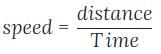All Exams >
Class 7 >
Science Class 7 >
All Questions
All questions of Motion and Time for Class 7 Exam
A car is moving with 72 km/hrs. The speed of the car in m/s is
- a)30 m/s
- b)20 m/s
- c)40 m/s
- d)25 m/s
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A car is moving with 72 km/hrs. The speed of the car in m/s is
a)
30 m/s
b)
20 m/s
c)
40 m/s
d)
25 m/s

|
Meera Reddy answered |
We know ,
1 km=1000m , 1 hour=3600s
1km/h=1000/3600m/s=5/18m/s
72km/h=72×5/18m/s
=4×5m/s
=20m/s.
1 km=1000m , 1 hour=3600s
1km/h=1000/3600m/s=5/18m/s
72km/h=72×5/18m/s
=4×5m/s
=20m/s.
The speed of the vehicle is recorded by
- a)Ammeter
- b)Odometer
- c)Speedometer
- d)Voltmeter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The speed of the vehicle is recorded by
a)
Ammeter
b)
Odometer
c)
Speedometer
d)
Voltmeter
|
|
Jyoti Kulkarni answered |
- The speedometer is a device found in vehicles that measures the current speed of the vehicle.
- It provides real-time information, allowing drivers to maintain safe speeds and abide by traffic regulations.
- Unlike an odometer, which measures distance traveled, the speedometer focuses solely on speed.
- Ammeter and voltmeter measure electrical current and voltage, respectively, and are not related to vehicle speed.
Topic in NCERT: Measuring Speed
Line in NCERT: "The speedometer records the speed directly in km/h."
Change in position with respect to the surroundings is called
- a)Acceleration
- b)Speed
- c)Momentum
- d)Force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Change in position with respect to the surroundings is called
a)
Acceleration
b)
Speed
c)
Momentum
d)
Force

|
Lakshmi Reddy answered |
The change in position with respect to the surroundings is called Speed
- Speed is the measure of how quickly an object moves from one position to another. It is calculated as the distance traveled divided by the time taken to travel that distance.
Line in NCERT: "The distance moved by an object in a unit time is called its speed."
The basic unit of speed is:
- a)km/min
- b)m/min
- c)km/h
- d)m/s
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic unit of speed is:
a)
km/min
b)
m/min
c)
km/h
d)
m/s

|
Kavya Rane answered |
The basic unit of distance is metre (m). The basic unit of time is second (s). Since we know that s=d/t. Therefore, the basic unit of speed is m/s.
So option D is the correct answer.
Speed time graph is straight line for- a)Non-uniform motion
- b)Constant motion Uniform motion
- c)Uniform motion
- d)Accelerated motion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Speed time graph is straight line for
a)
Non-uniform motion
b)
Constant motion Uniform motion
c)
Uniform motion
d)
Accelerated motion

|
Kiran Bajaj answered |
When the slope of distance-time graph is a straight line parallel to time axis, the object is moving with uniform motion.
What is the speed of a car that travels 15 km in 20 minutes, expressed in km/h?
- a)35 km/h
- b)40 km/h
- c)45 km/h
- d)50 km/h
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the speed of a car that travels 15 km in 20 minutes, expressed in km/h?
a)
35 km/h
b)
40 km/h
c)
45 km/h
d)
50 km/h
|
|
Vidhi bajaj answered |
Calculation:
- Distance traveled = 15 km
- Time taken = 20 minutes = 20/60 hours = 1/3 hours
Formula:
- Speed = Distance/Time
Calculation:
- Speed = 15 km / (1/3) hours
- Speed = 15 km * 3
- Speed = 45 km/h
Therefore, the speed of the car that travels 15 km in 20 minutes is 45 km/h.
- Distance traveled = 15 km
- Time taken = 20 minutes = 20/60 hours = 1/3 hours
Formula:
- Speed = Distance/Time
Calculation:
- Speed = 15 km / (1/3) hours
- Speed = 15 km * 3
- Speed = 45 km/h
Therefore, the speed of the car that travels 15 km in 20 minutes is 45 km/h.
The distance-time graph of the non-uniform motion is a _________ line- a)straight
- b)straight then curved
- c)curved
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance-time graph of the non-uniform motion is a _________ line
a)
straight
b)
straight then curved
c)
curved
d)
none of these

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
The distance-time graph of the non-uniform motion is a curved line as it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, hence option A is correct.
Which of the following motions is characterized by an object moving back and forth along the same path?- a)Circular motion
- b)Linear motion
- c)Oscillatory motion
- d)Random motion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Circular motion
b)
Linear motion
c)
Oscillatory motion
d)
Random motion
|
|
Vaibhav Goyal answered |
Understanding Oscillatory Motion
Oscillatory motion is a specific type of movement where an object moves back and forth along the same path. This motion can be observed in various everyday scenarios and is characterized by a repetitive cycle.
Key Characteristics of Oscillatory Motion:
- Back and Forth Movement: The defining feature of oscillatory motion is that the object returns to its original position after moving in one direction, then reverses to move in the opposite direction.
- Examples: Common examples include a swinging pendulum, vibrations of a guitar string, or the motion of a spring when compressed and released.
- Time Period: This motion is periodic, meaning it occurs in cycles over a fixed time interval, known as the time period.
- Equilibrium Position: The object oscillates around a central point or equilibrium position, where it would be at rest if not for the oscillatory forces acting on it.
Why Other Motions Are Not Oscillatory:
- Circular Motion: In circular motion, an object moves in a circular path, which does not involve returning along the same path.
- Linear Motion: Linear motion involves movement in a straight line, without the back-and-forth characteristic of oscillatory motion.
- Random Motion: Random motion lacks any predictable pattern, unlike the orderly back-and-forth nature of oscillatory motion.
In summary, oscillatory motion is distinct due to its repetitive back-and-forth movement along the same path, making option 'C' the correct answer.
Oscillatory motion is a specific type of movement where an object moves back and forth along the same path. This motion can be observed in various everyday scenarios and is characterized by a repetitive cycle.
Key Characteristics of Oscillatory Motion:
- Back and Forth Movement: The defining feature of oscillatory motion is that the object returns to its original position after moving in one direction, then reverses to move in the opposite direction.
- Examples: Common examples include a swinging pendulum, vibrations of a guitar string, or the motion of a spring when compressed and released.
- Time Period: This motion is periodic, meaning it occurs in cycles over a fixed time interval, known as the time period.
- Equilibrium Position: The object oscillates around a central point or equilibrium position, where it would be at rest if not for the oscillatory forces acting on it.
Why Other Motions Are Not Oscillatory:
- Circular Motion: In circular motion, an object moves in a circular path, which does not involve returning along the same path.
- Linear Motion: Linear motion involves movement in a straight line, without the back-and-forth characteristic of oscillatory motion.
- Random Motion: Random motion lacks any predictable pattern, unlike the orderly back-and-forth nature of oscillatory motion.
In summary, oscillatory motion is distinct due to its repetitive back-and-forth movement along the same path, making option 'C' the correct answer.
Which of the following is an example of non-uniform motion?- a)Movement of an asteroid
- b)A car coming to a halt
- c)A bouncing ball
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of non-uniform motion?
a)
Movement of an asteroid
b)
A car coming to a halt
c)
A bouncing ball
d)
All of these
|
|
Aryan Mukherjee answered |
Non-uniform Motion:
Movement of an asteroid, a car coming to a halt, and a bouncing ball are all examples of non-uniform motion. Non-uniform motion refers to an object moving at varying speeds or changing its direction over time.
Movement of an Asteroid:
- An asteroid moving through space does not maintain a constant speed as it is influenced by gravitational forces from other celestial bodies. It may speed up or slow down as it travels through the solar system.
A Car Coming to a Halt:
- When a car is slowing down to come to a stop, it is experiencing non-uniform motion. Initially, the car is moving at a certain speed, but as the brakes are applied, the speed decreases until it eventually comes to a complete stop.
A Bouncing Ball:
- A bouncing ball is another example of non-uniform motion. When a ball is thrown or dropped, it accelerates towards the ground due to gravity. Upon hitting the ground, it bounces back up, changing its speed and direction multiple times during the bouncing process.
Conclusion:
- All three examples exhibit non-uniform motion because they involve changes in speed or direction over time. Understanding non-uniform motion is essential in physics as it helps to describe the motion of objects in real-world scenarios.
A train travels at a speed of 60 km/h. How far will it travel in 4 hours?- a)15 km
- b)230 km
- c)60km
- d)240km
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A train travels at a speed of 60 km/h. How far will it travel in 4 hours?
a)
15 km
b)
230 km
c)
60km
d)
240km

|
Uday Gupta answered |
Understanding Speed, Time, and Distance
To determine how far a train will travel, we can use the fundamental relationship between speed, time, and distance, expressed by the formula:
Distance = Speed × Time
In this scenario:
- The speed of the train is 60 km/h.
- The time of travel is 4 hours.
Calculating the Distance
Now, let's perform the calculation step-by-step:
- Speed = 60 km/h
- Time = 4 hours
Using the formula:
- Distance = Speed × Time
- Distance = 60 km/h × 4 hours
Performing the Multiplication
- Distance = 240 km
This means that the train will cover a distance of 240 kilometers in 4 hours at a speed of 60 km/h.
Choosing the Correct Option
Now, let's compare the calculated distance with the given options:
- a) 15 km
- b) 230 km
- c) 60 km
- d) 240 km
The correct answer is option 'D' - 240 km.
Conclusion
To sum up, by multiplying the speed of the train by the time traveled, we found that the train travels a total of 240 kilometers in 4 hours. Understanding this relationship is essential in solving problems related to speed, time, and distance.
To determine how far a train will travel, we can use the fundamental relationship between speed, time, and distance, expressed by the formula:
Distance = Speed × Time
In this scenario:
- The speed of the train is 60 km/h.
- The time of travel is 4 hours.
Calculating the Distance
Now, let's perform the calculation step-by-step:
- Speed = 60 km/h
- Time = 4 hours
Using the formula:
- Distance = Speed × Time
- Distance = 60 km/h × 4 hours
Performing the Multiplication
- Distance = 240 km
This means that the train will cover a distance of 240 kilometers in 4 hours at a speed of 60 km/h.
Choosing the Correct Option
Now, let's compare the calculated distance with the given options:
- a) 15 km
- b) 230 km
- c) 60 km
- d) 240 km
The correct answer is option 'D' - 240 km.
Conclusion
To sum up, by multiplying the speed of the train by the time traveled, we found that the train travels a total of 240 kilometers in 4 hours. Understanding this relationship is essential in solving problems related to speed, time, and distance.
A scooterist travels at 30 km/h along a straight path for 20 minutes. What is the distance traveled?- a)10 km
- b)1.5 km
- c)6 km
- d)90 km
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A scooterist travels at 30 km/h along a straight path for 20 minutes. What is the distance traveled?
a)
10 km
b)
1.5 km
c)
6 km
d)
90 km

|
Tutorpedia Coaching answered |
If the scooter is travelling at precisely 30km/h in a perfectly straight line.
We know 1 hour=60 minutes
Therefore to calculate the distance traveled in the started fraction of the hour.
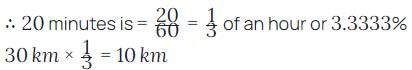
Therefore 10km is the distance traveled in 20 minutes of travelling at a speed of 30km/h
We know 1 hour=60 minutes
Therefore to calculate the distance traveled in the started fraction of the hour.
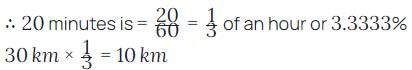
Therefore 10km is the distance traveled in 20 minutes of travelling at a speed of 30km/h
Car travels first 60 km of a distance in 1 hr, next 70 km of the distance in next hour and remaining 20 km distance in final hour. Find its type of motion
- a)uniform motion
- b)non-uniform motion
- c)either uniform or non-uniform motion
- d)neither uniform nor non-uniform motion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Car travels first 60 km of a distance in 1 hr, next 70 km of the distance in next hour and remaining 20 km distance in final hour. Find its type of motion
a)
uniform motion
b)
non-uniform motion
c)
either uniform or non-uniform motion
d)
neither uniform nor non-uniform motion
|
|
Sharada patil answered |
Uniform motion vs Non-uniform motion
Uniform motion refers to the motion of an object where it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. On the other hand, non-uniform motion refers to the motion of an object where it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
Analysis of the given scenario
Let's analyze the given scenario step by step to determine whether the motion of the car is uniform or non-uniform.
1. In the first hour, the car travels a distance of 60 km.
2. In the second hour, the car travels a distance of 70 km.
3. In the final hour, the car travels a distance of 20 km.
Calculating the time intervals
To determine whether the distances covered by the car are equal or not, we need to calculate the time intervals for each distance.
1. The car covers the first 60 km in 1 hour, so the time interval for this distance is 1 hour.
2. The car covers the next 70 km in the next hour, so the time interval for this distance is also 1 hour.
3. The car covers the remaining 20 km in the final hour, so the time interval for this distance is again 1 hour.
Comparing the distances covered
Now, let's compare the distances covered by the car in each time interval.
1. In the first hour, the car covers 60 km.
2. In the second hour, the car covers 70 km.
3. In the final hour, the car covers 20 km.
Conclusion
From the analysis, we can see that the car covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. Therefore, the motion of the car is non-uniform.
Explanation of the correct answer
The correct answer is option 'B' - non-uniform motion. This is because the car covers unequal distances (60 km, 70 km, and 20 km) in equal intervals of time (1 hour each). In uniform motion, the distances covered by an object in equal intervals of time would be the same.
Uniform motion refers to the motion of an object where it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time. On the other hand, non-uniform motion refers to the motion of an object where it covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
Analysis of the given scenario
Let's analyze the given scenario step by step to determine whether the motion of the car is uniform or non-uniform.
1. In the first hour, the car travels a distance of 60 km.
2. In the second hour, the car travels a distance of 70 km.
3. In the final hour, the car travels a distance of 20 km.
Calculating the time intervals
To determine whether the distances covered by the car are equal or not, we need to calculate the time intervals for each distance.
1. The car covers the first 60 km in 1 hour, so the time interval for this distance is 1 hour.
2. The car covers the next 70 km in the next hour, so the time interval for this distance is also 1 hour.
3. The car covers the remaining 20 km in the final hour, so the time interval for this distance is again 1 hour.
Comparing the distances covered
Now, let's compare the distances covered by the car in each time interval.
1. In the first hour, the car covers 60 km.
2. In the second hour, the car covers 70 km.
3. In the final hour, the car covers 20 km.
Conclusion
From the analysis, we can see that the car covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time. Therefore, the motion of the car is non-uniform.
Explanation of the correct answer
The correct answer is option 'B' - non-uniform motion. This is because the car covers unequal distances (60 km, 70 km, and 20 km) in equal intervals of time (1 hour each). In uniform motion, the distances covered by an object in equal intervals of time would be the same.
If a simple pendulum completes 20 oscillations in 32 seconds, what is its time period?
- a)1.6 s
- b)2.0 s
- c)2.5 s
- d)3.2 s
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If a simple pendulum completes 20 oscillations in 32 seconds, what is its time period?
a)
1.6 s
b)
2.0 s
c)
2.5 s
d)
3.2 s

|
Coachify answered |
Time period ?= Total time/Number of oscillations
= 32s/20
=1.6 s
T= 1.6 s
= 32s/20
=1.6 s
T= 1.6 s
Rajdhini express moves at a speed of 150 km/h. How long will it take to cover a distance of 15 km?- a)1.125 h
- b)2.125 h
- c)3.125 h
- d)0.1 h
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Rajdhini express moves at a speed of 150 km/h. How long will it take to cover a distance of 15 km?
a)
1.125 h
b)
2.125 h
c)
3.125 h
d)
0.1 h

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
Given,
speed v = 150 km/h
distance cover = displacement d=15 km (Assume express is not changing its direction)
speed v = 150 km/h
distance cover = displacement d=15 km (Assume express is not changing its direction)
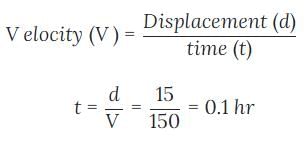
Time taken t = 0.1 hr
Which of the following does not express a time interval?- a)Time of the first bell in the school
- b)A day
- c)A second
- d)A school period
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not express a time interval?
a)
Time of the first bell in the school
b)
A day
c)
A second
d)
A school period
|
|
Sunehri Choudhary answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'A' - Time of the first bell in the school.
Time intervals:
Time intervals refer to a specific duration or period of time. They measure the amount of time between two points or events.
Options:
a) Time of the first bell in the school:
This option does not express a time interval. It refers to a specific point in time when the first bell rings in the school. It does not indicate a duration or a period of time. Therefore, it is not an example of a time interval.
b) A day:
A day represents a time interval. It refers to a period of 24 hours, starting from midnight and ending at the next midnight. It is a commonly used unit of time to measure the duration of various activities or events.
c) A second:
A second is another example of a time interval. It is a unit of time measurement in the International System of Units (SI). It represents a duration of 1/60th of a minute or 1/3,600th of an hour. It is commonly used to measure short durations or intervals.
d) A school period:
A school period is also a time interval. It refers to a specific duration of time allocated for a particular subject or activity in a school. It can vary in length depending on the school's schedule and may range from a few minutes to an hour.
Conclusion:
Out of the given options, the only one that does not express a time interval is option 'A' - Time of the first bell in the school. This option refers to a specific point in time rather than a duration or period of time.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Time of the first bell in the school.
Time intervals:
Time intervals refer to a specific duration or period of time. They measure the amount of time between two points or events.
Options:
a) Time of the first bell in the school:
This option does not express a time interval. It refers to a specific point in time when the first bell rings in the school. It does not indicate a duration or a period of time. Therefore, it is not an example of a time interval.
b) A day:
A day represents a time interval. It refers to a period of 24 hours, starting from midnight and ending at the next midnight. It is a commonly used unit of time to measure the duration of various activities or events.
c) A second:
A second is another example of a time interval. It is a unit of time measurement in the International System of Units (SI). It represents a duration of 1/60th of a minute or 1/3,600th of an hour. It is commonly used to measure short durations or intervals.
d) A school period:
A school period is also a time interval. It refers to a specific duration of time allocated for a particular subject or activity in a school. It can vary in length depending on the school's schedule and may range from a few minutes to an hour.
Conclusion:
Out of the given options, the only one that does not express a time interval is option 'A' - Time of the first bell in the school. This option refers to a specific point in time rather than a duration or period of time.
The earliest clocks for measuring time during day were- a)Sand clocks
- b)Pendulum clocks
- c)Sundials
- d)Stop watches
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The earliest clocks for measuring time during day were
a)
Sand clocks
b)
Pendulum clocks
c)
Sundials
d)
Stop watches

|
Rainbow Rise Classes answered |
Sundials utilize the position of the sun to cast a shadow, indicating the time, and are considered one of the first devices used to measure time, dating back to ancient Egypt.
- Sand clocks: While ancient, sand clocks are not considered the earliest timekeeping devices.
- Pendulum clocks: These were developed much later than sundials.
- Stopwatches: Stopwatches are designed to measure specific time intervals, not the time of day, and came about even later than pendulum clocks.
Topic in NCERT: Units of time and speed
Line in NCERT: "Sundials"
Chapter doubts & questions for Motion and Time - Science Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 7 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Motion and Time - Science Class 7 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 7 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Science Class 7
112 videos|275 docs|28 tests
|
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup