All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions >
All Questions
All questions of Principles of Inheritance & Variation for NEET Exam
Match column -I with column-ii and select the correct option from the codes given below
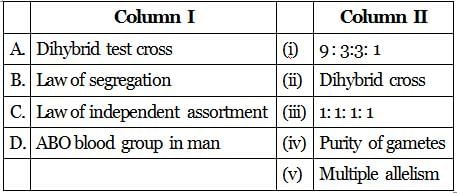
- a)A - (i), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (v)
- b)A - (i), B - (iv), C - (ii), D - (v)
- c)A - (iii), B - (ii), C - (iv), D - (v)
- d)A - (ii), B - (v), C - (iii), D - (i)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column -I with column-ii and select the correct option from the codes given below

a)
A - (i), B - (iv), C - (iii), D - (v)
b)
A - (i), B - (iv), C - (ii), D - (v)
c)
A - (iii), B - (ii), C - (iv), D - (v)
d)
A - (ii), B - (v), C - (iii), D - (i)

|
Lead Academy answered |
Dihybrid Cross is a genetic cross or breeding experiment in which two individuals or parent organisms that differ in two specific traits or alleles are crossed to observe the inheritance patterns of these traits in their offspring.
Law of Segregation, proposed by Gregor Mendel, is one of the fundamental principles of classical genetics. It states that during the formation of gametes (sperm and egg cells), the two alleles (gene variants) for a given trait segregate or separate from each other, with each gamete receiving one allele. This law is also known as 'Law of Purity of Gametes'.
Law of Independent Assortment, also formulated by Gregor Mendel, is another fundamental principle of genetics. It states that genes located on different, non-homologous chromosomes segregate independently during the formation of gametes. In other words, the inheritance of one gene does not affect the inheritance of another gene, assuming they are located on different chromosomes. This law contributes to the genetic diversity of offspring by allowing for the assortment of different combinations of alleles. Dihybrid crosses are used to study the independent assortment of genes located on different chromosomes and help determine the probability of particular combinations of traits occurring in the offspring.
ABO Blood Group in Humans, is a classification system for human blood types based on the presence or absence of specific antigens (A and B) on the surface of red blood cells. This is an example of multiple allelism. This system is one of the most important in blood transfusion and transplantation medicine. There are four main blood types in the ABO system:
- Type A: Red blood cells have A antigens on their surface.
- Type B: Red blood cells have B antigens on their surface.
- Type AB: Red blood cells have both A and B antigens on their surface.
- Type O: Red blood cells have neither A nor B antigens on their surface.
Number of autosomes present in liver cells of a human female is- a)22 autosomes
- b)22 pairs
- c)23 autosomes
- d)23 pairs
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Number of autosomes present in liver cells of a human female is
a)
22 autosomes
b)
22 pairs
c)
23 autosomes
d)
23 pairs
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
In humans, number of autosomes are 2n = 44 or 22 pairs regardless of the sex.
What can be the blood group of offspring when both parents have AB blood group? - a)AB only
- b)A, B and AB
- c)A, B, AB and O
- d)A and B only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What can be the blood group of offspring when both parents have AB blood group?
a)
AB only
b)
A, B and AB
c)
A, B, AB and O
d)
A and B only
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
When both parents have blood group AB(IAIB) then offsprings can have blood groups A(IAIA),B(IBIB) or AB(IAIB) but not O as allele i is not present in any of the parents.
In maize, coloured endosperm (C) is dominant over colourless (c); and full endosperm (R) is dominant over shrunken (r). When a dihybrid of F1 generation were test crossed, it produced four phenotypes in the following percentage:Coloured full 48%, Coloured shrunken 5%,
Colourless full 7%, and Colourless shrunken 40%.From this data, what will be the distance between two non-allelic genes?- a)48 units
- b)5 units
- c)7 units
- d)12 units
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In maize, coloured endosperm (C) is dominant over colourless (c); and full endosperm (R) is dominant over shrunken (r). When a dihybrid of F1 generation were test crossed, it produced four phenotypes in the following percentage:
Coloured full 48%, Coloured shrunken 5%,
Colourless full 7%, and Colourless shrunken 40%.
Colourless full 7%, and Colourless shrunken 40%.
From this data, what will be the distance between two non-allelic genes?
a)
48 units
b)
5 units
c)
7 units
d)
12 units
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Given that recombination percentage is 7% and 5%, therefore, total recombinants would be 7 + 5 = 12%. It is known that one map unit is the distance that yields 1% recombinant chromosomes. Hence the distance between two non-allelic genes is 12 map units.
The percentage of ab gamete produced by AaBb parent will be- a)25%
- b)50%
- c)75%
- d)12.5%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The percentage of ab gamete produced by AaBb parent will be
a)
25%
b)
50%
c)
75%
d)
12.5%
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Gametes produced by AaBb parent would be 25 % AB, 25 % aB, 25 % Ab and 25 % ab.
The characters which appear in the first filial generation are called- a)recessive characters
- b)dominant characters
- c)holandric characters
- d)lethal characters
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The characters which appear in the first filial generation are called
a)
recessive characters
b)
dominant characters
c)
holandric characters
d)
lethal characters
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
In heterozygous individuals or hybrids, out of the two factors or alleles representing the alternate traits of a character, one is dominant and expresses itself in the hybrid or F1 generation. The other factor or allele is recessive and does not show its effect in the heterozygous individual (Principle of dominance).
In mice, black coat colour (allele B) is dominant to brown coat colour (allele b). The offspring of a cross between a black mouse (BB) and a brown mouse (bb) were allowed to interbreed. What percentage of the progeny would have black coats?- a)25%
- b)50%
- c)75%
- d)100%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In mice, black coat colour (allele B) is dominant to brown coat colour (allele b). The offspring of a cross between a black mouse (BB) and a brown mouse (bb) were allowed to interbreed. What percentage of the progeny would have black coats?
a)
25%
b)
50%
c)
75%
d)
100%
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
The cross between black mouse (BB) and a brown mouse (bb) and the inbreeding of their hybrid progeny is shown below
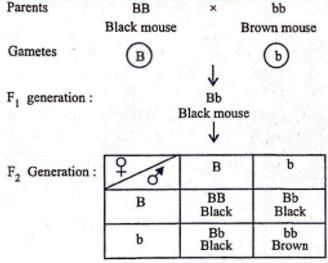
Hence, phenotypic raio is 3 black : 1 brown i.e, 75 % of the progeny would have black coat.
Fused ear lobes appear in the progeny due to an autosomal recessive gene. Work out the genotypes of members in the given pedigree.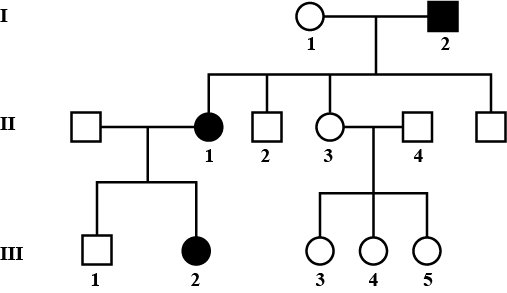
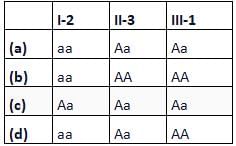
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Fused ear lobes appear in the progeny due to an autosomal recessive gene. Work out the genotypes of members in the given pedigree.


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Given pedigree chart for fused ear lobes (autosomal recessive trait) can be explained as follows:
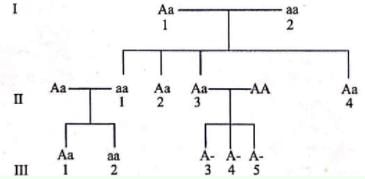
If four o'clock plants, the gene for red flower colour (R) is incompletely dominant over the gene for white flower colour (r), hence the plants heterozygous for flower colour (Rr) have pink flower. What will be the ratio of offsprings in a cross between the red flowers and pink flowers?- a)75% red flower, 25% pink flowers
- b)All red flowers
- c)50% red flowers, 50% pink flowers
- d)Red : pink : white :: 1 : 2 : 1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If four o'clock plants, the gene for red flower colour (R) is incompletely dominant over the gene for white flower colour (r), hence the plants heterozygous for flower colour (Rr) have pink flower. What will be the ratio of offsprings in a cross between the red flowers and pink flowers?
a)
75% red flower, 25% pink flowers
b)
All red flowers
c)
50% red flowers, 50% pink flowers
d)
Red : pink : white :: 1 : 2 : 1
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Incomplete dominance is reported in flowers of Merabilis jalapa (four o' clock)When red flower are crossed with pink flowers 50 % red flowers and 50 % pink flowers are obtained
Choose the correct statement about recombination and linkage- a)Complete linkage results in higher non-parental gene combinations than parental type
- b)Recombination results in the generation of parental gene combinations
- c)Genetic maps are constructed by using the frequency of recombination between gene pairs
- d)T.H. Morgan constructed the first chromosome map
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Complete linkage results in higher non-parental gene combinations than parental type
b)
Recombination results in the generation of parental gene combinations
c)
Genetic maps are constructed by using the frequency of recombination between gene pairs
d)
T.H. Morgan constructed the first chromosome map
|
|
Prashanth Menon answered |
Understanding Genetic Maps and Recombination
Genetic mapping is a fundamental concept in genetics that helps to determine the location of genes on chromosomes. The correct statement among the options given is:
Genetic maps are constructed by using the frequency of recombination between gene pairs.
Explanation of Option C
- **Recombination and Linkage**: Recombination occurs during meiosis when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This process leads to the formation of new allele combinations. The frequency of recombination between two genes is inversely related to their physical distance on a chromosome.
- **Construction of Genetic Maps**: Genetic maps utilize the frequency of recombination to estimate the relative positions of genes. The more frequently two genes recombine, the farther apart they are likely to be. This is quantified as a percentage, known as recombination frequency, which helps in constructing a map.
- **T.H. Morgan's Contribution**: T.H. Morgan was pivotal in demonstrating the principles of linkage and recombination. He used fruit flies (Drosophila) to show how genes are inherited and developed the first chromosome maps based on recombination frequencies.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- **Option A**: Complete linkage results in only parental types, not higher non-parental combinations.
- **Option B**: Recombination generates non-parental combinations rather than parental ones.
- **Option D**: While Morgan constructed the first chromosome map, the statement does not directly relate to the role of recombination frequency, making option C the most accurate.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of recombination in genetic mapping is crucial for grasping how traits are inherited and how genetic diversity arises in populations.
Genetic mapping is a fundamental concept in genetics that helps to determine the location of genes on chromosomes. The correct statement among the options given is:
Genetic maps are constructed by using the frequency of recombination between gene pairs.
Explanation of Option C
- **Recombination and Linkage**: Recombination occurs during meiosis when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material. This process leads to the formation of new allele combinations. The frequency of recombination between two genes is inversely related to their physical distance on a chromosome.
- **Construction of Genetic Maps**: Genetic maps utilize the frequency of recombination to estimate the relative positions of genes. The more frequently two genes recombine, the farther apart they are likely to be. This is quantified as a percentage, known as recombination frequency, which helps in constructing a map.
- **T.H. Morgan's Contribution**: T.H. Morgan was pivotal in demonstrating the principles of linkage and recombination. He used fruit flies (Drosophila) to show how genes are inherited and developed the first chromosome maps based on recombination frequencies.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- **Option A**: Complete linkage results in only parental types, not higher non-parental combinations.
- **Option B**: Recombination generates non-parental combinations rather than parental ones.
- **Option D**: While Morgan constructed the first chromosome map, the statement does not directly relate to the role of recombination frequency, making option C the most accurate.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of recombination in genetic mapping is crucial for grasping how traits are inherited and how genetic diversity arises in populations.
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, when heterozygous Round Yellow are self crossed, Round Green offsprings are represented by the genotype- a)RrYy, RrYY, RRYy
- b)Rryy, Rryy, rryy
- c)rrYy, rrYY
- d)Rryy, RRyy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In Mendelian dihybrid cross, when heterozygous Round Yellow are self crossed, Round Green offsprings are represented by the genotype
a)
RrYy, RrYY, RRYy
b)
Rryy, Rryy, rryy
c)
rrYy, rrYY
d)
Rryy, RRyy
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
A typical Mendelian dihybrid cross between yellow round (dominant) and green wrinkled (recessive plants) can be represented as follows:
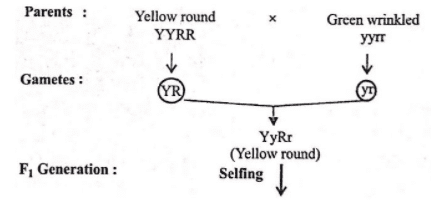
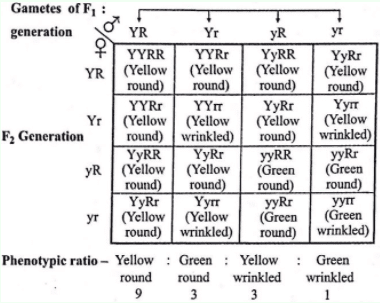
Thus, round green (green round) offsprings are represented by genotypes yyRR and yyRr (or RRyy and Rryy).
A man having the genotype EEFfGgHH can produce P number of genetically different sperms, and a woman of genotype liLLMmNn can generate Q number of genetically different eggs. Determine the values P and Q.- a)P = 4, Q = 4
- b)P = 4,Q = 8
- c)P = 8, Q = 4
- d)P = 8,Q = 8
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A man having the genotype EEFfGgHH can produce P number of genetically different sperms, and a woman of genotype liLLMmNn can generate Q number of genetically different eggs. Determine the values P and Q.
a)
P = 4, Q = 4
b)
P = 4,Q = 8
c)
P = 8, Q = 4
d)
P = 8,Q = 8
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
Types of gametes = 2n, where n is number of heterozygous loci. Thus, man will produe 22 = 4 types of gametes and woman will produce 23 = 8 types of gametes.
A child has blood group O. If the father has blood group A and mother blood group B, work out the genotypes of the parents- a)IAIA and iBi
- b)IAi and IBi
- c)IAi and ii
- d)ii and IBIB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A child has blood group O. If the father has blood group A and mother blood group B, work out the genotypes of the parents
a)
I
AIA and iBib)
IAi and IBi
c)
IAi and ii
d)
ii and IBIB
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
If father has blood group 'A', mother has blood group 'B', and the child with blood group 'O' appears in progeny, this means that the parents are heterozygous.
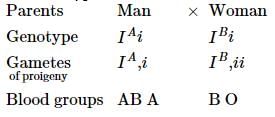
In Antirrhinum (dog flower), phenotypic ratio in F2 generation for the inheritance of flower colour would be- a)3:1
- b)1:2:1
- c)1:1
- d)2:1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Antirrhinum (dog flower), phenotypic ratio in F2 generation for the inheritance of flower colour would be
a)
3:1
b)
1:2:1
c)
1:1
d)
2:1
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The inheritance of flower colour in the Antirrhinum majus (snapdragon or dog flower) is an example of incomplete or partial dominance. Incomplete dominance is the phenomenon in which neither of the two alleles of a gene is completely dominant over the other. In a cross between true-breeding redflowered (RR) and true-breeding white-flowered plants (rr), the F1 plants obtained were pink (Rr) coloured. When the F1 plants were self-pollinated, the F2 generation resulted in the ratio, 1(RR) Red : 2(Rr) Pink : 1(rr) White. The phenotypic ratios had changed from the normal 3:1 dominant : recessive ratio to 1:2:1. R was not completely dominant over r and this made it possible to distinguish Rr (pink) from RR (red) and rr (white).
Law of independent assortment can be explained with the help of- a)dihybrid cross
- b)test cross
- c)back cross
- d)monohybrid cross
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Law of independent assortment can be explained with the help of
a)
dihybrid cross
b)
test cross
c)
back cross
d)
monohybrid cross
|
|
Bhavya Pillai answered |
Explanation of Law of Independent Assortment with Dihybrid Cross:
Dihybrid Cross:
In a dihybrid cross, two different traits are studied simultaneously. For example, if we consider pea plants, we can study the inheritance of seed color (yellow or green) and seed shape (round or wrinkled) at the same time.
Law of Independent Assortment:
According to the law of independent assortment, alleles of different genes assort independently of each other during gamete formation. This means that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another trait.
Illustration with Dihybrid Cross:
When we perform a dihybrid cross between two heterozygous pea plants (YyRr x YyRr), where Y stands for yellow seed color, y stands for green seed color, R stands for round seed shape and r stands for wrinkled seed shape, we can observe the law of independent assortment in action.
Outcome of Dihybrid Cross:
The offspring of the dihybrid cross will exhibit a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, which means that 9 individuals will have both dominant traits, 3 individuals will have one dominant and one recessive trait, 3 individuals will have the other pair of dominant and recessive traits, and 1 individual will have both recessive traits.
Conclusion:
By observing the phenotypic ratio in the offspring of a dihybrid cross, we can understand how the law of independent assortment works. This phenomenon demonstrates how genes located on different chromosomes are inherited independently of each other, following Mendel's principles of inheritance.
Dihybrid Cross:
In a dihybrid cross, two different traits are studied simultaneously. For example, if we consider pea plants, we can study the inheritance of seed color (yellow or green) and seed shape (round or wrinkled) at the same time.
Law of Independent Assortment:
According to the law of independent assortment, alleles of different genes assort independently of each other during gamete formation. This means that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of another trait.
Illustration with Dihybrid Cross:
When we perform a dihybrid cross between two heterozygous pea plants (YyRr x YyRr), where Y stands for yellow seed color, y stands for green seed color, R stands for round seed shape and r stands for wrinkled seed shape, we can observe the law of independent assortment in action.
Outcome of Dihybrid Cross:
The offspring of the dihybrid cross will exhibit a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, which means that 9 individuals will have both dominant traits, 3 individuals will have one dominant and one recessive trait, 3 individuals will have the other pair of dominant and recessive traits, and 1 individual will have both recessive traits.
Conclusion:
By observing the phenotypic ratio in the offspring of a dihybrid cross, we can understand how the law of independent assortment works. This phenomenon demonstrates how genes located on different chromosomes are inherited independently of each other, following Mendel's principles of inheritance.
Read the given statements and select the correct option
Statement 1: The law of segregation is one of the most important contributions to the biology
Statement 2: It introduced the concept of heredity factors as discrete physical entities which do not become blended.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option
Statement 1: The law of segregation is one of the most important contributions to the biology
Statement 2: It introduced the concept of heredity factors as discrete physical entities which do not become blended.
Statement 1: The law of segregation is one of the most important contributions to the biology
Statement 2: It introduced the concept of heredity factors as discrete physical entities which do not become blended.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The principlem of segregation is the most fundamental principle of heredity that has universal application with no exception. Some workers like Bateson call the principal of segregation as the principle of purity of gametes because segregation of the two Mendelian factors of a trait result result in ametes receiving only one factor out of a pair. As a result gametes are always pure for a character. It is also known as law of non-mixing of alleles and can be demostrated through a monohybrid cross.
Andalusian fowls have two pure forms — black and white. If black forms (BB) and white forms (WW) are crossed, F1 individuals appear blue coloured (BW), due to incomplete dominance. Which of the following would be an outcome of a cross between black form and blue form?- a)1 Black : 2 Blue : 1 White
- b)2 Black : 1 Blue
- c)1 Black : 2 Blue
- d)1 Black : 1 Blue
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Andalusian fowls have two pure forms — black and white. If black forms (BB) and white forms (WW) are crossed, F1 individuals appear blue coloured (BW), due to incomplete dominance. Which of the following would be an outcome of a cross between black form and blue form?
a)
1 Black : 2 Blue : 1 White
b)
2 Black : 1 Blue
c)
1 Black : 2 Blue
d)
1 Black : 1 Blue
|
|
Meera Singh answered |
The cross between blue (BW) and black (BB) forms can be shown as :
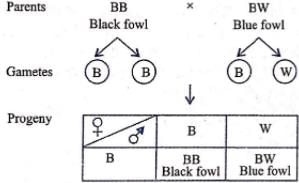
Thus, black and blue individuals are produced in the ratio of 1:1
What is the probability of production of dwarf offsprings in a cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants?- a)Zero
- b)50%
- c)25%
- d)100%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the probability of production of dwarf offsprings in a cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants?
a)
Zero
b)
50%
c)
25%
d)
100%
|
|
Moumita Datta answered |
The probability of production of dwarf offspring in a cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants can be determined using the principles of Mendelian genetics and Punnett squares.
Mendelian Genetics and Punnett Squares:
Mendelian genetics is the study of how traits are inherited from one generation to the next. It is based on the principles proposed by Gregor Mendel, who performed experiments with pea plants in the 19th century. Mendel's laws state that traits are determined by genes, and these genes are inherited in predictable patterns.
A Punnett square is a tool used to determine the possible combinations of alleles (alternative forms of a gene) that can be produced from a cross between two individuals. It allows us to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
Cross Between Two Heterozygous Tall Pea Plants:
In this case, both pea plants are heterozygous for the tall trait. The tall trait is dominant over the dwarf trait, where T represents the allele for tall and t represents the allele for dwarf.
The genotypes of the two parents can be represented as follows:
Parent 1: Tt
Parent 2: Tt
Creating a Punnett Square:
To determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring, we can create a Punnett square.
T t
T TT Tt
t Tt tt
Possible Combinations:
From the Punnett square, we can see that there are four possible combinations of alleles in the offspring:
- 1 TT (tall)
- 2 Tt (tall)
- 1 tt (dwarf)
Probability of Dwarf Offspring:
Out of the four possible combinations, only one combination (tt) represents the dwarf phenotype. Therefore, the probability of producing a dwarf offspring is 1 out of 4 possible combinations, which is 1/4 or 25%.
Conclusion:
The probability of production of dwarf offspring in a cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants is 25%. This is because the dwarf trait is recessive, and both parents carry one copy of the recessive allele.
Mendelian Genetics and Punnett Squares:
Mendelian genetics is the study of how traits are inherited from one generation to the next. It is based on the principles proposed by Gregor Mendel, who performed experiments with pea plants in the 19th century. Mendel's laws state that traits are determined by genes, and these genes are inherited in predictable patterns.
A Punnett square is a tool used to determine the possible combinations of alleles (alternative forms of a gene) that can be produced from a cross between two individuals. It allows us to determine the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring.
Cross Between Two Heterozygous Tall Pea Plants:
In this case, both pea plants are heterozygous for the tall trait. The tall trait is dominant over the dwarf trait, where T represents the allele for tall and t represents the allele for dwarf.
The genotypes of the two parents can be represented as follows:
Parent 1: Tt
Parent 2: Tt
Creating a Punnett Square:
To determine the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring, we can create a Punnett square.
T t
T TT Tt
t Tt tt
Possible Combinations:
From the Punnett square, we can see that there are four possible combinations of alleles in the offspring:
- 1 TT (tall)
- 2 Tt (tall)
- 1 tt (dwarf)
Probability of Dwarf Offspring:
Out of the four possible combinations, only one combination (tt) represents the dwarf phenotype. Therefore, the probability of producing a dwarf offspring is 1 out of 4 possible combinations, which is 1/4 or 25%.
Conclusion:
The probability of production of dwarf offspring in a cross between two heterozygous tall pea plants is 25%. This is because the dwarf trait is recessive, and both parents carry one copy of the recessive allele.
Mendel law of independent assortment does not hold true for the genes that are located closely on- a)same chromosome
- b)non-homologous chromosomes
- c)X - chromosome
- d)autosomes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mendel law of independent assortment does not hold true for the genes that are located closely on
a)
same chromosome
b)
non-homologous chromosomes
c)
X - chromosome
d)
autosomes
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
As per linkage experiments carried out by Morgan, the two linked genes do not always segregate independently of each other and F2 ratio deviated very significantly from 9:3:3:1 ratio (expected when two genes are independent). Hence, if linkage was known at the time of Mendel, he would riot have been able to explain law of independent assortment.
What will be the distribution of phenotypic features in the first filial generation after a cross between a homozygous female and a heterozygous male for a single locus?- a)3:1
- b)1:2:1
- c)1:1
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the distribution of phenotypic features in the first filial generation after a cross between a homozygous female and a heterozygous male for a single locus?
a)
3:1
b)
1:2:1
c)
1:1
d)
None of these
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
F1 or first filial or progeny is the generation of hybrids produced from a cross between the genetically different individuals called parents. A cross between homozygous and heterozygous parents for a single locus will produce 1:1 ratio of phenotypic features in F1 generation.
In mice, Y is the dominant allele for yellow fur and y is the recessive allele for grey fur. Since Y is lethal when homozygous, the result of cross Yy x Yy will be- a)3 yellow : 1 grey
- b)2 yellow : 1 grey
- c)1 yellow : 1 grey
- d)1 yellow : 2 grey
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In mice, Y is the dominant allele for yellow fur and y is the recessive allele for grey fur. Since Y is lethal when homozygous, the result of cross Yy x Yy will be
a)
3 yellow : 1 grey
b)
2 yellow : 1 grey
c)
1 yellow : 1 grey
d)
1 yellow : 2 grey
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Given, that Y is dominant for yellow fur and y is recessive for grey fur, the cross between Yy and Yy will produce ratio of 1YY:2Yy:1yy. But as Y is lethal in homozygous condition, hence phenotypic ratio would be 2 yellow (Yy):1 grey (yy).
Today ________ are extensively used as a _______ point in the sequencing of whole genome- a)Pedigree charts, conclusive
- b)Genetic maps, starting
- c)Pedigree charts, starting
- d)Genetic maps, conclusive
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Pedigree charts, conclusive
b)
Genetic maps, starting
c)
Pedigree charts, starting
d)
Genetic maps, conclusive
|
|
Amar Mehra answered |
Understanding Genetic Maps
Genetic maps are crucial tools in the field of genomics, especially when it comes to sequencing whole genomes.
Definition of Genetic Maps
- Genetic maps represent the arrangement of genes and genetic markers on chromosomes.
- They are based on the frequency of recombination between genetic markers during gamete formation.
Role as a Starting Point
- Genetic maps serve as a foundational resource in genome sequencing projects.
- They help researchers identify the locations of genes and other important sequences, guiding the sequencing process.
Importance in Whole Genome Sequencing
- By providing a reference framework, genetic maps simplify the complex task of sequencing entire genomes.
- They enable the alignment of sequenced data to known genetic locations, enhancing accuracy.
Comparison with Pedigree Charts
- Pedigree charts illustrate family relationships and inheritance patterns but do not provide the genomic context necessary for sequencing.
- They are more useful in genetic counseling and tracing inheritance rather than in the technical aspects of genome sequencing.
Conclusion
- The statement's correct answer is "Genetic maps, starting" because genetic maps are indeed the essential tools that provide a starting point in the sequencing of whole genomes.
- Their utility in mapping genetic information makes them indispensable in modern genetics research.
Overall, understanding the role of genetic maps not only clarifies their significance in sequencing but also highlights their foundational importance in genomic studies.
Genetic maps are crucial tools in the field of genomics, especially when it comes to sequencing whole genomes.
Definition of Genetic Maps
- Genetic maps represent the arrangement of genes and genetic markers on chromosomes.
- They are based on the frequency of recombination between genetic markers during gamete formation.
Role as a Starting Point
- Genetic maps serve as a foundational resource in genome sequencing projects.
- They help researchers identify the locations of genes and other important sequences, guiding the sequencing process.
Importance in Whole Genome Sequencing
- By providing a reference framework, genetic maps simplify the complex task of sequencing entire genomes.
- They enable the alignment of sequenced data to known genetic locations, enhancing accuracy.
Comparison with Pedigree Charts
- Pedigree charts illustrate family relationships and inheritance patterns but do not provide the genomic context necessary for sequencing.
- They are more useful in genetic counseling and tracing inheritance rather than in the technical aspects of genome sequencing.
Conclusion
- The statement's correct answer is "Genetic maps, starting" because genetic maps are indeed the essential tools that provide a starting point in the sequencing of whole genomes.
- Their utility in mapping genetic information makes them indispensable in modern genetics research.
Overall, understanding the role of genetic maps not only clarifies their significance in sequencing but also highlights their foundational importance in genomic studies.
Inheritance of roan coat in cattle is an example of- a)incomplete dominance
- b)codominance
- c)multiple allelism
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inheritance of roan coat in cattle is an example of
a)
incomplete dominance
b)
codominance
c)
multiple allelism
d)
none of these
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Coat colour in short-horned cattle is an exampl of co-dominance. If a cattle with black coat is crossed with a cattle with white coat, the F1 hybrids possess neither black nor white coat colour, but have roan coat colour, where black and white patches appear separately. The effect is produced due to juxtaposition of small patches of red and white colour. Hence the alleles which are able to express themselves independently when present together are called codominant alleles and the inheritance pattern is called co-dominance. On inbreeding, the roan hybrids produce three types of cattle — red, roan and white in the ratio of 1:2:1.
Morgan observed tight linkage in Drosophila with only 1.3 percent recombination for- a)White eye and yellow body
- b)Normal wing and yellow body
- c)White eye and miniature wing
- d)Yellow body and miniature wing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
White eye and yellow body
b)
Normal wing and yellow body
c)
White eye and miniature wing
d)
Yellow body and miniature wing

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Morgan observed that white eye and yellow body traits in Drosophila were very tightly linked, with a low recombination frequency of only 1.3 percent, indicating very close linkage.
What proportion of the offsprings obtained from cross AABBCC x AaBbCc will be completely heterozygous for all the genes segregated independently?- a)1/8
- b)1/4
- c)1/2
- d)1/16
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What proportion of the offsprings obtained from cross AABBCC x AaBbCc will be completely heterozygous for all the genes segregated independently?
a)
1/8
b)
1/4
c)
1/2
d)
1/16
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Since one parent is homozygous AABBCC the genotype formed will be only 1 type i.e. ABC. The other parent is heterozygous for all genes. About 1/8th or 12.5% of total offspring will be heterozygous at all three-locus.
Read the given paragraph to answer
In a certain plant, yellow fruit colour (Y) is dominant to green fruit colour (y) and round shape (R) is dominant to oval shape (r). The two genes involved are located on different chromosomes.Which of the following is correct for the condition when plant YyRr is back crossed with the double recessive parent?- a)9:3:3:1 ratio of phenotypes only
- b)9:3:3:1 ratio of genotypes only
- c)1:1:1:1 ratio of phenotypes only
- d)1:1:1:1 ratio of phenotypes and genotypes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given paragraph to answer
In a certain plant, yellow fruit colour (Y) is dominant to green fruit colour (y) and round shape (R) is dominant to oval shape (r). The two genes involved are located on different chromosomes.
In a certain plant, yellow fruit colour (Y) is dominant to green fruit colour (y) and round shape (R) is dominant to oval shape (r). The two genes involved are located on different chromosomes.
Which of the following is correct for the condition when plant YyRr is back crossed with the double recessive parent?
a)
9:3:3:1 ratio of phenotypes only
b)
9:3:3:1 ratio of genotypes only
c)
1:1:1:1 ratio of phenotypes only
d)
1:1:1:1 ratio of phenotypes and genotypes
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
When YyRr is crossed with double recessive parent then genotypic and phenotypic ratio will be 1:1:1:1
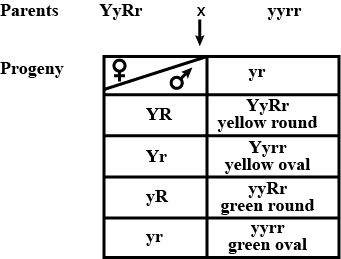
Phenotypic ratio = 1 yellow round : 1 yellow oval : 1 green round : 1 green and oval. This represent a test cross.
Depending upon the distance between any two genes which is inversely proportional to the strength of linkage, cross overs will vary from
- a)50−100%
- b)0−50%
- c)75−100%
- d)100−150%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Depending upon the distance between any two genes which is inversely proportional to the strength of linkage, cross overs will vary from
a)
50−100%
b)
0−50%
c)
75−100%
d)
100−150%
|
|
Isha Khanna answered |
It is not possible to determine the exact number of crossovers based solely on the distance between two genes. The frequency of crossovers is influenced by several factors, including the specific genetic loci involved, the presence of recombination hotspots, and other genetic and environmental factors.
A couple has six daughters. What is the possibility of their having a girl next time?- a)10%
- b)50%
- c)90%
- d)100%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A couple has six daughters. What is the possibility of their having a girl next time?
a)
10%
b)
50%
c)
90%
d)
100%
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
The possibility of having a girl or boy child is equal i.e., 50% as 50% male gametes are Y type and 50% are X type. Fusion of egg with X type sperm will produce a girl child.
Morgan coined the term recombination to describe- a)Physical association of genes on a chromosome
- b)Generation of new traits by mutation
- c)Linkage of two genes on different chromosomes
- d)Generation of non-parental gene combinations
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Physical association of genes on a chromosome
b)
Generation of new traits by mutation
c)
Linkage of two genes on different chromosomes
d)
Generation of non-parental gene combinations

|
Lead Academy answered |
Morgan coined the term "recombination" to describe the generation of new, non-parental gene combinations due to crossing over during meiosis.
question 3 question is incomplete
ChatGPT
Apologies for the incomplete question. Here is the revised and complete version of
question 3 question is incomplete
ChatGPT
Apologies for the incomplete question. Here is the revised and complete version of
Which of the following statements accurately describes linked genes?- a)Linked genes are located near each other on the same chromosome, violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate together during meiosis.
- b)Linked genes are located on different chromosomes, violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate independently.
- c)Linked genes are located near each other on the same chromosome, do not violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate independently.
- d)Linked genes are located on different chromosomes, do not violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate together during meiosis.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Linked genes are located near each other on the same chromosome, violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate together during meiosis.
b)
Linked genes are located on different chromosomes, violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate independently.
c)
Linked genes are located near each other on the same chromosome, do not violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate independently.
d)
Linked genes are located on different chromosomes, do not violate the law of independent assortment, and segregate together during meiosis.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Linked genes are those located near each other on the same chromosome. This proximity means that they do not assort independently and tend to segregate together during meiosis, which violates the law of independent assortment. Thus, Option A accurately describes linked genes.
Linkage was described by Morgan in Drosophila. Which of the following combinations are correct?- a)(ii), (iv), (v)
- b)(i), (iii)
- c)(i), (iii), (v)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
(ii), (iv), (v)
b)
(i), (iii)
c)
(i), (iii), (v)
d)
(i) and (iv)

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Morgan observed that in his experiments with Drosophila, the F2 generation did not exhibit the expected 9:3:3:1 ratio due to linkage, with parental combinations being more frequent than recombinants. He attributed linkage to the physical association of genes on the same chromosome, not their chemical association. Thus, options (i) and (iii) are correct.
What is incorrect for genetic maps?- a)Alfred Sturtevant prepared it for the first time using monohybrid test cross
- b)It is a measure of the distance between genes present on the same chromosome
- c)Stronger the linkage lesser is the distance between two genes
- d)It was extensively used in the case of the Human Genome Sequencing Project
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Alfred Sturtevant prepared it for the first time using monohybrid test cross
b)
It is a measure of the distance between genes present on the same chromosome
c)
Stronger the linkage lesser is the distance between two genes
d)
It was extensively used in the case of the Human Genome Sequencing Project

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
Genetic maps are indeed a measure of gene distance on the same chromosome, and they are used in genome sequencing projects. The incorrect statement is Option A, as Alfred Sturtevant used a dihybrid test cross to create genetic maps, not a monohybrid test cross.
"When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters." The statement is independent of the other pair of characters. The statement explains which of the following laws/principles of Mendel?- a)Principle of paired factors
- b)Principle of dominance
- c)Law of segregation
- d)Law of independent assortment
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
"When two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters." The statement is independent of the other pair of characters. The statement explains which of the following laws/principles of Mendel?
a)
Principle of paired factors
b)
Principle of dominance
c)
Law of segregation
d)
Law of independent assortment
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Cross involving two contrasting character is called dihybrid cross or a two factor cross. The two factors of each trait assort at random and independent of the factors of other traits at the time of meiosis (gametogenesis) and get randomly as well as independently rearranged in the offspring producing both parental and new combinations of traits. This forms the basis of the law of independent assortment given by Mendel.
Genes which code for a pair of contrasting traits are known as- a)dominant genes
- b)alleles
- c)linked genes
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Genes which code for a pair of contrasting traits are known as
a)
dominant genes
b)
alleles
c)
linked genes
d)
none of these
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Genes are the units of inheritance and contain the information that is required to express a particular trait in an organism. Alternating form if a single gene which code for pair of contrasting traits are known as alleles, i.e, tall and drawf are alleles determining the height of pea plant.
A tobacco plant heterozygous for a recessive character is self-pollinated and 1200 seeds are subsequently germinated. Flow many seedlings would have the parental genotype?- a)1250
- b)600
- c)300
- d)2250
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A tobacco plant heterozygous for a recessive character is self-pollinated and 1200 seeds are subsequently germinated. Flow many seedlings would have the parental genotype?
a)
1250
b)
600
c)
300
d)
2250
|
|
Anshika Ahuja answered |
Given information:
- A tobacco plant is heterozygous for a recessive character.
- The plant is self-pollinated.
- 1200 seeds are germinated.
To solve the problem, we need to use the principles of Mendelian genetics and Punnett squares.
Step-by-step solution:
1. Write down the genotype of the parent plant:
- Let's use A to represent the dominant allele and a to represent the recessive allele. The parent plant is heterozygous, so its genotype is Aa.
2. Create a Punnett square to show the possible gametes and offspring:
| | A | a |
|----|---|---|
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | aA | aa |
- Each box represents a possible offspring genotype that can result from the combination of the parent's gametes.
- The probability of each genotype occurring can be calculated by multiplying the probabilities of the corresponding gametes.
3. Determine the probability of each genotype:
- In this case, we want to know the probability of the parental genotype (Aa) occurring.
- We can see from the Punnett square that there are two Aa offspring genotypes out of four possible genotypes, so the probability is 2/4 or 1/2.
4. Calculate the number of offspring with the parental genotype:
- We know that there are 1200 seeds germinated, so we can use the probability we calculated in step 3 to find the expected number of Aa offspring.
- Expected number of Aa offspring = probability of Aa genotype x total number of offspring
- Expected number of Aa offspring = 1/2 x 1200 = 600
5. Choose the correct answer:
- The question asks how many seedlings would have the parental genotype, which is Aa.
- From step 4, we know that the expected number of Aa offspring is 600. Therefore, the correct answer is B, 600.
- A tobacco plant is heterozygous for a recessive character.
- The plant is self-pollinated.
- 1200 seeds are germinated.
To solve the problem, we need to use the principles of Mendelian genetics and Punnett squares.
Step-by-step solution:
1. Write down the genotype of the parent plant:
- Let's use A to represent the dominant allele and a to represent the recessive allele. The parent plant is heterozygous, so its genotype is Aa.
2. Create a Punnett square to show the possible gametes and offspring:
| | A | a |
|----|---|---|
| A | AA | Aa |
| a | aA | aa |
- Each box represents a possible offspring genotype that can result from the combination of the parent's gametes.
- The probability of each genotype occurring can be calculated by multiplying the probabilities of the corresponding gametes.
3. Determine the probability of each genotype:
- In this case, we want to know the probability of the parental genotype (Aa) occurring.
- We can see from the Punnett square that there are two Aa offspring genotypes out of four possible genotypes, so the probability is 2/4 or 1/2.
4. Calculate the number of offspring with the parental genotype:
- We know that there are 1200 seeds germinated, so we can use the probability we calculated in step 3 to find the expected number of Aa offspring.
- Expected number of Aa offspring = probability of Aa genotype x total number of offspring
- Expected number of Aa offspring = 1/2 x 1200 = 600
5. Choose the correct answer:
- The question asks how many seedlings would have the parental genotype, which is Aa.
- From step 4, we know that the expected number of Aa offspring is 600. Therefore, the correct answer is B, 600.
Refer the given statements and select the correct option,
(i) Percentage of homozygous dominant individuals obtained by selfing Aa individuals is 25%.
(ii) Types of genetically different gametes produced by genotype AABbcc are 2.
(iii) Phenotypic ratio of monohybrid F2 progeny in case of Mirabilis jalapa is 3:1.- a)All the statements are true
- b)Statements (i) and (ii) are true, but statement (iii) is false
- c)Statements (i) and (iii) are true, but statement (ii) is false
- d)Statements (ii) and (iii) are true, but statement (i) is false
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer the given statements and select the correct option,
(i) Percentage of homozygous dominant individuals obtained by selfing Aa individuals is 25%.
(ii) Types of genetically different gametes produced by genotype AABbcc are 2.
(iii) Phenotypic ratio of monohybrid F2 progeny in case of Mirabilis jalapa is 3:1.
(i) Percentage of homozygous dominant individuals obtained by selfing Aa individuals is 25%.
(ii) Types of genetically different gametes produced by genotype AABbcc are 2.
(iii) Phenotypic ratio of monohybrid F2 progeny in case of Mirabilis jalapa is 3:1.
a)
All the statements are true
b)
Statements (i) and (ii) are true, but statement (iii) is false
c)
Statements (i) and (iii) are true, but statement (ii) is false
d)
Statements (ii) and (iii) are true, but statement (i) is false
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
The phenotypic ratio of monohybrid F2 generation in case of Mirabilis jalapa is 1 Red : 2 Pink : 1 White, due to incomplete dominance.
XO type of sex determination and XY type of sex determination are the examples of- a)male heterogamety
- b)female heterogamety
- c)male homogamety
- d)both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
XO type of sex determination and XY type of sex determination are the examples of
a)
male heterogamety
b)
female heterogamety
c)
male homogamety
d)
both (b) and (c)
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In XO type and XY type sex determining mechanisms, males produce two different types of gametes, (a) either with or without X-chromosome (XO type), (b) some gametes with X-chromosome and some with Y-chromosome (XY type). Such type of sex determination mechanism is designated to be the example of male heterogamety. In both, females are homogametic and produce X type of gametes in both the cases and have XX genotype.
Select the incorrect statement regarding pedigree analysis- a)Solid symbols show unaffected individuals
- b)Proband is the person from which case history starts
- c)It is useful for genetic counsellors
- d)It is an alalysis of traits in several generations of a family
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement regarding pedigree analysis
a)
Solid symbols show unaffected individuals
b)
Proband is the person from which case history starts
c)
It is useful for genetic counsellors
d)
It is an alalysis of traits in several generations of a family
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In pedigree analysis, solid symbol shows affected individuals.
If both parents are carriers for thalassaemia, which is an autosomal recessive disorder, what are the chances of pregnancy resulting in an affected child?- a)25%
- b)100%
- c)No chance
- d)50%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If both parents are carriers for thalassaemia, which is an autosomal recessive disorder, what are the chances of pregnancy resulting in an affected child?
a)
25%
b)
100%
c)
No chance
d)
50%
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Thalassemia-autosomal-linked recessive
AA-Normal
Aa-Carrier
aa-Disease
Affected = 1/4 = 25%
An autosomal recessive disorder like thalassemia is caused by abnormalities in both members of a pair of genes. Both parents may carry a single dose of the gene on one chromosome but have a normal gene on the other chromosome, which prevents the appearance of the disease in the carrier parent. A child must get one abnormal gene from each parent in order to be affected by the disease. Parents who are both carriers of an autosomal recessive disorder have a 25% risk of producing an offspring affected by the disease and a 50% risk of producing normal-appearing carriers.
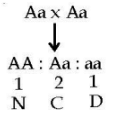
AA-Normal
Aa-Carrier
aa-Disease
Affected = 1/4 = 25%
An autosomal recessive disorder like thalassemia is caused by abnormalities in both members of a pair of genes. Both parents may carry a single dose of the gene on one chromosome but have a normal gene on the other chromosome, which prevents the appearance of the disease in the carrier parent. A child must get one abnormal gene from each parent in order to be affected by the disease. Parents who are both carriers of an autosomal recessive disorder have a 25% risk of producing an offspring affected by the disease and a 50% risk of producing normal-appearing carriers.
Which of the following is incorrect regarding ZW-ZZ type of sex determination?- a)It occurs in birds and some reptiles
- b)Females are homogametic and males are heterogametic
- c)1:1 sex ratio is produced in the offsprings
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is incorrect regarding ZW-ZZ type of sex determination?
a)
It occurs in birds and some reptiles
b)
Females are homogametic and males are heterogametic
c)
1:1 sex ratio is produced in the offsprings
d)
All of these
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
In ZW - ZZ type of sex determination, the male has two homomorphic sex chromosomes (ZZ) and is homogametic, and the female has two heteromorphic sex chromosomes (ZW) and is heterogametic. There are, thus, two types of eggs : with Z and with W, and only one type of sperms, i.e., each with Z. Fertilisation of an egg with Z chromosome by a sperm with Z chromosome gives a zygote with ZZ chromosomes (male). Fertilisation of an egg with W chromosome by a sperm with Z chromosome yields a zygote with ZW chromosomes (female). This mechanism operates in some vertebrates (fishes, reptiles and birds).
An allele is said to be recessive, when it is expressed in- a)heterozygous condition only
- b)homozygous condition only
- c)F3 generation
- d)both homozygous and heterozygous conditions
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An allele is said to be recessive, when it is expressed in
a)
heterozygous condition only
b)
homozygous condition only
c)
F3 generation
d)
both homozygous and heterozygous conditions
|
|
Nilanjan Kapoor answered |
Understanding Recessive Alleles
Recessive alleles are a fundamental concept in genetics. They play a crucial role in determining phenotypes, or observable traits, of an organism.
Definition of Recessive Alleles
- An allele is termed "recessive" when its effects are masked by the presence of a dominant allele in a heterozygous condition.
- For a recessive allele to manifest its traits, it must be present in a homozygous condition, meaning two copies of the recessive allele are required.
Homozygous vs. Heterozygous Conditions
- Homozygous Condition:
- An organism possesses two identical alleles for a particular gene (e.g., aa).
- The recessive trait is expressed when both alleles are recessive.
- Heterozygous Condition:
- An organism carries one dominant and one recessive allele (e.g., Aa).
- The dominant allele will overshadow the recessive allele, preventing its expression.
Expression of Recessive Traits
- A recessive trait is only observable in the homozygous condition.
- Therefore, the correct answer to the original question is option 'B', as recessive alleles are expressed only when an individual has two copies of that allele.
Conclusion
Understanding the interaction between dominant and recessive alleles is essential for predicting inheritance patterns in genetics. Recessive traits require a specific genetic configuration (homozygous) to be expressed, distinguishing them from dominant traits, which can manifest even in a single copy.
Recessive alleles are a fundamental concept in genetics. They play a crucial role in determining phenotypes, or observable traits, of an organism.
Definition of Recessive Alleles
- An allele is termed "recessive" when its effects are masked by the presence of a dominant allele in a heterozygous condition.
- For a recessive allele to manifest its traits, it must be present in a homozygous condition, meaning two copies of the recessive allele are required.
Homozygous vs. Heterozygous Conditions
- Homozygous Condition:
- An organism possesses two identical alleles for a particular gene (e.g., aa).
- The recessive trait is expressed when both alleles are recessive.
- Heterozygous Condition:
- An organism carries one dominant and one recessive allele (e.g., Aa).
- The dominant allele will overshadow the recessive allele, preventing its expression.
Expression of Recessive Traits
- A recessive trait is only observable in the homozygous condition.
- Therefore, the correct answer to the original question is option 'B', as recessive alleles are expressed only when an individual has two copies of that allele.
Conclusion
Understanding the interaction between dominant and recessive alleles is essential for predicting inheritance patterns in genetics. Recessive traits require a specific genetic configuration (homozygous) to be expressed, distinguishing them from dominant traits, which can manifest even in a single copy.
Which of the following cross will give tall and dwarf pea plants in same proportions?- a)TT x tt
- b)Tt x tt
- c)TT x Tt
- d)tt x tt
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following cross will give tall and dwarf pea plants in same proportions?
a)
TT x tt
b)
Tt x tt
c)
TT x Tt
d)
tt x tt
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
This is an example of a test cross in which a cross is made between heterozygous tall and homozygous dwarf individuals, tall and dwarf plants are obtained in the same proportions.
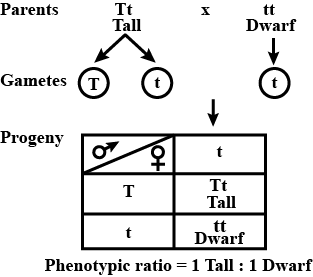
Inheritance of which of the following traits is shown in the given cross?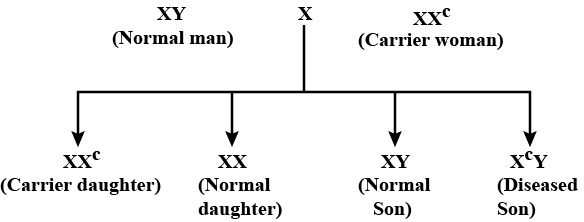
- a)X-linked dominant trait
- b)X-linked recessive trait
- c)Autosomal recessive trait
- d)Autosomal dominant trait
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inheritance of which of the following traits is shown in the given cross?

a)
X-linked dominant trait
b)
X-linked recessive trait
c)
Autosomal recessive trait
d)
Autosomal dominant trait
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
- In the given cross, passing of disease is from carrier female to male progeny (criss-cross inheritance). Any trait that shows criss-cross inheritance is located on the sex chromosome.
- Presence of a single recessive gene i.e. Xc in carrier individuals (XXC) does not cause the disease, thus the trait is recessive.
In fruit flies, the long wing is dominant to the vestigial wing. When heterozygous long-winged flies were crossed with vestigial-winged flies, 192 offsprings were produced. Of these, 101 had long wings and 91 had vestigial wings. If an exact Mendelian ratio had been obtained, then the number of each phenotype would have been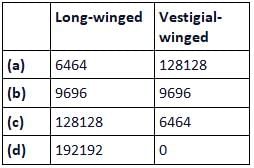
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In fruit flies, the long wing is dominant to the vestigial wing. When heterozygous long-winged flies were crossed with vestigial-winged flies, 192 offsprings were produced. Of these, 101 had long wings and 91 had vestigial wings. If an exact Mendelian ratio had been obtained, then the number of each phenotype would have been

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
A cross between heterozygous long-winged flies and (homozygous) vestigial winged flies represents an example of test cross, in which the exact Mendelian ratio of 1:1 is obtained, i.e. 96 long-winged flies and 96 vestigial winged flies.
Complete the given table showing different possililities of genotypes and their corresponding blood group, by selecting the correct option
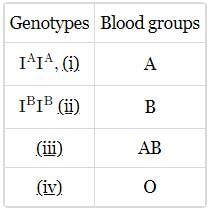
- a)(i) - IAIA, (ii) - IBIB, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - ii
- b)(i) - IAIA, (ii) - IBIB, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - IAi
- c)(i) - IAi, (ii) - IBi, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - ii
- d)(i) - IAi, (ii) - IBi, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - IBi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Complete the given table showing different possililities of genotypes and their corresponding blood group, by selecting the correct option

a)
(i) - IAIA, (ii) - IBIB, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - ii
b)
(i) - IAIA, (ii) - IBIB, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - IAi
c)
(i) - IAi, (ii) - IBi, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - ii
d)
(i) - IAi, (ii) - IBi, (iii) - IAIB, (iv) - IBi
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
- This case where three alleles are present in one gene is called co-dominance, The gene I has three forms and when either A or B is expressed in the gene then either A or B blood group is expressed respectively.
- When both A and B are present then it results in the AB blood group. The i allele represents the recessive form and codes for O blood group and will be expressed only in the dominant recessive genotype expression.
In the following pedigree chart, the mutant trait is shaded black. The gene responsible for the trait is 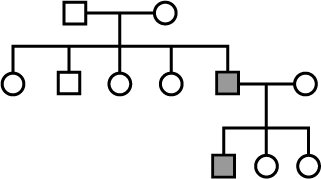
- a)dominant and sex linked
- b)dominant and autosomal
- c)recessive and sex linked
- d)recessive and autosomal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following pedigree chart, the mutant trait is shaded black. The gene responsible for the trait is

a)
dominant and sex linked
b)
dominant and autosomal
c)
recessive and sex linked
d)
recessive and autosomal
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The given trait cannot be sex-linked as sex-linked traits follow criss-cross inheritance and in the given pedigree, no criss-cross inheritance is being followed. The trait exhibited in pedigree chart is autosomal recessive. An autosomal recessive trait appears in case of marriage between two heterozygous individuals (Aa x Aa=3Aa+1aa), a recessive individual with hybrid (Aa x aa=2Aa+2aa) and two recessives (aa x aa= all aa). It expresses its effect only in pure or homozygous state.
If the trait had been controlled by dominant gene, then one of the parent must have possessed the dominant gene and hence the disease.
question 1:
Select the correct statement from the ones given below with respect to dihybrid cross.- a)Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show higher recombinations
- b)Genes far apart on the same chromosome show very few recombinations
- c)Genes loosely linked on the same chromosome show similar recombinations as the tightly linked ones
- d)Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement from the ones given below with respect to dihybrid cross.
a)
Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show higher recombinations
b)
Genes far apart on the same chromosome show very few recombinations
c)
Genes loosely linked on the same chromosome show similar recombinations as the tightly linked ones
d)
Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
In a dihybrid cross, tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations because they are so close together that they tend to be inherited as a unit. This is consistent with Option D, which accurately describes the nature of tightly linked genes. Options A, B, and C do not correctly describe the behavior of linked genes.
True-breeding red-eyed Drosophila flies with plain thoraxes were crossed with pink-eyed flies with striped thoraxesRed eye plain thorax × Pink eye striped thoraxThe F1 flies were then test crossed against the double recessive.
The following F2 generation resulted from the cross: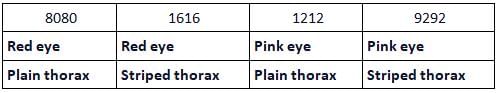 What percentage number of recombinants resulted from the test cross ?
What percentage number of recombinants resulted from the test cross ?- a)12
- b)14
- c)16
- d)28
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
True-breeding red-eyed Drosophila flies with plain thoraxes were crossed with pink-eyed flies with striped thoraxes
Red eye plain thorax × Pink eye striped thorax
The F1 flies were then test crossed against the double recessive.
The following F2 generation resulted from the cross:
The following F2 generation resulted from the cross:

What percentage number of recombinants resulted from the test cross ?
a)
12
b)
14
c)
16
d)
28
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Recombinants obtained from the cross are 16 red eye striped thorax flies and 12 pink eye plain thorax flies.
Total number of flies =200
Total number of recombinants =28
Therefore, percentage of recombinants
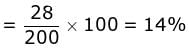
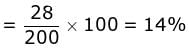
When a cross is made between a tall plant with yellow seeds (Tt Yy) and a tall plant with green seeds (Tt yy), what is true regarding the proportions of phenotypes of the offsprings in F1 generation?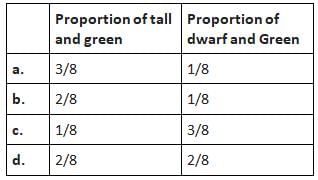
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a cross is made between a tall plant with yellow seeds (Tt Yy) and a tall plant with green seeds (Tt yy), what is true regarding the proportions of phenotypes of the offsprings in F1 generation?

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
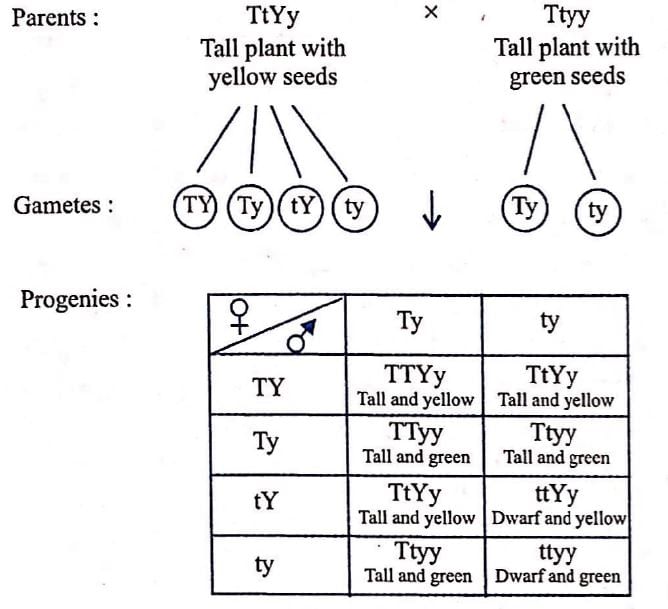
A cross between a tall plant with yellow seeds (TtYy) and a tall plant with green seeds (Ttyy) will be:
Pnenotypic ratio is
Tall and yellow : Tall and green : Dwarf and yellow : Dwarf and green :: 3 : 3: 1: 1 or 3/8, 3/8,1/8,1/8.
Tall and yellow : Tall and green : Dwarf and yellow : Dwarf and green :: 3 : 3: 1: 1 or 3/8, 3/8,1/8,1/8.
Chapter doubts & questions for Principles of Inheritance & Variation - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Principles of Inheritance & Variation - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup