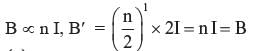All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Olympiad for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Magnetic Effects of Electric Current for Class 10 Exam
Permanent magnets are made up of- a)Ferronite (alloy of Fe, Ni and Mg)
- b)Alnico (alloy of Al, Ni and Co)
- c)Iron ore
- d)Bauxite ore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Permanent magnets are made up of
a)
Ferronite (alloy of Fe, Ni and Mg)
b)
Alnico (alloy of Al, Ni and Co)
c)
Iron ore
d)
Bauxite ore
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Permanent magnets are made from special alloys (ferromagnetic materials) such as iron, nickel and cobalt, several alloys of rare-earth metals and minerals such as lodestone.
What is the potential difference of current in Indian household circuit?- a)220 V
- b)240 V
- c)330 V
- d)440 V
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the potential difference of current in Indian household circuit?
a)
220 V
b)
240 V
c)
330 V
d)
440 V
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Potential difference between a live wire and a neutral wire in a domestic circuits it 220 V and the frequency of an AC is 50 Hz.
The direction of magnetic field pattern produced by a straight wire can be determined with which one of the following rules ?- a)Thumb rule
- b)Fleming’s left hand rule
- c)Fleming’s right hand rule
- d)Any of the these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The direction of magnetic field pattern produced by a straight wire can be determined with which one of the following rules ?
a)
Thumb rule
b)
Fleming’s left hand rule
c)
Fleming’s right hand rule
d)
Any of the these
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
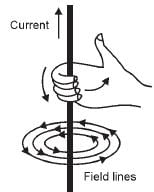
As per the Right-Hand thumb rule, the direction of curling of fingers of the right hand gives the direction of magnetic field lines.
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, then- a)Speed of the particle is changed
- b)Speed of the particle remains the same
- c)Direction of the particle remains unchanged
- d)Acceleration of the particle remain unchanged
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, then
a)
Speed of the particle is changed
b)
Speed of the particle remains the same
c)
Direction of the particle remains unchanged
d)
Acceleration of the particle remain unchanged
|
|
Anika malhotra answered |
Explanation:
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, the speed of the particle remains the same. This is known as the magnetic force or the Lorentz force.
Key Points:
The following factors contribute to the speed of the particle remaining the same:
1. Magnetic Force: When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, it experiences a force known as the magnetic force. This force acts at right angles to the motion of the particle and the magnetic field.
2. Circular Path: The magnetic force causes the charged particle to move in a circular path. This circular motion is due to the continuous deflection of the particle by the magnetic force.
3. Centripetal Force: In a circular motion, there is a force called the centripetal force that continuously pulls the particle towards the center of the circular path. This force is provided by the magnetic force acting as the centripetal force.
4. Constant Speed: The centripetal force required to keep the particle in a circular path is provided by the magnetic force. As long as the magnetic force remains constant, the speed of the particle remains the same.
5. No Change in Energy: Since the speed of the particle remains the same, there is no change in its kinetic energy. The work done by the magnetic force is zero, as the force is always perpendicular to the displacement of the particle.
Conclusion:
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, the speed of the particle remains the same. This is due to the magnetic force causing the particle to move in a circular path, with the centripetal force provided by the magnetic force. As a result, there is no change in the speed or kinetic energy of the particle.
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, the speed of the particle remains the same. This is known as the magnetic force or the Lorentz force.
Key Points:
The following factors contribute to the speed of the particle remaining the same:
1. Magnetic Force: When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, it experiences a force known as the magnetic force. This force acts at right angles to the motion of the particle and the magnetic field.
2. Circular Path: The magnetic force causes the charged particle to move in a circular path. This circular motion is due to the continuous deflection of the particle by the magnetic force.
3. Centripetal Force: In a circular motion, there is a force called the centripetal force that continuously pulls the particle towards the center of the circular path. This force is provided by the magnetic force acting as the centripetal force.
4. Constant Speed: The centripetal force required to keep the particle in a circular path is provided by the magnetic force. As long as the magnetic force remains constant, the speed of the particle remains the same.
5. No Change in Energy: Since the speed of the particle remains the same, there is no change in its kinetic energy. The work done by the magnetic force is zero, as the force is always perpendicular to the displacement of the particle.
