All Exams >
Mechanical Engineering >
Manufacturing Engineering >
All Questions
All questions of Computer Integrated Manufacturing for Mechanical Engineering Exam
The following device is used for transmitting energy in CNC machine tools:- a)pulley and belt
- b)gears
- c)screw and nut assembly
- d)recirculating ball screw and nut assembly
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The following device is used for transmitting energy in CNC machine tools:
a)
pulley and belt
b)
gears
c)
screw and nut assembly
d)
recirculating ball screw and nut assembly
|
|
Anmol Saini answered |
Conventional lead screw and its nut assembly is not suitable for CNC machine tools because of its lesser power transmitting capacity, lesser accuracy due to backlash and higher frictional forces. To avoid these problems, the recirculating ball screw and nut assembly is used as energy transmitting device in CNC machining
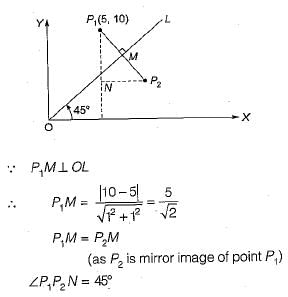
In a CAD package, mirror image of a 2D point P(5, 10) is to be obtained about a line which passes through the origin and makes an angle of 450 counterclockwise with the X-axis. The coordinates of the transformed point will be- a)(7.5, 5)
- b)(10, 5)
- c)(7.5, -5)
- d)(10, -5)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In a CAD package, mirror image of a 2D point P(5, 10) is to be obtained about a line which passes through the origin and makes an angle of 450 counterclockwise with the X-axis. The coordinates of the transformed point will be
a)
(7.5, 5)
b)
(10, 5)
c)
(7.5, -5)
d)
(10, -5)

|
Anmol Roy answered |
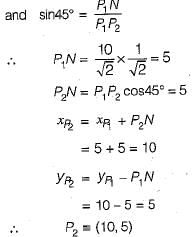
The following system of instructions is used on the tape of NC machine tools:- a)Numeric
- b)Alphanumeric
- c)Binary numbers
- d)Binary coded decimals
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following system of instructions is used on the tape of NC machine tools:
a)
Numeric
b)
Alphanumeric
c)
Binary numbers
d)
Binary coded decimals

|
Arya Menon answered |
In NCmachine tools, the binary systems is used. In this system, the base of the system is 2 and only two characters, 0 and 1, are needed. The binary system is tedious to use in everyday life, but very suitable in the numerical control of machine tools.
Miscellaneous function for coolant ON is- a)M 08
- b)MOO
- c)M 03
- d)M 30
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Miscellaneous function for coolant ON is
a)
M 08
b)
MOO
c)
M 03
d)
M 30

|
Gauri Roy answered |
M 00 - Programme stop
M 01 - Optional stop
M 02 - End of programme
M 03-Spindle on CW
M 04 - Spindle on CCW
M 05 - Spindle off
M 0 8 -C o o la nt on
M 09 - Coolant off
M 17 - Chip conveyor on
M 18 - Chip conveyor off
M 30 - End of tape and tape rewind
M 39 - Auto recycl
M 01 - Optional stop
M 02 - End of programme
M 03-Spindle on CW
M 04 - Spindle on CCW
M 05 - Spindle off
M 0 8 -C o o la nt on
M 09 - Coolant off
M 17 - Chip conveyor on
M 18 - Chip conveyor off
M 30 - End of tape and tape rewind
M 39 - Auto recycl
The main function of a spindle in CNC machine is- a)holding the job
- b)holding the tool
- c)holding and centering the job
- d)holding and rotating the job about central axis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The main function of a spindle in CNC machine is
a)
holding the job
b)
holding the tool
c)
holding and centering the job
d)
holding and rotating the job about central axis
|
|
Mansi Rane answered |
The main functions of the spindle are: (i) Centering the job or the tool (ii) holding the job or the tool (iii) rotating the job or.the tool
The operation of NC machine tools is based on- a)feedback system
- b)numerical controls
- c)a series of coded instructions
- d)digitization
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The operation of NC machine tools is based on
a)
feedback system
b)
numerical controls
c)
a series of coded instructions
d)
digitization
|
|
Kiran Basu answered |
Understanding NC Machine Tools
NC (Numerical Control) machine tools are a crucial part of modern manufacturing processes. They operate based on a series of coded instructions that dictate how the machine should perform various tasks.
What are Coded Instructions?
- Coded instructions are the fundamental elements of NC technology.
- These instructions are typically written in a programming language called G-code.
- Each line of G-code corresponds to specific movements or actions the machine should execute, such as cutting, drilling, or milling.
