Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > The focal length of the eye lens increases wh...
Start Learning for Free
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
- a)Are released and lens becomes thinner
- b)Contract and lens becomes thicker
- c)Are released and lens becomes thicker
- d)Contract and lens becomes thinner
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are relea...
Understanding Eye Lens and Focal Length
The eye lens plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. The focal length of the eye lens changes based on the activity of the ciliary muscles surrounding it.
Mechanism of Eye Lens Adjustment
- Ciliary Muscles: These muscles control the shape of the lens. When they contract or relax, they affect the lens's curvature and consequently its focal length.
- Focal Length: The distance over which light rays converge. A shorter focal length allows for focusing on nearby objects, while a longer focal length is necessary for distant objects.
Impact of Ciliary Muscle Action
- When Muscles Contract: The ciliary muscles tighten, pulling the lens into a more rounded shape. This increases the lens's thickness and reduces the focal length, allowing us to focus on nearby objects.
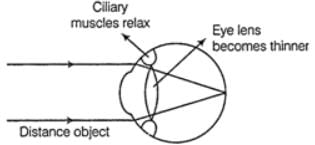
- When Muscles Are Released: The ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to become thinner. This increases the focal length, enabling the eye to focus on distant objects effectively.
Correct Option Explanation
- The correct answer is option A: "Are released and lens becomes thinner."
- Release of Muscles: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thinner, which leads to an increase in focal length.
- Effect on Vision: This adjustment is essential for viewing distant objects clearly.
Conclusion
In summary, the focal length of the eye lens increases when the ciliary muscles are released, allowing the lens to become thinner. Understanding this mechanism is vital for grasping how our vision works in relation to different distances.
The eye lens plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, allowing us to see clearly. The focal length of the eye lens changes based on the activity of the ciliary muscles surrounding it.
Mechanism of Eye Lens Adjustment
- Ciliary Muscles: These muscles control the shape of the lens. When they contract or relax, they affect the lens's curvature and consequently its focal length.
- Focal Length: The distance over which light rays converge. A shorter focal length allows for focusing on nearby objects, while a longer focal length is necessary for distant objects.
Impact of Ciliary Muscle Action
- When Muscles Contract: The ciliary muscles tighten, pulling the lens into a more rounded shape. This increases the lens's thickness and reduces the focal length, allowing us to focus on nearby objects.
- When Muscles Are Released: The ciliary muscles relax, allowing the lens to become thinner. This increases the focal length, enabling the eye to focus on distant objects effectively.
Correct Option Explanation
- The correct answer is option A: "Are released and lens becomes thinner."
- Release of Muscles: When the ciliary muscles are relaxed, the eye lens becomes thinner, which leads to an increase in focal length.
- Effect on Vision: This adjustment is essential for viewing distant objects clearly.
Conclusion
In summary, the focal length of the eye lens increases when the ciliary muscles are released, allowing the lens to become thinner. Understanding this mechanism is vital for grasping how our vision works in relation to different distances.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are relea...
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles relaxed and becomes thinner. The sharp image of the distant object is formed at the retina. This enables us to focus accurately on distant objects.


|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Question Description
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye musclesa)Are released and lens becomes thinnerb)Contract and lens becomes thickerc)Are released and lens becomes thickerd)Contract and lens becomes thinnerCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















