All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Past Year Papers >
All Questions
All questions of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants for NEET Exam
Which one of the following is represented by Calvin cycle? [1996]- a)Reductive carboxylation
- b)Oxidative carboxylation
- c)Photophosphorylation
- d)Oxidative phosphorylation.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is represented by Calvin cycle? [1996]
a)
Reductive carboxylation
b)
Oxidative carboxylation
c)
Photophosphorylation
d)
Oxidative phosphorylation.

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
In dark phase of calvin cycle of photosynthesis the CO2 is reduced to Glucose in stroma of chloroplast, making use of the ATP & NADPH2, (available from light phase).
The C4 plants are photosynthetically more efficient than C3 plants because:- a)the CO2 compensation point is more
- b)CO2 generated during photorespiration is trapped and recycled through PEP carboxylase
- c)the CO2 efflux is not prevented
- d)they have more chloroplasts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The C4 plants are photosynthetically more efficient than C3 plants because:
a)
the CO2 compensation point is more
b)
CO2 generated during photorespiration is trapped and recycled through PEP carboxylase
c)
the CO2 efflux is not prevented
d)
they have more chloroplasts
|
|
Neha Dasgupta answered |
Based on metabolic activities in plants, they are broadly classified into CAM, C3, C4, etc. These are pathways for carbon fixation during photosynthesis.
In C3 plants, chloroplasts are not present in the bundle sheath cells. Whereas, it is present in C4 plants.
Also, In C4 plants, photosynthesis occurs even when pores called stomata are closed.
C4 plants show high efficiency in photosynthesis than the C3 plants because they contain more chloroplasts.
In C3 plants, chloroplasts are not present in the bundle sheath cells. Whereas, it is present in C4 plants.
Also, In C4 plants, photosynthesis occurs even when pores called stomata are closed.
C4 plants show high efficiency in photosynthesis than the C3 plants because they contain more chloroplasts.
C4 plants are more efficient in photosynthesis than C3 plants due to: [2010]
- a)Higher leaf area
- b)Lower rate of photorespiration
- c)Presence of thin cuticle
- d)
Presence of larger number of chloroplasts in the leaf cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
C4 plants are more efficient in photosynthesis than C3 plants due to: [2010]
a)
Higher leaf area
b)
Lower rate of photorespiration
c)
Presence of thin cuticle
d)
Presence of larger number of chloroplasts in the leaf cells

|
Yash Saha answered |
Like Plants, alage have cell walls contain either polysaccharides such as cellulose (a glucan) or a variety of glycoproteins or both. The inclusion of additional polysaccharide in algal cell walls is used as a feature for algal taxonomy. Mannas form microbibrils in the cell walls of a number of marine green alge including those from the genera Codium, Acetabularia as well as in the walls of some red algae including those from the gera Codium, Acteabularia as well as in the walls of some red algae like Porpyra.
The first stable product of CO2 fixation in sorghum is: [2021]- a)Succinic acid
- b)Phosphoglyceric acid
- c)Pyruvic acid
- d)Oxaloacetic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The first stable product of CO2 fixation in sorghum is: [2021]
a)
Succinic acid
b)
Phosphoglyceric acid
c)
Pyruvic acid
d)
Oxaloacetic acid
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
- You may like to cut a section of the leaves of C4 plants – maize or sorghum – to observe the Kranz anatomy and the distribution of mesophyll cells.
- The C4 acid OAA is formed in the mesophyll cells.
As compared to a C3 – plant, how many additional molecules of ATP are needed for net production of one molecule of hexose sugar by C4 – plants: [2005]- a)two
- b)six
- c)twelve
- d)zero
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
As compared to a C3 – plant, how many additional molecules of ATP are needed for net production of one molecule of hexose sugar by C4 – plants: [2005]
a)
two
b)
six
c)
twelve
d)
zero

|
Bhargavi Choudhury answered |
Equation for C4 pathway 6 PEP + 6 RuBP + 6CO2 + 30 ATP + 12 NADPH 6PEP + 6 RuBP + C6H12O6 + 30 ADP + 30 H3PO4 + 12 NADP+
The net reaction of C3 dark fixation is 6RuBP + 6CO2 + 18ATP + 12 NADPH 6 RuBP + C6H12O6 + 18 ADP + 18 P + 12 NADP+
The net reaction of C3 dark fixation is 6RuBP + 6CO2 + 18ATP + 12 NADPH 6 RuBP + C6H12O6 + 18 ADP + 18 P + 12 NADP+
The specific characteristic of C4-plants is [1995]- a)bulliform cells
- b)isobilateral leaf
- c)kranz anatomy
- d)parallel veins configuration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The specific characteristic of C4-plants is [1995]
a)
bulliform cells
b)
isobilateral leaf
c)
kranz anatomy
d)
parallel veins configuration

|
Harshitha Dey answered |
Anatomy of leaves of C4– plant is called kranz anatomy. In the mesophyll cells of these plants pallisade tissue is absent.
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in photosynthesis of : [2010]- a)Bryophyte
- b)Gymnosperm
- c)Angiosperm
- d)Alga
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PGA as the first CO2 fixation product was discovered in photosynthesis of : [2010]
a)
Bryophyte
b)
Gymnosperm
c)
Angiosperm
d)
Alga

|
Sarthak Saini answered |
Phosphoglyceric and (PGA) is the first stable product of photosynthesis. It was first discovered by Calvin, Benson and their colleagues in Chlorella, algae.
Photosynthesis in C4 plants is relatively less limited by atmospheric CO2 levels because:[2005]- a)Effective pumping of CO2 into bundle sheath cells.
- b)Rubisco in C4 plants has higher affinity for CO2.
- c)Four carbon acids are the primary initial CO2 fixation products.
- d)The primary fixation of CO2 is mediated via PEP carboxylase.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthesis in C4 plants is relatively less limited by atmospheric CO2 levels because:
[2005]
a)
Effective pumping of CO2 into bundle sheath cells.
b)
Rubisco in C4 plants has higher affinity for CO2.
c)
Four carbon acids are the primary initial CO2 fixation products.
d)
The primary fixation of CO2 is mediated via PEP carboxylase.

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
In C4 plants, initial fixation of carbon dioxide occurs in mesophyll cells. The primary acceptor of CO2 is phosphoenol pyruvate or PEP. It combines with carbon dioxide in the presence of PEP carboxylase or Pepcase to form oxaloacetate.
C4 plants are more efficient in picking up CO2 even when it is found in low concentration because of the high affinity of PEP case.
C4 plants are more efficient in picking up CO2 even when it is found in low concentration because of the high affinity of PEP case.
A process that makes important difference between C3 and C4 plants is : [2012]- a)Transpiration
- b)Glycolysis
- c)Photosynthesis
- d)Photorespiration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A process that makes important difference between C3 and C4 plants is : [2012]
a)
Transpiration
b)
Glycolysis
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Photorespiration

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Photorespiration is absent is C4 plants. Photorespiration does not produce energy or reducing power. Rather, it consumes energy. Further, it undoes the work of photosynthesis. There is 25% loss of fixed CO2. Therefore, photorespiration is a highly wasteful process. This happens only in case of C3 plants.
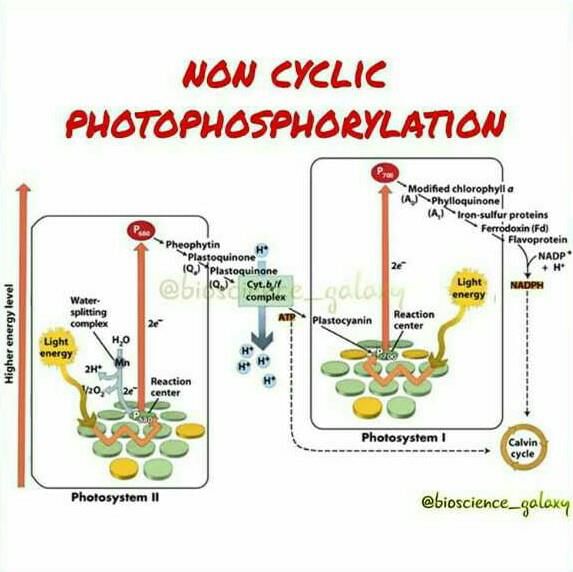
Which one occurs both during cyclic and noncyclic modes of photophosphorylation? [1994]
- a)Involvement of both PS I and PS II
- b)Formation of ATP
- c)Release of O2
- d)Formation of NADPH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one occurs both during cyclic and noncyclic modes of photophosphorylation? [1994]
a)
Involvement of both PS I and PS II
b)
Formation of ATP
c)
Release of O2
d)
Formation of NADPH

|
Lekshmi Banerjee answered |
The only process that occurs in both cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation is the formation of ATP.
Plants adapted to low light intensity have [2004]- a)larger photosynthetic unit size that the sun plants
- b)higher rate of CO2 fixation that the sun plants
- c)more extended root system
- d)leaves modified to spines
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plants adapted to low light intensity have [2004]
a)
larger photosynthetic unit size that the sun plants
b)
higher rate of CO2 fixation that the sun plants
c)
more extended root system
d)
leaves modified to spines

|
Sneha Basak answered |
They have larger photosynthetic unit size so that they can absorb maximum amount of light of the Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR) for photosynthesis.
How many turns of Calvin cycle yield one molecule of glucose ? [1996, 2000]- a)Eight
- b)Two
- c)Six
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many turns of Calvin cycle yield one molecule of glucose ? [1996, 2000]
a)
Eight
b)
Two
c)
Six
d)
Four

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Each turn of Calvin cycle generates one carbon atom hence six turns of the cycle is required to generate one molecule of hexose sugar glucose.
The oxygenation activity of RuBisCo enzyme in photorespiration leads to the formation of: [2020]- a)1 molecule of 6-C compound
- b)1 molecule of 4-C compound and 1 molecule of 2-C compound
- c)2 molecules of 3-C compound
- d)1 molecule of 3-C compound
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxygenation activity of RuBisCo enzyme in photorespiration leads to the formation of: [2020]
a)
1 molecule of 6-C compound
b)
1 molecule of 4-C compound and 1 molecule of 2-C compound
c)
2 molecules of 3-C compound
d)
1 molecule of 3-C compound
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Photorespiration is the light dependent process. At high temperature, RuBP carboxylase functions as oxygenase and instead of fixing carbon dioxide (C3 cycle), oxidises ribulose 1, 5-biphosphate to produce a 3-carbon phosphoglyceric acid and a 2-carbon phosphoglycolate.
Cyclic photophosphorylation results in the formation of [2009]- a)ATP and NADPH
- b)ATP, NADPH and O2
- c)ATP
- d)NADPH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cyclic photophosphorylation results in the formation of [2009]
a)
ATP and NADPH
b)
ATP, NADPH and O2
c)
ATP
d)
NADPH

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
Cyclic photophosphorylation results in the formation of ATP. This process is called photophosphorylation, which occurs in two different ways. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is considered by biologists to be the energy currency of life. It is the high-energy molecule that stores the energy we need to do just about everything we do. It is present in the cytoplasm and nucleoplasm of every cell, and essentially all the physiological mechanisms that require energy for operation obtain it directly from the stored ATP.
Which fractions of the visible spectrum of solar radiations are primarily absorbed by carotenoids of the higher plants? [2003]- a)Violet and blue
- b)Blue and green
- c)Green and red
- d)Red and violet
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which fractions of the visible spectrum of solar radiations are primarily absorbed by carotenoids of the higher plants? [2003]
a)
Violet and blue
b)
Blue and green
c)
Green and red
d)
Red and violet

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Carotenoids are a group of yellow, red and orange pigments which function as acessary pigments and protect chlorophyll molecules from destruction by intensive light rays. Carotenoids have three absorption peaks in the blue-violet range of the spectrum.
Which element is located at the centre of the porphyrin ring in chlorophyll ? [2003]- a)Manganese
- b)Calcium
- c)Magnesium
- d)Potassium
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which element is located at the centre of the porphyrin ring in chlorophyll ? [2003]
a)
Manganese
b)
Calcium
c)
Magnesium
d)
Potassium

|
Arindam Khanna answered |
A non ionic Mg atom is held in the centre of porphyrin (of chlorophyll) held by N atom of pyrrole ring.
Which enzyme is most abudantly found on earth?[1999]- a)Catalase
- b)Rubisco
- c)Nitrogenase
- d)Invertase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which enzyme is most abudantly found on earth?[1999]
a)
Catalase
b)
Rubisco
c)
Nitrogenase
d)
Invertase
|
|
Nitya Saha answered |
Most abundantly found enzyme on earth: Rubisco
Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the most abundant enzyme on earth. It plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis, which is responsible for converting carbon dioxide into organic compounds essential for plant growth.
Importance of Rubisco:
- Rubisco is involved in the first major step of carbon fixation during photosynthesis.
- It catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, leading to the production of 3-phosphoglycerate, a crucial intermediate in the Calvin cycle.
- Without Rubisco, plants would not be able to efficiently fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, leading to a decrease in plant growth and productivity.
Abundance of Rubisco:
- Rubisco is found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
- It is estimated that Rubisco accounts for approximately 30-50% of total soluble protein in plant leaves.
- Due to its high abundance and essential role in photosynthesis, Rubisco is considered the most abundant enzyme on earth.
In conclusion, Rubisco is the most abundantly found enzyme on earth due to its critical role in carbon fixation during photosynthesis. Its high abundance in plant tissues highlights its importance in sustaining life on our planet.
Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase) is the most abundant enzyme on earth. It plays a crucial role in the process of photosynthesis, which is responsible for converting carbon dioxide into organic compounds essential for plant growth.
Importance of Rubisco:
- Rubisco is involved in the first major step of carbon fixation during photosynthesis.
- It catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, leading to the production of 3-phosphoglycerate, a crucial intermediate in the Calvin cycle.
- Without Rubisco, plants would not be able to efficiently fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, leading to a decrease in plant growth and productivity.
Abundance of Rubisco:
- Rubisco is found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria.
- It is estimated that Rubisco accounts for approximately 30-50% of total soluble protein in plant leaves.
- Due to its high abundance and essential role in photosynthesis, Rubisco is considered the most abundant enzyme on earth.
In conclusion, Rubisco is the most abundantly found enzyme on earth due to its critical role in carbon fixation during photosynthesis. Its high abundance in plant tissues highlights its importance in sustaining life on our planet.
The principle of limiting factors was proposed by[1996]- a)Blackman
- b)Hill
- c)Arnol
- d)Liebig
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The principle of limiting factors was proposed by[1996]
a)
Blackman
b)
Hill
c)
Arnol
d)
Liebig

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
The principle of limiting factors was formulated by Blackmann (1905). It states that when a process is conditioned as to its rapidity by a number of separate factors, the rate of process is limited by the pace of slowest factor.
Photorespiration is favoured by [1996]- a)high O2 and low CO2
- b)low light and high O2
- c) low temperature and high O2
- d)low O2 and high CO2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Photorespiration is favoured by [1996]
a)
high O2 and low CO2
b)
low light and high O2
c)
low temperature and high O2
d)
low O2 and high CO2

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
Photorespiratory loss of CO2 occurs when RUBISCO starts functioning as an oxygenase instead of carboxylase under conditions of high O2 and low CO2. It involves three organelles chloroplast, mitochondria and peroxisomes. Half of the photosynthetically fixed carbon (in the form of RUBP) may be lost into the atmosphere through this process and no ATP formation occurs.
In C3 plants, the first stable product of photosynthesis during the dark reaction is [2004]- a)Malic acid
- b)Oxaloacetic acid
- c)3-phosphoglyceric acid
- d)Phosphoglyceraldehyde
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In C3 plants, the first stable product of photosynthesis during the dark reaction is [2004]
a)
Malic acid
b)
Oxaloacetic acid
c)
3-phosphoglyceric acid
d)
Phosphoglyceraldehyde

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3 carbon compound is the first product formed in the C3 cycle. It is then converted to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Oxaloacetic acid, 4 carbon compound is the first product formed in C4 cycle. It is then converted to malic acid.
Pigment acting as a reaction centre during photosynthesis is [1994]- a)Carotene
- b)Phytochrome
- c)P700
- d)Cytochrome
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pigment acting as a reaction centre during photosynthesis is [1994]
a)
Carotene
b)
Phytochrome
c)
P700
d)
Cytochrome

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
P700 consists of a chl a and chl b molecules and is named after maximum absorption by pigment or photocentre at that wavelength.
CAM helps the plants in : [2011]- a)conserving water
- b)secondary growth
- c)disease resistance
- d)reproduction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
CAM helps the plants in : [2011]
a)
conserving water
b)
secondary growth
c)
disease resistance
d)
reproduction

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
CAM plants are most common in arid environments. Being able to keep stomata closed during the hottest and driest part of the day reduces the loss of water through evapotranspiration.
In leaves of C4 plants malic acid synthesis during CO2 fixation occurs in [2008]- a)epidermal cells
- b)mesophyll cells
- c)bundle sheath
- d)guard cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In leaves of C4 plants malic acid synthesis during CO2 fixation occurs in [2008]
a)
epidermal cells
b)
mesophyll cells
c)
bundle sheath
d)
guard cells

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
In leaves of C4 plants, malic acid synthesis during CO2 fixation occurs in mesophyll cells. The mesophyll cells perform C4 cycle and the cells of bundle sheath perform C3 cycle. CO2 taken from the atmosphere is accepted by phosphoenol pyruvic acid (PEP) present in the chloroplasts of mesophyll cell of these leaves, leading to the formation of a 4-C compound, oxaloacetic acid (OAA). This acid is converted to another 4-C acid, the malic acid which enters into the chloroplast of bundle sheath cells and these undergoes oxidative decarboxylation yielding pyruvic acid (3C - compound) and CO2.
The wavelength of light absorbed by Pr form of phytochrome is [2007]- a)680 nm
- b)720 nm
- c)620 nm
- d)640 nm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The wavelength of light absorbed by Pr form of phytochrome is [2007]
a)
680 nm
b)
720 nm
c)
620 nm
d)
640 nm

|
Yash Saha answered |
The Pr form absorbs light between 660 to 680 nm and absorbs at a peak of 666 nm. It is the form synthesized in darkgrown seedlings. When Pr absorbs red light, it is converted to the Pfr form.
During photorespiration, the oxygen consuming reaction(s) occur in [2006]- a)stroma of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
- b)grana of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
- c)stroma of chloroplasts
- d)stroma of chloroplasts and mitochondria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During photorespiration, the oxygen consuming reaction(s) occur in [2006]
a)
stroma of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
b)
grana of chloroplasts and peroxisomes
c)
stroma of chloroplasts
d)
stroma of chloroplasts and mitochondria

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The first reaction of photorespiration occur in stroma of chloroplast. In this reaction the RuBP(Ribulose 1-5 biphosphate) consume one oxygen molecule in presence of enzyme Rubisco.
In peroxisome the glycolate transferred from chloroplast takes up O2 and formed the glyoxylate whereas the H2O2 release as byproduct.
In peroxisome the glycolate transferred from chloroplast takes up O2 and formed the glyoxylate whereas the H2O2 release as byproduct.
Fixation of one CO2 molecule through Calvin cycle requires [2000]- a)1 ATP and 2NADPH2
- b)2ATP and 2NADPH2
- c)3ATP and 2NADPH2
- d)2ATP and 1NADPH2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Fixation of one CO2 molecule through Calvin cycle requires [2000]
a)
1 ATP and 2NADPH2
b)
2ATP and 2NADPH2
c)
3ATP and 2NADPH2
d)
2ATP and 1NADPH2

|
Moumita Khanna answered |
2 ATP are required during conversion of PGA to 1, 3-diphosphoglyceric acid and 1 ATP during conversion of glyceraldehyde phosphate to ribulose biphosphate. 2NADH2 molecules are utilised for converting 1, 3-diphosphoglyceric acid to glyceraldehyde phosphate.
Bundle sheath cells [NEET Kar. 2013]- a)Are rich in RuBisCO
- b)Are rich in PEP carboxylase
- c)Lack RuBisCO
- d)Lack both RuBisCO and PEP carboxylase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bundle sheath cells [NEET Kar. 2013]
a)
Are rich in RuBisCO
b)
Are rich in PEP carboxylase
c)
Lack RuBisCO
d)
Lack both RuBisCO and PEP carboxylase

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
In C4 plants, bundle sheath cells are rich in RuBisCO, but lack PEPcase. The CO2 released in the bundle sheath cells enters the C3 or the Calvin pathway, common to all plants. Thus, the basic pathway that results in the formation of sugars, the calvin pathway is common to the C3 and C4 plants.
In photosystem-1the first electron acceptor is [2006]
- a)Cytochrome
- b)Plastocyanin
- c)An iron-sulphur protein
- d)Ferredoxin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In photosystem-1the first electron acceptor is [2006]
a)
Cytochrome
b)
Plastocyanin
c)
An iron-sulphur protein
d)
Ferredoxin
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Cytochrome
Photosystem I is located in the outer surface of the thylakoid and the photosystem II is located towards the inner side of the thylakoid membrane. The first electron acceptor in the case of photosystem I is Cytochrome.
Photosynthetically active radiation is represented by the range of wavelength of [1996, 2004, 05]- a)340-450 nm
- b)400-700 nm
- c)500-600 nm
- d)400-950 nm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthetically active radiation is represented by the range of wavelength of [1996, 2004, 05]
a)
340-450 nm
b)
400-700 nm
c)
500-600 nm
d)
400-950 nm

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Photosynthesis takes place only in the visible part (400 - 700 nm wavelength) of electromagnetic radiations. Hence this component comprises the photosynthetically active radiation.
Which pair is wrong? [2001]- a)C3 – Maize
- b)C4 – Kranz anatomy
- c)Calvin cycle – PGA
- d)Hatch and Slack Pathway – Oxalo acetic Acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which pair is wrong? [2001]
a)
C3 – Maize
b)
C4 – Kranz anatomy
c)
Calvin cycle – PGA
d)
Hatch and Slack Pathway – Oxalo acetic Acid

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
Maize is a C4 plant carrying out Hatch and Slack pathway. These plants show Kranz anatomy and overcome photorespiration.
In photosynthesis energy from light reaction to dark reaction is transferred in the form of [2002]
- a)ADP
- b)ATP
- c)RuDP
- d)Chlorophyll
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In photosynthesis energy from light reaction to dark reaction is transferred in the form of [2002]
a)
ADP
b)
ATP
c)
RuDP
d)
Chlorophyll

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
ATP molecules produced in the light reaction are used in the dark reaction to fix CO2 to form organic compound.
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in: [2005]- a)grana
- b)pyrenoid
- c)stroma
- d)both grana and stroma
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Chlorophyll in chloroplasts is located in: [2005]
a)
grana
b)
pyrenoid
c)
stroma
d)
both grana and stroma

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Internally a chloroplast contains a matrix or stroma which is similar to cytoplasm in its constitution. It contains DNA, RNA, ribsomes, enzymes for CO2 assimilation, proteins, starch grains and fat droplets or plastoglobuli.
In the matrix or stroma embedded a number of flattened membranous sacs called thylakoids or lamellae. At places the thylakoids are aggregated to form stacks called grana.
In the matrix or stroma embedded a number of flattened membranous sacs called thylakoids or lamellae. At places the thylakoids are aggregated to form stacks called grana.
Chapter doubts & questions for Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - NEET Past Year Papers 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants - NEET Past Year Papers in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup