All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Breathing and Exchange of Gases for NEET Exam
The alveoli of lungs are lined by- a)Squamous epithelium
- b)Columnar epithelium
- c)Cuboidal epithelium
- d)Simple epithelium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The alveoli of lungs are lined by
a)
Squamous epithelium
b)
Columnar epithelium
c)
Cuboidal epithelium
d)
Simple epithelium
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
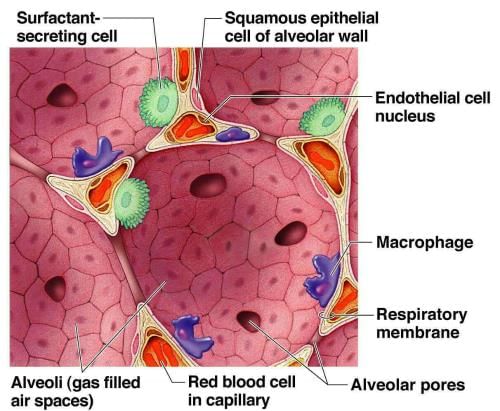
- The respiratory or gas-exchange surface consists of millions of small sacs, or alveoli, lined by a simple squamous epithelium.
- This epithelium is exceedingly thin to facilitate the diffusion of oxygen and CO2.
- The alveolar walls also contain cuboidal surfactant-secreting cells.
In frog cutaneous respiration takes place- a)In water
- b)On land
- c)In hibernation
- d)All (Always)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In frog cutaneous respiration takes place
a)
In water
b)
On land
c)
In hibernation
d)
All (Always)
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Frog Respiration. The frog has three respiratory surfaces on its body that it uses to exchange gas with the surroundings: the skin, in the lungs and on the lining of the mouth. While completely submerged all of the frog's repiration takes place through the skin.
Residual volume is- a)Greater than inspiratory volume
- b)Greater than tidal volume
- c)Greater than vital capacity
- d)Lesser than tidal volume
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Residual volume is
a)
Greater than inspiratory volume
b)
Greater than tidal volume
c)
Greater than vital capacity
d)
Lesser than tidal volume
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
- Tidal volume is approximately 500ml while residual volume is 1100-1200 ml.
- Therefore the residual volume is greater than tidal volume.
The term ‘Glycolysis’ has originated from the Greek words:
- a)Glyco and lysis
- b)Glycose and lysis
- c)Glykos and lysis
- d)Glyko and lysis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The term ‘Glycolysis’ has originated from the Greek words:
a)
Glyco and lysis
b)
Glycose and lysis
c)
Glykos and lysis
d)
Glyko and lysis
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
He word glycolysis is of Greek origin, where 'glykos' means sweet, and 'lysis' means splitting. Hence, Glycolysis literally means "sugar splitting" or "sugar breaking"; this accurately describes the process of glycolysis, in which a 6-carbon sugar molecule is broken down into two 3-carbon molecules. There are three stages in glycolysis which are Investment stage, Splitting stage and Energy Yielding stage. Glycolysis consists of ten separate reactions, each catalyzed by a different enzyme.
Oxygen in expired air- a)10%
- b)16%
- c)19%
- d)4%
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen in expired air
a)
10%
b)
16%
c)
19%
d)
4%

|
Syed Hussain answered |
After a human breathes in Earth's air (roughly 78 percent nitrogen and 21 percent oxygen), he or she exhales a mixture of compounds similar to the air inhaled: 78 percent nitrogen, 16 percent oxygen, 0.09 percent argon, and four percent carbon dioxide.
The pharynx opens into the larynx by a slit-like aperture called
a) Bronchusb)Epiglottisc)Glottisd) TracheaCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Nasopharynx lined by ciliated pseudostratified epithelia, oropharynx and laryngopharynx lined by non keratinized epithelium. Mouth serves as an alternate route for air when nasal chambers are blocked. Foramen by which pharynx opens into larynx called glottis. In general it remains open. During swallowing it is closed. It provides passage for air. Pharyns leads into the oesophagus through an aperture called gullet. In general condition it remains closed and opens at the time of swallowing. During swallowing epiglottis closes the glottis.
Intercostal muscles occur in [1988]- a)abdomen
- b)thigh
- c)ribs
- d)diaphragm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Intercostal muscles occur in [1988]
a)
abdomen
b)
thigh
c)
ribs
d)
diaphragm

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
Intercostal muscles (External intercostal & Internal intercostal) are attached with the ribs which help in the movement of rib cage during breathing.
Respiration is- a)Physical process
- b)Chemical process
- c)Physico chemical process
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiration is
a)
Physical process
b)
Chemical process
c)
Physico chemical process
d)
None
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Respiration is the biochemical process in which the cells of an organism obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (the currency of energy in cells).
When we examine the equation for cellular respiration, we see that the reactants are glucose and oxygen (for aerobic respiration), and the products are carbon dioxide, water, and ATP. Note the number of oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water molecules involved in each 'turn' of the process.
Very high number of alveoli present in a lung is meant for- a)More space for increasing volume of inspired air
- b)More area for diffusion
- c)Making the organ spongy
- d)Increasing nerve supply
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Very high number of alveoli present in a lung is meant for
a)
More space for increasing volume of inspired air
b)
More area for diffusion
c)
Making the organ spongy
d)
Increasing nerve supply
|
|
Tejas Kumar answered |
Explanation:
Alveoli are tiny air sacs present in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. The number of alveoli present in the lungs is very high, which serves the purpose of providing a large surface area for diffusion of gases. This is important because the process of respiration involves the exchange of gases between the lungs and blood. The alveoli provide a large surface area for this exchange to occur efficiently.
More area for diffusion:
The high number of alveoli in the lungs provides a large surface area for diffusion of gases. Oxygen from the air diffuses through the alveolar walls and into the bloodstream. At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the bloodstream and into the alveoli to be exhaled out of the body.
More space for increasing volume of inspired air:
The high number of alveoli also allows for the lungs to expand and increase in volume when we inhale, allowing for more air to enter the lungs. This is important for efficient gas exchange as it ensures that more oxygen can be taken in and more carbon dioxide can be expelled.
Making the organ spongy:
The high number of alveoli in the lungs also gives the organ a spongy texture. This allows the lungs to be flexible and accommodate changes in volume during breathing.
Increasing nerve supply:
While the high number of alveoli does not directly increase the nerve supply to the lungs, it does allow for more efficient gas exchange. This ensures that the body's cells receive the oxygen they need and allows for the removal of carbon dioxide, which can have harmful effects on the body if allowed to build up.
In summary, the high number of alveoli in the lungs provides a large surface area for diffusion of gases, allows for more space for increasing volume of inspired air, gives the organ a spongy texture, and allows for more efficient gas exchange, which is important for the body's overall health and function.
Alveoli are tiny air sacs present in the lungs where gas exchange occurs. The number of alveoli present in the lungs is very high, which serves the purpose of providing a large surface area for diffusion of gases. This is important because the process of respiration involves the exchange of gases between the lungs and blood. The alveoli provide a large surface area for this exchange to occur efficiently.
More area for diffusion:
The high number of alveoli in the lungs provides a large surface area for diffusion of gases. Oxygen from the air diffuses through the alveolar walls and into the bloodstream. At the same time, carbon dioxide diffuses out of the bloodstream and into the alveoli to be exhaled out of the body.
More space for increasing volume of inspired air:
The high number of alveoli also allows for the lungs to expand and increase in volume when we inhale, allowing for more air to enter the lungs. This is important for efficient gas exchange as it ensures that more oxygen can be taken in and more carbon dioxide can be expelled.
Making the organ spongy:
The high number of alveoli in the lungs also gives the organ a spongy texture. This allows the lungs to be flexible and accommodate changes in volume during breathing.
Increasing nerve supply:
While the high number of alveoli does not directly increase the nerve supply to the lungs, it does allow for more efficient gas exchange. This ensures that the body's cells receive the oxygen they need and allows for the removal of carbon dioxide, which can have harmful effects on the body if allowed to build up.
In summary, the high number of alveoli in the lungs provides a large surface area for diffusion of gases, allows for more space for increasing volume of inspired air, gives the organ a spongy texture, and allows for more efficient gas exchange, which is important for the body's overall health and function.
In humans, which among these is not a step in respiration?- a)Utilisation of CO2 by cells for catabolic reactions
- b)Pulmonary ventilation
- c)Transport of gases by blood
- d)Alveolar diffusion of O2 and CO2
- e)Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In humans, which among these is not a step in respiration?
a)
Utilisation of CO2 by cells for catabolic reactions
b)
Pulmonary ventilation
c)
Transport of gases by blood
d)
Alveolar diffusion of O2 and CO2
e)
Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
- Out of the given options, the processes or steps that are included as parts of the respiration in humans include alveolar diffusion of O2 and CO2, transport of gases by blood, and diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues among others.
- However, the utilization of CO2 by cells for catabolic reactions is not considered a part of respiration in humans.
So, the correct answer is 'The utilisation of CO2 by cells for catabolic reactions'.
Blood analysis of a patient reveals an unusually high quantity of carboxyhaemoglobin content. Which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of [2004]- a)carbon disulphide
- b)chloroform
- c)carbon dioxide
- d)carbon monoxide
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blood analysis of a patient reveals an unusually high quantity of carboxyhaemoglobin content. Which of the following conclusions is most likely to be correct?The patient has been inhaling polluted air containing unusually high content of [2004]
a)
carbon disulphide
b)
chloroform
c)
carbon dioxide
d)
carbon monoxide

|
Ayush Chavan answered |
Carboxyhaemoglobin is the stable product formed by the association of CO and Hb in the blood. The association of carbon dioxide and haemoglobin forms carbamino haemoglobin.
In the process of transport of CO2 which phenomenon occurs between RBCs and plasma- a)Osmosis
- b)Adsorption
- c)Chloride shift
- d)Absorption
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the process of transport of CO2 which phenomenon occurs between RBCs and plasma
a)
Osmosis
b)
Adsorption
c)
Chloride shift
d)
Absorption
|
|
Gayatri Pillai answered |
**Chloride Shift in the Transport of CO2 between RBCs and Plasma**
The correct phenomenon that occurs between red blood cells (RBCs) and plasma during the transport of carbon dioxide (CO2) is the **chloride shift**.
During gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen (O2) is taken up by hemoglobin in the RBCs, while CO2 is released from the tissues and diffuses into the blood. CO2 is mainly transported in the blood in three forms: dissolved CO2, bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), and carbamino compounds.
**Chloride Shift Process:**
1. **CO2 Loading in the Tissues:** In the tissues, CO2 diffuses into the RBCs and reacts with water (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) through the action of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
2. **Formation of Bicarbonate Ions:** Carbonic acid (H2CO3) dissociates into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+). The bicarbonate ions are then transported out of the RBCs into the plasma in exchange for chloride ions (Cl-) through a process called the chloride shift.
3. **Reverse Chloride Shift in the Lungs:** In the lungs, where the partial pressure of CO2 is lower, the reverse process occurs. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) are transported back into the RBCs in exchange for chloride ions (Cl-) from the plasma.
4. **CO2 Unloading in the Lungs:** Inside the RBCs, carbonic acid (H2CO3) is formed again, which then dissociates into CO2 and water (H2O) due to the action of carbonic anhydrase. The CO2 is then released from the RBCs into the alveoli of the lungs, where it can be exhaled.
**Purpose of the Chloride Shift:**
The chloride shift plays a crucial role in CO2 transport as it helps maintain the electrochemical balance and pH of the RBCs. By exchanging bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) for chloride ions (Cl-), it prevents the accumulation of excess bicarbonate ions in the RBCs and maintains the electrical neutrality of the cells. This is important for the proper functioning of various cellular processes.
In summary, during the transport of CO2 between RBCs and plasma, the chloride shift is the phenomenon where bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) are exchanged for chloride ions (Cl-) to facilitate the movement of CO2 out of the tissues and into the lungs. This process helps maintain the electrochemical balance and pH within the RBCs.
The correct phenomenon that occurs between red blood cells (RBCs) and plasma during the transport of carbon dioxide (CO2) is the **chloride shift**.
During gas exchange in the lungs, oxygen (O2) is taken up by hemoglobin in the RBCs, while CO2 is released from the tissues and diffuses into the blood. CO2 is mainly transported in the blood in three forms: dissolved CO2, bicarbonate ions (HCO3-), and carbamino compounds.
**Chloride Shift Process:**
1. **CO2 Loading in the Tissues:** In the tissues, CO2 diffuses into the RBCs and reacts with water (H2O) to form carbonic acid (H2CO3) through the action of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase.
2. **Formation of Bicarbonate Ions:** Carbonic acid (H2CO3) dissociates into bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+). The bicarbonate ions are then transported out of the RBCs into the plasma in exchange for chloride ions (Cl-) through a process called the chloride shift.
3. **Reverse Chloride Shift in the Lungs:** In the lungs, where the partial pressure of CO2 is lower, the reverse process occurs. Bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) are transported back into the RBCs in exchange for chloride ions (Cl-) from the plasma.
4. **CO2 Unloading in the Lungs:** Inside the RBCs, carbonic acid (H2CO3) is formed again, which then dissociates into CO2 and water (H2O) due to the action of carbonic anhydrase. The CO2 is then released from the RBCs into the alveoli of the lungs, where it can be exhaled.
**Purpose of the Chloride Shift:**
The chloride shift plays a crucial role in CO2 transport as it helps maintain the electrochemical balance and pH of the RBCs. By exchanging bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) for chloride ions (Cl-), it prevents the accumulation of excess bicarbonate ions in the RBCs and maintains the electrical neutrality of the cells. This is important for the proper functioning of various cellular processes.
In summary, during the transport of CO2 between RBCs and plasma, the chloride shift is the phenomenon where bicarbonate ions (HCO3-) are exchanged for chloride ions (Cl-) to facilitate the movement of CO2 out of the tissues and into the lungs. This process helps maintain the electrochemical balance and pH within the RBCs.
In Man, the structure with a function similar to spiracles of cockroach are- a)Lungs
- b)Alveoli
- c)Bronchioles
- d)Nostrils
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In Man, the structure with a function similar to spiracles of cockroach are
a)
Lungs
b)
Alveoli
c)
Bronchioles
d)
Nostrils

|
Santosh Kumar answered |
Respiratory tubules open outside the body by the spiracles in CockroachEach spiracle open into a large chamber called atrium or tracheal chamber as like nostril.
The pneumotaxic centre is present in- a)Medulla
- b)Cerebrum
- c)Cerebellum
- d)Pons varolii
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The pneumotaxic centre is present in
a)
Medulla
b)
Cerebrum
c)
Cerebellum
d)
Pons varolii
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The pneumotaxic center is located in the upper part of the pons i.e pons varolii. Its nuclei are the subparabrachial nucleus and the medial parabrachial nucleus. The pneumotaxic center controls both the rate and the pattern of breathing.
Respiratory quotient is defined as:
- a)volume of CO2 evolved - volume of O2 consumed.
- b)Volume of O2 consumed/Volume of CO2 evolved.
- c)Volume of CO2 evolved/Volume of O2 consumed.
- d)Volume of O2 evolved/Volume of CO2 consumed.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiratory quotient is defined as:
a)
volume of CO2 evolved - volume of O2 consumed.
b)
Volume of O2 consumed/Volume of CO2 evolved.
c)
Volume of CO2 evolved/Volume of O2 consumed.
d)
Volume of O2 evolved/Volume of CO2 consumed.
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The respiratory quotient (RQ) is the ratio of CO2 produced to O2 consumed while food is being metabolized.
RQ = CO2 eliminated/O2 consumed
- Respiratory quotient (RQ) is a term used in physiology to describe the ratio of the volume of carbon dioxide (CO2) evolved to the volume of oxygen (O2) consumed during respiration. It is used to determine the type of fuel (carbohydrates, fats, or proteins) being used by an organism for energy production.
- Option A, volume of CO2 evolved - volume of O2 consumed, is not a correct answer as it does not represent the ratio of CO2 evolved to O2 consumed.
- Option B, Volume of O2 consumed/Volume of CO2 evolved, is not a correct answer as it represents the reciprocal of the actual respiratory quotient, and therefore is not the correct definition of RQ.
- Option D, Volume of O2 evolved/Volume of CO2 consumed, is not a correct answer as it represents the reciprocal of the actual respiratory quotient, and therefore is not the correct definition of RQ.
Therefore, the correct answer is C: Volume of CO2 evolved/Volume of O2 consumed, which represents the actual definition of respiratory quotient, a ratio of CO2 evolved to O2 consumed during respiration.
A person breathes in some volume of air by forced inspiration after having a forced expiration. This quantity of air taken in is- a)Total lung capacity
- b)Vital capacity
- c)Inspiratory capacity
- d)Tidal volume
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person breathes in some volume of air by forced inspiration after having a forced expiration. This quantity of air taken in is
a)
Total lung capacity
b)
Vital capacity
c)
Inspiratory capacity
d)
Tidal volume
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The maximum volume of air that a person can breathe in after forced expiration or the maximum volume of air that a person can breathe out after forced inspiration is called vital capacity. The value of vital capacity varies from 3400 mL to 4800 mi- On the other hand, tidal volume is the air inspired or expired during normal breathing. Total lung capacity is the volume of air present in lungs and respiratory passage after maximum inspiration. Whereas, inspiratory capacity is total volume of air that a person can inspire after normal inspiration.
Which one is the cofactor of carbonic anhydrase?- a)Cu
- b)Zn
- c)Fe
- d)Mg
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is the cofactor of carbonic anhydrase?
a)
Cu
b)
Zn
c)
Fe
d)
Mg
|
|
Janani Singh answered |
Cofactor of carbonic anhydrase
Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions. It is present in red blood cells and plays a crucial role in the transportation of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. The cofactor of carbonic anhydrase is Zn (zinc).
Explanation
Carbonic anhydrase requires a metal ion cofactor for its activity. The metal ion binds to the active site of the enzyme and participates in the catalytic reaction. Several metal ions have been found to be cofactors of carbonic anhydrase, including Cu (copper), Fe (iron), Mg (magnesium), and Zn (zinc). However, Zn is the most common and important cofactor of carbonic anhydrase.
Zinc ion (Zn2+) acts as a Lewis acid and binds to a water molecule, which then acts as a base to facilitate the transfer of a proton from carbonic acid to water, forming bicarbonate and a hydronium ion. The hydronium ion is then removed by another water molecule, regenerating the active site of the enzyme.
Zinc is essential for the activity of carbonic anhydrase, and its deficiency can lead to severe metabolic disorders such as osteoporosis, growth retardation, and immune dysfunction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cofactor of carbonic anhydrase is Zn (zinc). Zinc is essential for the activity of the enzyme, and its deficiency can lead to severe health problems.
Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ions. It is present in red blood cells and plays a crucial role in the transportation of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. The cofactor of carbonic anhydrase is Zn (zinc).
Explanation
Carbonic anhydrase requires a metal ion cofactor for its activity. The metal ion binds to the active site of the enzyme and participates in the catalytic reaction. Several metal ions have been found to be cofactors of carbonic anhydrase, including Cu (copper), Fe (iron), Mg (magnesium), and Zn (zinc). However, Zn is the most common and important cofactor of carbonic anhydrase.
Zinc ion (Zn2+) acts as a Lewis acid and binds to a water molecule, which then acts as a base to facilitate the transfer of a proton from carbonic acid to water, forming bicarbonate and a hydronium ion. The hydronium ion is then removed by another water molecule, regenerating the active site of the enzyme.
Zinc is essential for the activity of carbonic anhydrase, and its deficiency can lead to severe metabolic disorders such as osteoporosis, growth retardation, and immune dysfunction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the cofactor of carbonic anhydrase is Zn (zinc). Zinc is essential for the activity of the enzyme, and its deficiency can lead to severe health problems.
The most important function of diaphragm of mammals is- a)To devide the body cavity into compartments
- b)To protect lungs
- c)To aid in respiration
- d)To aid in ventilation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most important function of diaphragm of mammals is
a)
To devide the body cavity into compartments
b)
To protect lungs
c)
To aid in respiration
d)
To aid in ventilation

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscular structure. It separates the thoracic and the abdominal region of the body.
The main function of the diaphragm is to aid in ventilation. During the process of inspiration and expiration, it contracts and relaxes simultaneously to change the volume of thoracic cavity which creates a pressure difference between the lungs and outer atmosphere which helps to inhale and exhale.
During inspiration the diaphragm contracts and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, and decreases the pressure inside the lungs, thus the air enters inside the lungs.
During expiration the diaphragm relaxes and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, and increase the pressure inside the lungs, thus the air is forced out of the lungs.
So, the correct answer is option D.
The main function of the diaphragm is to aid in ventilation. During the process of inspiration and expiration, it contracts and relaxes simultaneously to change the volume of thoracic cavity which creates a pressure difference between the lungs and outer atmosphere which helps to inhale and exhale.
During inspiration the diaphragm contracts and increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, and decreases the pressure inside the lungs, thus the air enters inside the lungs.
During expiration the diaphragm relaxes and decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity, and increase the pressure inside the lungs, thus the air is forced out of the lungs.
So, the correct answer is option D.
If TLC is 5500ml, IRV is 2950ml, ERV is 900ml and TV is 500ml then what will be value of RV ?- a)2550ml
- b)1100ml
- c)1200ml
- d)1150ml
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If TLC is 5500ml, IRV is 2950ml, ERV is 900ml and TV is 500ml then what will be value of RV ?
a)
2550ml
b)
1100ml
c)
1200ml
d)
1150ml
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
RV = TLC - IRV – ERV– TV. On substituting the values, we get 1150ml.
Lungs have a large number of narrow tubes called- a)Bronchi
- b)Alveoli
- c)Bronchioles
- d)Tracheae
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lungs have a large number of narrow tubes called
a)
Bronchi
b)
Alveoli
c)
Bronchioles
d)
Tracheae
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The narrow tubes found inside lungs are called bronchioles.
When we breathe, air travels from the nose or mouth, and goes down the trachea and reaches the part called carina. From here the tube branches into two, creating two bronchi that lead to left and right lung each. From there onwards, the bronchi split into smaller and smaller bronchioles until it terminates in the alveoli where gas exchange occurs.
The carbon dioxide is transported via blood to lungs as [1995]- a)dissolved in blood plasma
- b)in the form of carbonic acid only
- c)in combination with haemoglobin only
- d)carbaminohaemoglobin and as carbonic acid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The carbon dioxide is transported via blood to lungs as [1995]
a)
dissolved in blood plasma
b)
in the form of carbonic acid only
c)
in combination with haemoglobin only
d)
carbaminohaemoglobin and as carbonic acid

|
Deepak Joshi answered |
Carbon dioxide is transported via blood to lungs mostly as carbaminohaemoglobin and carbonic acid. It is released in lungs in exchange with oxygen.
Habit of Cigarette smoking can lead to :- a)loss of cilia lining the respiratory tract
- b)all of the following
- c)coughing
- d)emphysema
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Habit of Cigarette smoking can lead to :
a)
loss of cilia lining the respiratory tract
b)
all of the following
c)
coughing
d)
emphysema
|
|
Syed Aakif answered |
Because which contains Nictogen and other harmful compounts which can affect our whole body it supress our body function
How much oxygen, blood supplies to tissues in one circulation- a)75%
- b)1.34%
- c)25%
- d)7%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How much oxygen, blood supplies to tissues in one circulation
a)
75%
b)
1.34%
c)
25%
d)
7%
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Blood supplies approximately 25% of oxygen to the tissues in one circulation as the partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood is 75-95mmHg.
Which one of the following mammalian cells is not capable of metabolising glucose to carbon-dioxide aerobically? [2007]- a)unstraited muscle cells
- b)liver cells
- c)red blood cells
- d)white blood
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following mammalian cells is not capable of metabolising glucose to carbon-dioxide aerobically? [2007]
a)
unstraited muscle cells
b)
liver cells
c)
red blood cells
d)
white blood

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
Since RBCS do not have mitochondria so they can respire only anaerobically.
Which one of the following mammalian cells is not capable of metabolising glucose to carbon dioxide aerobically?- a)Unstriated muscle cells
- b)White blood cells
- c)Liver cells
- d)Red blood cells
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following mammalian cells is not capable of metabolising glucose to carbon dioxide aerobically?
a)
Unstriated muscle cells
b)
White blood cells
c)
Liver cells
d)
Red blood cells
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Cell organelles and nucleus are absent in mature red blood cells, therefore, aerobic respiration do not take place.
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin is- a)Sigmoid
- b)Hyperbolic
- c)Linear
- d)Hypobolic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen dissociation curve of haemoglobin is
a)
Sigmoid
b)
Hyperbolic
c)
Linear
d)
Hypobolic

|
Shyamal Modak. answered |
Acc. to NCERT it is sigmoid.
NCERT page 274 section 17.4.1. Transport of O2
fig. 17.5
NCERT page 274 section 17.4.1. Transport of O2
fig. 17.5
Which one of the following is a possibility for most of us in regard to breathing, by making a conscious effort? [2011M]
- a)One can breathe out air totally without oxygen.
- b)One can consiously breathe in and breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone, without moving the ribs at all
- c)One can breathe out air through eustachian tubes by closing both the nose and the mouth.
- d)The lungs can be made fully empty by forcefully breathing out all air from them
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is a possibility for most of us in regard to breathing, by making a conscious effort? [2011M]
a)
One can breathe out air totally without oxygen.
b)
One can consiously breathe in and breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone, without moving the ribs at all
c)
One can breathe out air through eustachian tubes by closing both the nose and the mouth.
d)
The lungs can be made fully empty by forcefully breathing out all air from them

|
Naveen Menon answered |
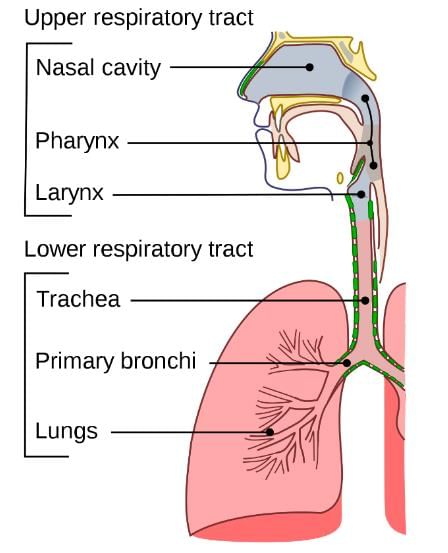
The process of breathing involves the pathway of the human respiratory system and includes the nasal cavities, oral cavities, pharynx, trachea, primary bronchi, secondary bronchi and lungs with bronchioles and alveoli present. Breathing is a 2-fold process which includes breathing in and breathing out. During this process, the diaphragm which is the dome-shaped sheet of muscle located below the lungs contracts and expands along with the intercostal muscles to force air in and out of the lungs. Since intercostal muscles are also involved in the process of respiration, deeper respiration results in the movement of ribs too. Hence most of us can consciously breathe in and breathe out by moving the diaphragm alone.
Inhibitory centre and pneumotaxis centre concerned with
- a)Respiration
- b)Digestion
- c)Reflexaction
- d)Breathing
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Inhibitory centre and pneumotaxis centre concerned with
a)
Respiration
b)
Digestion
c)
Reflexaction
d)
Breathing
|
|
Akshay Chavan answered |
Inhibitory centre and pneumotaxis centre are both located in the brainstem and are involved in the regulation of breathing.
Inhibitory Centre:
- Located in the medulla oblongata
- Responsible for controlling the rate and depth of breathing
- Activated when levels of carbon dioxide in the blood increase, leading to an increase in respiratory rate to remove excess carbon dioxide
- Also activated when levels of oxygen in the blood decrease, leading to an increase in respiratory rate to increase oxygen intake
Pneumotaxis Centre:
- Located in the pons region of the brainstem
- Responsible for controlling the duration of each breath
- Activated by signals from the inhibitory centre
- Helps fine-tune the breathing rate and depth by adjusting the inspiratory and expiratory volumes
In summary, the inhibitory centre and pneumotaxis centre work together to regulate breathing, ensuring that the body receives enough oxygen and removes excess carbon dioxide.
Inhibitory Centre:
- Located in the medulla oblongata
- Responsible for controlling the rate and depth of breathing
- Activated when levels of carbon dioxide in the blood increase, leading to an increase in respiratory rate to remove excess carbon dioxide
- Also activated when levels of oxygen in the blood decrease, leading to an increase in respiratory rate to increase oxygen intake
Pneumotaxis Centre:
- Located in the pons region of the brainstem
- Responsible for controlling the duration of each breath
- Activated by signals from the inhibitory centre
- Helps fine-tune the breathing rate and depth by adjusting the inspiratory and expiratory volumes
In summary, the inhibitory centre and pneumotaxis centre work together to regulate breathing, ensuring that the body receives enough oxygen and removes excess carbon dioxide.
The structure which prevents the entry of food into respiratory tract is- a)pharynx
- b)Larynx
- c)Glottis
- d)Epiglottis
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The structure which prevents the entry of food into respiratory tract is
a)
pharynx
b)
Larynx
c)
Glottis
d)
Epiglottis

|
Srishti Dam answered |
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap of cartilage located behind the tongue, at the top of the larynx, or voice box. The main function of the epiglottis is to seal off the windpipe during eating, so that food is not accidentally inhaled.
Epiglottis is made of stratified columnar epithelium tissue (non-ciliated) .
Epiglottis is made of stratified columnar epithelium tissue (non-ciliated) .
Emphysema is a- a)Pulmonary disease
- b)Cardiovascular disease
- c)Neural disease
- d)Renal disease
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Emphysema is a
a)
Pulmonary disease
b)
Cardiovascular disease
c)
Neural disease
d)
Renal disease
|
|
Kaneez Fatima answered |
Panacinar emphysema(panlobular emphysema): is an abnormal weakening & enlargement of all alveoli distal to the terminal bronchioles, including respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs & alveoli the entire acinus is affected by dilation & destruction.
What percentage of CO2 flows in blood in form of bicarbonates- a)7%
- b)23%
- c)50%
- d)70%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What percentage of CO2 flows in blood in form of bicarbonates
a)
7%
b)
23%
c)
50%
d)
70%

|
Shyamal Modak. answered |
It is written in NCERT. Ans. is D
For proper transport of O2 and CO2 blood should be- a)Slightly acidic
- b)Strongly acidic
- c)Strongly alkaline
- d)Slightly alkaline
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For proper transport of O2 and CO2 blood should be
a)
Slightly acidic
b)
Strongly acidic
c)
Strongly alkaline
d)
Slightly alkaline
|
|
Rishabh Shah answered |
Explanation:
Transport of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood is a crucial process for the proper functioning of the body. The pH of the blood plays a significant role in this process.
Acidic and alkaline conditions:
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, less than 7 being acidic, and greater than 7 being alkaline. Blood pH is tightly regulated, with a normal range of 7.35 to 7.45.
Blood pH and transport of O2 and CO2:
The transport of O2 and CO2 in the blood is facilitated by the binding of these gases to hemoglobin (Hb) and other proteins. The binding of O2 to Hb is influenced by the pH of the blood. In an acidic environment, Hb has a higher affinity for O2, which means it binds more readily. On the other hand, in an alkaline environment, Hb has a lower affinity for O2, which means it releases O2 more readily.
Similarly, the transport of CO2 in the blood is also influenced by the pH of the blood. CO2 can combine with water (H2O) in the blood to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which can then dissociate into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). In an acidic environment, there are more H+ ions, which combine with HCO3- to form H2CO3 and release CO2. In an alkaline environment, there are fewer H+ ions, which means more HCO3- is available to combine with H+ ions and form H2CO3, which can then be converted back to CO2.
Slightly alkaline pH:
From the above explanation, it is clear that blood pH should be slightly alkaline (between 7.35 to 7.45) for the proper transport of O2 and CO2. This pH range ensures that Hb binds O2 readily in the lungs (where the pH is slightly more alkaline) and releases O2 readily in the tissues (where the pH is slightly more acidic). It also ensures that CO2 is released readily in the lungs (where the pH is slightly more acidic) and transported to the lungs as HCO3- (where the pH is slightly more alkaline).
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (Slightly alkaline).
Transport of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood is a crucial process for the proper functioning of the body. The pH of the blood plays a significant role in this process.
Acidic and alkaline conditions:
pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being neutral, less than 7 being acidic, and greater than 7 being alkaline. Blood pH is tightly regulated, with a normal range of 7.35 to 7.45.
Blood pH and transport of O2 and CO2:
The transport of O2 and CO2 in the blood is facilitated by the binding of these gases to hemoglobin (Hb) and other proteins. The binding of O2 to Hb is influenced by the pH of the blood. In an acidic environment, Hb has a higher affinity for O2, which means it binds more readily. On the other hand, in an alkaline environment, Hb has a lower affinity for O2, which means it releases O2 more readily.
Similarly, the transport of CO2 in the blood is also influenced by the pH of the blood. CO2 can combine with water (H2O) in the blood to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which can then dissociate into hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). In an acidic environment, there are more H+ ions, which combine with HCO3- to form H2CO3 and release CO2. In an alkaline environment, there are fewer H+ ions, which means more HCO3- is available to combine with H+ ions and form H2CO3, which can then be converted back to CO2.
Slightly alkaline pH:
From the above explanation, it is clear that blood pH should be slightly alkaline (between 7.35 to 7.45) for the proper transport of O2 and CO2. This pH range ensures that Hb binds O2 readily in the lungs (where the pH is slightly more alkaline) and releases O2 readily in the tissues (where the pH is slightly more acidic). It also ensures that CO2 is released readily in the lungs (where the pH is slightly more acidic) and transported to the lungs as HCO3- (where the pH is slightly more alkaline).
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (Slightly alkaline).
Oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve will shift to right on decrease of- a)Acidity
- b)Carbon dioxide concentration
- c)Both 1 & 2
- d)pH
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Oxygen haemoglobin dissociation curve will shift to right on decrease of
a)
Acidity
b)
Carbon dioxide concentration
c)
Both 1 & 2
d)
pH
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
The strength with which oxygen binds to hemoglobin is affected by several factors. These factors shift or reshape the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. A rightward shift indicates that the hemoglobin under study has a decreased affinity for oxygen.
Which of the following statement is true about Trachea, in a respiratory system?- a)It functions as passages of air to each alveolus.
- b)It functions for sound production.
- c)It acts as a passage for air to bronchi.
- d)It lowers the surface tension.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement is true about Trachea, in a respiratory system?
a)
It functions as passages of air to each alveolus.
b)
It functions for sound production.
c)
It acts as a passage for air to bronchi.
d)
It lowers the surface tension.
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The trachea serves as a passage for air, moistens and warms it while it passes into the lungs, and protects the respiratory surface from an accumulation of foreign particles.

Which one of the following organs in the human body is most affected due to shortage of oxygen? [1999]- a)intestine
- b)skin
- c)kidney
- d)brain
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following organs in the human body is most affected due to shortage of oxygen? [1999]
a)
intestine
b)
skin
c)
kidney
d)
brain

|
Rajeev Sharma answered |
Brain is the most vital organ. It stops functioning in the absence of O2.
R.Q. for glucose is:a) 1b) 0.5c) 2d) 0.05Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Anchal Maurya answered |
R.Q (respiratory quetiont )=no.of total molecules of CO2 released in rxn/no. of O2 involved
in glucose rxn
C6H12O6+6O2-->6CO2 +6H2O+energy
so R. Q.=6/6
R.Q.=1
in glucose rxn
C6H12O6+6O2-->6CO2 +6H2O+energy
so R. Q.=6/6
R.Q.=1
Which one of the following statement is correct?- a)Chest expands because air enters into the lungs
- b)Air enters into the lungs because chest expands
- c)The muscles of the diaphragm contracts because air enters into the lungs
- d)All of the above statements are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statement is correct?
a)
Chest expands because air enters into the lungs
b)
Air enters into the lungs because chest expands
c)
The muscles of the diaphragm contracts because air enters into the lungs
d)
All of the above statements are correct

|
Pragati Mishra answered |
Inhalation or inspiration is an active process.
we ,with the help of the intercoastal muscles, increase the volume of thoracic cavity ,thus increasing the volume of lungs. This creates a negative pressure inside the lungs as compared to external surrounding and therefore due to negative pressure, air comes inside the lungs.
we ,with the help of the intercoastal muscles, increase the volume of thoracic cavity ,thus increasing the volume of lungs. This creates a negative pressure inside the lungs as compared to external surrounding and therefore due to negative pressure, air comes inside the lungs.
Expiratory muscles contract at the time of
- a)Deep inspiration
- b)Normal inspiration and expiration
- c)Forceful expiration
- d)Normal expiration
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Expiratory muscles contract at the time of
a)
Deep inspiration
b)
Normal inspiration and expiration
c)
Forceful expiration
d)
Normal expiration
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Expiration muscles come into action when you force expiration. The expiratory muscles are the abdominal muscles and intercostals. It is rare if a patient is contracting abdominal muscles for quiet breathing and he is trying to force expiration.
Expiration involves
- a)Relaxation of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
- b)Contraction of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
- c)Contraction of diaphragm muscles
- d)Contraction of intercostal muscles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Expiration involves
a)
Relaxation of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
b)
Contraction of diaphragm and intercostal muscles
c)
Contraction of diaphragm muscles
d)
Contraction of intercostal muscles
|
|
Priyanka Nath answered |
Expiration is a process by which the foul air (carbon dioxide) is expelled out from the lungs. It is a passive process which occurs in the diaphragm and internal intercostal muscles in the following manner-
i) Diaphragm: The muscle fibres of the diaphragm relax making it convex, decreasing the volume of tge thoracic activity.
ii) Internal intercostal muscles: These muscles contract so that they pull the ribs downward and inward decreasing the size of the thoracic activity. So, the correct answer is option (A) .
i) Diaphragm: The muscle fibres of the diaphragm relax making it convex, decreasing the volume of tge thoracic activity.
ii) Internal intercostal muscles: These muscles contract so that they pull the ribs downward and inward decreasing the size of the thoracic activity. So, the correct answer is option (A) .
The quantity 1200 ml in the respiratory volumes of a normal human adult refers to [1996]
- a)residual volume
- b)maximum air that can be breathed in and breathed out
- c)expiratory reserve volume
- d)total lung capacity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The quantity 1200 ml in the respiratory volumes of a normal human adult refers to [1996]
a)
residual volume
b)
maximum air that can be breathed in and breathed out
c)
expiratory reserve volume
d)
total lung capacity

|
Maitri Mukherjee answered |
The total volume of air that can be expelled from the lungs after maximum inspiration and then expiring to the maximum is known as the vital capacity. The volume of air that remains inside lungs at the end of maximum forceful expiration is the residual volume. Expiratory reserve volume is the maximum extra volume of air that can be expired by forceful expiration after a normal tidal expiration. Total lung capacity is the maximum volume of air that can be contained in the lungs after maximum inspiration.
Lungs are made up of air-filled sacs, the alveoli. They do not collapse even after forceful expiration, because of:- a)Expiratory reserve volume
- b)Residual volume
- c)Inspiratory reserve volume
- d)Tidal volume
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Lungs are made up of air-filled sacs, the alveoli. They do not collapse even after forceful expiration, because of:
a)
Expiratory reserve volume
b)
Residual volume
c)
Inspiratory reserve volume
d)
Tidal volume
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- The volume of air remaining in the lungs even after a forcible expiration is called residual volume.
- This residual volume prevents the lungs from collapsing.
Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in- a)humans
- b)frog [1990]
- c)rabbit
- d)lizard
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Skin is an accessory organ of respiration in
a)
humans
b)
frog [1990]
c)
rabbit
d)
lizard

|
Arya Khanna answered |
In addition to lungs, skin is also an organ of respiration in frog. It is practically the only mode of respiration when the frog is under water or hibernating. Skin is richly supplied with blood and is permeable to gases. That is way frogs always stay near water to keep their skin moist. It is further kept moist by secretion of mucus from its glands, and does not become dry out of water.
The alveolar epithelium in the lungs is[1990]- a)nonciliated columnar
- b)nonciliated squamous
- c)ciliated columnar
- d)ciliated squamous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The alveolar epithelium in the lungs is[1990]
a)
nonciliated columnar
b)
nonciliated squamous
c)
ciliated columnar
d)
ciliated squamous

|
Dipanjan Chawla answered |
The very thin alveolar wall (about 0.0001 mm) is composed of moist, nonciliated, squamous epithelial cells.
"Emphysema" is a condition in which -- a)Repiratoy centre inhibited
- b)Lot of fluid in the lungs
- c)The walls seperating the alveoli break
- d)Lungs have more O2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
"Emphysema" is a condition in which -
a)
Repiratoy centre inhibited
b)
Lot of fluid in the lungs
c)
The walls seperating the alveoli break
d)
Lungs have more O2
|
|
Tanvi Dear answered |
When any person consume cigarette then it harms the inner wall of alveoli so in response of it alveoli secrete some chemicals which destroy the smoked particles present near by alveolar wall but with them wall also ruptures .it leads to decresing surface area of alveoli which makes difficult to respire ..And this infectious condition is emphysema .
Hope It Helps Uh
Hope It Helps Uh
Respiration in mature mammalian erythrocytes are __________
- a)Anaerobic
- b)Absent
- c)Sometimes aerobic and sometimes anaerobic
- d)Aerobic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiration in mature mammalian erythrocytes are __________
a)
Anaerobic
b)
Absent
c)
Sometimes aerobic and sometimes anaerobic
d)
Aerobic
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Sometimes aerobic and sometimes anaerobic.
If expiratory reserve volume is 1100 ml residual volume is 1200 ml and tidal volume is 500 ml, what shall be the functional residual capacity- a)1600 ml
- b)2800 ml
- c)2300 ml
- d)1200 ml
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If expiratory reserve volume is 1100 ml residual volume is 1200 ml and tidal volume is 500 ml, what shall be the functional residual capacity
a)
1600 ml
b)
2800 ml
c)
2300 ml
d)
1200 ml
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC) is the volume of air that will remain in the lungs after a normal expiration. This includes expiratory reserve volume i.e. 1100ml plus 1200ml or 2300ml.
Chapter doubts & questions for Breathing and Exchange of Gases - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Breathing and Exchange of Gases - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily














