All Exams >
Class 6 >
Science Olympiad Class 6 >
All Questions
All questions of The World of Living for Class 6 Exam
Which of the following joints and their parts enable a bowler to bowl, while playing cricket?- a)Ball and socket joint at shoulder.
- b)Hinge joint at elbow.
- c)Hinge joint at shoulder.
- d)Ball and socket joint at elbow.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following joints and their parts enable a bowler to bowl, while playing cricket?
a)
Ball and socket joint at shoulder.
b)
Hinge joint at elbow.
c)
Hinge joint at shoulder.
d)
Ball and socket joint at elbow.

|
Manasa Chauhan answered |
Our shoulder has the ball and socket joint that allows circular movement. When you bowl while playing cricket, you rotate your hand in full circle.
Which parts of the fish helps it to move forward?- a)Hands and fins
- b)Legs and fins
- c)Gills and fins
- d)Fins and tail
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which parts of the fish helps it to move forward?
a)
Hands and fins
b)
Legs and fins
c)
Gills and fins
d)
Fins and tail

|
Anoushka Sharma answered |
Fins help the fish to move in water. The forward movement of the fish starts with front and sideways push of the tail. The flexible and strong tail fin of the fish pushes the water and propels the fish forward.
Which body system holds our body upright?- a)Circulatory system
- b)Muscular system
- c)Nervous system
- d)Skeletal system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which body system holds our body upright?
a)
Circulatory system
b)
Muscular system
c)
Nervous system
d)
Skeletal system

|
Sagar Mehta answered |
The skeletal system is the framework of bones that support our body and keeps it upright.
Which joint allows movement in one direction only?- a)Ball and socket joint
- b)Hinge joint
- c)Pivot joint
- d)Gliding joint
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which joint allows movement in one direction only?
a)
Ball and socket joint
b)
Hinge joint
c)
Pivot joint
d)
Gliding joint

|
Moumita Desai answered |
Hinge joint allows back and forth movement only. Bones in the knee, elbow, finger, and toes have hinge joint.
Which of the following plants exhibits a fibrous root system?- a) Carrot
- b) Radish
- c) Grass
- d) Beetroot
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following plants exhibits a fibrous root system?
a)
Carrot
b)
Radish
c)
Grass
d)
Beetroot
|
|
Satish Thube answered |
C grass is the correct option for guessing here is a tip p-f-m ,r-t-d r means reticulate venation p-parallel venation f-fibrous root t-taproot d-dicotyledons m-monocotyledons
Which part of the plant is responsible for photosynthesis?- a)Root
- b)Stem
- c)Leaf
- d)Flower
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the plant is responsible for photosynthesis?
a)
Root
b)
Stem
c)
Leaf
d)
Flower

|
EduRev Class 6 answered |
Leaves contain chlorophyll and are the main site for photosynthesis, the process by which plants make their food.
Which of the following organisms has a backbone?- a)Spider
- b)Starfish
- c)Snake
- d)Snail
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organisms has a backbone?
a)
Spider
b)
Starfish
c)
Snake
d)
Snail
|
|
Akshita Sarkar answered |
The correct answer is option 'C', which is the snake.
Explanation:
Explanation:
Which joint is present at the knee and arm?- a)Ball and socket joint.
- b)Pivot joint
- c)Hinge joint
- d)Fixed joint
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which joint is present at the knee and arm?
a)
Ball and socket joint.
b)
Pivot joint
c)
Hinge joint
d)
Fixed joint

|
Anoushka Sharma answered |
The bones in elbow have hinge joint that allows only back and forth movement.
In flowering plants, which part is often brightly colored to attract pollinators?- a) Sepal
- b) Petal
- c) Stamen
- d) Pistil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In flowering plants, which part is often brightly colored to attract pollinators?
a)
Sepal
b)
Petal
c)
Stamen
d)
Pistil

|
EduRev Class 6 answered |
Petals are typically colorful and serve to attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies. The vibrant colors and patterns of petals are important for ensuring successful pollination, which is crucial for the reproductive success of flowering plants.
The following aquatic animals are grouped according to their breathing adaptations. Which group of animals does not breathe in the same way?- a)Water stick insect, water scorpion
- b)Tubifex worm, tadpole
- c)Crab, wood louse
- d)Water spider, great diving beetle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following aquatic animals are grouped according to their breathing adaptations. Which group of animals does not breathe in the same way?
a)
Water stick insect, water scorpion
b)
Tubifex worm, tadpole
c)
Crab, wood louse
d)
Water spider, great diving beetle
|
|
Debanshi Roy answered |
Breathing Adaptations in Aquatic Animals
Aquatic animals have different adaptations for breathing in water due to the difference in their respiratory systems. Let's analyze the given options to determine the group of animals that do not breathe in the same way.
a) Water stick insect, water scorpion
- Both water stick insects and water scorpions are insects that live in freshwater habitats. They both have a specialized structure called a spiracle, which allows them to breathe air. They come to the water surface to take in oxygen through their spiracles.
b) Tubifex worm, tadpole
- Tubifex worms are small aquatic worms that live in the mud or sediment of freshwater environments. They respire through their body surface and obtain oxygen dissolved in the water. Tubifex worms do not have specialized breathing structures.
- Tadpoles, on the other hand, are the larval stage of amphibians, such as frogs. They have gills that allow them to extract oxygen directly from the water. Tadpoles respire by pumping water over their gills, extracting oxygen, and expelling carbon dioxide.
c) Crab, wood louse
- Crabs are crustaceans that live in marine and freshwater habitats. They have gills, which are specialized respiratory structures that extract oxygen from the water. Crabs breathe by pumping water over their gills, allowing oxygen exchange to occur.
- Woodlice, also known as roly-polies or pill bugs, are terrestrial crustaceans. They have a modified respiratory system called a pseudotrachea, which allows them to breathe air. Woodlice breathe by absorbing oxygen through their pseudotrachea.
d) Water spider, great diving beetle
- Water spiders are spiders that live in freshwater habitats. They build underwater webs and create air bubbles to breathe. They carry air bubbles trapped in their body hairs and use them as a respiratory supply.
- Great diving beetles are aquatic insects that live in freshwater. They have spiracles, similar to water stick insects and water scorpions, which allow them to breathe air. Great diving beetles come to the water surface to replenish their air supply.
From the given options, it is clear that the group of animals that does not breathe in the same way are the Tubifex worm and tadpole. While Tubifex worms respire through their body surface, tadpoles have gills for extracting oxygen from the water. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Aquatic animals have different adaptations for breathing in water due to the difference in their respiratory systems. Let's analyze the given options to determine the group of animals that do not breathe in the same way.
a) Water stick insect, water scorpion
- Both water stick insects and water scorpions are insects that live in freshwater habitats. They both have a specialized structure called a spiracle, which allows them to breathe air. They come to the water surface to take in oxygen through their spiracles.
b) Tubifex worm, tadpole
- Tubifex worms are small aquatic worms that live in the mud or sediment of freshwater environments. They respire through their body surface and obtain oxygen dissolved in the water. Tubifex worms do not have specialized breathing structures.
- Tadpoles, on the other hand, are the larval stage of amphibians, such as frogs. They have gills that allow them to extract oxygen directly from the water. Tadpoles respire by pumping water over their gills, extracting oxygen, and expelling carbon dioxide.
c) Crab, wood louse
- Crabs are crustaceans that live in marine and freshwater habitats. They have gills, which are specialized respiratory structures that extract oxygen from the water. Crabs breathe by pumping water over their gills, allowing oxygen exchange to occur.
- Woodlice, also known as roly-polies or pill bugs, are terrestrial crustaceans. They have a modified respiratory system called a pseudotrachea, which allows them to breathe air. Woodlice breathe by absorbing oxygen through their pseudotrachea.
d) Water spider, great diving beetle
- Water spiders are spiders that live in freshwater habitats. They build underwater webs and create air bubbles to breathe. They carry air bubbles trapped in their body hairs and use them as a respiratory supply.
- Great diving beetles are aquatic insects that live in freshwater. They have spiracles, similar to water stick insects and water scorpions, which allow them to breathe air. Great diving beetles come to the water surface to replenish their air supply.
From the given options, it is clear that the group of animals that does not breathe in the same way are the Tubifex worm and tadpole. While Tubifex worms respire through their body surface, tadpoles have gills for extracting oxygen from the water. Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
An organism X can walk, and climb on a surface and can also fly in the air. Which organism is X?
- a)Cockroach
- b)Bat
- c)Lizard
- d)Snail
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An organism X can walk, and climb on a surface and can also fly in the air. Which organism is X?
a)
Cockroach
b)
Bat
c)
Lizard
d)
Snail

|
Rishika Chopra answered |
Cockroach can walk, climb and can also fly in air. The muscles in the breast region move the legs for walking while another set of breast muscles move the wings during flying.
Which animal moves by using tiny bristles on its body?- a)Cockroach
- b)Earthworm
- c)Fish
- d)Snail
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which animal moves by using tiny bristles on its body?
a)
Cockroach
b)
Earthworm
c)
Fish
d)
Snail
|
|
Edgy Education answered |
Earthworms move using tiny bristles called setae, which grip the ground during movement.
Topic in NCERT: Gait of animals
Line in NCERT: "Under its body, it has a large number of tiny bristles (hair like structures) projecting out. The bristles are connected with muscles. The bristles help to get a good grip on the ground."
Line in NCERT: "Under its body, it has a large number of tiny bristles (hair like structures) projecting out. The bristles are connected with muscles. The bristles help to get a good grip on the ground."
Skeletal and muscular systems work together to enable the body to move. What is the main function of the skeletal system in relationship to the muscular system?- a)To provide attachment points for muscles.
- b)To assist muscles in growth and development.
- c)To produce muscle cells inside the bone marrow.
- d)To produce enzymes that help muscles repair themselves.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Skeletal and muscular systems work together to enable the body to move. What is the main function of the skeletal system in relationship to the muscular system?
a)
To provide attachment points for muscles.
b)
To assist muscles in growth and development.
c)
To produce muscle cells inside the bone marrow.
d)
To produce enzymes that help muscles repair themselves.

|
Harshad Shah answered |
Skeletal system provides attachment points for muscles.
Which of the following are characteristics of living beings ?(i) Respiration
(ii) Reproduction
(iii) Adaptation
(iv) ExcretionChoose the correct answer from the options below:- a)(i), (ii) and (iv) only
- b)(i) and (ii) only
- c)(ii) and (iv) only
- d)(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are characteristics of living beings ?
(i) Respiration
(ii) Reproduction
(iii) Adaptation
(iv) Excretion
(ii) Reproduction
(iii) Adaptation
(iv) Excretion
Choose the correct answer from the options below:
a)
(i), (ii) and (iv) only
b)
(i) and (ii) only
c)
(ii) and (iv) only
d)
(i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
All these features - respiration (the process of exchanging gases), reproduction (producing offspring), adaptation (ability to adjust to the environment), and excretion (removal of metabolic waste) - are essential characteristics of living organisms.
Which plant system is characterized by a single, thick root?- a)Grass
- b)Carrot
- c)Wheat
- d)Maize
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant system is characterized by a single, thick root?
a)
Grass
b)
Carrot
c)
Wheat
d)
Maize
|
|
Mahesh Chavan answered |
Understanding Plant Systems
Plants have various root systems that help them adapt to their environments. One of these systems is characterized by a single, thick root, commonly known as a taproot system.
What is a Taproot System?
- A taproot system consists of a main root that grows deeper into the soil, providing stability and anchorage to the plant.
- The thick main root is often accompanied by smaller lateral roots that spread out horizontally.
Characteristics of Carrot (Option B)
- The carrot (Daucus carota) is a classic example of a plant with a taproot system.
- The thick, orange root that we eat is actually the storage organ of the plant, designed to store nutrients and energy.
- Carrots thrive in well-drained soils, allowing their taproots to grow deep and access water and nutrients.
Comparison with Other Options
- Grass (Option A): Grass typically has a fibrous root system, which consists of many thin roots that spread out close to the surface.
- Wheat (Option C): Wheat also possesses a fibrous root system that helps it anchor and absorb moisture efficiently.
- Maize (Option D): Similar to wheat, maize (corn) has a fibrous root system, with many roots that grow shallow and wide.
Conclusion
In summary, the carrot is the correct answer because it features a single, thick taproot, distinguishing it from grasses, wheat, and maize, which all have fibrous root systems. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate the diversity in plant adaptations and growth strategies.
Plants have various root systems that help them adapt to their environments. One of these systems is characterized by a single, thick root, commonly known as a taproot system.
What is a Taproot System?
- A taproot system consists of a main root that grows deeper into the soil, providing stability and anchorage to the plant.
- The thick main root is often accompanied by smaller lateral roots that spread out horizontally.
Characteristics of Carrot (Option B)
- The carrot (Daucus carota) is a classic example of a plant with a taproot system.
- The thick, orange root that we eat is actually the storage organ of the plant, designed to store nutrients and energy.
- Carrots thrive in well-drained soils, allowing their taproots to grow deep and access water and nutrients.
Comparison with Other Options
- Grass (Option A): Grass typically has a fibrous root system, which consists of many thin roots that spread out close to the surface.
- Wheat (Option C): Wheat also possesses a fibrous root system that helps it anchor and absorb moisture efficiently.
- Maize (Option D): Similar to wheat, maize (corn) has a fibrous root system, with many roots that grow shallow and wide.
Conclusion
In summary, the carrot is the correct answer because it features a single, thick taproot, distinguishing it from grasses, wheat, and maize, which all have fibrous root systems. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate the diversity in plant adaptations and growth strategies.
Identify the part of the plant that is primarily responsible for reproduction.- a) Leaf
- b) Stem
- c) Root
- d) Flower
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the part of the plant that is primarily responsible for reproduction.
a)
Leaf
b)
Stem
c)
Root
d)
Flower
|
|
Saptarshi Das answered |
Understanding Plant Reproduction
The flower is the primary reproductive structure in flowering plants (angiosperms). Its complex structure facilitates various processes crucial for reproduction.
Key Functions of the Flower
- Attraction of Pollinators:
Flowers are often brightly colored and fragrant, attracting insects and animals, which help in the process of pollination.
- Pollination:
This is the transfer of pollen from the male part (anther) to the female part (stigma) of the flower. It can occur via wind, water, or animals.
- Fertilization:
After pollination, pollen travels down the style to the ovary, where fertilization occurs. This leads to the formation of seeds.
- Seed Production:
Once fertilized, the ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary matures into a fruit, which helps in seed dispersal.
Other Plant Parts and Their Roles
- Leaves:
Primarily responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy for the plant.
- Stems:
Support the plant, transport nutrients and water between roots and leaves, but do not play a direct role in reproduction.
- Roots:
Anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil, but they are not involved in the reproductive process.
Conclusion
In summary, the flower is essential for the reproductive cycle of flowering plants, making it the correct answer. Understanding its role helps us appreciate the complexity and beauty of plant life.
The flower is the primary reproductive structure in flowering plants (angiosperms). Its complex structure facilitates various processes crucial for reproduction.
Key Functions of the Flower
- Attraction of Pollinators:
Flowers are often brightly colored and fragrant, attracting insects and animals, which help in the process of pollination.
- Pollination:
This is the transfer of pollen from the male part (anther) to the female part (stigma) of the flower. It can occur via wind, water, or animals.
- Fertilization:
After pollination, pollen travels down the style to the ovary, where fertilization occurs. This leads to the formation of seeds.
- Seed Production:
Once fertilized, the ovule develops into a seed, and the ovary matures into a fruit, which helps in seed dispersal.
Other Plant Parts and Their Roles
- Leaves:
Primarily responsible for photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy for the plant.
- Stems:
Support the plant, transport nutrients and water between roots and leaves, but do not play a direct role in reproduction.
- Roots:
Anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil, but they are not involved in the reproductive process.
Conclusion
In summary, the flower is essential for the reproductive cycle of flowering plants, making it the correct answer. Understanding its role helps us appreciate the complexity and beauty of plant life.
Which part of the plant contains the seeds after fertilization?- a) Leaf
- b) Stem
- c) Flower
- d) Root
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the plant contains the seeds after fertilization?
a)
Leaf
b)
Stem
c)
Flower
d)
Root

|
Get Idea answered |
Seeds develop within the ovary of the flower after the process of fertilization. This reproductive part is crucial for the propagation of the plant, as seeds will eventually grow into new plants under favorable conditions.
What function do veins serve in leaves?- a) Absorb sunlight
- b) Transport water and nutrients
- c) Perform photosynthesis
- d) Store food
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What function do veins serve in leaves?
a)
Absorb sunlight
b)
Transport water and nutrients
c)
Perform photosynthesis
d)
Store food

|
Rohini Seth answered |
Veins in leaves are essential for transporting water and nutrients to the leaf tissues and carrying the synthesized food back to other parts of the plant. This vascular network is crucial for maintaining the plant's health and facilitating its metabolic processes.
Four groups of mice were taken for an experiment. One group was control group and other three were test groups. The test groups consume different amounts of sweetener in their food. The control group is the one that receives:- a)10 mg/day of sweetener
- b)50 mg/day of sweetener
- c)No sweetener
- d)Extra food
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Four groups of mice were taken for an experiment. One group was control group and other three were test groups. The test groups consume different amounts of sweetener in their food. The control group is the one that receives:
a)
10 mg/day of sweetener
b)
50 mg/day of sweetener
c)
No sweetener
d)
Extra food

|
EduRev Class 6 answered |
The control group in the experiment is the group that serves as a comparison to the test groups. It does not receive any sweetener in its food. The other three test groups consume different amounts of sweetener in their food.
Test groups:
- Group A: This test group receives 10 mg/day of sweetener in their food.
- Group B: This test group receives 50 mg/day of sweetener in their food.
- Group C: This test group does not receive any sweetener in their food.
- Group D: This test group receives extra food, but no sweetener.
Explanation:
- The purpose of having a control group is to provide a baseline for comparison. By not giving any sweetener to the control group, any changes observed in the test groups can be attributed to the sweetener and not other factors.
- Group A and Group B are the test groups that receive different amounts of sweetener in their food. These groups are used to study the effects of different dosages of sweetener.
- Group C is the control group that does not receive any sweetener. By comparing the results of Group C with the test groups, the researchers can determine the impact of the sweetener on various factors.
- Group D is not a test group related to the sweetener. It receives extra food, but no sweetener. This group may serve as a control group for other factors being studied in the experiment.
In conclusion, the control group in this experiment is the one that does not receive any sweetener in their food (Group C).
Following are some features of plants(i) They lose a lot of water through transpiration.
(ii) Their leaves are always broad and flat.
(iii) They lose very little water through transpiration.
(iv) Their roots grow very deep into the soil.Which of the combination of above features are typical of desert plants?- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Following are some features of plants
(i) They lose a lot of water through transpiration.
(ii) Their leaves are always broad and flat.
(iii) They lose very little water through transpiration.
(iv) Their roots grow very deep into the soil.
(ii) Their leaves are always broad and flat.
(iii) They lose very little water through transpiration.
(iv) Their roots grow very deep into the soil.
Which of the combination of above features are typical of desert plants?
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(iii) and (iv)
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
(iii) Plants lose a significant amount of water through transpiration, a process where water evaporates from the leaves.
(iv) Plants often have deep roots that aid in anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from deeper soil layers.
(iv) Plants often have deep roots that aid in anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients from deeper soil layers.
Fishes have scales on their body. This helps them to _________- a)Remain in the same place in water
- b)Balance themselves in water
- c)Change directions in water
- d)Swim in water
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Fishes have scales on their body. This helps them to _________
a)
Remain in the same place in water
b)
Balance themselves in water
c)
Change directions in water
d)
Swim in water

|
EduRev Class 6 answered |
Scales provide fish with protection and buoyancy, assisting them in maintaining their position in water without constantly expending energy to swim or balance.
Excretion, irritability and reproduction are characteristics of:- a)All animals and plants
- b)Animals only
- c)Plants only
- d)All animals and some plants only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Excretion, irritability and reproduction are characteristics of:
a)
All animals and plants
b)
Animals only
c)
Plants only
d)
All animals and some plants only
|
|
Mansi nambiar answered |
Plants and animals have all the following characteristics: excretion, irritability and reproduction. Let's talk firstly about the plants.
Plants can excrete through stomatal pores in the leaves. The main metabolic reactions that occur in a plant that produces these residues are cellular respiration and photosynthesis. However, this place isn't the only that works as a way of excretion. Plants also excrete solid or slimy things. Talking about irritability, plants can have a reaction about all kind of stimulus, as chemical as phisical. For instance, the lights, the weather, animals around it, temperature and chemical changes inside the plants. About reproduction, plants can reproduce inside the gyno, the female sexual organ of plants. The gynoecium consists of the ovary, which produces and stores the eggs. In the eggs there are also the sex cells of the plant. Now talking about the animals, they have all sort of process, but is more complex than plants. You have about nine phylus in Animal Kingdom, and all sort of phylus has your unique excretion, irritability and reproduction.
Plants can excrete through stomatal pores in the leaves. The main metabolic reactions that occur in a plant that produces these residues are cellular respiration and photosynthesis. However, this place isn't the only that works as a way of excretion. Plants also excrete solid or slimy things. Talking about irritability, plants can have a reaction about all kind of stimulus, as chemical as phisical. For instance, the lights, the weather, animals around it, temperature and chemical changes inside the plants. About reproduction, plants can reproduce inside the gyno, the female sexual organ of plants. The gynoecium consists of the ovary, which produces and stores the eggs. In the eggs there are also the sex cells of the plant. Now talking about the animals, they have all sort of process, but is more complex than plants. You have about nine phylus in Animal Kingdom, and all sort of phylus has your unique excretion, irritability and reproduction.
What is the role of sepals in a flower?- a) Protect the bud
- b) Attract pollinators
- c) Produce pollen
- d) Support the ovary
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the role of sepals in a flower?
a)
Protect the bud
b)
Attract pollinators
c)
Produce pollen
d)
Support the ovary

|
Kds Coaching answered |
Sepals are typically green and serve to protect the flower bud before it blooms. They shield the delicate petals and reproductive structures from environmental damage and dehydration, ensuring the flower can develop properly.
Which part of the plant is primarily responsible for anchoring it to the ground?- a)Leaf
- b)Stem
- c)Root
- d)Flower
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the plant is primarily responsible for anchoring it to the ground?
a)
Leaf
b)
Stem
c)
Root
d)
Flower

|
Get Idea answered |
The root of the plant plays a crucial role in anchoring it to the soil, providing stability and support.
Additionally, roots are vital for absorbing water and essential nutrients from the soil,
which are necessary for the plant's growth and development.
Additionally, roots are vital for absorbing water and essential nutrients from the soil,
which are necessary for the plant's growth and development.
What is the function of xylem in plants?- a) Transport food
- b) Transport water and minerals
- c) Photosynthesis
- d) Reproduction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the function of xylem in plants?
a)
Transport food
b)
Transport water and minerals
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Reproduction
|
|
Sagnik Saha answered |
Function of Xylem in Plants
Xylem is a crucial tissue in vascular plants, primarily responsible for the transport of water and minerals. Here’s a detailed explanation of its function:
Water Transport
- Xylem transports water from the roots to various parts of the plant, including stems and leaves.
- This process occurs through a mechanism called transpiration, where water evaporates from the leaf surface, creating a negative pressure that pulls water upward.
Mineral Transport
- Along with water, xylem also carries essential minerals and nutrients absorbed from the soil.
- These minerals include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and others that are vital for plant growth and development.
Structural Support
- Besides transport, xylem provides structural support to the plant.
- Its cell walls are thickened and lignified, helping to maintain the plant's upright position and withstand various environmental stresses.
Importance in Plant Growth
- The efficient transport of water and minerals is critical for photosynthesis, the process by which plants make their food.
- Adequate water supply helps in nutrient absorption and promotes overall plant health and growth.
In summary, the primary function of xylem is to transport water and minerals, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding the role of xylem is essential for appreciating how plants thrive and maintain their physiological processes.
Xylem is a crucial tissue in vascular plants, primarily responsible for the transport of water and minerals. Here’s a detailed explanation of its function:
Water Transport
- Xylem transports water from the roots to various parts of the plant, including stems and leaves.
- This process occurs through a mechanism called transpiration, where water evaporates from the leaf surface, creating a negative pressure that pulls water upward.
Mineral Transport
- Along with water, xylem also carries essential minerals and nutrients absorbed from the soil.
- These minerals include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and others that are vital for plant growth and development.
Structural Support
- Besides transport, xylem provides structural support to the plant.
- Its cell walls are thickened and lignified, helping to maintain the plant's upright position and withstand various environmental stresses.
Importance in Plant Growth
- The efficient transport of water and minerals is critical for photosynthesis, the process by which plants make their food.
- Adequate water supply helps in nutrient absorption and promotes overall plant health and growth.
In summary, the primary function of xylem is to transport water and minerals, making option 'B' the correct answer. Understanding the role of xylem is essential for appreciating how plants thrive and maintain their physiological processes.
What is the primary role of phloem in plants?- a) Transport food
- b) Transport water
- c) Provide support
- d) Absorb nutrients
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary role of phloem in plants?
a)
Transport food
b)
Transport water
c)
Provide support
d)
Absorb nutrients
|
|
Lekshmi Sen answered |
Primary Role of Phloem in Plants
Phloem is a vital tissue in vascular plants, primarily responsible for the transport of food. Let's explore its role in detail.
Food Transport
- Phloem is responsible for transporting organic nutrients, particularly sugars produced through photosynthesis in the leaves.
- The sugars move from the leaves, where they are synthesized, to other parts of the plant that require energy, like roots, stems, and developing fruits.
- This process is called translocation, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive the necessary nutrients to grow and function effectively.
Structure of Phloem
- Phloem consists of specialized cells, including sieve elements and companion cells.
- Sieve elements form tubes that allow the smooth flow of nutrients, while companion cells help in the loading and unloading of sugars.
Importance of Phloem
- Phloem plays a crucial role in the overall health and survival of plants by distributing energy-rich compounds.
- A healthy phloem system supports growth, reproduction, and resilience against environmental stresses.
Comparison with Other Plant Tissues
- Unlike xylem, which transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, phloem's primary function centers on distributing food.
- This distinction emphasizes the unique and essential role of phloem in plant physiology.
In summary, phloem's primary role in plants is the transport of food, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive the nutrients necessary for growth and vitality. Understanding this function is crucial for appreciating how plants sustain themselves and thrive in their environments.
Phloem is a vital tissue in vascular plants, primarily responsible for the transport of food. Let's explore its role in detail.
Food Transport
- Phloem is responsible for transporting organic nutrients, particularly sugars produced through photosynthesis in the leaves.
- The sugars move from the leaves, where they are synthesized, to other parts of the plant that require energy, like roots, stems, and developing fruits.
- This process is called translocation, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive the necessary nutrients to grow and function effectively.
Structure of Phloem
- Phloem consists of specialized cells, including sieve elements and companion cells.
- Sieve elements form tubes that allow the smooth flow of nutrients, while companion cells help in the loading and unloading of sugars.
Importance of Phloem
- Phloem plays a crucial role in the overall health and survival of plants by distributing energy-rich compounds.
- A healthy phloem system supports growth, reproduction, and resilience against environmental stresses.
Comparison with Other Plant Tissues
- Unlike xylem, which transports water and minerals from the roots to the leaves, phloem's primary function centers on distributing food.
- This distinction emphasizes the unique and essential role of phloem in plant physiology.
In summary, phloem's primary role in plants is the transport of food, ensuring that all parts of the plant receive the nutrients necessary for growth and vitality. Understanding this function is crucial for appreciating how plants sustain themselves and thrive in their environments.
Which joint allows movement in all directions?- a)Hinge
- b)Pivot
- c)Ball and socket
- d)Gliding
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which joint allows movement in all directions?
a)
Hinge
b)
Pivot
c)
Ball and socket
d)
Gliding
|
|
Sneha Rane answered |
The correct answer is option 'C' - Ball and socket joint.
Ball and socket joints are unique in that they allow movement in all directions. These joints are found in our bodies and provide a wide range of motion, allowing us to perform various activities and movements. Let's explore the characteristics and examples of ball and socket joints in more detail.
Characteristics of ball and socket joints:
- Structure: Ball and socket joints consist of a rounded end of one bone (ball) that fits into a cup-shaped cavity (socket) of another bone.
- Range of motion: These joints have the greatest range of motion compared to other types of joints, enabling movement in multiple directions, including rotation, flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
- Stability: The ball and socket joint provides stability due to the deep socket and the surrounding ligaments and muscles that support the joint.
Examples of ball and socket joints:
1. Shoulder joint: The shoulder joint is a classic example of a ball and socket joint. The rounded head of the humerus bone fits into the shallow socket of the scapula bone. This joint allows movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation of the arm.
2. Hip joint: The hip joint is another prominent example of a ball and socket joint. The rounded head of the femur bone fits into the deep socket of the pelvis bone. This joint permits movements like flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation of the leg.
Advantages of ball and socket joints:
- Wide range of motion: Ball and socket joints allow for a vast range of motion, facilitating movements required for daily activities and sports.
- Increased stability: The structure of ball and socket joints provides stability, preventing dislocation and ensuring proper alignment during movement.
- Weight-bearing capacity: Ball and socket joints are designed to bear weight, enabling us to walk, run, and perform weight-bearing activities.
Conclusion:
Ball and socket joints are unique in their ability to allow movement in all directions. The shoulder and hip joints are prominent examples of ball and socket joints in our bodies. These joints provide a wide range of motion, stability, and weight-bearing capacity, making them crucial for our everyday activities and movements.
Ball and socket joints are unique in that they allow movement in all directions. These joints are found in our bodies and provide a wide range of motion, allowing us to perform various activities and movements. Let's explore the characteristics and examples of ball and socket joints in more detail.
Characteristics of ball and socket joints:
- Structure: Ball and socket joints consist of a rounded end of one bone (ball) that fits into a cup-shaped cavity (socket) of another bone.
- Range of motion: These joints have the greatest range of motion compared to other types of joints, enabling movement in multiple directions, including rotation, flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction.
- Stability: The ball and socket joint provides stability due to the deep socket and the surrounding ligaments and muscles that support the joint.
Examples of ball and socket joints:
1. Shoulder joint: The shoulder joint is a classic example of a ball and socket joint. The rounded head of the humerus bone fits into the shallow socket of the scapula bone. This joint allows movements such as flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation of the arm.
2. Hip joint: The hip joint is another prominent example of a ball and socket joint. The rounded head of the femur bone fits into the deep socket of the pelvis bone. This joint permits movements like flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation of the leg.
Advantages of ball and socket joints:
- Wide range of motion: Ball and socket joints allow for a vast range of motion, facilitating movements required for daily activities and sports.
- Increased stability: The structure of ball and socket joints provides stability, preventing dislocation and ensuring proper alignment during movement.
- Weight-bearing capacity: Ball and socket joints are designed to bear weight, enabling us to walk, run, and perform weight-bearing activities.
Conclusion:
Ball and socket joints are unique in their ability to allow movement in all directions. The shoulder and hip joints are prominent examples of ball and socket joints in our bodies. These joints provide a wide range of motion, stability, and weight-bearing capacity, making them crucial for our everyday activities and movements.
Look at the following pictures carefully.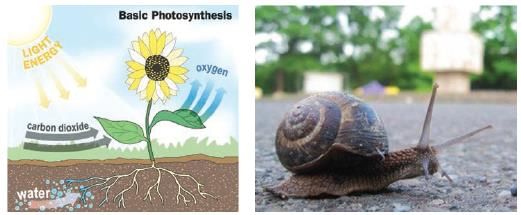 Q. The two living organisms in these pictures are_____________ and the common life process that occurs in both the living organism is_________________ .
Q. The two living organisms in these pictures are_____________ and the common life process that occurs in both the living organism is_________________ .- a)Plant and mushroom, respiration
- b)Plant and animal, photosynthesis
- c)Plant and snail, mobility
- d)Plant and snail, excretion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Look at the following pictures carefully.

Q. The two living organisms in these pictures are_____________ and the common life process that occurs in both the living organism is_________________ .
a)
Plant and mushroom, respiration
b)
Plant and animal, photosynthesis
c)
Plant and snail, mobility
d)
Plant and snail, excretion

|
Vp Classes answered |
The two organisms in the pictures are likely a plant and a snail. Both organisms perform excretion, which is the process of removing waste products from the body. Plants excrete excess water and gases like oxygen, while snails excrete waste through their digestive system. Therefore, the common life process is excretion.
Choose the set that represents only the biotic components of a habitat.- a)Tiger, Deer, Grass, Soil
- b)Rocks, Soil, Plants, Air
- c)Sand, Turtle, Crab, Rocks
- d)Aquatic plant, Fish, Frog, Insect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the set that represents only the biotic components of a habitat.
a)
Tiger, Deer, Grass, Soil
b)
Rocks, Soil, Plants, Air
c)
Sand, Turtle, Crab, Rocks
d)
Aquatic plant, Fish, Frog, Insect

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
Biotic components refer to living organisms in an ecosystem. In this set, aquatic plants, fish, frogs, and insects are all living organisms, representing the biotic components of a habitat.
Which of the following is an incorrect statement about excretion?
- a)Excretion takes place in plants.
- b)Excretion takes place both in plants and animals.
- c)Excretion is the process of getting rid of excess water
- d)Secretion is one method of excretion.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an incorrect statement about excretion?
a)
Excretion takes place in plants.
b)
Excretion takes place both in plants and animals.
c)
Excretion is the process of getting rid of excess water
d)
Secretion is one method of excretion.
|
|
Jay Goyal answered |
Excretion is the process by which waste substances, such as metabolic waste and toxins, are eliminated from the body or organism. It is an essential function for maintaining homeostasis in both plants and animals. However, the incorrect statement about excretion is option C, which states that excretion is the process of getting rid of excess water only.
- Excretion in Plants:
Plants also undergo excretion, although their excretory system is different from animals. In plants, excretion mainly occurs through the stomata, which are small openings on the surface of leaves and stems. These stomata allow for the exchange of gases during photosynthesis but also facilitate the release of waste products, such as oxygen and water vapor. Additionally, plants excrete waste substances, such as resins, gums, and alkaloids, through specialized structures like lenticels and glandular trichomes.
- Excretion in Animals:
Animals have more complex excretory systems, including organs specifically dedicated to excretion. The main excretory organs in animals are the kidneys, which filter waste products from the blood and form urine. The urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, plays a crucial role in eliminating nitrogenous waste, excess water, and other waste substances from the body. Apart from the kidneys, other organs like the skin, lungs, and liver also contribute to excretion.
- Secretion as a Method of Excretion:
Secretion is one of the processes by which excretion occurs. It involves the release of specific substances produced by cells or glands into body fluids, such as blood or digestive juices, for elimination. For example, the liver secretes bile, which is involved in the excretion of waste products like bilirubin and cholesterol. Similarly, the sweat glands in the skin secrete sweat, which helps in the excretion of water, salts, and urea. Thus, secretion is a method through which excretion takes place in animals.
Therefore, option C, which suggests that excretion is only the process of getting rid of excess water, is incorrect. Excretion involves the elimination of various waste substances and toxins from the body, and it occurs in both plants and animals through different mechanisms.
- Excretion in Plants:
Plants also undergo excretion, although their excretory system is different from animals. In plants, excretion mainly occurs through the stomata, which are small openings on the surface of leaves and stems. These stomata allow for the exchange of gases during photosynthesis but also facilitate the release of waste products, such as oxygen and water vapor. Additionally, plants excrete waste substances, such as resins, gums, and alkaloids, through specialized structures like lenticels and glandular trichomes.
- Excretion in Animals:
Animals have more complex excretory systems, including organs specifically dedicated to excretion. The main excretory organs in animals are the kidneys, which filter waste products from the blood and form urine. The urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, plays a crucial role in eliminating nitrogenous waste, excess water, and other waste substances from the body. Apart from the kidneys, other organs like the skin, lungs, and liver also contribute to excretion.
- Secretion as a Method of Excretion:
Secretion is one of the processes by which excretion occurs. It involves the release of specific substances produced by cells or glands into body fluids, such as blood or digestive juices, for elimination. For example, the liver secretes bile, which is involved in the excretion of waste products like bilirubin and cholesterol. Similarly, the sweat glands in the skin secrete sweat, which helps in the excretion of water, salts, and urea. Thus, secretion is a method through which excretion takes place in animals.
Therefore, option C, which suggests that excretion is only the process of getting rid of excess water, is incorrect. Excretion involves the elimination of various waste substances and toxins from the body, and it occurs in both plants and animals through different mechanisms.
Which of the following organisms is not ultimately dependent on the sun as a source of energy?- a)A night-blooming flower is pollinated by night-flying bats
- b)An underground earthworm avoids the sun
- c)A cave fish feeds on debris that washes down to it
- d)No, all the organisms are ultimately dependent on the sun
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organisms is not ultimately dependent on the sun as a source of energy?
a)
A night-blooming flower is pollinated by night-flying bats
b)
An underground earthworm avoids the sun
c)
A cave fish feeds on debris that washes down to it
d)
No, all the organisms are ultimately dependent on the sun
|
|
Meena Yadav answered |
Option 'D' is the correct answer.
Which part of the flower develops into fruit?- a) Petal
- b) Sepal
- c) Ovary
- d) Stamen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the flower develops into fruit?
a)
Petal
b)
Sepal
c)
Ovary
d)
Stamen
|
|
Pritam Kulkarni answered |
Understanding Flower Structure and Fruit Development
Flowers are crucial reproductive structures in flowering plants, and they contain several parts, each with specific functions. One of the key components of a flower is the ovary.
Role of the Ovary
- The ovary is located at the base of the flower and is part of the female reproductive organ known as the pistil.
- It contains ovules, which are the potential seeds of the plant.
- After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds, while the ovary itself matures into the fruit.
Process of Fruit Development
- After pollination, when pollen grains fertilize the ovules within the ovary, the ovules develop into seeds.
- The ovary starts to grow and transform into fruit, which serves to protect the developing seeds and aid in their dispersal.
- The fruit can take many forms, such as fleshy fruits (like apples) or dry fruits (like nuts).
Importance of Fruit
- Fruits play a vital role in the life cycle of plants by facilitating seed dispersal.
- Animals eat the fruit, and through digestion, they help spread the seeds away from the parent plant, promoting genetic diversity and colonization of new areas.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question about which part of the flower develops into fruit is indeed the ovary (option C), as it is essential for the production and protection of seeds post-fertilization.
Flowers are crucial reproductive structures in flowering plants, and they contain several parts, each with specific functions. One of the key components of a flower is the ovary.
Role of the Ovary
- The ovary is located at the base of the flower and is part of the female reproductive organ known as the pistil.
- It contains ovules, which are the potential seeds of the plant.
- After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds, while the ovary itself matures into the fruit.
Process of Fruit Development
- After pollination, when pollen grains fertilize the ovules within the ovary, the ovules develop into seeds.
- The ovary starts to grow and transform into fruit, which serves to protect the developing seeds and aid in their dispersal.
- The fruit can take many forms, such as fleshy fruits (like apples) or dry fruits (like nuts).
Importance of Fruit
- Fruits play a vital role in the life cycle of plants by facilitating seed dispersal.
- Animals eat the fruit, and through digestion, they help spread the seeds away from the parent plant, promoting genetic diversity and colonization of new areas.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question about which part of the flower develops into fruit is indeed the ovary (option C), as it is essential for the production and protection of seeds post-fertilization.
Which type of plant typically has leaves with parallel veins?- a) Monocots
- b) Dicots
- c) Gymnosperms
- d) Bryophytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of plant typically has leaves with parallel veins?
a)
Monocots
b)
Dicots
c)
Gymnosperms
d)
Bryophytes

|
Geetika Patel answered |
Understanding Plant Types
Plants are categorized into different groups based on their characteristics. One of the primary classifications is between monocots and dicots.
Monocots: Characteristics
- Parallel Veins: Monocots, or monocotyledons, are characterized by leaves that have parallel veins. This means that the veins run parallel to each other along the length of the leaf.
- Examples: Common examples of monocots include grasses, lilies, and orchids.
- Other Features: Monocots typically have flower parts in multiples of three, a single cotyledon (seed leaf), and fibrous root systems.
Dicots: Characteristics
- Net-like Veins: In contrast, dicots, or dicotyledons, have leaves with a branching, net-like vein pattern.
- Examples: Examples of dicots include roses, sunflowers, and oak trees.
- Other Features: Dicots usually have flower parts in multiples of four or five, two cotyledons, and taproot systems.
Conclusion
The distinct leaf vein patterns are a key identifier between monocots and dicots. Monocots, with their parallel veins, are a unique and important group of flowering plants. Understanding these differences helps in the study of botany and plant biology.
Plants are categorized into different groups based on their characteristics. One of the primary classifications is between monocots and dicots.
Monocots: Characteristics
- Parallel Veins: Monocots, or monocotyledons, are characterized by leaves that have parallel veins. This means that the veins run parallel to each other along the length of the leaf.
- Examples: Common examples of monocots include grasses, lilies, and orchids.
- Other Features: Monocots typically have flower parts in multiples of three, a single cotyledon (seed leaf), and fibrous root systems.
Dicots: Characteristics
- Net-like Veins: In contrast, dicots, or dicotyledons, have leaves with a branching, net-like vein pattern.
- Examples: Examples of dicots include roses, sunflowers, and oak trees.
- Other Features: Dicots usually have flower parts in multiples of four or five, two cotyledons, and taproot systems.
Conclusion
The distinct leaf vein patterns are a key identifier between monocots and dicots. Monocots, with their parallel veins, are a unique and important group of flowering plants. Understanding these differences helps in the study of botany and plant biology.
What term describes the small openings on the surface of leaves that facilitate gas exchange?- a) Stomata
- b) Chloroplasts
- c) Veins
- d) Petioles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What term describes the small openings on the surface of leaves that facilitate gas exchange?
a)
Stomata
b)
Chloroplasts
c)
Veins
d)
Petioles
|
|
Manoj Iyer answered |
Understanding Stomata
Stomata are tiny openings located on the surface of leaves that play a crucial role in the process of gas exchange in plants.
Key Functions of Stomata:
- Gas Exchange: Stomata allow carbon dioxide (CO2) to enter the leaf for photosynthesis, which is essential for the plant's growth and energy production. At the same time, oxygen (O2), a byproduct of photosynthesis, exits the leaf through these openings.
- Transpiration: Stomata also facilitate transpiration, the process by which water vapor is released from the plant into the atmosphere. This helps in cooling the plant and maintaining its water balance.
- Regulation: The opening and closing of stomata are regulated by guard cells. These specialized cells surround each stoma and control its size, responding to environmental conditions such as light, humidity, and CO2 concentration.
Other Options Explained:
- Chloroplasts: These are organelles within plant cells responsible for photosynthesis but do not facilitate gas exchange.
- Veins: Plant veins transport water and nutrients but are not involved in gas exchange.
- Petioles: The petiole is the stalk that attaches the leaf to the stem, serving a structural role rather than a function in gas exchange.
In conclusion, stomata are essential for the survival of plants, enabling them to take in necessary gases and release byproducts efficiently. Their unique structure and function make them vital components of the leaf's anatomy.
Stomata are tiny openings located on the surface of leaves that play a crucial role in the process of gas exchange in plants.
Key Functions of Stomata:
- Gas Exchange: Stomata allow carbon dioxide (CO2) to enter the leaf for photosynthesis, which is essential for the plant's growth and energy production. At the same time, oxygen (O2), a byproduct of photosynthesis, exits the leaf through these openings.
- Transpiration: Stomata also facilitate transpiration, the process by which water vapor is released from the plant into the atmosphere. This helps in cooling the plant and maintaining its water balance.
- Regulation: The opening and closing of stomata are regulated by guard cells. These specialized cells surround each stoma and control its size, responding to environmental conditions such as light, humidity, and CO2 concentration.
Other Options Explained:
- Chloroplasts: These are organelles within plant cells responsible for photosynthesis but do not facilitate gas exchange.
- Veins: Plant veins transport water and nutrients but are not involved in gas exchange.
- Petioles: The petiole is the stalk that attaches the leaf to the stem, serving a structural role rather than a function in gas exchange.
In conclusion, stomata are essential for the survival of plants, enabling them to take in necessary gases and release byproducts efficiently. Their unique structure and function make them vital components of the leaf's anatomy.
Based on the diagrams of the dolphin and the fish (not drawn to scale), which characteristic they share in common?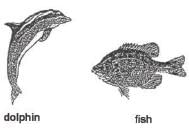
1. They both have whiskers.
2. Each has a tail to propel itself forward in the water.
3. Both have gills to breath.
4. Both are warm blooded.- a)Only 2
- b)1 and 4 only
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)3 and 4 only
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the diagrams of the dolphin and the fish (not drawn to scale), which characteristic they share in common?

1. They both have whiskers.
2. Each has a tail to propel itself forward in the water.
3. Both have gills to breath.
4. Both are warm blooded.
a)
Only 2
b)
1 and 4 only
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
3 and 4 only
|
|
Eduskill Classes answered |
- Option 1 (Whiskers): Dolphins do not have whiskers, so this statement is incorrect.
- Option 2 (Tail to propel forward in water): Both dolphins and fish have tails that they use to propel themselves forward in the water. This is a common characteristic.
- Option 3 (Gills to breathe): Fish have gills to breathe underwater, but dolphins are mammals and breathe through lungs, so they do not have gills.
- Option 4 (Warm-blooded): Dolphins are warm-blooded mammals, but fish are cold-blooded, so this statement is incorrect for fish.
Thus, the correct answer is Option A: Only 2, because both dolphins and fish have tails to propel themselves in water.
These living organisms excrete uric acid:- a)Birds and lizards
- b)Birds and reptiles
- c)Birds
- d)A and B both
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
These living organisms excrete uric acid:
a)
Birds and lizards
b)
Birds and reptiles
c)
Birds
d)
A and B both

|
Yogesh Sangwan answered |
Beacause all organisams excerete uric acid
Some green beans were placed on some damp cotton wool in a dish and placed in a dark corner. A few days later, the beans started to grow into seedlings. The beans get their food for growth from the ________________.- a)Air
- b)Cotton wool
- c)Seed-leaves
- d)Water used to damp the cotton wool
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Some green beans were placed on some damp cotton wool in a dish and placed in a dark corner. A few days later, the beans started to grow into seedlings. The beans get their food for growth from the ________________.
a)
Air
b)
Cotton wool
c)
Seed-leaves
d)
Water used to damp the cotton wool
|
|
Debanshi Roy answered |
The correct answer is option 'C', which states that the seedlings get their food for growth from the seed-leaves.
Explanation:
When green beans are placed on damp cotton wool and left in a dark corner, they start to grow into seedlings after a few days. This process is known as germination. During germination, the seed undergoes various changes to develop into a seedling.
During the early stages of germination, the seed absorbs water from the damp cotton wool. This water activates enzymes within the seed, which then trigger metabolic processes. As a result, the seed begins to break down stored food reserves to provide energy for growth.
The stored food reserves in the seed are located in the seed-leaves, also known as cotyledons. These cotyledons contain stored carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, which serve as the initial source of nutrition for the developing seedling. The cotyledons provide the necessary nutrients for the seedling until it can establish its own root system and start absorbing nutrients from the soil.
The cotyledons also serve another important function during germination. They emerge from the seed coat and become the first leaves of the seedling. These seed-leaves are usually thick and fleshy, allowing them to store a significant amount of food reserves. As the seedling grows, it uses the stored food reserves in the cotyledons to produce energy for photosynthesis and to develop its roots, stem, and true leaves.
In summary, the seed-leaves (cotyledons) of the green beans provide the initial source of food for the growing seedling during germination. They contain stored carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids that are broken down and used by the seedling until it can establish its own source of nutrition through photosynthesis and nutrient absorption from the soil.
Explanation:
When green beans are placed on damp cotton wool and left in a dark corner, they start to grow into seedlings after a few days. This process is known as germination. During germination, the seed undergoes various changes to develop into a seedling.
During the early stages of germination, the seed absorbs water from the damp cotton wool. This water activates enzymes within the seed, which then trigger metabolic processes. As a result, the seed begins to break down stored food reserves to provide energy for growth.
The stored food reserves in the seed are located in the seed-leaves, also known as cotyledons. These cotyledons contain stored carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids, which serve as the initial source of nutrition for the developing seedling. The cotyledons provide the necessary nutrients for the seedling until it can establish its own root system and start absorbing nutrients from the soil.
The cotyledons also serve another important function during germination. They emerge from the seed coat and become the first leaves of the seedling. These seed-leaves are usually thick and fleshy, allowing them to store a significant amount of food reserves. As the seedling grows, it uses the stored food reserves in the cotyledons to produce energy for photosynthesis and to develop its roots, stem, and true leaves.
In summary, the seed-leaves (cotyledons) of the green beans provide the initial source of food for the growing seedling during germination. They contain stored carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids that are broken down and used by the seedling until it can establish its own source of nutrition through photosynthesis and nutrient absorption from the soil.
What is the primary function of the stem in a plant?- a)Absorption of water
- b)Support and transport
- c)Photosynthesis
- d)Reproduction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of the stem in a plant?
a)
Absorption of water
b)
Support and transport
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Reproduction

|
EduRev Class 6 answered |
The stem serves as the main support structure of a plant, elevating leaves and flowers to access sunlight while transporting water, nutrients, and food between the roots and other parts of the plant.This vital function ensures that all parts of the plant receive the necessary resources for survival.
Which of the following moves by contraction and expansion of the body?- a)Snake
- b)Earthworm
- c)Snail
- d)Crab
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following moves by contraction and expansion of the body?
a)
Snake
b)
Earthworm
c)
Snail
d)
Crab

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
- Earthworm: Earthworms move by contracting and expanding their body segments. They have circular and longitudinal muscles.
The correct answer is C: Earthworm.
The correct answer is C: Earthworm.
Which part of the skeleton protects the brain?- a)Spine
- b)Rib cage
- c)Skull
- d)Pelvis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the skeleton protects the brain?
a)
Spine
b)
Rib cage
c)
Skull
d)
Pelvis

|
Get Idea answered |
The skull is a bony structure that serves to protect the brain from injury.
Key points:
- The skull is composed of multiple bones joined together.
- It encases and safeguards the brain, a vital organ.
Topic in NCERT: Fixed joints
Line in NCERT: "The skull is made up of many bones joined together. It encloses and protects a very important part of the body, the brain."
Samantha found a healthy plant with red leaves in her garden. She said that the plant is not able to make food because its leaves are not green. Is Samantha correct?
- a)Yes. The plant does not have green leaves. Hence, it will not make its own food but gets its food from the ground
- b)No. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is hidden under the red pigment in the leaves. Hence, the plant can still make food.
- c)No. Even though the plant has no green leaves, it can still make food through its underground stem
- d)Yes. The plant does not have green leaves. Hence, it does not have chlorophyll to absorb sunlight to make food
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Samantha found a healthy plant with red leaves in her garden. She said that the plant is not able to make food because its leaves are not green. Is Samantha correct?
a)
Yes. The plant does not have green leaves. Hence, it will not make its own food but gets its food from the ground
b)
No. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is hidden under the red pigment in the leaves. Hence, the plant can still make food.
c)
No. Even though the plant has no green leaves, it can still make food through its underground stem
d)
Yes. The plant does not have green leaves. Hence, it does not have chlorophyll to absorb sunlight to make food
|
|
Pallavi Roy answered |
Answer:
Explanation:
The correct answer is option D: No. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is hidden under the red pigment in the leaves. Hence, the plant can still make food.
Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis:
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells. It is essential for the process of photosynthesis, which is how plants make their own food. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and converts it into chemical energy, which is used to produce glucose and oxygen.
Red Leaves:
In this scenario, Samantha found a healthy plant with red leaves in her garden. While it is true that most plants have green leaves due to the presence of chlorophyll, there are some plants that have leaves of different colors, such as red. The red color in these leaves is due to the presence of other pigments, such as anthocyanins, which can mask the green color of chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll Hidden:
Even though the leaves of the plant are red, it does not mean that it is unable to make food. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is still present in the leaves but is hidden by the red pigment. This means that the plant is still capable of absorbing sunlight and carrying out photosynthesis, even though its leaves are not green.
Conclusion:
Samantha is incorrect in her statement that the plant is not able to make food because its leaves are not green. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is hidden under the red pigment in the leaves, allowing the plant to still carry out photosynthesis and make its own food. The plant may have adapted to have red leaves for various reasons, such as attracting pollinators or protecting against excessive sunlight.
Explanation:
The correct answer is option D: No. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is hidden under the red pigment in the leaves. Hence, the plant can still make food.
Chlorophyll and Photosynthesis:
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant cells. It is essential for the process of photosynthesis, which is how plants make their own food. During photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs sunlight and converts it into chemical energy, which is used to produce glucose and oxygen.
Red Leaves:
In this scenario, Samantha found a healthy plant with red leaves in her garden. While it is true that most plants have green leaves due to the presence of chlorophyll, there are some plants that have leaves of different colors, such as red. The red color in these leaves is due to the presence of other pigments, such as anthocyanins, which can mask the green color of chlorophyll.
Chlorophyll Hidden:
Even though the leaves of the plant are red, it does not mean that it is unable to make food. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is still present in the leaves but is hidden by the red pigment. This means that the plant is still capable of absorbing sunlight and carrying out photosynthesis, even though its leaves are not green.
Conclusion:
Samantha is incorrect in her statement that the plant is not able to make food because its leaves are not green. The green pigment, chlorophyll, is hidden under the red pigment in the leaves, allowing the plant to still carry out photosynthesis and make its own food. The plant may have adapted to have red leaves for various reasons, such as attracting pollinators or protecting against excessive sunlight.
Which of the following is classified as a modified stem?- a)Carrot
- b)Potato
- c)Spinach
- d)Radish
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is classified as a modified stem?
a)
Carrot
b)
Potato
c)
Spinach
d)
Radish

|
Coders Trust answered |
Explanation:
- Carrot – a modified root (taproot storing food).
- Potato – a modified stem (underground stem called a tuber; has nodes, internodes, and “eyes” which are axillary buds).
- Spinach – leafy vegetable, normal leaves (not a modified stem).
- Radish – a modified root (taproot storing food).
Read the features of a plant as given below:
1. They have waxy upper surface.
2. Leaves are large and flat.
3. Roots are much reduced in size.
4. Stems are generally long and narrow.Q. To which of the following habitats does this plant belong?- a)Polar region
- b)Desert
- c)Aquatic
- d)Tropical rainforest
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the features of a plant as given below:
1. They have waxy upper surface.
2. Leaves are large and flat.
3. Roots are much reduced in size.
4. Stems are generally long and narrow.
1. They have waxy upper surface.
2. Leaves are large and flat.
3. Roots are much reduced in size.
4. Stems are generally long and narrow.
Q. To which of the following habitats does this plant belong?
a)
Polar region
b)
Desert
c)
Aquatic
d)
Tropical rainforest
|
|
Maya Mehta answered |
Answer:
Plant Features:
1. They have waxy upper surface.
2. Leaves are large and flat.
3. Roots are much reduced in size.
4. Stems are generally long and narrow.
Explanation:
To determine the habitat of a plant based on its features, we need to analyze the characteristics and match them with the conditions found in different habitats.
1. Waxy Upper Surface:
Plants with a waxy upper surface on their leaves generally have this adaptation to prevent water loss. The waxy cuticle acts as a barrier, reducing transpiration and preventing dehydration. This adaptation is common in plants that thrive in dry environments.
2. Large and Flat Leaves:
Large and flat leaves are beneficial for capturing sunlight for photosynthesis. These types of leaves are commonly found in plants that require a lot of sunlight. They have a larger surface area, allowing them to absorb more sunlight for energy production.
3. Reduced Size of Roots:
When roots are reduced in size, it indicates that the plant does not require extensive root systems to absorb water and nutrients. This adaptation is often found in plants that grow in environments where water availability is limited or inconsistent.
4. Long and Narrow Stems:
Plants with long and narrow stems are usually adapted to habitats with limited space or where competition for light is high. These types of stems allow the plant to grow upwards towards sunlight, maximizing their exposure to light.
Habitat Conclusion:
Based on the given features, the plant with a waxy upper surface, large and flat leaves, reduced size of roots, and long and narrow stems is most likely adapted to an aquatic habitat.
In an aquatic habitat, plants need to adapt to living in or near water. The waxy upper surface helps prevent waterlogging and enables the plant to float or remain submerged. The large and flat leaves allow for efficient photosynthesis in water where light is often limited. The reduced size of roots is common in aquatic plants as they can obtain nutrients directly from the water. Lastly, the long and narrow stems help the plant reach the water's surface to capture sunlight.
Therefore, option c) Aquatic is the correct answer based on the given plant features.
Plant Features:
1. They have waxy upper surface.
2. Leaves are large and flat.
3. Roots are much reduced in size.
4. Stems are generally long and narrow.
Explanation:
To determine the habitat of a plant based on its features, we need to analyze the characteristics and match them with the conditions found in different habitats.
1. Waxy Upper Surface:
Plants with a waxy upper surface on their leaves generally have this adaptation to prevent water loss. The waxy cuticle acts as a barrier, reducing transpiration and preventing dehydration. This adaptation is common in plants that thrive in dry environments.
2. Large and Flat Leaves:
Large and flat leaves are beneficial for capturing sunlight for photosynthesis. These types of leaves are commonly found in plants that require a lot of sunlight. They have a larger surface area, allowing them to absorb more sunlight for energy production.
3. Reduced Size of Roots:
When roots are reduced in size, it indicates that the plant does not require extensive root systems to absorb water and nutrients. This adaptation is often found in plants that grow in environments where water availability is limited or inconsistent.
4. Long and Narrow Stems:
Plants with long and narrow stems are usually adapted to habitats with limited space or where competition for light is high. These types of stems allow the plant to grow upwards towards sunlight, maximizing their exposure to light.
Habitat Conclusion:
Based on the given features, the plant with a waxy upper surface, large and flat leaves, reduced size of roots, and long and narrow stems is most likely adapted to an aquatic habitat.
In an aquatic habitat, plants need to adapt to living in or near water. The waxy upper surface helps prevent waterlogging and enables the plant to float or remain submerged. The large and flat leaves allow for efficient photosynthesis in water where light is often limited. The reduced size of roots is common in aquatic plants as they can obtain nutrients directly from the water. Lastly, the long and narrow stems help the plant reach the water's surface to capture sunlight.
Therefore, option c) Aquatic is the correct answer based on the given plant features.
Which of the following animals have the correct form of adaptation?- a)Camel: bristles on his feet
- b)Whale: blow holes in its head
- c)Mudskipper: lungs for breathing
- d)Birds: compact bones
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following animals have the correct form of adaptation?
a)
Camel: bristles on his feet
b)
Whale: blow holes in its head
c)
Mudskipper: lungs for breathing
d)
Birds: compact bones
|
|
Nilanjan Unni answered |
**Adaptations in Animals**
**Introduction:**
Adaptations are modifications or traits that help organisms survive and thrive in their specific environments. Different animals have different adaptations that enable them to meet the challenges of their habitats. In this question, we are asked to identify the animal that has the correct form of adaptation out of the given options. Let's analyze each option to find the correct answer.
**a) Camel: bristles on its feet:**
Camels have several adaptations that enable them to survive in the desert. However, bristles on their feet are not one of them. The bristles on a camel's feet are actually protective hairs that help prevent sand from entering their hooves, which is important for walking in sandy environments. Therefore, this adaptation is incorrect in the context of the question.
**b) Whale: blowholes in its head:**
Whales are marine mammals that have evolved to live in water. One of their most distinctive adaptations is the presence of blowholes in their heads. These blowholes are specialized nostrils that allow whales to breathe air at the water's surface without having to fully expose their bodies. This adaptation is crucial for their survival and is the correct answer to the question.
**c) Mudskipper: lungs for breathing:**
Mudskippers are unique fish that can survive out of water for extended periods of time. They have adapted to their muddy habitats by developing lungs, which allow them to breathe air. This adaptation is useful for mudskippers when they are in areas with low oxygen levels or when the water dries up. However, in the context of the question, this adaptation is incorrect as it does not match with the given animal.
**d) Birds: compact bones:**
Birds have a variety of adaptations that enable them to fly and live in different environments. One of these adaptations is having hollow or pneumatic bones. These bones are lightweight and filled with air sacs, which help reduce the bird's overall weight, making it easier for them to fly. Compact bones, on the other hand, are denser and heavier, and not a correct adaptation for birds.
**Conclusion:**
Out of the given options, the correct animal with the appropriate adaptation is the whale, which has blowholes in its head. This adaptation allows whales to breathe air at the water's surface, making it easier for them to survive in their marine environment.
**Introduction:**
Adaptations are modifications or traits that help organisms survive and thrive in their specific environments. Different animals have different adaptations that enable them to meet the challenges of their habitats. In this question, we are asked to identify the animal that has the correct form of adaptation out of the given options. Let's analyze each option to find the correct answer.
**a) Camel: bristles on its feet:**
Camels have several adaptations that enable them to survive in the desert. However, bristles on their feet are not one of them. The bristles on a camel's feet are actually protective hairs that help prevent sand from entering their hooves, which is important for walking in sandy environments. Therefore, this adaptation is incorrect in the context of the question.
**b) Whale: blowholes in its head:**
Whales are marine mammals that have evolved to live in water. One of their most distinctive adaptations is the presence of blowholes in their heads. These blowholes are specialized nostrils that allow whales to breathe air at the water's surface without having to fully expose their bodies. This adaptation is crucial for their survival and is the correct answer to the question.
**c) Mudskipper: lungs for breathing:**
Mudskippers are unique fish that can survive out of water for extended periods of time. They have adapted to their muddy habitats by developing lungs, which allow them to breathe air. This adaptation is useful for mudskippers when they are in areas with low oxygen levels or when the water dries up. However, in the context of the question, this adaptation is incorrect as it does not match with the given animal.
**d) Birds: compact bones:**
Birds have a variety of adaptations that enable them to fly and live in different environments. One of these adaptations is having hollow or pneumatic bones. These bones are lightweight and filled with air sacs, which help reduce the bird's overall weight, making it easier for them to fly. Compact bones, on the other hand, are denser and heavier, and not a correct adaptation for birds.
**Conclusion:**
Out of the given options, the correct animal with the appropriate adaptation is the whale, which has blowholes in its head. This adaptation allows whales to breathe air at the water's surface, making it easier for them to survive in their marine environment.
Organisms that obtain their food from others are called- a)Autotrophs
- b)Consumer
- c)Producer
- d)Scavengers
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms that obtain their food from others are called
a)
Autotrophs
b)
Consumer
c)
Producer
d)
Scavengers

|
Coders Trust answered |
Organisms that obtain their food from other organisms are called consumers. Consumers depend on other organisms for their food, either by eating plants (herbivores), other animals (carnivores), or both (omnivores).
- Autotrophs (Option A) are organisms that can produce their own food, such as plants that use photosynthesis.
- Producers (Option C) are also autotrophs, such as plants and some bacteria, that produce their own food and serve as the base of the food chain.
- Scavengers (Option D) are a type of consumer that feed on dead organisms.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B: Consumer.
What are the two main components of a stamen?- a)Ovary and style
- b)Anther and filament
- c)Petal and sepal
- d)Stigma and ovule
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer??
What are the two main components of a stamen?
a)
Ovary and style
b)
Anther and filament
c)
Petal and sepal
d)
Stigma and ovule
|
|
Ishaan Chawla answered |
Understanding the Stamen
The stamen is a crucial part of a flower's reproductive system. It consists of two main components: the anther and the filament.
Components of Stamen
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option (a) "Ovary and style" refers to parts of the pistil, which is the female reproductive structure of the flower.
- Option (c) "Petal and sepal" are parts of the flower that are primarily involved in attracting pollinators and protecting the reproductive organs but are not part of the stamen.
- Option (d) "Stigma and ovule" are also components of the pistil, with the stigma receiving pollen and the ovule developing into seeds after fertilization.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'B' because the anther and filament are the two defining components that make up a stamen, highlighting its role in the male reproductive process of flowering plants.
The stamen is a crucial part of a flower's reproductive system. It consists of two main components: the anther and the filament.
Components of Stamen
- Anther:
- The anther is the part of the stamen that produces pollen grains, which contain the male gametes (sperm cells) necessary for fertilization.
- It is typically located at the top of the stamen and is often yellow or orange, making it easily identifiable. - Filament:
- The filament is a slender stalk that supports the anther and holds it in a position where pollinators can easily access the pollen.
- It connects the anther to the base of the flower, ensuring that the pollen is available for transfer to the stigma of the pistil during pollination.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option (a) "Ovary and style" refers to parts of the pistil, which is the female reproductive structure of the flower.
- Option (c) "Petal and sepal" are parts of the flower that are primarily involved in attracting pollinators and protecting the reproductive organs but are not part of the stamen.
- Option (d) "Stigma and ovule" are also components of the pistil, with the stigma receiving pollen and the ovule developing into seeds after fertilization.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'B' because the anther and filament are the two defining components that make up a stamen, highlighting its role in the male reproductive process of flowering plants.
What is the main function of root hairs?- a) Absorb light
- b) Absorb water and nutrients
- c) Protect the root
- d) Store food
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main function of root hairs?
a)
Absorb light
b)
Absorb water and nutrients
c)
Protect the root
d)
Store food

|
Get Idea answered |
Root hairs significantly increase the surface area of the root, enhancing the plant's ability to absorb water and essential nutrients from the soil. This increased absorption capability is vital for the plant's growth and overall health.
What part of the plant is responsible for losing water vapor through small pores?- a) Root
- b) Stem
- c) Leaf
- d) Flower
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What part of the plant is responsible for losing water vapor through small pores?
a)
Root
b)
Stem
c)
Leaf
d)
Flower

|
Get Idea answered |
Leaves lose water vapor through tiny openings called stomata. This process, known as transpiration, helps regulate water loss and maintains the plant's temperature while also facilitating the uptake of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
Chapter doubts & questions for The World of Living - Science Olympiad Class 6 2025 is part of Class 6 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 6 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The World of Living - Science Olympiad Class 6 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 6 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Olympiad Class 6
70 videos|150 docs|104 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