How Do They Work?
- The coded instructions are fed into the machine's controller, which interprets them.
- The controller translates these codes into mechanical movements, guiding the machine's tools along predetermined paths.
- This allows for high precision and repeatability in manufacturing processes.
Advantages of Coded Instructions
- **Automation**: The use of coded instructions allows for the automation of complex machining tasks, reducing human intervention.
- **Precision**: Coded commands enable accurate execution of designs, ensuring consistent quality in production.
- **Flexibility**: Adjusting the code allows easy modifications to the manufacturing process without needing to change the machine setup.
Conclusion
In summary, the operation of NC machine tools fundamentally relies on a series of coded instructions. This method not only enhances efficiency and precision but also provides the flexibility needed in modern manufacturing environments. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer for understanding NC machine tools.
NC (Numerical Control) machine tools are a crucial part of modern manufacturing processes. They operate based on a series of coded instructions that dictate how the machine should perform various tasks.
What are Coded Instructions?
- Coded instructions are the fundamental elements of NC technology.
- These instructions are typically written in a programming language called G-code.
- Each line of G-code corresponds to specific movements or actions the machine should execute, such as cutting, drilling, or milling.
How Do They Work?
- The coded instructions are fed into the machine's controller, which interprets them.
- The controller translates these codes into mechanical movements, guiding the machine's tools along predetermined paths.
- This allows for high precision and repeatability in manufacturing processes.
Advantages of Coded Instructions
- **Automation**: The use of coded instructions allows for the automation of complex machining tasks, reducing human intervention.
- **Precision**: Coded commands enable accurate execution of designs, ensuring consistent quality in production.
- **Flexibility**: Adjusting the code allows easy modifications to the manufacturing process without needing to change the machine setup.
Conclusion
In summary, the operation of NC machine tools fundamentally relies on a series of coded instructions. This method not only enhances efficiency and precision but also provides the flexibility needed in modern manufacturing environments. Therefore, option 'C' is the correct answer for understanding NC machine tools.
What is BLU in numerical control of machining?- a)unit of displacement
- b)closed loop system indicator
- c)just a control system
- d)interpolator
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is BLU in numerical control of machining?
a)
unit of displacement
b)
closed loop system indicator
c)
just a control system
d)
interpolator
|
|
Shreya Kulkarni answered |
Displacement are expressed in part programmes by integers. Each unit corresponds to the position resolution of the axes of motion and will be referred to as the basic length-unit (BLU). The BLU is the smallest length of motion that can be repeatably sensed in the machine
In APT language, the cutter motion in incremental coordinate mode is addressed as- a)GO TO/.......
- b)GO/TO.........
- c)GO DLTA/.......
- d)GO FWD/.........
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In APT language, the cutter motion in incremental coordinate mode is addressed as
a)
GO TO/.......
b)
GO/TO.........
c)
GO DLTA/.......
d)
GO FWD/.........
|
|
Nishanth Basu answered |
Introduction to APT Language and Incremental Coordinate Mode:
APT (Automatically Programmed Tool) is a high-level programming language that is used to control and program machine tools, such as milling machines and lathes. It allows users to define the tool's movements and operations by specifying the desired coordinates and motions.
In APT language, the cutter motion can be controlled in two different coordinate modes: incremental and absolute. In incremental coordinate mode, the tool's position is defined relative to its current position, while in absolute coordinate mode, the tool's position is defined with respect to a fixed reference point.
Addressing Cutter Motion in APT Language:
When addressing the cutter motion in APT language, the correct syntax to be used in incremental coordinate mode is "GO/TO". This syntax is used to specify the desired position that the tool should move to.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
The correct answer, option 'B' - GO/TO, is the appropriate syntax to address the cutter motion in incremental coordinate mode.
This syntax consists of the following components:
1. "GO": This keyword is used to indicate that the tool should move to the specified position.
2. "/": This character is used to separate the keyword "GO" from the keyword "TO".
3. "TO": This keyword is used to specify the target position that the tool should move to.
By using the "GO/TO" syntax, the APT program can accurately control the tool's movements in incremental coordinate mode. The program will calculate the relative position based on the current tool position and move the tool accordingly.
Advantages of Using Incremental Coordinate Mode:
1. Flexibility: Incremental coordinate mode allows for more flexibility in programming as the tool's position is defined relative to its current position. This makes it easier to perform complex machining operations.
2. Error Correction: Since the tool's position is defined incrementally, any errors or interruptions during machining can be easily corrected by specifying a new relative position.
3. Reduced Programming Effort: Incremental coordinate mode eliminates the need for repeatedly specifying the absolute position of the tool, resulting in shorter and more concise programs.
