All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Ecosystem for NEET Exam
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is- a)1 - 5%
- b)2 - 10%
- c)less than 50%
- d)approx 100%
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is
a)
1 - 5%
b)
2 - 10%
c)
less than 50%
d)
approx 100%
|
|
Lakshmi Deshpande answered |
The percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is less than 50%. PAR refers to the portion of sunlight that is within the wavelength range of 400 to 700 nanometers, which is the range most effectively used by plants for photosynthesis.
Here is a detailed explanation:
1. Definition of PAR:
- PAR is the range of light wavelengths that are absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in plants, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis.
- PAR is typically measured in micromoles per square meter per second (µmol/m²/s).
2. Components of solar radiation:
- Solar radiation is composed of various wavelengths, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light.
- Only a small portion of solar radiation falls within the PAR range.
3. Wavelengths of PAR:
- The PAR range is defined as 400 to 700 nanometers (nm), which corresponds to the visible light spectrum.
- Within this range, different wavelengths of light have varying effects on plant growth and development.
4. Importance of PAR for photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, using water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll, the primary pigment in plants, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue (400-500 nm) and red (600-700 nm) regions of the spectrum.
- Therefore, light within the PAR range is crucial for driving photosynthesis.
5. Percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation:
- While the exact percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation varies depending on factors such as atmospheric conditions and time of day, it is generally accepted to be less than 50%.
- This means that more than half of the solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface falls outside the PAR range.
6. Utilization of non-PAR wavelengths:
- Plants can also utilize certain wavelengths of light outside the PAR range, such as UV and IR light, for various physiological processes.
- UV light, for example, can stimulate the production of protective compounds in plants, while IR light can affect plant growth and development.
In conclusion, the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is less than 50%. This indicates that a significant portion of solar radiation falls outside the PAR range, highlighting the importance of considering the entire spectrum of light when studying plant responses to sunlight.
Here is a detailed explanation:
1. Definition of PAR:
- PAR is the range of light wavelengths that are absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in plants, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis.
- PAR is typically measured in micromoles per square meter per second (µmol/m²/s).
2. Components of solar radiation:
- Solar radiation is composed of various wavelengths, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light.
- Only a small portion of solar radiation falls within the PAR range.
3. Wavelengths of PAR:
- The PAR range is defined as 400 to 700 nanometers (nm), which corresponds to the visible light spectrum.
- Within this range, different wavelengths of light have varying effects on plant growth and development.
4. Importance of PAR for photosynthesis:
- Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy, using water and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen.
- Chlorophyll, the primary pigment in plants, absorbs light most efficiently in the blue (400-500 nm) and red (600-700 nm) regions of the spectrum.
- Therefore, light within the PAR range is crucial for driving photosynthesis.
5. Percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation:
- While the exact percentage of PAR in incident solar radiation varies depending on factors such as atmospheric conditions and time of day, it is generally accepted to be less than 50%.
- This means that more than half of the solar radiation that reaches the Earth's surface falls outside the PAR range.
6. Utilization of non-PAR wavelengths:
- Plants can also utilize certain wavelengths of light outside the PAR range, such as UV and IR light, for various physiological processes.
- UV light, for example, can stimulate the production of protective compounds in plants, while IR light can affect plant growth and development.
In conclusion, the percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) in the incident solar radiation is less than 50%. This indicates that a significant portion of solar radiation falls outside the PAR range, highlighting the importance of considering the entire spectrum of light when studying plant responses to sunlight.
Study the following statements and select the incorrect one.- a)Shorter food chains provide more energy as compared to longer food chains
- b)Ecological factors connected with physical geography of earth are called topographic factors
- c)The pyramid of biomass is upright in a grassland ecosystem and the pyramid of numbers is upright in a parasitic food chain
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements and select the incorrect one.
a)
Shorter food chains provide more energy as compared to longer food chains
b)
Ecological factors connected with physical geography of earth are called topographic factors
c)
The pyramid of biomass is upright in a grassland ecosystem and the pyramid of numbers is upright in a parasitic food chain
d)
None of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Pyramid of biomass for terrestrial ecosystems (grasslands, forests) the biomass generally decreases at each higher trophic level from plants via herbivores to carnivores. This is evident from the fact that the terrestrial producers’ viz. grasses, trees and shrubs have a much higher biomass than the animals that consume them, such as deer, zebras and insects. A single plant or animal in a parasitic food chain may support numerous parasites, which might be further supporting a larger number of hyperparasites. Thus, the pyramid of numbers in a parasitic food chain is inverted.
So the correct option is 'the pyramid of biomass is upright in a grassland ecosystem and the pyramid of number is upright in a parasitic food chain'.
So the correct option is 'the pyramid of biomass is upright in a grassland ecosystem and the pyramid of number is upright in a parasitic food chain'.
Which food chain is the major conduit for energy flow in an aquatic ecosystem?- a)Grazing food chain (GFC)
- b)Detritus food chain (DFC)
- c)Both GFC and DFC
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Grazing food chain (GFC)
b)
Detritus food chain (DFC)
c)
Both GFC and DFC
d)
None of the above

|
EduRev NEET answered |
In an aquatic ecosystem, the grazing food chain (GFC) is the major pathway for energy flow, whereas the detritus food chain plays a smaller role compared to terrestrial ecosystems.
In an aquatic ecosystem, the organism present at the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands is?- a)Phytolanktons
- b)Large fishes
- c)Sea gulls
- d)Zooplanktons
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In an aquatic ecosystem, the organism present at the trophic level equivalent to cows in grasslands is?
a)
Phytolanktons
b)
Large fishes
c)
Sea gulls
d)
Zooplanktons
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In an aquatic ecosystem, the important herbivores are zooplankton, larvae, tadpoles, etc. Cows in grasslands also act as herbivores as these feed on producers. Thus, both cows and zooplankton occupy second trophic level in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem respectively.
Which group of organisms in the pond ecosystem is primarily responsible for the decomposition of dead matter?- a)Phytoplankton
- b)Zooplankton
- c)Algae
- d)Fungi and bacteria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Phytoplankton
b)
Zooplankton
c)
Algae
d)
Fungi and bacteria
|
|
Sahil Basu answered |
Role of Decomposers in Pond Ecosystem
In a pond ecosystem, the decomposition of dead organic matter is crucial for nutrient recycling. This process is primarily facilitated by fungi and bacteria, making them the key decomposers in such environments.
Importance of Decomposers
Decomposers play several vital roles in maintaining the health of the ecosystem:
Comparison with Other Organisms
While phytoplankton and algae are primary producers that convert sunlight into energy, and zooplankton are consumers that feed on these producers, they do not play significant roles in decomposition:
Conclusion
In summary, fungi and bacteria are essential for decomposition in pond ecosystems, enabling nutrient recycling and supporting overall ecological balance.
In a pond ecosystem, the decomposition of dead organic matter is crucial for nutrient recycling. This process is primarily facilitated by fungi and bacteria, making them the key decomposers in such environments.
Importance of Decomposers
Decomposers play several vital roles in maintaining the health of the ecosystem:
- Breaking Down Organic Matter: Fungi and bacteria break down dead plants and animals, recycling essential nutrients back into the ecosystem.
- Nutrient Release: As these organisms decompose organic materials, they release nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for the growth of aquatic plants.
- Soil and Water Quality: The decomposition process helps improve soil quality and can enhance water clarity by reducing organic waste.
- Energy Flow: Decomposers are integral to the energy flow in the ecosystem. By breaking down dead matter, they convert it into forms that can be utilized by primary producers like phytoplankton.
Comparison with Other Organisms
While phytoplankton and algae are primary producers that convert sunlight into energy, and zooplankton are consumers that feed on these producers, they do not play significant roles in decomposition:
- Phytoplankton: Primarily photosynthetic and contribute to oxygen production.
- Zooplankton: Heterotrophic and consume phytoplankton, but do not decompose dead matter.
- Algae: Also producers that depend on sunlight and nutrients but are not involved in decomposition.
Conclusion
In summary, fungi and bacteria are essential for decomposition in pond ecosystems, enabling nutrient recycling and supporting overall ecological balance.
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Pyramids of energy and yearly biomass production can never be inverted, since this would violate the laws of thermodynamics.
(ii) Pyramids of standing crop and numbers can be inverted, since the number of organisms at a time does not indicate the amount of energy flowing through the system.
(iii) There are certain limitations of ecological pyramids such as they do not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
(iv) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(iii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements and select the incorrect ones.
(i) Pyramids of energy and yearly biomass production can never be inverted, since this would violate the laws of thermodynamics.
(ii) Pyramids of standing crop and numbers can be inverted, since the number of organisms at a time does not indicate the amount of energy flowing through the system.
(iii) There are certain limitations of ecological pyramids such as they do not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
(iv) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
(i) Pyramids of energy and yearly biomass production can never be inverted, since this would violate the laws of thermodynamics.
(ii) Pyramids of standing crop and numbers can be inverted, since the number of organisms at a time does not indicate the amount of energy flowing through the system.
(iii) There are certain limitations of ecological pyramids such as they do not take into account the same species belonging to two or more trophic levels.
(iv) Saprophytes are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(iii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
None of these
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The second law of thermodynamics states that whenever energy is transformed, there is a loss energy through the release of heat. This occurs when energy is transferred between trophic levels as illustrated in a food web. When one animal feeds off another, there is a loss of heat (energy) in the process. Additional loss of energy occurs during respiration and movement. Hence, more and more energy is lost as one moves up through trophic levels. If this pyramid is inverterved, it would violate the law of thermodynamics. Hence the pyramid can never be inverted.
The pyramid of numbers depicts the relationship in terms of the number of producers, herbivores and the carnivores at their successive trophic levels. There is a decrease in the number of individuals from the lower to the higher trophic levels. The number pyramid varies from ecosystem to ecosystem. Since the amount if energy flowing through the system is not indicated, the pyramid can be inverted.
These are the diagrammatic illustrations of connection between different trophic levels in terms of energy, biomass and number of an organism. The base of each pyramid represents the producers or the first trophic level. Apex represents tertiary or top level consumers. If any species belongs to two or more trophic level, it can causes differences and issues in energy flow and numbers.
Saprophytes are organisms which feed on dead and decaying matter and these pyramid exhibit interaction between the living components and decomposers interact with dead organisms at all level. This makes it difficult to place it in the ecological pyramid. Hence, they are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
So the correct option is 'none of these'.
The pyramid of numbers depicts the relationship in terms of the number of producers, herbivores and the carnivores at their successive trophic levels. There is a decrease in the number of individuals from the lower to the higher trophic levels. The number pyramid varies from ecosystem to ecosystem. Since the amount if energy flowing through the system is not indicated, the pyramid can be inverted.
These are the diagrammatic illustrations of connection between different trophic levels in terms of energy, biomass and number of an organism. The base of each pyramid represents the producers or the first trophic level. Apex represents tertiary or top level consumers. If any species belongs to two or more trophic level, it can causes differences and issues in energy flow and numbers.
Saprophytes are organisms which feed on dead and decaying matter and these pyramid exhibit interaction between the living components and decomposers interact with dead organisms at all level. This makes it difficult to place it in the ecological pyramid. Hence, they are not given any place in ecological pyramids even though they play a vital role in the ecosystem.
So the correct option is 'none of these'.
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(i), (ii) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct ones.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
(i) A given species may occupy more than one trophic level in the same ecosystem at the same time.
(ii) Productivity of an aquatic ecosystem is less than that of a terrestrial ecosystem.
(iii) Producers constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Decomposers and detritivores constitute the first trophic level of a detritus food chain.
Mr. X is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying- a)first trophic level
- b)second trophic level
- c)third trophic level
- d)fourth trophic level
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mr. X is eating curd/yoghurt. For this food intake in a food chain he should be considered as occupying
a)
first trophic level
b)
second trophic level
c)
third trophic level
d)
fourth trophic level
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Mr. X eating curd / yoghurt should be considered as occupying third trophic level. Producers or greeen plants (first trophic level) are consumed by herbivore (second trophic level). And from them curd, yoghurt (made from dairy breed) is consumed by third trophic level like man.
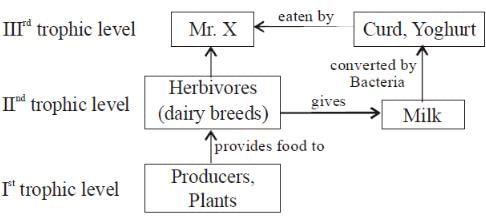

What describes the movement of energy in the pond ecosystem?- a)Bidirectional flow between trophic levels
- b)Cyclical within the same trophic level
- c)Unidirectional towards higher trophic levels
- d)Stagnant at the autotrophic level
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Bidirectional flow between trophic levels
b)
Cyclical within the same trophic level
c)
Unidirectional towards higher trophic levels
d)
Stagnant at the autotrophic level

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
In the pond ecosystem, there is a unidirectional movement of energy towards higher trophic levels, starting from autotrophs to heterotrophs, and energy is eventually dissipated as heat.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: In an aquatic ecosystem, pyramid of biomass is inverted.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: In an aquatic ecosystem, pyramid of biomass is inverted.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.
Statement 1: In an aquatic ecosystem, pyramid of biomass is inverted.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Rahul Das answered |
Statement 1: In an aquatic ecosystem, pyramid of biomass is inverted.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.
The correct option is A) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
Explanation:
Aquatic Ecosystem and Pyramid of Biomass:
An aquatic ecosystem refers to any environment that is primarily water-based and includes both freshwater and marine ecosystems. The pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the total biomass at each trophic level (feeding level) in an ecosystem. It shows the amount of living material (biomass) present in each trophic level.
Inverted Pyramid of Biomass:
In an aquatic ecosystem, the pyramid of biomass is often inverted. This means that the biomass of consumers (herbivores and carnivores) is greater than the biomass of producers (plants and algae). This is in contrast to a typical pyramid of biomass in a terrestrial ecosystem, where the biomass of producers is greater than the biomass of consumers.
Explanation for Statement 1:
The inverted pyramid of biomass in aquatic ecosystems can be attributed to the high turnover rate of producers and the rapid growth and reproduction of consumers. In aquatic ecosystems, producers such as phytoplankton and algae have a short lifespan and high turnover rate. They are constantly being consumed by herbivores, leading to a high biomass of consumers compared to producers.
Explanation for Statement 2:
Biomass is the total mass of living organisms in a given area or volume. It depends on the reproductive potential and longevity of individuals in an ecosystem. Reproductive potential refers to the ability of individuals to produce offspring, while longevity refers to the lifespan of individuals. In aquatic ecosystems, consumers often have higher reproductive potential and shorter lifespans compared to producers. This leads to a higher biomass of consumers and an inverted pyramid of biomass.
In conclusion, both statements are correct, and statement 2 provides a correct explanation for statement 1. The inverted pyramid of biomass in aquatic ecosystems can be attributed to the high turnover rate of producers and the higher reproductive potential and shorter lifespans of consumers.
Statement 2: Biomass depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of individuals.
The correct option is A) Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
Explanation:
Aquatic Ecosystem and Pyramid of Biomass:
An aquatic ecosystem refers to any environment that is primarily water-based and includes both freshwater and marine ecosystems. The pyramid of biomass is a graphical representation of the total biomass at each trophic level (feeding level) in an ecosystem. It shows the amount of living material (biomass) present in each trophic level.
Inverted Pyramid of Biomass:
In an aquatic ecosystem, the pyramid of biomass is often inverted. This means that the biomass of consumers (herbivores and carnivores) is greater than the biomass of producers (plants and algae). This is in contrast to a typical pyramid of biomass in a terrestrial ecosystem, where the biomass of producers is greater than the biomass of consumers.
Explanation for Statement 1:
The inverted pyramid of biomass in aquatic ecosystems can be attributed to the high turnover rate of producers and the rapid growth and reproduction of consumers. In aquatic ecosystems, producers such as phytoplankton and algae have a short lifespan and high turnover rate. They are constantly being consumed by herbivores, leading to a high biomass of consumers compared to producers.
Explanation for Statement 2:
Biomass is the total mass of living organisms in a given area or volume. It depends on the reproductive potential and longevity of individuals in an ecosystem. Reproductive potential refers to the ability of individuals to produce offspring, while longevity refers to the lifespan of individuals. In aquatic ecosystems, consumers often have higher reproductive potential and shorter lifespans compared to producers. This leads to a higher biomass of consumers and an inverted pyramid of biomass.
In conclusion, both statements are correct, and statement 2 provides a correct explanation for statement 1. The inverted pyramid of biomass in aquatic ecosystems can be attributed to the high turnover rate of producers and the higher reproductive potential and shorter lifespans of consumers.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.- a)Both statement 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
- b)Both statement 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
- c)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- d)Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.
Statement 1: Herbivores are also called as first-order consumers.
Statement 2: Herbivores obtain their food directly from plants.
a)
Both statement 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1
b)
Both statement 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1
c)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
d)
Both statement 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
First-order consumers are animals that eat plants called herbivores. They are the first step in the food chain.
Organisms which are associated with first as well as third trophic level are- a)macrophytes
- b)phytoplanktons
- c)chemoautotrophs
- d)insectivorous plants
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Organisms which are associated with first as well as third trophic level are
a)
macrophytes
b)
phytoplanktons
c)
chemoautotrophs
d)
insectivorous plants
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Trophic level is a functional level. A single species may occupy more than one trophic level. Insectivorous plants are producers, occupying first trophic level. They also eat insects and thus, occupy third trophic level also.
If 10 joules of energy is available at the producer level, then amount of energy present at the level of secondary consumer is- a)10 J
- b)1 J
- c)0.1 J
- d)0.01 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If 10 joules of energy is available at the producer level, then amount of energy present at the level of secondary consumer is
a)
10 J
b)
1 J
c)
0.1 J
d)
0.01 J
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Only 10 % of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next trophic level of a food chain (ten percent law, given by Linderman). In present case, energy available at producer level is 10 J. Hence energy at primary consumer level would be 1 H (10% of 10 J). Similarly, at secondary consumer level, energy present will be 0.1 J (100 % of 1 J).
In a grassland ecosystem, if the number of primary producers is approximately 6 million plants, the number of the top carnivores (in million), which may be supported by it may be ________ million.- a)3
- b)30
- c)6
- d)60
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a grassland ecosystem, if the number of primary producers is approximately 6 million plants, the number of the top carnivores (in million), which may be supported by it may be ________ million.
a)
3
b)
30
c)
6
d)
60
|
|
Devika Ahuja answered |
Calculation of the number of top carnivores supported by the grassland ecosystem:
1. Trophic levels in a grassland ecosystem:
- Primary producers (plants) are at the first trophic level.
- Herbivores are at the second trophic level.
- Carnivores (including top carnivores) are at higher trophic levels.
2. Energy transfer in an ecosystem:
- Only about 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
- This means that a large number of primary producers are needed to support a smaller number of herbivores and an even smaller number of top carnivores.
3. Calculation:
- If there are 6 million primary producers, and assuming a 10% energy transfer efficiency, the number of herbivores supported would be 6 million / 10 = 0.6 million.
- Similarly, the number of top carnivores supported by the herbivores would be 0.6 million / 10 = 0.06 million, which is equal to 60,000 top carnivores.
Therefore, the number of top carnivores (in million) supported by the grassland ecosystem would be 3 million (Option A).
1. Trophic levels in a grassland ecosystem:
- Primary producers (plants) are at the first trophic level.
- Herbivores are at the second trophic level.
- Carnivores (including top carnivores) are at higher trophic levels.
2. Energy transfer in an ecosystem:
- Only about 10% of energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
- This means that a large number of primary producers are needed to support a smaller number of herbivores and an even smaller number of top carnivores.
3. Calculation:
- If there are 6 million primary producers, and assuming a 10% energy transfer efficiency, the number of herbivores supported would be 6 million / 10 = 0.6 million.
- Similarly, the number of top carnivores supported by the herbivores would be 0.6 million / 10 = 0.06 million, which is equal to 60,000 top carnivores.
Therefore, the number of top carnivores (in million) supported by the grassland ecosystem would be 3 million (Option A).
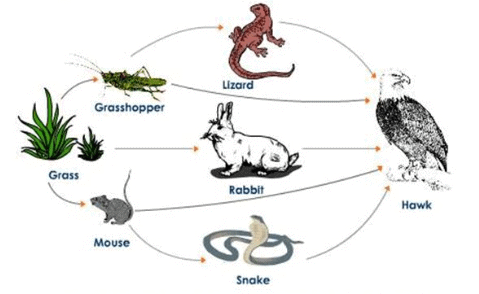
In the given food web, an increase in the population of hawks will not result in
- a)decrease in the population of rabbits and snakes
- b)increase in the population of producers
- c)increase in the population of grasshoppers
- d)decrease in the population of lizards
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given food web, an increase in the population of hawks will not result in
a)
decrease in the population of rabbits and snakes
b)
increase in the population of producers
c)
increase in the population of grasshoppers
d)
decrease in the population of lizards
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
If population of hawks would increase, they would feed on more lizards which will result in decrease of lizard population.
What is the primary function of the solar input in the pond ecosystem?- a)It facilitates the growth of bottom-dwelling forms.
- b)It drives the photosynthetic activity of autotrophs.
- c)It controls the decomposition rate of organic matter.
- d)It increases the water temperature to optimum levels for fungi.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It facilitates the growth of bottom-dwelling forms.
b)
It drives the photosynthetic activity of autotrophs.
c)
It controls the decomposition rate of organic matter.
d)
It increases the water temperature to optimum levels for fungi.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
The primary function of the solar input in the pond ecosystem is to drive the photosynthetic activity of autotrophs such as phytoplankton and certain algae, enabling them to convert inorganic substances into organic material, which is essential for the functioning of the ecosystem.
What role do autotrophs play in an aquatic ecosystem such as a pond?- a)They decompose organic material.
- b)They consume other organisms.
- c)They convert inorganic into organic material using sunlight.
- d)They regulate the temperature of the pond.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
They decompose organic material.
b)
They consume other organisms.
c)
They convert inorganic into organic material using sunlight.
d)
They regulate the temperature of the pond.

|
Stepway Academy answered |
In an aquatic ecosystem like a pond, autotrophs such as phytoplankton and certain algae use the radiant energy from the sun to convert inorganic substances into organic material, supporting the base of the food web.
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that is captured by plants in synthesis of organic matter is?- a)50-70%
- b)30-40%
- c)80-100%
- d)2-10%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) that is captured by plants in synthesis of organic matter is?
a)
50-70%
b)
30-40%
c)
80-100%
d)
2-10%
|
|
Mohd Parvez answered |
According to NCERT page number 245 chapter ecosystems incident solar radiation less than 50% of its photosynthetically active radiation Then option D will correct.
Less than 50% Aisa ek hi option h jisme kam hai
Less than 50% Aisa ek hi option h jisme kam hai
Study the food web given below and answer the questions that follow.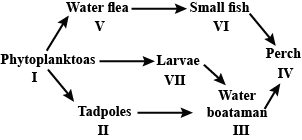 Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?
Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?- a)II and V
- b)III and VI
- c)VII only
- d)IV only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the food web given below and answer the questions that follow.

Which of the following organisms in the given food web acts as a secondary consumer?
a)
II and V
b)
III and VI
c)
VII only
d)
IV only
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
In the given food web, organisms I (phytoplanktons) act as producers, organisms II, V and VII act as primary consumers as they feed on producers, organisms III and VI act as secondary consumers as they upon primary consumers, and organism IV acts as a tertiary consumer.
Study the following ecological pyramids carefully.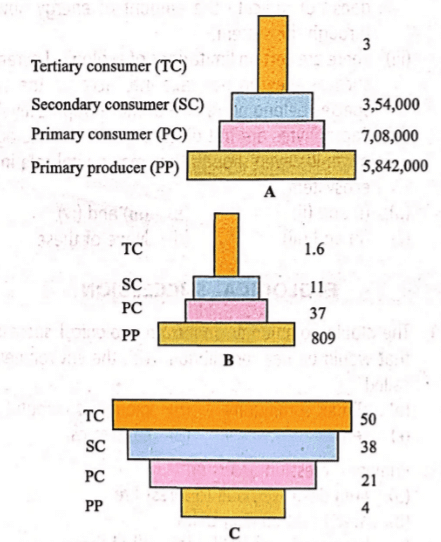 Match the following statements (i),(ii) and (iii) with given pyramids A, B and C and select the correct answer.
Match the following statements (i),(ii) and (iii) with given pyramids A, B and C and select the correct answer.
(i) Inverted pyramid of biomass depicting small standing crop of phytoplanktons supporting a large standing crop of zooplanktons
(ii) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem showing about 6 million producers
(iii) Upright pyramid of biomass- a)A−(ii), B−(iii), C−(i)
- b)A−(ii), B−(i), C−(iii)
- c)A−(i), B−(iii), C−(ii)
- d)A−(i), B−(ii), C−(iii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following ecological pyramids carefully.

Match the following statements (i),(ii) and (iii) with given pyramids A, B and C and select the correct answer.
(i) Inverted pyramid of biomass depicting small standing crop of phytoplanktons supporting a large standing crop of zooplanktons
(ii) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem showing about 6 million producers
(iii) Upright pyramid of biomass
(i) Inverted pyramid of biomass depicting small standing crop of phytoplanktons supporting a large standing crop of zooplanktons
(ii) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem showing about 6 million producers
(iii) Upright pyramid of biomass
a)
A−(ii), B−(iii), C−(i)
b)
A−(ii), B−(i), C−(iii)
c)
A−(i), B−(iii), C−(ii)
d)
A−(i), B−(ii), C−(iii)
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
When the biomass of producer is less and that of the consumer is more the pyramid will have an inverted shape. It occurs in a pond and lake ecosystem. Here the biomass of diatoms in planktons is negligible as compared to their date of crustaceans and small fishes. inverted pyramid soil found in that ecosystem where the number and biomass of producers of more and those of consumers are less.
In most of the ecosystems, the number of the biomass of producers is more than those of a consumer is less. This type of ecosystem has a pyramid where the apex is pointed upwards. This type of pyramid is known as upright pyramid.
In some ecosystem, the number of the producers is more than the consumers. The apex is pointed upwards. This is known as the upright pyramid of the number. Found in the grassland ecosystem.
In most of the ecosystems, the number of the biomass of producers is more than those of a consumer is less. This type of ecosystem has a pyramid where the apex is pointed upwards. This type of pyramid is known as upright pyramid.
In some ecosystem, the number of the producers is more than the consumers. The apex is pointed upwards. This is known as the upright pyramid of the number. Found in the grassland ecosystem.
Given food web contains some missing organisms, (1), (2), (3) and (4). Identify these organisms and select the correct answer.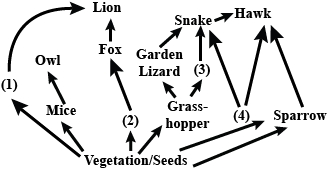
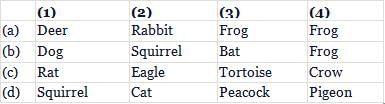
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given food web contains some missing organisms, (1), (2), (3) and (4). Identify these organisms and select the correct answer.


a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
A lion feeds on a deer.
Deer are the primary consumer.
Fox acts a secondary consumer and feeds on a primary consumer such as Rabbit.
Frog feeds on a grasshopper and acts as a primary consumer.
Rat acts as prey for both Snake and a hawk.
Deer are the primary consumer.
Fox acts a secondary consumer and feeds on a primary consumer such as Rabbit.
Frog feeds on a grasshopper and acts as a primary consumer.
Rat acts as prey for both Snake and a hawk.
What term is used to describe the vertical distribution of different species occupying various levels in an ecosystem?- a)Biodiversity
- b)Stratification
- c)Succession
- d)Composition
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What term is used to describe the vertical distribution of different species occupying various levels in an ecosystem?
a)
Biodiversity
b)
Stratification
c)
Succession
d)
Composition

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification. For example, trees occupy top vertical strata or layer of a forest, shrubs the second and herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layers.
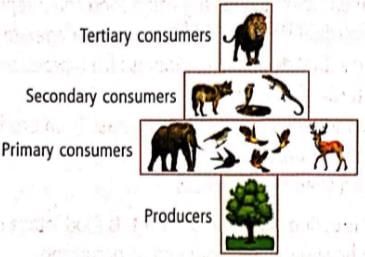
The given pyramid best represents
- a)pyramid of energy in forest ecosystem
- b)pyramid of biomass in forest ecosystem
- c)pyramid of numbers in grassland ecosystem
- d)pyramid of numbers in forest ecosystem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The given pyramid best represents


a)
pyramid of energy in forest ecosystem
b)
pyramid of biomass in forest ecosystem
c)
pyramid of numbers in grassland ecosystem
d)
pyramid of numbers in forest ecosystem
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Pyramid of numbers in a forest ecosystem is spindle shaped. In a forest ecosystem, number of producers is lesser but supports a greater number of herbivores. Which in turn support a fewer number of carnivores. This results in spindle shaped structure of pyramid of numbers.
Given figure represents a pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem
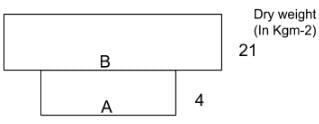 Identify A and B and select the correct answer.
Identify A and B and select the correct answer.
(i) A is the crop which supports and B is the crop which is supported.
(ii) A is the crop which is supported and B is the crop which supports.
(iii) A is phytoplanktons and B is zooplanktons.
(iv) A is zooplanktons and B is phytoplanktons.- a)(i) and (iv)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(i) and (iii)
- d)(ii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Given figure represents a pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem


Identify A and B and select the correct answer.
(i) A is the crop which supports and B is the crop which is supported.
(ii) A is the crop which is supported and B is the crop which supports.
(iii) A is phytoplanktons and B is zooplanktons.
(iv) A is zooplanktons and B is phytoplanktons.
(i) A is the crop which supports and B is the crop which is supported.
(ii) A is the crop which is supported and B is the crop which supports.
(iii) A is phytoplanktons and B is zooplanktons.
(iv) A is zooplanktons and B is phytoplanktons.
a)
(i) and (iv)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(i) and (iii)
d)
(ii) and (iv)
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
The given pyramid represents pyramid of biomass in an aquatic ecosystem. In this pyramid, biomass of phytoplanktons, i.e., producers (represented by A) is smaller than that of zooplanktons, i.e., primary consumers (represented by B). Phytoplanktons support zooplanktons as the latter feed upon them.
Which kind of pyramid is represented by the given figure?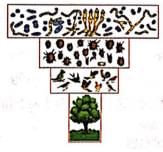
- a)Inverted pyramid of numbers
- b)Inverted pyramid of biomass
- c)Inverted pyramid of energy
- d)Both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which kind of pyramid is represented by the given figure?

a)
Inverted pyramid of numbers
b)
Inverted pyramid of biomass
c)
Inverted pyramid of energy
d)
Both (a) and (b)
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Given pyramid is pyramid of numbers in a parasitic food chain. In a parasitic food chain, the pyramid of numbers is inverted. This is due to the fact that a single plant may support the growth of many herbivores and each herbivore in turn may provide nutrition to several parasites, which in turn support many hyper-parasites. Thus, from the producer towards consumers, the number of organisms gradually increase, making the pyramid inverted in shape.
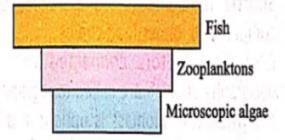
In an open ocean, the biomass of primary producers (microscopic algae) is often lower than the biomass of higher trophic levels (zooplanktons and fish), as illustrated below by an inverted pyramid of biomass. How can there be enough food in an open ocean to support the higher trophic levels?
- a)The microscopic primary producers are a source of food of high quality
- b)The microscopic primary producers have high rates of growth and reproduction
- c)The microscopic primary producers are less abundant
- d)The higher trophic levels are cold-blooded animals which do not require much food
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In an open ocean, the biomass of primary producers (microscopic algae) is often lower than the biomass of higher trophic levels (zooplanktons and fish), as illustrated below by an inverted pyramid of biomass. How can there be enough food in an open ocean to support the higher trophic levels?


a)
The microscopic primary producers are a source of food of high quality
b)
The microscopic primary producers have high rates of growth and reproduction
c)
The microscopic primary producers are less abundant
d)
The higher trophic levels are cold-blooded animals which do not require much food
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
In an open ocean, the large numbers of phytoplankton quickly complete their life cycles and sets of new population or crops of phytoplankton are formed every few hours or days. Thus, the cumulative energy contents that these generation after generation of phytoplankton trap in course of a year is certainly much more than trapped by only a few generations of herbivorous fishes in the corresponding time and space. The energy content trapped by the carnivores living on the herbivorous fishes is the leat.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.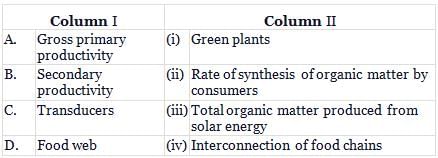
- a)A−(i),B−(ii),C−(iii),D−(iv)
- b)A−(iii),B−(ii),C−(i),D−(iv)
- c)A−(iii),B−(iv),C−(i),D−(ii)
- d)A−(ii),B−(i),C−(iv),D−(iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the given codes.

a)
A−(i),B−(ii),C−(iii),D−(iv)
b)
A−(iii),B−(ii),C−(i),D−(iv)
c)
A−(iii),B−(iv),C−(i),D−(ii)
d)
A−(ii),B−(i),C−(iv),D−(iii)

|
Lead Academy answered |
To match column I with column II correctly:
- Gross primary productivity: Total organic matter produced from solar energy (iii)
- Secondary productivity: Rate of synthesis of organic matter by consumers (ii)
- Transducers: Green plants (i)
- Food web: Interconnection of food chains (iv)
Therefore, the correct match is:
B: A - (iii), B - (ii), C - (i), D - (iv).
This arrangement aligns with the definitions and roles of each concept in ecological systems, ensuring efficient energy flow and understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
- Gross primary productivity: Total organic matter produced from solar energy (iii)
- Secondary productivity: Rate of synthesis of organic matter by consumers (ii)
- Transducers: Green plants (i)
- Food web: Interconnection of food chains (iv)
Therefore, the correct match is:
B: A - (iii), B - (ii), C - (i), D - (iv).
This arrangement aligns with the definitions and roles of each concept in ecological systems, ensuring efficient energy flow and understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
Given figure represents food chains of a deciduous woodland linked together to form a food web.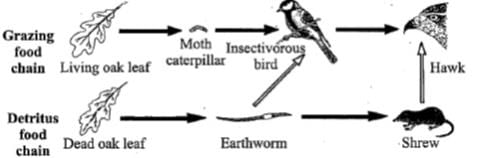 Which of the following constitute first trophic level of the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain respectively?
Which of the following constitute first trophic level of the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain respectively? - a)Living oak leaf and dead oak leaf
- b)Living oak leaf and earthworm
- c)Moth caterpillar and earthworm
- d)Living oak left in both
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Given figure represents food chains of a deciduous woodland linked together to form a food web.

Which of the following constitute first trophic level of the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain respectively?
a)
Living oak leaf and dead oak leaf
b)
Living oak leaf and earthworm
c)
Moth caterpillar and earthworm
d)
Living oak left in both
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
In grazing food chain (GFC), producers constitute the first trophic level whereas detritus food chain (DFC) begins with detritus or dead organic matter.
What kind of pyramid is represented by the given figure?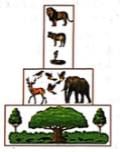
- a)Pyramid of numbers in a forest ecosystem
- b)Pyramid of numbers in a parasitic food chain
- c)Pyramid of biomass in a forest ecosystem
- d)It is a wrong pyramid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What kind of pyramid is represented by the given figure?

a)
Pyramid of numbers in a forest ecosystem
b)
Pyramid of numbers in a parasitic food chain
c)
Pyramid of biomass in a forest ecosystem
d)
It is a wrong pyramid
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Pyramids of biomass are comparatively more fundamental, as they, instead of geometric factor, show the quantitative relationships of the standing crops. In grassland and forest, there is generally a gradual decrease in biomass of organisms at successive levels from the producers to the top carnivores. Thus, pyramids of biomass and number are upright in terrestrial ecosystems.
Which one of the following animals may occupy more than one trophic levels in the same ecosystem at the same time?- a)Sparrow
- b)Lion
- c)Goat
- d)Frog
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following animals may occupy more than one trophic levels in the same ecosystem at the same time?
a)
Sparrow
b)
Lion
c)
Goat
d)
Frog
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A single species may occupy more than one trophic level. Sparrow being omnivorous can be a primary consumer if it feeds on seeds, fruits and peas or a secondary consumer if it feeds on insects and worms.
Chapter doubts & questions for Ecosystem - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Ecosystem - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