Conclusion:
When a charged particle moves perpendicular to a magnetic field, the speed of the particle remains the same. This is due to the magnetic force causing the particle to move in a circular path, with the centripetal force provided by the magnetic force. As a result, there is no change in the speed or kinetic energy of the particle.
In case of a current-carrying circular coil, the magnetic field is maximum- a)At its centre
- b)At the ends of the coil
- c)Any where inside the coil
- d)Outside the coil
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of a current-carrying circular coil, the magnetic field is maximum
a)
At its centre
b)
At the ends of the coil
c)
Any where inside the coil
d)
Outside the coil
|
|
Rajni kumar answered |
Magnetic Field of a Current-Carrying Circular Coil
When examining a circular coil carrying an electric current, it is essential to understand how the magnetic field behaves within and around the coil.
Magnetic Field Characteristics
- When current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field.
- The direction of this magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand grip rule: if you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the current, your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field lines.
Maximum Magnetic Field at the Center
- The magnetic field strength is not uniform throughout the coil.
- It reaches its maximum strength at the center of the coil due to the cumulative effect of the magnetic fields generated by each segment of the coil.
- At the center, all the magnetic field lines generated by the coil loops add together constructively, leading to a stronger magnetic field.
Magnetic Field at Other Locations
- At the ends of the coil, the magnetic field strength decreases because the contributions from the individual loops do not align as effectively.
- Inside the coil but away from the center, the magnetic field is still present but weaker than at the center.
- Outside the coil, the magnetic field is significantly weaker and disperses into the surrounding area.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the magnetic field is indeed maximum at the center of a current-carrying circular coil, reaffirming option 'A' as the correct answer. Understanding these principles is crucial for grasping the fundamentals of electromagnetism in physics.
When examining a circular coil carrying an electric current, it is essential to understand how the magnetic field behaves within and around the coil.
Magnetic Field Characteristics
- When current flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field.
- The direction of this magnetic field can be determined using the right-hand grip rule: if you curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the current, your thumb points in the direction of the magnetic field lines.
Maximum Magnetic Field at the Center
- The magnetic field strength is not uniform throughout the coil.
- It reaches its maximum strength at the center of the coil due to the cumulative effect of the magnetic fields generated by each segment of the coil.
- At the center, all the magnetic field lines generated by the coil loops add together constructively, leading to a stronger magnetic field.
Magnetic Field at Other Locations
- At the ends of the coil, the magnetic field strength decreases because the contributions from the individual loops do not align as effectively.
- Inside the coil but away from the center, the magnetic field is still present but weaker than at the center.
- Outside the coil, the magnetic field is significantly weaker and disperses into the surrounding area.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the magnetic field is indeed maximum at the center of a current-carrying circular coil, reaffirming option 'A' as the correct answer. Understanding these principles is crucial for grasping the fundamentals of electromagnetism in physics.
What is the current rating of power switch current in our household circuit?- a)5 A
- b)10 A
- c)15 A
- d)20 A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the current rating of power switch current in our household circuit?
a)
5 A
b)
10 A
c)
15 A
d)
20 A
|
|
Mira nambiar answered |
Understanding Household Circuit Ratings
In most household circuits, the power switch current rating is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. The common ratings you might encounter include 5 A, 10 A, 15 A, and 20 A.
Standard Current Ratings
- 5 A: This rating is typically used for low-power devices such as lamps and small electronics.
- 10 A: This can handle moderate loads like kitchen appliances, but it’s not sufficient for higher power devices.
- 15 A: This is the most common rating for a standard household circuit in many countries. It can effectively support larger appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, and washing machines.
- 20 A: This is used for heavy-duty appliances, such as air conditioners or electric ovens, which require more current to operate safely.
Why is 15 A the Correct Answer?
The choice of 15 A as the standard rating stems from the need for balance between safety and functionality:
- Safety: A 15 A rating prevents overheating and potential fire hazards by limiting the current that can flow through the circuit.
- Versatility: It provides adequate supply for a variety of household appliances without the risk of overloading the circuit.
Conclusion
In summary, while 5 A and 10 A are suitable for low to moderate power devices, the 15 A rating is widely adopted for general household use, accommodating a range of appliances safely. The 20 A rating is reserved for specialized, high-power equipment.
In most household circuits, the power switch current rating is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. The common ratings you might encounter include 5 A, 10 A, 15 A, and 20 A.
Standard Current Ratings
- 5 A: This rating is typically used for low-power devices such as lamps and small electronics.
- 10 A: This can handle moderate loads like kitchen appliances, but it’s not sufficient for higher power devices.
- 15 A: This is the most common rating for a standard household circuit in many countries. It can effectively support larger appliances like refrigerators, microwaves, and washing machines.
- 20 A: This is used for heavy-duty appliances, such as air conditioners or electric ovens, which require more current to operate safely.
Why is 15 A the Correct Answer?
The choice of 15 A as the standard rating stems from the need for balance between safety and functionality:
- Safety: A 15 A rating prevents overheating and potential fire hazards by limiting the current that can flow through the circuit.
- Versatility: It provides adequate supply for a variety of household appliances without the risk of overloading the circuit.
Conclusion
In summary, while 5 A and 10 A are suitable for low to moderate power devices, the 15 A rating is widely adopted for general household use, accommodating a range of appliances safely. The 20 A rating is reserved for specialized, high-power equipment.
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform horizontal magnetic field whose magnitude in Tesla is- a)2 T
- b)0.65 T
- c)1.3 T
- d)0.55 T
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A straight wire of mass 200 g and length 1.5 m carries a current of 2A. It is suspended in mid air by a uniform horizontal magnetic field whose magnitude in Tesla is
a)
2 T
b)
0.65 T
c)
1.3 T
d)
0.55 T
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
It has been found that Force (F) acting on a current-carrying conductor placed on a magnetic field, in a direction perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field, is directly proportional to the current, length of the conductor and magnitude of the field F = k I l B. In SI units, constant k = 1 Also, Force acting on a suspended mass = mg ⇒ mg = I l b
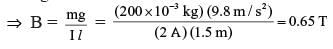
Commercial electric motors do not use- a)An electromagnet to rotate the armature
- b)Effectively large number of turns of conducting wire in the current-carrying coil
- c)A permanent magnet to rotate the armature
- d)A soft iron core on which the coil is wound
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Commercial electric motors do not use
a)
An electromagnet to rotate the armature
b)
Effectively large number of turns of conducting wire in the current-carrying coil
c)
A permanent magnet to rotate the armature
d)
A soft iron core on which the coil is wound
|
|
Gopika dasgupta answered |
Understanding Electric Motors
Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using electromagnetic principles. In commercial electric motors, various components play crucial roles in their functionality.
Components of Electric Motors
- Electromagnet:
- Most electric motors use electromagnets to generate the magnetic field required for rotation. This field interacts with the armature to produce motion.
- Conducting Wire:
- A large number of turns of conducting wire are used in the coil. This increases the magnetic field strength when electric current passes through, enhancing the motor's efficiency.
- Soft Iron Core:
- The coil is often wound around a soft iron core, which amplifies the magnetic field. This core helps in directing the magnetic lines of force, improving the motor's performance.
Why Permanent Magnets Are Less Common
- Permanent Magnet Use:
- In commercial electric motors, the use of permanent magnets to rotate the armature is not typical. While some motors, like small DC motors, might feature permanent magnets, most larger and more complex motors rely on electromagnets for better control and efficiency.
- Flexibility and Control:
- Electromagnets allow for adjustable magnetic fields, which enable precise control over speed and torque. This flexibility is essential in industrial applications, making electromagnets more favorable than permanent magnets.
Conclusion
In summary, commercial electric motors primarily utilize electromagnets, conducting wire coils, and soft iron cores, rather than permanent magnets, to achieve efficient and controllable motion. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'C'.
Electric motors are devices that convert electrical energy into mechanical energy using electromagnetic principles. In commercial electric motors, various components play crucial roles in their functionality.
Components of Electric Motors
- Electromagnet:
- Most electric motors use electromagnets to generate the magnetic field required for rotation. This field interacts with the armature to produce motion.
- Conducting Wire:
- A large number of turns of conducting wire are used in the coil. This increases the magnetic field strength when electric current passes through, enhancing the motor's efficiency.
- Soft Iron Core:
- The coil is often wound around a soft iron core, which amplifies the magnetic field. This core helps in directing the magnetic lines of force, improving the motor's performance.
Why Permanent Magnets Are Less Common
- Permanent Magnet Use:
- In commercial electric motors, the use of permanent magnets to rotate the armature is not typical. While some motors, like small DC motors, might feature permanent magnets, most larger and more complex motors rely on electromagnets for better control and efficiency.
- Flexibility and Control:
- Electromagnets allow for adjustable magnetic fields, which enable precise control over speed and torque. This flexibility is essential in industrial applications, making electromagnets more favorable than permanent magnets.
Conclusion
In summary, commercial electric motors primarily utilize electromagnets, conducting wire coils, and soft iron cores, rather than permanent magnets, to achieve efficient and controllable motion. Thus, the correct answer to the question is option 'C'.
An electric bulb rated 220 V is connected to 220 V, 5 Hz AC source. The bulb- a)Does not glow
- b)Glows immediately
- c)Glows continuously
- d)Gets fused
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric bulb rated 220 V is connected to 220 V, 5 Hz AC source. The bulb
a)
Does not glow
b)
Glows immediately
c)
Glows continuously
d)
Gets fused
|
|
Sudha gupta answered |
Explanation:
The given question is related to the working of an electric bulb when connected to an AC source. Let us understand the answer to the question in detail.
The working of an electric bulb:
An electric bulb consists of a filament made up of tungsten wire which is enclosed in a glass bulb filled with an inert gas like argon. When an electric current flows through the filament, it gets heated up and produces light. The amount of light produced depends on the temperature of the filament. When the temperature of the filament reaches a certain level, it starts glowing and emits light.
Working of AC source:
An AC source is a source of electrical energy that produces an alternating current. In an AC source, the direction of current changes periodically. The frequency of the current is measured in Hertz (Hz) and indicates the number of cycles per second.
Answer to the question:
When an electric bulb rated 220 V is connected to a 220 V, 5 Hz AC source, the bulb glows immediately. This is because the voltage of the AC source is equal to the rated voltage of the bulb. As soon as the current flows through the filament, it gets heated up and starts emitting light. The frequency of the AC source does not affect the working of the bulb as long as the voltage is within the rated value.
Options other than B:
a) Does not glow: This option is incorrect as the bulb will glow when connected to an AC source of the same voltage.
c) Glows continuously: This option is incorrect as the bulb will glow as long as it is connected to the AC source. It will not glow continuously without any power source.
d) Gets fused: This option is incorrect as the bulb will not get fused unless the voltage of the AC source exceeds the rated voltage of the bulb.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, an electric bulb rated 220 V will immediately start glowing when connected to a 220 V, 5 Hz AC source. The frequency of the AC source does not affect the working of the bulb as long as the voltage is within the rated value.
The given question is related to the working of an electric bulb when connected to an AC source. Let us understand the answer to the question in detail.
The working of an electric bulb:
An electric bulb consists of a filament made up of tungsten wire which is enclosed in a glass bulb filled with an inert gas like argon. When an electric current flows through the filament, it gets heated up and produces light. The amount of light produced depends on the temperature of the filament. When the temperature of the filament reaches a certain level, it starts glowing and emits light.
Working of AC source:
An AC source is a source of electrical energy that produces an alternating current. In an AC source, the direction of current changes periodically. The frequency of the current is measured in Hertz (Hz) and indicates the number of cycles per second.
Answer to the question:
When an electric bulb rated 220 V is connected to a 220 V, 5 Hz AC source, the bulb glows immediately. This is because the voltage of the AC source is equal to the rated voltage of the bulb. As soon as the current flows through the filament, it gets heated up and starts emitting light. The frequency of the AC source does not affect the working of the bulb as long as the voltage is within the rated value.
Options other than B:
a) Does not glow: This option is incorrect as the bulb will glow when connected to an AC source of the same voltage.
c) Glows continuously: This option is incorrect as the bulb will glow as long as it is connected to the AC source. It will not glow continuously without any power source.
d) Gets fused: This option is incorrect as the bulb will not get fused unless the voltage of the AC source exceeds the rated voltage of the bulb.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, an electric bulb rated 220 V will immediately start glowing when connected to a 220 V, 5 Hz AC source. The frequency of the AC source does not affect the working of the bulb as long as the voltage is within the rated value.
To which wire amongst the following, an electric fuse connected?- a)Neutral
- b)Earth
- c)Live
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To which wire amongst the following, an electric fuse connected?
a)
Neutral
b)
Earth
c)
Live
d)
None of these
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
Electric fuses are always connected in series with the live wire. Electric fuses are always connected in series with the live wire.
A straight wire of diameter 2.5 mm carrying a current of 2 A is replaced by another thick wire of 5 mm diameter. The strength of the magnetic field far away is- a)Twice the earlier value
- b)One-half of the earlier value
- c)One-quarter of the earlier value
- d)Same as the earlier value
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A straight wire of diameter 2.5 mm carrying a current of 2 A is replaced by another thick wire of 5 mm diameter. The strength of the magnetic field far away is
a)
Twice the earlier value
b)
One-half of the earlier value
c)
One-quarter of the earlier value
d)
Same as the earlier value
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Magnetic field due to current-carrying wire is independent of its diameter or cross-sectional area of so long as the current remains the same.
An induced emf is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. The magnetic field of induced emf does not depend on- a)The number of turns in the coil
- b)The speed with which the magnet is moved
- c)The strength of the magnet
- d)The resistivity of the material of the coil
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An induced emf is produced when a magnet is plunged into a coil. The magnetic field of induced emf does not depend on
a)
The number of turns in the coil
b)
The speed with which the magnet is moved
c)
The strength of the magnet
d)
The resistivity of the material of the coil
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Resistivity of the coil will determine the resistance of the coil and the induced current through it.
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each- a)Two revolutions
- b)One revolution
- c)Half revolution
- d)One-fourth of revolution
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes once in each
a)
Two revolutions
b)
One revolution
c)
Half revolution
d)
One-fourth of revolution
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
The direction of the induced current varies once every half revolution when a rectangular coil is rotated in a magnetic field. As a consequence, the current in the coil continues to flow in the same direction.
An AC of frequency 50 Hz changes its polarity after every- a)1/25 second
- b)1/50 second
- c)1/75 second
- d)1/100 second
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An AC of frequency 50 Hz changes its polarity after every
a)
1/25 second
b)
1/50 second
c)
1/75 second
d)
1/100 second
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
In India the frequency of AC is 50 Hz which means that AC changes its polarity after 1/100 s
(i.e., 100 times per second) as it complete one cycle i.e., from + ve to –ve and from –ve to + ve 1/50 sec.
(i.e., 100 times per second) as it complete one cycle i.e., from + ve to –ve and from –ve to + ve 1/50 sec.
What material is used to make a fuse wire ?- a)Alloy of Ni, Al, and Co
- b)Alloy of Fe, Cu and Ni
- c)Alloy of Pb and Sn
- d)Alloy of Pb and Fe
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What material is used to make a fuse wire ?
a)
Alloy of Ni, Al, and Co
b)
Alloy of Fe, Cu and Ni
c)
Alloy of Pb and Sn
d)
Alloy of Pb and Fe
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Fuse wire is made of an alloy of lead (75%) and tin (25%) which melts at around 200 °C.
Which of the following fact(s) is/are true about a natural magnet?- a)It is a piece of iron ore magnet Fe3O4 having attractive and directive property.
- b)When suspended freely, it points in the north-south direction.
- c)It is also called lodestone.
- d)All of the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following fact(s) is/are true about a natural magnet?
a)
It is a piece of iron ore magnet Fe3O4 having attractive and directive property.
b)
When suspended freely, it points in the north-south direction.
c)
It is also called lodestone.
d)
All of the above.
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
- A naturally magnetized piece of mineral magnetite is called a lodestone. They are called natural magnets, and they can attract iron. The magnetism property was first discovered in antiquity via lodestones. in which the Middle English refers to the "course stone" or "leading stone"
- Artificial magnets are stronger than naturally occurring magnets like lodestone.
- Again artificial magnets are classified into two types, permanent magnets, and electromagnets.
- Permanent magnets are made of carbon steel or different metal alloys like AlNiCo which is an alloy of Aluminium, Nickel, and Cobalt; or even a nonmetal like a ferrite which can be very strongly magnetized.
- Electromagnets have low carbon steel or special alloys of steel it have a coil of current-carrying material wrapped around them.
A dynamo- a)Creates electrical energy
- b)Creates mechanical energy
- c)Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
- d)Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A dynamo
a)
Creates electrical energy
b)
Creates mechanical energy
c)
Converts mechanical energy into electrical energy
d)
Converts electrical energy into mechanical energy
|
|
Priyanka Kapoor answered |
Generally, a small dynamo requires a permanent magnet. Using Faraday's law of induction, rotating a coil of wire and magnetic fields to convert mechanical rotation into a direct electric current. Thus, a dynamo converts mechanical energy to electrical energy.
The rate of change of flux is greater in case when a magnet is moved towards a coil ______.- a)Very quickly
- b)Very slowly
- c)Moderately
- d)No change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The rate of change of flux is greater in case when a magnet is moved towards a coil ______.
a)
Very quickly
b)
Very slowly
c)
Moderately
d)
No change
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
emf induced is proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux.
When a magnet is moved towards the coil quickly, the rate of change of flux is larger than if the magnetic is moved slowly, thus larger emf is induced due to the quick movement of the coil.
When a magnet is moved towards the coil quickly, the rate of change of flux is larger than if the magnetic is moved slowly, thus larger emf is induced due to the quick movement of the coil.
Which of these factors affect(s) the strength of an electromagnet?- a)The number of turns in a coil
- b)The current flowing in the coil
- c)The length of gap between its poles
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these factors affect(s) the strength of an electromagnet?
a)
The number of turns in a coil
b)
The current flowing in the coil
c)
The length of gap between its poles
d)
All of these
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The four main factors that affect the strength of an electromagnet are the loop count, the current, the wire size, and the presence of an iron core.
When a charged particle moving with the same velocity is subjected to magnetic field, the force acting on it is non-zero. This implies that- a)Angle between them can have any value other than 0° and 180°
- b)Angle between them can have any value other than 90°
- c)Angle between them is necessarily 90°
- d)Angle between them is either 0° or 90°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a charged particle moving with the same velocity is subjected to magnetic field, the force acting on it is non-zero. This implies that
a)
Angle between them can have any value other than 0° and 180°
b)
Angle between them can have any value other than 90°
c)
Angle between them is necessarily 90°
d)
Angle between them is either 0° or 90°
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
No force acts on a charged particle when it is moving either parallel (0°) or antiparallel (180°) to the magnetic field. In all other cases, the charged particle experience a force.
The magnetic field at a distance of 10 cm from a long wire carrying current is 2 tesla. The magnetic field at a distance of 20 cm is- a)0.5 T
- b)1 T
- c)1.5 T
- d)2 T
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic field at a distance of 10 cm from a long wire carrying current is 2 tesla. The magnetic field at a distance of 20 cm is
a)
0.5 T
b)
1 T
c)
1.5 T
d)
2 T
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Magnetic field ∝ 1/r
When r doubles (10 cm to 20 cm), the magnetic field becomes half (2 T → 1 T)
When r doubles (10 cm to 20 cm), the magnetic field becomes half (2 T → 1 T)
What type of material is used in the core of an electromagnet?- a)Soft iron
- b)Steel
- c)Alloy
- d)Non-metal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What type of material is used in the core of an electromagnet?
a)
Soft iron
b)
Steel
c)
Alloy
d)
Non-metal
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
The most suitable material to be used as the core of an electromagnet is soft iron and it has high permeability but its availability and cost makes it uneconomical.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current- a)Is zero
- b)Decreases as we move towards its end
- c)Increasing as we move towards its end
- d)Is uniform at all points
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid carrying current
a)
Is zero
b)
Decreases as we move towards its end
c)
Increasing as we move towards its end
d)
Is uniform at all points
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
The magnetic field for a point inside a long straight current-carrying solenoid is double then for a point situated at one of its ends.
Which polarity is developed on the face of the solenoid when a north pole of a magnet is moving towards it?
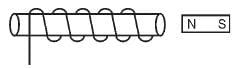
- a)North pole
- b)South pole
- c)Neutral
- d)Can’t be found
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which polarity is developed on the face of the solenoid when a north pole of a magnet is moving towards it?


a)
North pole
b)
South pole
c)
Neutral
d)
Can’t be found
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
When Magnet moves with its North pole towards the coil, emf is induced in the coil as the magnetic flux through the coil changes. So, when seeing from magnet side the direction of induced current appears to be Anticlockwise.
Chapter doubts & questions for Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Science Olympiad for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Science Olympiad for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily