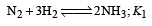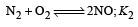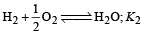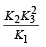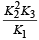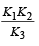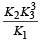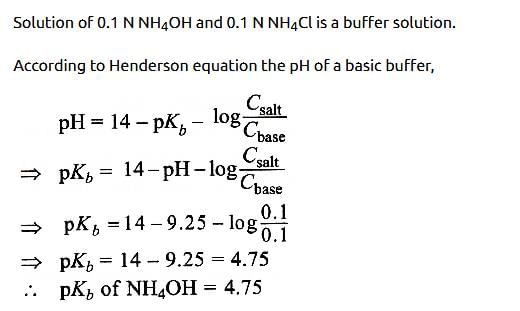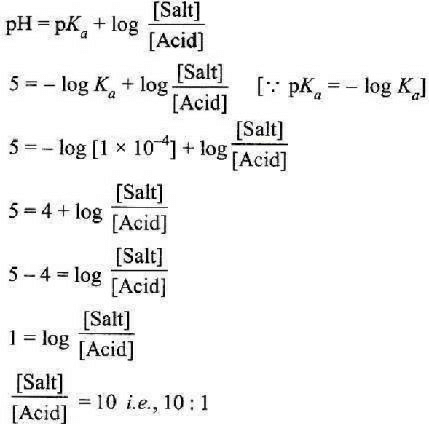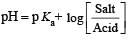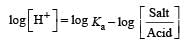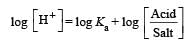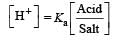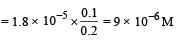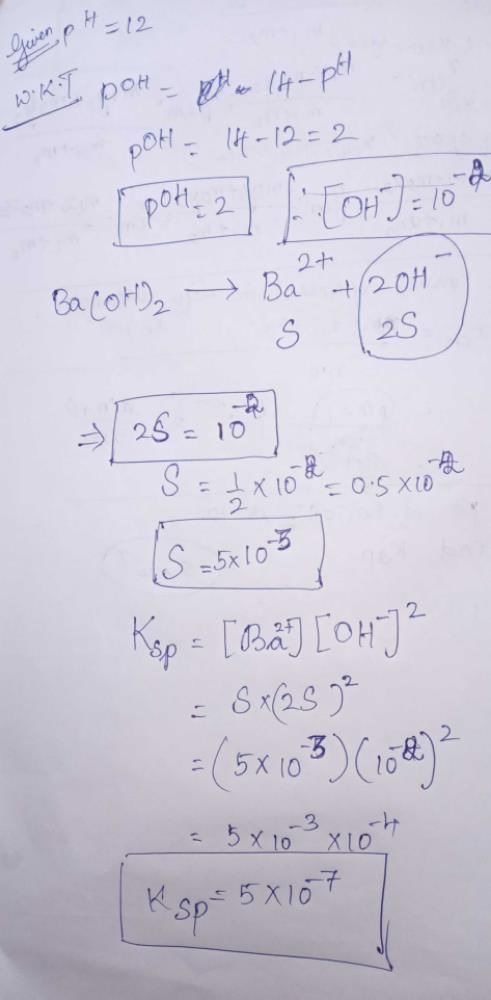All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Equilibrium for NEET Exam
Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis acid? [2010]- a)NH3
- b)H2O
- c)B2H6
- d)CH4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following molecular hydrides acts as a Lewis acid? [2010]
a)
NH3
b)
H2O
c)
B2H6
d)
CH4

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
Boron in B2H6 is electron deficient
In a buffer solution containing equal concentration of B– and HB, the Kb for B– is 10–10. The pH of buffer solution is : [2010]- a)10
- b)7
- c)6
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a buffer solution containing equal concentration of B– and HB, the Kb for B– is 10–10. The pH of buffer solution is : [2010]
a)
10
b)
7
c)
6
d)
4

|
Nilotpal Gupta answered |
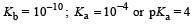
For the buffer solution containing equal concentration of B– and HB
pH = pKa + log 1
pH = pKa = 4
The octahedral complex ion [ CoCl2(NH3)4]+ i.e., tetra amminedichloro cobalt (III) ion exists as cis and trans isomers.
pH = pKa + log 1
pH = pKa = 4
The octahedral complex ion [ CoCl2(NH3)4]+ i.e., tetra amminedichloro cobalt (III) ion exists as cis and trans isomers.
Identify the correct order of solubility in aqueous medium: [NEET 2013]- a)ZnS > Na2S > CuS
- b)Na2S > CuS > ZnS
- c)Na2S > ZnS > CuS
- d)CuS > ZnS > Na2S
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the correct order of solubility in aqueous medium: [NEET 2013]
a)
ZnS > Na2S > CuS
b)
Na2S > CuS > ZnS
c)
Na2S > ZnS > CuS
d)
CuS > ZnS > Na2S

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
Solubility of alkali metal is maximum among the following. Among ZnS (1.7 × 10–5) & CuS (8 × 10–37) ZnS has higher value of Ksp.
The values of Kp1 and Kp2 for the reactions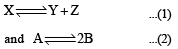 are in the ratio of 9 : 1. If degree of dissociation of X and A be equal, then total pressure at equilibrium (1) and (2) are in the ratio :
are in the ratio of 9 : 1. If degree of dissociation of X and A be equal, then total pressure at equilibrium (1) and (2) are in the ratio :- a)3 : 1
- b)1 : 9
- c)36 : 1
- d)1 : 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The values of Kp1 and Kp2 for the reactions
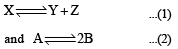
are in the ratio of 9 : 1. If degree of dissociation of X and A be equal, then total pressure at equilibrium (1) and (2) are in the ratio :
a)
3 : 1
b)
1 : 9
c)
36 : 1
d)
1 : 1
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Given reaction are

Let the total pressure for reaction (i) and (ii) be P1 and P2 respectively, then
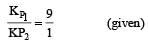
After dissociation,
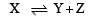
At equilibrium (1–α) α α
[Let 1 mole of X dissociate with α as degree of dissociation ]
Total number of moles = 1– α + α + α = (1+α)
[Let 1 mole of X dissociate with α as degree of dissociation ]
Total number of moles = 1– α + α + α = (1+α)
Thus 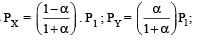
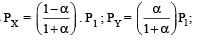
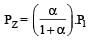
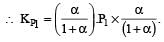
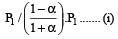
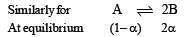
We have,
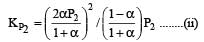
Dividing (i) by (ii), we get
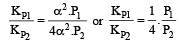
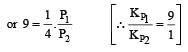
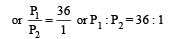
i.e. Option (c) is correct answer.
Accumulation of lactic acid (HC3H5O3), a monobasic acid in tissues leads to pain and a feeling of fatigue. In a 0.10 M aqueous solution, lactic acid is 3.7% dissociated. The value of dissociation constant, Ka, for this acid will be: [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)2.8 × 10–4
- b)1.4 × 10–5
- c)1.4 × 10–4
- d)3.7 × 10–4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Accumulation of lactic acid (HC3H5O3), a monobasic acid in tissues leads to pain and a feeling of fatigue. In a 0.10 M aqueous solution, lactic acid is 3.7% dissociated. The value of dissociation constant, Ka, for this acid will be: [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
2.8 × 10–4
b)
1.4 × 10–5
c)
1.4 × 10–4
d)
3.7 × 10–4

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Degree of dissociation, α = 3.7 = 0.037
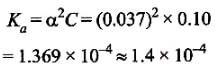
Equimolar solutions of the following substances were prepared separately. Which one of these will record the highest pH value ? [2012]- a)BaCl2
- b)AlCl3
- c)LiCl
- d)BeCl2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Equimolar solutions of the following substances were prepared separately. Which one of these will record the highest pH value ? [2012]
a)
BaCl2
b)
AlCl3
c)
LiCl
d)
BeCl2

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
(AlCl3, LiCl & BeCl2) ) all these solutions are acidic due to cationic hydrolysis, where as BaCl2, is salt of strong base and strong acid, hence its solution will almost neutral i.e., pH ≈ 7.
At 100°C the Kw of water is 55 times its value at 25°C. What will be the pH of neutral solution? (log 55 = 1.74) [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)6.13
- b)7.00
- c)7.87
- d)5.13
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At 100°C the Kw of water is 55 times its value at 25°C. What will be the pH of neutral solution? (log 55 = 1.74) [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
6.13
b)
7.00
c)
7.87
d)
5.13

|
Krish Khanna answered |
Kw at 25°C = 1 × 10–14 At 25ºC
Kw = [H+] [OH–] = 10–14 At 100°C (given) Kw = [H+] [OH–] = 55 × 10–14
∵ for a neutral solution [H+] = [OH–]
∴ [H+]2 = 55 × 10–14
or [H+] = (55 × 10–14)1/2
∵ pH = – log [H+]
On taking log on both side – log [H+] = –log (55 × 10–14)1/2
∵ for a neutral solution [H+] = [OH–]
∴ [H+]2 = 55 × 10–14
or [H+] = (55 × 10–14)1/2
∵ pH = – log [H+]
On taking log on both side – log [H+] = –log (55 × 10–14)1/2
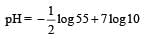
pH = – 0.87 + 7
= 6.13
= 6.13
Buffer solutions have con stant acidity and alkalinity because [2012]- a)these give unionised acid or base on reaction with added acid or alkali.
- b)acids and a lkalies in these solutions are shielded from attack by other ions.
- c)they have large excess of H+ or OH– ions
- d)they have fixed value of pH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Buffer solutions have con stant acidity and alkalinity because [2012]
a)
these give unionised acid or base on reaction with added acid or alkali.
b)
acids and a lkalies in these solutions are shielded from attack by other ions.
c)
they have large excess of H+ or OH– ions
d)
they have fixed value of pH
|
|
Yash Modi answered |
Buffer solutions are those whose pH is almost constant due to the presence of mechanisms to control its fluctuation. This is due to the presence of excess of either excess of H+ or OH- etc. so that there is no effect when some of either of them may enter from outside. Eg. blood in human body is at constant pH of about 7.4. It uses H+ and HCO3- ions to regulate any change in it's pH (like during respiration)
A weak acid, HA, has a Ka of 1.00 × 10–5. If 0.100 mole of this acid dissolved in one litre of water, the percentage of acid dissociated at equilbrium is closest to [2007]- a)1.00%
- b)99.9%
- c)0.100%
- d)99.0%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A weak acid, HA, has a Ka of 1.00 × 10–5. If 0.100 mole of this acid dissolved in one litre of water, the percentage of acid dissociated at equilbrium is closest to [2007]
a)
1.00%
b)
99.9%
c)
0.100%
d)
99.0%

|
Shivani Rane answered |
Given Ka = 1.00×10–5, C= 0.100 mol for a weak electrolyte, degree of dissociation
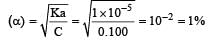
Which one of the following orders of acid strength is correct? [2003]- a)RCOOH > HC ≡ CH > HOH > ROH
- b)RCOOH > ROH > HOH > HC≡CH
- c)RCOOH > HOH > ROH > HC ≡ CH
- d)RCOOH > HOH > HC ≡ CH > ROH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following orders of acid strength is correct? [2003]
a)
RCOOH > HC ≡ CH > HOH > ROH
b)
RCOOH > ROH > HOH > HC≡CH
c)
RCOOH > HOH > ROH > HC ≡ CH
d)
RCOOH > HOH > HC ≡ CH > ROH

|
Aashna Mukherjee answered |
The higher is the tendency to donate proton, stronger is the acid. Thus the correct order is R – COOH > HOH > R – OH > CH ≡ CH depending upon the rate of donation of proton.
The dissociation equilibrium of a gas AB2 can be represented as : [2008]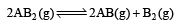 The degree of dissociation is ‘x’ and is small compared to 1. The expression relating the degree of dissociation (x) with equilibrium constant Kp and total pressure P is :
The degree of dissociation is ‘x’ and is small compared to 1. The expression relating the degree of dissociation (x) with equilibrium constant Kp and total pressure P is :- a)(2Kp/P)
- b)(2Kp/P)1/3
- c)(2Kp/P)1/2
- d)(Kp/P)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The dissociation equilibrium of a gas AB2 can be represented as : [2008]
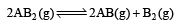
The degree of dissociation is ‘x’ and is small compared to 1. The expression relating the degree of dissociation (x) with equilibrium constant Kp and total pressure P is :
a)
(2Kp/P)
b)
(2Kp/P)1/3
c)
(2Kp/P)1/2
d)
(Kp/P)
|
|
Nishtha Choudhary answered |
For the reaction
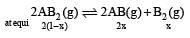
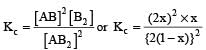
= x3 [(1–x) can be neglected in denominator
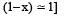
The partial pressure at equilibrium are calculated on the basis of total number of moles at equilibrium.
Total number of moles
Total number of moles
= 2 (1–x) + 2x + x = (2 + x)
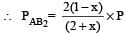 where P is the total pressure.
where P is the total pressure.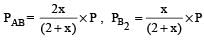
Since x is very small so can be neglected in denominator Thus, we get
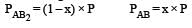
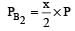
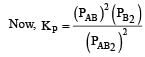
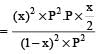
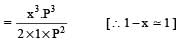
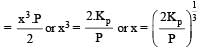
H2S gas when passed through a solution of cations containing HCl precipitates the cations of second group of qualitative analysis but not those belonging to the fourth group. It is be cau se [2005]- a)presence of HCl decr eases the sulphide ion concentration.
- b)solubility product of group II sulph ides is more than that of group IV sulphides.
- c)presence of HCl increases the sulphide ion concentration.
- d)sulphides of group IV cations are unstable in HCl.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
H2S gas when passed through a solution of cations containing HCl precipitates the cations of second group of qualitative analysis but not those belonging to the fourth group. It is be cau se [2005]
a)
presence of HCl decr eases the sulphide ion concentration.
b)
solubility product of group II sulph ides is more than that of group IV sulphides.
c)
presence of HCl increases the sulphide ion concentration.
d)
sulphides of group IV cations are unstable in HCl.

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
IVth group needs higher S2– i on concentration. In presence of HCl, the dissociation of H2S decreases hence produces less amount of sulphide ions due to common ion effect, thus HCl decreases the solubility of H2S which is sufficient to precipitate IInd group radicals.
In qualitative analysis, the metals of Group I can be separated from other ions by precipitating them as chloride salts. A solution initially contains Ag+ and Pb2+ at a concentration of 0.10 M. Aqueous HCl is added to this solution until the Cl– concentration is 0.10 M. What will the concentrations of Ag+ and Pb2+ be at equilibrium?
(Ksp for AgCl = 1.8 × 10–10,
Ksp for PbCl2 = 1.7 × 10–5) [2011M]- a)[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–7 M ; [Pb2+] = 1.7 × 10–6 M
- b)[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–11 M ; [Pb2+] = 8.5 × 10–5 M
- c)[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–9 M ; [Pb2+] = 1.7 × 10–3 M
- d)[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–11 M ; [Pb2+] = 8.5 × 10–4 M
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In qualitative analysis, the metals of Group I can be separated from other ions by precipitating them as chloride salts. A solution initially contains Ag+ and Pb2+ at a concentration of 0.10 M. Aqueous HCl is added to this solution until the Cl– concentration is 0.10 M. What will the concentrations of Ag+ and Pb2+ be at equilibrium?
(Ksp for AgCl = 1.8 × 10–10,
Ksp for PbCl2 = 1.7 × 10–5) [2011M]
(Ksp for AgCl = 1.8 × 10–10,
Ksp for PbCl2 = 1.7 × 10–5) [2011M]
a)
[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–7 M ; [Pb2+] = 1.7 × 10–6 M
b)
[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–11 M ; [Pb2+] = 8.5 × 10–5 M
c)
[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–9 M ; [Pb2+] = 1.7 × 10–3 M
d)
[Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–11 M ; [Pb2+] = 8.5 × 10–4 M

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
Ksp = [Ag+] [Cl–] 1.8 × 10–10 = [Ag+] [0.1] [Ag+] = 1.8 × 10–9 M
Ksp = [Pb+2] [Cl–]2 1.7 × 10–5 = [Pb+2] [0.1]2 [Pb+2] = 1.7 × 10–3 M
Ksp = [Pb+2] [Cl–]2 1.7 × 10–5 = [Pb+2] [0.1]2 [Pb+2] = 1.7 × 10–3 M
Which has the highest value of pH? [2002]- a)CH3COOK
- b)Na2CO3
- c)NH4Cl
- d)NaNO3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which has the highest value of pH? [2002]
a)
CH3COOK
b)
Na2CO3
c)
NH4Cl
d)
NaNO3
|
|
Amrita Gupta answered |
Explanation:
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or alkalinity. It is a scale that ranges from 0 to 14, where pH 7 is considered neutral. A pH less than 7 is acidic, while a pH greater than 7 is alkaline.
To determine which compound has the highest value of pH among the given options, we need to understand the nature of these compounds and their behavior in water.
a) CH3COOK (Potassium acetate):
Potassium acetate is a salt of a weak acid (acetic acid) and a strong base (potassium hydroxide). When it dissolves in water, it undergoes hydrolysis.
The hydrolysis of potassium acetate produces acetate ions (CH3COO-) and potassium ions (K+).
The acetate ion is the conjugate base of the weak acid acetic acid, which means it can accept protons (H+) from water and increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in the solution.
The presence of hydroxide ions increases the pH of the solution, making it slightly alkaline. However, the pH of potassium acetate solution is not as high as the other options.
b) Na2CO3 (Sodium carbonate):
Sodium carbonate is a salt of a weak base (carbonic acid) and a strong base (sodium hydroxide). When it dissolves in water, it dissociates into carbonate ions (CO32-) and sodium ions (Na+).
The carbonate ion is a strong base and can accept protons from water, increasing the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in the solution.
As a result, the presence of hydroxide ions significantly increases the pH of the solution, making it highly alkaline.
Therefore, sodium carbonate has the highest value of pH among the given options.
c) NH4Cl (Ammonium chloride):
Ammonium chloride is a salt of a weak base (ammonia) and a strong acid (hydrochloric acid). When it dissolves in water, it dissociates into ammonium ions (NH4+) and chloride ions (Cl-).
The ammonium ion is a weak acid and can donate protons to water, increasing the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+).
The presence of hydronium ions decreases the pH of the solution, making it slightly acidic.
d) NaNO3 (Sodium nitrate):
Sodium nitrate is a salt of a strong acid (nitric acid) and a strong base (sodium hydroxide). When it dissolves in water, it dissociates into nitrate ions (NO3-) and sodium ions (Na+).
The nitrate ion is a neutral species and does not significantly affect the pH of the solution.
Therefore, sodium nitrate does not have a particularly high or low pH value.
In conclusion, among the given options, sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) has the highest value of pH.
Calculate the pOH of a solution at 25°C that contains 1× 10–10 M of hydronium ions, i.e. H3O+.- a)4.000
- b)9.0000 [2007]
- c)1.000
- d)7.000
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the pOH of a solution at 25°C that contains 1× 10–10 M of hydronium ions, i.e. H3O+.
a)
4.000
b)
9.0000 [2007]
c)
1.000
d)
7.000

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
To calculate the pOH of a solution at 25°C, you need to know the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in the solution.
The pOH is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydroxide ion concentration. The formula to calculate pOH is:
pOH = -log[OH-]
If you do not have the concentration of hydroxide ions, you will need additional information to calculate it.
The pOH is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the hydroxide ion concentration. The formula to calculate pOH is:
pOH = -log[OH-]
If you do not have the concentration of hydroxide ions, you will need additional information to calculate it.
Which one of the following compounds is not a protonic acid? [2003]- a)SO2 (OH)2
- b)B (OH)3
- c)PO (OH)3
- d)SO (OH)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following compounds is not a protonic acid? [2003]
a)
SO2 (OH)2
b)
B (OH)3
c)
PO (OH)3
d)
SO (OH)2

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
B(OH)3 does not provide H+ ions in water instead it accepts OH– ion and hence it is Lewis acid
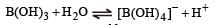
A buffer solution is prepared in which the concentration of NH3 is 0.30M and the concentration of NH4+ is 0.20 M. If the equilibrium constant, Kb for NH3 equals 1.8 × 10–5, what is the pH of this solution ? (log 2.7 = 0.433). [2011]- a)9.08
- b)9.43
- c)11.72
- d)8.73
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A buffer solution is prepared in which the concentration of NH3 is 0.30M and the concentration of NH4+ is 0.20 M. If the equilibrium constant, Kb for NH3 equals 1.8 × 10–5, what is the pH of this solution ? (log 2.7 = 0.433). [2011]
a)
9.08
b)
9.43
c)
11.72
d)
8.73

|
Aniket Chawla answered |
Given [NH3] = 0.3 M, [NH4+] = 0.2 M, Kb = 1.8 × 10–5.
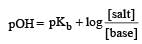
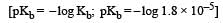
∴ pKb = 4.74
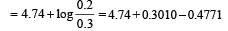
= 4.56
pH = 14 – 4.56 = 9.436
pH = 14 – 4.56 = 9.436
The values of Ksp of CaCO3 and CaC2O4 are 4.7 × 10–9 and 1.3 × 10–9 respectively at 25°C. If the mixture of these two is washed with water, what is the concentration of Ca2+ ions in water? [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)7.746 × 10–5 M
- b)5.831 × 10–5 M
- c)6.856 × 10–5 M
- d)3.606 × 10–5 M
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The values of Ksp of CaCO3 and CaC2O4 are 4.7 × 10–9 and 1.3 × 10–9 respectively at 25°C. If the mixture of these two is washed with water, what is the concentration of Ca2+ ions in water? [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
7.746 × 10–5 M
b)
5.831 × 10–5 M
c)
6.856 × 10–5 M
d)
3.606 × 10–5 M

|
Muskaan Basak answered |
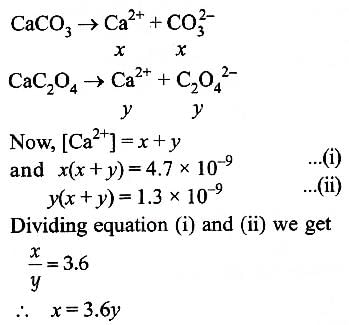
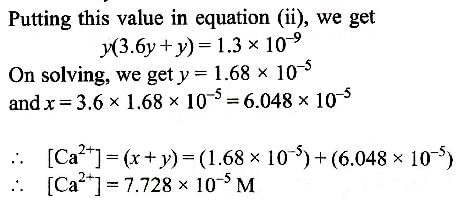
The ionization constant of ammonium hydroxide is 1.77 × 10–5 at 298 K. Hydrolysis constant of ammonium chloride is: [2009]- a)6.50 × 10– 12
- b)5.65 × 10–13
- c)5.65 × 10–12
- d)5.65 × 10–10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The ionization constant of ammonium hydroxide is 1.77 × 10–5 at 298 K. Hydrolysis constant of ammonium chloride is: [2009]
a)
6.50 × 10– 12
b)
5.65 × 10–13
c)
5.65 × 10–12
d)
5.65 × 10–10

|
Nayanika Reddy answered |
Ammonium chloride is a salt of weak base and strong acid. In this case hydrolysis constant Kh can be calculated as
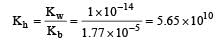
Equal volumes of three acid solutions of pH 3, 4 and 5 are mixed in a vessel. What will be the H+ ion concentration in the mixture ? [2008]- a)1.11 × 10–4 M
- b)3.7 × 10–4 M
- c)3.7 × 10– 3 M
- d)1.11× 10–3 M
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Equal volumes of three acid solutions of pH 3, 4 and 5 are mixed in a vessel. What will be the H+ ion concentration in the mixture ? [2008]
a)
1.11 × 10–4 M
b)
3.7 × 10–4 M
c)
3.7 × 10– 3 M
d)
1.11× 10–3 M

|
Prisha Singh answered |
[H3O]+ for a solution having pH = 3 is given by [H3O]+ = 1×10–3 moles/litre
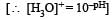
Similarly for solution having pH = 4, [H3O]+ = 1 × 10–4 moles/ litre and for pH=5 [H3O+] = 1×10–5 moles/ litre Let the volume of each solution in mixture be IL, then total volume of mixture solution L = (1 + 1 + 1) L =3L
Total [H3O]+ ion present in mixture solution = (10–3 + 10–4 + 10–5) moles Then [H3O]+ ion concentration of mixture solution
Total [H3O]+ ion present in mixture solution = (10–3 + 10–4 + 10–5) moles Then [H3O]+ ion concentration of mixture solution
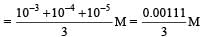
= 0.00037 M = 3.7 ×10–4 M.
For the reaction [2006]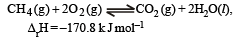 Which of the following statements is not true ?
Which of the following statements is not true ?- a)The equilibrium constant for the reaction is given by
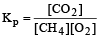
- b)Addition of CH4(g) or O2(g) at equilibrium will cause a shift to the right
- c)The reaction is exothermic
- d)At equilibrium, the concentrations of CO2(g) and H2O(l) are not equal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction [2006]
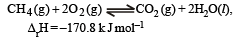
Which of the following statements is not true ?
a)
The equilibrium constant for the reaction is given by 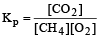
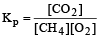
b)
Addition of CH4(g) or O2(g) at equilibrium will cause a shift to the right
c)
The reaction is exothermic
d)
At equilibrium, the concentrations of CO2(g) and H2O(l) are not equal

|
Dipika Das answered |
First option is incorrect as the value of KP given is wrong. It should have been
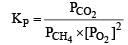
If the concentration of OH– ions in the reaction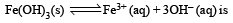 decreased by
decreased by 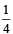 times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]
times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]- a)8 times
- b)16 times
- c)64 times
- d)4 times
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the concentration of OH– ions in the reaction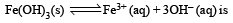 decreased by
decreased by 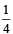 times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]
times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]
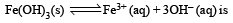 decreased by
decreased by 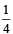 times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]
times, then equilibriumconcentration of Fe3+ will increase by : [2008]a)
8 times
b)
16 times
c)
64 times
d)
4 times

|
Dipika Das answered |
For this reaction Keq. is given by
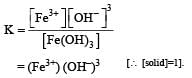
If (OH–) is decreased by 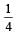 times then forreaction equilibrium constant to remain constant, we have to increase the concentration of [Fe3+] by a factor of 43 i.e 4× 4 × = 64. Thus option (c) is correct answer.
times then forreaction equilibrium constant to remain constant, we have to increase the concentration of [Fe3+] by a factor of 43 i.e 4× 4 × = 64. Thus option (c) is correct answer.
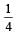 times then forreaction equilibrium constant to remain constant, we have to increase the concentration of [Fe3+] by a factor of 43 i.e 4× 4 × = 64. Thus option (c) is correct answer.
times then forreaction equilibrium constant to remain constant, we have to increase the concentration of [Fe3+] by a factor of 43 i.e 4× 4 × = 64. Thus option (c) is correct answer.Equimolar solutions of the following were prepared in water separately. Which one of the solutions will record the highest pH ? [2008]- a)SrCl2
- b)BaCl2
- c)MgCl2
- d)CaCl2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Equimolar solutions of the following were prepared in water separately. Which one of the solutions will record the highest pH ? [2008]
a)
SrCl2
b)
BaCl2
c)
MgCl2
d)
CaCl2

|
Pooja Saha answered |
The highest pH will be recorded by the most basic solution. The basic nature of hydroxides of alkaline earth metals increase as we move from Mg to Ba and thus the solution of BaCl2 in water will be most basic and so it will have highest pH.
Which of the following molecules acts as a Lewis acid ?[2009]- a)(CH3)2 O
- b)(CH3)3 P
- c)(CH3)3 N
- d)(CH3)3 B
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following molecules acts as a Lewis acid ?[2009]
a)
(CH3)2 O
b)
(CH3)3 P
c)
(CH3)3 N
d)
(CH3)3 B

|
Snehal Shah answered |
(CH3)3 B - is an electron deficient, th us behave as a lewis acid.
The reaction quotient (Q) for the reaction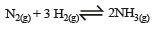 is given by
is given by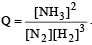 The reaction will proceed from right to left if [2003]where Kc is the equilibrium constant
The reaction will proceed from right to left if [2003]where Kc is the equilibrium constant- a)Q = 0
- b)Q = Kc
- c)Q < Kc
- d)Q > Kc
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction quotient (Q) for the reaction
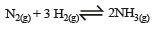
is given by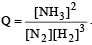
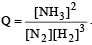
The reaction will proceed from right to left if [2003]
where Kc is the equilibrium constant
a)
Q = 0
b)
Q = Kc
c)
Q < Kc
d)
Q > Kc

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
For reaction to proceed from right to left
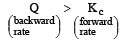 i.e the reaction will be fast in backward direction i.e rb > rf.
i.e the reaction will be fast in backward direction i.e rb > rf.Given that the equilibrium constant for the reaction 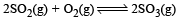 has a value of 278 at a particular temperature. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature ?
has a value of 278 at a particular temperature. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature ?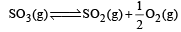 [2012 M]
[2012 M]- a)1.8 × 10–3
- b)3.6 × 10–3
- c)6.0 × 10–2
- d)1.3 × 10–5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given that the equilibrium constant for the reaction 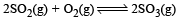 has a value of 278 at a particular temperature. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature ?
has a value of 278 at a particular temperature. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature ?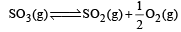 [2012 M]
[2012 M]
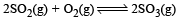 has a value of 278 at a particular temperature. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature ?
has a value of 278 at a particular temperature. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature ?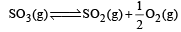 [2012 M]
[2012 M]a)
1.8 × 10–3
b)
3.6 × 10–3
c)
6.0 × 10–2
d)
1.3 × 10–5

|
Jatin Chakraborty answered |
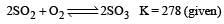
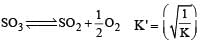
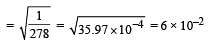
Which of the following pairs constitutes a buffer?- a)NaOH and NaCl [2006]
- b)HNO3 and NH4NO3
- c)HCl and KCl
- d)HNO2 and NaNO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs constitutes a buffer?
a)
NaOH and NaCl [2006]
b)
HNO3 and NH4NO3
c)
HCl and KCl
d)
HNO2 and NaNO2

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
HNO2 is a weak acid and NaNO2 is salt of that weak acid and strong base (NaOH).
What is the correct relation ship between the pHs of isomolar solutions of sodium oxide (pH1), sodium sulphide (pH2), sodium selenide (pH3) and sodium telluride (pH4)? [2 00 5]- a)pH1 > pH2 > pH3 > pH4
- b)pH1 > pH2 ≈ pH3 > pH4
- c)pH1 < pH2 < pH3 < pH4
- d)pH1 < pH2 < pH3 ≈ pH4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the correct relation ship between the pHs of isomolar solutions of sodium oxide (pH1), sodium sulphide (pH2), sodium selenide (pH3) and sodium telluride (pH4)? [2 00 5]
a)
pH1 > pH2 > pH3 > pH4
b)
pH1 > pH2 ≈ pH3 > pH4
c)
pH1 < pH2 < pH3 < pH4
d)
pH1 < pH2 < pH3 ≈ pH4

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
The solution formed from isomolar solutions of sodium oxide, sodium sulphide, sodium selenide H2O, H2S, H2Se & H2Te respectively.
As the acidic strengh increases from H2O to H2Te thus pH decreases and hence the correct of pHs is pH1 > pH2 > pH3 > pH4.
As the acidic strengh increases from H2O to H2Te thus pH decreases and hence the correct of pHs is pH1 > pH2 > pH3 > pH4.
Given the reaction between 2 gases represented by A2 and B2 to give the compound AB(g).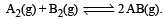 At equilibrium, the concentration
At equilibrium, the concentration
of A2 = 3.0 × 10–3 M
of B2= 4.2 × 10–3 M
of AB = 2.8 × 10–3 M
lf the reaction takes place in a sealed vessel at 527°C, then the value of KC will be : [2012 M]- a)2.0
- b)1.9
- c)0.62
- d)4.5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given the reaction between 2 gases represented by A2 and B2 to give the compound AB(g).
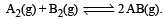
At equilibrium, the concentration
of A2 = 3.0 × 10–3 M
of B2= 4.2 × 10–3 M
of AB = 2.8 × 10–3 M
lf the reaction takes place in a sealed vessel at 527°C, then the value of KC will be : [2012 M]
of A2 = 3.0 × 10–3 M
of B2= 4.2 × 10–3 M
of AB = 2.8 × 10–3 M
lf the reaction takes place in a sealed vessel at 527°C, then the value of KC will be : [2012 M]
a)
2.0
b)
1.9
c)
0.62
d)
4.5

|
Ayush Sengupta answered |

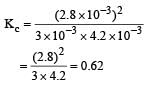
The dissociation constants for acetic acid and HCN at 25°C are 1.5 × 10–5 and 4.5 × 10–10 respectively. The equilibrium constant for the equilibrium [2009] 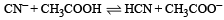 would be:
would be:- a)3.0 × 10– 5
- b)3.0 × 10– 4
- c)3.0 × 104
- d)3.0 × 105
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The dissociation constants for acetic acid and HCN at 25°C are 1.5 × 10–5 and 4.5 × 10–10 respectively. The equilibrium constant for the equilibrium [2009] 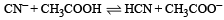 would be:
would be:
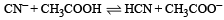 would be:
would be:a)
3.0 × 10– 5
b)
3.0 × 10– 4
c)
3.0 × 104
d)
3.0 × 105
|
|
Sayan Sengupto answered |
Option 3 is right ans
The rapid change of pH near the stoichiometric point of an acid-base titration is the basis of indicator detection. pH of the solution is related to ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate acid (HIn) and base (In–) forms of the indicator by the expression [2004]- a)
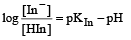
- b)
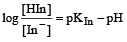
- c)
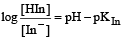
- d)
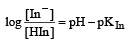
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The rapid change of pH near the stoichiometric point of an acid-base titration is the basis of indicator detection. pH of the solution is related to ratio of the concentrations of the conjugate acid (HIn) and base (In–) forms of the indicator by the expression [2004]
a)
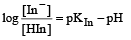
b)
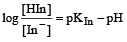
c)
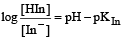
d)
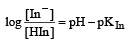
|
|
Raza Great answered |
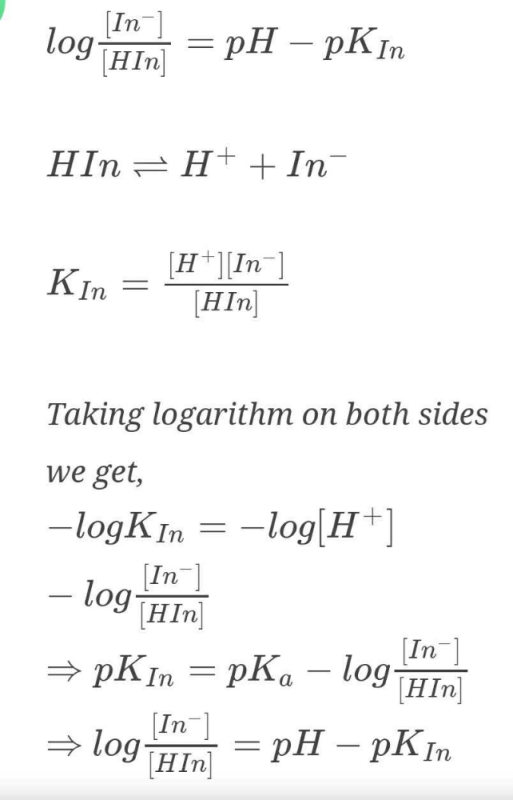
The solubility product of AgI at 25ºC is 1.0 × 10–16 mol2 L–2. The solubiliy of AgI in 10–4 N solution of KI at 25ºC is approximately(in mol L–1) [2003]- a)1.0 × 10–8
- b)1.0 × 10–16
- c)1.0 × 10–12
- d)1.0 × 10–10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The solubility product of AgI at 25ºC is 1.0 × 10–16 mol2 L–2. The solubiliy of AgI in 10–4 N solution of KI at 25ºC is approximately(in mol L–1) [2003]
a)
1.0 × 10–8
b)
1.0 × 10–16
c)
1.0 × 10–12
d)
1.0 × 10–10

|
Rhea Sarkar answered |
Ksp for AgI = 1 × 10–16 In solution of KI, I– would be due to the both AgI and KI, 10–4 solution KI would provide = 10–4 I–
AgI would provide, say = x I– (x is solubility of AgI)
AgI would provide, say = x I– (x is solubility of AgI)
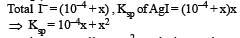
as x is very small ∴ x2 can be ignored
∴ 10–4 x = 10–16
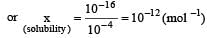
Which of these is least likely to act as Lewis base? [NEET 2013]- a)F–
- b)BF3
- c)PF3
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is least likely to act as Lewis base? [NEET 2013]
a)
F–
b)
BF3
c)
PF3
d)
CO

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
BF3 is Lewis acid(e– pair acceptor)
The reaction 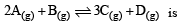 begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression [2010]
begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression [2010]- a)[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(0.75)2 (0.25)]
- b)[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(1.00)2 (1.00)]
- c)[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(0.50)2 (0.75)]
- d)[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(0.50)2 (0.25)]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction 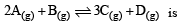 begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression [2010]
begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression [2010]
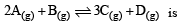 begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression [2010]
begun with the concentrations of A and B both at an initial value of 1.00 M. When equilibrium is reached, the concentration of D is measured and found to be 0.25 M. The value for the equilibrium constant for this reaction is given by the expression [2010]a)
[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(0.75)2 (0.25)]
b)
[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(1.00)2 (1.00)]
c)
[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(0.50)2 (0.75)]
d)
[(0.75)3 (0.25)] ÷ [(0.50)2 (0.25)]

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
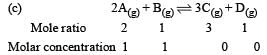

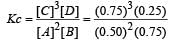
If pH of a saturated solution of Ba (OH)2 is 12, the value of its K(sp) is : [2010]- a)4.00 × 10-6M3
- b)4.00 × 10–7 M3
- c)5.00 × 10-6M3
- d)5.00 × 10-7M3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If pH of a saturated solution of Ba (OH)2 is 12, the value of its K(sp) is : [2010]
a)
4.00 × 10-6M3
b)
4.00 × 10–7 M3
c)
5.00 × 10-6M3
d)
5.00 × 10-7M3
|
|
Nikhil Dasgupta answered |
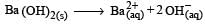
pH = 12 or pOH = 2
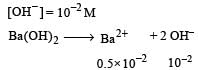
[∴ Concentration of Ba 2+ is half of OH-]
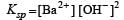
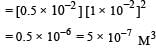
In which of the following equilibrium Kc and Kp are not equal? [2010]- a)
- b)
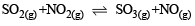
- c)
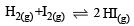
- d)
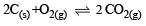
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following equilibrium Kc and Kp are not equal? [2010]
a)
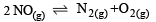
b)
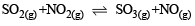
c)
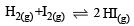
d)
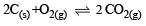

|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
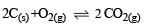
Δn = 2 – 1 = + 1
∴ Kc and Kp are not equal.
At 25°C, the dissociation con stant of a base, BOH, is 1. 0 x 10-12. The concentration of hydroxyl ions in 0.01 M aqueous solution of the base would be [2005]- a)1.0 x 10-5 mol L-1
- b)1.0 x 10-6 mol L-1
- c)2.0 x 10-6 mol L-1
- d)1.0 x 10-7 mol L-1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At 25°C, the dissociation con stant of a base, BOH, is 1. 0 x 10-12. The concentration of hydroxyl ions in 0.01 M aqueous solution of the base would be [2005]
a)
1.0 x 10-5 mol L-1
b)
1.0 x 10-6 mol L-1
c)
2.0 x 10-6 mol L-1
d)
1.0 x 10-7 mol L-1

|
Krish Saha answered |

The hydrogen ion concentration of a 10–8 M HCl aqueous solution at 298 K (Kw = 10–14) is [2006]- a)11 × 10–8 M
- b)9.525 × 10–8 M
- c)1.0 × 10–8 M
- d)1.0 × 10–6 M
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The hydrogen ion concentration of a 10–8 M HCl aqueous solution at 298 K (Kw = 10–14) is [2006]
a)
11 × 10–8 M
b)
9.525 × 10–8 M
c)
1.0 × 10–8 M
d)
1.0 × 10–6 M

|
Pooja Saha answered |
For a solution of 10–8 M HCl [H+] = 10–8 [H+] of water = 10–7
Total [H+] = 10–7 + 10–8 = 10 × 10–8 + 10–8
10–8 (10 + 1) = 11 × 10–8
Total [H+] = 10–7 + 10–8 = 10 × 10–8 + 10–8
10–8 (10 + 1) = 11 × 10–8
The value of equilibrium constant of the reaction
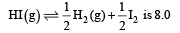 [2008]
[2008]
The equilibrium constant of the reaction 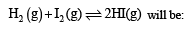
- a)
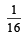
- b)
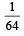
- c)16
- d)
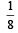
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The value of equilibrium constant of the reaction
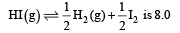 [2008]
[2008]
The equilibrium constant of the reaction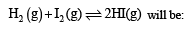
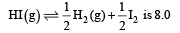 [2008]
[2008]The equilibrium constant of the reaction
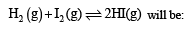
a)
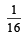
b)
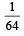
c)
16
d)
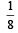
|
|
Niti Patel answered |
Given : Equilibrium constant (K1) for the reaction
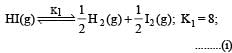
To find equilibrium constant for the following reaction
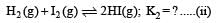
For this multiply (i) by 2, we get
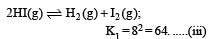
[Note: When the equation for an equilibrium is multiplied by a factor, the equilibrium constant must be raised to the power equal to the factor]
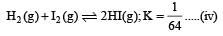
Now reverse equation (iii), we get
[Note: For a reversible reaction, the equilibrium constant of the backward reaction is inverse of the equilibrium constant for the forward reaction.] Equation (iv) is the same as the required equation (ii), thus K2 for equation (ii) is 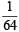 i.e.
i.e.
option (b) is correct.
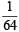 i.e.
i.e.option (b) is correct.
Chapter doubts & questions for Equilibrium - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Equilibrium - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily