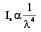All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Olympiad for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Human Eye and Colourful World for Class 10 Exam
If A is angle of prism D is angle of deviation, i is angle of incidence and e is the angle of emergence through a prism, then the correct relation between the four angles is- a)A + i = D + e
- b)A + D = i + e
- c)A + e = D + i
- d)A + i + e = D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If A is angle of prism D is angle of deviation, i is angle of incidence and e is the angle of emergence through a prism, then the correct relation between the four angles is
a)
A + i = D + e
b)
A + D = i + e
c)
A + e = D + i
d)
A + i + e = D
|
|
Aman Rane answered |
Relation between angles in a prism:
In optics, when light passes through a prism, it undergoes refraction which causes the light ray to bend. The bending of light depends on the angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of deviation, and angle of the prism.
Angle of Incidence (i):
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal to the surface of the prism at the point of incidence.
Angle of Deviation (D):
The angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray when passing through the prism.
Angle of Emergence (e):
The angle of emergence is the angle between the emergent ray and the normal to the surface of the prism at the point of emergence.
Angle of Prism (A):
The angle of prism is the angle between the two refracting surfaces of the prism.
Relation between the angles:
The correct relation between the four angles is given by option B, which states that "A * D = i * e".
Explanation:
When light passes through a prism, it undergoes refraction twice, once at each surface of the prism. The angle of incidence and angle of emergence are measured with respect to the normal to the surface of the prism at the point of incidence and emergence respectively.
The angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. This angle depends on both the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence.
The angle of prism is a fixed angle, determined by the geometry of the prism.
According to Snell's law of refraction, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of emergence is constant for a given pair of media. This means that the product of the angle of incidence and angle of emergence is constant.
Mathematically, we can write it as:
sin(i)/sin(e) = constant
Now, let's consider the angles A, D, i, and e. The angle of deviation D depends on both the angle of incidence i and angle of emergence e. We can write it as:
D = i + e - A
Rearranging the equation, we get:
D = (i - A) + (e - A)
Now, substituting the value of (i - A) as x and (e - A) as y, we get:
D = x + y
This means that the angle of deviation D is the sum of the differences between the angle of incidence and the angle of prism, and the angle of emergence and the angle of prism.
Therefore, we can conclude that A * D = i * e, which is the correct relation between the angles.
In optics, when light passes through a prism, it undergoes refraction which causes the light ray to bend. The bending of light depends on the angle of incidence, angle of emergence, angle of deviation, and angle of the prism.
Angle of Incidence (i):
The angle of incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the normal to the surface of the prism at the point of incidence.
Angle of Deviation (D):
The angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray when passing through the prism.
Angle of Emergence (e):
The angle of emergence is the angle between the emergent ray and the normal to the surface of the prism at the point of emergence.
Angle of Prism (A):
The angle of prism is the angle between the two refracting surfaces of the prism.
Relation between the angles:
The correct relation between the four angles is given by option B, which states that "A * D = i * e".
Explanation:
When light passes through a prism, it undergoes refraction twice, once at each surface of the prism. The angle of incidence and angle of emergence are measured with respect to the normal to the surface of the prism at the point of incidence and emergence respectively.
The angle of deviation is the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. This angle depends on both the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence.
The angle of prism is a fixed angle, determined by the geometry of the prism.
According to Snell's law of refraction, the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of emergence is constant for a given pair of media. This means that the product of the angle of incidence and angle of emergence is constant.
Mathematically, we can write it as:
sin(i)/sin(e) = constant
Now, let's consider the angles A, D, i, and e. The angle of deviation D depends on both the angle of incidence i and angle of emergence e. We can write it as:
D = i + e - A
Rearranging the equation, we get:
D = (i - A) + (e - A)
Now, substituting the value of (i - A) as x and (e - A) as y, we get:
D = x + y
This means that the angle of deviation D is the sum of the differences between the angle of incidence and the angle of prism, and the angle of emergence and the angle of prism.
Therefore, we can conclude that A * D = i * e, which is the correct relation between the angles.
The far point of a myopic eye is at 50 cm. The power of the lens to correct his vision is- a)– 4 D
- b)– 2 D
- c)+ 2 D
- d)+ 4 D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The far point of a myopic eye is at 50 cm. The power of the lens to correct his vision is
a)
– 4 D
b)
– 2 D
c)
+ 2 D
d)
+ 4 D
|
|
Damini singhania answered |
To determine the power of the lens required to correct a myopic eye, we need to find the focal length of the lens that will bring the far point of the eye to infinity (normal vision).
The far point of the myopic eye is at 50 cm, which means the lens needs to bring this point to infinity. The focal length (f) of the lens can be found using the formula:
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
Where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance.
In this case, the image distance (v) is infinity since we want the far point to be at infinity. The object distance (u) is 50 cm.
1/f = 1/infinity - 1/50
1/f = 0 - 1/50
1/f = -1/50
To solve for f, we take the reciprocal of both sides:
f = -50
The negative sign indicates that the lens is concave (diverging) since it needs to spread out the light rays to bring the far point to infinity.
The power (P) of a lens is given by the formula:
P = 1/f
Substituting the value of f:
P = 1/-50
P = -1/50
Therefore, the power of the lens required to correct the myopic eye is -1/50 diopters.
The far point of the myopic eye is at 50 cm, which means the lens needs to bring this point to infinity. The focal length (f) of the lens can be found using the formula:
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
Where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance.
In this case, the image distance (v) is infinity since we want the far point to be at infinity. The object distance (u) is 50 cm.
1/f = 1/infinity - 1/50
1/f = 0 - 1/50
1/f = -1/50
To solve for f, we take the reciprocal of both sides:
f = -50
The negative sign indicates that the lens is concave (diverging) since it needs to spread out the light rays to bring the far point to infinity.
The power (P) of a lens is given by the formula:
P = 1/f
Substituting the value of f:
P = 1/-50
P = -1/50
Therefore, the power of the lens required to correct the myopic eye is -1/50 diopters.
Human eye is more or less like a- a)Microscope
- b)Telescope
- c)Camera
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Human eye is more or less like a
a)
Microscope
b)
Telescope
c)
Camera
d)
None of these
|
|
Khusboo bhatia answered |
Similarity between Human Eye and Camera
Human eye is more like a camera because both have the ability to capture images and focus on objects. Here are some key similarities between the human eye and a camera:
1. Lens System
- Both the human eye and a camera have a lens system that helps in focusing light onto a light-sensitive surface.
- The lens in the human eye is called the cornea and the lens in a camera can be adjusted to focus on objects at different distances.
2. Aperture
- Both the human eye and a camera have an aperture that controls the amount of light entering the system.
- The iris in the human eye acts like an aperture by adjusting the size of the pupil, while a camera has a physical aperture that can be adjusted.
3. Light-sensitive Surface
- In both the human eye and a camera, the light is focused onto a light-sensitive surface where the image is formed.
- The retina in the human eye functions as the light-sensitive surface, while a camera uses a digital sensor or film.
4. Image Processing
- Both the human eye and a camera process the captured images to form a clear and detailed image.
- The human brain processes the visual information received by the eye, while a camera processes the captured image using software algorithms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the human eye shares similarities with a microscope and telescope in terms of its ability to focus on objects, it is most closely related to a camera due to its structure and functioning as a tool for capturing and processing images.
Human eye is more like a camera because both have the ability to capture images and focus on objects. Here are some key similarities between the human eye and a camera:
1. Lens System
- Both the human eye and a camera have a lens system that helps in focusing light onto a light-sensitive surface.
- The lens in the human eye is called the cornea and the lens in a camera can be adjusted to focus on objects at different distances.
2. Aperture
- Both the human eye and a camera have an aperture that controls the amount of light entering the system.
- The iris in the human eye acts like an aperture by adjusting the size of the pupil, while a camera has a physical aperture that can be adjusted.
3. Light-sensitive Surface
- In both the human eye and a camera, the light is focused onto a light-sensitive surface where the image is formed.
- The retina in the human eye functions as the light-sensitive surface, while a camera uses a digital sensor or film.
4. Image Processing
- Both the human eye and a camera process the captured images to form a clear and detailed image.
- The human brain processes the visual information received by the eye, while a camera processes the captured image using software algorithms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the human eye shares similarities with a microscope and telescope in terms of its ability to focus on objects, it is most closely related to a camera due to its structure and functioning as a tool for capturing and processing images.
Angle of deviation through a prism of angle 60°, when angles of incidence and emergence are 40° each is- a)40°
- b)20°
- c)60°
- d)30°
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Angle of deviation through a prism of angle 60°, when angles of incidence and emergence are 40° each is
a)
40°
b)
20°
c)
60°
d)
30°
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
A = 60°, ∠i= ∠e = 40°
As A + D = i + e
∴ 60° = D = 40° + 40° ⇒ D = 80° – 60° = 20°
As A + D = i + e
∴ 60° = D = 40° + 40° ⇒ D = 80° – 60° = 20°
Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in formation of a rainbow ?
- a)Reflection, refraction and dispersion
- b)Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
- c)Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
- d)Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in formation of a rainbow ?
a)
Reflection, refraction and dispersion
b)
Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
c)
Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
d)
Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
In the formation of a rainbow, sun rays
through rain drops undergo first refraction, then dispersion and finally internal reflection before coming out of the rain droplets.
through rain drops undergo first refraction, then dispersion and finally internal reflection before coming out of the rain droplets.
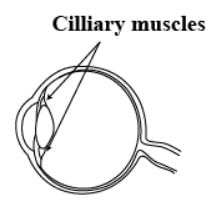
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles- a)Are released and lens becomes thinner
- b)Contract and lens becomes thicker
- c)Are released and lens becomes thicker
- d)Contract and lens becomes thinner
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
a)
Are released and lens becomes thinner
b)
Contract and lens becomes thicker
c)
Are released and lens becomes thicker
d)
Contract and lens becomes thinner
|
|
Nishant chauhan answered |
Understanding Eye Lens and Focal Length
The eye lens plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. The focal length of the eye lens changes based on the activity of the ciliary muscles surrounding it.
Mechanism of Eye Lens Adjustment
- Ciliary Muscles: These muscles control the shape of the lens. When they contract or relax, they affect the lens's curvature and consequently its focal length.
- Focal Length: The distance over which light rays converge. A shorter focal length allows for focusing on nearby objects, while a longer focal length is necessary for distant objects.
Impact of Ciliary Muscle Action
- When Muscles Contract: The ciliary muscles tighten, pulling the lens into a more rounded shape. This increases the lens's thickness and reduces the focal length, allowing us to focus on nearby objects.
- When Muscles Are Released: The ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to become thinner. This increases the focal length, enabling the eye to focus on distant objects effectively.
Correct Option Explanation
- The correct answer is option A: "Are released and lens becomes thinner."
- Release of Muscles: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thinner, which leads to an increase in focal length.
- Effect on Vision: This adjustment is essential for viewing distant objects clearly.
Conclusion
In summary, the focal length of the eye lens increases when the ciliary muscles are released, allowing the lens to become thinner. Understanding this mechanism is vital for grasping how our vision works in relation to different distances.
The eye lens plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. The focal length of the eye lens changes based on the activity of the ciliary muscles surrounding it.
Mechanism of Eye Lens Adjustment
- Ciliary Muscles: These muscles control the shape of the lens. When they contract or relax, they affect the lens's curvature and consequently its focal length.
- Focal Length: The distance over which light rays converge. A shorter focal length allows for focusing on nearby objects, while a longer focal length is necessary for distant objects.
Impact of Ciliary Muscle Action
- When Muscles Contract: The ciliary muscles tighten, pulling the lens into a more rounded shape. This increases the lens's thickness and reduces the focal length, allowing us to focus on nearby objects.
- When Muscles Are Released: The ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to become thinner. This increases the focal length, enabling the eye to focus on distant objects effectively.
Correct Option Explanation
- The correct answer is option A: "Are released and lens becomes thinner."
- Release of Muscles: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thinner, which leads to an increase in focal length.
- Effect on Vision: This adjustment is essential for viewing distant objects clearly.
Conclusion
In summary, the focal length of the eye lens increases when the ciliary muscles are released, allowing the lens to become thinner. Understanding this mechanism is vital for grasping how our vision works in relation to different distances.
How many times does a ray of light bend on passing through prism ?- a)once
- b)twice
- c)thrice
- d)four times
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many times does a ray of light bend on passing through prism ?
a)
once
b)
twice
c)
thrice
d)
four times
|
|
Sahana dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
A ray of light passing through a prism undergoes bending or refraction. Refraction is the change in direction of a ray of light as it passes from one medium to another medium with a different refractive index.
Prism:
- A prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light.
- It has two triangular bases and three rectangular faces.
- The shape of the prism causes the light to refract or bend as it passes through.
Refraction in Prism:
- When a ray of light enters a prism, it first undergoes refraction at the first surface of the prism.
- The ray of light bends towards the base of the prism due to the change in the refractive index.
- After refraction, the light continues to travel through the prism and reaches the second surface.
- At the second surface, the light undergoes refraction again, but this time it bends away from the base of the prism.
- The angle of deviation depends on the angle of incidence and the refractive indices of the prism and the surrounding medium.
Number of Times Light Bends:
- When a ray of light passes through a prism, it bends twice.
- The first bending occurs at the entrance surface, where the light bends towards the base of the prism.
- The second bending occurs at the exit surface, where the light bends away from the base of the prism.
- Therefore, a ray of light passing through a prism bends twice.
Conclusion:
- A ray of light passing through a prism bends twice, once at the entrance surface and once at the exit surface.
- This bending or refraction is due to the change in the refractive index of the prism.
- Understanding the refraction of light through a prism is important in the study of optics and the behavior of light.
A ray of light passing through a prism undergoes bending or refraction. Refraction is the change in direction of a ray of light as it passes from one medium to another medium with a different refractive index.
Prism:
- A prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light.
- It has two triangular bases and three rectangular faces.
- The shape of the prism causes the light to refract or bend as it passes through.
Refraction in Prism:
- When a ray of light enters a prism, it first undergoes refraction at the first surface of the prism.
- The ray of light bends towards the base of the prism due to the change in the refractive index.
- After refraction, the light continues to travel through the prism and reaches the second surface.
- At the second surface, the light undergoes refraction again, but this time it bends away from the base of the prism.
- The angle of deviation depends on the angle of incidence and the refractive indices of the prism and the surrounding medium.
Number of Times Light Bends:
- When a ray of light passes through a prism, it bends twice.
- The first bending occurs at the entrance surface, where the light bends towards the base of the prism.
- The second bending occurs at the exit surface, where the light bends away from the base of the prism.
- Therefore, a ray of light passing through a prism bends twice.
Conclusion:
- A ray of light passing through a prism bends twice, once at the entrance surface and once at the exit surface.
- This bending or refraction is due to the change in the refractive index of the prism.
- Understanding the refraction of light through a prism is important in the study of optics and the behavior of light.
At noon, the sun appears white as- a)Blue colour is scattered the most
- b)Red colour is scattered the most
- c)All the colours of white light are scattered away
- d)Light is least scattered
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At noon, the sun appears white as
a)
Blue colour is scattered the most
b)
Red colour is scattered the most
c)
All the colours of white light are scattered away
d)
Light is least scattered
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
At noon because the sun is overhead, the light is scattered the least and hence appears white. When it is overhead, it has lesser air to travel through and the scattering from dust and other particles is reduced if the distance to be travelled in air is reduced.
The essential condition for Rayleigh’s elastic scattering is- a)Size of scatterer (x) must be much less then the wavelength of light (λ) incident i.e., x << λ
- b)x >> λ
- c)x = λ
- d)independent of x and λ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The essential condition for Rayleigh’s elastic scattering is
a)
Size of scatterer (x) must be much less then the wavelength of light (λ) incident i.e., x << λ
b)
x >> λ
c)
x = λ
d)
independent of x and λ
|
|
Avantika nair answered |
Scattering is that the size of the scattering particles must be much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light. This condition is known as the Rayleigh criterion.
In Rayleigh scattering, the incident light interacts with the scattering particles, causing them to scatter the light in all directions. The scattering is more pronounced in the shorter wavelengths of the visible spectrum, such as blue and violet light.
The size of the scattering particles being much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light is crucial because it affects the intensity and direction of the scattered light. When the particle size is much larger than the wavelength, the scattering behavior changes, leading to different scattering phenomena.
The Rayleigh criterion is important in various natural phenomena, such as the blue color of the sky, where the scattering of shorter wavelengths of sunlight by atmospheric particles causes the blue light to be scattered more than other colors. It is also relevant in other fields, including optics, telecommunications, and remote sensing, where the scattering of light is of interest.
Overall, the essential condition for Rayleigh scattering is that the size of the scattering particles must be much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light to observe the characteristic scattering behavior.
In Rayleigh scattering, the incident light interacts with the scattering particles, causing them to scatter the light in all directions. The scattering is more pronounced in the shorter wavelengths of the visible spectrum, such as blue and violet light.
The size of the scattering particles being much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light is crucial because it affects the intensity and direction of the scattered light. When the particle size is much larger than the wavelength, the scattering behavior changes, leading to different scattering phenomena.
The Rayleigh criterion is important in various natural phenomena, such as the blue color of the sky, where the scattering of shorter wavelengths of sunlight by atmospheric particles causes the blue light to be scattered more than other colors. It is also relevant in other fields, including optics, telecommunications, and remote sensing, where the scattering of light is of interest.
Overall, the essential condition for Rayleigh scattering is that the size of the scattering particles must be much smaller than the wavelength of the incident light to observe the characteristic scattering behavior.
______ is at the lower end and ______ is at the upper end of the visible spectrum.- a)Violet, red
- b)Red, blue
- c)Red, violet
- d)Blue, red
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
______ is at the lower end and ______ is at the upper end of the visible spectrum.
a)
Violet, red
b)
Red, blue
c)
Red, violet
d)
Blue, red
|
|
Ramya sengupta answered |
The visible spectrum:
The visible spectrum refers to the range of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It consists of various colors that we can perceive, ranging from red to violet.
The lower end of the visible spectrum:
At the lower end of the visible spectrum, we find the color violet. Violet light has the shortest wavelength and highest frequency among the visible colors. It can be seen at the end of a rainbow or when sunlight passes through a prism, causing the colors to separate.
The upper end of the visible spectrum:
At the upper end of the visible spectrum, we find the color red. Red light has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency among the visible colors. It can also be seen in a rainbow, appearing at the opposite end of violet.
The correct answer:
The correct answer to the question is option 'A', which states that violet is at the lower end and red is at the upper end of the visible spectrum. This is because violet light has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency compared to red light.
The visible spectrum refers to the range of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It consists of various colors that we can perceive, ranging from red to violet.
The lower end of the visible spectrum:
At the lower end of the visible spectrum, we find the color violet. Violet light has the shortest wavelength and highest frequency among the visible colors. It can be seen at the end of a rainbow or when sunlight passes through a prism, causing the colors to separate.
The upper end of the visible spectrum:
At the upper end of the visible spectrum, we find the color red. Red light has the longest wavelength and lowest frequency among the visible colors. It can also be seen in a rainbow, appearing at the opposite end of violet.
The correct answer:
The correct answer to the question is option 'A', which states that violet is at the lower end and red is at the upper end of the visible spectrum. This is because violet light has a shorter wavelength and higher frequency compared to red light.
The longest visible wavelength 800.0Å is of ______ colour- a)Violet
- b)Red
- c)Green
- d)Orange
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The longest visible wavelength 800.0Å is of ______ colour
a)
Violet
b)
Red
c)
Green
d)
Orange
|
|
Ramya sengupta answered |
The longest visible wavelength is approximately 800 nanometers (nm).
The function of iris is to regulate the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of- a)Pupil
- b)Cornea
- c)Iris
- d)Retina
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The function of iris is to regulate the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of
a)
Pupil
b)
Cornea
c)
Iris
d)
Retina

|
Dhruba Nambiar answered |
The Function of Iris in Regulating Light Entering the Eye
The iris is a colored, ring-shaped membrane behind the cornea of the eye. Its main function is to regulate the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil.
Regulating Pupil Size
- The pupil is the black circular opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye.
- The iris contains muscles that control the size of the pupil.
- In bright light, the iris constricts the pupil, making it smaller to reduce the amount of light entering the eye.
- In dim light, the iris dilates the pupil, making it larger to allow more light to enter.
Protecting the Eye
- The iris also plays a role in protecting the eye from potentially harmful levels of light.
- By adjusting the size of the pupil, the iris helps to regulate the amount of light that reaches the retina at the back of the eye.
- This helps to prevent damage to the sensitive cells in the retina that are responsible for vision.
Importance of Iris Function
- The ability of the iris to regulate the amount of light entering the eye is crucial for maintaining clear vision in varying lighting conditions.
- Without this function, the eye would be overwhelmed by too much light in bright conditions or struggle to see in low light situations.
- The iris works in conjunction with other parts of the eye, such as the cornea and lens, to ensure that light is focused properly on the retina for clear vision.
The iris is a colored, ring-shaped membrane behind the cornea of the eye. Its main function is to regulate the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil.
Regulating Pupil Size
- The pupil is the black circular opening in the center of the iris through which light enters the eye.
- The iris contains muscles that control the size of the pupil.
- In bright light, the iris constricts the pupil, making it smaller to reduce the amount of light entering the eye.
- In dim light, the iris dilates the pupil, making it larger to allow more light to enter.
Protecting the Eye
- The iris also plays a role in protecting the eye from potentially harmful levels of light.
- By adjusting the size of the pupil, the iris helps to regulate the amount of light that reaches the retina at the back of the eye.
- This helps to prevent damage to the sensitive cells in the retina that are responsible for vision.
Importance of Iris Function
- The ability of the iris to regulate the amount of light entering the eye is crucial for maintaining clear vision in varying lighting conditions.
- Without this function, the eye would be overwhelmed by too much light in bright conditions or struggle to see in low light situations.
- The iris works in conjunction with other parts of the eye, such as the cornea and lens, to ensure that light is focused properly on the retina for clear vision.
Which phenomenon is not explained on scattering of light ?- a)Red colour of danger signals
- b)Blue colour of the clear sky
- c)White colour of clouds
- d)Advanced sunrise
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phenomenon is not explained on scattering of light ?
a)
Red colour of danger signals
b)
Blue colour of the clear sky
c)
White colour of clouds
d)
Advanced sunrise
|
|
Nilima iyer answered |
Explanation:
Scattering of light:
Scattering of light refers to the process in which light is deflected or scattered in various directions when it interacts with particles or objects in its path. This phenomenon explains several natural phenomena and colors we observe in our surroundings.
Red color of danger signals:
The red color of danger signals is a result of the scattering of light. When sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere, it undergoes scattering due to the presence of air molecules and other particles. The scattering of shorter wavelength colors like blue and green is more prominent, while longer wavelength colors like red are scattered less. As a result, the scattered light appears to be predominantly red, which is why danger signals are usually red in color.
Blue color of the clear sky:
The blue color of the clear sky is also a result of the scattering of light. The Earth's atmosphere contains tiny molecules, such as nitrogen and oxygen, that scatter short wavelength light more efficiently than long wavelength light. When sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the shorter wavelength colors like blue and violet are scattered in all directions. This scattered light is what we perceive as the blue color of the sky.
White color of clouds:
Clouds appear white because of the scattering of light by water droplets or ice crystals present in them. When sunlight passes through the clouds, the water droplets or ice crystals scatter all wavelengths of light equally. As a result, the scattered light appears white.
Advanced sunrise:
The phenomenon of advanced sunrise is not directly related to the scattering of light. An advanced sunrise occurs when the sun appears to rise earlier than its actual position due to atmospheric refraction. Atmospheric refraction is the bending of light as it passes through the Earth's atmosphere. This bending causes the sun to appear higher in the sky than it actually is, resulting in an advanced sunrise.
In conclusion, the scattering of light explains the red color of danger signals, the blue color of the clear sky, and the white color of clouds. However, the advanced sunrise is not directly related to the scattering of light.
Scattering of light:
Scattering of light refers to the process in which light is deflected or scattered in various directions when it interacts with particles or objects in its path. This phenomenon explains several natural phenomena and colors we observe in our surroundings.
Red color of danger signals:
The red color of danger signals is a result of the scattering of light. When sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere, it undergoes scattering due to the presence of air molecules and other particles. The scattering of shorter wavelength colors like blue and green is more prominent, while longer wavelength colors like red are scattered less. As a result, the scattered light appears to be predominantly red, which is why danger signals are usually red in color.
Blue color of the clear sky:
The blue color of the clear sky is also a result of the scattering of light. The Earth's atmosphere contains tiny molecules, such as nitrogen and oxygen, that scatter short wavelength light more efficiently than long wavelength light. When sunlight passes through the atmosphere, the shorter wavelength colors like blue and violet are scattered in all directions. This scattered light is what we perceive as the blue color of the sky.
White color of clouds:
Clouds appear white because of the scattering of light by water droplets or ice crystals present in them. When sunlight passes through the clouds, the water droplets or ice crystals scatter all wavelengths of light equally. As a result, the scattered light appears white.
Advanced sunrise:
The phenomenon of advanced sunrise is not directly related to the scattering of light. An advanced sunrise occurs when the sun appears to rise earlier than its actual position due to atmospheric refraction. Atmospheric refraction is the bending of light as it passes through the Earth's atmosphere. This bending causes the sun to appear higher in the sky than it actually is, resulting in an advanced sunrise.
In conclusion, the scattering of light explains the red color of danger signals, the blue color of the clear sky, and the white color of clouds. However, the advanced sunrise is not directly related to the scattering of light.
A glass prism has- a)Six rectangular surfaces
- b)Four rectangular surfaces
- c)Two triangular bases and their rectangular surfaces
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A glass prism has
a)
Six rectangular surfaces
b)
Four rectangular surfaces
c)
Two triangular bases and their rectangular surfaces
d)
None of these
|
|
Gauri reddy answered |
Understanding the Structure of a Glass Prism
A glass prism is a transparent optical element that refracts light. To comprehend its structure, let's analyze its surfaces.
Key Components of a Glass Prism
- Triangular Bases: A standard glass prism has two triangular bases. These bases are the top and bottom surfaces of the prism.
- Rectangular Lateral Surfaces: In addition to the triangular bases, a prism has three rectangular lateral surfaces that connect the corresponding sides of the triangular bases.
Total Number of Surfaces
- Counting Surfaces:
- 2 triangular surfaces (the bases)
- 3 rectangular surfaces (the sides connecting the bases)
Thus, the total number of surfaces is 5 (2 triangular + 3 rectangular).
Conclusion
Given the options provided:
- a) Six rectangular surfaces – Incorrect, as there are not six rectangular surfaces.
- b) Four rectangular surfaces – Incorrect, as there are three rectangular surfaces.
- c) Two triangular bases and their rectangular surfaces – Correct, since it accurately describes the structure of a prism.
- d) None of these – Incorrect, as option c is correct.
In summary, option 'C' accurately reflects that a glass prism consists of two triangular bases and three rectangular lateral surfaces, making it the right choice. Always remember that understanding the basic geometry of shapes enhances our grasp of their properties and functions.
A glass prism is a transparent optical element that refracts light. To comprehend its structure, let's analyze its surfaces.
Key Components of a Glass Prism
- Triangular Bases: A standard glass prism has two triangular bases. These bases are the top and bottom surfaces of the prism.
- Rectangular Lateral Surfaces: In addition to the triangular bases, a prism has three rectangular lateral surfaces that connect the corresponding sides of the triangular bases.
Total Number of Surfaces
- Counting Surfaces:
- 2 triangular surfaces (the bases)
- 3 rectangular surfaces (the sides connecting the bases)
Thus, the total number of surfaces is 5 (2 triangular + 3 rectangular).
Conclusion
Given the options provided:
- a) Six rectangular surfaces – Incorrect, as there are not six rectangular surfaces.
- b) Four rectangular surfaces – Incorrect, as there are three rectangular surfaces.
- c) Two triangular bases and their rectangular surfaces – Correct, since it accurately describes the structure of a prism.
- d) None of these – Incorrect, as option c is correct.
In summary, option 'C' accurately reflects that a glass prism consists of two triangular bases and three rectangular lateral surfaces, making it the right choice. Always remember that understanding the basic geometry of shapes enhances our grasp of their properties and functions.
The change in focal length of an eye lens to focus the image of the objects at varying distances is done by the action of- a)Retina
- b)Ciliary muscles
- c)Iris
- d)Pupil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The change in focal length of an eye lens to focus the image of the objects at varying distances is done by the action of
a)
Retina
b)
Ciliary muscles
c)
Iris
d)
Pupil
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
The ciliary muscles change the focal length of the eye lens to focus objects at variable distances.

The splitting up of the light into its constituent colours, and the coloured bands so obtained on the screen are called- a)Dispersion
- b)Scattering
- c)Spectrum
- d)Refraction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The splitting up of the light into its constituent colours, and the coloured bands so obtained on the screen are called
a)
Dispersion
b)
Scattering
c)
Spectrum
d)
Refraction
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Dispersion is the phenomenon of splitting of polychromatic light into its constituent colours. The band of colours obtained on the screen on passing white light through a prism is called a spectrum.
The property of eye which is used in cinematography is- a)Persistence of vision
- b)Power of accommodation
- c)Colour blindness
- d)Range of vision
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The property of eye which is used in cinematography is
a)
Persistence of vision
b)
Power of accommodation
c)
Colour blindness
d)
Range of vision
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Animation works by using an optical illusion. Film theorists often refer to this illusion of movement as the persistence of vision. The persistence of vision works because the human eye and brain can only process 10 to 12 separate images per second, retaining an image for up to a fifteenth of a second.
Persistence of vision is the eye's ability to keep seeing an image of an object for a fraction of a second after the object has disappeared from view. The principle of persistence of vision is used in making motion pictures and animated cartoons.
Persistence of vision is the eye's ability to keep seeing an image of an object for a fraction of a second after the object has disappeared from view. The principle of persistence of vision is used in making motion pictures and animated cartoons.
In passing through a glass prism, a ray of light undergoes how many refractions ?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In passing through a glass prism, a ray of light undergoes how many refractions ?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
A ray of light undergoes two refractions at the two faces of the prism
The deviation of a ray of light passing through a prism depends on- a)angle of prism
- b)nature of material of the prism
- c)angle of incidence of the ray
- d)all of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The deviation of a ray of light passing through a prism depends on
a)
angle of prism
b)
nature of material of the prism
c)
angle of incidence of the ray
d)
all of the above
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
- The angle of incidenc: As the angle of incidence increases, first the angle of deviation decreases and reaches to a minimum value for a certain angle of incidence. By further increasing the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation is found to increase.
- The material of prism (i.e., on refractive index): For a given angle of incidence, the prism with a higher refractive index produces a greater deviation than the prism which has a lower refractive index.
- Angle of prism: Angle of deviation increases with the increase in the angle of prism.
The cells which enable us to distinguish between different colours are- a)Rod shaped
- b)Cone shaped
- c)Both types of cells
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cells which enable us to distinguish between different colours are
a)
Rod shaped
b)
Cone shaped
c)
Both types of cells
d)
None of these
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Cone cells, or cones, are one of three types of photoreceptor cells in the retina of mammalian eyes(e.g. the human eye). They are responsible for color vision and they function best in relatively bright light.
Blue colour of clear sky is on account of- a)Scattering of sunlight
- b)Dispersion
- c)Atmospheric refraction
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Blue colour of clear sky is on account of
a)
Scattering of sunlight
b)
Dispersion
c)
Atmospheric refraction
d)
None of these
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Gases and particles in Earth's atmosphere scatter sunlight in all directions. Blue light is scattered more than other colors because it travels as shorter, smaller waves. This is why we see a blue sky most of the time.
The cause of advanced sunrise and delayed sunset is- a)Scattering of sunlight
- b)Dispersion
- c)Atmospheric refraction
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cause of advanced sunrise and delayed sunset is
a)
Scattering of sunlight
b)
Dispersion
c)
Atmospheric refraction
d)
None of these
|
|
Meera Rana answered |
The sun is visible to us about 2 minutes before the actual sunrise, and about 2 minutes after the actual sunset because of atmospheric refraction.
Cataract is a flow that arises when eye lens of person becomes- a)Hazy (opaque)
- b)Transparent
- c)Black
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Cataract is a flow that arises when eye lens of person becomes
a)
Hazy (opaque)
b)
Transparent
c)
Black
d)
None of these
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
The crystalline lens of some people in old age becomes hazy or even opaque. This happens because of the development of a membrane over it when it happens the person is said to have a cataract.
Chapter doubts & questions for Human Eye and Colourful World - Science Olympiad for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Human Eye and Colourful World - Science Olympiad for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup