All Exams >
Class 7 >
Science Class 7 >
All Questions
All questions of Respiration in Organisms for Class 7 Exam
During exhalation, the ribs move
- a)Outwards
- b)Downwards
- c)Upwards
- d)To normal position
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During exhalation, the ribs move
a)
Outwards
b)
Downwards
c)
Upwards
d)
To normal position
|
|
Disha Iyer answered |
During exhalation, i.e. releasing air during respiration, the ribs move downwards to reduce the volume of the thoracic cavity.
During exhalation, your diaphragm relaxes and moves upward into the chest cavity. The intercostal muscles between the ribs also relax to reduce the space in the chest cavity. As they relax they position the rib cage downwards and inwards.
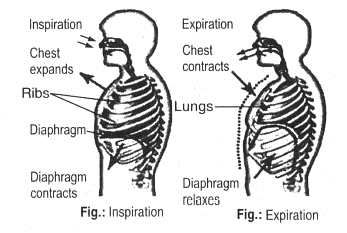
During exhalation, your diaphragm relaxes and moves upward into the chest cavity. The intercostal muscles between the ribs also relax to reduce the space in the chest cavity. As they relax they position the rib cage downwards and inwards.

Identify X in the given equation of aerobic respiration.
Glucose + X → CO2 + H20 + Energy
- a)Water
- b)Oxygen
- c)Ethyl alcohol
- d)Nitrogen
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify X in the given equation of aerobic respiration.
Glucose + X → CO2 + H20 + Energy
a)
Water
b)
Oxygen
c)
Ethyl alcohol
d)
Nitrogen

|
Anushka Kaur answered |
The given equation represents aerobic respiration. X is oxygen in the given equation.
In insects, air enters the body through
- a)Spiracles
- b)Gills
- c)Lungs
- d)Skin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In insects, air enters the body through
a)
Spiracles
b)
Gills
c)
Lungs
d)
Skin

|
Maitri Sarkar answered |
Insect bodies have openings, called spiracles, along the thorax and abdomen. These openings connect to the tubular network, allowing oxygen to pass into the body, regulating the diffusion of CO2 and water vapor.

Inhalation is the
- a)Release of oxygen
- b)Intake of carbon dioxide
- c)Intake of oxygen
- d)Release of carbon dioxide
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Inhalation is the
a)
Release of oxygen
b)
Intake of carbon dioxide
c)
Intake of oxygen
d)
Release of carbon dioxide

|
Prateek Sharma answered |
The part of breathing during which oxygen rich air is taken in is called inhalation.
Which of the following organisms respire through tracheal system?- a)Earthworm
- b)Cockroach
- c)Fish
- d)Frog
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following organisms respire through tracheal system?
a)
Earthworm
b)
Cockroach
c)
Fish
d)
Frog

|
Sai Kumar answered |
Tracheal respiration is found in cockroach.
Which of the following statements is correct for anaerobic respiration?
- a)Food is broken down in the absence of oxygen to release energy.
- b)Breakdown of food occurs in presence of oxygen.
- c)It produces large amount of energy compared to aerobic respiration.
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is correct for anaerobic respiration?
a)
Food is broken down in the absence of oxygen to release energy.
b)
Breakdown of food occurs in presence of oxygen.
c)
It produces large amount of energy compared to aerobic respiration.
d)
None of these

|
Yash Kapoor answered |
Food is broken down in the absence of oxygen to form alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy in anaerobic respiration.
Identify the labelled parts P, Q and R in the figure given below.
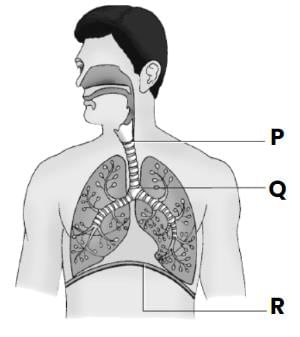
- a)P- Bronchus; Q- Bronchiole, R- Alveolus
- b)P- Trachea; Q- Alveolus, R- Bronchus
- c)P- Bronchus; Q- Bronchiole, R- Diaphragm
- d)P- Trachea; Q- Bronchus, R- Diaphragm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the labelled parts P, Q and R in the figure given below.

a)
P- Bronchus; Q- Bronchiole, R- Alveolus
b)
P- Trachea; Q- Alveolus, R- Bronchus
c)
P- Bronchus; Q- Bronchiole, R- Diaphragm
d)
P- Trachea; Q- Bronchus, R- Diaphragm

|
Learning Education answered |
The trachea, commonly known as the windpipe, is a tube about 4 inches long and less than an inch in diameter in most people. The trachea begins just under the larynx (voice box) and runs down behind the breastbone (sternum). The trachea then divides into two smaller tubes called bronchi: one bronchus for each lung.
The alveoli are where the lungs and the blood exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and breathing out.
The diaphragm is an unpaired, dome shaped skeletal muscle that is located in the trunk. It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities from each other by closing the inferior thoracic aperture. The diaphragm is the primary muscle that is active in inspiration.
The alveoli are where the lungs and the blood exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide during the process of breathing in and breathing out.
The diaphragm is an unpaired, dome shaped skeletal muscle that is located in the trunk. It separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities from each other by closing the inferior thoracic aperture. The diaphragm is the primary muscle that is active in inspiration.
What happens when we breathe in?(i) Size of our chest increases.(ii) Size of our chest decreases.(iii) Carbon dioxide is removed from our body(iv) Air enters our lungs.- a)(i) and (iii) are correct
- b)(i) and (iv) are correct
- c)(ii) and (iii) are correct
- d)(ii) and (iv) are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when we breathe in?
(i) Size of our chest increases.
(ii) Size of our chest decreases.
(iii) Carbon dioxide is removed from our body
(iv) Air enters our lungs.
a)
(i) and (iii) are correct
b)
(i) and (iv) are correct
c)
(ii) and (iii) are correct
d)
(ii) and (iv) are correct
|
|
Sahana Iyer answered |
When we breathe in air. Air enters lungs and there is an increase in the size of the chest.
What will happen when the thin rubber sheet is pulled downwards as shown in figure given below? 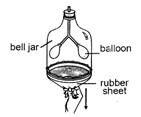
- a)Nothing will happen.
- b)The balloon will burst.
- c)The balloon will be deflated.
- d)The balloon will be inflated.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What will happen when the thin rubber sheet is pulled downwards as shown in figure given below?

a)
Nothing will happen.
b)
The balloon will burst.
c)
The balloon will be deflated.
d)
The balloon will be inflated.

|
Sreemoyee Nair answered |
When rubber sheet is pulled downwards, air enters into the balloon.
What will happen when diaphragm relaxes and curves upwards?- a)Air is forced out of the lungs.
- b)The rib cage goes up and outward.
- c)The volume of the thoracic cavity increases.
- d)Air pressure inside the thoracic cavity decreases.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will happen when diaphragm relaxes and curves upwards?
a)
Air is forced out of the lungs.
b)
The rib cage goes up and outward.
c)
The volume of the thoracic cavity increases.
d)
Air pressure inside the thoracic cavity decreases.

|
Sreemoyee Nair answered |
When structure P (diaphragm) relaxes and curve upwards air is forced out of the lungs.
When we inhale, we breathe in air into the lungs. What do we breathe out when we exhale?- a)Only oxygen gas.
- b)Only hydrogen gas.
- c)Air that has more oxygen than inhaled air.
- d)Air that has more carbon dioxide than inhaled air.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When we inhale, we breathe in air into the lungs. What do we breathe out when we exhale?
a)
Only oxygen gas.
b)
Only hydrogen gas.
c)
Air that has more oxygen than inhaled air.
d)
Air that has more carbon dioxide than inhaled air.

|
Abhay Menon answered |
During exhalation or expiration we breathe out air rich in carbon dioxide.
Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing a race?
- a)To reduce muscle cramps
- b)To supply more oxygen to the cells
- c)To expel excess carbon dioxide
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why does an athlete breathe faster and deeper than usual after finishing a race?
a)
To reduce muscle cramps
b)
To supply more oxygen to the cells
c)
To expel excess carbon dioxide
d)
None of these
|
|
Lakshya Sagare answered |
An athlete breathes faster and deeper than usual after finishing a race because their body needs to intake more oxygen to compensate for the oxygen debt incurred during the intense physical activity. This helps in the removal of lactic acid and the replenishment of oxygen levels in the muscles.
What is the normal range of breathing rate per minute for an average adult at rest?
- a)9-12
- b)15-18
- c)21-24
- d)30-33
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the normal range of breathing rate per minute for an average adult at rest?
a)
9-12
b)
15-18
c)
21-24
d)
30-33

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
The normal breathing rate for an average adult at rest is 15-18 breaths per minute. This rate can vary based on factors such as age, fitness level, and overall health.
The classification table given below shows how different organisms breathe. Which of these organisms are correctly represented by X, Y and Z?
Which of these organisms are correctly represented by X, Y and Z? - a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The classification table given below shows how different organisms breathe.

Which of these organisms are correctly represented by X, Y and Z?
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Anoushka Bajaj answered |
In the given table tadpole respires through gills, whale by lungs and earthworm through skin.
Which of these are parts of the human respiratory system?(i) Larynx (ii) Nostrils(iii) Gullet(iv) Windpipe(v) Lungs- a)(ii) and (v) only
- b)(i), (ii), (iv) and (v) only
- c)(i), (iv) and (v) only
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these are parts of the human respiratory system?
(i) Larynx
(ii) Nostrils
(iii) Gullet
(iv) Windpipe
(v) Lungs
a)
(ii) and (v) only
b)
(i), (ii), (iv) and (v) only
c)
(i), (iv) and (v) only
d)
All of the above
|
|
Aurora Institute answered |
Parts of Respiratory System includes:
- External nostrils – For the intake of air.
- Nasal chamber – which is lined with hair and mucus to filter the air from dust and dirt.
- Pharynx – It is a passage behind the nasal chamber and serves as the common passageway for both air and food.
- Larynx – Known as the soundbox as it houses the vocal chords, which are paramount in the generation of sound.
- Epiglottis – It is a flap-like structure that covers the glottis and prevents the entry of food into the windpipe.
- Trachea – It is a long tube passing through the mid-thoracic cavity.
- Bronchi – The trachea divides into left and right bronchi.
- Bronchioles – Each bronchus is further divided into finer channels known as bronchioles.
- Alveoli – The bronchioles terminate in balloon-like structures known as the alveoli.
- Lungs – Humans have a pair of lungs, which are sac-like structures and covered by a double-layered membrane known as pleura.
Breathing involves inspiration and expiration process. Which of the following take place during inspiration?- a)Ribs move downward and outward.
- b)Ribs move upward and inward.
- c)Ribs move downward and inward.
- d)Ribs move upward and outward.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Breathing involves inspiration and expiration process. Which of the following take place during inspiration?
a)
Ribs move downward and outward.
b)
Ribs move upward and inward.
c)
Ribs move downward and inward.
d)
Ribs move upward and outward.

|
Pranjal Banerjee answered |
During inspiration ribs move upward and outward.
Why do we get, muscle cramps after heavy exercise?- a)It is due to the partial breakdown of glucose to produce lactic acid.
- b)It is due to the complete breakdown of glucose to produce lactic acid.
- c)It is due to the muscle cells that respire in the presence of oxygen.
- d)It is due to the increased supply of oxygen to muscle cells.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Why do we get, muscle cramps after heavy exercise?
a)
It is due to the partial breakdown of glucose to produce lactic acid.
b)
It is due to the complete breakdown of glucose to produce lactic acid.
c)
It is due to the muscle cells that respire in the presence of oxygen.
d)
It is due to the increased supply of oxygen to muscle cells.

|
Abhay Menon answered |
In muscle cells partial breakdown of glucose produces lactic acid.
What is the process in cells where breakdown of food happens with the use of oxygen called?- a)Aerobic respiration
- b)Anaerobic respiration
- c)Photosynthesis
- d)Cell division
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the process in cells where breakdown of food happens with the use of oxygen called?
a)
Aerobic respiration
b)
Anaerobic respiration
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Cell division
|
|
Gayatri Mukherjee answered |
Understanding Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration is the process by which cells break down food molecules in the presence of oxygen to release energy. This process is crucial for the survival of most living organisms, as it provides the energy required for various cellular activities.
Key Features of Aerobic Respiration:
- **Oxygen Requirement:**
Aerobic respiration occurs only in the presence of oxygen. This is a key differentiator from anaerobic respiration, which happens without oxygen.
- **Energy Production:**
The main purpose of aerobic respiration is to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell. One glucose molecule can yield up to 36-38 ATP molecules during aerobic respiration.
- **Process Overview:**
The process involves several steps, mainly:
- **Glycolysis:** This occurs in the cytoplasm, where glucose is partially broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
- **Krebs Cycle:** In the mitochondria, pyruvate is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and transferring energy to electron carriers.
- **Electron Transport Chain:** This final stage occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, allowing ATP to be produced efficiently.
Importance of Aerobic Respiration:
- **Sustains Life:**
It provides the energy necessary for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells.
- **Waste Products:**
The by-products of aerobic respiration, primarily carbon dioxide and water, are less toxic compared to those produced during anaerobic respiration.
In summary, aerobic respiration is a vital process that utilizes oxygen to efficiently break down food and produce energy, sustaining life in various organisms.
Aerobic respiration is the process by which cells break down food molecules in the presence of oxygen to release energy. This process is crucial for the survival of most living organisms, as it provides the energy required for various cellular activities.
Key Features of Aerobic Respiration:
- **Oxygen Requirement:**
Aerobic respiration occurs only in the presence of oxygen. This is a key differentiator from anaerobic respiration, which happens without oxygen.
- **Energy Production:**
The main purpose of aerobic respiration is to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of the cell. One glucose molecule can yield up to 36-38 ATP molecules during aerobic respiration.
- **Process Overview:**
The process involves several steps, mainly:
- **Glycolysis:** This occurs in the cytoplasm, where glucose is partially broken down into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
- **Krebs Cycle:** In the mitochondria, pyruvate is further broken down, releasing carbon dioxide and transferring energy to electron carriers.
- **Electron Transport Chain:** This final stage occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, allowing ATP to be produced efficiently.
Importance of Aerobic Respiration:
- **Sustains Life:**
It provides the energy necessary for growth, repair, and maintenance of cells.
- **Waste Products:**
The by-products of aerobic respiration, primarily carbon dioxide and water, are less toxic compared to those produced during anaerobic respiration.
In summary, aerobic respiration is a vital process that utilizes oxygen to efficiently break down food and produce energy, sustaining life in various organisms.
Which of the following animals breathe through skin as well as through lungs?- a)Fish
- b)Frog
- c)Cockroach
- d)Earthworm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following animals breathe through skin as well as through lungs?
a)
Fish
b)
Frog
c)
Cockroach
d)
Earthworm

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
Animals that breathe through skin as well as through lungs:
- Frog: Frogs are amphibians that have the ability to breathe through their skin as well as through their lungs. Their skin is thin and moist, allowing for gas exchange to occur. This is especially important for frogs when they are underwater or in environments with low oxygen levels.
Explanation:
- Frogs have a specialized skin that is permeable to gases, allowing them to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide through their skin.
- When frogs are on land, they primarily use their lungs to breathe. However, when they are in water or in damp environments, they rely more on their skin for respiration.
- This dual breathing system allows frogs to adapt to different environments and survive in a variety of conditions.
Conclusion:
- In conclusion, frogs are a unique example of animals that can breathe through their skin as well as through their lungs, showcasing their remarkable adaptation to varying habitats.
Yeasts are single-celled organisms that respire anaerobically and yield _____ and ________during this process.
- a)Water and Carbon Dioxide
- b)Oxygen and Alcohol
- c)Nitrogen and Carbon Dioxide
- d)Alcohol and Carbon Dioxide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Yeasts are single-celled organisms that respire anaerobically and yield _____ and ________during this process.
a)
Water and Carbon Dioxide
b)
Oxygen and Alcohol
c)
Nitrogen and Carbon Dioxide
d)
Alcohol and Carbon Dioxide
|
|
Priya Mukherjee answered |
Yeast Respiration and Alcohol Production
Anaerobic respiration in yeasts is known as fermentation, which produces alcohol as a byproduct. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Yeast Cells
- Yeasts are single-celled organisms that can respire anaerobically when oxygen is not present.
- They have the ability to convert sugars into energy without the need for oxygen through fermentation.
Anaerobic Respiration
- In the absence of oxygen, yeasts undergo anaerobic respiration to generate energy.
- This process involves breaking down sugars (such as glucose) into simpler compounds to release energy.
Alcohol Production
- During anaerobic respiration, yeasts produce alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
- The alcohol produced by yeasts is commonly used in the production of alcoholic beverages such as beer and wine.
Final Product
- The main product of anaerobic respiration in yeasts is alcohol, which is utilized in various industrial and culinary processes.
- This process is essential for the fermentation of sugars into alcohol, making yeasts valuable organisms in biotechnology and food production.
Anaerobic respiration in yeasts is known as fermentation, which produces alcohol as a byproduct. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Yeast Cells
- Yeasts are single-celled organisms that can respire anaerobically when oxygen is not present.
- They have the ability to convert sugars into energy without the need for oxygen through fermentation.
Anaerobic Respiration
- In the absence of oxygen, yeasts undergo anaerobic respiration to generate energy.
- This process involves breaking down sugars (such as glucose) into simpler compounds to release energy.
Alcohol Production
- During anaerobic respiration, yeasts produce alcohol (ethanol) and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
- The alcohol produced by yeasts is commonly used in the production of alcoholic beverages such as beer and wine.
Final Product
- The main product of anaerobic respiration in yeasts is alcohol, which is utilized in various industrial and culinary processes.
- This process is essential for the fermentation of sugars into alcohol, making yeasts valuable organisms in biotechnology and food production.
Plants breathe through their stomata located in their- a)Leaves
- b)Stem
- c)Flowers
- d)Roots
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plants breathe through their stomata located in their
a)
Leaves
b)
Stem
c)
Flowers
d)
Roots

|
Indu Gupta answered |
Stomata are microscopic pores found on the surface of leaves and are responsible for gas exchange.
They allow plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis and respiration.
They allow plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis and respiration.
The following word equation shows a chemical process that take place in an organism Y.
 What is organism Y?
What is organism Y?
- a)Algae
- b)Protozoan
- c)Yeast
- d)Hydra
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The following word equation shows a chemical process that take place in an organism Y.

What is organism Y?
a)
Algae
b)
Protozoan
c)
Yeast
d)
Hydra

|
Sreemoyee Nair answered |
The given equation represents fermentation or anaerobic respiration. In the equation Y represents yeast.
What will happen when the thin rubber sheet is pushed upwards?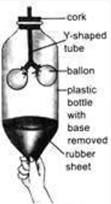
- a)Air is pulled in
- b)Air is forced out
- c)Air pressure in the bell jar increases
- d)No change
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What will happen when the thin rubber sheet is pushed upwards?

a)
Air is pulled in
b)
Air is forced out
c)
Air pressure in the bell jar increases
d)
No change

|
Learning Enablers answered |
In the given experimental setup when the rubber sheet is pushed upwards air is forced out.
Chapter doubts & questions for Respiration in Organisms - Science Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 7 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Respiration in Organisms - Science Class 7 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 7 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Class 7
112 videos|252 docs|28 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












