All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Biomolecules for NEET Exam
About 98 percent of the mass of every living organism is composed of just six element including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and
[2007]
- a)sulphur and magnesium
- b)magnesium and sodium
- c)phosphorus and calcium
- d)sulphur and phosphorus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
About 98 percent of the mass of every living organism is composed of just six element including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and
[2007]
a)
sulphur and magnesium
b)
magnesium and sodium
c)
phosphorus and calcium
d)
sulphur and phosphorus

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
It is calcium and phosphorus.
Which of the following are not secondary metabolites in plants? [2021]- a)Vinblastin, curcumin
- b)Rubber, gums
- c)Morphine, codeine
- d)Amino acids, glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are not secondary metabolites in plants? [2021]
a)
Vinblastin, curcumin
b)
Rubber, gums
c)
Morphine, codeine
d)
Amino acids, glucose
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
- Some Secondary Metabolites
- However, when one analyses plant, fungal and microbial cells, one would see thousands of compounds other than these called primary metabolites, e.g. alkaloids, flavonoids, rubber, essential oils, antibiotics, coloured pigments, scents, gums, spices.
- These are called secondary metabolites.
An organic substance bound to an enzyme and essential for its activity is called[2006]- a)Holoenzyme
- b)Apoenzyme
- c)Isoenzyme
- d)Coenzyme
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic substance bound to an enzyme and essential for its activity is called
[2006]
a)
Holoenzyme
b)
Apoenzyme
c)
Isoenzyme
d)
Coenzyme

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Coenzyme is an organic substance that enhances the action of an enzyme by binding with the protein molecule. Holoenzyme is a biochemically active compound formed by the combination of an enzyme with a coenzyme. Apoenzyme is the protein of an enzyme to which the coenzyme attaches to form an active enzyme Isoenzyme is one of the several forms of an enzyme that catalyse the same reaction but differ from each other in such properties as substrate affinity and maximum rates of enzyme substrate reaction.
Select the option which is not correct with respect to enzyme action: [2014]- a)Substrate binds with enzyme at its active site.
- b)Addition of lot of succinate does not reverse the inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate.
- c)A non-competitive inhibitor binds the enzyme at a site distinct from that which binds the substrate.
- d)Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the option which is not correct with respect to enzyme action: [2014]
a)
Substrate binds with enzyme at its active site.
b)
Addition of lot of succinate does not reverse the inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate.
c)
A non-competitive inhibitor binds the enzyme at a site distinct from that which binds the substrate.
d)
Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase.

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
(b) Inhibitions of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate is an example of competitive inhibition. Thus it is reversible reaction. On increasing the substrate (succinate) concentration the effect of inhibitor is removed and Vmax remain same.
Which of the following biomolecules does have phosphodiester bond ? [2015 RS]- a)Monosaccharides in a polysaccharide
- b)Amino acids in a polypeptide
- c)Nucleic acids in a nucleotide
- d)Fatty acids in a diglyceride
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following biomolecules does have phosphodiester bond ? [2015 RS]
a)
Monosaccharides in a polysaccharide
b)
Amino acids in a polypeptide
c)
Nucleic acids in a nucleotide
d)
Fatty acids in a diglyceride

|
Prisha Singh answered |
(c) Nucleic acids have phophodiester bond in a nucleotide.
Carrier ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like:[2010]- a)amino acids and glucose
- b)glucose and fatty acids
- c)fatty acids and glycerol
- d)fructose and some amino acids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Carrier ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like:
[2010]
a)
amino acids and glucose
b)
glucose and fatty acids
c)
fatty acids and glycerol
d)
fructose and some amino acids

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Massive ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like amino acid and glucose through Co transport.
A typical fat molecule is made up of [2016]- a)three glycerol molecules and one fatty acid molecule
- b)one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
- c)one glycerol and one fatty acid molecule
- d)three glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical fat molecule is made up of [2016]
a)
three glycerol molecules and one fatty acid molecule
b)
one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
c)
one glycerol and one fatty acid molecule
d)
three glycerol and three fatty acid molecules

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
(b) Fat molecules are made of atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms binds to the carbon, as pictorially depicted. A typical fat molecule has one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules.
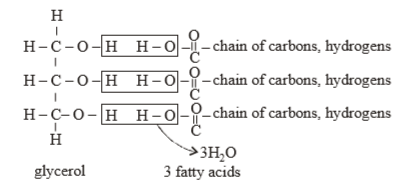

Which one of the following statements is wrong? [2016]- a)Sucrose is a disaccharide.
- b)Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
- c)Uracil is a pyrimidine.
- d)Glycine is a sulphur containing amino acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is wrong? [2016]
a)
Sucrose is a disaccharide.
b)
Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
c)
Uracil is a pyrimidine.
d)
Glycine is a sulphur containing amino acid.

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
(d) Glycine (abbreviated as Gly or G) is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins, and indeed is the smallest possible (having a hydrogen substituent as its side-chain). The formula is NH2CH2COOH. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG of the genetic code.
The enzyme that is not present in succus entericus is : [2015 RS]- a)nucleases
- b)nucleosidase
- c)lipase
- d)maltase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme that is not present in succus entericus is : [2015 RS]
a)
nucleases
b)
nucleosidase
c)
lipase
d)
maltase

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
(a) Succus entericus lacks enzyme nucleases
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both[2000]- a)are polymers of nucleotides
- b)are capable of replicating
- c)have similar sugars
- d)have similar pyrimidine bases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both
[2000]
a)
are polymers of nucleotides
b)
are capable of replicating
c)
have similar sugars
d)
have similar pyrimidine bases

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
DNA and RNA are both polymers of nucleotides . DNA has deoxyribose sugar while RNA has ribose sugar. DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil in place of thymine.
The essential chemical components of many coenzymes are :[NEET 2013]- a)Nucleic acids
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Vitamins
- d)Proteins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The essential chemical components of many coenzymes are :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Nucleic acids
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Vitamins
d)
Proteins

|
Yash Saha answered |
The essential chemical components of many enzymes are vitamins, e.g., coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and NADP contain vitamin niacin.
The enormous diversity of protein molecules is due mainly to the diversity of
[1998]
- a)amino groups on the amino acids
- b)R groups on the amino acids
- c)amino acid sequences within the protein molecule.
- d)peptide bonds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enormous diversity of protein molecules is due mainly to the diversity of
[1998]
a)
amino groups on the amino acids
b)
R groups on the amino acids
c)
amino acid sequences within the protein molecule.
d)
peptide bonds
|
|
Ankita Khaire answered |
Proteins are building blocks of the body. The proteins are made up of amino acids. The amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a protein. The amino acids consist of amine group made up of nitrogen and hydrogen and the carboxyl group at the end and a side chain of R group which is specific to a particular amino acid. This specific group brings a variability to the proteins. If R group is H it is glycine while if it is CH
2
it is alanine. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein. So, the correct answer is option D.
Which one of the following statements in incorrect? [2015 RS]- a)In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor molecule is not chemically changed by the enzyme.
- b)The competitive inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzymesubstrate complex.
- c)The presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate.
- d)A competitive inhibitor reacts reversibly with the enzyme to form an enzymeinhibitor complex.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements in incorrect? [2015 RS]
a)
In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor molecule is not chemically changed by the enzyme.
b)
The competitive inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzymesubstrate complex.
c)
The presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate.
d)
A competitive inhibitor reacts reversibly with the enzyme to form an enzymeinhibitor complex.
|
|
Anirban Nambiar answered |
Competitive Inhibition and Km
Competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where an inhibitor molecule, similar in structure to the substrate, competes with the substrate for binding to the active site of the enzyme. This type of inhibition does not chemically change the inhibitor or the enzyme.
The rate of breakdown of the enzyme substrate complex is affected by competitive inhibition because the inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding to the active site. However, the inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzyme itself.
In competitive inhibition, the presence of the inhibitor increases the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, meaning that the concentration of substrate required to reach half of the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the reaction is decreased. This is reflected in a decrease in the Michaelis constant (Km) of the enzyme for the substrate.
Therefore, the incorrect statement is option C, which states that the presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate. In fact, the presence of the competitive inhibitor increases the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, leading to a decrease in Km.
Competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where an inhibitor molecule, similar in structure to the substrate, competes with the substrate for binding to the active site of the enzyme. This type of inhibition does not chemically change the inhibitor or the enzyme.
The rate of breakdown of the enzyme substrate complex is affected by competitive inhibition because the inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding to the active site. However, the inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzyme itself.
In competitive inhibition, the presence of the inhibitor increases the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, meaning that the concentration of substrate required to reach half of the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the reaction is decreased. This is reflected in a decrease in the Michaelis constant (Km) of the enzyme for the substrate.
Therefore, the incorrect statement is option C, which states that the presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate. In fact, the presence of the competitive inhibitor increases the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, leading to a decrease in Km.
Macro molecule chitin is :
[NEET 2013]
- a)Phosphorus containing polysaccharide
- b)Sulphur containing polysaccharide
- c)Simple polysaccharide
- d)Nitrogen containing polysaccharide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Macro molecule chitin is :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Phosphorus containing polysaccharide
b)
Sulphur containing polysaccharide
c)
Simple polysaccharide
d)
Nitrogen containing polysaccharide

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Explanation:
Chitin is the most abundant amino polysaccharide polymer found in nature, and it is the building material that gives crustaceans, insects, and fungi their exoskeletons and cell walls their strength.
Chitin is the most abundant amino polysaccharide polymer found in nature, and it is the building material that gives crustaceans, insects, and fungi their exoskeletons and cell walls their strength.
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing modified polysaccharide made up of units of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (more precisely, 2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-D-glucose).
Final answer: Macromolecule chitin is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
Final answer: Macromolecule chitin is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
A polysaccharide, which is synthesized and stored in liver cells, is[1995]- a)lactose
- b)galactose
- c)arabinose
- d)glycogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A polysaccharide, which is synthesized and stored in liver cells, is
[1995]
a)
lactose
b)
galactose
c)
arabinose
d)
glycogen

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Glycogen is a polysaccharide, which is synthesized and stored in the liver. It is released into the blood by breakdown of simple glucose, and energy is released.
Which of the following glucose transporters is insulin-dependent? [2019]- a)GLUT IV
- b)GLUT I
- c)GLUT II
- d)GLUT III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following glucose transporters is insulin-dependent? [2019]
a)
GLUT IV
b)
GLUT I
c)
GLUT II
d)
GLUT III
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
GLUT stands for glucose transport protein channel. They are of different types. Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT IV) is a protein encoded in humans by the SLC2A4 gene. It is insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscles.
The two functional groups characteristic of sugars are [2018]- a)Hydroxyl and methyl
- b)Carbonyl and methyl
- c)Carbonyl and phosphate
- d)Carbonyl and hydroxyl
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The two functional groups characteristic of sugars are [2018]
a)
Hydroxyl and methyl
b)
Carbonyl and methyl
c)
Carbonyl and phosphate
d)
Carbonyl and hydroxyl
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Carbohydrates (commonly called sugars) are chemically defined as polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketones. All sugar molecules have one carbonyl group (-CO-) in addition to hydroxyl group (OH) on other carbon atoms.
The introduction of t-DNA into plants involves: [2015 RS]- a)Altering the pH of the soil, then heat shocking the plants
- b)Exposing the plants to cold for a brief period
- c)Allowing the plant roots to stand in water
- d)Infection of the plant by Agrobacterium tumefaciens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The introduction of t-DNA into plants involves: [2015 RS]
a)
Altering the pH of the soil, then heat shocking the plants
b)
Exposing the plants to cold for a brief period
c)
Allowing the plant roots to stand in water
d)
Infection of the plant by Agrobacterium tumefaciens

|
Palak Khanna answered |
(d) Agrobacterium tumefaciens introduces tDNA into the plant.
The two polypeptides of human insulin are linked together by [2016]- a)hydrogen bonds
- b)phosphodiester bond
- c)covalent bond
- d)disulphide bridges
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The two polypeptides of human insulin are linked together by [2016]
a)
hydrogen bonds
b)
phosphodiester bond
c)
covalent bond
d)
disulphide bridges

|
Diya Datta answered |
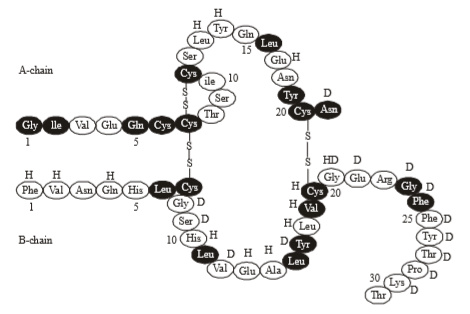
(d) Insulin is a hormone consisting of 2 polypeptide chains. Each chain is composed of a specific sequence of amino acid residues connected by peptide bonds. In humans, chain A has 21 amino acids, and chain B has 30. Post translational modifications result in the connection of these two chains by disulfide bridges. Cysteine residues on A7 and B7, as well as A20 to B19 are covalently connected by disulfide bridges
The figure shows a hypothetical tetrapeptide portion of a protein with parts labelled A-D. Which one of the following option is correct?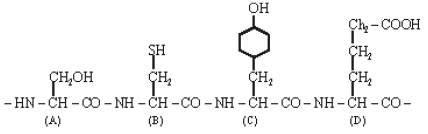 [NEET Kar. 2013]
[NEET Kar. 2013]- a)A is the sulphur containing amino acid -methionine
- b)D is the acidic amino acid - glutamic acid'
- c)C is an aromatic amino acid -tryptophan
- d)A is the C - terminal amino acid and D is N terminal amino acid
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure shows a hypothetical tetrapeptide portion of a protein with parts labelled A-D. Which one of the following option is correct?

[NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
A is the sulphur containing amino acid -methionine
b)
D is the acidic amino acid - glutamic acid'
c)
C is an aromatic amino acid -tryptophan
d)
A is the C - terminal amino acid and D is N terminal amino acid
|
|
Shreya Saini answered |
Which one of the following biomolecules is correctly characterized?[2012M]- a)Lecithin - A phosphorylated glyceride found in cell membrane.
- b)Palmitic acid - An unsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms.
- c)Adenylic acid - Adenosine with a glucose phosphate molecule.
- d)Alanine amino acid - Contains an amino group and an acidic group anywhere in the molecule.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following biomolecules is correctly characterized?
[2012M]
a)
Lecithin - A phosphorylated glyceride found in cell membrane.
b)
Palmitic acid - An unsaturated fatty acid with 18 carbon atoms.
c)
Adenylic acid - Adenosine with a glucose phosphate molecule.
d)
Alanine amino acid - Contains an amino group and an acidic group anywhere in the molecule.
|
|
Abhijeet Iyer answered |
Understanding Lecithin
Lecithin is a vital biomolecule, particularly in cell membranes. It is a type of phospholipid that plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of cellular membranes.
Characteristics of Lecithin
- Phosphorylated Glyceride: Lecithin is indeed a phosphorylated glyceride, which means it contains a glycerol backbone, fatty acids, and a phosphate group.
- Role in Cell Membranes: Its amphipathic nature (having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts) allows it to form bilayers that are essential for cell membrane integrity.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
- Palmitic Acid: This is a saturated fatty acid with 16 carbon atoms, not 18. It is not classified as unsaturated.
- Adenylic Acid: This compound is known as AMP (adenosine monophosphate). It consists of an adenosine molecule and one phosphate group, not a glucose phosphate molecule.
- Alanine Amino Acid: While alanine does contain an amino group (NH2) and a carboxylic acid group (COOH), the statement is misleading because these groups are specific to the alpha carbon of the amino acid, not "anywhere in the molecule."
Conclusion
In summary, option A is correct because it accurately describes lecithin as a phosphorylated glyceride found in cell membranes, highlighting its essential role in cellular structure. The other options misrepresent the chemical nature or structure of the biomolecules.
Lecithin is a vital biomolecule, particularly in cell membranes. It is a type of phospholipid that plays a crucial role in maintaining the structure and function of cellular membranes.
Characteristics of Lecithin
- Phosphorylated Glyceride: Lecithin is indeed a phosphorylated glyceride, which means it contains a glycerol backbone, fatty acids, and a phosphate group.
- Role in Cell Membranes: Its amphipathic nature (having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts) allows it to form bilayers that are essential for cell membrane integrity.
Why Other Options are Incorrect
- Palmitic Acid: This is a saturated fatty acid with 16 carbon atoms, not 18. It is not classified as unsaturated.
- Adenylic Acid: This compound is known as AMP (adenosine monophosphate). It consists of an adenosine molecule and one phosphate group, not a glucose phosphate molecule.
- Alanine Amino Acid: While alanine does contain an amino group (NH2) and a carboxylic acid group (COOH), the statement is misleading because these groups are specific to the alpha carbon of the amino acid, not "anywhere in the molecule."
Conclusion
In summary, option A is correct because it accurately describes lecithin as a phosphorylated glyceride found in cell membranes, highlighting its essential role in cellular structure. The other options misrepresent the chemical nature or structure of the biomolecules.
A phosphoglycerate is always made up of :[NEET 2013]- a)only an unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached
- b)a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached
- c)a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a phosphate group which is also attached to a glycerol molecule.
- d)only a saturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A phosphoglycerate is always made up of :
[NEET 2013]
a)
only an unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached
b)
a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached
c)
a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a phosphate group which is also attached to a glycerol molecule.
d)
only a saturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached

|
Kajal Bose answered |
A saturated or unsaturated fatty acid esterified to a glycerol molecule to which a phosphate group is also attached forms phosphoglycerides. Phosphoglycerides are major structural components of cell membranes. They are, therefore, also called membrane lipids. Lecithin is one example.
Enzymes, vitamins and hormones can be classified into a single category of biological chemicals, because all of these[2005]- a)help in regulating metabolism
- b)are exclusively synthesized in the body of a living organism as at present
- c)are conjugated proteins
- d)enhance oxidative metabolism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes, vitamins and hormones can be classified into a single category of biological chemicals, because all of these
[2005]
a)
help in regulating metabolism
b)
are exclusively synthesized in the body of a living organism as at present
c)
are conjugated proteins
d)
enhance oxidative metabolism

|
Kajal Bose answered |
Help in regulating metabolism.
Which form of RNA has a structure resembling clover leaf ?[2004]- a)rRNA
- b)hn RNA
- c)m RNA
- d)t RNA
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which form of RNA has a structure resembling clover leaf ?
[2004]
a)
rRNA
b)
hn RNA
c)
m RNA
d)
t RNA

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
rRNA occurs inside ribosomes. m RNA brings information from DNA to polypeptides. hnRNA are heterogenous nuclear RNA.
The amino acid Tryptophan is the precursor for the synthesis of [2016]- a)Melatonin and Serotonin
- b)Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine
- c)Estrogen and Progesterone
- d)Cortisol and Cortisone
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The amino acid Tryptophan is the precursor for the synthesis of [2016]
a)
Melatonin and Serotonin
b)
Thyroxine and Triiodothyronine
c)
Estrogen and Progesterone
d)
Cortisol and Cortisone

|
Shounak Nair answered |
(a) Tryptophan is a precursor to neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin. Thyroxine (3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine) is produced by follicular cells of the thyroid gland. It is produced as the precursor thyroglobulin. Estrogen is biosynthesized from progesterone (arrived at in two steps from cholesterol, via intermediate pregnenolone). Cortisone is one of several end-products of a process called steroidogenesis. Cortisol is produced in the adrenal cortex of kidney.
Which one of the following hydrolyses internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain?[2005]- a)Lipase
- b)Protease
- c)Endonuclease
- d)Exonuclease
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following hydrolyses internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain?
[2005]
a)
Lipase
b)
Protease
c)
Endonuclease
d)
Exonuclease

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Endonucleases hydrolyse internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain (i.e. DNA). While exonucleases hydrolyse terminal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain (i.e., DNA).
Enzymes increase the rate of reaction by______.- a)increasing temperature and pH
- b) increasing activation energy
- c)lowering activation energy
- d)decreasing temperature and pH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes increase the rate of reaction by______.
a)
increasing temperature and pH
b)
increasing activation energy
c)
lowering activation energy
d)
decreasing temperature and pH
|
|
Bhavya Pillai answered |
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions within cells. Enzymes are mostly proteins that catalyze chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur.
Explanation:
Enzymes lower activation energy:
Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction. In a chemical reaction, the reactant molecules need to collide with each other with sufficient energy to overcome the energy barrier and form the product. Enzymes lower the activation energy by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction to occur. This alternate pathway requires less energy, and hence the reaction proceeds at a faster rate.
Example:
The breakdown of sucrose into glucose and fructose requires an input of energy. In the presence of the enzyme sucrase, the activation energy required for the reaction is lowered, and the reaction occurs spontaneously.
Enzymes are specific:
Enzymes are specific to the reaction they catalyze, and they bind to the reactants at a specific site called the active site. The shape of the active site is complementary to the shape of the reactant molecule, and this specificity ensures that only the correct reactants bind to the enzyme.
Example:
The enzyme lactase catalyzes the breakdown of lactose into glucose and galactose. Lactase specifically binds to the lactose molecule, and the reaction occurs at a faster rate.
Enzymes are not consumed in the reaction:
Enzymes are not consumed in the reaction, and they can be used to catalyze the same reaction repeatedly. Enzymes are not changed by the reaction, and they can be reused multiple times.
Example:
The enzyme catalase catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Catalase is not consumed in the reaction, and it can be used to catalyze the same reaction repeatedly.
In conclusion, enzymes increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. This allows the reaction to occur at a faster rate.
Explanation:
Enzymes lower activation energy:
Activation energy is the energy required to initiate a chemical reaction. In a chemical reaction, the reactant molecules need to collide with each other with sufficient energy to overcome the energy barrier and form the product. Enzymes lower the activation energy by providing an alternate pathway for the reaction to occur. This alternate pathway requires less energy, and hence the reaction proceeds at a faster rate.
Example:
The breakdown of sucrose into glucose and fructose requires an input of energy. In the presence of the enzyme sucrase, the activation energy required for the reaction is lowered, and the reaction occurs spontaneously.
Enzymes are specific:
Enzymes are specific to the reaction they catalyze, and they bind to the reactants at a specific site called the active site. The shape of the active site is complementary to the shape of the reactant molecule, and this specificity ensures that only the correct reactants bind to the enzyme.
Example:
The enzyme lactase catalyzes the breakdown of lactose into glucose and galactose. Lactase specifically binds to the lactose molecule, and the reaction occurs at a faster rate.
Enzymes are not consumed in the reaction:
Enzymes are not consumed in the reaction, and they can be used to catalyze the same reaction repeatedly. Enzymes are not changed by the reaction, and they can be reused multiple times.
Example:
The enzyme catalase catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. Catalase is not consumed in the reaction, and it can be used to catalyze the same reaction repeatedly.
In conclusion, enzymes increase the rate of reaction by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. This allows the reaction to occur at a faster rate.
Transition state str ucture of the substrate formed during an enzymatic reaction is :[NEET 2013]- a)permanent but unstable
- b)transient and unstable
- c)permanent and stable
- d)transient but stable
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Transition state str ucture of the substrate formed during an enzymatic reaction is :
[NEET 2013]
a)
permanent but unstable
b)
transient and unstable
c)
permanent and stable
d)
transient but stable

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Transition state structure formed during an enzymatic reaction is transient and unstable.
Which of the following statements regarding enzyme inhibition is correct?[2005]- a)Competitive inhibition is seen when a substrate competes with an enzyme for binding to an inhibitor protein.
- b)Competitive inhibition is seen when the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site on the enzyme.
- c)Non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme can be overcome by adding large amount of substrate.
- d)Non-competitive inhibitors often bind to the enzyme irreversibly.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding enzyme inhibition is correct?
[2005]
a)
Competitive inhibition is seen when a substrate competes with an enzyme for binding to an inhibitor protein.
b)
Competitive inhibition is seen when the substrate and the inhibitor compete for the active site on the enzyme.
c)
Non-competitive inhibition of an enzyme can be overcome by adding large amount of substrate.
d)
Non-competitive inhibitors often bind to the enzyme irreversibly.

|
Sneha Basak answered |
In competitive inhibition the inhibitor resembles the substrate in structure and hence compete for the active site of the enzyme.
Antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule means that- a)the phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole)
- b)the phosphate groups of two DNA strands, at their ends. share the same position
- c)one strand turns clockwise
- d)one strand turns anti-clockwise
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule means that
a)
the phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole)
b)
the phosphate groups of two DNA strands, at their ends. share the same position
c)
one strand turns clockwise
d)
one strand turns anti-clockwise
|
|
Saif Khan answered |
Antiparallel strands of a DNA molecule means that the phosphate groups at the start of two DNA strands are in opposite position (pole). DNA is composed of two polynucleotide strands, which form what looks like a ladder. The two polynucleotide strands run 'antiparallel' to each other, with nitrogenous bases projecting inwards. The term 'antiparallel' means that the strands run in opposite directions, parallel to one another. The antiparallel strands twist in a complete DNA structure, forming a double helix. It runs 3'-5' and 5'-3' linkage. The 5' and 3' mean "five prime" and "three prime", which indicate the carbon numbers in the DNA's sugar backbone. The 5' carbon has a phosphate group attached to it and the 3' carbon a hydroxyl (-OH) group. This asymmetry gives a DNA strand a "direction".,,..
Which of the following is the simplest amino acid?[2005]- a)Alanine
- b)Asparagine
- c)Glycine
- d)Tyrosine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the simplest amino acid?
[2005]
a)
Alanine
b)
Asparagine
c)
Glycine
d)
Tyrosine
|
|
Shreya Singh answered |
Glycine is the simplest aminoacid..as its variable group R consists of H.....
Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on earth, are produced by :[2005]- a)some bacteria, algae and green plant cells
- b)fungi, algae and green plant cells
- c)all bacteria, fungi and algae
- d)viruses, fungi and bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates, the most abundant biomolecules on earth, are produced by :
[2005]
a)
some bacteria, algae and green plant cells
b)
fungi, algae and green plant cells
c)
all bacteria, fungi and algae
d)
viruses, fungi and bacteria

|
Yash Saha answered |
Some bacteria (such as Rhodopseudomonas), algae and green plants cell produces carbohydrates.
Identify the basic amino acid from the following [2020]- a)Lysine
- b)Valine
- c)Tyrosine
- d)Glutamic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the basic amino acid from the following [2020]
a)
Lysine
b)
Valine
c)
Tyrosine
d)
Glutamic acid
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Lysine is the basic amino acid. Valine is neutral amino acid. Tyrosine is aromatic amino acid. Glutamic acid is acidic amino acid.
Enzymes having slightly different molecular structure but performing identical activity are[1991]- a)Holoenzymes
- b)Isoenzymes
- c)Apoenzymes
- d)Coenzymes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzymes having slightly different molecular structure but performing identical activity are
[1991]
a)
Holoenzymes
b)
Isoenzymes
c)
Apoenzymes
d)
Coenzymes

|
Yash Saha answered |
There are certain enzymes which have slightly different molecular structure but have similar catalytic function such enzymes are known as isoenzymes. Holoenzymes is the active compound formed by combination of a coenzyme and an apoenzyme. Apoenzyme is the protein component of an enzyme, to which the coenzyme attaches to form an active enzyme. Coenzyme are organic non-protein molecules that bind with the protein molecule (apoenzyme) to form the active enzyme (holoenzyme).
Which one is the most abundant protein in the animal world
[2012]
- a)Trypsin
- b)Haemoglobin
- c)Collagen
- d)Insulin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is the most abundant protein in the animal world
[2012]
a)
Trypsin
b)
Haemoglobin
c)
Collagen
d)
Insulin

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Collagen is the most abundant protein of animal world. Rubisco (ribulose biphosphte carboxylase - oxygenase) is not only the most abundant protein in plants but also the whole biosphere.
Which of the following statements aboutenzymes is wrong? [NEETKar. 2013]- a)Enzymes require optimum pH and temperature for maximum activity
- b)Enzymes are denatured at high temperatures
- c)Enzymes are mostly proteins but some are lipids also
- d)Enzymes are highly specific
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements aboutenzymes is wrong?
[NEETKar. 2013]
a)
Enzymes require optimum pH and temperature for maximum activity
b)
Enzymes are denatured at high temperatures
c)
Enzymes are mostly proteins but some are lipids also
d)
Enzymes are highly specific

|
Kajal Bose answered |
Almost all enzymes are proteins. There are some nucleic acids that behave like enzymes. There are called ribozyme (also called RNA enzyme or catalytic RNA).
Which of the following is required as inducer(s) for the expression of Lac operon ? [2016]- a)Glucose
- b)Galactose
- c)Lactose
- d)Lactose and galactose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is required as inducer(s) for the expression of Lac operon ? [2016]
a)
Glucose
b)
Galactose
c)
Lactose
d)
Lactose and galactose

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
(c) Lac operon is an inducible operon. Lactose is the substrate for the enzyme betagalactosidase and it also regulates switching on and off of the operon. Hence, it is termed as inducer. Inducers function by disabling repressors. The gene is expressed because an inducer binds to the repressor. The binding of the inducer to the repressor prevents the repressor from binding to the operator. RNA polymerase can then begin to transcribe operon genes.
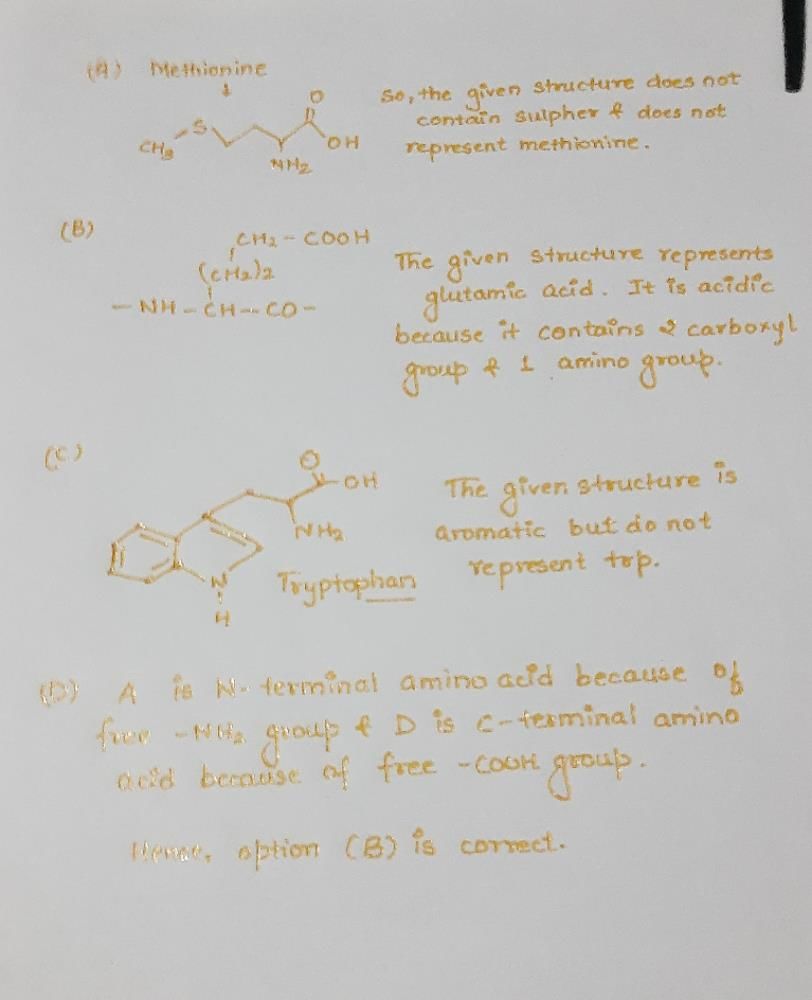
Which one of the following structural formulae of two organic compounds is correctly identified along with its related function ?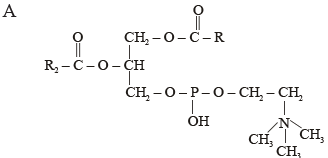
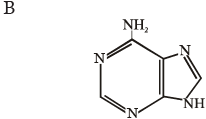 [2011]
[2011]- a)B : Adenine — a nucleotide that makes up nucleic acids
- b)A: Triglyceride — major source of energy
- c)B : Uracil — a component of DNA
- d)A: Lecithin — a component of cell membrane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following structural formulae of two organic compounds is correctly identified along with its related function ?


[2011]
a)
B : Adenine — a nucleotide that makes up nucleic acids
b)
A: Triglyceride — major source of energy
c)
B : Uracil — a component of DNA
d)
A: Lecithin — a component of cell membrane

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Lecithin is a fat like substance called a phospholipid, which is a part of plasma membrane.
A competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase is[2008]- a)Malonate
- b)Oxaloacetate
- c)m-ketoglutarate
- d)Malate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase is
[2008]
a)
Malonate
b)
Oxaloacetate
c)
m-ketoglutarate
d)
Malate

|
Subham Chavan answered |
Malonate is a powerful inhibitor of cellular respiration, because it binds to the active site of the succinate dehydrogenase in the citric acid cycle but does not react, thereby competes with succinate, since it does not have the -CH2-CH2- group as in succinate which is required for dehydrogenation. For the oxidative phosphorylation reaction, malonate is an inhibitor for complex II which again contain succinate dehydrogenase.
The catalytic efficiency of two different enzymes can be compared by the[2005]- a)formation of the product
- b)pH optimum value
- c)Km value
- d)molecular size of the enzyme
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The catalytic efficiency of two different enzymes can be compared by the
[2005]
a)
formation of the product
b)
pH optimum value
c)
Km value
d)
molecular size of the enzyme

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Km (Michealis Menten constant). It is defined as that substrate concentration at which under optimum conditions the rate of an enzyme catalysed reaction reaches half the maximum rate. Km is inversely proportional to affinity of enzyme for its substrate.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biomolecules - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biomolecules - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










