Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Questions > Plants breathe through their stomata located ...
Start Learning for Free
Plants breathe through their stomata located in their
- a)Leaves
- b)Stem
- c)Flowers
- d)Roots
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)F...
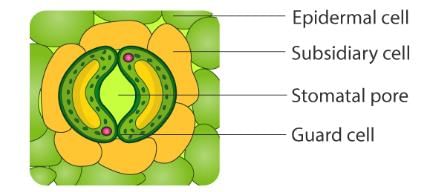
Stomata are microscopic pores found on the surface of leaves and are responsible for gas exchange.
They allow plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis and respiration.
They allow plants to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, playing a crucial role in photosynthesis and respiration.
Most Upvoted Answer
Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)F...
Understanding Plant Breathing
Plants play a crucial role in our ecosystem, and one of their vital processes is respiration, which occurs primarily through structures called stomata.
What Are Stomata?
- Stomata are tiny openings located mainly on the surfaces of leaves.
- They consist of two specialized cells called guard cells that control their opening and closing.
Role of Stomata in Breathing
- Gas Exchange: Stomata facilitate the exchange of gases, allowing carbon dioxide (CO2) to enter the leaf for photosynthesis and oxygen (O2) to exit as a by-product.
- Transpiration: They also play a key role in transpiration, where water vapor is released, helping in nutrient uptake and temperature regulation.
Location of Stomata
- While stomata can be found on stems and sometimes flowers, their primary and most abundant location is on the leaves.
- This positioning maximizes their exposure to sunlight and air, optimizing photosynthesis.
Importance of Leaves in Plant Breathing
- Photosynthesis: Leaves are the main sites for photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into energy, necessitating the need for stomata for gas exchange.
- Adaptations: Different plants have adapted the number and size of stomata based on their environment, ensuring efficient breathing under varying conditions.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A'—leaves, as they house the stomata that enable plants to breathe effectively and perform essential life processes.
Plants play a crucial role in our ecosystem, and one of their vital processes is respiration, which occurs primarily through structures called stomata.
What Are Stomata?
- Stomata are tiny openings located mainly on the surfaces of leaves.
- They consist of two specialized cells called guard cells that control their opening and closing.
Role of Stomata in Breathing
- Gas Exchange: Stomata facilitate the exchange of gases, allowing carbon dioxide (CO2) to enter the leaf for photosynthesis and oxygen (O2) to exit as a by-product.
- Transpiration: They also play a key role in transpiration, where water vapor is released, helping in nutrient uptake and temperature regulation.
Location of Stomata
- While stomata can be found on stems and sometimes flowers, their primary and most abundant location is on the leaves.
- This positioning maximizes their exposure to sunlight and air, optimizing photosynthesis.
Importance of Leaves in Plant Breathing
- Photosynthesis: Leaves are the main sites for photosynthesis, where sunlight is converted into energy, necessitating the need for stomata for gas exchange.
- Adaptations: Different plants have adapted the number and size of stomata based on their environment, ensuring efficient breathing under varying conditions.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'A'—leaves, as they house the stomata that enable plants to breathe effectively and perform essential life processes.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Question Description
Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 7.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Plants breathe through their stomata located in theira)Leavesb)Stemc)Flowersd)RootsCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 7 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















