All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Biomolecules for NEET Exam
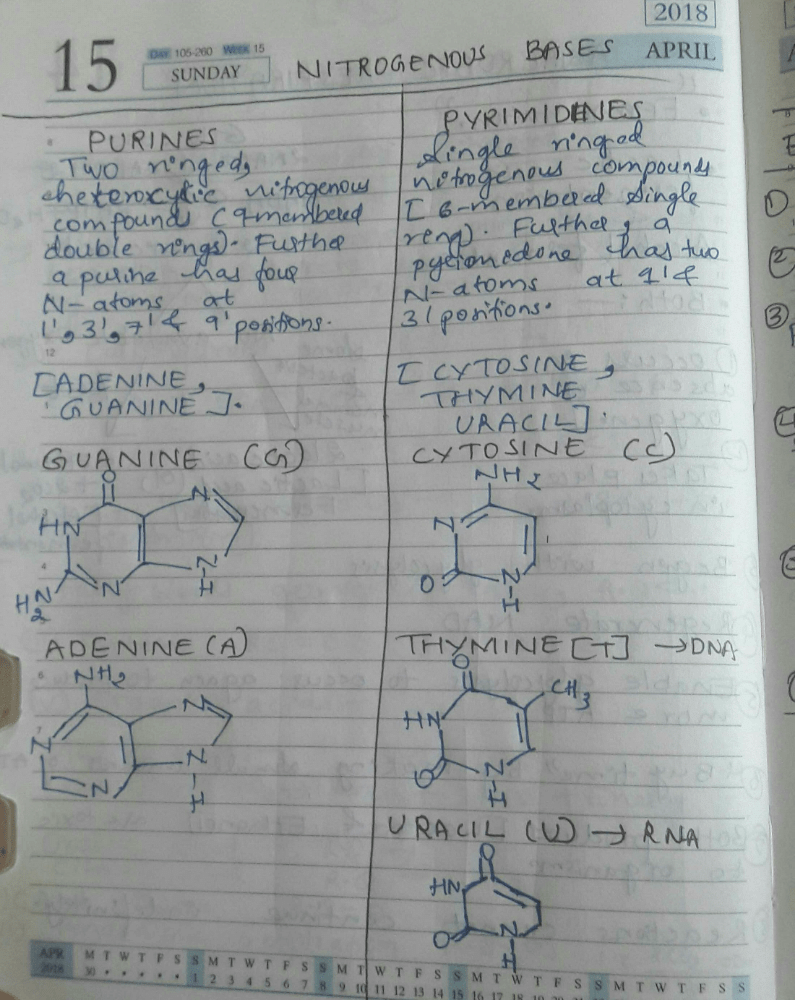
Which is true about enzymes?a)All enzymes are ... moreproteins.b)All proteins are enzymes.c)All enzymes are not proteins.d)All enzymes are vitamins.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Most enzymes are proteins, although a few are catalytic RNA molecules. The latter are called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures.
Cellulose is made up of- a)Fructose
- b)Glucose
- c)Sucrose
- d)Ribose
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cellulose is made up of
a)
Fructose
b)
Glucose
c)
Sucrose
d)
Ribose
|
|
Ayush Chauhan answered |
Cellulose is a third polymer made from beta glucose molecules and the polymer molecules are straight cellulose serves a very different purpose in nature to starch and glycogen it make up the cell walls in plant cell.
The number of amino acids found in proteins are- a)20
- b)21
- c)18
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The number of amino acids found in proteins are
a)
20
b)
21
c)
18
d)
16
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Proteinogenic amino acids are amino acids that are incorporated biosynthetically into proteins during translation. ... Throughout known life, there are 22 genetically encoded (proteinogenic) amino acids, 20 in the standard genetic code and an additional 2 that can be incorporated by special translation mechanisms.
A homopolymer has only one type of building block called a monomer repeated ‘n’ number of times. A heteropolymer has more than one type of monomer. Proteins are heteropolymers made of amino acids. While a nucleic acid like DNA or RNA is made of only 4 types of nucleotide monomers, proteins are made of- a)20 types of monomers
- b)3 types of monomers
- c)40 types of monomers
- d)Only one type of monomer
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A homopolymer has only one type of building block called a monomer repeated ‘n’ number of times. A heteropolymer has more than one type of monomer. Proteins are heteropolymers made of amino acids. While a nucleic acid like DNA or RNA is made of only 4 types of nucleotide monomers, proteins are made of
a)
20 types of monomers
b)
3 types of monomers
c)
40 types of monomers
d)
Only one type of monomer

|
Syed Hussain answered |
In living systems, like our own bodies, these larger molecules include carbohydrates, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins. The monomers of these organic groups are: Carbohydrates - monosaccharides. Lipids - glycerol and fatty acids
About 98 percent of the mass of every living organism is composed of just six element including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and
[2007]
- a)sulphur and magnesium
- b)magnesium and sodium
- c)phosphorus and calcium
- d)sulphur and phosphorus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
About 98 percent of the mass of every living organism is composed of just six element including carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and
[2007]
a)
sulphur and magnesium
b)
magnesium and sodium
c)
phosphorus and calcium
d)
sulphur and phosphorus

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
It is calcium and phosphorus.
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is- a)Protein
- b)Lipid
- c)Steroids
- d)Cellulose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is
a)
Protein
b)
Lipid
c)
Steroids
d)
Cellulose
|
|
Raghavendra Datta answered |
The most abundant organic molecule present on earth is cellulose.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is found in the cell walls of plants. It is composed of repeating units of glucose molecules that are linked together to form long chains. These chains are then arranged in a way that gives cellulose its characteristic strength and rigidity.
Why is Cellulose Abundant on Earth?
Cellulose is abundant on earth for several reasons:
1. It is found in the cell walls of plants - Plants are the most abundant form of life on earth, and cellulose is a major component of their cell walls. This means that there is a huge amount of cellulose present on earth.
2. It is resistant to degradation - Unlike other organic molecules, cellulose is highly resistant to degradation by enzymes and other biological processes. This means that it can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to its abundance.
3. It is a major component of biomass - Cellulose is a major component of the biomass of plants. When plants die and decompose, the cellulose in their cell walls is broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by other organisms. This means that there is a constant supply of cellulose being produced and broken down on earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule present on earth due to its presence in the cell walls of plants, its resistance to degradation, and its role as a major component of biomass.
What is Cellulose?
Cellulose is a complex carbohydrate that is found in the cell walls of plants. It is composed of repeating units of glucose molecules that are linked together to form long chains. These chains are then arranged in a way that gives cellulose its characteristic strength and rigidity.
Why is Cellulose Abundant on Earth?
Cellulose is abundant on earth for several reasons:
1. It is found in the cell walls of plants - Plants are the most abundant form of life on earth, and cellulose is a major component of their cell walls. This means that there is a huge amount of cellulose present on earth.
2. It is resistant to degradation - Unlike other organic molecules, cellulose is highly resistant to degradation by enzymes and other biological processes. This means that it can persist in the environment for a long time, contributing to its abundance.
3. It is a major component of biomass - Cellulose is a major component of the biomass of plants. When plants die and decompose, the cellulose in their cell walls is broken down into smaller molecules that can be used by other organisms. This means that there is a constant supply of cellulose being produced and broken down on earth.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulose is the most abundant organic molecule present on earth due to its presence in the cell walls of plants, its resistance to degradation, and its role as a major component of biomass.
The bacterial cell wall is formed of- a)Cellulose
- b)Hemicellulose
- c)Peptidoglycan
- d)Glycogen
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bacterial cell wall is formed of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Hemicellulose
c)
Peptidoglycan
d)
Glycogen
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan (also called murein), which is made from polysaccharide chains cross-linked by unusual peptides containing D-amino acids. Bacterial cell walls are different from the cell walls of plants and fungi which are made of cellulose and chitin, respectively.
An ester bond is present between- a)Amino acids
- b)Nucleoside
- c)Nucleotide
- d)Monosaccharides
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An ester bond is present between
a)
Amino acids
b)
Nucleoside
c)
Nucleotide
d)
Monosaccharides

|
Syed Hussain answered |
Phosphodiester bond definition. A bondbetween a two sugar groups and a phosphate group; such bonds form the sugar-phosphate-sugar backbone of DNA and RNA. A diester bond (between phosphoric acid and two sugar molecules) linking two nucleotides together to form the nucleotide polymers DNA and RNA.
Double hydrogen bond occurs in DNA between- a)Adenine and guanine
- b)Thymine and cytosine
- c)Adenine and thymine
- d)Uracil and thymine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Double hydrogen bond occurs in DNA between
a)
Adenine and guanine
b)
Thymine and cytosine
c)
Adenine and thymine
d)
Uracil and thymine
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The complementary base pairs of guanine with cytosine and adenine with thymine connect to one another using hydrogen bonds. In addition to holding the DNA strands together, the hydrogen bonding between the complementary bases also sequester the bases in the interior of the double helix. Since, the option of Guanine and Cytosine is not provided. Hence, the correct option is Option C.
A segment of DNA has 120 adenine and 120 cytosine bases. The total number of nucleotides present in the segment is- a)480
- b)240
- c)60
- d)120
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A segment of DNA has 120 adenine and 120 cytosine bases. The total number of nucleotides present in the segment is
a)
480
b)
240
c)
60
d)
120
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
According to Chargaff’s rule, the amount of adenine is always equal to that of thymine and the amount of guanine is always equal to that of cytosine.
A = T(120), G = C(120)
The total number of nucleotides would be 120 × 4 = 480.
The plant cell wall are made up of- a)Cellulose
- b)Starch
- c)Glycogen Bacteria
- d)Inulin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The plant cell wall are made up of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Starch
c)
Glycogen Bacteria
d)
Inulin

|
Srishti Sen answered |
Plant cell walls are made of cellulose. Paper made from plant pulp is cellulose.
The oils have- a)High melting point
- b)Low melting point
- c)Optimum melting point
- d)No melting point
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The oils have
a)
High melting point
b)
Low melting point
c)
Optimum melting point
d)
No melting point
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Oils have lower melting point (e.g., gingely oil) and hence remain as oil in winters.
Which of the following are not secondary metabolites in plants? [2021]- a)Vinblastin, curcumin
- b)Rubber, gums
- c)Morphine, codeine
- d)Amino acids, glucose
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are not secondary metabolites in plants? [2021]
a)
Vinblastin, curcumin
b)
Rubber, gums
c)
Morphine, codeine
d)
Amino acids, glucose
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
- Some Secondary Metabolites
- However, when one analyses plant, fungal and microbial cells, one would see thousands of compounds other than these called primary metabolites, e.g. alkaloids, flavonoids, rubber, essential oils, antibiotics, coloured pigments, scents, gums, spices.
- These are called secondary metabolites.
Protein synthesis in an animal cell takes place[1997] - a)only in the cytoplasm
- b)in the nucleolus as well as in cytoplasm
- c)in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
- d)only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Protein synthesis in an animal cell takes place
[1997]
a)
only in the cytoplasm
b)
in the nucleolus as well as in cytoplasm
c)
in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
d)
only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
In the cytoplasm protein synthesis is restricted to the ribosomes. Mitochondria being a semiautonomous organelle, has its own genetic machinery to synthesize its proteins.
Which one is true for ATP?- a)ATP is organic ions of enzyme.
- b)ATP is a coenzyme.
- c)ATP is an enzyme
- d)ATP is a prosthetic part of an enzyme.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is true for ATP?
a)
ATP is organic ions of enzyme.
b)
ATP is a coenzyme.
c)
ATP is an enzyme
d)
ATP is a prosthetic part of an enzyme.
|
|
Hitakshi HTG answered |
Adenosine triphosphate, also known as molecular unit of currency, is a coenzyme of vast importance in the transfer of chemical energy derived from biochemical oxidations and it also transports energy within cells for metabolism. Thus, option 'B' is the right answer.
An organic substance bound to an enzyme and essential for its activity is called[2006]- a)Holoenzyme
- b)Apoenzyme
- c)Isoenzyme
- d)Coenzyme
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An organic substance bound to an enzyme and essential for its activity is called
[2006]
a)
Holoenzyme
b)
Apoenzyme
c)
Isoenzyme
d)
Coenzyme

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Coenzyme is an organic substance that enhances the action of an enzyme by binding with the protein molecule. Holoenzyme is a biochemically active compound formed by the combination of an enzyme with a coenzyme. Apoenzyme is the protein of an enzyme to which the coenzyme attaches to form an active enzyme Isoenzyme is one of the several forms of an enzyme that catalyse the same reaction but differ from each other in such properties as substrate affinity and maximum rates of enzyme substrate reaction.
Select the option which is not correct with respect to enzyme action: [2014]- a)Substrate binds with enzyme at its active site.
- b)Addition of lot of succinate does not reverse the inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate.
- c)A non-competitive inhibitor binds the enzyme at a site distinct from that which binds the substrate.
- d)Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the option which is not correct with respect to enzyme action: [2014]
a)
Substrate binds with enzyme at its active site.
b)
Addition of lot of succinate does not reverse the inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate.
c)
A non-competitive inhibitor binds the enzyme at a site distinct from that which binds the substrate.
d)
Malonate is a competitive inhibitor of succinic dehydrogenase.

|
Abhijeet Goyal answered |
(b) Inhibitions of succinic dehydrogenase by malonate is an example of competitive inhibition. Thus it is reversible reaction. On increasing the substrate (succinate) concentration the effect of inhibitor is removed and Vmax remain same.
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example, some function as enzymes. Which one of the following represents an additional function which some proteins discharge?- a)Antibiotics
- b)Pigments making colours of flowers
- c)Hormones
- d)Pigments conferring colour to skin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example, some function as enzymes. Which one of the following represents an additional function which some proteins discharge?
a)
Antibiotics
b)
Pigments making colours of flowers
c)
Hormones
d)
Pigments conferring colour to skin
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Proteins perform many physiological functions. For example, some proteins function as enzymes. Hormones represents an additional function that some proteins discharge (like insulin).
Enormous diversity of protein molecules is due to- a)R groups of amino acids
- b)Sequence of amino acids
- c)Peptide bonds
- d)Amino groups of amino acids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Enormous diversity of protein molecules is due to
a)
R groups of amino acids
b)
Sequence of amino acids
c)
Peptide bonds
d)
Amino groups of amino acids
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The third is tertiary; this is the folding of the secondary structures into the final 3D structure of a protein. Amino acids have properties that guide this; some interact easily with water (hydrophilic) and these orient themselves on the outside of a protein, while others don't interact well with water (hydrophobic) and will try to get themselves on the inside of the folded structure where they will be protected. Hydrophobicity/philicity is the major driving force in protein folding but other bonds will also be formed between amino acids like S-S linkages, other ionic bonds and HYDROGEN BONDS (tons of these are made). These smaller interactions generally stabilize the protein and keep it folded in the most ideal conformation possible.
The enzyme which cuts DNA is- a)DNA polymerase
- b)DNA ligase
- c)Restriction endonucleases
- d)DNA lyase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme which cuts DNA is
a)
DNA polymerase
b)
DNA ligase
c)
Restriction endonucleases
d)
DNA lyase
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Restriction Endonucleases are enzyme which scan DNA molecules for a particular nucleotide sequence. These are called Recognition Sequences.Once the Endonuclease finds this sequence it halts ans cuts the strand.Thus,the correct option is "C".
The enzyme found functional in lysosome is- a)Acid phosphataseLyases
- b)Lyases
- c)Oxidoreductase
- d)Basic phosphatase
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme found functional in lysosome is
a)
Acid phosphatase
Lyases
b)
Lyases
c)
Oxidoreductase
d)
Basic phosphatase
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
A lysosome is a membrane-bound organelle found in nearly all animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules.
Which of the following biomolecules does have phosphodiester bond ? [2015 RS]- a)Monosaccharides in a polysaccharide
- b)Amino acids in a polypeptide
- c)Nucleic acids in a nucleotide
- d)Fatty acids in a diglyceride
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following biomolecules does have phosphodiester bond ? [2015 RS]
a)
Monosaccharides in a polysaccharide
b)
Amino acids in a polypeptide
c)
Nucleic acids in a nucleotide
d)
Fatty acids in a diglyceride

|
Prisha Singh answered |
(c) Nucleic acids have phophodiester bond in a nucleotide.
Most abundant organic compound on earth is[2001]- a)Protein
- b)Cellulose
- c)Lipids
- d)Steroids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most abundant organic compound on earth is
[2001]
a)
Protein
b)
Cellulose
c)
Lipids
d)
Steroids

|
Maya Sengupta answered |
Cellulose is the most abundant organic compound, most abundant polysaccharide and most abundant bipolymer found on earth.
Carrier ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like:[2010]- a)amino acids and glucose
- b)glucose and fatty acids
- c)fatty acids and glycerol
- d)fructose and some amino acids
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Carrier ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like:
[2010]
a)
amino acids and glucose
b)
glucose and fatty acids
c)
fatty acids and glycerol
d)
fructose and some amino acids

|
Mrinalini Bajaj answered |
Massive ions like Na+ facilitate the absorption of substances like amino acid and glucose through Co transport.
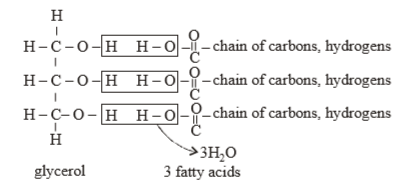
A typical fat molecule is made up of [2016]- a)three glycerol molecules and one fatty acid molecule
- b)one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
- c)one glycerol and one fatty acid molecule
- d)three glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical fat molecule is made up of [2016]
a)
three glycerol molecules and one fatty acid molecule
b)
one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules
c)
one glycerol and one fatty acid molecule
d)
three glycerol and three fatty acid molecules

|
Priyanka Iyer answered |
(b) Fat molecules are made of atoms of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen and oxygen atoms binds to the carbon, as pictorially depicted. A typical fat molecule has one glycerol and three fatty acid molecules.

Which one of the following statements is wrong? [2016]- a)Sucrose is a disaccharide.
- b)Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
- c)Uracil is a pyrimidine.
- d)Glycine is a sulphur containing amino acid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is wrong? [2016]
a)
Sucrose is a disaccharide.
b)
Cellulose is a polysaccharide.
c)
Uracil is a pyrimidine.
d)
Glycine is a sulphur containing amino acid.

|
Pooja Choudhary answered |
(d) Glycine (abbreviated as Gly or G) is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins, and indeed is the smallest possible (having a hydrogen substituent as its side-chain). The formula is NH2CH2COOH. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG of the genetic code.
The enzyme that is not present in succus entericus is : [2015 RS]- a)nucleases
- b)nucleosidase
- c)lipase
- d)maltase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The enzyme that is not present in succus entericus is : [2015 RS]
a)
nucleases
b)
nucleosidase
c)
lipase
d)
maltase

|
Mahesh Saini answered |
(a) Succus entericus lacks enzyme nucleases
Enzyme amylase belongs to- a)Hydrolases
- b)Transferases
- c)Isomerases
- d)Oxidoreductases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enzyme amylase belongs to
a)
Hydrolases
b)
Transferases
c)
Isomerases
d)
Oxidoreductases
|
|
Ragini Shukla answered |
Hydrolase are the enzyme which breaks down the large molecules into smaller ones with the help of hydrogen and hydroxyl groups of water molecule this phenomena is known as hydrolysis. Amylase is the enzyme produced by the salivary gland and helps in breaking down the starch into glucose. Amylase catalysis the hydrolysis of starch into sugar (glucose).
Amylase is also found in germinating seeds.
Amylase is also found in germinating seeds.
Which enzyme is concerned with the transfer of electrons?
- a)Dehydrogenase
- b)Transaminase
- c)Hydrolase
- d) Desmolase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which enzyme is concerned with the transfer of electrons?
a)
Dehydrogenase
b)
Transaminase
c)
Hydrolase
d)
Desmolase
|
|
Leelu Bhai answered |
Transaminase are the enzymes concerned with transfer of atoms or group of atoms or electrons.. so, option B is correct not A
DNA nucleotides are attached by
- a)Hydrogen bond
- b)Covalent bond
- c)Van der Waals bond
- d)Electrovalent bond
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
DNA nucleotides are attached by
a)
Hydrogen bond
b)
Covalent bond
c)
Van der Waals bond
d)
Electrovalent bond
|
|
Gopikas S answered |
Explanation: DNA nucleotides are attached by the Hydrogen bond. A nucleotide is the basic unit of polynucleotide chain of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) or RNA (Ribonucleic acid).
The nitrogenous bases are found in the strand's inward direction. The nitrogenous bases of the two antiparallel strands form hydrogen bonds, resulting in the formation of two helical strands.
The nitrogenous bases used in DNA (double-stranded helical structure) are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T).
Adenine is joined to thymine with two hydrogen bonds, whereas guanine is joined to cytosine by three hydrogen bonds.
Thus, DNA nucleotides are attached by Hydrogen bond.
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both[2000]- a)are polymers of nucleotides
- b)are capable of replicating
- c)have similar sugars
- d)have similar pyrimidine bases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both
[2000]
a)
are polymers of nucleotides
b)
are capable of replicating
c)
have similar sugars
d)
have similar pyrimidine bases

|
Ritika Khanna answered |
DNA and RNA are both polymers of nucleotides . DNA has deoxyribose sugar while RNA has ribose sugar. DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil in place of thymine.
Collagen is[2002]- a)fibrous protein
- b)globular protein
- c)lipid
- d)carbohydrate
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Collagen is
[2002]
a)
fibrous protein
b)
globular protein
c)
lipid
d)
carbohydrate

|
Arnav Iyer answered |
Collagen is a major fibrous protein of connective tissue occuring as white fibres produced by fibroblast.
The nucleotide chemical components are- a)Heterocyclic compounds, sugar and phosphate
- b)Sugar and Phosphate
- c)Heterocyclic compounds and sugar
- d)Phosphate and heterocyclic compounds
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The nucleotide chemical components are
a)
Heterocyclic compounds, sugar and phosphate
b)
Sugar and Phosphate
c)
Heterocyclic compounds and sugar
d)
Phosphate and heterocyclic compounds

|
Akshat Chavan answered |
The nucleotide has three chemically distinct components. One is a heterocyclic compound, the second is a monosaccharide and the third a phosphoric acid or phosphate.
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both[2000]- a)are polymers of nucleotides
- b)are capable of replicating
- c)have similar sugars
- d)have similar pyrimidine bases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both
[2000]
a)
are polymers of nucleotides
b)
are capable of replicating
c)
have similar sugars
d)
have similar pyrimidine bases

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
DNA and RNA are both polymers of nucleotides . DNA has deoxyribose sugar while RNA has ribose sugar. DNA has thymine while RNA has uracil in place of thymine.
The enormous diversity of protein molecules is due mainly to the diversity of
[1998]
- a)amino groups on the amino acids
- b)R groups on the amino acids
- c)amino acid sequences within the protein molecule
- d)peptide bonds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enormous diversity of protein molecules is due mainly to the diversity of
[1998]
a)
amino groups on the amino acids
b)
R groups on the amino acids
c)
amino acid sequences within the protein molecule
d)
peptide bonds

|
Prashanth Dasgupta answered |
There are only 20 amino acids . These can be arranged in different order in the polypeptide chain to form a diverse array of proteins.
The essential chemical components of many coenzymes are :[NEET 2013]- a)Nucleic acids
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Vitamins
- d)Proteins
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The essential chemical components of many coenzymes are :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Nucleic acids
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Vitamins
d)
Proteins

|
Yash Saha answered |
The essential chemical components of many enzymes are vitamins, e.g., coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and NADP contain vitamin niacin.
The enormous diversity of protein molecules is due mainly to the diversity of
[1998]
- a)amino groups on the amino acids
- b)R groups on the amino acids
- c)amino acid sequences within the protein molecule.
- d)peptide bonds
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The enormous diversity of protein molecules is due mainly to the diversity of
[1998]
a)
amino groups on the amino acids
b)
R groups on the amino acids
c)
amino acid sequences within the protein molecule.
d)
peptide bonds
|
|
Ankita Khaire answered |
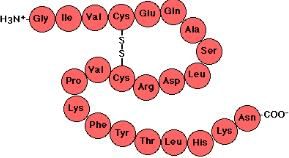
Proteins are building blocks of the body. The proteins are made up of amino acids. The amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds to form a protein. The amino acids consist of amine group made up of nitrogen and hydrogen and the carboxyl group at the end and a side chain of R group which is specific to a particular amino acid. This specific group brings a variability to the proteins. If R group is H it is glycine while if it is CH
2
it is alanine. The sequence of amino acids determines the protein. So, the correct answer is option D.
Which one of the following statements in incorrect? [2015 RS]- a)In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor molecule is not chemically changed by the enzyme.
- b)The competitive inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzymesubstrate complex.
- c)The presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate.
- d)A competitive inhibitor reacts reversibly with the enzyme to form an enzymeinhibitor complex.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements in incorrect? [2015 RS]
a)
In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor molecule is not chemically changed by the enzyme.
b)
The competitive inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzymesubstrate complex.
c)
The presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate.
d)
A competitive inhibitor reacts reversibly with the enzyme to form an enzymeinhibitor complex.
|
|
Anirban Nambiar answered |
Competitive Inhibition and Km
Competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where an inhibitor molecule, similar in structure to the substrate, competes with the substrate for binding to the active site of the enzyme. This type of inhibition does not chemically change the inhibitor or the enzyme.
The rate of breakdown of the enzyme substrate complex is affected by competitive inhibition because the inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding to the active site. However, the inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzyme itself.
In competitive inhibition, the presence of the inhibitor increases the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, meaning that the concentration of substrate required to reach half of the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the reaction is decreased. This is reflected in a decrease in the Michaelis constant (Km) of the enzyme for the substrate.
Therefore, the incorrect statement is option C, which states that the presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate. In fact, the presence of the competitive inhibitor increases the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, leading to a decrease in Km.
Competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where an inhibitor molecule, similar in structure to the substrate, competes with the substrate for binding to the active site of the enzyme. This type of inhibition does not chemically change the inhibitor or the enzyme.
The rate of breakdown of the enzyme substrate complex is affected by competitive inhibition because the inhibitor competes with the substrate for binding to the active site. However, the inhibitor does not affect the rate of breakdown of the enzyme itself.
In competitive inhibition, the presence of the inhibitor increases the apparent affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, meaning that the concentration of substrate required to reach half of the maximum velocity (Vmax) of the reaction is decreased. This is reflected in a decrease in the Michaelis constant (Km) of the enzyme for the substrate.
Therefore, the incorrect statement is option C, which states that the presence of the competitive inhibitor decreases the Km of the enzyme for the substrate. In fact, the presence of the competitive inhibitor increases the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, leading to a decrease in Km.
Macro molecule chitin is :
[NEET 2013]
- a)Phosphorus containing polysaccharide
- b)Sulphur containing polysaccharide
- c)Simple polysaccharide
- d)Nitrogen containing polysaccharide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Macro molecule chitin is :
[NEET 2013]
a)
Phosphorus containing polysaccharide
b)
Sulphur containing polysaccharide
c)
Simple polysaccharide
d)
Nitrogen containing polysaccharide

|
Pooja Saha answered |
Explanation:
Chitin is the most abundant amino polysaccharide polymer found in nature, and it is the building material that gives crustaceans, insects, and fungi their exoskeletons and cell walls their strength.
Chitin is the most abundant amino polysaccharide polymer found in nature, and it is the building material that gives crustaceans, insects, and fungi their exoskeletons and cell walls their strength.
Chitin is a nitrogen-containing modified polysaccharide made up of units of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (more precisely, 2-(acetylamino)-2-deoxy-D-glucose).
Final answer: Macromolecule chitin is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
Final answer: Macromolecule chitin is a nitrogen-containing polysaccharide
Which one is not a denaturing factor for protein?- a)High energy radiation
- b)High pressure
- c)Drastic change in pH
- d)High temperature
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not a denaturing factor for protein?
a)
High energy radiation
b)
High pressure
c)
Drastic change in pH
d)
High temperature

|
Prasenjit Pillai answered |
Protein molecules get denatured due to high temperature, very high or low pH and high energy radiation but there is no effect due to high pressure.
Which of the following is not a conjugated protein?- a)Peptone
- b)Glycoprotein
- c)Chromoprotein
- d)Lipoprotein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a conjugated protein?
a)
Peptone
b)
Glycoprotein
c)
Chromoprotein
d)
Lipoprotein
|
|
Suyash Jain answered |
A conjugated protein is a protein that functions in interaction with other (non-polypeptide) chemical groups attached by covalent bonding or weak interactions.
. __________ is a globular protein of 6 kDa consisting of 51 amino acids arranged in 2 polypeptide chains held together by a disulphide bridge- a)Fibrinogen
- b)Keratin
- c)Insulin
- d)Glucagon
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
. __________ is a globular protein of 6 kDa consisting of 51 amino acids arranged in 2 polypeptide chains held together by a disulphide bridge
a)
Fibrinogen
b)
Keratin
c)
Insulin
d)
Glucagon
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Human insulin is a peptide hormone composed of 51 ammo acids and has a molecular weight of 5805 Da.(∼6 Kda). In this molecule, there are two polypeptide chains (A and B) held together by disulphide bridge.
The energy currency of cell is—- a)GDP
- b)ATP
- c)ADP
- d)NAD
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy currency of cell is—
a)
GDP
b)
ATP
c)
ADP
d)
NAD
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
When the ATP converts to ADP, the ATP is said to be spent. he molecule is used like a battery within cells and allows the consumption of one of its phosphorous molecules.The energy currency used by all cells from bacteria to man is adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Which is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms?- a)Lipids
- b)Proteins
- c)Ions
- d)Water
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms?
a)
Lipids
b)
Proteins
c)
Ions
d)
Water

|
Anand Jain answered |
Water is the most abundant chemical for the living organisms.
A polysaccharide, which is synthesized and stored in liver cells, is[1995]- a)lactose
- b)galactose
- c)arabinose
- d)glycogen
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A polysaccharide, which is synthesized and stored in liver cells, is
[1995]
a)
lactose
b)
galactose
c)
arabinose
d)
glycogen

|
Sneha Basak answered |
Glycogen is a polysaccharide, which is synthesized and stored in the liver. It is released into the blood by breakdown of simple glucose, and energy is released.
Which of the following glucose transporters is insulin-dependent? [2019]- a)GLUT IV
- b)GLUT I
- c)GLUT II
- d)GLUT III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following glucose transporters is insulin-dependent? [2019]
a)
GLUT IV
b)
GLUT I
c)
GLUT II
d)
GLUT III
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
GLUT stands for glucose transport protein channel. They are of different types. Glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT IV) is a protein encoded in humans by the SLC2A4 gene. It is insulin-regulated glucose transporter found primarily in adipose tissues and striated muscles.
A peptide bond is formed by the process of- a)Amination
- b)Rehydration
- c)Deamination
- d)Dehydration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A peptide bond is formed by the process of
a)
Amination
b)
Rehydration
c)
Deamination
d)
Dehydration
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A peptide bond is a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O). This is a dehydration synthesis reaction (also known as a condensation reaction), and usually occurs between amino acids.
In a DNA molecule, two strands are held by- a)Nitrogen bonds
- b)Phosphate bonds
- c)Carbon bonds
- d)Hydrogen bonds
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a DNA molecule, two strands are held by
a)
Nitrogen bonds
b)
Phosphate bonds
c)
Carbon bonds
d)
Hydrogen bonds
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
By hydrogen bonds between the two bases. Basically, the bases are ‘polar’, meaning they have slight differences in electrical charge at certain points. This allows them to attract one another like a balloon sticking to your hair.
Hydrogen bonds are weaker than the covalent bonds that hold the rest of the molecule together, making them easier to break and re-form.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biomolecules - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biomolecules - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup