Marginal cost = 30 = (x-80)/(4-2).
30 = (x-80)/2.
30 x 2 = x-80.
60 = x-80.
60+80 = x.
x = 140.
Hence, correct answer is option A.
At 4 units,
Let the required units be 'x' units at 4 units.
Marginal cost = 30 = (x-80)/(4-2).
30 = (x-80)/2.
30 x 2 = x-80.
60 = x-80.
60+80 = x.
x = 140.
Hence, correct answer is option A.
A firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of Rs. 150 and has to pay Rs. 350 to its fixed factors of production whether it produces or not. How much of the average total cost is made up of variable costs?- a)Rs. 200
- b)Rs. 50
- c)Rs. 300
- d)Rs. 100
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm producing 7 units of output has an average total cost of Rs. 150 and has to pay Rs. 350 to its fixed factors of production whether it produces or not. How much of the average total cost is made up of variable costs?
a)
Rs. 200
b)
Rs. 50
c)
Rs. 300
d)
Rs. 100

|
Akshay Das answered |
Given:
Average total cost = Rs. 150
Fixed cost = Rs. 350
Output produced = 7 units
To find:
Variable cost component in average total cost
Solution:
Total cost = Average total cost * Output produced
Total cost = Rs. 150 * 7
Total cost = Rs. 1050
Variable cost = Total cost - Fixed cost
Variable cost = Rs. 1050 - Rs. 350
Variable cost = Rs. 700
Variable cost component in average total cost = Variable cost / Output produced
Variable cost component in average total cost = Rs. 700 / 7
Variable cost component in average total cost = Rs. 100
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, Rs. 100.
Average total cost = Rs. 150
Fixed cost = Rs. 350
Output produced = 7 units
To find:
Variable cost component in average total cost
Solution:
Total cost = Average total cost * Output produced
Total cost = Rs. 150 * 7
Total cost = Rs. 1050
Variable cost = Total cost - Fixed cost
Variable cost = Rs. 1050 - Rs. 350
Variable cost = Rs. 700
Variable cost component in average total cost = Variable cost / Output produced
Variable cost component in average total cost = Rs. 700 / 7
Variable cost component in average total cost = Rs. 100
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, Rs. 100.
The marginal, average, and total product curves encountered by the firm producing in the short run exhibit all of the following relationships except:- a)when total product is rising, average and marginal product may be either rising or falling.
- b)when marginal product is negative, total product and average product are falling.
- c)when average product is at a maximum, marginal product equals average product, and total product is rising.
- d)when marginal product is at a maximum, average product equals marginal product, and total product is rising.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The marginal, average, and total product curves encountered by the firm producing in the short run exhibit all of the following relationships except:
a)
when total product is rising, average and marginal product may be either rising or falling.
b)
when marginal product is negative, total product and average product are falling.
c)
when average product is at a maximum, marginal product equals average product, and total product is rising.
d)
when marginal product is at a maximum, average product equals marginal product, and total product is rising.

|
Anand Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
Marginal product (MP), average product (AP), and total product (TP) are important concepts in the theory of production. The relationship between these three curves can reveal important information about the efficiency of production.
a) When total product is rising, average and marginal product may be either rising or falling:
- Total product (TP) is the total output of a firm, which increases as more inputs are added.
- Average product (AP) is the output per unit of input, which may increase initially as more inputs are added, but eventually reaches a maximum and then declines.
- Marginal product (MP) is the additional output produced by adding one more unit of input, which may increase initially as more inputs are added, but eventually reaches a maximum and then declines.
Therefore, when TP is rising, AP may be rising or falling, depending on whether the additional inputs are adding more or less than the average output per unit of input. Similarly, MP may be rising or falling, depending on whether the additional input is adding more or less than the previous unit.
b) When marginal product is negative, total product and average product are falling:
- When MP is negative, it means that the additional input is decreasing the overall output of the firm, which leads to a decline in TP.
- Since AP is calculated as TP divided by the number of inputs, it will also decline when TP is falling.
c) When average product is at a maximum, marginal product equals average product, and total product is rising:
- AP reaches a maximum when the additional input is adding the most output per unit of input, which means that MP equals AP at this point.
- This also means that the firm is producing at the most efficient level, and TP is rising as more inputs are added.
d) When marginal product is at a maximum, average product equals marginal product, and total product is rising:
- This statement is incorrect because it implies that MP is at a maximum when AP is equal to MP, which is not true.
- MP reaches a maximum when the additional input is adding the most output, which may occur at a different point than when AP is at a maximum.
- However, when MP is at a maximum, it does indicate that the firm is producing at the most efficient level, and TP is rising as more inputs are added.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, as it does not accurately describe the relationship between MP, AP, and TP.
Marginal product (MP), average product (AP), and total product (TP) are important concepts in the theory of production. The relationship between these three curves can reveal important information about the efficiency of production.
a) When total product is rising, average and marginal product may be either rising or falling:
- Total product (TP) is the total output of a firm, which increases as more inputs are added.
- Average product (AP) is the output per unit of input, which may increase initially as more inputs are added, but eventually reaches a maximum and then declines.
- Marginal product (MP) is the additional output produced by adding one more unit of input, which may increase initially as more inputs are added, but eventually reaches a maximum and then declines.
Therefore, when TP is rising, AP may be rising or falling, depending on whether the additional inputs are adding more or less than the average output per unit of input. Similarly, MP may be rising or falling, depending on whether the additional input is adding more or less than the previous unit.
b) When marginal product is negative, total product and average product are falling:
- When MP is negative, it means that the additional input is decreasing the overall output of the firm, which leads to a decline in TP.
- Since AP is calculated as TP divided by the number of inputs, it will also decline when TP is falling.
c) When average product is at a maximum, marginal product equals average product, and total product is rising:
- AP reaches a maximum when the additional input is adding the most output per unit of input, which means that MP equals AP at this point.
- This also means that the firm is producing at the most efficient level, and TP is rising as more inputs are added.
d) When marginal product is at a maximum, average product equals marginal product, and total product is rising:
- This statement is incorrect because it implies that MP is at a maximum when AP is equal to MP, which is not true.
- MP reaches a maximum when the additional input is adding the most output, which may occur at a different point than when AP is at a maximum.
- However, when MP is at a maximum, it does indicate that the firm is producing at the most efficient level, and TP is rising as more inputs are added.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D, as it does not accurately describe the relationship between MP, AP, and TP.
Units 0 1 2 3 4
Total Cost 20 30 40 45 50
What will be the AFC at 4 units of output?- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Units 0 1 2 3 4
Total Cost 20 30 40 45 50
What will be the AFC at 4 units of output?
Total Cost 20 30 40 45 50
What will be the AFC at 4 units of output?
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5

|
Ritika Iyer answered |
Calculation of AFC at 4 units of output:
- AFC (Average Fixed Cost) = Total Fixed Cost / Units of Output
- Total Fixed Cost = Total Cost - Total Variable Cost
- At 4 units of output, the total cost is 50 and given that the cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs, we need to determine the total fixed cost and variable cost.
- From the given data, we can see that the cost increases as the units of output increase, which means that the variable cost also increases.
- We can calculate the variable cost by subtracting the fixed cost from the total cost at any given level of output. For example, at 2 units of output, the variable cost is 30 - 20 = 10.
- To calculate the total fixed cost, we can subtract the variable cost from the total cost at the highest level of output (4 units): 50 - 45 = 5.
- Therefore, the AFC at 4 units of output is:
AFC = Total Fixed Cost / Units of Output
AFC = 5 / 4
AFC = 1.25 or 5/4
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (5).
- AFC (Average Fixed Cost) = Total Fixed Cost / Units of Output
- Total Fixed Cost = Total Cost - Total Variable Cost
- At 4 units of output, the total cost is 50 and given that the cost is the sum of fixed and variable costs, we need to determine the total fixed cost and variable cost.
- From the given data, we can see that the cost increases as the units of output increase, which means that the variable cost also increases.
- We can calculate the variable cost by subtracting the fixed cost from the total cost at any given level of output. For example, at 2 units of output, the variable cost is 30 - 20 = 10.
- To calculate the total fixed cost, we can subtract the variable cost from the total cost at the highest level of output (4 units): 50 - 45 = 5.
- Therefore, the AFC at 4 units of output is:
AFC = Total Fixed Cost / Units of Output
AFC = 5 / 4
AFC = 1.25 or 5/4
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (5).
The positively sloped (i.e. rising) part of the long run average total cost curve is due to which of the following?- a)Diseconomies of scale.
- b)Increasing returns.
- c)The firm being able to take advantage of large-scale production techniques as it expands its output.
- d)The increase in productivity that results from specialization.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The positively sloped (i.e. rising) part of the long run average total cost curve is due to which of the following?
a)
Diseconomies of scale.
b)
Increasing returns.
c)
The firm being able to take advantage of large-scale production techniques as it expands its output.
d)
The increase in productivity that results from specialization.

|
Lakshmi Kaur answered |
Explanation:
The long run average total cost (LRATC) curve shows the per-unit cost of producing a given level of output when the firm has the flexibility to adjust all of its inputs. The positively sloped part of the LRATC curve is called diseconomies of scale. It occurs when the firm's average total cost increases as the firm expands its output in the long run. This happens due to the following reasons:
1. Coordination problems: As the firm expands its output, it becomes more complex, and coordination problems arise, increasing the cost of production. This includes communication issues, delays in decision making, and conflicts between departments.
2. Management problems: As the firm expands, it becomes harder to manage efficiently, and the cost of management increases. This includes problems with delegation, supervision, and control.
3. Increasing input costs: As the firm expands, it may face increasing costs of inputs such as labor, raw materials, and energy, which increases the cost of production.
4. Diseconomies of specialization: As the firm becomes larger, it may become too specialized, and its employees may become less versatile, leading to a decline in productivity and an increase in costs.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the positively sloped part of the LRATC curve is due to the diseconomies of scale, which arise as the firm expands its output. These diseconomies can be due to coordination problems, management problems, increasing input costs, and diseconomies of specialization.
The long run average total cost (LRATC) curve shows the per-unit cost of producing a given level of output when the firm has the flexibility to adjust all of its inputs. The positively sloped part of the LRATC curve is called diseconomies of scale. It occurs when the firm's average total cost increases as the firm expands its output in the long run. This happens due to the following reasons:
1. Coordination problems: As the firm expands its output, it becomes more complex, and coordination problems arise, increasing the cost of production. This includes communication issues, delays in decision making, and conflicts between departments.
2. Management problems: As the firm expands, it becomes harder to manage efficiently, and the cost of management increases. This includes problems with delegation, supervision, and control.
3. Increasing input costs: As the firm expands, it may face increasing costs of inputs such as labor, raw materials, and energy, which increases the cost of production.
4. Diseconomies of specialization: As the firm becomes larger, it may become too specialized, and its employees may become less versatile, leading to a decline in productivity and an increase in costs.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the positively sloped part of the LRATC curve is due to the diseconomies of scale, which arise as the firm expands its output. These diseconomies can be due to coordination problems, management problems, increasing input costs, and diseconomies of specialization.
Increase in all input leading to less than proportional increase in output is called ______:- a)Increasing returns to scale
- b)Decreasing returns to scale
- c)Constant returns to scale
- d)Both increasing and decreasing returns to scale
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Increase in all input leading to less than proportional increase in output is called ______:
a)
Increasing returns to scale
b)
Decreasing returns to scale
c)
Constant returns to scale
d)
Both increasing and decreasing returns to scale
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
It occurs if a given percentage increase in all inputs results in a smaller percentage increase in output. The most common explanation for decreasing Returns involves organization factors in very large firms. ... As a result, proportional increases in output require more than proportional increases in inputs.
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 40 at 12 units. What will be the average fixed cost at 8 units:- a)Rs. 60
- b)Rs. 70
- c)Rs. 90
- d)Rs. 80
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm’s average fixed cost is Rs. 40 at 12 units. What will be the average fixed cost at 8 units:
a)
Rs. 60
b)
Rs. 70
c)
Rs. 90
d)
Rs. 80

|
Subhankar Sen answered |
Is an organization that provides goods or services to customers in exchange for payment. It can be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or other legal entity. Firms are typically created to generate profits for their owners or shareholders, but they can also be non-profit organizations that operate for the benefit of society. Firms can operate in a variety of industries, such as manufacturing, technology, healthcare, finance, and retail. They can be small and local or large and multinational, with operations in multiple countries.
In the first stage of law of variable proportions, total product increases at the ______
- a)Decreasing rate
- b)Increasing rate
- c)Constant rate
- d)Both A And B
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the first stage of law of variable proportions, total product increases at the ______
a)
Decreasing rate
b)
Increasing rate
c)
Constant rate
d)
Both A And B

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Explanation:
Law of Variable Proportions:
- The law of variable proportions is a fundamental principle in economics that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs in production.
- According to this law, as one input is varied while others are held constant, the output produced will change.
First Stage of Law of Variable Proportions:
- In the first stage of the law of variable proportions, total product increases at an increasing rate.
- This means that as more units of a variable input are added to the production process, the total output produced will increase at a faster rate.
- This stage is typically characterized by underutilization of fixed inputs and increasing specialization of labor.
Factors Influencing Total Product in the First Stage:
- In the first stage, the fixed inputs are being effectively utilized, and the variable input is being added in optimal proportions.
- As a result, the marginal product of the variable input is higher than the average product, leading to an increasing total product.
- This stage represents an efficient use of resources and a positive impact on overall productivity.
Implications of Increasing Rate of Total Product:
- The increasing rate of total product in the first stage indicates that the production process is operating efficiently and effectively.
- It suggests that the business is able to increase output by adding more units of the variable input without experiencing diminishing returns.
- This stage is crucial for maximizing production and achieving economies of scale.
In conclusion, the first stage of the law of variable proportions is characterized by an increasing rate of total product, which signifies optimal utilization of inputs and efficient production processes.
Law of Variable Proportions:
- The law of variable proportions is a fundamental principle in economics that describes the relationship between inputs and outputs in production.
- According to this law, as one input is varied while others are held constant, the output produced will change.
First Stage of Law of Variable Proportions:
- In the first stage of the law of variable proportions, total product increases at an increasing rate.
- This means that as more units of a variable input are added to the production process, the total output produced will increase at a faster rate.
- This stage is typically characterized by underutilization of fixed inputs and increasing specialization of labor.
Factors Influencing Total Product in the First Stage:
- In the first stage, the fixed inputs are being effectively utilized, and the variable input is being added in optimal proportions.
- As a result, the marginal product of the variable input is higher than the average product, leading to an increasing total product.
- This stage represents an efficient use of resources and a positive impact on overall productivity.
Implications of Increasing Rate of Total Product:
- The increasing rate of total product in the first stage indicates that the production process is operating efficiently and effectively.
- It suggests that the business is able to increase output by adding more units of the variable input without experiencing diminishing returns.
- This stage is crucial for maximizing production and achieving economies of scale.
In conclusion, the first stage of the law of variable proportions is characterized by an increasing rate of total product, which signifies optimal utilization of inputs and efficient production processes.
The Average fixed cost for producing on output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. ______.- a)50
- b)45
- c)25
- d)20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The Average fixed cost for producing on output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. ______.
a)
50
b)
45
c)
25
d)
20

|
Rajveer Yadav answered |
Given, the average fixed cost for producing 6 units of a product is Rs. 30.
We can use the formula for calculating average fixed cost:
Average fixed cost = Total fixed cost / Quantity
Let the total fixed cost be 'F' for producing 6 units of the product.
30 = F / 6
F = 180
So, the total fixed cost for producing 6 units is Rs. 180.
Now, we need to find the average fixed cost for producing 4 units.
Let the total fixed cost for producing 4 units be 'C'.
We know that the average fixed cost remains the same for different quantities of output.
So, we can use the same formula:
Average fixed cost = C / 4
But we know that the average fixed cost is Rs. 30.
So, we can write:
30 = C / 4
C = 120
Therefore, the total fixed cost for producing 4 units of the product is Rs. 120.
Now, we can calculate the average fixed cost for producing 4 units:
Average fixed cost = 120 / 4 = Rs. 30
Therefore, the answer is option B) 45.
We can use the formula for calculating average fixed cost:
Average fixed cost = Total fixed cost / Quantity
Let the total fixed cost be 'F' for producing 6 units of the product.
30 = F / 6
F = 180
So, the total fixed cost for producing 6 units is Rs. 180.
Now, we need to find the average fixed cost for producing 4 units.
Let the total fixed cost for producing 4 units be 'C'.
We know that the average fixed cost remains the same for different quantities of output.
So, we can use the same formula:
Average fixed cost = C / 4
But we know that the average fixed cost is Rs. 30.
So, we can write:
30 = C / 4
C = 120
Therefore, the total fixed cost for producing 4 units of the product is Rs. 120.
Now, we can calculate the average fixed cost for producing 4 units:
Average fixed cost = 120 / 4 = Rs. 30
Therefore, the answer is option B) 45.
The Law of Diminishing Returns is applicable in _________.- a)Only manufacturing industries
- b)Only Agriculture
- c)Neither in Agriculture nor in industries
- d)All Economic activities after a point
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Law of Diminishing Returns is applicable in _________.
a)
Only manufacturing industries
b)
Only Agriculture
c)
Neither in Agriculture nor in industries
d)
All Economic activities after a point
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Diminishing returns, also called law of diminishing returns or principle of diminishing marginal productivity, economic law stating that if one input in the production of a commodity is increased while all other inputs are held fixed, a point will eventually be reached at which additions of the input yield progressively smaller, or diminishing, increases in output.
Consider the following data 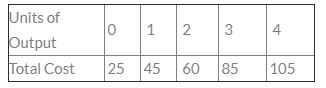 The Average Variable Cost (AVC) for an output of 4 units will be:-
The Average Variable Cost (AVC) for an output of 4 units will be:-- a)Rs. 20
- b)Rs. 30
- c)Rs. 25
- d)Rs. 26
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following data
The Average Variable Cost (AVC) for an output of 4 units will be:-
a)
Rs. 20
b)
Rs. 30
c)
Rs. 25
d)
Rs. 26

|
Jay Vyas answered |
At 0 units of output TC is equalls TFC and TFC is remains constant so TVC at 4 units =TC-TFC TVC = 105-25=80 AVC = TVC/Q AVC = 80/4 = 20 HENCE option A is correct
If the LAC curve falls as output expands, this is due to ______________________.- a)Law of Diminishing Returns
- b)Diseconomies of Scale
- c)Law of Variable Proportions
- d)Economies of Scale
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the LAC curve falls as output expands, this is due to ______________________.
a)
Law of Diminishing Returns
b)
Diseconomies of Scale
c)
Law of Variable Proportions
d)
Economies of Scale

|
Srsps answered |
Long-run average cost is the cost per unit of output reasonable when all factors of production are variable. Long-Run Average cost is of 'U' shaped because of returns to scale. In the establishment, firms enjoy lots of economies to scale so its cost curve is downward sloping. Increasing income to scale applies when firms enjoy economies to scale. In the beginning, the factors of production are not exhausted.
Find AFC of 3 units.
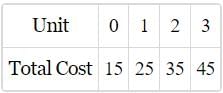
- a)5
- b)10
- c)15
- d)25
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Find AFC of 3 units.


a)
5
b)
10
c)
15
d)
25

|
Srsps answered |
AFC (Average Fixed Cost) is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost by the quantity of output produced.
Formula: AFC = Total Fixed Cost / Quantity of Output
Fixed costs are those costs that do not change with the level of output, such as rent, salaries, and equipment costs. These costs are incurred even if no output is produced. By dividing the total fixed cost by the quantity of output, you can determine the average fixed cost per unit of output.
Correct option is A.
Formula: AFC = Total Fixed Cost / Quantity of Output
Fixed costs are those costs that do not change with the level of output, such as rent, salaries, and equipment costs. These costs are incurred even if no output is produced. By dividing the total fixed cost by the quantity of output, you can determine the average fixed cost per unit of output.
Correct option is A.
The average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. _________.- a)50
- b)45
- c)25
- d)20
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product by a firm is Rs. 30. The same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. _________.
a)
50
b)
45
c)
25
d)
20

|
Stuti Desai answered |
Given:
- Average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product = Rs. 30
To find:
- Same cost for producing an output of 4 units
Solution:
The average fixed cost (AFC) is the total fixed cost (TFC) divided by the quantity of output (Q).
Therefore, the TFC for producing 6 units can be calculated as follows:
AFC = TFC / Q
Rs. 30 = TFC / 6
TFC = Rs. 180
Now, let's find the AFC for producing 4 units:
AFC = TFC / Q
AFC = Rs. 180 / 4
AFC = Rs. 45
Therefore, the same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. 45.
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
- Average fixed cost for producing an output of 6 units of a product = Rs. 30
To find:
- Same cost for producing an output of 4 units
Solution:
The average fixed cost (AFC) is the total fixed cost (TFC) divided by the quantity of output (Q).
Therefore, the TFC for producing 6 units can be calculated as follows:
AFC = TFC / Q
Rs. 30 = TFC / 6
TFC = Rs. 180
Now, let's find the AFC for producing 4 units:
AFC = TFC / Q
AFC = Rs. 180 / 4
AFC = Rs. 45
Therefore, the same cost for producing an output of 4 units will be Rs. 45.
Hence, option (b) is the correct answer.
AFC curve is: - a)Convex & downward sloping
- b)Concave & downward sloping
- c)Convex & upward sloping
- d)Concave & upward rising
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
AFC curve is:
a)
Convex & downward sloping
b)
Concave & downward sloping
c)
Convex & upward sloping
d)
Concave & upward rising

|
Dipika Kaur answered |
To the origin
b)Concave to the origin
c)U-shaped
d)A straight line
Answer: b) Concave to the origin.
b)Concave to the origin
c)U-shaped
d)A straight line
Answer: b) Concave to the origin.
In the short run, when the output of a firm increases, its average fixed cost :- a)increases.
- b)decreases.
- c)remains constant.
- d)first declines and then rises.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the short run, when the output of a firm increases, its average fixed cost :
a)
increases.
b)
decreases.
c)
remains constant.
d)
first declines and then rises.

|
Mehul Saini answered |
Explanation:
Average fixed cost (AFC) is the fixed cost per unit of output. It is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost (TFC) by the total output (Q).
Formula: AFC = TFC/Q
Short Run: In the short run, at least one factor of production is fixed and cannot be changed. For example, a firm may have a fixed amount of capital such as a building, machinery or land.
When the output of a firm increases, the average fixed cost will decrease due to the spreading effect of fixed cost over a larger output.
Example:
Suppose a firm has a fixed cost of $1000 and produces 100 units of output, then AFC will be:
AFC = TFC/Q = $1000/100 = $10
If the firm increases its output to 200 units, then AFC will be:
AFC = TFC/Q = $1000/200 = $5
Therefore, as the output increases, the fixed cost is spread over a larger number of units, reducing the average fixed cost.
Conclusion:
In the short run, when the output of a firm increases, its average fixed cost decreases. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer.
Average fixed cost (AFC) is the fixed cost per unit of output. It is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost (TFC) by the total output (Q).
Formula: AFC = TFC/Q
Short Run: In the short run, at least one factor of production is fixed and cannot be changed. For example, a firm may have a fixed amount of capital such as a building, machinery or land.
When the output of a firm increases, the average fixed cost will decrease due to the spreading effect of fixed cost over a larger output.
Example:
Suppose a firm has a fixed cost of $1000 and produces 100 units of output, then AFC will be:
AFC = TFC/Q = $1000/100 = $10
If the firm increases its output to 200 units, then AFC will be:
AFC = TFC/Q = $1000/200 = $5
Therefore, as the output increases, the fixed cost is spread over a larger number of units, reducing the average fixed cost.
Conclusion:
In the short run, when the output of a firm increases, its average fixed cost decreases. Therefore, option 'B' is the correct answer.
Suppose the total cost production of a commodity ‘x’ is Rs. 1, 25,000 out of which Implicit cost is Rs. 35,000 and normal profit is Rs. 25,000. What would be the explicit cost of commodity x?- a)Rs. 90,000
- b)Rs. 65,000
- c)Rs. 1, 00,000
- d)Rs. 60,000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Suppose the total cost production of a commodity ‘x’ is Rs. 1, 25,000 out of which Implicit cost is Rs. 35,000 and normal profit is Rs. 25,000. What would be the explicit cost of commodity x?
a)
Rs. 90,000
b)
Rs. 65,000
c)
Rs. 1, 00,000
d)
Rs. 60,000

|
Arka Tiwari answered |
125000-25000-35000 = 65000 = explicit cost.
Total cost = implicit cost + explicit cost.
Total cost = implicit cost + explicit cost.
Calculate total cost of 4 units: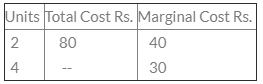
- a)140
- b)120
- c)50
- d)40
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate total cost of 4 units:
a)
140
b)
120
c)
50
d)
40

|
Manasvi Khemani answered |
MC=30 change in quantity = 2 MC =change in total cost÷change in output30=change in total cost, ÷ 230*2=change in TC60= change in TCSo, TC of 4 unit =TC of initial unit +change in TC80+60=140
Returns to scale will said to be in operation when quantity of: - a)All inputs are changed
- b)All inputs are changed in already established proportion
- c)All inputs are not changed
- d)One input is changed while quantity of all other inputs remain the same
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Returns to scale will said to be in operation when quantity of:
a)
All inputs are changed
b)
All inputs are changed in already established proportion
c)
All inputs are not changed
d)
One input is changed while quantity of all other inputs remain the same

|
Raghav Ghoshal answered |
Explanation:
Returns to scale is a concept that measures how the output of a production process changes when all inputs are changed. It refers to the relationship between the scale of production and the output produced.
Definition of Returns to Scale:
Returns to scale refers to the rate at which output increases when all inputs are increased by the same proportion.
Types of Returns to Scale:
There are three types of returns to scale:
1. Increasing returns to scale: When the output increases by more than the proportionate increase in all inputs.
2. Constant returns to scale: When the output increases by the same proportion as the increase in all inputs.
3. Decreasing returns to scale: When the output increases by less than the proportionate increase in all inputs.
Answer:
The correct answer is 'B'. When all inputs are changed in already established proportion, returns to scale will be in operation. This means that the rate at which output increases will be the same as the rate at which all inputs are increased.
Explanation of Other Options:
A) All inputs are changed: This option is not correct because it does not specify the proportion in which the inputs are changed.
C) All inputs are not changed: This option is not correct because returns to scale refers to the rate at which output changes when all inputs are changed.
D) One input is changed while the quantity of all other inputs remain the same: This option is not correct because returns to scale refers to the relationship between the scale of production and the output produced when all inputs are changed.
Returns to scale is a concept that measures how the output of a production process changes when all inputs are changed. It refers to the relationship between the scale of production and the output produced.
Definition of Returns to Scale:
Returns to scale refers to the rate at which output increases when all inputs are increased by the same proportion.
Types of Returns to Scale:
There are three types of returns to scale:
1. Increasing returns to scale: When the output increases by more than the proportionate increase in all inputs.
2. Constant returns to scale: When the output increases by the same proportion as the increase in all inputs.
3. Decreasing returns to scale: When the output increases by less than the proportionate increase in all inputs.
Answer:
The correct answer is 'B'. When all inputs are changed in already established proportion, returns to scale will be in operation. This means that the rate at which output increases will be the same as the rate at which all inputs are increased.
Explanation of Other Options:
A) All inputs are changed: This option is not correct because it does not specify the proportion in which the inputs are changed.
C) All inputs are not changed: This option is not correct because returns to scale refers to the rate at which output changes when all inputs are changed.
D) One input is changed while the quantity of all other inputs remain the same: This option is not correct because returns to scale refers to the relationship between the scale of production and the output produced when all inputs are changed.
A production function is defined as the relationship between ________.- a)The quantity of physical inputs and physical output of a firm
- b)Stock of inputs and stock of output
- c)Prices of inputs and output
- d)Price and supply of a firm.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A production function is defined as the relationship between ________.
a)
The quantity of physical inputs and physical output of a firm
b)
Stock of inputs and stock of output
c)
Prices of inputs and output
d)
Price and supply of a firm.
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
In simple words, production function refers to the functional relationship between the quantity of a good produced (output) and factors of production (inputs).
“The production function is purely a technical relation which connects factor inputs and output.” Prof. Koutsoyiannis
Defined production function as “the relation between a firm’s physical production (output) and the material factors of production (inputs).” Prof. Watson
In this way, production function reflects how much output we can expect if we have so much of labour and so much of capital as well as of labour etc. In other words, we can say that production function is an indicator of the physical relationship between the inputs and output of a firm.
The reason behind physical relationship is that money prices do not appear in it. However, here one thing that becomes most important to quote is that like demand function a production function is for a definite period.
It shows the flow of inputs resulting into a flow of output during some time.
A firm producers 10 units of a commodity at an average total cost of Rs. 200 and with a fixed cost of Rs. 500. Find out the component of average variable cost in the total cost:- a)Rs. 300
- b)Rs. 200
- c)Rs. 150
- d)Rs. 100
Correct answer is 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm producers 10 units of a commodity at an average total cost of Rs. 200 and with a fixed cost of Rs. 500. Find out the component of average variable cost in the total cost:
a)
Rs. 300
b)
Rs. 200
c)
Rs. 150
d)
Rs. 100

|
Ritika Iyer answered |
Given information:
- Number of units produced = 10
- Average total cost = Rs. 200
- Fixed cost = Rs. 500
To find out the component of average variable cost in the total cost, we need to calculate the average variable cost first.
Average variable cost (AVC) = Total variable cost / Number of units produced
Total cost = Total fixed cost + Total variable cost
Average total cost (ATC) = Total cost / Number of units produced
Since we know the value of ATC and fixed cost, we can calculate the value of total variable cost.
Total cost = Total fixed cost + Total variable cost
ATC * Number of units produced = Fixed cost + Total variable cost
Rs. 200 * 10 = Rs. 500 + Total variable cost
Total variable cost = Rs. 1500 - Rs. 500
Total variable cost = Rs. 1000
Now, we can calculate the value of AVC.
AVC = Total variable cost / Number of units produced
AVC = Rs. 1000 / 10
AVC = Rs. 100
Therefore, the component of average variable cost in the total cost is Rs. 150 (ATC - AVC).
Answer: Option (c) Rs. 150.
- Number of units produced = 10
- Average total cost = Rs. 200
- Fixed cost = Rs. 500
To find out the component of average variable cost in the total cost, we need to calculate the average variable cost first.
Average variable cost (AVC) = Total variable cost / Number of units produced
Total cost = Total fixed cost + Total variable cost
Average total cost (ATC) = Total cost / Number of units produced
Since we know the value of ATC and fixed cost, we can calculate the value of total variable cost.
Total cost = Total fixed cost + Total variable cost
ATC * Number of units produced = Fixed cost + Total variable cost
Rs. 200 * 10 = Rs. 500 + Total variable cost
Total variable cost = Rs. 1500 - Rs. 500
Total variable cost = Rs. 1000
Now, we can calculate the value of AVC.
AVC = Total variable cost / Number of units produced
AVC = Rs. 1000 / 10
AVC = Rs. 100
Therefore, the component of average variable cost in the total cost is Rs. 150 (ATC - AVC).
Answer: Option (c) Rs. 150.
Which curve is never U-shaped?- a)ATC curve
- b)AVC curve
- c)AFC curve
- d)MC curve
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which curve is never U-shaped?
a)
ATC curve
b)
AVC curve
c)
AFC curve
d)
MC curve

|
Mihir Banerjee answered |
Explanation:
The U-shaped curve is a characteristic of the average variable cost (AVC) and average total cost (ATC) curves. However, the average fixed cost (AFC) and marginal cost (MC) curves do not exhibit a U-shape.
Average Fixed Cost (AFC) Curve:
The average fixed cost (AFC) curve is a rectangular hyperbola. It slopes downwards to the right but never touches the horizontal axis. This is because fixed costs remain constant, no matter what the level of output is. Therefore, as output increases, the fixed cost per unit decreases. AFC is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost by the level of output.
AFC = Total Fixed Cost / Quantity
As the level of output increases, the denominator increases, and hence the AFC decreases. Since the curve slopes downwards to the right, it never exhibits a U-shape.
Marginal Cost (MC) Curve:
The marginal cost (MC) curve is the slope of the total cost (TC) curve. It shows the additional cost incurred in producing one more unit of output. MC is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in output.
MC = Change in Total Cost / Change in Quantity
The MC curve is U-shaped if the marginal product of labor (MPL) curve is diminishing. This is because the additional output produced by each additional unit of labor decreases, leading to an increase in marginal cost. However, if the MPL curve is increasing or constant, the MC curve is not U-shaped.
Conclusion:
The AFC and MC curves do not exhibit a U-shape, while the ATC and AVC curves do. This is because fixed costs do not change with the level of output, and the MC curve is not always affected by diminishing marginal returns.
The U-shaped curve is a characteristic of the average variable cost (AVC) and average total cost (ATC) curves. However, the average fixed cost (AFC) and marginal cost (MC) curves do not exhibit a U-shape.
Average Fixed Cost (AFC) Curve:
The average fixed cost (AFC) curve is a rectangular hyperbola. It slopes downwards to the right but never touches the horizontal axis. This is because fixed costs remain constant, no matter what the level of output is. Therefore, as output increases, the fixed cost per unit decreases. AFC is calculated by dividing the total fixed cost by the level of output.
AFC = Total Fixed Cost / Quantity
As the level of output increases, the denominator increases, and hence the AFC decreases. Since the curve slopes downwards to the right, it never exhibits a U-shape.
Marginal Cost (MC) Curve:
The marginal cost (MC) curve is the slope of the total cost (TC) curve. It shows the additional cost incurred in producing one more unit of output. MC is calculated by dividing the change in total cost by the change in output.
MC = Change in Total Cost / Change in Quantity
The MC curve is U-shaped if the marginal product of labor (MPL) curve is diminishing. This is because the additional output produced by each additional unit of labor decreases, leading to an increase in marginal cost. However, if the MPL curve is increasing or constant, the MC curve is not U-shaped.
Conclusion:
The AFC and MC curves do not exhibit a U-shape, while the ATC and AVC curves do. This is because fixed costs do not change with the level of output, and the MC curve is not always affected by diminishing marginal returns.
Average Fixed Cost = Rs. 20Quantity Produced = 10 units What will be the Average Fixed Cost of 20th unit?- a)Rs. 10
- b)Rs. 20
- c)Rs. 5
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Average Fixed Cost = Rs. 20Quantity Produced = 10 units What will be the Average Fixed Cost of 20th unit?
a)
Rs. 10
b)
Rs. 20
c)
Rs. 5
d)
None
|
|
Vivek Vivek answered |
AFC IS EQUAL AT ANY UNIT
SO AFC OF 20th UNIT=20
With fixed cost of Rs. 400, a firm has an average total cost of Rs. 3 and an average variable cost of Rs. 2.50. Its output is _________.- a)200 units
- b)400 units
- c)800 units
- d)1600 units
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
With fixed cost of Rs. 400, a firm has an average total cost of Rs. 3 and an average variable cost of Rs. 2.50. Its output is _________.
a)
200 units
b)
400 units
c)
800 units
d)
1600 units

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Average Total Costs = Rs.3
Average Variable Cost of Rs. 2.50
Average total costs = Average variable cost + Average Fixed Cost
Rs.3 = Rs.2.50 + AFC
AFC = Rs.3 - Rs.2.5
AFC = Rs.0.5
Average Fixed Cost = Total Fixed Cost/Total Quantity
Fixed Cost = Rs.400
AFC = Rs.0.5
Total No. of Quantity = Total Fixed Cost/AFC
Total No. of Quantity = Rs.400/0.5
Total No. of Quantity = 800 units
correct answer is 800 units.
correct answer is 800 units.
Average Revenue Curve is also known as _________.- a)Profit Curve
- b)Demand Curve.
- c)Supply Curve
- d)Average Cost Curve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Average Revenue Curve is also known as _________.
a)
Profit Curve
b)
Demand Curve.
c)
Supply Curve
d)
Average Cost Curve

|
Jyoti Nair answered |
Average Revenue Curve as Demand Curve
Definition: Average revenue is the revenue earned per unit of output sold. It is calculated by dividing the total revenue by the total quantity sold.
Average Revenue Curve: The average revenue curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the revenue earned per unit sold. It is a downward-sloping curve that reflects the law of demand, which states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases.
Relation with Demand Curve: The average revenue curve is also known as the demand curve because it shows the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices. It is the same as the demand curve because the price that consumers are willing to pay for a good or service is the same as the revenue that producers earn from selling that good or service.
Uses: The average revenue curve is an important tool for businesses to use in determining the optimal price to charge for their goods or services. By analyzing the relationship between price and quantity demanded, businesses can determine the price that will maximize their revenue and profitability.
Definition: Average revenue is the revenue earned per unit of output sold. It is calculated by dividing the total revenue by the total quantity sold.
Average Revenue Curve: The average revenue curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a good or service and the revenue earned per unit sold. It is a downward-sloping curve that reflects the law of demand, which states that as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded decreases.
Relation with Demand Curve: The average revenue curve is also known as the demand curve because it shows the quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices. It is the same as the demand curve because the price that consumers are willing to pay for a good or service is the same as the revenue that producers earn from selling that good or service.
Uses: The average revenue curve is an important tool for businesses to use in determining the optimal price to charge for their goods or services. By analyzing the relationship between price and quantity demanded, businesses can determine the price that will maximize their revenue and profitability.
External economies accrue due to ________:- a)Increasing returns to scale
- b)Increasing returns to factor
- c)Law of variable proportion
- d)Low cost
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
External economies accrue due to ________:
a)
Increasing returns to scale
b)
Increasing returns to factor
c)
Law of variable proportion
d)
Low cost

|
Saumya Khanna answered |
External economies due to increasing returns to scale
Definition: External economies refer to the benefits that are enjoyed by an entire industry or region as a result of the growth of a particular firm or industry.
Increasing returns to scale: Increasing returns to scale occur when the increase in the quantity of inputs used in production results in a more than proportionate increase in output. In other words, when a firm expands its production, its cost per unit of output decreases, and it becomes more efficient.
Explanation: When there is increasing returns to scale, the cost per unit of output decreases as the industry expands. This means that as the industry grows, the cost of production for every firm in the industry decreases. This, in turn, benefits the entire industry, and every firm operating in it.
For example, if the automobile industry in a particular region grows, there will be an increase in the demand for auto parts and services. This would result in a decrease in the cost of production and an increase in efficiency for all firms that produce auto parts and services in that region. This decrease in cost and increase in efficiency would benefit not only the firms but also the consumers, who would be able to buy auto parts and services at a lower cost.
Conclusion: Therefore, external economies accrue due to increasing returns to scale. As the industry grows, the cost of production decreases, and efficiency increases, benefiting the entire industry, and every firm operating in it.
Definition: External economies refer to the benefits that are enjoyed by an entire industry or region as a result of the growth of a particular firm or industry.
Increasing returns to scale: Increasing returns to scale occur when the increase in the quantity of inputs used in production results in a more than proportionate increase in output. In other words, when a firm expands its production, its cost per unit of output decreases, and it becomes more efficient.
Explanation: When there is increasing returns to scale, the cost per unit of output decreases as the industry expands. This means that as the industry grows, the cost of production for every firm in the industry decreases. This, in turn, benefits the entire industry, and every firm operating in it.
For example, if the automobile industry in a particular region grows, there will be an increase in the demand for auto parts and services. This would result in a decrease in the cost of production and an increase in efficiency for all firms that produce auto parts and services in that region. This decrease in cost and increase in efficiency would benefit not only the firms but also the consumers, who would be able to buy auto parts and services at a lower cost.
Conclusion: Therefore, external economies accrue due to increasing returns to scale. As the industry grows, the cost of production decreases, and efficiency increases, benefiting the entire industry, and every firm operating in it.
What will be the AFC of 2 units according to the table given below :
Output 0 1 2
Total cost (in Rs.) 580 689 850- a)105
- b)135
- c)235
- d)290
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the AFC of 2 units according to the table given below :
Output 0 1 2
Total cost (in Rs.) 580 689 850
Output 0 1 2
Total cost (in Rs.) 580 689 850
a)
105
b)
135
c)
235
d)
290

|
Niharika Joshi answered |
Calculation of Average Fixed Cost (AFC) of 2 units :
Given,
Total cost for producing 2 units = Rs. 850
Total cost for producing 1 unit = Rs. 689
Total fixed cost for producing 2 units = Total cost for producing 2 units - Total variable cost for producing 2 units
= Rs. 850 - (Rs. 689 x 2)
= Rs. 850 - Rs. 1378
= - Rs. 528
As total fixed cost can not be negative, it means there is some calculation error in the given table.
Therefore, the answer cannot be determined from the given table.
Given,
Total cost for producing 2 units = Rs. 850
Total cost for producing 1 unit = Rs. 689
Total fixed cost for producing 2 units = Total cost for producing 2 units - Total variable cost for producing 2 units
= Rs. 850 - (Rs. 689 x 2)
= Rs. 850 - Rs. 1378
= - Rs. 528
As total fixed cost can not be negative, it means there is some calculation error in the given table.
Therefore, the answer cannot be determined from the given table.
A forms AFC is Rs. 200 at 10 units of output what will be it at 20 units of output?- a)500
- b)100
- c)150
- d)200
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A forms AFC is Rs. 200 at 10 units of output what will be it at 20 units of output?
a)
500
b)
100
c)
150
d)
200

|
Lekshmi Mehta answered |
Calculation:
- AFC = Total Fixed Costs / Units of Output
- AFC at 10 units of output = Rs. 200 / 10 = Rs. 20
- AFC at 20 units of output = Rs. 200 / 20 = Rs. 10
Explanation:
- AFC stands for Average Fixed Cost, which is the fixed cost per unit of output.
- In this case, the AFC is given as Rs. 200 at 10 units of output, which means that the total fixed cost is Rs. 200 and the number of units produced is 10.
- To calculate the AFC at 20 units of output, we need to divide the total fixed cost by the number of units produced, which gives us Rs. 200 / 20 = Rs. 10.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which states that the AFC at 20 units of output is Rs. 10.
Conclusion:
- It is important to understand the concept of average fixed cost in order to solve this problem.
- By using the formula for AFC, we can easily calculate the fixed cost per unit of output at different levels of production.
- In this case, the AFC decreases as the number of units produced increases, which is a common trend in most production processes.
- AFC = Total Fixed Costs / Units of Output
- AFC at 10 units of output = Rs. 200 / 10 = Rs. 20
- AFC at 20 units of output = Rs. 200 / 20 = Rs. 10
Explanation:
- AFC stands for Average Fixed Cost, which is the fixed cost per unit of output.
- In this case, the AFC is given as Rs. 200 at 10 units of output, which means that the total fixed cost is Rs. 200 and the number of units produced is 10.
- To calculate the AFC at 20 units of output, we need to divide the total fixed cost by the number of units produced, which gives us Rs. 200 / 20 = Rs. 10.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option B, which states that the AFC at 20 units of output is Rs. 10.
Conclusion:
- It is important to understand the concept of average fixed cost in order to solve this problem.
- By using the formula for AFC, we can easily calculate the fixed cost per unit of output at different levels of production.
- In this case, the AFC decreases as the number of units produced increases, which is a common trend in most production processes.
As output increases, average fixed cost: - a)Remains constant
- b)Starts falling
- c)Start rising
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As output increases, average fixed cost:
a)
Remains constant
b)
Starts falling
c)
Start rising
d)
None

|
Geetika Basak answered |
Explanation:
Average fixed cost (AFC) is the total fixed cost divided by the quantity produced. As output increases, the total fixed cost remains fixed, but the average fixed cost decreases.
Reasons:
There are several reasons why average fixed cost decreases as output increases:
1. Spread Over a Larger Output: Fixed costs are spread over a larger number of units as output increases. This means that the average fixed cost per unit decreases.
2. Economies of Scale: As a firm produces more output, it may benefit from economies of scale. This means that the cost per unit of output decreases as output increases.
3. Specialization of Labor: As output increases, the firm may be able to specialize the work of its employees more effectively. This can lead to higher productivity and lower costs per unit of output.
Graphical Representation:
The graphical representation of the AFC curve is a rectangular hyperbola, which means that as output increases, AFC approaches zero but never reaches it.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, as output increases, average fixed cost decreases due to spreading fixed costs over a larger output, benefiting from economies of scale, and specialization of labor.
Average fixed cost (AFC) is the total fixed cost divided by the quantity produced. As output increases, the total fixed cost remains fixed, but the average fixed cost decreases.
Reasons:
There are several reasons why average fixed cost decreases as output increases:
1. Spread Over a Larger Output: Fixed costs are spread over a larger number of units as output increases. This means that the average fixed cost per unit decreases.
2. Economies of Scale: As a firm produces more output, it may benefit from economies of scale. This means that the cost per unit of output decreases as output increases.
3. Specialization of Labor: As output increases, the firm may be able to specialize the work of its employees more effectively. This can lead to higher productivity and lower costs per unit of output.
Graphical Representation:
The graphical representation of the AFC curve is a rectangular hyperbola, which means that as output increases, AFC approaches zero but never reaches it.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, as output increases, average fixed cost decreases due to spreading fixed costs over a larger output, benefiting from economies of scale, and specialization of labor.
Which of the following statements concerning the long-run average cost curve is false?- a)It represents the least-cost input combination for producing each level of output.
- b)It is derived from a series of short-run average cost curves.
- c)The short-run cost curve at the minimum point of the long-run average cost curve represents the least–cost plant size for all levels of output.
- d)As output increases, the amount of capital employed by the firm increases along the curve.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements concerning the long-run average cost curve is false?
a)
It represents the least-cost input combination for producing each level of output.
b)
It is derived from a series of short-run average cost curves.
c)
The short-run cost curve at the minimum point of the long-run average cost curve represents the least–cost plant size for all levels of output.
d)
As output increases, the amount of capital employed by the firm increases along the curve.

|
Ankita Mukherjee answered |
Ans.
Option

Cost in terms of pain, discomfort, disability involved in supplying the various factors of production by their owners are termed as________.- a)Social Cost
- b)Explicit Cost
- c)Real Cost
- d)Implicit Cost
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cost in terms of pain, discomfort, disability involved in supplying the various factors of production by their owners are termed as________.
a)
Social Cost
b)
Explicit Cost
c)
Real Cost
d)
Implicit Cost
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
REAL COST
The overall actual expense involved in creating a good or service for sale to consumers. The real cost of production for a business typically includes the value of all tangible resources such as raw materials and labor that are used in the production process.
The overall actual expense involved in creating a good or service for sale to consumers. The real cost of production for a business typically includes the value of all tangible resources such as raw materials and labor that are used in the production process.
Marginal cost changes due to change in ________ cost.- a)Total
- b)Fixed
- c)Average
- d)Variable
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Marginal cost changes due to change in ________ cost.
a)
Total
b)
Fixed
c)
Average
d)
Variable
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Although the marginal cost measures the change in the total cost with respect to a change in the production output level, a change in fixed costs does not affect the marginal cost. For example, if there are only fixed costs associated with producing goods, the marginal cost of production is zero. If the fixed costs were to double, the marginal cost of production is still zero. The change in the total cost is always equal to zero when there is an absence of variable costs. The marginal cost of production measures the change in total cost with respect to a change in production levels and fixed costs do not change with production levels.
However, the marginal cost of production is affected when there are variable costs associated with production. For example, suppose the fixed costs for a computer manufacturer are $100, and the cost of producing computers is variable. The total cost of production for 20 computers is $1,100. The total cost for producing 21 computers is $1,120. Therefore, the marginal cost of producing computer 21 is $20.
Chapter doubts & questions for Theory of Production and Cost - Business Economics for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Theory of Production and Cost - Business Economics for CA Foundation in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Business Economics for CA Foundation
86 videos|200 docs|58 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup














