All Exams >
Class 6 >
Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 >
All Questions
All questions of Light, Shadow and Reflections for Class 6 Exam
To see a shadow we need- a)A source of light and translucent object
- b)A source of light and transparent object
- c)A source of light and an opaque object
- d)Many source of light and opaque object
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To see a shadow we need
a)
A source of light and translucent object
b)
A source of light and transparent object
c)
A source of light and an opaque object
d)
Many source of light and opaque object
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
A shadow is formed only when a source of light is obstructed by an opaque object.
In the morning, when the sun rises in the east, your shadow will be seen on the- a)North
- b)West
- c)South
- d)East
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the morning, when the sun rises in the east, your shadow will be seen on the
a)
North
b)
West
c)
South
d)
East
|
|
Divya kulkarni answered |
In the morning, when the sun rises in the east, your shadow will be seen on the west, i.e. on the opposite side.
What is formed when an opaque object blocks the path of light?- a)Reflection
- b)Refraction
- c)Shadow
- d)Image
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Reflection
b)
Refraction
c)
Shadow
d)
Image

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
When light is blocked by an opaque object, a shadow is formed on the opposite side of the light source.
Study the set-up below. 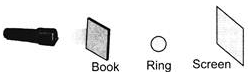 How will the shadow look like?
How will the shadow look like?- a)
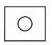
- b)
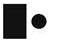
- c)
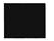
- d)
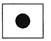
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the set-up below.

How will the shadow look like?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Book is an opaque object and hence does not allow the light of torch to pass through it. As there is no light on the ring, hence no image will be formed and the screen will remain dark due to absence of any light ray.
Geeta placed three objects made of different materials as shown in the figure. She observed a bright spot of light at (II) but (III) would not get any spot.-Then,
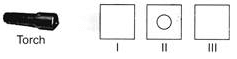
- a)(I) and (II) are made of transparent materials and (III) is made of opaque material.
- b)(I) is made of transparent material, (II) is made of translucent material and (III) is made of opaque material.
- c)(I) is made of transparent material, (II) is made of opaque material and (III) is made of either transparent or opaque or translucent material.
- d)(I) and (II) are made of opaque material and (III) is made of transparent material.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Geeta placed three objects made of different materials as shown in the figure. She observed a bright spot of light at (II) but (III) would not get any spot.-Then,

a)
(I) and (II) are made of transparent materials and (III) is made of opaque material.
b)
(I) is made of transparent material, (II) is made of translucent material and (III) is made of opaque material.
c)
(I) is made of transparent material, (II) is made of opaque material and (III) is made of either transparent or opaque or translucent material.
d)
(I) and (II) are made of opaque material and (III) is made of transparent material.

|
Subham Nair answered |
Transparent material allows light to pass through it and opaque object obstructs it.
A girl is 4 m away from the plane mirror. If she moves few steps closer to the mirror, what will happen to the image size in the mirror? 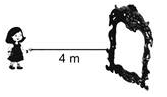
- a)The size of image will decrease.
- b)The size of image will increase.
- c)The size of image will be the same.
- d)Cannot say.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A girl is 4 m away from the plane mirror. If she moves few steps closer to the mirror, what will happen to the image size in the mirror?

a)
The size of image will decrease.
b)
The size of image will increase.
c)
The size of image will be the same.
d)
Cannot say.

|
Anoushka Banerjee answered |
The image formed in the plane mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
Three sticks are placed in an open field as shown in figure. Which of the following sticks will form the shadow of equal length? 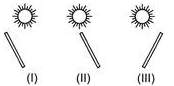
- a)Only sticks (I) and (II)
- b)Only sticks (II) and (III)
- c)Only sticks (I) and (III)
- d)All sticks (I), (II) and (III).
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Three sticks are placed in an open field as shown in figure. Which of the following sticks will form the shadow of equal length?

a)
Only sticks (I) and (II)
b)
Only sticks (II) and (III)
c)
Only sticks (I) and (III)
d)
All sticks (I), (II) and (III).

|
Gopal Ghoshal answered |
The length of the shadow changes according to the position of the source of light, i.e., the sun with respect to the object.
The diagram shows an object O viewed using two mirrors. A person looks into the mirrors as shown. At which position is the image of O seen? 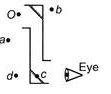
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The diagram shows an object O viewed using two mirrors. A person looks into the mirrors as shown. At which position is the image of O seen?

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d

|
Arjun Desai answered |
1) Consider the object O and the mirror at the top... . The image formed will be equal distance perpendicular to the mirror (follows the 5 characteristics of mirror image). Let the image be O’.2) Now treat O’ as the new object and consider the mirror at the bottom. Likewise apply the same principle, the image of O’ is now at position D. Alternatively, a fast and simple way is based on the concept that to our eyes, light seems to travel in straight line. Hence to our eyes, the image of O is directly in front.
Which of the following statements is true about shadows?- a)They are always colored
- b)They are always smaller than the object
- c)They can change size and shape
- d)They are formed only during the day
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
They are always colored
b)
They are always smaller than the object
c)
They can change size and shape
d)
They are formed only during the day

|
Vp Classes answered |
Shadows can vary in size and shape depending on the position and distance of the light source relative to the object.
Which of the following is a natural source of light?- a)Candle
- b)Sun
- c)Electric bulb
- d)Torch
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Candle
b)
Sun
c)
Electric bulb
d)
Torch

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
The Sun is a natural source of light, while candles, electric bulbs, and torches are artificial sources.
Which of the following materials is best suited for making a pinhole camera?- a)Transparent plastic
- b)Cardboard box
- c)Metal sheet
- d)Glass jar
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Transparent plastic
b)
Cardboard box
c)
Metal sheet
d)
Glass jar

|
Vp Classes answered |
A cardboard box is opaque and easy to manipulate, making it ideal for constructing a pinhole camera.
What happens to the size of a shadow when the light source is moved closer to the object?- a)It becomes larger
- b)It becomes smaller
- c)It remains the same
- d)It disappears
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It becomes larger
b)
It becomes smaller
c)
It remains the same
d)
It disappears

|
Coachify answered |
As the light source moves closer, the shadow enlarges due to the increased divergence of light rays.
Which of the following is NOT an example of a luminous object?- a)Sun
- b)Firefly
- c)Moon
- d)Lit candle
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Sun
b)
Firefly
c)
Moon
d)
Lit candle
|
|
Nilanjan Unni answered |
Luminous vs. Non-Luminous Objects
Luminous objects are those that emit light on their own. In contrast, non-luminous objects do not produce light; instead, they reflect light from luminous sources. Let's analyze the options provided:
Examples of Luminous Objects:
- Sun: The Sun is a massive ball of gas that generates light through nuclear fusion. It is the primary source of light for our solar system.
- Firefly: Fireflies are insects that produce light through a chemical reaction in their bodies. This natural phenomenon is known as bioluminescence.
- Lit Candle: A lit candle emits light due to the combustion of wax. The flame produces a bright glow, making it luminous.
Why the Moon is Non-Luminous:
- Moon: The Moon does not produce its own light. Instead, it reflects light from the Sun. When we see the Moon shining in the night sky, we are actually seeing sunlight that is bouncing off its surface.
Conclusion:
In summary, the correct answer is option 'C' (Moon) because it is a non-luminous object. The Moon's brightness is a result of reflecting sunlight, while the Sun, firefly, and lit candle are all examples of luminous objects that emit their own light. Understanding the distinction between these types of objects is crucial in studying light and its sources.
Luminous objects are those that emit light on their own. In contrast, non-luminous objects do not produce light; instead, they reflect light from luminous sources. Let's analyze the options provided:
Examples of Luminous Objects:
- Sun: The Sun is a massive ball of gas that generates light through nuclear fusion. It is the primary source of light for our solar system.
- Firefly: Fireflies are insects that produce light through a chemical reaction in their bodies. This natural phenomenon is known as bioluminescence.
- Lit Candle: A lit candle emits light due to the combustion of wax. The flame produces a bright glow, making it luminous.
Why the Moon is Non-Luminous:
- Moon: The Moon does not produce its own light. Instead, it reflects light from the Sun. When we see the Moon shining in the night sky, we are actually seeing sunlight that is bouncing off its surface.
Conclusion:
In summary, the correct answer is option 'C' (Moon) because it is a non-luminous object. The Moon's brightness is a result of reflecting sunlight, while the Sun, firefly, and lit candle are all examples of luminous objects that emit their own light. Understanding the distinction between these types of objects is crucial in studying light and its sources.
A solid transparent sphere has a small opaque dot at its centre. When observed from outside, the apparent position of the dot will be- a)Closer to the eye than its actual position.
- b)The same as its actual position.
- c)Farther away from the eye than its actual position.
- d)None of these.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A solid transparent sphere has a small opaque dot at its centre. When observed from outside, the apparent position of the dot will be
a)
Closer to the eye than its actual position.
b)
The same as its actual position.
c)
Farther away from the eye than its actual position.
d)
None of these.

|
Siddharth Chavan answered |
As u = 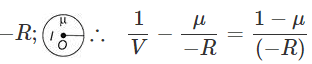
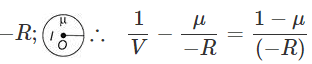
⇒ v = −R
Read the given statements and select the correct option,
Statement 1: Rahul placed a colored plastic bottle in front of the beam of a torch light. Then he placed a transparent sheet of same size on the other side of bottle. No shadow will form on the screen.
Statement 2: Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially. - a)Both statements 1 and 2 are true and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are true but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
- d)Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option,
Statement 1: Rahul placed a colored plastic bottle in front of the beam of a torch light. Then he placed a transparent sheet of same size on the other side of bottle. No shadow will form on the screen.
Statement 2: Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially.
Statement 1: Rahul placed a colored plastic bottle in front of the beam of a torch light. Then he placed a transparent sheet of same size on the other side of bottle. No shadow will form on the screen.
Statement 2: Translucent objects allow light to pass through them partially.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are true and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are true but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is true but statement 2 is false.
d)
Statement 1 is false but statement 2 is true.

|
Upasana Basak answered |
A colored plastic bottle is an opaque material. When a light beam is incident on it, a shadow will form on the screen can easily pass through the transparent material.
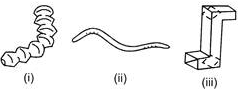 Which of the items above will allow you to see around a corner from where you are standing?
Which of the items above will allow you to see around a corner from where you are standing?- a)(i) only
- b)(iii) only
- c)(i) and (ii)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

Which of the items above will allow you to see around a corner from where you are standing?
a)
(i) only
b)
(iii) only
c)
(i) and (ii)
d)
(i) and (iii)

|
Harshad Saha answered |
Figure (iii) is periscope which is used to see around the corners. It is based upon the principle of rectilinear propagation of light and reflection of light.
Which of the following statements is true?
- a)The image formed by a pinhole camera is inverted because light travels in a straight line.
- b)Light does not change its direction on reflection.
- c)As we move the object away from the light source, the shadow of the object becomes smaller.
- d)Reflection is possible only from unpolished surface.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true?
a)
The image formed by a pinhole camera is inverted because light travels in a straight line.
b)
Light does not change its direction on reflection.
c)
As we move the object away from the light source, the shadow of the object becomes smaller.
d)
Reflection is possible only from unpolished surface.

|
Rajat Menon answered |
Light changes its direction after reflection. As we move the object away from the light source, the shadow becomes larger as the distance between object and the light source increases. Reflection is possible from rough surface also.
Riya and Priya were sitting around a round table. They noticed that they could see their own and each other's image onto the table top. Then table top is made of- a)Unpolished wood, covered with white cloth
- b)Polished glass of red colour
- c)Glass covered with cellophane paper
- d)Smoked glass covered with green colour cloth.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Riya and Priya were sitting around a round table. They noticed that they could see their own and each other's image onto the table top. Then table top is made of
a)
Unpolished wood, covered with white cloth
b)
Polished glass of red colour
c)
Glass covered with cellophane paper
d)
Smoked glass covered with green colour cloth.

|
Shruti Mishra answered |
Polished glass of red colour reflects some of the light incident on it so images of the both persons are formed on it.
Which of the following is a luminous object?- a)Moon
- b)Wooden box
- c)Tube light
- d)Ceramic plate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Moon
b)
Wooden box
c)
Tube light
d)
Ceramic plate

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
A luminous object emits its own light. A tube light is a source of light, whereas the Moon, wooden box, and ceramic plate do not emit light on their own.
What type of object allows all light to pass through it?- a)Opaque
- b)Translucent
- c)Transparent
- d)Reflective
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Opaque
b)
Translucent
c)
Transparent
d)
Reflective

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Transparent objects allow all light to pass through them, enabling clear visibility of objects on the other side.
Why do shadows change shape when an object is rotated?- a)Because the color of the light changes
- b)Because the position of the light source changes
- c)Because the shape of the object changes
- d)Because the distance between the object and light source changes
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Because the color of the light changes
b)
Because the position of the light source changes
c)
Because the shape of the object changes
d)
Because the distance between the object and light source changes

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Shadows change shape when an object is rotated because the distance between the object and the light source changes. This affects the angle at which light hits the object, thereby altering the shape and size of the shadow. For instance, rotating a book while it is under a light source will change the shape of the shadow on the ground.
When Abhishek looked at a lighted torch through an object he could see a faint glow, but not the torch. The object is- a)Transparent
- b)Opaque
- c)Translucent
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When Abhishek looked at a lighted torch through an object he could see a faint glow, but not the torch. The object is
a)
Transparent
b)
Opaque
c)
Translucent
d)
None of these

|
Subham Verma answered |
Translucent objects allow only a small part of light to pass through them.
What happens to light when it strikes a plane mirror?- a)It refracts
- b)It absorbs
- c)It reflects
- d)It diffuses
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It refracts
b)
It absorbs
c)
It reflects
d)
It diffuses
|
|
Rounak Patel answered |
What Happens to Light on Striking a Plane Mirror?
When light strikes a plane mirror, the primary phenomenon observed is reflection. Here’s a detailed explanation of this process:
Reflection of Light
- Definition: Reflection occurs when light rays bounce back from a surface.
- Plane Mirror Characteristics: A plane mirror has a flat, smooth surface that reflects light uniformly.
Law of Reflection
- Incident Ray: The incoming light ray that strikes the mirror is called the incident ray.
- Reflected Ray: The light ray that bounces back is known as the reflected ray.
- Normal Line: An imaginary line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
- Angle of Incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal line.
- Angle of Reflection: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal line.
- Key Principle: The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Why Reflection Occurs?
- Smooth Surface: The smooth surface of a plane mirror allows for a clear reflection, as all incident rays reflect at the same angle.
- Visual Clarity: This property makes mirrors effective for producing clear images, as they redirect light without scattering.
Conclusion
In summary, when light strikes a plane mirror, it reflects back, allowing us to see clear images. The correct answer to the question is option 'C', as reflection is the primary interaction of light with a plane mirror. This fundamental concept is crucial in understanding how mirrors work and is foundational in the study of optics.
When light strikes a plane mirror, the primary phenomenon observed is reflection. Here’s a detailed explanation of this process:
Reflection of Light
- Definition: Reflection occurs when light rays bounce back from a surface.
- Plane Mirror Characteristics: A plane mirror has a flat, smooth surface that reflects light uniformly.
Law of Reflection
- Incident Ray: The incoming light ray that strikes the mirror is called the incident ray.
- Reflected Ray: The light ray that bounces back is known as the reflected ray.
- Normal Line: An imaginary line perpendicular to the surface at the point of incidence.
- Angle of Incidence: The angle between the incident ray and the normal line.
- Angle of Reflection: The angle between the reflected ray and the normal line.
- Key Principle: The angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
Why Reflection Occurs?
- Smooth Surface: The smooth surface of a plane mirror allows for a clear reflection, as all incident rays reflect at the same angle.
- Visual Clarity: This property makes mirrors effective for producing clear images, as they redirect light without scattering.
Conclusion
In summary, when light strikes a plane mirror, it reflects back, allowing us to see clear images. The correct answer to the question is option 'C', as reflection is the primary interaction of light with a plane mirror. This fundamental concept is crucial in understanding how mirrors work and is foundational in the study of optics.
Which material is an example of a translucent object?- a)Clear plastic sheet
- b)Frosted glass
- c)Aluminum foil
- d)Mirror
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Clear plastic sheet
b)
Frosted glass
c)
Aluminum foil
d)
Mirror

|
Coachify answered |
Translucent objects allow some light to pass through but scatter it, making frosted glass a good example.
Which of the following is NOT necessary for the formation of a shadow?- a)Light source
- b)Opaque object
- c)Transparent screen
- d)Surface to cast the shadow
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Light source
b)
Opaque object
c)
Transparent screen
d)
Surface to cast the shadow

|
Vp Classes answered |
A transparent screen is not required for a shadow, but a light source, an opaque object, and a surface are essential.
Vijay puts some water into four cups made of steel, porcelain, glass, frosted glass. Which one of these cups will allow him to see the level of the water clearly?- a)Glass cup
- b)Steel cup
- c)Porcelain cup
- d)Frosted glass cup
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vijay puts some water into four cups made of steel, porcelain, glass, frosted glass. Which one of these cups will allow him to see the level of the water clearly?
a)
Glass cup
b)
Steel cup
c)
Porcelain cup
d)
Frosted glass cup

|
Shilpa Dasgupta answered |
Glass is a transparent material. It allows light to pass through it.
The image formed in water is:- a)Erect
- b)Diminished
- c)Inverted
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The image formed in water is:
a)
Erect
b)
Diminished
c)
Inverted
d)
None of these
|
|
Nishtha Mukherjee answered |
Understanding Image Formation in Water
When we discuss how images are formed when looking through water, it’s essential to consider the properties of light and how it behaves when it passes through different mediums.
How Light Interacts with Water
- Light travels at different speeds in different mediums.
- When light enters water from air, it bends (refracts) due to the change in speed.
Characteristics of the Image Formed
- Erect Image: When an object is placed in water, the image formed is upright or erect. This means the orientation of the image matches that of the object.
- Diminished Size: The image may appear smaller than the actual object, but it remains upright.
Why is the Image Erect?
- This happens because of the way light rays converge after passing through the water.
- When observing an object submerged in water, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction create an effect that keeps the image upright.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when viewing an object submerged in water, the image formed is erect due to the refraction of light. This unique property of light allows us to see objects clearly even when they are partially covered by water.
Thus, the correct answer is indeed option 'A': the image formed in water is erect.
When we discuss how images are formed when looking through water, it’s essential to consider the properties of light and how it behaves when it passes through different mediums.
How Light Interacts with Water
- Light travels at different speeds in different mediums.
- When light enters water from air, it bends (refracts) due to the change in speed.
Characteristics of the Image Formed
- Erect Image: When an object is placed in water, the image formed is upright or erect. This means the orientation of the image matches that of the object.
- Diminished Size: The image may appear smaller than the actual object, but it remains upright.
Why is the Image Erect?
- This happens because of the way light rays converge after passing through the water.
- When observing an object submerged in water, the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction create an effect that keeps the image upright.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when viewing an object submerged in water, the image formed is erect due to the refraction of light. This unique property of light allows us to see objects clearly even when they are partially covered by water.
Thus, the correct answer is indeed option 'A': the image formed in water is erect.
What kinds of objects do not allow light to pass through them?- a)Transparent
- b)Translucent
- c)Opaque
- d)Luminous
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What kinds of objects do not allow light to pass through them?
a)
Transparent
b)
Translucent
c)
Opaque
d)
Luminous
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
- Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them.
- Examples include materials like wood, metal, and stone.
- When light hits an opaque object, it is either absorbed or reflected, preventing any transmission.
- In contrast, transparent objects (like glass) let light through, while translucent objects (like frosted glass) allow some light but scatter it.
- Understanding these differences helps in various applications, from construction to design.
- Examples include materials like wood, metal, and stone.
- When light hits an opaque object, it is either absorbed or reflected, preventing any transmission.
- In contrast, transparent objects (like glass) let light through, while translucent objects (like frosted glass) allow some light but scatter it.
- Understanding these differences helps in various applications, from construction to design.
What happens when light falls on a mirror?- a)It gets absorbed
- b)It passes through the mirror
- c)It changes direction and gets reflected
- d)It disappears
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when light falls on a mirror?
a)
It gets absorbed
b)
It passes through the mirror
c)
It changes direction and gets reflected
d)
It disappears

|
Torcia Education answered |
- When light falls on a mirror, it changes direction and bounces back. This is called reflection.
- Imagine light as a bouncing ball hitting a wall and coming back.
- The mirror acts like that wall for light. It reflects the light so we can see things in it, just like when you look at your face in a mirror.
What is the main difference between a shadow and a reflection?- a)Shadows are colored; reflections are not
- b)Shadows are formed by opaque objects; reflections by smooth surfaces
- c)Shadows require a screen; reflections do not
- d)Shadows are always smaller; reflections are always larger
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Shadows are colored; reflections are not
b)
Shadows are formed by opaque objects; reflections by smooth surfaces
c)
Shadows require a screen; reflections do not
d)
Shadows are always smaller; reflections are always larger

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
Shadows occur when an opaque object blocks light, while reflections are formed on smooth surfaces by the bouncing of light.
When you see your face in a mirror, what you see is a _______.- a)Shadow
- b)Reflection
- c)Tree
- d)Building
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When you see your face in a mirror, what you see is a _______.
a)
Shadow
b)
Reflection
c)
Tree
d)
Building

|
Keystone Instructors answered |
When you look at yourself in a mirror, the image you see is called a reflection. It's like a copy of how you look, but in the mirror.
How can you see a reflection in a mirror?- a)By using a bright light source to illuminate the mirror
- b)By placing an object near the mirror in a dark room
- c)By directing light onto the mirror
- d)By keeping the mirror in complete darkness
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How can you see a reflection in a mirror?
a)
By using a bright light source to illuminate the mirror
b)
By placing an object near the mirror in a dark room
c)
By directing light onto the mirror
d)
By keeping the mirror in complete darkness

|
Future Foundation Institute answered |
You can see a reflection in a mirror by directing light onto the mirror. The mirror reflects the light that hits it, allowing you to see the reflected image. Mirrors change the direction of light rays that hit their surface, which is why we can see clear images of objects in front of them.
Objects like the sun that give out their own light are called ______ objects.- a)Transparent
- b)Luminous
- c)Opaque
- d)Translucent
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Objects like the sun that give out their own light are called ______ objects.
a)
Transparent
b)
Luminous
c)
Opaque
d)
Translucent
|
|
Bibek Verma answered |
Understanding Luminous Objects
Objects that emit their own light are classified as luminous objects. The sun is the most prominent example of a luminous object, but there are many others like stars and certain types of artificial lights.
Definition of Luminous Objects
- Luminous objects generate light through various processes, such as nuclear fusion in stars or electrical energy in light bulbs.
- They are distinct from other types of objects that either reflect or transmit light.
Comparison with Other Object Types
- Transparent Objects: These allow light to pass through without scattering. Examples include clear glass and clean water. They do not emit their own light.
- Opaque Objects: These do not allow light to pass through. They either absorb or reflect light. Common examples are wood and metal.
- Translucent Objects: These permit some light to pass through, but not clearly. Frosted glass is a typical example. Like transparent objects, they do not produce their own light.
Why Option B is Correct
- The question asks for objects that generate their own light, making option B (luminous) the correct choice.
- Understanding the distinction between luminous and non-luminous objects is key to grasping basic concepts in physics and astronomy.
In summary, luminous objects like the sun are essential in our universe, providing light and energy, unlike transparent, opaque, or translucent objects, which interact with light differently.
Objects that emit their own light are classified as luminous objects. The sun is the most prominent example of a luminous object, but there are many others like stars and certain types of artificial lights.
Definition of Luminous Objects
- Luminous objects generate light through various processes, such as nuclear fusion in stars or electrical energy in light bulbs.
- They are distinct from other types of objects that either reflect or transmit light.
Comparison with Other Object Types
- Transparent Objects: These allow light to pass through without scattering. Examples include clear glass and clean water. They do not emit their own light.
- Opaque Objects: These do not allow light to pass through. They either absorb or reflect light. Common examples are wood and metal.
- Translucent Objects: These permit some light to pass through, but not clearly. Frosted glass is a typical example. Like transparent objects, they do not produce their own light.
Why Option B is Correct
- The question asks for objects that generate their own light, making option B (luminous) the correct choice.
- Understanding the distinction between luminous and non-luminous objects is key to grasping basic concepts in physics and astronomy.
In summary, luminous objects like the sun are essential in our universe, providing light and energy, unlike transparent, opaque, or translucent objects, which interact with light differently.
What type of image is formed by a plane mirror?- a)Real and inverted
- b)Virtual and upright
- c)Real and upright
- d)Virtual and inverted
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Real and inverted
b)
Virtual and upright
c)
Real and upright
d)
Virtual and inverted
|
|
Kalyan Sengupta answered |
Understanding Image Formation by a Plane Mirror
When light rays hit a plane mirror, they reflect off the surface, creating an image. The characteristics of this image can be understood through the following points:
1. Type of Image
- The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual.
- This means that the image cannot be projected onto a screen; it appears to be behind the mirror.
2. Orientation of the Image
- The image is also upright.
- This means that the image maintains the same orientation as the object, which is particularly noticeable in everyday use, like when looking at oneself in a mirror.
3. Characteristics of Virtual Images
- Virtual images, like those formed by plane mirrors, are formed by the apparent divergence of light rays.
- They are always located at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
4. Comparison with Other Image Types
- Real images are formed by the convergence of light rays and can be projected onto a screen. They are typically inverted.
- In contrast, images produced by plane mirrors differ significantly from real images, as they are neither converged nor inverted.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer to the question is option B: Virtual and upright. This is a fundamental concept in optics, making plane mirrors fascinating in their simplicity and utility in daily life.
When light rays hit a plane mirror, they reflect off the surface, creating an image. The characteristics of this image can be understood through the following points:
1. Type of Image
- The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual.
- This means that the image cannot be projected onto a screen; it appears to be behind the mirror.
2. Orientation of the Image
- The image is also upright.
- This means that the image maintains the same orientation as the object, which is particularly noticeable in everyday use, like when looking at oneself in a mirror.
3. Characteristics of Virtual Images
- Virtual images, like those formed by plane mirrors, are formed by the apparent divergence of light rays.
- They are always located at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
4. Comparison with Other Image Types
- Real images are formed by the convergence of light rays and can be projected onto a screen. They are typically inverted.
- In contrast, images produced by plane mirrors differ significantly from real images, as they are neither converged nor inverted.
Conclusion
Thus, the correct answer to the question is option B: Virtual and upright. This is a fundamental concept in optics, making plane mirrors fascinating in their simplicity and utility in daily life.
Which of the following explains why air is not visible?- a)It is nearly a perfect transparent substance.
- b)It neither absorbs nor reflects light.
- c)It transmits whole of light.
- d)All of these.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following explains why air is not visible?
a)
It is nearly a perfect transparent substance.
b)
It neither absorbs nor reflects light.
c)
It transmits whole of light.
d)
All of these.

|
Tanishq Dasgupta answered |
An object is visible, when it either absorbs light or reflects light. Air is not visible because it neither absorbs nor reflects light.
Which of the following statements is not true?- a)A cylindrical object can cast a rectangular as well as a circular shadow.
- b)Polished surface produces a clear image.
- c)The umbra is the region of a shadow which is grey in colour.
- d)Light travels in a straight line.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not true?
a)
A cylindrical object can cast a rectangular as well as a circular shadow.
b)
Polished surface produces a clear image.
c)
The umbra is the region of a shadow which is grey in colour.
d)
Light travels in a straight line.

|
Gunjan Lakhani answered |
- A: A cylindrical object can cast a rectangular as well as a circular shadow.
This is true. Depending on the angle of the light source and the orientation of the cylindrical object, it can cast both rectangular (if the object is viewed from the side) and circular (if viewed from the top) shadows. - B: Polished surface produces a clear image.
This is true. A polished surface causes specular reflection, which creates clear and sharp images, as it reflects light in parallel directions. - C: The umbra is the region of a shadow which is grey in colour.
This is false. The umbra is the darkest part of a shadow, where the light source is completely blocked. It is typically black or very dark, not grey. The penumbra is the lighter, greyish region of the shadow, where some, but not all, of the light is blocked. - D: Light travels in a straight line.
This is true. In the absence of obstacles or medium changes, light travels in a straight line.
Thus, the statement that is not true is C: The umbra is the region of a shadow which is grey in colour.
You are standing upright in a room in front of a vertical mirror. In this mirror, you can see from your position, only the upper two- third part of your body. You wish to see the full image of your body in the mirror. Which combination of the following three courses of action will achieve this?
I. Move away from the mirror
II. Move towards the mirror
III. Use a mirror whose height will allow you to see your full image - a)I only
- b)II only
- c)Either I or III
- d)III only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
You are standing upright in a room in front of a vertical mirror. In this mirror, you can see from your position, only the upper two- third part of your body. You wish to see the full image of your body in the mirror. Which combination of the following three courses of action will achieve this?
I. Move away from the mirror
II. Move towards the mirror
III. Use a mirror whose height will allow you to see your full image
I. Move away from the mirror
II. Move towards the mirror
III. Use a mirror whose height will allow you to see your full image
a)
I only
b)
II only
c)
Either I or III
d)
III only

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
- Mirror Size and Position: To see your full image, the mirror must be at least half your height.
- Action I (Move Away): Moving away increases the field of view, allowing you to see more of yourself. Thus, moving away can help you see your full image if the mirror is tall enough.
- Action III (Use Taller Mirror): A taller mirror ensures you see your entire reflection regardless of distance.
- Conclusion: Either moving away (I) or using a taller mirror (III) will allow you to see your full image. Thus, the correct answer is C.
- Action I (Move Away): Moving away increases the field of view, allowing you to see more of yourself. Thus, moving away can help you see your full image if the mirror is tall enough.
- Action III (Use Taller Mirror): A taller mirror ensures you see your entire reflection regardless of distance.
- Conclusion: Either moving away (I) or using a taller mirror (III) will allow you to see your full image. Thus, the correct answer is C.
What causes the images to appear upside down in a pinhole camera?- a)The light is bent by a lens
- b)The small size of the pinhole
- c)The light travels in straight lines
- d)The camera is not properly aligned
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The light is bent by a lens
b)
The small size of the pinhole
c)
The light travels in straight lines
d)
The camera is not properly aligned
|
|
Rounak Chawla answered |
Understanding the Pinhole Camera
A pinhole camera is a simple type of camera that operates without a lens, using only a small opening (the pinhole) to let light in. The unique characteristic of images produced by a pinhole camera is that they appear upside down. Let's explore why this happens.
Light Travels in Straight Lines
- The primary reason images appear upside down in a pinhole camera is that light travels in straight lines.
- When light rays from an object pass through the pinhole, they cross over each other.
- For example, light from the top of an object travels downwards to the bottom of the image plane, and light from the bottom travels upwards to the top of the image plane.
Formation of the Upside-Down Image
- As a result of this crossing of light rays, the image on the opposite side of the pinhole is inverted.
- This means that everything you see through the pinhole appears flipped both horizontally and vertically.
Other Options Explained
- Option a) "The light is bent by a lens" is incorrect because a pinhole camera does not use a lens.
- Option b) "The small size of the pinhole" does not directly cause the inversion; it merely affects the sharpness and brightness of the image.
- Option d) "The camera is not properly aligned" is irrelevant to the fundamental principle of how light behaves in relation to the pinhole.
Understanding this principle helps clarify how simple optical devices like the pinhole camera work and why they produce unique visual effects.
A pinhole camera is a simple type of camera that operates without a lens, using only a small opening (the pinhole) to let light in. The unique characteristic of images produced by a pinhole camera is that they appear upside down. Let's explore why this happens.
Light Travels in Straight Lines
- The primary reason images appear upside down in a pinhole camera is that light travels in straight lines.
- When light rays from an object pass through the pinhole, they cross over each other.
- For example, light from the top of an object travels downwards to the bottom of the image plane, and light from the bottom travels upwards to the top of the image plane.
Formation of the Upside-Down Image
- As a result of this crossing of light rays, the image on the opposite side of the pinhole is inverted.
- This means that everything you see through the pinhole appears flipped both horizontally and vertically.
Other Options Explained
- Option a) "The light is bent by a lens" is incorrect because a pinhole camera does not use a lens.
- Option b) "The small size of the pinhole" does not directly cause the inversion; it merely affects the sharpness and brightness of the image.
- Option d) "The camera is not properly aligned" is irrelevant to the fundamental principle of how light behaves in relation to the pinhole.
Understanding this principle helps clarify how simple optical devices like the pinhole camera work and why they produce unique visual effects.
Why do shadows appear on a screen but not in the air?- a)Shadows are blocked by the air
- b)The light is scattered in the air
- c)Shadows need a surface to form
- d)The screen is not transparent
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Shadows are blocked by the air
b)
The light is scattered in the air
c)
Shadows need a surface to form
d)
The screen is not transparent

|
Rahul Kumar answered |
Shadows appear on a screen because shadows need a surface to be formed and visible. When light is obstructed by an opaque object, it creates a shadow that can be seen on a surface or screen where the light is blocked. In the air, shadows are not visible because there is no surface to capture and display them.
What is the main difference between a translucent and a transparent object?- a)Translucent objects allow all light through while transparent objects allow partial light
- b)Transparent objects allow all light through while translucent objects allow partial light
- c)Both objects allow light through but in different amounts
- d)There is no difference between translucent and transparent objects
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Translucent objects allow all light through while transparent objects allow partial light
b)
Transparent objects allow all light through while translucent objects allow partial light
c)
Both objects allow light through but in different amounts
d)
There is no difference between translucent and transparent objects

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
The main difference between translucent and transparent objects is that transparent objects allow all light to pass through clearly, allowing you to see through them without distortion. In contrast, translucent objects allow only partial light to pass through, making objects on the other side appear blurry or unclear.
What property of light explains the formation of shadows?- a)Light travels in a straight line
- b)Light bends around objects
- c)Light scatters in all directions
- d)Light changes speed in different media
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Light travels in a straight line
b)
Light bends around objects
c)
Light scatters in all directions
d)
Light changes speed in different media

|
Dr Manju Sen answered |
Shadows are formed because light travels in straight lines and cannot bend around opaque objects.
In a pinhole camera, how does the image appear?- a)Upright and magnified
- b)Inverted and smaller
- c)Upright and smaller
- d)Inverted and same size
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Upright and magnified
b)
Inverted and smaller
c)
Upright and smaller
d)
Inverted and same size

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
The pinhole camera forms an inverted and smaller image due to the straight-line propagation of light through the small hole.
Which of the following is an example of an opaque object?- a)Clear glass
- b)Butter paper
- c)Wooden screen
- d)Soap bubble
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Clear glass
b)
Butter paper
c)
Wooden screen
d)
Soap bubble

|
Coachify answered |
Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through them, making a wooden screen an example of an opaque object.
Which phenomenon explains why we can see our reflection in a mirror?- a)Refraction
- b)Diffusion
- c)Reflection
- d)Absorption
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Refraction
b)
Diffusion
c)
Reflection
d)
Absorption

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
The reflection of light on smooth surfaces like mirrors enables us to see our image.
Which of the following materials would cast the darkest shadow?- a)Clear plastic
- b)Wax paper
- c)Cardboard
- d)Thin cloth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Clear plastic
b)
Wax paper
c)
Cardboard
d)
Thin cloth

|
Praveen Kumar answered |
Cardboard is completely opaque and blocks all light, casting the darkest shadow.
There is no dark shadow formed by the glass when light is shone on it. This is because 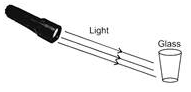
- a)It is not night time yet.
- b)The light is not strong enough.
- c)The glass is a transparent object.
- d)The distance between glass and screen is very large.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
There is no dark shadow formed by the glass when light is shone on it. This is because

a)
It is not night time yet.
b)
The light is not strong enough.
c)
The glass is a transparent object.
d)
The distance between glass and screen is very large.

|
Vaibhav Shah answered |
The shadows are formed when the opaque object cuts off the light from the source. Since glass is transparent, it allows the light to pass through it. So no dark shadow is formed.
Which of the following allows light to pass through it easily?- a)A metal plate
- b)A glass tumbler
- c)A book
- d)A wooden block
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following allows light to pass through it easily?
a)
A metal plate
b)
A glass tumbler
c)
A book
d)
A wooden block
|
|
Kiran Reddy answered |
A glass tumbler is a transparent substance which allows light to pass through it easily.
Chapter doubts & questions for Light, Shadow and Reflections - Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 2025 is part of Class 6 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 6 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Light, Shadow and Reflections - Online MCQ Tests for Class 6 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 6 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









