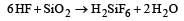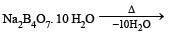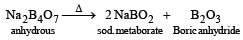All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of The p-Block Elements (Group 13 & 14) for NEET Exam
An example of a double salt is [1989]- a)Bleaching powder
- b)K4[Fe(CN)6]
- c)Hypo
- d)Potash Alum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An example of a double salt is [1989]
a)
Bleaching powder
b)
K4[Fe(CN)6]
c)
Hypo
d)
Potash Alum

|
Surbhi Das answered |
Potash Alum, K2SO4. Al2(SO4). 24H2O is a double salt.
The substance used as a smoke screen in warfare is[1989]- a)SiCl4
- b)PH3
- c)PCl5
- d)Acetylene
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The substance used as a smoke screen in warfare is[1989]
a)
SiCl4
b)
PH3
c)
PCl5
d)
Acetylene

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
SiCl4 gets hydrolysed in moist air and gives white fumes which are used as a smoke screen in warfare.
Which of these is not a monomer for a high molecular mass silicone polymer? [NEET 2013]- a)Me2SiCl2
- b)Me3SiCl
- c)PhSiCl3
- d)MeSiCl3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is not a monomer for a high molecular mass silicone polymer? [NEET 2013]
a)
Me2SiCl2
b)
Me3SiCl
c)
PhSiCl3
d)
MeSiCl3

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Since Me3SiCl contains only one Cl, therefore it can’t form high molecular mass silicon polymer. It can form only dimer.
Glass is a [1991]- a)Liquid
- b)Solid
- c)Supercooled liquid
- d)Transparent organic polymer
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Glass is a [1991]
a)
Liquid
b)
Solid
c)
Supercooled liquid
d)
Transparent organic polymer

|
Yash Saha answered |
Glass is a super cooled liquid.
The basic structural unit of silicates is : [NEET 2013]- a)SiO44-
- b)SiO32-
- c)SiO24-
- d)SiO
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic structural unit of silicates is : [NEET 2013]
a)
SiO44-
b)
SiO32-
c)
SiO24-
d)
SiO

|
Anand Jain answered |
SiO44– is basic structural unit of silicates.
Which of the following structure is similar to graphite? [NEET 2013]- a)B
- b)B4C
- c)B2H6
- d)BN
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following structure is similar to graphite? [NEET 2013]
a)
B
b)
B4C
c)
B2H6
d)
BN

|
Arnab Iyer answered |
Boron nitride (BN) is known as inorganic graphite. The most stable form is hexagonal one. It has layered structure similar to graphite.

Which one of the following statements about the zeolites is false ? [2004]
- a)They are used as cation exchangers
- b)They have open structure which enables them to take up small molecules
- c)none of the SiO44- units are replaced by AlO45- and AlO69- ions in zeolites
- d)Zeolites are aluminosilicates having three dimensional network
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about the zeolites is false ? [2004]
a)
They are used as cation exchangers
b)
They have open structure which enables them to take up small molecules
c)
none of the SiO44- units are replaced by AlO45- and AlO69- ions in zeolites
d)
Zeolites are aluminosilicates having three dimensional network

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Zeolite are microporous crystalline solid with well defined structure. They contain silicon, aluminium and oxygen in their framework and cations, water & other molecules within their pores. The general formula of zeolite is Mx/y[(AlO2)x(SiO2)y]. mH2O.
Aluminium is extracted from alumina (Al2O3) by electrolysis of a molten mixture of : [2012]- a)Al2O3 + HF + NaAlF4
- b)Al2O3 + CaF2 + NaAlF4
- c)Al2O3 + Na3AlF6 + CaF2
- d)Al2O3 + KF + Na3AlF6
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Aluminium is extracted from alumina (Al2O3) by electrolysis of a molten mixture of : [2012]
a)
Al2O3 + HF + NaAlF4
b)
Al2O3 + CaF2 + NaAlF4
c)
Al2O3 + Na3AlF6 + CaF2
d)
Al2O3 + KF + Na3AlF6

|
Sinjini Datta answered |
Extraction of Aluminium from Alumina (Al2O3)
Aluminium is an important metal that is widely used in various industries due to its low density, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is extracted from its ore, alumina (Al2O3), through a process called electrolysis. The correct combination of molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis is given in option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF2.
Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3)
The extraction of aluminium from alumina involves the process of electrolysis. In this process, a molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is used as an electrolyte. The following steps explain the extraction process in detail:
1. Formation of Cryolite (Na3AlF6):
- Cryolite is a mineral that is added to the mixture to lower the melting point of alumina and improve its conductivity.
- Na3AlF6 is formed by the reaction between alumina and sodium fluoride (NaF).
- 2 Al2O3 + 6 NaF → 2 Na3AlF6 + 3 O2
2. Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3):
- The mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is heated to a high temperature to form a molten electrolyte.
- The mixture is then placed in an electrolytic cell, which consists of a carbon anode and a carbon cathode.
- The carbon anode is connected to the positive terminal of a power supply, while the carbon cathode is connected to the negative terminal.
- The molten mixture acts as the electrolyte, and alumina is dissolved in it.
- When an electric current is passed through the electrolyte, the following reactions occur:
- At the anode (oxidation): 2 O2- → O2 + 4 e-
- At the cathode (reduction): 4 Al3+ + 12 e- → 4 Al
- The oxygen ions (O2-) are attracted to the anode and combine to form oxygen gas (O2), which is released.
- The aluminium ions (Al3+) are attracted to the cathode and gain electrons to form aluminium metal (Al), which is deposited on the cathode.
Advantages of the Molten Mixture
The molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 has several advantages for the extraction of aluminium:
- Lower Melting Point: The addition of cryolite (Na3AlF6) lowers the melting point of alumina, reducing the amount of energy required for the process.
- Improved Conductivity: The presence of the molten mixture enhances the conductivity of the electrolyte, allowing for efficient electrolysis.
- Electrolyte Stability: The molten mixture remains stable at high temperatures, ensuring the continuous flow of current and the extraction of aluminium.
Conclusion
The correct combination of the molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium from alumina (Al2O3) is option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF
Aluminium is an important metal that is widely used in various industries due to its low density, high strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. It is extracted from its ore, alumina (Al2O3), through a process called electrolysis. The correct combination of molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium by electrolysis is given in option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF2.
Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3)
The extraction of aluminium from alumina involves the process of electrolysis. In this process, a molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is used as an electrolyte. The following steps explain the extraction process in detail:
1. Formation of Cryolite (Na3AlF6):
- Cryolite is a mineral that is added to the mixture to lower the melting point of alumina and improve its conductivity.
- Na3AlF6 is formed by the reaction between alumina and sodium fluoride (NaF).
- 2 Al2O3 + 6 NaF → 2 Na3AlF6 + 3 O2
2. Electrolysis of Alumina (Al2O3):
- The mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 is heated to a high temperature to form a molten electrolyte.
- The mixture is then placed in an electrolytic cell, which consists of a carbon anode and a carbon cathode.
- The carbon anode is connected to the positive terminal of a power supply, while the carbon cathode is connected to the negative terminal.
- The molten mixture acts as the electrolyte, and alumina is dissolved in it.
- When an electric current is passed through the electrolyte, the following reactions occur:
- At the anode (oxidation): 2 O2- → O2 + 4 e-
- At the cathode (reduction): 4 Al3+ + 12 e- → 4 Al
- The oxygen ions (O2-) are attracted to the anode and combine to form oxygen gas (O2), which is released.
- The aluminium ions (Al3+) are attracted to the cathode and gain electrons to form aluminium metal (Al), which is deposited on the cathode.
Advantages of the Molten Mixture
The molten mixture of alumina, Na3AlF6, and CaF2 has several advantages for the extraction of aluminium:
- Lower Melting Point: The addition of cryolite (Na3AlF6) lowers the melting point of alumina, reducing the amount of energy required for the process.
- Improved Conductivity: The presence of the molten mixture enhances the conductivity of the electrolyte, allowing for efficient electrolysis.
- Electrolyte Stability: The molten mixture remains stable at high temperatures, ensuring the continuous flow of current and the extraction of aluminium.
Conclusion
The correct combination of the molten mixture for the extraction of aluminium from alumina (Al2O3) is option 'C', which consists of Al2O3, Na3AlF6, and CaF
Name the type of the structure of silicate in which one oxygen atom of [SiO4]4– is shared ? [2011]- a)Linear chain silicate
- b)Sheet silicate
- c)Pyrosilicate
- d)Three dimensional
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the type of the structure of silicate in which one oxygen atom of [SiO4]4– is shared ? [2011]
a)
Linear chain silicate
b)
Sheet silicate
c)
Pyrosilicate
d)
Three dimensional
|
|
Amrutha Das answered |
The type of structure where one oxygen atom of [SiO4]4- is shared with another tetrahedron is called a sheet structure or a layered structure.
Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in diamond ? [1992]- a)Ionic
- b)Covalent
- c)Dipolar
- d)vander Waals.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following types of forces bind together the carbon atoms in diamond ? [1992]
a)
Ionic
b)
Covalent
c)
Dipolar
d)
vander Waals.

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
In diamond each carbon atom is sp 3 hybridized and thus forms covalent bonds with four other carbon atoms lying at the corners of a regular tetrahedron.
Water gas is produced by [1992]- a)Passing steam through a red hot coke bed
- b)Saturating hydrogen with moisture
- c)Mixing oxygen and hydrogen in the ratio of 1 : 2
- d)Heating a mixture of CO2 and CH4 in petroleum refineries.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water gas is produced by [1992]
a)
Passing steam through a red hot coke bed
b)
Saturating hydrogen with moisture
c)
Mixing oxygen and hydrogen in the ratio of 1 : 2
d)
Heating a mixture of CO2 and CH4 in petroleum refineries.

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Water gas is made by blowing steam through the layer of incandescent coal.
The tendency of BF3, BCl3 and BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence- a)BCl3 > BF3 > BBr3 [2010]
- b)BBr3 > BCl2 > BF3
- c)BBr3 > BF3 > BCl3
- d)BF3 > BCl3 > BBr3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The tendency of BF3, BCl3 and BBr3 to behave as Lewis acid decreases in the sequence
a)
BCl3 > BF3 > BBr3 [2010]
b)
BBr3 > BCl2 > BF3
c)
BBr3 > BF3 > BCl3
d)
BF3 > BCl3 > BBr3

|
Yash Saha answered |
As the size of halogen atom increases, the acidic strength of boron halides increases. Thus, BF3 is the weakest Lewis acid. This is because of the pπ - pπ back bonding between the fully-filled unutilised 2p orbitals of F and vacant 2p orbitals of boron which makes BF3 less electron deficient. Such back donation is not possible in case of BCl3 or BBr3 due to the larger energy difference between their orbitals. Thus, these are more electron deficient. Since on moving are more electron deficient. Since on moving down the group the energy difference increases, Thus, the tendency to behave as Lewis acid follows the order
BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
BBr3 > BCl3 > BF3
The straight chain polymer is formed by:[2009]- a)hydrolysis of CH3SiCl3 followed by condensation polymerisation
- b)hydrolysis of (CH3)4 Si by addition polymerisation
- c)hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerisation
- d)hydrolysis of (CH3)3SiCl followed by condensation polymerisation
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The straight chain polymer is formed by:[2009]
a)
hydrolysis of CH3SiCl3 followed by condensation polymerisation
b)
hydrolysis of (CH3)4 Si by addition polymerisation
c)
hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerisation
d)
hydrolysis of (CH3)3SiCl followed by condensation polymerisation

|
Manisha Choudhary answered |
Hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerisation is the correct process for the formation of a straight chain polymer.
Explanation:
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a compound reacts with water to form new compounds. In this case, (CH3)2SiCl2 undergoes hydrolysis to form (CH3)2Si(OH)2, also known as dimethylsilanediol.
Condensation polymerisation is a process in which monomers join together to form a polymer with the elimination of a small molecule such as water. In this case, the dimethylsilanediol monomers undergo condensation polymerisation to form a straight chain polymer.
Here is a detailed explanation of each step:
1. Hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2:
(CH3)2SiCl2 + 2H2O → (CH3)2Si(OH)2 + 2HCl
In this step, (CH3)2SiCl2 reacts with water to form (CH3)2Si(OH)2 and hydrochloric acid (HCl) as a byproduct.
2. Condensation polymerisation:
(CH3)2Si(OH)2 + (CH3)2Si(OH)2 → -[(CH3)2Si-O-Si(CH3)2]- + 2H2O
In this step, the dimethylsilanediol monomers, (CH3)2Si(OH)2, react with each other to form a straight chain polymer, -[(CH3)2Si-O-Si(CH3)2]-, also known as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) or silicone. This reaction involves the elimination of water molecules.
The resulting polymer, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), is a straight chain polymer with repeating units of (-Si-O-)n, where n represents the number of repeating units. PDMS is commonly used in various applications, including lubricants, adhesives, sealants, and coatings, due to its unique properties such as high thermal stability, low surface tension, and excellent electrical insulation.
In conclusion, the correct process for the formation of a straight chain polymer is the hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerisation. This process results in the formation of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) or silicone.
Explanation:
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a compound reacts with water to form new compounds. In this case, (CH3)2SiCl2 undergoes hydrolysis to form (CH3)2Si(OH)2, also known as dimethylsilanediol.
Condensation polymerisation is a process in which monomers join together to form a polymer with the elimination of a small molecule such as water. In this case, the dimethylsilanediol monomers undergo condensation polymerisation to form a straight chain polymer.
Here is a detailed explanation of each step:
1. Hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2:
(CH3)2SiCl2 + 2H2O → (CH3)2Si(OH)2 + 2HCl
In this step, (CH3)2SiCl2 reacts with water to form (CH3)2Si(OH)2 and hydrochloric acid (HCl) as a byproduct.
2. Condensation polymerisation:
(CH3)2Si(OH)2 + (CH3)2Si(OH)2 → -[(CH3)2Si-O-Si(CH3)2]- + 2H2O
In this step, the dimethylsilanediol monomers, (CH3)2Si(OH)2, react with each other to form a straight chain polymer, -[(CH3)2Si-O-Si(CH3)2]-, also known as polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) or silicone. This reaction involves the elimination of water molecules.
The resulting polymer, polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), is a straight chain polymer with repeating units of (-Si-O-)n, where n represents the number of repeating units. PDMS is commonly used in various applications, including lubricants, adhesives, sealants, and coatings, due to its unique properties such as high thermal stability, low surface tension, and excellent electrical insulation.
In conclusion, the correct process for the formation of a straight chain polymer is the hydrolysis of (CH3)2SiCl2 followed by condensation polymerisation. This process results in the formation of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) or silicone.
Which statement is wrong? [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Feldspars are not aluminosilicates
- b)Beryl is an example of cyclic silicate
- c)Mg2SiO4 is orthosilicate
- d)Basic structural unit in silicates is the SiO4 tetrahedron
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statement is wrong? [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Feldspars are not aluminosilicates
b)
Beryl is an example of cyclic silicate
c)
Mg2SiO4 is orthosilicate
d)
Basic structural unit in silicates is the SiO4 tetrahedron

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
Feldspars are aluminosilicates.
Al2O3 can be converted to anhydrous AlCl3 by heating [2006]- a)Al2O3 with NaCl in solid state
- b)a mixture of Al2O3 and carbon in dry Cl2 gas
- c)Al2O3 with Cl2 gas
- d)Al2O3 with HCl gas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Al2O3 can be converted to anhydrous AlCl3 by heating [2006]
a)
Al2O3 with NaCl in solid state
b)
a mixture of Al2O3 and carbon in dry Cl2 gas
c)
Al2O3 with Cl2 gas
d)
Al2O3 with HCl gas

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Al2O3 can be converted to anhydrous AlCl3 by heating a mixture of Al2O3 and carbon in dry Cl2

Which of the following statements about H3BO3 is not correct ? [1994]- a)It is a strong tribasic acid
- b)It is prepared by acidifying an aqueous solution of borax
- c)It has a layer structure in which planar BO3 units are joined by hydrogen bonds
- d)It does not act as proton donor but acts as a Lewis acid by accepting a lone pair of electrons
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about H3BO3 is not correct ? [1994]
a)
It is a strong tribasic acid
b)
It is prepared by acidifying an aqueous solution of borax
c)
It has a layer structure in which planar BO3 units are joined by hydrogen bonds
d)
It does not act as proton donor but acts as a Lewis acid by accepting a lone pair of electrons

|
Vaibhav Basu answered |
H3BO3 is a weak monobasic acid.
In graphite, electrons are [1994]- a)Localised on every third C-atom
- b)Present in anti-bonding orbital
- c)Localised on each C-atom
- d)Spread out between the structure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In graphite, electrons are [1994]
a)
Localised on every third C-atom
b)
Present in anti-bonding orbital
c)
Localised on each C-atom
d)
Spread out between the structure

|
Soumya Ahuja answered |
In graphite, each carbon is sp2 -hybridized and the single occupied unhybridized porbitals of C-atoms overlap side wise to give π -electron cloud which is delocalized and thus the electrons are spread out between the structure.
Chapter doubts & questions for The p-Block Elements (Group 13 & 14) - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The p-Block Elements (Group 13 & 14) - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily