All Exams >
CA Foundation >
Business Economics for CA Foundation >
All Questions
All questions of Price Determination in Different Markets for CA Foundation Exam
In monopolistic competition excess capacity in the firm _______.
a)Never Existsb)Sometimes Existsc)Always Existsd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Excess capacity refers to a situation where a firm is producing at a lower scale of output than it has been designed for. Context: ... It may arise because as demand increases, firms have to invest and expand capacity in lumpy or indivisible portions.
Under which Market Situation demand curve is linear and parallel to X-axis:- a)Perfect competition
- b)Monopoly
- c)Monopolistic Competition
- d)Oligopoly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Under which Market Situation demand curve is linear and parallel to X-axis:
a)
Perfect competition
b)
Monopoly
c)
Monopolistic Competition
d)
Oligopoly

|
Anand Dasgupta answered |
The demand curve under perfect competition is a horizontal linear line parallel to x-axis which means that the price of the commodity remains the same and any amount of quantity can be sold at this prevailing price in the market but a little variation in the price will lead to a fall in demand to zero.
Under Monopolistic competition the cross elasticity of demand for the product of a single firm would be: - a)Infinite
- b)Highly elastic
- c)Highly inelastic
- d)Zero
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Under Monopolistic competition the cross elasticity of demand for the product of a single firm would be:
a)
Infinite
b)
Highly elastic
c)
Highly inelastic
d)
Zero
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
The cross elasticity of demand for the product of a monopolist with respect to a fall in the price of the other products in the economy is very low or zero.
In monopolistic competition the cross elasticity of demand for the product of a single firm with respect to a change in the price of other products made in the monopolistic ‘group’ is very high.
If the price of crackers goes up when the price of cheese goes down, crackers and cheese are
a)complements.b)substitutes.
c)both substitutes and complements.d)inferior goods.Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
A complementary good is a good whose use is related to the use of an associated or paired good. Two goods (A and B) are complementary if using more of good A requires the use of more of good B. For example, the demand for one good (printers) generates demand for the other (ink cartridges).
Assume that when price is Rs. 20, quantity demanded is 9 units, and when price is Rs. 19, quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units.- a)Rs. 20
- b)Rs. 19
- c)Rs. 10
- d)Re. 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that when price is Rs. 20, quantity demanded is 9 units, and when price is Rs. 19, quantity demanded is 10 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 9 units to 10 units.
a)
Rs. 20
b)
Rs. 19
c)
Rs. 10
d)
Re. 1
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
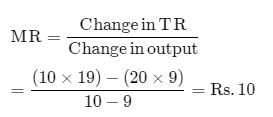
If a seller obtains Rs. 3,000 after selling 50 units and Rs. 3,100 after selling 52 units, then marginal revenue will be- a)Rs. 59.62
- b)Rs. 50.00
- c)Rs. 60.00
- d)Rs. 59.80
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a seller obtains Rs. 3,000 after selling 50 units and Rs. 3,100 after selling 52 units, then marginal revenue will be
a)
Rs. 59.62
b)
Rs. 50.00
c)
Rs. 60.00
d)
Rs. 59.80

|
Srsps answered |
The marginal revenue (MR) is calculated as the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity sold. In this case, the total revenue changes from Rs. 3,000 to Rs. 3,100 as the quantity sold increases from 50 to 52 units. Therefore, the marginal revenue is (3,100 - 3,000) / (52 - 50) = Rs. 50.00. The correct answer is indeed option 2.
Assume that when price is Rs.20, quantity demanded is 15 units, and when price is Rs.18, quantity demanded is 16 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 15 units to 16 units?- a)Rs. 18
- b)Rs. 16
- c)Rs. 12
- d)Rs. 28
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that when price is Rs.20, quantity demanded is 15 units, and when price is Rs.18, quantity demanded is 16 units. Based on this information, what is the marginal revenue resulting from an increase in output from 15 units to 16 units?
a)
Rs. 18
b)
Rs. 16
c)
Rs. 12
d)
Rs. 28

|
Nitin Kumar answered |
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned by producing and selling one more unit of output. It is calculated as the change in total revenue divided by the change in quantity.
Given that when the price is Rs.20, the quantity demanded is 15 units, and when the price is Rs.18, the quantity demanded is 16 units.
To calculate marginal revenue, we need to first calculate the total revenue at each level of output.
At a price of Rs.20, the total revenue is 20 x 15 = Rs.300
At a price of Rs.18, the total revenue is 18 x 16 = Rs.288
The change in total revenue from producing one more unit of output is Rs.288 - Rs.300 = -Rs.12
The change in quantity is 16 - 15 = 1
Therefore, the marginal revenue is -Rs.12/1 = -Rs.12
Hence, the correct answer is option C, which is Rs.12.
Given that when the price is Rs.20, the quantity demanded is 15 units, and when the price is Rs.18, the quantity demanded is 16 units.
To calculate marginal revenue, we need to first calculate the total revenue at each level of output.
At a price of Rs.20, the total revenue is 20 x 15 = Rs.300
At a price of Rs.18, the total revenue is 18 x 16 = Rs.288
The change in total revenue from producing one more unit of output is Rs.288 - Rs.300 = -Rs.12
The change in quantity is 16 - 15 = 1
Therefore, the marginal revenue is -Rs.12/1 = -Rs.12
Hence, the correct answer is option C, which is Rs.12.
Which of the following falls under micro economics?- a)National income
- b)General price level
- c)Factor pricing
- d)National saving and investment
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following falls under micro economics?
a)
National income
b)
General price level
c)
Factor pricing
d)
National saving and investment

|
Dhruba Choudhary answered |
Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics
Before answering the question, it is important to understand the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics is the study of individual economic agents such as households, firms, and markets, while macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including issues such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Answer
Out of the options given, factor pricing falls under microeconomics.
Explanation
Factor pricing refers to the determination of the prices of factors of production such as labor, capital, and land. It is a study of how markets allocate resources and how the prices of goods and services are determined. This falls under the purview of microeconomics as it deals with the behavior of individual firms and households in the market.
In contrast, national income, general price level, and national saving and investment are macroeconomic concepts as they deal with the overall performance of the economy as a whole. National income refers to the total value of goods and services produced in a country in a given period, while general price level refers to the average level of prices of goods and services in the economy. National saving and investment refer to the total amount of savings and investments made by the entire economy.
Conclusion
In summary, factor pricing falls under microeconomics as it deals with the behavior of individual firms and households in the market. The other options, national income, general price level, and national saving and investment, fall under macroeconomics as they deal with the overall performance of the economy as a whole.
Before answering the question, it is important to understand the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics is the study of individual economic agents such as households, firms, and markets, while macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole, including issues such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
Answer
Out of the options given, factor pricing falls under microeconomics.
Explanation
Factor pricing refers to the determination of the prices of factors of production such as labor, capital, and land. It is a study of how markets allocate resources and how the prices of goods and services are determined. This falls under the purview of microeconomics as it deals with the behavior of individual firms and households in the market.
In contrast, national income, general price level, and national saving and investment are macroeconomic concepts as they deal with the overall performance of the economy as a whole. National income refers to the total value of goods and services produced in a country in a given period, while general price level refers to the average level of prices of goods and services in the economy. National saving and investment refer to the total amount of savings and investments made by the entire economy.
Conclusion
In summary, factor pricing falls under microeconomics as it deals with the behavior of individual firms and households in the market. The other options, national income, general price level, and national saving and investment, fall under macroeconomics as they deal with the overall performance of the economy as a whole.
Price discrimination is possible only when. - a)Goods are homogeneous
- b)Seller is alone
- c)Market is controlled by the government
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Price discrimination is possible only when.
a)
Goods are homogeneous
b)
Seller is alone
c)
Market is controlled by the government
d)
None of the above

|
Sparsh Chauhan answered |
The correct option is Option A.
Price discrimination is when the same good is sold at different prices to different consumers.
Price discrimination occur only under imperfect markets such as Monopoly, Oligopoly, Monopolistic competition etc.
It cannot occur under Perfect competition market structure as there are a large number of buyers. So if a firm charges a higher price the consumer will go to the other sellers.
The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly assumes that- a)response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease.
- b)response to a price increase is more than the response to a price decrease.
- c)elasticity of demand is constant regardless of whether price increases or decreases.
- d)elasticity of demand is perfectly elastic if price increases and perfectly inelastic if price decreases.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly assumes that
a)
response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease.
b)
response to a price increase is more than the response to a price decrease.
c)
elasticity of demand is constant regardless of whether price increases or decreases.
d)
elasticity of demand is perfectly elastic if price increases and perfectly inelastic if price decreases.
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
The oligopolist faces a kinked‐demand curve because of competition from other oligopolists in the market. If the oligopolist increases its price above the equilibrium price P, it is assumed that the other oligopolists in the market will not follow with price increases of their own.
Market which have two firms are known as: - a)Oligopoly
- b)Duopoly
- c)Monopsony
- d)Oligopsony
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Market which have two firms are known as:
a)
Oligopoly
b)
Duopoly
c)
Monopsony
d)
Oligopsony

|
Divya Dasgupta answered |
Duopoly Market
A duopoly market is a market in which two firms dominate the market. In this market, the actions of one firm have a significant impact on the other firm. The main characteristics of a duopoly market are:
1. Interdependence: The two firms in a duopoly market are interdependent. This means that the decisions of one firm affect the decisions of the other firm.
2. Competition: The two firms in a duopoly market compete with each other. They try to gain a larger market share by offering better products or services.
3. Barriers to entry: There are significant barriers to entry in a duopoly market. This makes it difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete with the existing firms.
Examples of Duopoly Markets
Some examples of duopoly markets are:
1. Soft drinks: Coca-Cola and PepsiCo dominate the soft drinks market.
2. Aircraft manufacturing: Boeing and Airbus dominate the aircraft manufacturing market.
3. Operating systems: Microsoft and Apple dominate the operating systems market.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Duopoly Markets
Advantages of duopoly markets are:
1. Innovation: The two firms in a duopoly market are motivated to innovate and improve their products or services to gain a larger market share.
2. Competitive pricing: The two firms in a duopoly market compete with each other, which can lead to competitive pricing.
Disadvantages of duopoly markets are:
1. Limited choices: Consumers have limited choices in a duopoly market, as there are only two firms dominating the market.
2. Collusion: The two firms in a duopoly market may collude to fix prices or limit production, which can harm consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a market which has two firms dominating it is known as a duopoly market. In this market, the two firms are interdependent and compete with each other. There are significant barriers to entry in a duopoly market, which can limit competition. Duopoly markets have advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to weigh them before making any decision.
A duopoly market is a market in which two firms dominate the market. In this market, the actions of one firm have a significant impact on the other firm. The main characteristics of a duopoly market are:
1. Interdependence: The two firms in a duopoly market are interdependent. This means that the decisions of one firm affect the decisions of the other firm.
2. Competition: The two firms in a duopoly market compete with each other. They try to gain a larger market share by offering better products or services.
3. Barriers to entry: There are significant barriers to entry in a duopoly market. This makes it difficult for new firms to enter the market and compete with the existing firms.
Examples of Duopoly Markets
Some examples of duopoly markets are:
1. Soft drinks: Coca-Cola and PepsiCo dominate the soft drinks market.
2. Aircraft manufacturing: Boeing and Airbus dominate the aircraft manufacturing market.
3. Operating systems: Microsoft and Apple dominate the operating systems market.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Duopoly Markets
Advantages of duopoly markets are:
1. Innovation: The two firms in a duopoly market are motivated to innovate and improve their products or services to gain a larger market share.
2. Competitive pricing: The two firms in a duopoly market compete with each other, which can lead to competitive pricing.
Disadvantages of duopoly markets are:
1. Limited choices: Consumers have limited choices in a duopoly market, as there are only two firms dominating the market.
2. Collusion: The two firms in a duopoly market may collude to fix prices or limit production, which can harm consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a market which has two firms dominating it is known as a duopoly market. In this market, the two firms are interdependent and compete with each other. There are significant barriers to entry in a duopoly market, which can limit competition. Duopoly markets have advantages and disadvantages, and it is important to weigh them before making any decision.
Mixed economy means:- a)Coexistence of both private and public sector
- b)Coexistence of poor and rich people
- c)Both (a) and (b)
- d)None.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mixed economy means:
a)
Coexistence of both private and public sector
b)
Coexistence of poor and rich people
c)
Both (a) and (b)
d)
None.

|
Sparsh Chauhan answered |
Mixed economy means the coexistence of both the private and public sectors in an economy. In other words, it is an economic system where both the market forces and the government play important roles in the allocation and distribution of resources.
Private sector
The private sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and operated by individuals or companies for profit. This includes businesses such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. In a mixed economy, the private sector plays a vital role in creating jobs, producing goods and services, and generating economic growth.
Public sector
The public sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and operated by the government. This includes government agencies, public utilities, and other government-run organizations. In a mixed economy, the government plays a crucial role in providing essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development.
Benefits of a mixed economy
1. Economic growth: A mixed economy allows for a significant level of economic growth as it provides a balance between the private sector's profit motive and the government's social welfare objectives.
2. Job creation: As both the private and public sectors are involved in the economy, there are more opportunities for job creation, leading to reduced unemployment rates.
3. Social welfare: The government's involvement in a mixed economy ensures that essential services such as healthcare and education are accessible to all, regardless of their financial status.
4. Innovation: The private sector's profit motive encourages innovation and new product development, leading to increased competition and a better standard of living.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mixed economy is an economic system that combines elements of both the private and public sectors to provide a balance between economic growth and social welfare. It provides opportunities for job creation, innovation, and essential services, making it a popular economic system worldwide.
Private sector
The private sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and operated by individuals or companies for profit. This includes businesses such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. In a mixed economy, the private sector plays a vital role in creating jobs, producing goods and services, and generating economic growth.
Public sector
The public sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and operated by the government. This includes government agencies, public utilities, and other government-run organizations. In a mixed economy, the government plays a crucial role in providing essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development.
Benefits of a mixed economy
1. Economic growth: A mixed economy allows for a significant level of economic growth as it provides a balance between the private sector's profit motive and the government's social welfare objectives.
2. Job creation: As both the private and public sectors are involved in the economy, there are more opportunities for job creation, leading to reduced unemployment rates.
3. Social welfare: The government's involvement in a mixed economy ensures that essential services such as healthcare and education are accessible to all, regardless of their financial status.
4. Innovation: The private sector's profit motive encourages innovation and new product development, leading to increased competition and a better standard of living.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a mixed economy is an economic system that combines elements of both the private and public sectors to provide a balance between economic growth and social welfare. It provides opportunities for job creation, innovation, and essential services, making it a popular economic system worldwide.
In a perfectly competitive market the demand curve of a firm is:-- a)Elastic
- b)Perfectly elastic
- c)Inelastic
- d)Perfectly inelastic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a perfectly competitive market the demand curve of a firm is:-
a)
Elastic
b)
Perfectly elastic
c)
Inelastic
d)
Perfectly inelastic

|
Tanya Mishra answered |
As AR curve is parallel to x axis due to constant price thus it is perfectly elastic
The demand curve of oligopoly is: - a)Horizontal
- b)Vertical
- c)Kinked
- d)Rising left to right
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The demand curve of oligopoly is:
a)
Horizontal
b)
Vertical
c)
Kinked
d)
Rising left to right

|
Arnab Nambiar answered |
In an oligopolistic market, the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease.
An increase in supply with unchanged demand leads to:- a)Rise in price and fall in quantity
- b)Fall in both price and quantity
- c)Rise in both price and quantity
- d)Fall in price and rise in quantity
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An increase in supply with unchanged demand leads to:
a)
Rise in price and fall in quantity
b)
Fall in both price and quantity
c)
Rise in both price and quantity
d)
Fall in price and rise in quantity

|
Nilanjan Saha answered |
Explanation:
When there is an increase in supply with unchanged demand, the market equilibrium shifts to the right, which means that the supply curve shifts to the right. This creates a situation where there is more supply than demand in the market. The following are the possible outcomes:
Fall in price: When there is an excess supply of goods, suppliers tend to lower the price of their goods to attract more buyers. This leads to a fall in the price of the goods.
Rise in quantity: When the price of goods falls, buyers tend to buy more of the goods. This leads to a rise in the quantity demanded of the goods.
Rise in quantity supplied: Suppliers tend to increase their supply of goods in response to the fall in price. This leads to a rise in the quantity supplied of the goods.
Fall in price and rise in quantity: The above outcomes lead to a fall in price and a rise in quantity supplied and demanded. This is represented by a movement along the demand and supply curve.
Therefore, the correct answer is 'D' - Fall in price and rise in quantity.
When there is an increase in supply with unchanged demand, the market equilibrium shifts to the right, which means that the supply curve shifts to the right. This creates a situation where there is more supply than demand in the market. The following are the possible outcomes:
Fall in price: When there is an excess supply of goods, suppliers tend to lower the price of their goods to attract more buyers. This leads to a fall in the price of the goods.
Rise in quantity: When the price of goods falls, buyers tend to buy more of the goods. This leads to a rise in the quantity demanded of the goods.
Rise in quantity supplied: Suppliers tend to increase their supply of goods in response to the fall in price. This leads to a rise in the quantity supplied of the goods.
Fall in price and rise in quantity: The above outcomes lead to a fall in price and a rise in quantity supplied and demanded. This is represented by a movement along the demand and supply curve.
Therefore, the correct answer is 'D' - Fall in price and rise in quantity.
Price taker firms _________- a)Do not advertise their product because it misleads the customers
- b)Advertise their products to boost the level of demand
- c)Do not advertise but give gifts along with the sold items to attract customers
- d)Do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Price taker firms _________
a)
Do not advertise their product because it misleads the customers
b)
Advertise their products to boost the level of demand
c)
Do not advertise but give gifts along with the sold items to attract customers
d)
Do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
What is a 'Price-Taker' ... All economic participants are considered to be price-takers in a market of perfect competition, or one in which all companies sell an identical product, there are no barriers to entry or exit, every company has a relatively small market share, and all buyers have full information of the market.
Under ________ market condition, firms make normal profit in the long run:- a)Perfect competition
- b)Monopoly
- c)Oligopoly
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Under ________ market condition, firms make normal profit in the long run:
a)
Perfect competition
b)
Monopoly
c)
Oligopoly
d)
None

|
Vaishnavi Joshi answered |
Perfect Competition and Normal Profit:
Perfect competition is a market situation where there are a large number of buyers and sellers, and every seller sells an identical product. In a perfectly competitive market, firms make normal profit in the long run.
Normal profit refers to the minimum amount of profit required to keep the firm in business. It is the opportunity cost of the resources used in the production process. In other words, normal profit is the cost of the entrepreneur's time and effort in managing the business.
Under perfect competition, firms earn normal profit in the long run because of the following reasons:
1. No Entry Barriers: In a perfectly competitive market, there are no entry barriers. Any firm can enter or exit the market without incurring any costs. This means that if a firm is making supernormal profit, new firms will enter the market, and the supply will increase, reducing the price and profit margins of the existing firms.
2. Homogeneous Product: In a perfectly competitive market, all firms sell an identical product. This means that consumers do not have any preferences for a particular brand or product. As a result, firms cannot charge a higher price than their competitors, and the price is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
3. Perfect Information: In a perfectly competitive market, all firms and consumers have perfect information about the price and quality of the product. This means that firms cannot charge a higher price than their competitors, and consumers can easily switch to another firm if they find a better deal.
4. No Market Power: In a perfectly competitive market, no firm has market power. This means that firms cannot influence the price of the product by their actions. They have to accept the market price, which is determined by the forces of demand and supply.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, under perfect competition, firms make normal profit in the long run because of the absence of entry barriers, the homogeneity of the product, perfect information, and the absence of market power. This means that firms cannot earn supernormal profit, which is the excess of revenue over the opportunity cost of resources used in the production process.
Perfect competition is a market situation where there are a large number of buyers and sellers, and every seller sells an identical product. In a perfectly competitive market, firms make normal profit in the long run.
Normal profit refers to the minimum amount of profit required to keep the firm in business. It is the opportunity cost of the resources used in the production process. In other words, normal profit is the cost of the entrepreneur's time and effort in managing the business.
Under perfect competition, firms earn normal profit in the long run because of the following reasons:
1. No Entry Barriers: In a perfectly competitive market, there are no entry barriers. Any firm can enter or exit the market without incurring any costs. This means that if a firm is making supernormal profit, new firms will enter the market, and the supply will increase, reducing the price and profit margins of the existing firms.
2. Homogeneous Product: In a perfectly competitive market, all firms sell an identical product. This means that consumers do not have any preferences for a particular brand or product. As a result, firms cannot charge a higher price than their competitors, and the price is determined by the market forces of demand and supply.
3. Perfect Information: In a perfectly competitive market, all firms and consumers have perfect information about the price and quality of the product. This means that firms cannot charge a higher price than their competitors, and consumers can easily switch to another firm if they find a better deal.
4. No Market Power: In a perfectly competitive market, no firm has market power. This means that firms cannot influence the price of the product by their actions. They have to accept the market price, which is determined by the forces of demand and supply.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, under perfect competition, firms make normal profit in the long run because of the absence of entry barriers, the homogeneity of the product, perfect information, and the absence of market power. This means that firms cannot earn supernormal profit, which is the excess of revenue over the opportunity cost of resources used in the production process.
A competitive firm in the short run incure losses. The firm continue production, if:- a)P>AVC
- b)P=AVC
- c)P<AVC
- d)P>=AVC
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A competitive firm in the short run incure losses. The firm continue production, if:
a)
P>AVC
b)
P=AVC
c)
P<AVC
d)
P>=AVC

|
Gopal Sen answered |
Is greater than AVC
b)P is greater than ATC
c)P is greater than MC
d)All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
Explanation:
In the short run, a competitive firm will incur losses if its total revenue (TR) is less than its total variable costs (TVC). However, the firm may still continue production if it can cover its variable costs and contribute towards covering its fixed costs.
a) If P is greater than AVC (average variable cost), the firm can cover its variable costs and may continue production to contribute towards covering its fixed costs.
b) If P is greater than ATC (average total cost), the firm can cover both its variable and fixed costs and may continue production.
c) If P is greater than MC (marginal cost), the firm is generating revenue that is greater than the additional cost of producing one more unit and may continue production to maximize its profits.
Therefore, if any of the above conditions are met, the firm may continue production despite incurring losses in the short run.
b)P is greater than ATC
c)P is greater than MC
d)All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
Explanation:
In the short run, a competitive firm will incur losses if its total revenue (TR) is less than its total variable costs (TVC). However, the firm may still continue production if it can cover its variable costs and contribute towards covering its fixed costs.
a) If P is greater than AVC (average variable cost), the firm can cover its variable costs and may continue production to contribute towards covering its fixed costs.
b) If P is greater than ATC (average total cost), the firm can cover both its variable and fixed costs and may continue production.
c) If P is greater than MC (marginal cost), the firm is generating revenue that is greater than the additional cost of producing one more unit and may continue production to maximize its profits.
Therefore, if any of the above conditions are met, the firm may continue production despite incurring losses in the short run.
Which one of the following statement is Incorrect?- a)Competitive firms are price takers and not price makers
- b)Price discrimination is possible in monopoly only
- c)Duopoly may lead to monopoly
- d)Competitive firm always seeks to discriminate prices
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is Incorrect?
a)
Competitive firms are price takers and not price makers
b)
Price discrimination is possible in monopoly only
c)
Duopoly may lead to monopoly
d)
Competitive firm always seeks to discriminate prices

|
Freedom Institute answered |
Explanation:The incorrect statement is:D: Competitive firm always seeks to discriminate pricesHere's why the other statements are correct:A: Competitive firms are price takers and not price makers- In a perfectly competitive market, individual firms have no control over the market price.- They must accept the market price as given and adjust their output levels accordingly.B: Price discrimination is possible in monopoly only- Price discrimination occurs when a firm charges different prices to different consumers for the same good or service.- This is possible in a monopoly because the firm has market power and can control the price of the product.- In competitive markets, firms cannot practice price discrimination as they have no control over the market price.C: Duopoly may lead to monopoly- A duopoly is a market structure where there are only two firms dominating the market.- If one firm acquires the other or if the two firms collude to act as a single entity, the market structure can transition into a monopoly.
In the long run monopolist can - a)Incur losses
- b)Must earn super normal profits
- c)Wants to shut-down
- d)Earns only normal profits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the long run monopolist can
a)
Incur losses
b)
Must earn super normal profits
c)
Wants to shut-down
d)
Earns only normal profits

|
Srsps answered |
As you can see above, there are two alternative cases for the determination of Equilibrium in Monopoly:
- With normal profits
- With super-normal profits
Given, AR = 5 and Elasticity of demand = 2 Find MR.- a)+2.5
- b)-2.5
- c)+1.5
- d)+2.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given, AR = 5 and Elasticity of demand = 2 Find MR.
a)
+2.5
b)
-2.5
c)
+1.5
d)
+2.0

|
Ayush Mishra answered |
MR=AR(e -1)/e =5(2-1)/2 =2.5
__________ is the price at which demand for a commodity is equal to its supply: - a)Normal Price
- b)Equilibrium Price
- c)Short run Price
- d)Secular Price
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
__________ is the price at which demand for a commodity is equal to its supply:
a)
Normal Price
b)
Equilibrium Price
c)
Short run Price
d)
Secular Price

|
Pallabi Khanna answered |
The price at which quantity demanded of a commodity is equal to its quantity supplied is called the equilibrium price.
In market, the price and output equilibrium is determined on the basis of:- a)Total revenue and total cost
- b)Total cost and marginal cost
- c)Marginal revenue and marginal cost
- d)Only marginal cost.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In market, the price and output equilibrium is determined on the basis of:
a)
Total revenue and total cost
b)
Total cost and marginal cost
c)
Marginal revenue and marginal cost
d)
Only marginal cost.
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
In a perfectly competitive market, price equals marginal cost and firms earn an economic profit of zero. In a monopoly, the price is set above marginal cost and the firm earns a positive economic profit. Perfect competition produces an equilibrium in which the price and quantity of a good is economically efficient.
Competitive firms in the long run earn: - a)Super normal profit
- b)Normal profit
- c)Losses
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Competitive firms in the long run earn:
a)
Super normal profit
b)
Normal profit
c)
Losses
d)
None

|
Mahesh Chakraborty answered |
In the long run, with the entry of new firms in the industry, the price of the product will go down as a result of the increase in supply of output and also the cost will go up as a result of more intensive competition for factors of production. The firms will continue entering the industry until the price is equal to average cost so that all firms are earning only normal profits.
MR of n the unit is given by: - a)TRn/ TRn-1
- b)TRn + TRn-1
- c)TRn - TRn-1
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
MR of n the unit is given by:
a)
TRn/ TRn-1
b)
TRn + TRn-1
c)
TRn - TRn-1
d)
All of these
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
The dalton, symbol Da, is also sometimes used as a unit of molar mass, especially in biochemistry, with the definition 1 Da = 1 g/mol, despite the fact that it is strictly a unit of mass (1 Da = 1 u = 1.660 538 921(73)X10−27 kg).
Profits of the firm will be more at:
- a)MR=MC
- b)Additional revenue from extra unit equals its additional cost
- c)Both of above
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Profits of the firm will be more at:
a)
MR=MC
b)
Additional revenue from extra unit equals its additional cost
c)
Both of above
d)
None

|
Ruchi Mishra answered |
Profit Maximization at MR=MC
When a firm is producing a certain level of output, it aims to maximize its profits. The firm can achieve profit maximization at the point where its Marginal Revenue (MR) equals Marginal Cost (MC). This is the point where the firm can earn the maximum amount of profit.
Explanation:
MR is the additional revenue earned by the firm by selling one more unit of output. MC is the additional cost incurred by the firm by producing one more unit of output. A firm can increase its profits by increasing its output until MR equals MC. At this point, the firm is producing the exact amount of output where the additional revenue earned by producing one more unit is equal to the additional cost incurred by producing one more unit.
If the firm produces less than the point where MR equals MC, then producing one more unit will increase its revenue more than its cost, so the firm can increase its profits by producing more. But if the firm produces more than the point where MR equals MC, then producing one more unit will increase its cost more than its revenue, so the firm can increase its profits by producing less.
Therefore, it is important for a firm to produce at the point where MR equals MC to maximize its profits. This is because at this point, the firm is producing the exact amount of output where the additional revenue earned is equal to the additional cost incurred, so the firm can earn the maximum amount of profit.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A', i.e., profits of the firm will be more at MR=MC.
When a firm is producing a certain level of output, it aims to maximize its profits. The firm can achieve profit maximization at the point where its Marginal Revenue (MR) equals Marginal Cost (MC). This is the point where the firm can earn the maximum amount of profit.
Explanation:
MR is the additional revenue earned by the firm by selling one more unit of output. MC is the additional cost incurred by the firm by producing one more unit of output. A firm can increase its profits by increasing its output until MR equals MC. At this point, the firm is producing the exact amount of output where the additional revenue earned by producing one more unit is equal to the additional cost incurred by producing one more unit.
If the firm produces less than the point where MR equals MC, then producing one more unit will increase its revenue more than its cost, so the firm can increase its profits by producing more. But if the firm produces more than the point where MR equals MC, then producing one more unit will increase its cost more than its revenue, so the firm can increase its profits by producing less.
Therefore, it is important for a firm to produce at the point where MR equals MC to maximize its profits. This is because at this point, the firm is producing the exact amount of output where the additional revenue earned is equal to the additional cost incurred, so the firm can earn the maximum amount of profit.
Conclusion:
Hence, the correct answer is option 'A', i.e., profits of the firm will be more at MR=MC.
Price taker firms _________- a)Do not advertise their product because it misleads the customers
- b)Advertise their products to boost the level of demand
- c)Do not advertise but give gifts along with the sold items to attract customers
- d)Do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Price taker firms _________
a)
Do not advertise their product because it misleads the customers
b)
Advertise their products to boost the level of demand
c)
Do not advertise but give gifts along with the sold items to attract customers
d)
Do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price

|
Dipika Kaur answered |
Price taker firms do not advertise because they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price.
Price taker firms are firms that operate in perfectly competitive markets. In such markets, there are numerous buyers and sellers, and no single firm has the power to influence the market price. As a result, price taker firms have to accept the market price as given and adjust their output accordingly. This means that they have no control over the price at which they sell their products.
Reasons why price taker firms do not advertise:
1. No control over price: Price taker firms cannot set the price for their products. They have to accept the prevailing market price, which is determined by the overall supply and demand in the market. Since advertising typically involves promoting products at a specific price, it would be futile for price taker firms to advertise because they cannot guarantee that the advertised price will align with the market price.
2. Perfect competition: Perfectly competitive markets have many firms selling homogeneous products. In such markets, consumers are price sensitive and are likely to choose the product with the lowest price. Price taker firms, therefore, compete solely on price. Advertising would not provide any competitive advantage as it would not influence the price or product differentiation.
3. Unnecessary cost: Advertising can be expensive, especially for firms with limited resources. Price taker firms, which operate on thin profit margins, may not have the financial capacity to invest in advertising. Since they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price, there is no need for them to incur additional costs on advertising.
4. Word-of-mouth and reputation: In perfectly competitive markets, reputation and word-of-mouth play a crucial role in attracting customers. If a price taker firm consistently offers high-quality products at competitive prices, it is likely to build a positive reputation among customers. This reputation can lead to customer loyalty and word-of-mouth referrals, which can drive sales without the need for advertising.
In conclusion, price taker firms do not advertise because they have no control over the price, operate in perfectly competitive markets, and can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price. Advertising would not provide any competitive advantage and would be an unnecessary cost for these firms. They rely on reputation and word-of-mouth to attract customers in their quest to maximize sales and profits.
Price taker firms are firms that operate in perfectly competitive markets. In such markets, there are numerous buyers and sellers, and no single firm has the power to influence the market price. As a result, price taker firms have to accept the market price as given and adjust their output accordingly. This means that they have no control over the price at which they sell their products.
Reasons why price taker firms do not advertise:
1. No control over price: Price taker firms cannot set the price for their products. They have to accept the prevailing market price, which is determined by the overall supply and demand in the market. Since advertising typically involves promoting products at a specific price, it would be futile for price taker firms to advertise because they cannot guarantee that the advertised price will align with the market price.
2. Perfect competition: Perfectly competitive markets have many firms selling homogeneous products. In such markets, consumers are price sensitive and are likely to choose the product with the lowest price. Price taker firms, therefore, compete solely on price. Advertising would not provide any competitive advantage as it would not influence the price or product differentiation.
3. Unnecessary cost: Advertising can be expensive, especially for firms with limited resources. Price taker firms, which operate on thin profit margins, may not have the financial capacity to invest in advertising. Since they can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price, there is no need for them to incur additional costs on advertising.
4. Word-of-mouth and reputation: In perfectly competitive markets, reputation and word-of-mouth play a crucial role in attracting customers. If a price taker firm consistently offers high-quality products at competitive prices, it is likely to build a positive reputation among customers. This reputation can lead to customer loyalty and word-of-mouth referrals, which can drive sales without the need for advertising.
In conclusion, price taker firms do not advertise because they have no control over the price, operate in perfectly competitive markets, and can sell as much as they wish at the prevailing price. Advertising would not provide any competitive advantage and would be an unnecessary cost for these firms. They rely on reputation and word-of-mouth to attract customers in their quest to maximize sales and profits.
Monopolistic Competitive firms ______. - a)Are small in size
- b)Have small share in total market
- c)Are very large in size
- d)Both (A) and (B)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Monopolistic Competitive firms ______.
a)
Are small in size
b)
Have small share in total market
c)
Are very large in size
d)
Both (A) and (B)

|
Madhavan Malik answered |
A monopolistic competitive industry has the following features:
Many firms.
Freedom of entry and exit.
Firms produce differentiated products.
Firms have price inelastic demand; they are price makers because the good is highly differentiated
Firms make normal profits in the long run but could make supernormal profits in the short term
Firms are allocatively and productively inefficient.
AR is also known as:- a)price
- b)income
- c)revenue
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
AR is also known as:
a)
price
b)
income
c)
revenue
d)
none of the above

|
Mrinalini Iyer answered |
AR or Average Revenue is a term used in economics and business to refer to the amount of revenue generated per unit of output sold. It is calculated by dividing total revenue by the quantity of goods or services sold. AR is also known as price, as it represents the price at which each unit of output is sold.
Explanation:
AR is a crucial metric for businesses as it helps them to determine the price at which they should sell their products or services. It is important for businesses to set their prices at a level that maximizes their revenue and profits. By calculating AR, businesses can determine the optimal price point that will help them achieve this goal.
AR is calculated by dividing total revenue by the quantity of goods or services sold. For example, if a company sells 100 units of a product at a price of $10 per unit, its total revenue would be $1000. Dividing this by the quantity sold (100), we get an AR of $10 per unit.
AR is also important for businesses to monitor over time. If a company notices a decline in its AR, it may indicate that its prices are too high and it needs to lower them to remain competitive. On the other hand, if AR is increasing, it may indicate that the company is successfully increasing its prices or selling higher-priced products, which can lead to higher profits.
In conclusion, AR is a key metric for businesses to monitor and use in their pricing strategy. It is also a useful tool for investors and analysts to evaluate a company's financial performance.
Explanation:
AR is a crucial metric for businesses as it helps them to determine the price at which they should sell their products or services. It is important for businesses to set their prices at a level that maximizes their revenue and profits. By calculating AR, businesses can determine the optimal price point that will help them achieve this goal.
AR is calculated by dividing total revenue by the quantity of goods or services sold. For example, if a company sells 100 units of a product at a price of $10 per unit, its total revenue would be $1000. Dividing this by the quantity sold (100), we get an AR of $10 per unit.
AR is also important for businesses to monitor over time. If a company notices a decline in its AR, it may indicate that its prices are too high and it needs to lower them to remain competitive. On the other hand, if AR is increasing, it may indicate that the company is successfully increasing its prices or selling higher-priced products, which can lead to higher profits.
In conclusion, AR is a key metric for businesses to monitor and use in their pricing strategy. It is also a useful tool for investors and analysts to evaluate a company's financial performance.
Economic Problem arises when:- a)Wants are unlimited
- b)Resources are limited
- c)Alternative uses of resources
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Economic Problem arises when:
a)
Wants are unlimited
b)
Resources are limited
c)
Alternative uses of resources
d)
All of the above

|
Aarya Sharma answered |
The Economic Problem arises due to the interplay of two fundamental factors: unlimited wants and limited resources. This problem is faced by individuals, organizations, and countries alike.
Unlimited Wants
Human wants are endless. People always desire more goods and services than they can afford to acquire. Wants are not limited to basic necessities like food, clothing, and shelter. They also extend to luxury goods like expensive cars, houses, and vacations. Moreover, wants keep changing and evolving over time due to factors like changing lifestyles, peer pressure, and advertising.
Limited Resources
Resources are the means to satisfy human wants. They include land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. However, these resources are not unlimited. For instance, land is a finite resource, and its supply cannot be increased. Similarly, labor is limited by the size of the population, and capital is constrained by the amount of savings and investment.
Alternative Uses of Resources
Resources can be used in different ways to produce different goods and services. For example, a farmer can use his land to grow wheat, cotton, or sugarcane. Similarly, a factory can use its labor and capital to produce cars, computers, or smartphones. The problem arises when resources have to be allocated among alternative uses. Every choice involves an opportunity cost, which is the value of the next-best alternative forgone.
All of the Above
The Economic Problem arises due to the interaction of unlimited wants, limited resources, and alternative uses of resources. No society can satisfy all the wants of all its members with the limited resources at its disposal. Hence, choices have to be made about what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. These choices are guided by the principles of efficiency, equity, and sustainability.
Unlimited Wants
Human wants are endless. People always desire more goods and services than they can afford to acquire. Wants are not limited to basic necessities like food, clothing, and shelter. They also extend to luxury goods like expensive cars, houses, and vacations. Moreover, wants keep changing and evolving over time due to factors like changing lifestyles, peer pressure, and advertising.
Limited Resources
Resources are the means to satisfy human wants. They include land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship. However, these resources are not unlimited. For instance, land is a finite resource, and its supply cannot be increased. Similarly, labor is limited by the size of the population, and capital is constrained by the amount of savings and investment.
Alternative Uses of Resources
Resources can be used in different ways to produce different goods and services. For example, a farmer can use his land to grow wheat, cotton, or sugarcane. Similarly, a factory can use its labor and capital to produce cars, computers, or smartphones. The problem arises when resources have to be allocated among alternative uses. Every choice involves an opportunity cost, which is the value of the next-best alternative forgone.
All of the Above
The Economic Problem arises due to the interaction of unlimited wants, limited resources, and alternative uses of resources. No society can satisfy all the wants of all its members with the limited resources at its disposal. Hence, choices have to be made about what to produce, how to produce, and for whom to produce. These choices are guided by the principles of efficiency, equity, and sustainability.
Which market have characteristic of product differentiation?- a)Perfect Competition
- b)Monopoly
- c)Monopolistic Competition
- d)Oligopoly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which market have characteristic of product differentiation?
a)
Perfect Competition
b)
Monopoly
c)
Monopolistic Competition
d)
Oligopoly

|
Nilanjan Saha answered |
Market with Characteristic of Product Differentiation
Explanation:
Product differentiation is a marketing strategy in which a company tries to distinguish its product or service from competitors by adding features or characteristics that make it unique. This strategy is mostly used in monopolistic competition, where there are many firms in the market and each firm is trying to differentiate its product to attract customers.
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which there are many firms selling a differentiated product. The firms have some control over the price of the product, but the competition is still high as the products are close substitutes. In monopolistic competition, firms can differentiate their products based on quality, design, features, branding, packaging, and advertising.
For example, in the market for smartphones, there are many firms that sell smartphones with different features, designs, and brands. Each firm tries to differentiate its product to attract customers. Apple, Samsung, and Huawei are some of the popular brands that sell smartphones with different features and designs.
In monopolistic competition, firms can charge a slightly higher price for their differentiated product as customers may be willing to pay extra for the unique features. However, if the price is too high, customers may switch to a substitute product.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C', Monopolistic Competition, as it is the market structure that has the characteristic of product differentiation.
Explanation:
Product differentiation is a marketing strategy in which a company tries to distinguish its product or service from competitors by adding features or characteristics that make it unique. This strategy is mostly used in monopolistic competition, where there are many firms in the market and each firm is trying to differentiate its product to attract customers.
Monopolistic Competition
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which there are many firms selling a differentiated product. The firms have some control over the price of the product, but the competition is still high as the products are close substitutes. In monopolistic competition, firms can differentiate their products based on quality, design, features, branding, packaging, and advertising.
For example, in the market for smartphones, there are many firms that sell smartphones with different features, designs, and brands. Each firm tries to differentiate its product to attract customers. Apple, Samsung, and Huawei are some of the popular brands that sell smartphones with different features and designs.
In monopolistic competition, firms can charge a slightly higher price for their differentiated product as customers may be willing to pay extra for the unique features. However, if the price is too high, customers may switch to a substitute product.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C', Monopolistic Competition, as it is the market structure that has the characteristic of product differentiation.
Which of these are characteristics of Perfect competition. - a)Many Sellers & Buyers
- b)Homogeneous Product
- c)Free Entry and Exit
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these are characteristics of Perfect competition.
a)
Many Sellers & Buyers
b)
Homogeneous Product
c)
Free Entry and Exit
d)
All of the above

|
Freedom Institute answered |
The answer is D: All of the above. Perfect competition is an idealized market structure that serves as a benchmark for analyzing other market structures. It is characterized by the following features:Many Sellers & Buyers:- A large number of both sellers and buyers participate in the market- No single seller or buyer can influence the market price- Each participant is a price taker, meaning they have no control over the market priceHomogeneous Product:- The products offered by all sellers in the market are identical or very similar- Buyers have no preference between different sellers' products- This ensures that price is the only factor that influences buyers' decisionsFree Entry and Exit:- There are no barriers to entering or exiting the market- Firms can easily enter the market if they believe they can earn a profit- Similarly, firms can exit the market if they are not making a profit- This feature ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that profits are driven down to a normal level in the long runIn summary, perfect competition is characterized by many sellers and buyers, a homogeneous product, and free entry and exit. These features lead to a highly competitive market environment where firms are forced to operate efficiently and provide goods at a price determined by the market.
What should firm do when Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost?- a)Firm should expand output
- b)Effect should be made to make them equal
- c)Prices should be covered down
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What should firm do when Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost?
a)
Firm should expand output
b)
Effect should be made to make them equal
c)
Prices should be covered down
d)
All of these

|
Shivam Chawla answered |
When marginal revenue (MR) is greater than marginal cost (MC), it means that the firm is generating more revenue from selling an additional unit of output than the cost incurred in producing that unit. In such a scenario, the firm should expand its output to maximize its profits. Here are the reasons why:
1. Profit maximization: The ultimate goal of any firm is to maximize its profits. When MR>MC, producing one more unit of output will add more to the firm's revenue than its cost. Therefore, the firm should continue producing more output until MR=MC, which is the point of profit maximization.
2. Market demand: Marginal revenue is a function of market demand. When MR>MC, it indicates that the market is willing to pay a higher price for the additional output. Therefore, expanding output is a way of meeting the market demand and maximizing revenue.
3. Economies of scale: Expansion of output can lead to economies of scale, which means that the firm can produce more units at a lower cost per unit. This can further increase the firm's profitability.
4. Competitive advantage: Expanding output can also give the firm a competitive advantage by increasing its market share and reducing the cost per unit. This can help the firm to compete effectively with its rivals.
In conclusion, when MR>MC, the firm should expand its output to maximize profits, meet market demand, achieve economies of scale, and gain a competitive advantage.
1. Profit maximization: The ultimate goal of any firm is to maximize its profits. When MR>MC, producing one more unit of output will add more to the firm's revenue than its cost. Therefore, the firm should continue producing more output until MR=MC, which is the point of profit maximization.
2. Market demand: Marginal revenue is a function of market demand. When MR>MC, it indicates that the market is willing to pay a higher price for the additional output. Therefore, expanding output is a way of meeting the market demand and maximizing revenue.
3. Economies of scale: Expansion of output can lead to economies of scale, which means that the firm can produce more units at a lower cost per unit. This can further increase the firm's profitability.
4. Competitive advantage: Expanding output can also give the firm a competitive advantage by increasing its market share and reducing the cost per unit. This can help the firm to compete effectively with its rivals.
In conclusion, when MR>MC, the firm should expand its output to maximize profits, meet market demand, achieve economies of scale, and gain a competitive advantage.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Average revenue curve is also known as:
- A:
Profit curve
- B:
Demand curve
- C:
Supply curve
- D:
Average cost curve.
The answer is b.
Average revenue curve is also known as:
Profit curve
Demand curve
Supply curve
Average cost curve.

|
Abc answered |
Demand curve depicts the relation between quantity & price.........avg revenue = mrkt price of product....... therefore, avg revenue curve also called as demand curve :)
If price is forced to stay below equilibrium price: - a)Excess supply exists
- b)Excess demand exists
- c)Either (a) or (b)
- d)Neither (a) nor (b)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If price is forced to stay below equilibrium price:
a)
Excess supply exists
b)
Excess demand exists
c)
Either (a) or (b)
d)
Neither (a) nor (b)
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
If the market price is below the equilibrium price, quantity supplied is less than quantity demanded that is excess demand exists, creating a shortage. The market is not clear. It is in shortage. Market price will rise because of this shortage.
If a shortage exists, price must rise in order to entice additional supply and reduce quantity demanded until the shortage is eliminated.
Normative aspect of Economics is given by: - a)Marshall
- b)Robbins
- c)Adam Smith
- d)Samuelson
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Normative aspect of Economics is given by:
a)
Marshall
b)
Robbins
c)
Adam Smith
d)
Samuelson

|
Srsps answered |
Alfred Marshall was a British economist who proposed the definition of welfare according to which economics should be a science of creation of welfare for both human as well as society believed that the subject studies the creation of materialistic things in the economy for personal gains which is not good for the welfare of the society. Therefore, he proposed a normative definition on economics.
Supernormal profits occur, when: - a)Total revenue is equal to total cost
- b)Total revenue is equal to variable cost
- c)Average revenue is more than average cost
- d)Average revenue is equal to average cost
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Supernormal profits occur, when:
a)
Total revenue is equal to total cost
b)
Total revenue is equal to variable cost
c)
Average revenue is more than average cost
d)
Average revenue is equal to average cost

|
Maheshwar Goyal answered |
Supernormal profit is also called economic profit, and abnormal profit, and is earned when total revenue is greater than the total costs.
The demand curve of the firm and industry will be same in which form of market: - a)Monopolistic Competition
- b)Perfect Competition
- c)Monopoly
- d)Oligopoly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The demand curve of the firm and industry will be same in which form of market:
a)
Monopolistic Competition
b)
Perfect Competition
c)
Monopoly
d)
Oligopoly
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Perceived Demand for Firms in Different Competitive Settings. The demand curve faced by a perfectly competitive firm is perfectly elastic, meaning it can sell all the output it wishes at the prevailing market price. The demand curve faced by a monopoly is the market demand.
A monopolist is able to maximize his profits when : - a)His output is maximum
- b)He charges a high price
- c)His average cost is minimum
- d)His marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A monopolist is able to maximize his profits when :
a)
His output is maximum
b)
He charges a high price
c)
His average cost is minimum
d)
His marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
A monopolist is able to maximize its profits by setting the price at the level that will maximize its per-unit profit.setting output at MR = MC and setting price at the demand curve's highest point. producing maximum output where price is equal to its marginal cost.
In the long run: - a)Only demand can change
- b)Only supply can change
- c)Both demand and supply can change
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the long run:
a)
Only demand can change
b)
Only supply can change
c)
Both demand and supply can change
d)
None of these

|
Vaishnavi Gupta answered |
Demand and Supply in the Long Run
In the long run, both demand and supply can change. This is because the long run refers to a period of time where all factors of production are variable, meaning that both demand and supply can adjust to changes in the market.
Factors Influencing Demand
Demand can change due to various factors such as:
1. Changes in consumer preferences and tastes
2. Changes in population and demographics
3. Changes in income levels
4. Changes in prices of related goods
5. Changes in advertising and promotional activities
6. Changes in government policies and regulations
Factors Influencing Supply
Supply can change due to various factors such as:
1. Changes in technology
2. Changes in the cost of production
3. Changes in the availability of resources and raw materials
4. Changes in the number of firms in the industry
5. Changes in government policies and regulations
Impact of Changes in Demand and Supply
When there is a change in either demand or supply, the market equilibrium point shifts. This means that the quantity and price of the good or service will change. If demand increases, the equilibrium price and quantity will increase. If supply increases, the equilibrium price will decrease and quantity will increase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, in the long run, both demand and supply can change due to various factors. When there is a change in either demand or supply, the market equilibrium point shifts, leading to changes in price and quantity.
In the long run, both demand and supply can change. This is because the long run refers to a period of time where all factors of production are variable, meaning that both demand and supply can adjust to changes in the market.
Factors Influencing Demand
Demand can change due to various factors such as:
1. Changes in consumer preferences and tastes
2. Changes in population and demographics
3. Changes in income levels
4. Changes in prices of related goods
5. Changes in advertising and promotional activities
6. Changes in government policies and regulations
Factors Influencing Supply
Supply can change due to various factors such as:
1. Changes in technology
2. Changes in the cost of production
3. Changes in the availability of resources and raw materials
4. Changes in the number of firms in the industry
5. Changes in government policies and regulations
Impact of Changes in Demand and Supply
When there is a change in either demand or supply, the market equilibrium point shifts. This means that the quantity and price of the good or service will change. If demand increases, the equilibrium price and quantity will increase. If supply increases, the equilibrium price will decrease and quantity will increase.
Conclusion
In conclusion, in the long run, both demand and supply can change due to various factors. When there is a change in either demand or supply, the market equilibrium point shifts, leading to changes in price and quantity.
Oligopolistic industries are characterized by :- a)a few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry.
- b)a few large firms and no entry barriers.
- c)a large number of small firms and no entry barriers.
- d)one dominant firm and low entry barriers.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oligopolistic industries are characterized by :
a)
a few dominant firms and substantial barriers to entry.
b)
a few large firms and no entry barriers.
c)
a large number of small firms and no entry barriers.
d)
one dominant firm and low entry barriers.
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
The term oligopoly indicates: a few firms producing either a differentiated or a homogeneous product. Oligopolistic industries are characterized by: a few dominant firms and substantial entry barriers.
The study of inflation is part of:- a)Normative economics.
- b)Macroeconomics.
- c)Microeconomics.
- d)Descriptive economics.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The study of inflation is part of:
a)
Normative economics.
b)
Macroeconomics.
c)
Microeconomics.
d)
Descriptive economics.
|
|
Pvs Chaitanya answered |
Macro Economics means study of economy as whole
Inflation is calculated for the whole country. So the study of inflation is covers under "MACRO ECONOMICS"
Inflation is calculated for the whole country. So the study of inflation is covers under "MACRO ECONOMICS"
MR Curve = AR = Demand Curve is a feature of which kind of Market?
- a)Perfect Competition
- b)Monopoly
- c)Monopolistic
- d)Oligopoly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
MR Curve = AR = Demand Curve is a feature of which kind of Market?
a)
Perfect Competition
b)
Monopoly
c)
Monopolistic
d)
Oligopoly

|
Srsps answered |
Answer: B: MonopolyExplanation:In a Monopoly market, the following features are observed:- Single seller: There is only one firm or seller producing the product or offering the service.- No close substitutes: The product or service offered by the monopolist has no close substitutes, making it unique.- Price maker: The monopolist is the price maker and has control over the price of the product or service.- High barriers to entry: There are high barriers to entry for other firms, either in the form of legal restrictions or economies of scale.MR Curve = AR = Demand Curve:In a monopoly market, the Marginal Revenue (MR) curve, the Average Revenue (AR) curve, and the Demand curve are equal. This is because the monopolist is the sole seller and has control over the price. The demand for the product or service is determined by the price set by the monopolist. Since there is only one seller, the average revenue is equal to the price, and the marginal revenue is the additional revenue earned by selling one extra unit. Therefore, MR = AR = Demand Curve in a monopoly market.
In the ‘kinked-demand’ curve model, the upper portion of the demand curve is:- a)Elastic
- b)Inelastic
- c)Perfectly Elastic
- d)Unitary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the ‘kinked-demand’ curve model, the upper portion of the demand curve is:
a)
Elastic
b)
Inelastic
c)
Perfectly Elastic
d)
Unitary

|
Nilanjan Saha answered |
Context of artificial intelligence and machine learning, bias refers to systematic errors in the decision-making process of an algorithm or model that can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. These biases can be introduced at various stages of the development process, from the data collection and preprocessing phase to the selection of features and the choice of the model architecture. Bias can arise from a variety of sources, including data imbalance, sample selection bias, algorithmic bias, and societal bias. Addressing bias in AI and ML is crucial for ensuring fairness, transparency, and ethical use of these technologies.
“Price Discrimination” can be best exercised by the Seller in ________.- a)Oligopoly
- b)Monopoly
- c)Monopolistic competition
- d)Perfect competition
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
“Price Discrimination” can be best exercised by the Seller in ________.
a)
Oligopoly
b)
Monopoly
c)
Monopolistic competition
d)
Perfect competition
|
|
Nikita Singh answered |
Answer: B - MonopolyPrice discrimination is best exercised by the seller in a monopoly market structure. Here's why:1. Market Power:- In a monopoly, there is only one seller, which means the firm has significant market power and can control the price.- This allows the monopolist to charge different prices to different consumers based on their willingness to pay.2. Barriers to Entry:- Monopoly markets have high barriers to entry, which prevents new firms from entering the market and competing with the monopolist.- This allows the monopolist to exercise price discrimination without the fear of losing customers to competitors.3. Differentiated Demand:- In a monopoly, the seller can identify and segment consumers based on their demand and price elasticity.- This enables the monopolist to charge different prices to different consumer segments, maximizing profit.4. Limited Consumer Information:- In a monopoly, consumers may not have complete information about the product or its pricing.- This makes it easier for the monopolist to engage in price discrimination without customers being aware of the different prices charged.In contrast, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, and perfect competition market structures have multiple sellers, making it more difficult for any single firm to engage in price discrimination without facing competition or losing customers to other firms.
In perfect competition in the long run there will be no ________________ .- a)normal profits
- b)supernormal profits.
- c)production
- d)costs.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In perfect competition in the long run there will be no ________________ .
a)
normal profits
b)
supernormal profits.
c)
production
d)
costs.

|
Amrutha Goyal answered |
Perfect Competition and Supernormal Profits
Perfect Competition:
Perfect competition is a market structure where a large number of small firms sell homogenous products to a large number of buyers. In this market structure, no single firm can influence the market price as all firms are price takers. They have to accept the market price as given. The market is in equilibrium when the market price is equal to the equilibrium price where the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied.
Supernormal Profits:
Supernormal profits are also known as economic profits. These are the profits earned by a firm when its total revenue is greater than the total cost, both implicit and explicit. In other words, when the firm earns more than the opportunity cost of production, it is said to be earning supernormal profits.
Long Run:
The long run is a period of time where all the factors of production are variable. In the long run, a firm can enter or exit the market. In perfect competition, there are no barriers to entry or exit. Therefore, in the long run, the number of firms in the market can change.
No Supernormal Profits in Perfect Competition in the Long Run:
In perfect competition, firms earn normal profits in the long run. Normal profits are the minimum profits required to keep a firm in business. It is the opportunity cost of production. In other words, normal profits are the profits that a firm would earn in its next best alternative. In the long run, if a firm is earning supernormal profits, then new firms will enter the market. This will increase the supply of the product and decrease the market price. As a result, the profits of existing firms will decrease. This process will continue until all firms are earning normal profits.
Conclusion:
In perfect competition, there will be no supernormal profits in the long run as new firms will enter the market and increase the supply of the product. This will lead to a decrease in the market price and the profits of existing firms will decrease. Eventually, all firms will earn normal profits.
Perfect Competition:
Perfect competition is a market structure where a large number of small firms sell homogenous products to a large number of buyers. In this market structure, no single firm can influence the market price as all firms are price takers. They have to accept the market price as given. The market is in equilibrium when the market price is equal to the equilibrium price where the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied.
Supernormal Profits:
Supernormal profits are also known as economic profits. These are the profits earned by a firm when its total revenue is greater than the total cost, both implicit and explicit. In other words, when the firm earns more than the opportunity cost of production, it is said to be earning supernormal profits.
Long Run:
The long run is a period of time where all the factors of production are variable. In the long run, a firm can enter or exit the market. In perfect competition, there are no barriers to entry or exit. Therefore, in the long run, the number of firms in the market can change.
No Supernormal Profits in Perfect Competition in the Long Run:
In perfect competition, firms earn normal profits in the long run. Normal profits are the minimum profits required to keep a firm in business. It is the opportunity cost of production. In other words, normal profits are the profits that a firm would earn in its next best alternative. In the long run, if a firm is earning supernormal profits, then new firms will enter the market. This will increase the supply of the product and decrease the market price. As a result, the profits of existing firms will decrease. This process will continue until all firms are earning normal profits.
Conclusion:
In perfect competition, there will be no supernormal profits in the long run as new firms will enter the market and increase the supply of the product. This will lead to a decrease in the market price and the profits of existing firms will decrease. Eventually, all firms will earn normal profits.
Abnormal profits exist in the long run only under _______.- a)Perfect Competition
- b)Monopoly
- c)Monopolistic Competition
- d)Oligopoly
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Abnormal profits exist in the long run only under _______.
a)
Perfect Competition
b)
Monopoly
c)
Monopolistic Competition
d)
Oligopoly

|
Nitin Kumar answered |
Abnormal profits are profits that are earned by a firm over and above the normal level of profits that are earned in the industry. In the long run, abnormal profits are not sustainable as they attract new firms to enter the industry, which leads to an increase in competition and a reduction in prices.
Monopoly
Under a monopoly, a single firm has complete control over the market and can charge a price that is higher than the marginal cost of production. This leads to the firm earning abnormal profits in the short run. However, in the long run, new firms cannot enter the market due to barriers to entry, and the monopoly firm continues to earn abnormal profits.
Monopolistic Competition
Under monopolistic competition, there are many firms in the market, each offering a slightly differentiated product. This leads to firms having some degree of market power and being able to charge a price that is higher than the marginal cost of production. In the short run, firms can earn abnormal profits. However, in the long run, new firms can enter the market and offer similar products, leading to a reduction in the market power of existing firms and a reduction in prices.
Perfect Competition
Under perfect competition, there are many firms in the market, each offering a homogeneous product. Firms in a perfectly competitive market are price takers and cannot charge a price higher than the market price. This leads to firms earning only normal profits in the long run, as new firms can enter the market and offer the same product at the same price.
Oligopoly
Under oligopoly, there are a few firms in the market, and each firm has a significant degree of market power. This leads to firms being able to charge a price that is higher than the marginal cost of production. In the short run, firms can earn abnormal profits. However, in the long run, new firms cannot enter the market due to barriers to entry, and existing firms continue to earn abnormal profits.
Conclusion
Abnormal profits exist in the long run only under monopoly as new firms cannot enter the market due to barriers to entry, and the monopoly firm continues to earn abnormal profits. However, under perfect competition, firms can earn only normal profits in the long run, as new firms can enter the market and offer the same product at the same price.
Monopoly
Under a monopoly, a single firm has complete control over the market and can charge a price that is higher than the marginal cost of production. This leads to the firm earning abnormal profits in the short run. However, in the long run, new firms cannot enter the market due to barriers to entry, and the monopoly firm continues to earn abnormal profits.
Monopolistic Competition
Under monopolistic competition, there are many firms in the market, each offering a slightly differentiated product. This leads to firms having some degree of market power and being able to charge a price that is higher than the marginal cost of production. In the short run, firms can earn abnormal profits. However, in the long run, new firms can enter the market and offer similar products, leading to a reduction in the market power of existing firms and a reduction in prices.
Perfect Competition
Under perfect competition, there are many firms in the market, each offering a homogeneous product. Firms in a perfectly competitive market are price takers and cannot charge a price higher than the market price. This leads to firms earning only normal profits in the long run, as new firms can enter the market and offer the same product at the same price.
Oligopoly
Under oligopoly, there are a few firms in the market, and each firm has a significant degree of market power. This leads to firms being able to charge a price that is higher than the marginal cost of production. In the short run, firms can earn abnormal profits. However, in the long run, new firms cannot enter the market due to barriers to entry, and existing firms continue to earn abnormal profits.
Conclusion
Abnormal profits exist in the long run only under monopoly as new firms cannot enter the market due to barriers to entry, and the monopoly firm continues to earn abnormal profits. However, under perfect competition, firms can earn only normal profits in the long run, as new firms can enter the market and offer the same product at the same price.
When ________________________________ , we know that the firms are earning just normal profits.- a)AC = AR
- b)MC = MR
- c)MC = AC
- d)AR = MR
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When ________________________________ , we know that the firms are earning just normal profits.
a)
AC = AR
b)
MC = MR
c)
MC = AC
d)
AR = MR

|
Aarya Sharma answered |
Explanation:
When the average cost (AC) is equal to the average revenue (AR), it indicates that the firms are earning just normal profits. Let's break down the options to understand why option 'A' is the correct answer.
Option A: AC = AR
- Average cost (AC) is the total cost divided by the quantity produced.
- Average revenue (AR) is the total revenue divided by the quantity sold.
- When AC is equal to AR, it means that the price at which the firm is selling its goods or services is equal to the average cost of producing those goods or services.
- In this case, the firm is neither making a profit nor incurring a loss. It is earning just enough to cover all its costs and is therefore earning normal profits.
Option B: MC = MR
- Marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output.
- Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned from selling one more unit of output.
- When MC is equal to MR, it indicates that the firm is maximizing its profit by producing the quantity at which the marginal cost of production is equal to the marginal revenue generated from selling that additional unit.
- It does not necessarily indicate whether the firm is earning normal profits or abnormal profits.
Option C: MC = AC
- Marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output.
- Average cost (AC) is the total cost divided by the quantity produced.
- When MC is equal to AC, it signifies that the average cost of production is not changing as more units are produced.
- It does not necessarily indicate whether the firm is earning normal profits or abnormal profits.
Option D: AR = MR
- Average revenue (AR) is the total revenue divided by the quantity sold.
- Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned from selling one more unit of output.
- When AR is equal to MR, it implies that the firm is selling each unit at the same price and the additional revenue earned from selling one more unit is constant.
- It does not necessarily indicate whether the firm is earning normal profits or abnormal profits.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, when the average cost (AC) is equal to the average revenue (AR), it signifies that the firm is earning just normal profits. This is because the price at which the firm is selling its goods or services is equal to the average cost of producing those goods or services, indicating that the firm is covering all its costs and not making any additional profit.
When the average cost (AC) is equal to the average revenue (AR), it indicates that the firms are earning just normal profits. Let's break down the options to understand why option 'A' is the correct answer.
Option A: AC = AR
- Average cost (AC) is the total cost divided by the quantity produced.
- Average revenue (AR) is the total revenue divided by the quantity sold.
- When AC is equal to AR, it means that the price at which the firm is selling its goods or services is equal to the average cost of producing those goods or services.
- In this case, the firm is neither making a profit nor incurring a loss. It is earning just enough to cover all its costs and is therefore earning normal profits.
Option B: MC = MR
- Marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output.
- Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned from selling one more unit of output.
- When MC is equal to MR, it indicates that the firm is maximizing its profit by producing the quantity at which the marginal cost of production is equal to the marginal revenue generated from selling that additional unit.
- It does not necessarily indicate whether the firm is earning normal profits or abnormal profits.
Option C: MC = AC
- Marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output.
- Average cost (AC) is the total cost divided by the quantity produced.
- When MC is equal to AC, it signifies that the average cost of production is not changing as more units are produced.
- It does not necessarily indicate whether the firm is earning normal profits or abnormal profits.
Option D: AR = MR
- Average revenue (AR) is the total revenue divided by the quantity sold.
- Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned from selling one more unit of output.
- When AR is equal to MR, it implies that the firm is selling each unit at the same price and the additional revenue earned from selling one more unit is constant.
- It does not necessarily indicate whether the firm is earning normal profits or abnormal profits.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, when the average cost (AC) is equal to the average revenue (AR), it signifies that the firm is earning just normal profits. This is because the price at which the firm is selling its goods or services is equal to the average cost of producing those goods or services, indicating that the firm is covering all its costs and not making any additional profit.
Chapter doubts & questions for Price Determination in Different Markets - Business Economics for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Price Determination in Different Markets - Business Economics for CA Foundation in English & Hindi are available as part of CA Foundation exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Business Economics for CA Foundation
86 videos|200 docs|58 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












