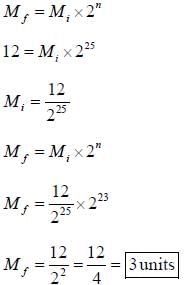All Exams >
Biotechnology Engineering (BT) >
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Biotechnology for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam
λ EMBL3 is used as a vector to clone 2000 bp fragments generated from a partial Sau3Al digest of the human genome (3 x 109 bp). We wish to isolate a gene contained completely on a 20,000 bp fragment. To have a 99% chance of isolating this gene in the λ EMBL3 recombinant genomic library, the number of independent clones to be examined are _______
Hint: (2 x 104 / 3 x 109) = 6.7 x 10-6 and ln(1 - 6.7 x 10-6) = In 0.9999 and In (0.01) = -4.61
Correct answer is '688000'. Can you explain this answer?
λ EMBL3 is used as a vector to clone 2000 bp fragments generated from a partial Sau3Al digest of the human genome (3 x 109 bp). We wish to isolate a gene contained completely on a 20,000 bp fragment. To have a 99% chance of isolating this gene in the λ EMBL3 recombinant genomic library, the number of independent clones to be examined are _______
Hint: (2 x 104 / 3 x 109) = 6.7 x 10-6 and ln(1 - 6.7 x 10-6) = In 0.9999 and In (0.01) = -4.61
Hint: (2 x 104 / 3 x 109) = 6.7 x 10-6 and ln(1 - 6.7 x 10-6) = In 0.9999 and In (0.01) = -4.61

|
Siddharth Majumdar answered |
The given sequence of the polypeptide Ala-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Arg-Pro-Val-Trp-Lys-Pro is treated with Trypsin in the laboratory. The number of fragments generated after treatment with trypsin will be ______________
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
The given sequence of the polypeptide Ala-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Arg-Pro-Val-Trp-Lys-Pro is treated with Trypsin in the laboratory. The number of fragments generated after treatment with trypsin will be ______________

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
Trypsin cuts at the C terminal of Lys or Arg but next a.a. should not be proline. And, also it is an endonuclease not exonuclease. So 2 fragments will be generated.
Which of the following is not correct about restriction enzymes- a)All restriction enzymes do not cut within recognition sites
- b)Restriction sites are always palindromic
- c)Restriction enzymes are synthesized in mammalian cells
- d)Two restriction enzymes can not cut at same sites
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not correct about restriction enzymes
a)
All restriction enzymes do not cut within recognition sites
b)
Restriction sites are always palindromic
c)
Restriction enzymes are synthesized in mammalian cells
d)
Two restriction enzymes can not cut at same sites

|
Madhavan Iyer answered |
Restriction enzymes are not synthesized by mammals but they form immune defence of bacterial cells. It is however true that every restriction site is palindromic, read same from both the ends. Two restriction enzymes can cut at same sites like isoschizomers. Also, there are three prominent classes of restriction enzymes, type I which cut 1000 bp away from recognition sites, type II which cut within the recognition sites, and type III which cut approximately 50 bp away from recognition sites, hence statement 1 is not correct.
What is drawback of Maxam-Gilbert method of DNA-sequencing?- a)It is not applicable for DNA sequencing, it is applicable for protein sequencing
- b)First nucleotide at the 3’ end of the DNA can not be sequenced by this method
- c)It can be applied only invivo condition
- d)It requires sequencing of both the strand to find out sequence of DNA.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is drawback of Maxam-Gilbert method of DNA-sequencing?
a)
It is not applicable for DNA sequencing, it is applicable for protein sequencing
b)
First nucleotide at the 3’ end of the DNA can not be sequenced by this method
c)
It can be applied only invivo condition
d)
It requires sequencing of both the strand to find out sequence of DNA.

|
Saranya Mehta answered |
In Maxam-Gilbert method of DNA-sequencing, the first nucleotide at 5’ can not be sequenced. So it requires sequencing of both the strand of DNA.
Which of the following statements about the chaotrophic agent is incorrect?- a)It leads to decrease in number of hydrogen bonds between solvent (water –water interactions)
- b)It leads to decrease in number/strength of hydrogen bonds between solvent (water –water interactions)
- c)They are also known as anti-kosmotropic agents
- d)It leads to increase in number/strength of hydrogen bonds between solvent (water –water interactions)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about the chaotrophic agent is incorrect?
a)
It leads to decrease in number of hydrogen bonds between solvent (water –water interactions)
b)
It leads to decrease in number/strength of hydrogen bonds between solvent (water –water interactions)
c)
They are also known as anti-kosmotropic agents
d)
It leads to increase in number/strength of hydrogen bonds between solvent (water –water interactions)

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
Chaotroph is a term used for agents such as urea that lead to denaturation and precipitation of biomolecules by enhancing solvent-solvent interactions and reducing solvent-solute interactions.
A restriction site “GAATTC” is recognized by an enzyme EcoRI, How many sites of this sequence are probable in a cloning vector, pBR322 of size 4361 bp.- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A restriction site “GAATTC” is recognized by an enzyme EcoRI, How many sites of this sequence are probable in a cloning vector, pBR322 of size 4361 bp.
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four

|
Jay Nambiar answered |
The probability of restriction site in a given DNA is calculated by formula
One in 4n, where n is the number of base pairs in a site
i.e. one site in 4096 bp,hence a DNA of size 4361 is likely to possess only one site based on random probability
One in 4n, where n is the number of base pairs in a site
i.e. one site in 4096 bp,hence a DNA of size 4361 is likely to possess only one site based on random probability
Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzyme?- a)5’CACGTA3’; CTCAGT5’
- b)5’CGTTCG3’; ATGGTA5’
- c)5’GAATTC3’; CTTAAG5’
- d)5’GATATC3’; CTACTA5’
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following palindromic base sequences in DNA can be easily cut at about the middle by some particular restriction enzyme?
a)
5’CACGTA3’; CTCAGT5’
b)
5’CGTTCG3’; ATGGTA5’
c)
5’GAATTC3’; CTTAAG5’
d)
5’GATATC3’; CTACTA5’

|
Sahana Sharma answered |
In given all four options
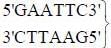 is the palindromic sequence because sequence same from both side in both strands.
is the palindromic sequence because sequence same from both side in both strands.
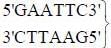 is the palindromic sequence because sequence same from both side in both strands.
is the palindromic sequence because sequence same from both side in both strands.Choose the correct statements about the recombinant expression of proteins- a)A human protein can never be expressed in a bacterial cell
- b)A marker gene such GFP is often used to confirm the expression
- c)A purification tag is often made up of poly His coding sequence in recombinant construct
- d)Disease causing viruses like small pox and adenovirus cannot be used as cloning vectors
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statements about the recombinant expression of proteins
a)
A human protein can never be expressed in a bacterial cell
b)
A marker gene such GFP is often used to confirm the expression
c)
A purification tag is often made up of poly His coding sequence in recombinant construct
d)
Disease causing viruses like small pox and adenovirus cannot be used as cloning vectors

|
Arnab Pillai answered |
Poly His can effectively bind with Ni column and helps in purification, while GFP or green fluorescent markers help in determining expression. Smallpox and adenovirus are commonly used for cloning and expression but, after removing the genes for pathogenicity.
Match the technique with its appropriate application from the list of options given below:
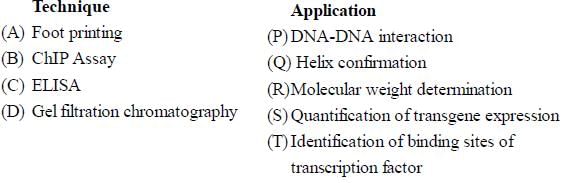
- a)A-T, B-Q, C-S, D-R
- b)A-T, B-T, C-S, D-R
- c)A-S, B-T, C-Q, D-R
- d)A-Q, B-S, C-R, D-T
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the technique with its appropriate application from the list of options given below:


a)
A-T, B-Q, C-S, D-R
b)
A-T, B-T, C-S, D-R
c)
A-S, B-T, C-Q, D-R
d)
A-Q, B-S, C-R, D-T
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
-
Footprinting (A): This technique, often referred to as "DNase footprinting," is used to study the binding sites of DNA-binding proteins such as transcription factors on DNA. So the appropriate match would be (T) Identification of binding sites of transcription factor.
-
ChIP Assay (B): Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay is used to investigate the interaction between proteins and DNA in the cell. This technique can identify the binding sites of DNA-associated proteins, such as transcription factors, on the genome. Therefore, the match is (T) Identification of binding sites of transcription factor.
-
ELISA (C): The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a test that uses antibodies and color change to identify a substance. It is commonly used for the detection and quantification of proteins, including hormones and antibodies. Thus, the match would be (S) Quantification of transgene expression if referring to a protein product of a transgene.
-
Gel Filtration Chromatography (D): This is a type of size exclusion chromatography that separates proteins based on their size, and it's often used for molecular weight determination. Therefore, the match is (R) Molecular weight determination.
So, the matches are:
- (A) Foot printing - (T) Identification of binding sites of transcription factor
- (B) ChIP Assay - (T) Identification of binding sites of transcription factor
- (C) ELISA - (S) Quantification of transgene expression
- (D) Gel Filtration Chromatography - (R) Molecular weight determination
Which of the following partial amino acid sequence from a protein whose gene you wish to clone would be most useful in designing an oligonucleotide probe to screen a cDNA library.
P = Met-Lev-Arg-Leu, Q = Met-Trp-Cys-Trp- a)Only P
- b)Only Q
- c)Both P & Q
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following partial amino acid sequence from a protein whose gene you wish to clone would be most useful in designing an oligonucleotide probe to screen a cDNA library.
P = Met-Lev-Arg-Leu, Q = Met-Trp-Cys-Trp
P = Met-Lev-Arg-Leu, Q = Met-Trp-Cys-Trp
a)
Only P
b)
Only Q
c)
Both P & Q
d)
None
|
|
Pooja Choudhury answered |
Met-Trp-Cys-Trp is the best choice for reverse translation into a DNA sequence because it contains fewer amino acid residues having multiple codon. Trp, Met have one codon each and cys has two, while Leu and Arg each have dic codon.
In any lab, a student performs a chymotrypsin digestion of the protein sequence
N-Lys-Arg-Phe-Pro-Glu-Tyro-Pro-Arg-Lys-Phe-C.
What will be the result?- a)No digestion occurs by chymotrypsin
- b)Because of the Pro after Phe, digestion does not occur
- c)Three fragments are generated
- d)2 fragments are generated
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
In any lab, a student performs a chymotrypsin digestion of the protein sequence
N-Lys-Arg-Phe-Pro-Glu-Tyro-Pro-Arg-Lys-Phe-C.
What will be the result?
N-Lys-Arg-Phe-Pro-Glu-Tyro-Pro-Arg-Lys-Phe-C.
What will be the result?
a)
No digestion occurs by chymotrypsin
b)
Because of the Pro after Phe, digestion does not occur
c)
Three fragments are generated
d)
2 fragments are generated

|
Sahana Roy answered |
Chymotrypsin cleaves at C terminal of aromatic amino acids but these amino acids should not be followed by proline.
Taq. polymerase is used in PCR. What is true about Taq. polymerase?- a)5’ - 3’ exonuclease activity is absent
- b)3’ - 5’ exonuclease activity is present
- c)5’ - 3’ exonuclease activity is present
- d)Isolated from Thermuselantas
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Taq. polymerase is used in PCR. What is true about Taq. polymerase?
a)
5’ - 3’ exonuclease activity is absent
b)
3’ - 5’ exonuclease activity is present
c)
5’ - 3’ exonuclease activity is present
d)
Isolated from Thermuselantas

|
Milan Majumdar answered |
Taq. polymerase has 5’-3’ polymerase as well as 5’-3’ exonuclease activity.
Which of the following is the proper order for vectors in terms of increasing cloning capacity?- a)BAC, Cosmid, Phage, Plasmid, YAC
- b)Plasmid, Phage, Cosmid, BAC, YAC
- c)Plasmid, Cosmid, Phage, BAC, YAC
- d)YAC, BAC, Cosmid, Phage, Plasmid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the proper order for vectors in terms of increasing cloning capacity?
a)
BAC, Cosmid, Phage, Plasmid, YAC
b)
Plasmid, Phage, Cosmid, BAC, YAC
c)
Plasmid, Cosmid, Phage, BAC, YAC
d)
YAC, BAC, Cosmid, Phage, Plasmid

|
Vaibhav Ghosh answered |
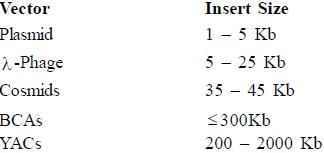
What is the clinical application of monoclonal antibodies?- a)Biosensors
- b)Transplant rejection
- c)Infectious disease
- d)Purification of drugs
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the clinical application of monoclonal antibodies?
a)
Biosensors
b)
Transplant rejection
c)
Infectious disease
d)
Purification of drugs

|
Shubham Rane answered |
Monoclonal antibodies have become an important tool in the field of medicine due to their clinical applications. One of the key applications of monoclonal antibodies is in the purification of drugs.
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that can mimic the immune system's ability to fight off harmful pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. These antibodies are designed to bind to specific molecules, known as antigens, which are present on the surface of cells or pathogens.
In the context of drug purification, monoclonal antibodies can be used to specifically bind and remove impurities from a drug formulation. This process is known as affinity chromatography.
Here is a detailed explanation of how monoclonal antibodies are used in the purification of drugs:
1. Affinity chromatography:
- Monoclonal antibodies are immobilized on a solid support, such as a column or resin.
- The drug formulation is passed through the column, allowing the monoclonal antibodies to specifically bind to the target drug molecules.
- Non-target molecules, including impurities, are washed away, while the target drug molecules remain bound to the monoclonal antibodies.
- The target drug molecules can then be eluted from the column, resulting in a purified drug formulation.
2. Specificity and selectivity:
- Monoclonal antibodies exhibit high specificity and selectivity towards their target molecules. This ensures that only the desired drug molecules are captured and purified, while other molecules are not affected.
- This specificity and selectivity is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry, as it allows for the production of pure and safe drugs.
3. Increased yield and purity:
- The use of monoclonal antibodies in drug purification can significantly increase the yield and purity of the final drug product.
- By selectively removing impurities, monoclonal antibodies help to ensure that the drug formulation meets the required quality standards.
4. Potential for personalized medicine:
- Monoclonal antibodies can be engineered to target specific molecules or cell types, allowing for personalized medicine.
- This means that drugs can be tailored to the individual patient, increasing their efficacy and reducing potential side effects.
In summary, the clinical application of monoclonal antibodies in the purification of drugs is an important process that allows for the production of pure and safe drug formulations. By selectively binding to target drug molecules and removing impurities, monoclonal antibodies help to increase the yield and purity of drugs, ensuring their effectiveness and safety for patients.
Monoclonal antibodies are laboratory-produced molecules that can mimic the immune system's ability to fight off harmful pathogens such as bacteria and viruses. These antibodies are designed to bind to specific molecules, known as antigens, which are present on the surface of cells or pathogens.
In the context of drug purification, monoclonal antibodies can be used to specifically bind and remove impurities from a drug formulation. This process is known as affinity chromatography.
Here is a detailed explanation of how monoclonal antibodies are used in the purification of drugs:
1. Affinity chromatography:
- Monoclonal antibodies are immobilized on a solid support, such as a column or resin.
- The drug formulation is passed through the column, allowing the monoclonal antibodies to specifically bind to the target drug molecules.
- Non-target molecules, including impurities, are washed away, while the target drug molecules remain bound to the monoclonal antibodies.
- The target drug molecules can then be eluted from the column, resulting in a purified drug formulation.
2. Specificity and selectivity:
- Monoclonal antibodies exhibit high specificity and selectivity towards their target molecules. This ensures that only the desired drug molecules are captured and purified, while other molecules are not affected.
- This specificity and selectivity is crucial in the pharmaceutical industry, as it allows for the production of pure and safe drugs.
3. Increased yield and purity:
- The use of monoclonal antibodies in drug purification can significantly increase the yield and purity of the final drug product.
- By selectively removing impurities, monoclonal antibodies help to ensure that the drug formulation meets the required quality standards.
4. Potential for personalized medicine:
- Monoclonal antibodies can be engineered to target specific molecules or cell types, allowing for personalized medicine.
- This means that drugs can be tailored to the individual patient, increasing their efficacy and reducing potential side effects.
In summary, the clinical application of monoclonal antibodies in the purification of drugs is an important process that allows for the production of pure and safe drug formulations. By selectively binding to target drug molecules and removing impurities, monoclonal antibodies help to increase the yield and purity of drugs, ensuring their effectiveness and safety for patients.
After using the Sanger method tor sequencing DNA (dideoxy nucleotide method), you observe the following autoradiogram
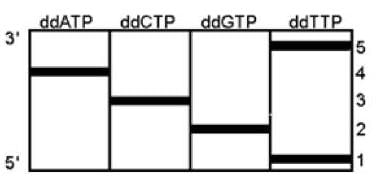 From the autoradiogram determine the base sequence of the template strand.
From the autoradiogram determine the base sequence of the template strand.- a)3'-TACGT-5'
- b)5'-TGCAT-3'
- c)3'-ACGTT-5'
- d)5'-ATGCA-3'
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
After using the Sanger method tor sequencing DNA (dideoxy nucleotide method), you observe the following autoradiogram


From the autoradiogram determine the base sequence of the template strand.
a)
3'-TACGT-5'
b)
5'-TGCAT-3'
c)
3'-ACGTT-5'
d)
5'-ATGCA-3'

|
Rohan Desai answered |
The Sangers gels are read from bottom to top to obtain a sequence of DNA. however this is the sequence of newly synthesized strand and template is complementary to this. On reading the gel from bottom we get 5 -TGC'AT-3 '. while complement ary to this would be 3’ACGTA5’, which can be written from 5’to 3’ as 5’ATGCA3’.
Consider the outcome of a reducing SDS-PAGE performed for a peptide performed from a purified fraction of a multisubunit peptide linked together by weak interactions as well as disulphide bridges. First lane represents the control group while the second lane represent proteins expressed under stress conditions. Considering that both samples had all the four peptides which were later confirmed by mass spectrometry.
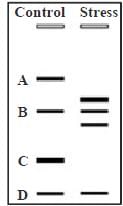 Which of the following statements can be speculated to be correct from the given data
Which of the following statements can be speculated to be correct from the given data- a)Peptide subunits B and D are not modified due to stress.
- b)Peptide subunit A is truncated or post tranlationally cleaved
- c)Peptide subunit A is under expressed/down regulated in stress condition
- d)Peptide B and D remain uncharged.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the outcome of a reducing SDS-PAGE performed for a peptide performed from a purified fraction of a multisubunit peptide linked together by weak interactions as well as disulphide bridges. First lane represents the control group while the second lane represent proteins expressed under stress conditions. Considering that both samples had all the four peptides which were later confirmed by mass spectrometry.


Which of the following statements can be speculated to be correct from the given data
a)
Peptide subunits B and D are not modified due to stress.
b)
Peptide subunit A is truncated or post tranlationally cleaved
c)
Peptide subunit A is under expressed/down regulated in stress condition
d)
Peptide B and D remain uncharged.

|
Bijoy Patel answered |
A change in protein molecular weight is reflected as shift in band position which may occur due to truncation or cleavage, while change in expression is reflected as intensity change of band.
Recognition sequence for some frequently used restriction endonucleases are given in the table. Find out which one is incorrectly matched.- a)

- b)
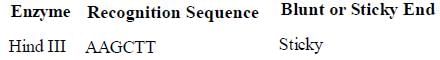
- c)
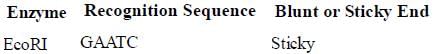
- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Recognition sequence for some frequently used restriction endonucleases are given in the table. Find out which one is incorrectly matched.
a)

b)
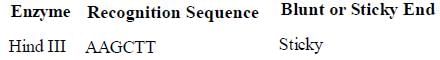
c)
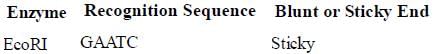
d)


|
Anisha Pillai answered |
The recognition site for EcoRI restriction site is GAATTC
Consider the outcome of a density gradient centrifugation for the separation of biomecules.
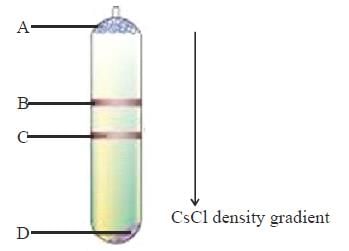 Which of the following captions correctly represent the separated biomolecules in a density gradient tube
Which of the following captions correctly represent the separated biomolecules in a density gradient tube- a)A – RNA, B – Linear DNA, C–Supercoiled DNA, D–Protein
- b)A – Protein, B – Linear DNA, C–Supercoiled DNA, D–RNA
- c)A – Protein, B – Supercoiled DNA, C–linear DNA, D–RNA
- d)A – Linear DNA, B – RNA, C–Supercoiled DNA, D–Protein
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the outcome of a density gradient centrifugation for the separation of biomecules.


Which of the following captions correctly represent the separated biomolecules in a density gradient tube
a)
A – RNA, B – Linear DNA, C–Supercoiled DNA, D–Protein
b)
A – Protein, B – Linear DNA, C–Supercoiled DNA, D–RNA
c)
A – Protein, B – Supercoiled DNA, C–linear DNA, D–RNA
d)
A – Linear DNA, B – RNA, C–Supercoiled DNA, D–Protein

|
Anirban Kapoor answered |
Proteins have least density around 1.55 g/cm3, followed by DNA (1.7) and maximum by RNA (1.8). Among linear and supercoiled DNA, EtBr binding is more in linear hence its density is lower than supercoiled.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biotechnology - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 2025 is part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biotechnology - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026
7 docs|34 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup