All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Body Fluids and Circulation for NEET Exam
Which of the following is not a granulocyte? [1997] - a)Lymphocyte
- b)Eosinophil
- c)Basophil
- d)Neutrophil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a granulocyte? [1997]
a)
Lymphocyte
b)
Eosinophil
c)
Basophil
d)
Neutrophil

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
White blood cells are of two types : (i) Granulocytes (with granular cytoplasm) - neutrophils, basophils and eosinophils. (ii) Agranulocytes (with clear cytoplasm) - Lymphocytes and monocytes
There is no DNA in: [2009]- a)mature RBCs
- b)a mature spermatozoan
- c)hair root
- d)an enucleated ovum
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
There is no DNA in: [2009]
a)
mature RBCs
b)
a mature spermatozoan
c)
hair root
d)
an enucleated ovum

|
Krish Chakraborty answered |
The chromatin material inside the nucleus is composed of DNA, some proteins and RNA. In fact it is DNA?protein complex basically. Thus, in an enucleated ovum, DNA will be absent. The mature RBCs, mature spermatozoan and root hair are nucleated, thus, contain DNA.
The life span of human W.B.C. is approximately [1997]- a)less than 10 days
- b)between 20 to 30 days
- c)between 2 to 3 months
- d)more than 4 months
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The life span of human W.B.C. is approximately [1997]
a)
less than 10 days
b)
between 20 to 30 days
c)
between 2 to 3 months
d)
more than 4 months
|
|
Vishal Kumar answered |
The life span of WBC ranges from 6 - 20 days, depending on the type, after which they are destroyed in the lymphatic system. When immature WBCs are first released from the bone marrow into the blood, they are called bands or stabs.
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which : [2011]- a)supply oxygenated blood to the different organs
- b)break up into capillaries which reunite to form a vein
- c)break up into capillaries which reunite to form one visceral organ
- d)carry blood from one visceral organ to another visceral organ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arteries are best defined as the vessels which : [2011]
a)
supply oxygenated blood to the different organs
b)
break up into capillaries which reunite to form a vein
c)
break up into capillaries which reunite to form one visceral organ
d)
carry blood from one visceral organ to another visceral organ
|
|
Bindu Bhavani answered |
Arteries supply blood to tissue by breaking into capillaries and deoxy blood from tissue is collected to form vein
Compared to blood our lymph has: [2009]- a)plasma without proteins
- b)more WBCs and no RBCs
- c)more RBCs and less WBCs
- d)no plasma
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Compared to blood our lymph has: [2009]
a)
plasma without proteins
b)
more WBCs and no RBCs
c)
more RBCs and less WBCs
d)
no plasma

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Lymph is a mobile connective tissue comprising lymph plasma and lymph corpuscles. Its composition is just like blood plasma except that it lacks RBCs and large plasma proteins.
Which one of the following vertebrate organs receives the oxygenated blood only ? [1996]- a)Gill
- b)Lung
- c)Liver
- d)Spleen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following vertebrate organs receives the oxygenated blood only ? [1996]
a)
Gill
b)
Lung
c)
Liver
d)
Spleen

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Spleen and brain are the organs which receive only oxygenated blood. In gills and lungs blood picks up oxygen.
Bundle of His is a network of [2003]- a)nerve fibres found throughout the heart
- b)muscle fibres distributed throughout the heart walls
- c)muscle fibres found only in the ventricle wall
- d)nerve fibres distributed in ventricles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bundle of His is a network of [2003]
a)
nerve fibres found throughout the heart
b)
muscle fibres distributed throughout the heart walls
c)
muscle fibres found only in the ventricle wall
d)
nerve fibres distributed in ventricles
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Bundle of His is a network of specialised conducting muscle fibres (Purkinje fibres) which transmit the impulse from AV node to all parts of both the ventricles.
In humans, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to. [2008]
- a)pushing open of the venous valves
- b)pressure difference between the caval and atrium
- c)stimulation of the sino auricular node
- d)suction pull
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In humans, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to. [2008]
a)
pushing open of the venous valves
b)
pressure difference between the caval and atrium
c)
stimulation of the sino auricular node
d)
suction pull

|
Ishani Nambiar answered |
In human, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to suction pull.
Which one of the following has an open circulatory system ? [2006]
- a)Periplaneta
- b)Hirudinaria
- c)Octopus
- d)Pheretima
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following has an open circulatory system ? [2006]
a)
Periplaneta
b)
Hirudinaria
c)
Octopus
d)
Pheretima

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Periplaneta (P. americana, the Indian Cockroach) is an insect & insects do not have closed blood circulation. Their blood (called haemolymph) even does not serve for respiration. They do not possess blood vessels in this circulatory system and hence it is an open system. Hirudinaria is a pure exception for having a closed circulatory system, even though it belongs to the phylum Annelida, which generally has an open circulatory system.
Bulk of carbon dioxide (CO2) released from body tissues into the blood is present as [2011M]- a)bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
- b)free CO2 in blood plasma
- c)70% carbamino- haemoglobin and 30% as bicarbonate
- d)carbamino-haemoglobin in RBCs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bulk of carbon dioxide (CO2) released from body tissues into the blood is present as [2011M]
a)
bicarbonate in blood plasma and RBCs
b)
free CO2 in blood plasma
c)
70% carbamino- haemoglobin and 30% as bicarbonate
d)
carbamino-haemoglobin in RBCs

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
At the tissue site where partial pressure of CO2, is high due to catabolism, CO2, diffuses into blood (RBCs and plasma) and forms HCO2 and IT. At the alveolar site where pCO2, is low, the reaction proceeds in the opposite direction leading to the formation of CO2, and CO2. Thus, CO2, trapped as bicarbonate at the tissue level and transported to the alveoli is released out as CO2
Which of the following statments is true for lymph? [2002]- a)WBC and serum
- b)all components of blood except RBCs and some proteins
- c)RBCs, WBCs and plasma
- d)RBCs proteins and platelets
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statments is true for lymph? [2002]
a)
WBC and serum
b)
all components of blood except RBCs and some proteins
c)
RBCs, WBCs and plasma
d)
RBCs proteins and platelets

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Lymph is colourless vascular connective tissue derived from tissue fluid. RBCs and platelets are absent. Only leucocytes and floating amoeboid lymphocytes are present.
The cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally. The doctors find that an artificial pacemaker is to be grafted in him. It is likely that it will be grafted at the site of- a)Atrioventricular bundle [2004]
- b)Purkinje system
- c)Sinuatrial node
- d)Atrioventricular node
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cardiac pacemaker in a patient fails to function normally. The doctors find that an artificial pacemaker is to be grafted in him. It is likely that it will be grafted at the site of
a)
Atrioventricular bundle [2004]
b)
Purkinje system
c)
Sinuatrial node
d)
Atrioventricular node

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
SA node is the natural pacemaker located in the right atrium. SA node initiates the cardiac impulse. So, artificial pacemaker will be grafted at the site of SA node
You are required to draw blood from a patient and to keep it in a test tube for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma. You are also provided with the following four types of test tubes. Which of them will you not use for the purpose? [2004]- a)Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate
- b)Chilled test tube
- c)Test tube containing heparin
- d)Test tube containing sodium oxalate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
You are required to draw blood from a patient and to keep it in a test tube for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma. You are also provided with the following four types of test tubes. Which of them will you not use for the purpose? [2004]
a)
Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate
b)
Chilled test tube
c)
Test tube containing heparin
d)
Test tube containing sodium oxalate
|
|
Avantika Roy answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'A' - Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate.
Reasons why this test tube cannot be used for the purpose are:
1. Calcium bicarbonate test tube is used for collecting blood for glucose estimation, not for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma.
2. Calcium bicarbonate is a chemical used to preserve blood for glucose estimation. It prevents the breakdown of glucose and stabilizes it for up to 48 hours. However, it can interfere with the analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma, leading to inaccurate results.
3. The other three test tubes - chilled test tube, test tube containing heparin, and test tube containing sodium oxalate are commonly used for collecting blood for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma.
- Chilled test tube is used for collecting blood for coagulation studies.
- Heparin test tube is used for collecting blood for plasma protein analysis and clotting factor assays.
- Sodium oxalate test tube is used for collecting blood for hematological tests like complete blood count (CBC) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Conclusion:
Thus, it is important to choose the appropriate test tube for the specific blood test required to ensure accurate results. In this case, the test tube containing calcium bicarbonate is not suitable for the analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma.
The correct answer is option 'A' - Test tube containing calcium bicarbonate.
Reasons why this test tube cannot be used for the purpose are:
1. Calcium bicarbonate test tube is used for collecting blood for glucose estimation, not for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma.
2. Calcium bicarbonate is a chemical used to preserve blood for glucose estimation. It prevents the breakdown of glucose and stabilizes it for up to 48 hours. However, it can interfere with the analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma, leading to inaccurate results.
3. The other three test tubes - chilled test tube, test tube containing heparin, and test tube containing sodium oxalate are commonly used for collecting blood for analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma.
- Chilled test tube is used for collecting blood for coagulation studies.
- Heparin test tube is used for collecting blood for plasma protein analysis and clotting factor assays.
- Sodium oxalate test tube is used for collecting blood for hematological tests like complete blood count (CBC) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Conclusion:
Thus, it is important to choose the appropriate test tube for the specific blood test required to ensure accurate results. In this case, the test tube containing calcium bicarbonate is not suitable for the analysis of blood corpuscles and plasma.
If due to some injury the chordae tendinae of the tricuspid valve of the human heart is partially non - functional, what will be the immediate effect? [2010]- a)The flow of blood into the aorta will be slowed down
- b)The ‘pacemaker’ will stop working
- c)The blood will tend to flow back into the left atrium
- d)The flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If due to some injury the chordae tendinae of the tricuspid valve of the human heart is partially non - functional, what will be the immediate effect? [2010]
a)
The flow of blood into the aorta will be slowed down
b)
The ‘pacemaker’ will stop working
c)
The blood will tend to flow back into the left atrium
d)
The flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
Tricuspid valve is the valve in the heart between the right atrium and right ventricle. The valve opens to allow blood to flow from atrium into the ventricle. Thus if tricuspid valve is partially nonfunctional, then the flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced
Which one of the following statements is incorrect ? [2006]
- a)In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues
- b)The residual air in lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals
- c)The principle of countercurrent flow facilitates efficient respiration in gills of fishes
- d)The presence of non-respiratory air sacs, increases the efficiency of respiration in birds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect ? [2006]
a)
In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues
b)
The residual air in lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals
c)
The principle of countercurrent flow facilitates efficient respiration in gills of fishes
d)
The presence of non-respiratory air sacs, increases the efficiency of respiration in birds
|
|
Ujwal Basu answered |
The residual air is the air that remains in the lungs after the most forceful expiration. The residual air remains in the lungs. Hence, it has no effect on respiration efficiency in mammals. The presence of non-respiratory air sacs increases the efficiency of respiration in birds. These air sacs increase the metabolic rate in birds. In insects, circulating body fluids serve to distribute oxygen to tissues. Countercurrent oxygen flow is the flow of blood through the gills in the opposite direction as the water flowing over the gills. This facilitates efficient respiration in gills of fishes.
Thus, the correct answer is 'The residual air in the lungs slightly decreases the efficiency of respiration in mammals.'
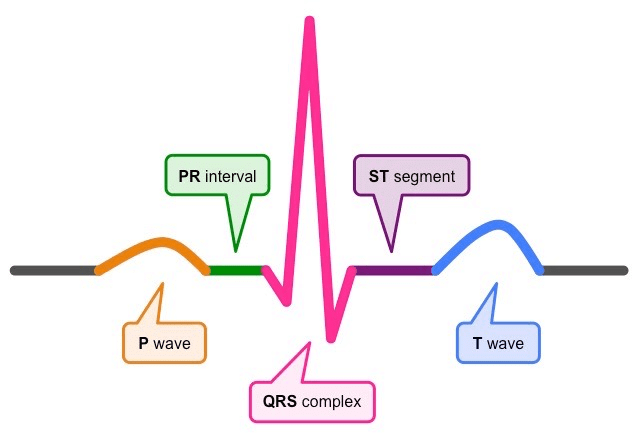
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?- a)S - start of systole [2009]
- b)T - end of diastole
- c)P - depolarisation of the atria
- d)R - repolarisation of ventricles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a standard ECG which one of the following alphabets is the correct representation of the respective activity of the human heart?
a)
S - start of systole [2009]
b)
T - end of diastole
c)
P - depolarisation of the atria
d)
R - repolarisation of ventricles

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
In a standard ECG, the P-wave is a small upward wave that indicates the depolarisation of the atria. This is caused by the activation of SA node.
Contraction of the ventricle in the heart begins by the command from [1999]- a)Chordae tendinae
- b)S.A. node
- c)Purkinje fibres
- d)A. V. node
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Contraction of the ventricle in the heart begins by the command from [1999]
a)
Chordae tendinae
b)
S.A. node
c)
Purkinje fibres
d)
A. V. node

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
SA is the site of generation of the rhythmic cardiac impulse. AV node is a compact mass of myogenic fibres which receives impulse from SA node and transmits it to ventricles. Purkinje fibres are in contact with the contractile muscles of the ventricular walls. Chordae tendinae are the muscles which keep the AV valves in position.
With respect to the ABO group, there are four major blood types because this blood group is determined by [1998]- a)three alleles, all of which are recessive
- b)three alleles, of which, two are recessive and the third is dominant
- c)three alleles, of which two are codominant and the third is recessive
- d)three alleles , all of which are codominant
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
With respect to the ABO group, there are four major blood types because this blood group is determined by [1998]
a)
three alleles, all of which are recessive
b)
three alleles, of which, two are recessive and the third is dominant
c)
three alleles, of which two are codominant and the third is recessive
d)
three alleles , all of which are codominant

|
Kajal Bose answered |
Blood group is determined by three alleles - IA, IB, and Io. Alleles IA and IB are codominant. Blood group A is determined by IA IA or IA Io. Blood group B is IB IB or IB Io. Blood group O is Io Io. Blood group AB is IA IB.
Impulse of heart beat originates from [2002]- a)S. A. node
- b)A. V. node
- c)Vagus nerve
- d)Cardiac nerve
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Impulse of heart beat originates from [2002]
a)
S. A. node
b)
A. V. node
c)
Vagus nerve
d)
Cardiac nerve

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
S.A node is called the pacemaker because it initiates the cardiac impulse AV node receives the impulse from the S.A node and transmits it to the ventricles
As the age advances, there is a gradual thinning of hair in human males. This is mainly because of lowered [2000]- a)blood supply
- b)synthesis of proteins
- c)synthesis of glycogen
- d)availability of energy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
As the age advances, there is a gradual thinning of hair in human males. This is mainly because of lowered [2000]
a)
blood supply
b)
synthesis of proteins
c)
synthesis of glycogen
d)
availability of energy

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Reduced protein synthesis causes thinning of hairs.
What is true about leucocytes ? [2000]- a)Their sudden fall in number is indication of blood cancer
- b)These are produced in thymus
- c)These are enucleated
- d)These can squeeze out through the capillary walls
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about leucocytes ? [2000]
a)
Their sudden fall in number is indication of blood cancer
b)
These are produced in thymus
c)
These are enucleated
d)
These can squeeze out through the capillary walls

|
Kunal Rane answered |
Leucocytes are colourless, nucleated amoeboid cells found in blood which are devoid of haemoglobin and are capable of coming out of blood capillaries through the process of diapedesis. Fall of WBC count is called leucopenia, and occurs due to folic acid deficiency and AIDS etc.
The blood cancer is known as [1995]- a)leukaemia
- b)thrombosis
- c)haemolysis
- d)haemophilia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The blood cancer is known as [1995]
a)
leukaemia
b)
thrombosis
c)
haemolysis
d)
haemophilia

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
The leukaemia is a type of blood cancer, which is characterized by an uncontrolled increase in the number (through mitosis) of leucocytes in the blood.
Systemic heart refers to [2003]- a)the two ventricles together in humans
- b)the heart that contracts under stimulation from nervous system
- c)left auricle and left ventricle in higher vertebrates
- d)entire heart in lower vertebrates
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Systemic heart refers to [2003]
a)
the two ventricles together in humans
b)
the heart that contracts under stimulation from nervous system
c)
left auricle and left ventricle in higher vertebrates
d)
entire heart in lower vertebrates

|
Anu Bajaj answered |
Higher vertebrates exhibit double circulation of blood namely systemic and pulmonary circulation. Systemic circulation involves the distribution of oxygenated blood via the aorta from the heart to all parts of the body, and the collection of deoxygenated blood from all parts of the body through the great veins into the heart. Pulmonary circulation denotes the route impure blood takes from the heart to the lungs for purification and then back to the heart, the left auricle receives oxygenated blood and passes it to the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the pure blood to all parts of the body through aorta. Hence these two chambers involved in systemic circulation are referred to as systemic heart.
What is true about RBCs in humans? [2010]- a)They carry about 20–25 per cent of CO2
- b)They transport 99.5 per cent of O2
- c)They transport about 80 per cent oxygen only and the rest 20 per cent of it is transported in dissolved state in blood plasma
- d)They do not carry CO2 at all
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is true about RBCs in humans? [2010]
a)
They carry about 20–25 per cent of CO2
b)
They transport 99.5 per cent of O2
c)
They transport about 80 per cent oxygen only and the rest 20 per cent of it is transported in dissolved state in blood plasma
d)
They do not carry CO2 at all

|
Palak Khanna answered |
Blood transports oxygen from respiratory organs to the tissue cells and also transports carbon dioxide from the tissue cells to the respiratory membrane. About 97% of oxygen is transported by RBCs in the blood while the remaining three percent of oxygen is carried in a dissolved state through plasma. Nearly 20-25% of carbon dioxide is transported by RBCs whereas 70% is carried as bicarbonate. About 7% of CO2 is carried in dissolved state through plasma.
The majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs- a)as bicarbonates [2006]
- b)as carbonates
- c)attached to hemoglobin
- d)dissolved in the blood
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs
a)
as bicarbonates [2006]
b)
as carbonates
c)
attached to hemoglobin
d)
dissolved in the blood
|
|
Sparsh Saha answered |
The majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs as bicarbonates. This process plays a crucial role in maintaining the acid-base balance in our body.
Transportation of Carbon Dioxide in the Body:
1. Production of Carbon Dioxide: During cellular respiration, our body cells produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the cells.
2. Conversion to Bicarbonate: Carbon dioxide diffuses into the red blood cells, where it combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) with the help of an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase. This reaction occurs rapidly and reversibly. Carbonic acid then dissociates into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+).
3. Transportation in the Blood: The majority of the bicarbonate ions formed are transported in the blood plasma. Bicarbonate ions are highly soluble and can be carried easily in the aqueous medium of the blood. They move from the red blood cells into the plasma, leading to the formation of chloride ions (Cl-) in the red blood cells to maintain electrical neutrality.
4. Exchange in the Lungs: As the blood reaches the lungs, the process is reversed. Bicarbonate ions diffuse back into the red blood cells, where they combine with hydrogen ions to form carbonic acid. Carbonic acid then breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide is then exhaled out of the lungs during expiration.
Significance of Bicarbonate Transport:
- Bicarbonate transport is essential for maintaining the acid-base balance in our body. It helps in preventing the accumulation of excess carbon dioxide, which could lead to respiratory acidosis.
- The rapid conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions allows for efficient transportation of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
- Bicarbonate ions are highly soluble in the blood plasma, enabling them to be readily transported without causing any issues or blockages in the circulatory system.
In conclusion, the majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs as bicarbonates. This process ensures the efficient removal of carbon dioxide waste from the body and plays a vital role in maintaining the acid-base balance.
Transportation of Carbon Dioxide in the Body:
1. Production of Carbon Dioxide: During cellular respiration, our body cells produce carbon dioxide as a waste product. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the cells.
2. Conversion to Bicarbonate: Carbon dioxide diffuses into the red blood cells, where it combines with water to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) with the help of an enzyme called carbonic anhydrase. This reaction occurs rapidly and reversibly. Carbonic acid then dissociates into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+).
3. Transportation in the Blood: The majority of the bicarbonate ions formed are transported in the blood plasma. Bicarbonate ions are highly soluble and can be carried easily in the aqueous medium of the blood. They move from the red blood cells into the plasma, leading to the formation of chloride ions (Cl-) in the red blood cells to maintain electrical neutrality.
4. Exchange in the Lungs: As the blood reaches the lungs, the process is reversed. Bicarbonate ions diffuse back into the red blood cells, where they combine with hydrogen ions to form carbonic acid. Carbonic acid then breaks down into carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide is then exhaled out of the lungs during expiration.
Significance of Bicarbonate Transport:
- Bicarbonate transport is essential for maintaining the acid-base balance in our body. It helps in preventing the accumulation of excess carbon dioxide, which could lead to respiratory acidosis.
- The rapid conversion of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions allows for efficient transportation of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
- Bicarbonate ions are highly soluble in the blood plasma, enabling them to be readily transported without causing any issues or blockages in the circulatory system.
In conclusion, the majority of carbon dioxide produced by our body cells is transported to the lungs as bicarbonates. This process ensures the efficient removal of carbon dioxide waste from the body and plays a vital role in maintaining the acid-base balance.
Given below is the ECG of a normal human. Which one of its components in human is correctly interpreted below
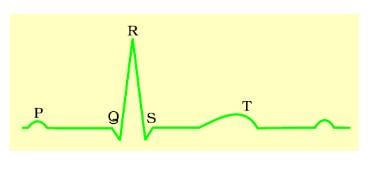
[2011M]a)Peak P and Peak R together-Systolic and diastolic blood pressuresb)Peak T - Initiation of total cardiac contractionc)Complex QRS-One complete Pulsed)Peak P- Initiation of left atrial contraction onlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?


|
Ruchi Chakraborty answered |
Peak P and Peak R together-Systolic and diastolic blood pressures
Sickle cell anaemia is induced by [2001]- a)change of amino acid in a-chain of haemoglobin
- b)change of amino acid in b-chain of haemoglobin
- c)change of amino acid in both a- and b-chain of haemoglobin
- d)change of amino acid in either a- or b-chain of haemoglobin
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Sickle cell anaemia is induced by [2001]
a)
change of amino acid in a-chain of haemoglobin
b)
change of amino acid in b-chain of haemoglobin
c)
change of amino acid in both a- and b-chain of haemoglobin
d)
change of amino acid in either a- or b-chain of haemoglobin

|
Arya Nair answered |
Sickle cell anaemia is a hereditary disorder of autosomal nature caused by mutation of the gene controlling b-chain of haemoglobin. It involves substitution of glutamine by valine.
Figure shows blood circulation in humans with labels A to D. Select the option which gives correct identification of label and functions of the part: [NEET Kar. 2013]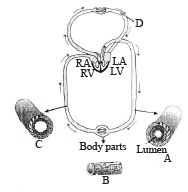
- a)A – Artery - thick walled and blood flows evenly
- b)B – Capillary - thin without muscle layers and wall two cell thick
- c)C – Vein - thin walled and blood flows in jerks/spurts
- d)D – Pulmonary vein - takes oxygenated blood to heart PO2 = 95 mmHg
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows blood circulation in humans with labels A to D. Select the option which gives correct identification of label and functions of the part: [NEET Kar. 2013]

a)
A – Artery - thick walled and blood flows evenly
b)
B – Capillary - thin without muscle layers and wall two cell thick
c)
C – Vein - thin walled and blood flows in jerks/spurts
d)
D – Pulmonary vein - takes oxygenated blood to heart PO2 = 95 mmHg

|
Anand Jain answered |
Arter y is blood vessel which receives blood from heart, has elastic thick wall shows jerky movements due to pumping activity of heart. Vein is a blood vessel which carries blood towards the heart, has wider lumen with internal valves where blood flows smoothly and slowly. Blood capillary is a very fine blood vessel which has a single layered wall. Pulmonary veins are the only veins which carry oxygenated blood. (PO2 = 95 mmHg, PCO2 = 40 mmHg)
The diagram given here is the standard ECG of a normal person, the P-wave represents the : [NEET 2013]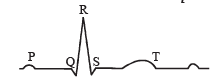
- a)Initiation of the ventricular contraction
- b)Beginning of the systole
- c)End of systole
- d)Contraction of both the atria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The diagram given here is the standard ECG of a normal person, the P-wave represents the : [NEET 2013]

a)
Initiation of the ventricular contraction
b)
Beginning of the systole
c)
End of systole
d)
Contraction of both the atria

|
Palak Khanna answered |
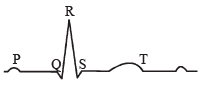
The P-wave represents the electrical excitation (or depolarisation) of the atria, which leads to the contraction of both the atria. The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
ABO blood groups in humans are controlled by the gene I. It has three alleles – IA IB and i. Since there are three different alleles, six different genotypes are possible. How many phenotypes can occur? [2010]- a)Three
- b)One
- c)Four
- d)Two
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ABO blood groups in humans are controlled by the gene I. It has three alleles – IA IB and i. Since there are three different alleles, six different genotypes are possible. How many phenotypes can occur? [2010]
a)
Three
b)
One
c)
Four
d)
Two

|
Anand Jain answered |
The three calle/es in ABO blood groups in humans can produce six different genotypes and four different phenotypes

Which one of the following human organs is often called the graveyard of RBCs?[2011M]- a)Gall bladder
- b)Kidney
- c)Spleen
- d)Liver
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following human organs is often called the graveyard of RBCs?[2011M]
a)
Gall bladder
b)
Kidney
c)
Spleen
d)
Liver

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Spleen is an organ of the lymphatic system located in the left side of the abdominal cavity under the diaphragm, the muscular partition between the abdomen and the chest. It is called graveyard of RBC because fragment of red blood cells, old and dead cells are constantly being removed from the blood streams by it.
‘Bundle of His’ is a part of which one of the following organs in humans? [2011]- a)Brain
- b)Heart
- c)Kidney
- d)Pancreas
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
‘Bundle of His’ is a part of which one of the following organs in humans? [2011]
a)
Brain
b)
Heart
c)
Kidney
d)
Pancreas

|
Tanya R answered |
Bundle of his is located in heart....these together forms purkinje fibers...check circulation unit of class 11 u will get a paragraph there
Which enzyme is responsible for the conversion of inactive fibrinogens to fibrins? [2021]- a)Epinephrine
- b)Thrombokinase
- c)Thrombin
- d)Renin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which enzyme is responsible for the conversion of inactive fibrinogens to fibrins? [2021]
a)
Epinephrine
b)
Thrombokinase
c)
Thrombin
d)
Renin
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Fibrins are formed by the conversion of inactive fibrinogens in the plasma by the enzyme thrombin.
The QRS complex in a standard ECG represents : [2020]- a)Depolarisation of ventricles
- b)Repolarisation of ventricles
- c)Repolarisation of auricles
- d)Depolarisation of auricles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The QRS complex in a standard ECG represents : [2020]
a)
Depolarisation of ventricles
b)
Repolarisation of ventricles
c)
Repolarisation of auricles
d)
Depolarisation of auricles
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after Q and marks the beginning of the systole.
Damage to thymus in a child may lead to: [2005]- a)a reduction in haemoglobin content of blood
- b)a reduction in stem cell production
- c)loss of antibody mediated immunity
- d)loss of cell mediated immunity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Damage to thymus in a child may lead to: [2005]
a)
a reduction in haemoglobin content of blood
b)
a reduction in stem cell production
c)
loss of antibody mediated immunity
d)
loss of cell mediated immunity

|
Yash Saha answered |
The thymus is a major gland of our immune system. The thymus is responsible for production of T (thymus dervied) lymphocytes from immature lymphocytes, a type of white blood cells responsible for cell mediated immunity. Cell mediated immunity is extremely important for raising immune response against bacteria, yeast, fungi, parasites and virus. It is also critical in protecting against cancer, autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, allergies etc.
An adult human with average health has systolic and diastolic pressures as [1998]- a)70 mm Hg and 120 mm Hg
- b)120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
- c)50 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
- d)80 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An adult human with average health has systolic and diastolic pressures as [1998]
a)
70 mm Hg and 120 mm Hg
b)
120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
c)
50 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg
d)
80 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
An adult human with average health has systolic and diastolic pressures as 120 mm Hg and 80 mm Hg respectively.
The most popularly known blood grouping is the ABO grouping. It is named ABO and not ABC, because “O” in it refers to having: [2009]- a)overdominance of this type on the genes for A and B types
- b)one antibody only - either anti - A or anti- B on the RBC;
- c)no antigens A and B on RBCs
- d)other antigens besides A and B on RBCs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most popularly known blood grouping is the ABO grouping. It is named ABO and not ABC, because “O” in it refers to having: [2009]
a)
overdominance of this type on the genes for A and B types
b)
one antibody only - either anti - A or anti- B on the RBC;
c)
no antigens A and B on RBCs
d)
other antigens besides A and B on RBCs

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
The ABO blood group system is the most important blood type system (or blood group system) in human blood transfusion. It is named ABO and not ABC, because blood group O (or blood group zero in some countries) individuals do not have either A or B antigens on the surface of their RBCs, but their blood serum contains IgM anti-A antibodies and anti-B antibodies against the A and B blood group antigens. Therefore, a group O individual can receive blood only from a group O individual, but can donate blood to individuals of any ABO blood group (ie A, B, O or AB).
The most active phagocytic white blood cells are: [2008]- a)neutrophils and eosinophils
- b)lymphocytes and macrophages
- c)eosinophils and lymphocytes
- d)neutrophils and monocytes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most active phagocytic white blood cells are: [2008]
a)
neutrophils and eosinophils
b)
lymphocytes and macrophages
c)
eosinophils and lymphocytes
d)
neutrophils and monocytes

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
The most active phagocytic white blood cells are neutrophils and monocytes. Neutrophil is a type of WBC (leucocyte) that has a lobed nucleus and granular cytoplasm. Neutrophils engulf bacteria and release various substance such as lysozyme and oxidizing agents. Monocyte is the largest form of WBC in vertebrates. It has a kidney shaped nucleus and is actively phagocytic, ingesting bacteria and cells debris.
In the ABO system of blood groups, if both antigens are present but no antibody, the blood group of the individual would be [2004]- a)B
- b)O
- c)AB
- d)A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the ABO system of blood groups, if both antigens are present but no antibody, the blood group of the individual would be [2004]
a)
B
b)
O
c)
AB
d)
A

|
Anirudh Datta answered |
Blood group AB is also known as the universal recipient.
Which one of the following statements about blood constituents and transport of respiratory gases is most accurate ? [1996]- a)RBCs transport oxygen whereas WBCs transport CO2 more and very little amount of oxygen
- b)RBCs transport oxygen whereas plasma transports carbon dioxide only
- c)RBCs as well as WBCs transport both oxygen and CO2
- d)RBCs as well as plasma transport both oxygen and CO2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements about blood constituents and transport of respiratory gases is most accurate ? [1996]
a)
RBCs transport oxygen whereas WBCs transport CO2 more and very little amount of oxygen
b)
RBCs transport oxygen whereas plasma transports carbon dioxide only
c)
RBCs as well as WBCs transport both oxygen and CO2
d)
RBCs as well as plasma transport both oxygen and CO2

|
Top Rankers answered |
About 97 per cent of O2 is transported by RBCs in the blood. The remaining 3 per cent of O2 is carried in a dissolved state through the plasma. Nearly 20-25 per cent of CO2 is transported by RBCs whereas 70 per cent of it is carried as bicarbonate. About 7 per cent of CO2 is carried in a dissolved state through plasma.
Which type of white blood cells are concerned with the release of histamine and the natural anti- coagulant heparin? [2008] - a)Neutrophils
- b)Basophils
- c)Eosinophils
- d)Monocytes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of white blood cells are concerned with the release of histamine and the natural anti- coagulant heparin? [2008]
a)
Neutrophils
b)
Basophils
c)
Eosinophils
d)
Monocytes

|
Anand Jain answered |
Basophil is a type of white blood cell (leucocyte) that has a lobed nucleus surrounded by granular cytoplasm. Basophils are produced continually by stem cells in the red bone marrow & move about in an amoeboid fashion. Like, mast cells, they produce histamine and heparin as part of the body’s defences at the site of an infection or injury.
In mammals, histamine is secreted by [1998]- a)histiocytes
- b)lymphocytes
- c)mast cells
- d)fibroblasts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In mammals, histamine is secreted by [1998]
a)
histiocytes
b)
lymphocytes
c)
mast cells
d)
fibroblasts

|
Ayush Choudhury answered |
Histamine is a potant vasodilator formed by decarboxylation of the amino acid histidine and released by mast cells in response to appropriate antigens.
Mast cells are especially prevalent in the connective tissue of the skin and respiratory tract and in surrounding blood vessels.
Mast cells are especially prevalent in the connective tissue of the skin and respiratory tract and in surrounding blood vessels.
Antigens are present [1995]- a)inside the nucleus
- b)on cell surface
- c)inside the cytoplasm
- d)on nuclear membrane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Antigens are present [1995]
a)
inside the nucleus
b)
on cell surface
c)
inside the cytoplasm
d)
on nuclear membrane

|
Dipanjan Mehta answered |
Antigens are foreign proteins, which stimulate specific immune response (antibody) against itself when introduced into the body. They are present on the surface of cell wall.
Which one of the following plasma proteins is involved in the coagulation of blood ? [2011]- a)an albumin
- b)serum amylase
- c)a globulin
- d)fibrinogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following plasma proteins is involved in the coagulation of blood ? [2011]
a)
an albumin
b)
serum amylase
c)
a globulin
d)
fibrinogen

|
Nilanjan Chakraborty answered |
Fibrinogen, the protein of blood plasma is converted to insoluble protein fibrin during the clotting process. The fibrinogen free fluid obtained after removal of the clot, called blood serum is plasma minus fibrinogen.
What would be the heart rate of a person if the cardiac output is 5 L, blood volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole is 100 mL and at the end of the ventricular systole is 50 mL? [2019]- a)125 beats per minute
- b)50 beats per minute
- c)75 beats per minute
- d)100 beats per minute
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What would be the heart rate of a person if the cardiac output is 5 L, blood volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole is 100 mL and at the end of the ventricular systole is 50 mL? [2019]
a)
125 beats per minute
b)
50 beats per minute
c)
75 beats per minute
d)
100 beats per minute
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Stroke volume = End diastolic volume - End systolic volume
= 100 - 50 = 50 mL
Cardiac output = Heart beat x stroke volume
∴ Heart beat = Cardiac output/Stroke volume = 5000 / 50 = 100 beats per minute
= 100 - 50 = 50 mL
Cardiac output = Heart beat x stroke volume
∴ Heart beat = Cardiac output/Stroke volume = 5000 / 50 = 100 beats per minute
A drop of each of the following, is placed separately on four slides. Which of them will not coagulate? [2007]- a)Blood serum
- b)Sample from the thoracic duct of lymphatic system
- c)Whole blood from pulmonary vein
- d)Blood plasma.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A drop of each of the following, is placed separately on four slides. Which of them will not coagulate? [2007]
a)
Blood serum
b)
Sample from the thoracic duct of lymphatic system
c)
Whole blood from pulmonary vein
d)
Blood plasma.
|
|
Shilpa Bose answered |
Explanation:
To understand why blood serum does not coagulate, we need to understand the composition of blood and the process of coagulation.
Blood Composition:
- Blood is composed of cells suspended in a liquid called plasma.
- Plasma is the liquid component of blood that contains various proteins, electrolytes, hormones, and waste products.
- Blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
Coagulation Process:
- Coagulation is a complex process that involves the formation of a blood clot to prevent excessive bleeding.
- It is initiated by a series of reactions that ultimately convert soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin, which forms a mesh-like structure to trap blood cells and stop bleeding.
Analysis of Options:
a) Blood serum: Blood serum is the liquid component of blood that remains after the clotting process. It does not contain fibrinogen, which is necessary for the formation of a blood clot. Therefore, blood serum does not coagulate.
b) Sample from the thoracic duct of the lymphatic system: The lymphatic system is a network of vessels that collects excess fluid and waste products from tissues. The sample from the thoracic duct may contain lymphocytes and other components, but it does not contain the necessary factors for coagulation. Therefore, it will not coagulate.
c) Whole blood from the pulmonary vein: Whole blood contains all the components of blood, including plasma, cells, and platelets. Therefore, it has the potential to coagulate.
d) Blood plasma: Blood plasma is the liquid component of blood that contains fibrinogen and other factors necessary for coagulation. Therefore, blood plasma has the potential to coagulate.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, blood serum will not coagulate because it does not contain fibrinogen, which is necessary for the coagulation process.
To understand why blood serum does not coagulate, we need to understand the composition of blood and the process of coagulation.
Blood Composition:
- Blood is composed of cells suspended in a liquid called plasma.
- Plasma is the liquid component of blood that contains various proteins, electrolytes, hormones, and waste products.
- Blood cells include red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
Coagulation Process:
- Coagulation is a complex process that involves the formation of a blood clot to prevent excessive bleeding.
- It is initiated by a series of reactions that ultimately convert soluble fibrinogen into insoluble fibrin, which forms a mesh-like structure to trap blood cells and stop bleeding.
Analysis of Options:
a) Blood serum: Blood serum is the liquid component of blood that remains after the clotting process. It does not contain fibrinogen, which is necessary for the formation of a blood clot. Therefore, blood serum does not coagulate.
b) Sample from the thoracic duct of the lymphatic system: The lymphatic system is a network of vessels that collects excess fluid and waste products from tissues. The sample from the thoracic duct may contain lymphocytes and other components, but it does not contain the necessary factors for coagulation. Therefore, it will not coagulate.
c) Whole blood from the pulmonary vein: Whole blood contains all the components of blood, including plasma, cells, and platelets. Therefore, it has the potential to coagulate.
d) Blood plasma: Blood plasma is the liquid component of blood that contains fibrinogen and other factors necessary for coagulation. Therefore, blood plasma has the potential to coagulate.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, blood serum will not coagulate because it does not contain fibrinogen, which is necessary for the coagulation process.
Pulmonary artery differ from pulmonary vein in having [2000]- a)no endothelium
- b)valves
- c)large lumen
- d)thick muscular walls
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Pulmonary artery differ from pulmonary vein in having [2000]
a)
no endothelium
b)
valves
c)
large lumen
d)
thick muscular walls

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
Arteries have thick wall and narrow lumen while veins have thin walls and large lumen. Arteries do not have valves.
Globulins contained in human blood plasma are primarily involved in : [2009]- a)osmotic balance of body fluids
- b)oxygen transport in the blood
- c)clotting of blood
- d)defence mechanisms of body
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Globulins contained in human blood plasma are primarily involved in : [2009]
a)
osmotic balance of body fluids
b)
oxygen transport in the blood
c)
clotting of blood
d)
defence mechanisms of body

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
Globulins contained in human blood plasma are primarily involved, in defence mechanism of body. Globulin is one of the two types of serum proteins, the other being albumin. Globulins can be divided into three fractions based on their electrophoretic mobility. Most of the alpha and beta globulins are synthesized by the liver, whereas gamma globulins are produced by lymphocytes and plasma cells in lymphoid tissue.
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding blood pressure ? [2011]- a)130/90 mmHg is considered high and requires treatment
- b)100/55 mmHg is considered an ideal blood pressure
- c)105/50 mm Hg makes one very active
- d)190/110 mmHg may harm vital organs like brain and kidney
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is correct regarding blood pressure ? [2011]
a)
130/90 mmHg is considered high and requires treatment
b)
100/55 mmHg is considered an ideal blood pressure
c)
105/50 mm Hg makes one very active
d)
190/110 mmHg may harm vital organs like brain and kidney
|
|
Asra Khatoon answered |
Hypertension is the term for blood pressure that is heigher than normal blood (120/80).In this measurement 120mm Hg is the systolic,or pumping, pressure and 80mmHg is the diastolic,or resting, pressure.If repeated checks of blood pressure of and individual is 240/90 or heigher,it shows hypertension.Blood pressure leads to heart diseases and also affects vital organs like brain and kidney.
Chapter doubts & questions for Body Fluids and Circulation - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Body Fluids and Circulation - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