Conclusion:
In APT language, the correct syntax to address the cutter motion in incremental coordinate mode is "GO/TO". This syntax allows the programmer to specify the desired position that the tool should move to, relative to its current position. By using incremental coordinate mode, programmers can achieve greater flexibility, error correction capabilities, and reduced programming effort.
APT (Automatically Programmed Tool) is a high-level programming language that is used to control and program machine tools, such as milling machines and lathes. It allows users to define the tool's movements and operations by specifying the desired coordinates and motions.
In APT language, the cutter motion can be controlled in two different coordinate modes: incremental and absolute. In incremental coordinate mode, the tool's position is defined relative to its current position, while in absolute coordinate mode, the tool's position is defined with respect to a fixed reference point.
Addressing Cutter Motion in APT Language:
When addressing the cutter motion in APT language, the correct syntax to be used in incremental coordinate mode is "GO/TO". This syntax is used to specify the desired position that the tool should move to.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
The correct answer, option 'B' - GO/TO, is the appropriate syntax to address the cutter motion in incremental coordinate mode.
This syntax consists of the following components:
1. "GO": This keyword is used to indicate that the tool should move to the specified position.
2. "/": This character is used to separate the keyword "GO" from the keyword "TO".
3. "TO": This keyword is used to specify the target position that the tool should move to.
By using the "GO/TO" syntax, the APT program can accurately control the tool's movements in incremental coordinate mode. The program will calculate the relative position based on the current tool position and move the tool accordingly.
Advantages of Using Incremental Coordinate Mode:
1. Flexibility: Incremental coordinate mode allows for more flexibility in programming as the tool's position is defined relative to its current position. This makes it easier to perform complex machining operations.
2. Error Correction: Since the tool's position is defined incrementally, any errors or interruptions during machining can be easily corrected by specifying a new relative position.
3. Reduced Programming Effort: Incremental coordinate mode eliminates the need for repeatedly specifying the absolute position of the tool, resulting in shorter and more concise programs.
Conclusion:
In APT language, the correct syntax to address the cutter motion in incremental coordinate mode is "GO/TO". This syntax allows the programmer to specify the desired position that the tool should move to, relative to its current position. By using incremental coordinate mode, programmers can achieve greater flexibility, error correction capabilities, and reduced programming effort.
The method by which the control system calculates the intermediate points and speed of the motor, is known as- a)control system
- b)director
- c)interpolator
- d)motion control system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The method by which the control system calculates the intermediate points and speed of the motor, is known as
a)
control system
b)
director
c)
interpolator
d)
motion control system

|
Lakshmi Datta answered |
Understanding the Role of an Interpolator
In control systems, particularly in mechanical engineering and robotics, the process of calculating intermediate points and motor speeds is crucial for smooth and accurate motion. This is where the term "interpolator" becomes significant.
What is an Interpolator?
- An interpolator is a component of a motion control system that determines the intermediate positions between a starting point and an endpoint.
- It calculates the required trajectory that the motor must follow, ensuring the movement is smooth and precise.
Functions of an Interpolator
- Trajectory Planning: It generates a path that the motor should follow, taking into account the desired speed and acceleration.
- Speed Control: The interpolator adjusts the speed of the motor at various points along the path to prevent jerky movements and ensure a gradual start and stop.
Importance in Control Systems
- Precision Motion: In applications like CNC machining and robotic arms, an interpolator is essential for achieving high accuracy in positioning.
- Efficiency: It optimizes the motion by minimizing travel time while adhering to speed and acceleration constraints.
Conclusion
The correct answer to the question regarding the method by which a control system calculates intermediate points and motor speed is indeed option 'C', the interpolator. By effectively managing the trajectory and speed, interpolators play a vital role in enhancing the performance of motion control systems.
In control systems, particularly in mechanical engineering and robotics, the process of calculating intermediate points and motor speeds is crucial for smooth and accurate motion. This is where the term "interpolator" becomes significant.
What is an Interpolator?
- An interpolator is a component of a motion control system that determines the intermediate positions between a starting point and an endpoint.
- It calculates the required trajectory that the motor must follow, ensuring the movement is smooth and precise.
Functions of an Interpolator
- Trajectory Planning: It generates a path that the motor should follow, taking into account the desired speed and acceleration.
- Speed Control: The interpolator adjusts the speed of the motor at various points along the path to prevent jerky movements and ensure a gradual start and stop.
Importance in Control Systems
- Precision Motion: In applications like CNC machining and robotic arms, an interpolator is essential for achieving high accuracy in positioning.
- Efficiency: It optimizes the motion by minimizing travel time while adhering to speed and acceleration constraints.
Conclusion
The correct answer to the question regarding the method by which a control system calculates intermediate points and motor speed is indeed option 'C', the interpolator. By effectively managing the trajectory and speed, interpolators play a vital role in enhancing the performance of motion control systems.
Conventional NC system is also known as:.- a)hardwired
- b)soft wired NC '
- c)computrised numerical control
- d)direct wired NC
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Conventional NC system is also known as:.
a)
hardwired
b)
soft wired NC '
c)
computrised numerical control
d)
direct wired NC

|
Jithin Choudhury answered |
Explanation:
Conventional NC system is a type of numerical control system that was used before the introduction of computerized numerical control (CNC) systems. It was developed in the 1950s and 1960s and was widely used in the manufacturing industry for controlling machine tools. It is also known as hardwired NC system because the instructions for controlling the machine tools were hardwired into the system.
Features of Conventional NC system:
1. Hardwired instructions: The instructions for controlling the machine tools were hardwired into the system. This means that the instructions were physically connected to the system and could not be changed or modified easily.
2. Limited functionality: The conventional NC system had limited functionality and could only perform simple tasks such as drilling, milling, and turning.
3. Limited memory: The system had limited memory capacity and could only store a limited number of instructions.
4. Low accuracy: The system had low accuracy because it relied on mechanical controls and did not have the advanced sensors and feedback systems that are found in modern CNC systems.
Advantages of Conventional NC system:
1. Cost-effective: Conventional NC systems were less expensive than the modern CNC systems.
2. Easy to use: The system was easy to use because the instructions were hardwired into the system and did not require programming skills.
3. Reliable: The system was reliable because it had fewer components and was less complex than modern CNC systems.
Disadvantages of Conventional NC system:
1. Limited functionality: The system had limited functionality and could only perform simple tasks.
2. Limited memory: The system had limited memory capacity and could only store a limited number of instructions.
3. Low accuracy: The system had low accuracy because it relied on mechanical controls and did not have the advanced sensors and feedback systems that are found in modern CNC systems.
Conclusion:
Conventional NC system was an important step in the evolution of numerical control systems. It paved the way for the development of modern CNC systems that are widely used in the manufacturing industry today. Although the conventional NC system had its limitations, it was cost-effective, easy to use, and reliable.
Conventional NC system is a type of numerical control system that was used before the introduction of computerized numerical control (CNC) systems. It was developed in the 1950s and 1960s and was widely used in the manufacturing industry for controlling machine tools. It is also known as hardwired NC system because the instructions for controlling the machine tools were hardwired into the system.
Features of Conventional NC system:
1. Hardwired instructions: The instructions for controlling the machine tools were hardwired into the system. This means that the instructions were physically connected to the system and could not be changed or modified easily.
2. Limited functionality: The conventional NC system had limited functionality and could only perform simple tasks such as drilling, milling, and turning.
3. Limited memory: The system had limited memory capacity and could only store a limited number of instructions.
4. Low accuracy: The system had low accuracy because it relied on mechanical controls and did not have the advanced sensors and feedback systems that are found in modern CNC systems.
Advantages of Conventional NC system:
1. Cost-effective: Conventional NC systems were less expensive than the modern CNC systems.
2. Easy to use: The system was easy to use because the instructions were hardwired into the system and did not require programming skills.
3. Reliable: The system was reliable because it had fewer components and was less complex than modern CNC systems.
Disadvantages of Conventional NC system:
1. Limited functionality: The system had limited functionality and could only perform simple tasks.
2. Limited memory: The system had limited memory capacity and could only store a limited number of instructions.
3. Low accuracy: The system had low accuracy because it relied on mechanical controls and did not have the advanced sensors and feedback systems that are found in modern CNC systems.
Conclusion:
Conventional NC system was an important step in the evolution of numerical control systems. It paved the way for the development of modern CNC systems that are widely used in the manufacturing industry today. Although the conventional NC system had its limitations, it was cost-effective, easy to use, and reliable.
Which of the following is not a NC programming language?- a)APT
- b)Automap
- c)Compact II
- d)Cobol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a NC programming language?
a)
APT
b)
Automap
c)
Compact II
d)
Cobol
|
|
Keerthana Joshi answered |
Answer:
NC programming, also known as numerical control programming, is a method of controlling machine tools and other manufacturing equipment using coded instructions. These instructions are typically generated using a programming language specifically designed for this purpose.
There are several programming languages that are commonly used for NC programming, such as APT, Automap, Compact II, and Cobol. However, Cobol is not a NC programming language. Here's why:
1. APT (Automatically Programmed Tool)
- APT is one of the oldest and most widely used programming languages for NC programming.
- It was developed in the late 1950s by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- APT uses a combination of English-like commands and mathematical expressions to specify the tool motions and operations required to produce a part.
2. Automap
- Automap is another popular NC programming language.
- It was developed by the Control Data Corporation (CDC) in the 1960s.
- Automap uses a simplified syntax, making it easier to learn and use compared to other NC programming languages.
3. Compact II
- Compact II is a programming language developed by GE Fanuc Automation.
- It is specifically designed for programming CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines.
- Compact II supports a wide range of machining operations and has advanced features for optimizing tool paths.
4. Cobol (Common Business-Oriented Language)
- Cobol is a high-level programming language primarily used for business applications.
- It was developed in the late 1950s by a committee of computer manufacturers and users.
- Cobol is not specifically designed for NC programming and does not have the necessary features and syntax to generate the required machine control codes.
In summary, while APT, Automap, and Compact II are all commonly used programming languages for NC programming, Cobol is not suitable for this purpose. Cobol is primarily used for business applications and lacks the necessary features and syntax to generate machine control codes for CNC machines and other manufacturing equipment.
NC programming, also known as numerical control programming, is a method of controlling machine tools and other manufacturing equipment using coded instructions. These instructions are typically generated using a programming language specifically designed for this purpose.
There are several programming languages that are commonly used for NC programming, such as APT, Automap, Compact II, and Cobol. However, Cobol is not a NC programming language. Here's why:
1. APT (Automatically Programmed Tool)
- APT is one of the oldest and most widely used programming languages for NC programming.
- It was developed in the late 1950s by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT).
- APT uses a combination of English-like commands and mathematical expressions to specify the tool motions and operations required to produce a part.
2. Automap
- Automap is another popular NC programming language.
- It was developed by the Control Data Corporation (CDC) in the 1960s.
- Automap uses a simplified syntax, making it easier to learn and use compared to other NC programming languages.
3. Compact II
- Compact II is a programming language developed by GE Fanuc Automation.
- It is specifically designed for programming CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines.
- Compact II supports a wide range of machining operations and has advanced features for optimizing tool paths.
4. Cobol (Common Business-Oriented Language)
- Cobol is a high-level programming language primarily used for business applications.
- It was developed in the late 1950s by a committee of computer manufacturers and users.
- Cobol is not specifically designed for NC programming and does not have the necessary features and syntax to generate the required machine control codes.
In summary, while APT, Automap, and Compact II are all commonly used programming languages for NC programming, Cobol is not suitable for this purpose. Cobol is primarily used for business applications and lacks the necessary features and syntax to generate machine control codes for CNC machines and other manufacturing equipment.
The interpolator in a CNC machine controls- a)spindie speed
- b)coolant flow
- c)feed rate
- d)tool change
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The interpolator in a CNC machine controls
a)
spindie speed
b)
coolant flow
c)
feed rate
d)
tool change
|
|
Mahi Kaur answered |
Understanding CNC Machine Interpolation
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines utilize interpolators to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of machining processes. The role of the interpolator is pivotal in controlling the movement of the machine's tool along specified paths.
What is Interpolation in CNC?
- Interpolation refers to the method by which a CNC machine calculates the intermediate points between two defined locations.
- It allows the machine to move smoothly and precisely between these points, following a predetermined tool path.
Feed Rate Control
- The feed rate is the speed at which the tool moves through the material.
- The interpolator is responsible for adjusting the feed rate according to the programmed path and desired machining parameters.
- By controlling the feed rate, the interpolator ensures optimal cutting conditions, improving surface finish and tool life.
Role of Interpolator
- The interpolator processes the CNC code (G-code) to determine how the machine should move.
- It calculates the necessary changes in position, ensuring that the tool follows the correct trajectory.
- This involves continuous adjustments to the feed rate, enabling the machine to adapt to varying material conditions and geometries.
Other Functions
- While the interpolator primarily focuses on feed rate, it can also indirectly influence other parameters like spindle speed and coolant flow by integrating with the machine's control system.
- However, the main function of the interpolator remains to ensure precise control of the feed rate during machining operations.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' because the interpolator plays a critical role in managing the feed rate, ensuring that the CNC machine operates efficiently and accurately throughout the machining process.
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines utilize interpolators to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of machining processes. The role of the interpolator is pivotal in controlling the movement of the machine's tool along specified paths.
What is Interpolation in CNC?
- Interpolation refers to the method by which a CNC machine calculates the intermediate points between two defined locations.
- It allows the machine to move smoothly and precisely between these points, following a predetermined tool path.
Feed Rate Control
- The feed rate is the speed at which the tool moves through the material.
- The interpolator is responsible for adjusting the feed rate according to the programmed path and desired machining parameters.
- By controlling the feed rate, the interpolator ensures optimal cutting conditions, improving surface finish and tool life.
Role of Interpolator
- The interpolator processes the CNC code (G-code) to determine how the machine should move.
- It calculates the necessary changes in position, ensuring that the tool follows the correct trajectory.
- This involves continuous adjustments to the feed rate, enabling the machine to adapt to varying material conditions and geometries.
Other Functions
- While the interpolator primarily focuses on feed rate, it can also indirectly influence other parameters like spindle speed and coolant flow by integrating with the machine's control system.
- However, the main function of the interpolator remains to ensure precise control of the feed rate during machining operations.
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' because the interpolator plays a critical role in managing the feed rate, ensuring that the CNC machine operates efficiently and accurately throughout the machining process.
Machining center is- a)an automatic tool changing unit
- b)a group of automatic machine tools
- c)a next logical step beyond NC machine
- d)an NC machine tool
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Machining center is
a)
an automatic tool changing unit
b)
a group of automatic machine tools
c)
a next logical step beyond NC machine
d)
an NC machine tool

|
Moumita Chopra answered |
Introduction:
A machining center is a type of machine tool used in the manufacturing industry for the production of precision components. It combines multiple machining operations into a single unit, offering high productivity, accuracy, and efficiency. In this response, we will explain why option 'A' - an automatic tool changing unit - is the correct answer.
Explanation:
1. Definition of a machining center:
A machining center is a highly automated machine tool that has the capability to perform various machining operations, such as milling, drilling, tapping, and turning, in a single setup. It is equipped with an automatic tool changing unit, which allows for the quick and efficient exchange of cutting tools.
2. Automatic tool changing unit:
The automatic tool changing unit is a vital component of a machining center. It consists of a tool magazine, where a variety of cutting tools are stored, and a tool changer, which is responsible for retrieving the required tool from the magazine and mounting it onto the machine's spindle. The tool changer is controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system, which ensures precise and reliable tool changes.
3. Advantages of automatic tool changing:
The automatic tool changing capability of a machining center offers several advantages, including:
- Increased productivity: With the ability to change tools automatically, machining centers can perform complex operations without the need for manual intervention. This leads to reduced setup times and increased production rates.
- Versatility: Machining centers can accommodate a wide range of cutting tools, allowing for the production of diverse components with different geometries and features. The automatic tool changing unit enables the machine to switch between tools seamlessly, enhancing its versatility.
- Accuracy and precision: By eliminating manual tool changes, machining centers minimize the risk of human error. The CNC system ensures that the tool is positioned accurately, resulting in consistent and precise machining operations.
- Reduced downtime: The automatic tool changing unit allows for rapid tool changes, minimizing downtime between machining operations. This leads to improved machine utilization and overall efficiency.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a machining center is a type of machine tool that incorporates an automatic tool changing unit. This capability enables the machine to perform various machining operations in a single setup, offering advantages such as increased productivity, versatility, accuracy, and reduced downtime. Therefore, option 'A' - an automatic tool changing unit - is the correct answer.
A machining center is a type of machine tool used in the manufacturing industry for the production of precision components. It combines multiple machining operations into a single unit, offering high productivity, accuracy, and efficiency. In this response, we will explain why option 'A' - an automatic tool changing unit - is the correct answer.
Explanation:
1. Definition of a machining center:
A machining center is a highly automated machine tool that has the capability to perform various machining operations, such as milling, drilling, tapping, and turning, in a single setup. It is equipped with an automatic tool changing unit, which allows for the quick and efficient exchange of cutting tools.
2. Automatic tool changing unit:
The automatic tool changing unit is a vital component of a machining center. It consists of a tool magazine, where a variety of cutting tools are stored, and a tool changer, which is responsible for retrieving the required tool from the magazine and mounting it onto the machine's spindle. The tool changer is controlled by a computer numerical control (CNC) system, which ensures precise and reliable tool changes.
3. Advantages of automatic tool changing:
The automatic tool changing capability of a machining center offers several advantages, including:
- Increased productivity: With the ability to change tools automatically, machining centers can perform complex operations without the need for manual intervention. This leads to reduced setup times and increased production rates.
- Versatility: Machining centers can accommodate a wide range of cutting tools, allowing for the production of diverse components with different geometries and features. The automatic tool changing unit enables the machine to switch between tools seamlessly, enhancing its versatility.
- Accuracy and precision: By eliminating manual tool changes, machining centers minimize the risk of human error. The CNC system ensures that the tool is positioned accurately, resulting in consistent and precise machining operations.
- Reduced downtime: The automatic tool changing unit allows for rapid tool changes, minimizing downtime between machining operations. This leads to improved machine utilization and overall efficiency.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, a machining center is a type of machine tool that incorporates an automatic tool changing unit. This capability enables the machine to perform various machining operations in a single setup, offering advantages such as increased productivity, versatility, accuracy, and reduced downtime. Therefore, option 'A' - an automatic tool changing unit - is the correct answer.
Feed drives in CNC milling are provided by- a)synchronous motor
- b)induction motors
- c)stepper motors
- d)servo motors
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Feed drives in CNC milling are provided by
a)
synchronous motor
b)
induction motors
c)
stepper motors
d)
servo motors
|
|
Nitin Joshi answered |
Feed drives in CNC milling are provided by servo motors.
Explanation:
CNC milling machines are equipped with different motors to provide motion control to the machine. Feed drives in CNC milling machines are responsible for controlling the movement of the cutting tool in the X, Y, and Z directions. These drives are powered by servo motors.
Servo motors are used to provide precise motion control in CNC milling machines. They are designed to provide accurate and repeatable positioning of the cutting tool. Servo motors are equipped with feedback devices that provide information about the position, speed, and acceleration of the motor shaft. This information is used by the CNC controller to adjust the motor's output and maintain precise positioning of the cutting tool.
Advantages of using Servo Motors:
1. High Precision: Servo motors are designed to deliver high precision and accuracy. They are capable of providing accurate positioning of the cutting tool, which is essential in CNC milling.
2. High Torque: Servo motors are capable of producing high torque at low speeds. This allows them to deliver the required power to move the cutting tool through the material being machined.
3. Fast Response Time: Servo motors are designed to provide fast response time, which is critical in CNC milling machines. They can quickly adjust their output to maintain precise positioning of the cutting tool.
4. High Reliability: Servo motors are highly reliable and can operate for long periods without requiring maintenance. They are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of CNC milling machines and deliver consistent performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, feed drives in CNC milling machines are provided by servo motors. These motors are capable of delivering high precision, high torque, fast response time, and high reliability, which are essential for CNC milling applications.
Explanation:
CNC milling machines are equipped with different motors to provide motion control to the machine. Feed drives in CNC milling machines are responsible for controlling the movement of the cutting tool in the X, Y, and Z directions. These drives are powered by servo motors.
Servo motors are used to provide precise motion control in CNC milling machines. They are designed to provide accurate and repeatable positioning of the cutting tool. Servo motors are equipped with feedback devices that provide information about the position, speed, and acceleration of the motor shaft. This information is used by the CNC controller to adjust the motor's output and maintain precise positioning of the cutting tool.
Advantages of using Servo Motors:
1. High Precision: Servo motors are designed to deliver high precision and accuracy. They are capable of providing accurate positioning of the cutting tool, which is essential in CNC milling.
2. High Torque: Servo motors are capable of producing high torque at low speeds. This allows them to deliver the required power to move the cutting tool through the material being machined.
3. Fast Response Time: Servo motors are designed to provide fast response time, which is critical in CNC milling machines. They can quickly adjust their output to maintain precise positioning of the cutting tool.
4. High Reliability: Servo motors are highly reliable and can operate for long periods without requiring maintenance. They are designed to withstand the harsh conditions of CNC milling machines and deliver consistent performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, feed drives in CNC milling machines are provided by servo motors. These motors are capable of delivering high precision, high torque, fast response time, and high reliability, which are essential for CNC milling applications.
Transfer machines can be defined as
- a)material processing machines
- b)material handling machines
- c)material processing and material handling machines
- d)component feeders for automatic assembly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Transfer machines can be defined as
a)
material processing machines
b)
material handling machines
c)
material processing and material handling machines
d)
component feeders for automatic assembly

|
Bijoy Chauhan answered |
Transfer machines are highly automated machines that can perform multiple operations on a workpiece in one cycle. These machines are used in mass production for high volume output. Transfer machines can be defined as material processing and material handling machines. This answer can be explained in the following points.
Material Processing Machines:
Transfer machines can perform various material processing operations such as drilling, tapping, milling, boring, reaming, and threading. These operations are performed on the workpiece that is mounted on a fixture or a pallet. The transfer machine moves the workpiece to different stations where each operation is performed by a separate tool. The workpiece is processed simultaneously at each station, resulting in a faster production rate.
Material Handling Machines:
Transfer machines can also be considered as material handling machines as they move the workpiece from one station to another. The transfer machine can be designed with various types of transfer systems such as rotary, linear or shuttle. These systems are used to move the workpiece from one station to another without manual intervention. The transfer machine can also be equipped with an automatic loading and unloading system, which further enhances the automation process.
Component Feeders for Automatic Assembly:
Transfer machines can also be used as component feeders for automatic assembly. The machine can be equipped with a vibratory feeder system that feeds the components to the machine. The transfer machine then assembles the components to form a finished product. This process is highly automated and can increase the production rate significantly.
In conclusion, transfer machines are material processing and material handling machines that can perform multiple operations on a workpiece in one cycle. These machines are highly automated and can be used for mass production.
Material Processing Machines:
Transfer machines can perform various material processing operations such as drilling, tapping, milling, boring, reaming, and threading. These operations are performed on the workpiece that is mounted on a fixture or a pallet. The transfer machine moves the workpiece to different stations where each operation is performed by a separate tool. The workpiece is processed simultaneously at each station, resulting in a faster production rate.
Material Handling Machines:
Transfer machines can also be considered as material handling machines as they move the workpiece from one station to another. The transfer machine can be designed with various types of transfer systems such as rotary, linear or shuttle. These systems are used to move the workpiece from one station to another without manual intervention. The transfer machine can also be equipped with an automatic loading and unloading system, which further enhances the automation process.
Component Feeders for Automatic Assembly:
Transfer machines can also be used as component feeders for automatic assembly. The machine can be equipped with a vibratory feeder system that feeds the components to the machine. The transfer machine then assembles the components to form a finished product. This process is highly automated and can increase the production rate significantly.
In conclusion, transfer machines are material processing and material handling machines that can perform multiple operations on a workpiece in one cycle. These machines are highly automated and can be used for mass production.
The criteria for selection of a CNC machine tool is- a)good quality production
- b)automatic production
- c)operator’sease
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The criteria for selection of a CNC machine tool is
a)
good quality production
b)
automatic production
c)
operator’sease
d)
all of these
|
|
Gayatri Dasgupta answered |
Criteria for Selection of a CNC Machine Tool
Selecting a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tool is a critical decision in manufacturing, and several factors come into play to ensure optimal performance and productivity. The correct answer, option 'D' - all of these, encompasses the essential criteria:
Good Quality Production
- Ensures high precision and accuracy in machining parts.
- Reduces the possibility of defects, leading to lower rework and scrap rates.
- Facilitates complex geometries that enhance product quality.
Automatic Production
- CNC machines operate automatically, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Increases production rates while maintaining consistent quality.
- Allows for the execution of repetitive tasks without fatigue, leading to higher efficiency.
Operator's Ease
- User-friendly interfaces and programming environments minimize the learning curve for operators.
- Enhances safety by reducing the operator's physical involvement in hazardous tasks.
- Streamlines workflow, allowing operators to focus on monitoring and quality control instead of manual operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the selection of a CNC machine tool should prioritize all these criteria. Good quality production ensures product excellence, automatic production enhances efficiency, and operator's ease contributes to a safer and more productive working environment. Together, these factors create a holistic approach to selecting the most suitable CNC machine tool for any manufacturing needs.
Selecting a CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine tool is a critical decision in manufacturing, and several factors come into play to ensure optimal performance and productivity. The correct answer, option 'D' - all of these, encompasses the essential criteria:
Good Quality Production
- Ensures high precision and accuracy in machining parts.
- Reduces the possibility of defects, leading to lower rework and scrap rates.
- Facilitates complex geometries that enhance product quality.
Automatic Production
- CNC machines operate automatically, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Increases production rates while maintaining consistent quality.
- Allows for the execution of repetitive tasks without fatigue, leading to higher efficiency.
Operator's Ease
- User-friendly interfaces and programming environments minimize the learning curve for operators.
- Enhances safety by reducing the operator's physical involvement in hazardous tasks.
- Streamlines workflow, allowing operators to focus on monitoring and quality control instead of manual operations.
Conclusion
In summary, the selection of a CNC machine tool should prioritize all these criteria. Good quality production ensures product excellence, automatic production enhances efficiency, and operator's ease contributes to a safer and more productive working environment. Together, these factors create a holistic approach to selecting the most suitable CNC machine tool for any manufacturing needs.
Chapter doubts & questions for Computer Integrated Manufacturing - Manufacturing Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Computer Integrated Manufacturing - Manufacturing Engineering in English & Hindi are available as part of Mechanical Engineering exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Manufacturing Engineering
56 videos|80 docs|29 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup