CA Foundation Exam > CA Foundation Questions > In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb...
Start Learning for Free
In the long run monopolist can
- a)Incur losses
- b)Must earn super normal profits
- c)Wants to shut-down
- d)Earns only normal profits
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal p...
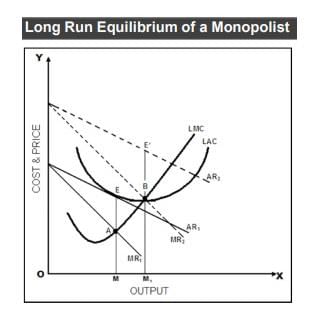
As you can see above, there are two alternative cases for the determination of Equilibrium in Monopoly:
- With normal profits
- With super-normal profits
Most Upvoted Answer
In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal p...
While a monopolist can maintain supernormal profits in the long run, it doesn’t necessarily make profits. A monopolist can be a loss making or revenue maximizing too. This is not possible under perfect competition. If abnormal profits are available in the long run, other firms will enter the competition with the result abnormal profits will be eliminated.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal p...
Monopolist must earn super normal profit because he is the only supplier of goods in the market. So customers has to purchase goods on that rate that monopolist has decided. Here monopolist would like to sale goods on high rate that is the cause of earning super profit of monopolist in long run monopoly.

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|
Question Description
In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. Information about In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for CA Foundation 2025 is part of CA Foundation preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the CA Foundation exam syllabus. Information about In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for CA Foundation 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for CA Foundation.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CA Foundation Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the long run monopolist cana)Incur lossesb)Must earn super normal profitsc)Wants to shut-downd)Earns only normal profitsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice CA Foundation tests.

|
Explore Courses for CA Foundation exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















