All Exams >
Class 6 >
Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 >
All Questions
All questions of Motion and Measurement of Distances for Class 6 Exam
Q. The movement of earth around the sun is an example ofa)Oscillatory motionb)Circular motionc)Translatory motiond)Periodic motionCorrect answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rajesh Khatri answered |
The answer is b.
A body moving along a circular pat is said to have a circular motion.
The distance of the moving body remains constant from a fixed point or axis, called the axis of rotation. The moving body changes its position during the motion. Thus the movement of earth around the sun is an example of Circular motion.
One cm is equal to- a)1 km
- b)1 m
- c)10 mm
- d)1000 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One cm is equal to
a)
1 km
b)
1 m
c)
10 mm
d)
1000 m

|
Moumita Desai answered |
One centimetre (cm) is equal to 10 mm.
One meter is equal to _____________ mm.- a)100
- b)1000
- c)10
- d)10000
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One meter is equal to _____________ mm.
a)
100
b)
1000
c)
10
d)
10000

|
Deepak Verma answered |
One meter is equal to 100 cm and one cm is equal to 10 mm. therefore, a meter is equal to 100 × 10 = 1000 mm.
Rahul and Ravi are playing in a ground. They start running from the same point X simultaneously in the ground and reach point Y at the same time by following paths marked 1 and 2 respectively, as shown in the figure.Q. Which of the following is correct statement for the given situation?- a)Rahul covers a longer distance with a lower speed.
- b)Rahul covers a longer distance with a higher speed.
- c)Rahul and Ravi both cover different distances with same speed.
- d)Ravi covers a shorter distance with higher speed.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rahul and Ravi are playing in a ground. They start running from the same point X simultaneously in the ground and reach point Y at the same time by following paths marked 1 and 2 respectively, as shown in the figure.
Q. Which of the following is correct statement for the given situation?
a)
Rahul covers a longer distance with a lower speed.
b)
Rahul covers a longer distance with a higher speed.
c)
Rahul and Ravi both cover different distances with same speed.
d)
Ravi covers a shorter distance with higher speed.

|
Nitin Iyer answered |
Rahul and Ravi both cover different distances XOY and XY respectively at the same time. Rahul covers more distance than Ravi in the same time. Hence Rahul covers longer distance with a higher speed.
One centimeter on a scale is divided into 20 equal divisions. The least count (minimum value) of this scale is
- a)20 cm
- b)1 cm
- c)0.1 cm
- d)0.05 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One centimeter on a scale is divided into 20 equal divisions. The least count (minimum value) of this scale is
a)
20 cm
b)
1 cm
c)
0.1 cm
d)
0.05 cm

|
Arjun Desai answered |
As 20 divisions = 1 cm
∴ 1 division = 1/20 cm
= 0.05cm
∴ 1 division = 1/20 cm
= 0.05cm
Length of curved line can be measured by using- a)Measuring rod
- b)Measuring tap
- c)Vernier scale
- d)Threads
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Length of curved line can be measured by using
a)
Measuring rod
b)
Measuring tap
c)
Vernier scale
d)
Threads

|
Jhanvi Banerjee answered |
Length of a curved line can be measured by using threads.
Study the given Venn diagram, Which of the motions described by different bodies are most likely to be I, II and III?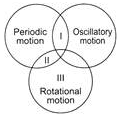
- a)

- b)

- c)
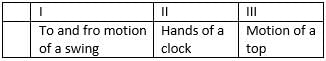
- d)

Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the given Venn diagram, Which of the motions described by different bodies are most likely to be I, II and III?

a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Option 1,2 and 3 are rotatory motion. Rotatory motion, also referred to as rotational motion or circular motion, is physical motion that happens when an object rotates or spins on an axis.
One kilometer is equal to- a)1000 m
- b)100 m
- c)10 m
- d)1000 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One kilometer is equal to
a)
1000 m
b)
100 m
c)
10 m
d)
1000 cm
|
|
Wahid Khan answered |
One kilometre is equal to 1000 meter.
A piece of thread folded 6 times is placed along a 15 cm long measuring scale as shown in the figure. The length of the thread is between

- a)0.15-0.50 m
- b)0.50m-1.0m
- c)1.0m-1.5m
- d)1.5m-2.0m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of thread folded 6 times is placed along a 15 cm long measuring scale as shown in the figure. The length of the thread is between

a)
0.15-0.50 m
b)
0.50m-1.0m
c)
1.0m-1.5m
d)
1.5m-2.0m

|
Subham Verma answered |
Length of each fold of thread placed along scale = 13.5 cm
As thread is folded 6 times
∴ Length of the thread = (13.5×6) cm
= 81 cm = 0.81 m
As thread is folded 6 times
∴ Length of the thread = (13.5×6) cm
= 81 cm = 0.81 m
If a book is 24 cm long, how many millimetres long is it?- a)240 mm
- b)2400 mm
- c)24 mm
- d)2.4 mm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
240 mm
b)
2400 mm
c)
24 mm
d)
2.4 mm

|
EduRev Class 6 answered |
To convert centimetres to millimetres, multiply by 10. Therefore, a book that is 24 cm long is 240 millimetres long (24 × 10 = 240).
In circular motion, the- a)Direction of motion is fixed
- b)Direction of motion changes continuously
- c)Acceleration is zero
- d)Velocity is constant.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In circular motion, the
a)
Direction of motion is fixed
b)
Direction of motion changes continuously
c)
Acceleration is zero
d)
Velocity is constant.
|
|
Muskaan Joshi answered |
Circular motion is the movement of an object along a circular path. In this type of motion, the object continuously changes its direction while maintaining a constant speed. The correct answer to the question is option 'B' - the direction of motion changes continuously. Let's understand why this is the correct answer in detail.
Direction of Motion
In circular motion, the object moves around a center point in a circular path. As it moves, the direction of the object constantly changes. At any given point on the circular path, the object is moving tangentially to that point. This means that the object is moving perpendicular to the radius of the circle at that point. Therefore, the direction of motion is not fixed but changes continuously.
Velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction. In circular motion, the object maintains a constant speed as it moves around the circle. However, the direction of motion changes continuously, which means the velocity of the object also changes. Therefore, the velocity is not constant in circular motion.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. In circular motion, even though the speed of the object remains constant, its direction changes continuously. This change in direction indicates a change in velocity. As a result, there is a non-zero acceleration in circular motion. The object is constantly accelerating towards the center of the circle, which is called centripetal acceleration.
Centripetal Force
The centripetal acceleration in circular motion is caused by a force called the centripetal force. This force acts towards the center of the circle, pulling the object inward. It is responsible for keeping the object in its circular path. Without this force, the object would move in a straight line tangent to the circle. The centripetal force is required to constantly change the object's direction of motion, thereby causing the continuous change in direction.
In conclusion, in circular motion, the direction of motion changes continuously, the velocity is not constant, and there is a non-zero acceleration. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
Direction of Motion
In circular motion, the object moves around a center point in a circular path. As it moves, the direction of the object constantly changes. At any given point on the circular path, the object is moving tangentially to that point. This means that the object is moving perpendicular to the radius of the circle at that point. Therefore, the direction of motion is not fixed but changes continuously.
Velocity
Velocity is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude (speed) and direction. In circular motion, the object maintains a constant speed as it moves around the circle. However, the direction of motion changes continuously, which means the velocity of the object also changes. Therefore, the velocity is not constant in circular motion.
Acceleration
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. In circular motion, even though the speed of the object remains constant, its direction changes continuously. This change in direction indicates a change in velocity. As a result, there is a non-zero acceleration in circular motion. The object is constantly accelerating towards the center of the circle, which is called centripetal acceleration.
Centripetal Force
The centripetal acceleration in circular motion is caused by a force called the centripetal force. This force acts towards the center of the circle, pulling the object inward. It is responsible for keeping the object in its circular path. Without this force, the object would move in a straight line tangent to the circle. The centripetal force is required to constantly change the object's direction of motion, thereby causing the continuous change in direction.
In conclusion, in circular motion, the direction of motion changes continuously, the velocity is not constant, and there is a non-zero acceleration. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B'.
From the following options, the movement of blades of a fan is- a)Periodic motion
- b)Non-periodic motion
- c)Rectilinear motion
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
From the following options, the movement of blades of a fan is
a)
Periodic motion
b)
Non-periodic motion
c)
Rectilinear motion
d)
All of these
|
|
Nishanth Iyer answered |
Understanding Periodic Motion
Periodic motion is defined as motion that repeats itself at regular intervals of time. This concept can be observed in various daily activities, one of which is the movement of fan blades.
Why Fan Blades Exhibit Periodic Motion
- Repetitive Movement:
The blades of a fan rotate around a fixed axis, completing a full revolution in a consistent timeframe. This consistent repetition characterizes periodic motion.
- Time Interval:
Each complete cycle of the fan blades returning to their original position occurs within a specific time interval, such as every second or two seconds, depending on the fan's speed.
- Predictable Pattern:
The motion can be predicted, as the blades will always return to the same position after a set duration. This predictability is a hallmark of periodic motion.
Comparing Other Types of Motion
- Non-Periodic Motion:
Unlike periodic motion, non-periodic motion does not follow a consistent pattern or interval. An example would be a person walking randomly in a park.
- Rectilinear Motion:
This type of motion involves movement in a straight line. Fan blades do not move in a straight line; they rotate in a circular path.
- Conclusion:
Since the movement of fan blades is consistent, repetitive, and predictable, it is classified as periodic motion.
Final Thoughts
In summary, the movement of fan blades is categorized as periodic motion because they rotate in a consistent manner, completing cycles at regular intervals. This understanding helps in recognizing how various objects move in our daily lives!
Periodic motion is defined as motion that repeats itself at regular intervals of time. This concept can be observed in various daily activities, one of which is the movement of fan blades.
Why Fan Blades Exhibit Periodic Motion
- Repetitive Movement:
The blades of a fan rotate around a fixed axis, completing a full revolution in a consistent timeframe. This consistent repetition characterizes periodic motion.
- Time Interval:
Each complete cycle of the fan blades returning to their original position occurs within a specific time interval, such as every second or two seconds, depending on the fan's speed.
- Predictable Pattern:
The motion can be predicted, as the blades will always return to the same position after a set duration. This predictability is a hallmark of periodic motion.
Comparing Other Types of Motion
- Non-Periodic Motion:
Unlike periodic motion, non-periodic motion does not follow a consistent pattern or interval. An example would be a person walking randomly in a park.
- Rectilinear Motion:
This type of motion involves movement in a straight line. Fan blades do not move in a straight line; they rotate in a circular path.
- Conclusion:
Since the movement of fan blades is consistent, repetitive, and predictable, it is classified as periodic motion.
Final Thoughts
In summary, the movement of fan blades is categorized as periodic motion because they rotate in a consistent manner, completing cycles at regular intervals. This understanding helps in recognizing how various objects move in our daily lives!
Hectare can be used to measure- a)Area of blackboard
- b)Volume of milk in a container
- c)Area of crop land
- d)Length of table top
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hectare can be used to measure
a)
Area of blackboard
b)
Volume of milk in a container
c)
Area of crop land
d)
Length of table top

|
Suyash Saini answered |
Hectare is unit for measuring large area as area of a crop land.
Which mode of transport uses a gas turbine engine?- a)Train
- b)Ship
- c)Airplane
- d)Bicycle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Train
b)
Ship
c)
Airplane
d)
Bicycle
|
|
Bibek Verma answered |
Introduction to Gas Turbine Engines
Gas turbine engines are powerful machines that convert fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. These engines are known for their efficiency and high power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for certain types of transport.
Transport Modes Using Gas Turbine Engines
- Airplane: The primary mode of transport that uses a gas turbine engine is the airplane.
- How It Works: In an airplane, the gas turbine engine, often referred to as a jet engine, works by drawing in air, compressing it, mixing it with fuel, and igniting the mixture. The high-speed exhaust gases then propel the aircraft forward.
- Advantages: Jet engines provide excellent thrust, enabling airplanes to achieve high speeds and altitudes. They are essential for commercial and military aviation.
Other Modes of Transport
- Train: Most trains operate using diesel engines or electric motors. However, some high-speed trains may utilize gas turbines, but these are less common.
- Ship: While many ships use diesel engines, some modern vessels, like naval ships, may use gas turbines for their propulsion systems. Yet, this is not the standard for all ships.
- Bicycle: Bicycles are human-powered vehicles and do not use engines at all, let alone gas turbine engines.
Conclusion
In summary, the most prominent mode of transport that utilizes gas turbine engines is the airplane. This technology plays a crucial role in enabling efficient and rapid air travel, distinguishing it from other transport methods.
Gas turbine engines are powerful machines that convert fuel into mechanical energy through combustion. These engines are known for their efficiency and high power-to-weight ratio, making them ideal for certain types of transport.
Transport Modes Using Gas Turbine Engines
- Airplane: The primary mode of transport that uses a gas turbine engine is the airplane.
- How It Works: In an airplane, the gas turbine engine, often referred to as a jet engine, works by drawing in air, compressing it, mixing it with fuel, and igniting the mixture. The high-speed exhaust gases then propel the aircraft forward.
- Advantages: Jet engines provide excellent thrust, enabling airplanes to achieve high speeds and altitudes. They are essential for commercial and military aviation.
Other Modes of Transport
- Train: Most trains operate using diesel engines or electric motors. However, some high-speed trains may utilize gas turbines, but these are less common.
- Ship: While many ships use diesel engines, some modern vessels, like naval ships, may use gas turbines for their propulsion systems. Yet, this is not the standard for all ships.
- Bicycle: Bicycles are human-powered vehicles and do not use engines at all, let alone gas turbine engines.
Conclusion
In summary, the most prominent mode of transport that utilizes gas turbine engines is the airplane. This technology plays a crucial role in enabling efficient and rapid air travel, distinguishing it from other transport methods.
Write the similarities and differences between the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan that has been switched on.- a)Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan has rotating blades.
- b)Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a circle.
- c)Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a circle, and a fan moves in a circle.
- d)Both have rectilinear motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a straight path.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan has rotating blades.
b)
Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a circle.
c)
Both have circular motion; a bicycle moves in a circle, and a fan moves in a circle.
d)
Both have rectilinear motion; a bicycle moves in a straight line, and a fan moves in a straight path.
|
|
Maya Mehta answered |
Similarities and Differences in Motion
When comparing the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan, it's important to understand how each operates in terms of movement.
Similarities
- Circular Motion:
- Both the bicycle and the ceiling fan exhibit circular motion at different points.
- While the fan blades rotate in a circular path, the bicycle can also move in a circular path when making turns or riding in a circle.
Differences
- Path of Motion:
- A bicycle primarily moves in a straight line when traveling from one point to another. However, it can also move in circles when the rider intentionally steers it that way.
- A ceiling fan, on the other hand, consistently rotates around a central axis, creating a circular motion at all times.
- Type of Motion:
- The bicycle's motion is not exclusively circular; it can be rectilinear (straight line) when moving directly forward or backward.
- The ceiling fan maintains a circular motion, as its blades spin around without deviating from that path.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'C' because both the bicycle and the ceiling fan can have circular motion; however, the bicycle's primary movement is often rectilinear unless it is maneuvering in a circular path. This contrast highlights the distinct nature of their movements while acknowledging that both can indeed exhibit circular motion under specific conditions.
When comparing the motion of a bicycle and a ceiling fan, it's important to understand how each operates in terms of movement.
Similarities
- Circular Motion:
- Both the bicycle and the ceiling fan exhibit circular motion at different points.
- While the fan blades rotate in a circular path, the bicycle can also move in a circular path when making turns or riding in a circle.
Differences
- Path of Motion:
- A bicycle primarily moves in a straight line when traveling from one point to another. However, it can also move in circles when the rider intentionally steers it that way.
- A ceiling fan, on the other hand, consistently rotates around a central axis, creating a circular motion at all times.
- Type of Motion:
- The bicycle's motion is not exclusively circular; it can be rectilinear (straight line) when moving directly forward or backward.
- The ceiling fan maintains a circular motion, as its blades spin around without deviating from that path.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'C' because both the bicycle and the ceiling fan can have circular motion; however, the bicycle's primary movement is often rectilinear unless it is maneuvering in a circular path. This contrast highlights the distinct nature of their movements while acknowledging that both can indeed exhibit circular motion under specific conditions.
While measuring the length of a wooden box, the reading at one end is 1.5 cm and the other end is 4.7 cm. What is the length of the wooden box?- a)4.7 cm
- b)1.5 cm
- c)3.2 cm
- d)6.2 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
While measuring the length of a wooden box, the reading at one end is 1.5 cm and the other end is 4.7 cm. What is the length of the wooden box?
a)
4.7 cm
b)
1.5 cm
c)
3.2 cm
d)
6.2 cm

|
Raj Mukherjee answered |
The length of the wooden box = Difference between the reading at both the ends = 4.7−1.5 = 3.2 cm
One hundred millimeters is equal to- a)10 dm
- b)100 dm
- c)1 m
- d)10 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One hundred millimeters is equal to
a)
10 dm
b)
100 dm
c)
1 m
d)
10 cm

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
- 100 millimeters (mm) is equal to 10 centimeters (cm) because 1 cm = 10 mm.
Let's verify the other options:
- A: 10 dm is incorrect because 1 dm (decimeter) = 100 mm, not 100 mm = 10 dm.
- B: 100 dm is incorrect because 100 millimeters is much smaller than 100 decimeters.
- C: 1 m is incorrect because 1 meter = 1000 mm, not 100 mm.
Thus, 100 mm = 10 cm is the correct answer.
Topic in NCERT: Units of Measurement
Line in NCERT: "Each metre (m) is divided into 100 equal divisions, called centimetre (cm)."
Which of the following statements is incorrect?- a)Motion of a vehicle on a straight road is not rectilinear motion.
- b)Motion of honeybees is the example of random motion.
- c)Cubit is the length of a forearm.
- d)Centigrade is not the SI unit of temperature.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
a)
Motion of a vehicle on a straight road is not rectilinear motion.
b)
Motion of honeybees is the example of random motion.
c)
Cubit is the length of a forearm.
d)
Centigrade is not the SI unit of temperature.
|
|
Divyansh Verma answered |
Rectilinear motion is another name for straight-line motion.
A moving swing has- a)Rectilinear motion
- b)Rotational motion
- c)Periodic motion
- d)Circular motion
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A moving swing has
a)
Rectilinear motion
b)
Rotational motion
c)
Periodic motion
d)
Circular motion

|
Indu Gupta answered |
A swing moves back and forth in a regular, repeating pattern, which is characteristic of periodic motion. This type of motion repeats at regular intervals, such as the swinging of a pendulum.
- A: Rectilinear motion refers to motion along a straight line, which is not the case for a swing.
- B: Rotational motion refers to motion around a fixed axis, like a spinning wheel, not the type of motion a swing exhibits.
- D: Circular motion refers to motion along a circular path, but a swing typically moves in a back-and-forth arc, not a full circle.
Thus, a moving swing exhibits periodic motion.
What kind of motion a bullet shows when fired from a gun?- a)Non-periodic motion.
- b)rectilinear motion
- c)Random motion
- d)Circulatory motion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What kind of motion a bullet shows when fired from a gun?
a)
Non-periodic motion.
b)
rectilinear motion
c)
Random motion
d)
Circulatory motion

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
When a bullet is fired from a gun, it typically moves in a straight line in the direction of the force applied by the gunpowder's explosion. This is known as rectilinear motion, which refers to motion along a straight path.
- A: Non-periodic motion refers to motion that does not repeat at regular intervals, which could describe some random or irregular movements, but the bullet's motion is more specific.
- C: Random motion refers to motion without a definite pattern or direction, which does not apply to a bullet's path.
- D: Circulatory motion is not a term used in the context of a bullet's movement, as a bullet moves in a straight line, not in a circular path.
Therefore, the bullet exhibits rectilinear motion.
Topic in NCERT: TYPES OF MOTION
Line in NCERT: "In all these examples we see that the objects move along a straight line. This type of motion is called rectilinear motion."
Which tool is best suited for measuring a curved line?- a)Ruler
- b)Metal rod
- c)Thread
- d)Yardstick
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which tool is best suited for measuring a curved line?
a)
Ruler
b)
Metal rod
c)
Thread
d)
Yardstick

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
For measuring a curved line, one can use a thread to get correct readings.
Four pieces of wooden sticks P, Q, R and S are placed along the length of 15 cm long scale as shown in figure. What is the average length of these sticks? 
- a)2.0 cm
- b)2.5 cm
- c)2.6 cm
- d)2.9 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Four pieces of wooden sticks P, Q, R and S are placed along the length of 15 cm long scale as shown in figure. What is the average length of these sticks?

a)
2.0 cm
b)
2.5 cm
c)
2.6 cm
d)
2.9 cm

|
Pragati Das answered |
P = 2.1 cm; Q = 3.0 cm; R = 3.1 cm; S = 2.5 cm
Average length of these sticks
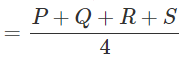
= 2.6cm
Average length of these sticks
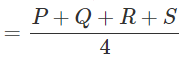
= 2.6cm
A pendulum swings backwards and forwards passing through Y, middle point of the oscillation. The first time the pendulum passes through Y, a stopwatch is started. 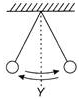 The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum?
The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum? - a)T/40
- b)T/21
- c)T/20
- d)T/10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A pendulum swings backwards and forwards passing through Y, middle point of the oscillation. The first time the pendulum passes through Y, a stopwatch is started.

The twenty-first time the pendulum pass through Y, the stopwatch is stopped. The reading is T. What is the time period of the pendulum?
a)
T/40
b)
T/21
c)
T/20
d)
T/10

|
Anagha Nambiar answered |
The time taken to complete one oscillation is called the time period of a pendulum.

Here the time period is the time taken to move from Y to B then back to A and then to Y. The reading of stopwatch = T Number of oscillations = 10

Here the time period is the time taken to move from Y to B then back to A and then to Y. The reading of stopwatch = T Number of oscillations = 10
∴ Time taken
= 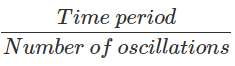 = T/10
= T/10
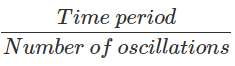 = T/10
= T/10Which of the following motions is/are periodic as well as oscillatory motion?
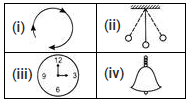
- a)(i), (ii) and (iii)
- b)(ii) only
- c)(i), (iii) and (iv)
- d)(iii) only
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following motions is/are periodic as well as oscillatory motion?

a)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
b)
(ii) only
c)
(i), (iii) and (iv)
d)
(iii) only

|
Subham Rane answered |
Only (ii) shows to and fro as well as interval. Hence, (ii) is the correct option.
Given figure shows a measuring cylinder (incm3) before and after the immersion of an irregular solid object. The volume of the object is 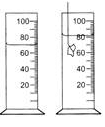
- a)82 cm3
- b)12 cm3
- c)30 cm3
- d)18 cm3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Given figure shows a measuring cylinder (incm3) before and after the immersion of an irregular solid object. The volume of the object is

a)
82 cm3
b)
12 cm3
c)
30 cm3
d)
18 cm3

|
Shounak Joshi answered |
Initial volume of water in the cylinder, (before the immersion of the object)
V1 = 70cm3
Final volume in the cylinder (after the immersion of the object)
V2 = 82cm3
Hence, volume of the object immersed in the cylinder = Final volume - Initial volume
= 82 cm3−70 cm3
= 12 cm3
V1 = 70cm3
Final volume in the cylinder (after the immersion of the object)
V2 = 82cm3
Hence, volume of the object immersed in the cylinder = Final volume - Initial volume
= 82 cm3−70 cm3
= 12 cm3
Two identical metal balls A and 8 moving in opposite directions with different speeds hit each other at point X as shown in the figure. Changes will most likely appear in their 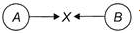 1. Shapes
1. Shapes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes- a)1 and 3
- b)2 and 3
- c)2 and 4
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two identical metal balls A and 8 moving in opposite directions with different speeds hit each other at point X as shown in the figure. Changes will most likely appear in their
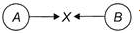
1. Shapes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes
2. Speeds
3. Directions
4. Volumes
a)
1 and 3
b)
2 and 3
c)
2 and 4
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
Sahil Desai answered |
In case of collision, changes are most likely to be appear in the speed and direction of both the balls.
Convert 3.75 metres into centimetres.- a)375 cm
- b)37.5 cm
- c)3.75 cm
- d)3750 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
375 cm
b)
37.5 cm
c)
3.75 cm
d)
3750 cm

|
Rahul Kumar answered |
To convert metres to centimetres, multiply by 100. Thus, 3.75 metres equals 375 centimetres (3.75 × 100 = 375).
Motion described by a simple pendulum is called- a)Periodic motion
- b)Rotatory motion
- c)curvilinear motion
- d)Rectilinear motion
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Motion described by a simple pendulum is called
a)
Periodic motion
b)
Rotatory motion
c)
curvilinear motion
d)
Rectilinear motion

|
Coachify answered |
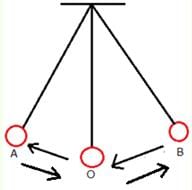
The motion of an object that repeats itself after regular intervals of time is called periodic motion.
The motion of simple pendulum is an example of periodic motion.
The motion of simple pendulum is an example of periodic motion.
Topic in NCERT: TYPES OF MOTION
Line in NCERT: "In some cases, an object repeats its motion after some time. This type of motion is called periodic motion."
The standard unit of length in the International System of Units (SI units) is _____.
- a)Centimeter
- b)Kilometer
- c)Meter
- d)Millimeter
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard unit of length in the International System of Units (SI units) is _____.
a)
Centimeter
b)
Kilometer
c)
Meter
d)
Millimeter

|
Keystone Instructors answered |
In the International System of Units (SI units), the standard unit of length is a meter. This is a measurement used to calculate distances. For example, the length of a room can be measured in meters which tells us how long it is.
What type of motion is characterized by objects moving along a straight line?- a)Circular motion
- b)Rectilinear motion
- c)Periodic motion
- d)Random motion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of motion is characterized by objects moving along a straight line?
a)
Circular motion
b)
Rectilinear motion
c)
Periodic motion
d)
Random motion

|
Keystone Instructors answered |
Rectilinear motion is when objects move along a straight line. This means they go in a straight direction without turning or going in circles.
The motion of a leaf falling from a tree is an example of which type of motion?- a)Circular motion
- b)Translatory motion
- c)Periodic motion
- d)Random motion
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Circular motion
b)
Translatory motion
c)
Periodic motion
d)
Random motion

|
Torcia Education answered |
The motion of a leaf falling from a tree is random because it does not follow a predictable or repetitive pattern. It is influenced by factors like wind and air resistance.
Which of the following is not a unit of length?- a)Inch
- b)Pound
- c)Yard
- d)Foot
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Inch
b)
Pound
c)
Yard
d)
Foot

|
Torcia Education answered |
Pound is not a unit of length; it is a unit of weight. Inch, yard, and foot are all units used to measure length.
Chapter doubts & questions for Motion and Measurement of Distances - Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 2025 is part of Class 6 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 6 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Motion and Measurement of Distances - Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 6 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days!
Study with 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos & Tests
10M+ students study on EduRev

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










