All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Olympiad for Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of Acids, Bases and Salts for Class 10 Exam
Lemon juice and coffee are- a)Both acidic
- b)Both basic
- c)Lemon juice is acidic, coffee is basic
- d)Lemon juice is basic, coffee is acidic
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lemon juice and coffee are
a)
Both acidic
b)
Both basic
c)
Lemon juice is acidic, coffee is basic
d)
Lemon juice is basic, coffee is acidic
|
|
Vivek Bansal answered |
Lemon juice and coffee are both acidic solutions. Lemon juice has a pH of 2, and coffee has a pH of 5.
If a few drops of a concentrated acid accidentally spill over the hand of a student, what should be done?- a)Wash the hand with saline solution
- b)Neutralise the acid with a strong alkali
- c)After washing with plenty of water apply solution of sodium hydroxide on the hand.
- d)Wash the hand immediately with plenty of water and apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a few drops of a concentrated acid accidentally spill over the hand of a student, what should be done?
a)
Wash the hand with saline solution
b)
Neutralise the acid with a strong alkali
c)
After washing with plenty of water apply solution of sodium hydroxide on the hand.
d)
Wash the hand immediately with plenty of water and apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
- If a few drops of a concentrated acid accidentally spill over the hand of a student, wash the hand immediately with plenty of water and apply a paste of sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- Water will dilute the acid and wash it out. Any remaining acid will be neutralized with sodium hydrogen carbonate. This will minimize the effect of acid and damage to the skin.
A salt on treatment with excess of ammonium hydroxide produces a complex tetraammine copper (II) ions. The salt contains- a)Cuprous ions
- b)Chloride ions
- c)Cupric ions
- d)Calcium ions
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A salt on treatment with excess of ammonium hydroxide produces a complex tetraammine copper (II) ions. The salt contains
a)
Cuprous ions
b)
Chloride ions
c)
Cupric ions
d)
Calcium ions

|
Bhavana Kaur answered |
The complex tetraammine copper (II) ions are formed when a salt is treated with an excess of ammonium hydroxide. The salt in question contains cupric ions. Let's break down the process and explain why the correct answer is option 'C'.
1. Formation of a Complex:
- When a salt is treated with excess ammonium hydroxide, the ammonia molecules act as ligands and form a complex with the metal ions present in the salt.
- In this case, the metal ion is copper (II) ion (Cu2+).
- The ammonia ligands coordinate with the copper (II) ion to form a complex called tetraammine copper (II) ions.
- The formula of this complex is [Cu(NH3)4]2+.
2. Identification of the Metal Ion:
- To determine the metal ion present in the starting salt, we need to consider the anion of the salt.
- The question does not provide information about the anion, so we cannot determine the exact salt.
- However, since the complex formed contains copper (II) ions, the starting salt must contain cupric ions (Cu2+).
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - cupric ions.
3. Explanation of Other Options:
a) Cuprous ions: Cuprous ions have a +1 charge (Cu+). However, the complex formed in this reaction contains copper (II) ions with a +2 charge (Cu2+), so cuprous ions are not present in the salt.
b) Chloride ions: Chloride ions (Cl-) are not involved in the formation of the complex. The complex is formed by the coordination of ammonia ligands with copper (II) ions.
d) Calcium ions: Calcium ions (Ca2+) are not involved in the reaction. The formation of the complex is specific to copper (II) ions.
In conclusion, when a salt is treated with excess ammonium hydroxide, it forms a complex tetraammine copper (II) ions. The starting salt contains cupric ions, and the correct answer is option 'C'.
1. Formation of a Complex:
- When a salt is treated with excess ammonium hydroxide, the ammonia molecules act as ligands and form a complex with the metal ions present in the salt.
- In this case, the metal ion is copper (II) ion (Cu2+).
- The ammonia ligands coordinate with the copper (II) ion to form a complex called tetraammine copper (II) ions.
- The formula of this complex is [Cu(NH3)4]2+.
2. Identification of the Metal Ion:
- To determine the metal ion present in the starting salt, we need to consider the anion of the salt.
- The question does not provide information about the anion, so we cannot determine the exact salt.
- However, since the complex formed contains copper (II) ions, the starting salt must contain cupric ions (Cu2+).
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - cupric ions.
3. Explanation of Other Options:
a) Cuprous ions: Cuprous ions have a +1 charge (Cu+). However, the complex formed in this reaction contains copper (II) ions with a +2 charge (Cu2+), so cuprous ions are not present in the salt.
b) Chloride ions: Chloride ions (Cl-) are not involved in the formation of the complex. The complex is formed by the coordination of ammonia ligands with copper (II) ions.
d) Calcium ions: Calcium ions (Ca2+) are not involved in the reaction. The formation of the complex is specific to copper (II) ions.
In conclusion, when a salt is treated with excess ammonium hydroxide, it forms a complex tetraammine copper (II) ions. The starting salt contains cupric ions, and the correct answer is option 'C'.
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of acid strength?- a)Acetic acid < water < Hydrochloric acid
- b)Hydrochloric acid < Water < Acetic acid
- c)Water < Acetic acid < Hydrochloric acid
- d)Water < Hydrochloric acid > Acetic acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gives the correct increasing order of acid strength?
a)
Acetic acid < water < Hydrochloric acid
b)
Hydrochloric acid < Water < Acetic acid
c)
Water < Acetic acid < Hydrochloric acid
d)
Water < Hydrochloric acid > Acetic acid

|
Avi Jain answered |
B)Formic acid
c)Citric acid
d)Oxalic acid
c)Citric acid
d)Oxalic acid
Washing soda (Na2CO3.10 H2O) on exposure to air gives- a)Na2CO3.9 H2O
- b)Na2CO3.7 H2O
- c)Na2CO3.5 H2O
- d)Na2CO3.H2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Washing soda (Na2CO3.10 H2O) on exposure to air gives
a)
Na2CO3.9 H2O
b)
Na2CO3.7 H2O
c)
Na2CO3.5 H2O
d)
Na2CO3.H2
|
|
Tarun Kapoor answered |
Answer:
Washing soda, also known as sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10 H2O), is a hydrate compound. This means that it contains water molecules as part of its crystal structure. When washing soda is exposed to air, it undergoes a process called efflorescence, where the water molecules in the compound are lost to the surrounding atmosphere.
Explanation:
Efflorescence
When a hydrate compound, such as washing soda, is exposed to air, the water molecules present in the compound can evaporate. This process is known as efflorescence. As a result of efflorescence, the compound loses some of its water molecules and its chemical formula changes.
Chemical formula of washing soda
The chemical formula of washing soda, Na2CO3.10 H2O, indicates that it contains 10 water molecules. However, on exposure to air, some of these water molecules are lost.
Changes in the chemical formula
As the water molecules evaporate, the chemical formula of the washing soda changes. The number of water molecules decreases and the chemical formula becomes Na2CO3.x H2O, where 'x' represents the remaining number of water molecules.
Correct answer
In this case, the correct answer is option 'D', Na2CO3.H2O. This implies that on exposure to air, washing soda loses all of its water molecules except for one. Therefore, the chemical formula becomes Na2CO3.H2O.
Conclusion
When washing soda (Na2CO3.10 H2O) is exposed to air, it undergoes efflorescence and loses some of its water molecules. The correct chemical formula for washing soda after exposure to air is Na2CO3.H2O.
Washing soda, also known as sodium carbonate decahydrate (Na2CO3.10 H2O), is a hydrate compound. This means that it contains water molecules as part of its crystal structure. When washing soda is exposed to air, it undergoes a process called efflorescence, where the water molecules in the compound are lost to the surrounding atmosphere.
Explanation:
Efflorescence
When a hydrate compound, such as washing soda, is exposed to air, the water molecules present in the compound can evaporate. This process is known as efflorescence. As a result of efflorescence, the compound loses some of its water molecules and its chemical formula changes.
Chemical formula of washing soda
The chemical formula of washing soda, Na2CO3.10 H2O, indicates that it contains 10 water molecules. However, on exposure to air, some of these water molecules are lost.
Changes in the chemical formula
As the water molecules evaporate, the chemical formula of the washing soda changes. The number of water molecules decreases and the chemical formula becomes Na2CO3.x H2O, where 'x' represents the remaining number of water molecules.
Correct answer
In this case, the correct answer is option 'D', Na2CO3.H2O. This implies that on exposure to air, washing soda loses all of its water molecules except for one. Therefore, the chemical formula becomes Na2CO3.H2O.
Conclusion
When washing soda (Na2CO3.10 H2O) is exposed to air, it undergoes efflorescence and loses some of its water molecules. The correct chemical formula for washing soda after exposure to air is Na2CO3.H2O.
When sodium hydroxide is added to ammonium carbonate salt and then a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid is brought near the test tube, we observe- a)Brick efflorescence
- b)Dense white fumes
- c)Reddish brown gas
- d)Yellowish green vapours
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When sodium hydroxide is added to ammonium carbonate salt and then a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid is brought near the test tube, we observe
a)
Brick efflorescence
b)
Dense white fumes
c)
Reddish brown gas
d)
Yellowish green vapours
|
|
Khusboo jain answered |
When sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is added to ammonium carbonate (NH4)2CO3 salt and a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) is brought near the test tube, we observe dense white fumes.
Explanation:
The reaction between sodium hydroxide and ammonium carbonate can be represented by the following chemical equation:
(NH4)2CO3 + 2NaOH → 2NH3 + 2H2O + Na2CO3
In this reaction, sodium hydroxide reacts with ammonium carbonate to produce ammonia gas (NH3), water (H2O), and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). The ammonia gas is released as a result of the reaction.
When a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid is brought near the test tube, it reacts with the ammonia gas produced in the previous step. The reaction between hydrochloric acid and ammonia can be represented as follows:
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
In this reaction, ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). This reaction is highly exothermic and releases heat.
The dense white fumes observed in this reaction are actually ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) being formed as a white solid. The fumes are formed due to the reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid. The white solid of ammonium chloride is formed as a result of the combination of ammonia gas and hydrochloric acid vapor.
The reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid is a classic example of a neutralization reaction. In this reaction, an acid (HCl) reacts with a base (NH3) to form a salt (NH4Cl) and water (H2O).
In summary, when sodium hydroxide is added to ammonium carbonate and a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid is brought near the test tube, we observe dense white fumes. These fumes are formed due to the reaction between ammonia gas produced from the reaction between sodium hydroxide and ammonium carbonate, and hydrochloric acid. The reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid leads to the formation of ammonium chloride, which appears as dense white fumes.
Explanation:
The reaction between sodium hydroxide and ammonium carbonate can be represented by the following chemical equation:
(NH4)2CO3 + 2NaOH → 2NH3 + 2H2O + Na2CO3
In this reaction, sodium hydroxide reacts with ammonium carbonate to produce ammonia gas (NH3), water (H2O), and sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). The ammonia gas is released as a result of the reaction.
When a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid is brought near the test tube, it reacts with the ammonia gas produced in the previous step. The reaction between hydrochloric acid and ammonia can be represented as follows:
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
In this reaction, ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to form ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). This reaction is highly exothermic and releases heat.
The dense white fumes observed in this reaction are actually ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) being formed as a white solid. The fumes are formed due to the reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid. The white solid of ammonium chloride is formed as a result of the combination of ammonia gas and hydrochloric acid vapor.
The reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid is a classic example of a neutralization reaction. In this reaction, an acid (HCl) reacts with a base (NH3) to form a salt (NH4Cl) and water (H2O).
In summary, when sodium hydroxide is added to ammonium carbonate and a glass rod dipped in dilute hydrochloric acid is brought near the test tube, we observe dense white fumes. These fumes are formed due to the reaction between ammonia gas produced from the reaction between sodium hydroxide and ammonium carbonate, and hydrochloric acid. The reaction between ammonia and hydrochloric acid leads to the formation of ammonium chloride, which appears as dense white fumes.
Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel. Its nature is- a)Acidic
- b)Basic
- c)Neutral
- d)Amphoteric
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel. Its nature is
a)
Acidic
b)
Basic
c)
Neutral
d)
Amphoteric
|
|
Divya shukla answered |
Calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel and its nature is basic.
Explanation:
1. Composition of Tooth Enamel:
Tooth enamel is the hard, outermost layer of the tooth that covers and protects the underlying dentin and pulp. It is primarily composed of hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline form of calcium phosphate. Hydroxyapatite is a mineral that gives tooth enamel its strength and hardness.
2. Nature of Calcium Phosphate:
Calcium phosphate is an inorganic compound that contains calcium ions (Ca2+) and phosphate ions (PO43-). It is classified as a basic compound because it can accept protons (H+) and increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution.
3. Acid-Base Properties:
Acidic compounds are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) in solution, while basic compounds release hydroxide ions (OH-). Neutral compounds have an equal concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). Amphoteric compounds can act as both acids and bases depending on the pH of the solution.
4. Tooth Enamel and pH:
Tooth enamel is constantly exposed to various acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, as well as acidic foods and drinks. The acids can demineralize the enamel, leading to tooth decay and cavities. However, tooth enamel also has the ability to remineralize itself to some extent through the uptake of minerals like calcium and phosphate ions.
5. Role of Calcium Phosphate:
Calcium phosphate plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and strength of tooth enamel. When the pH in the mouth becomes acidic, calcium phosphate in the enamel can release calcium ions and phosphate ions. These ions can combine with hydroxide ions (OH-) from saliva to form hydroxyapatite crystals, which remineralize the enamel and restore its hardness.
6. Conclusion:
In conclusion, calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel and its nature is basic. It plays a vital role in maintaining the strength and integrity of tooth enamel by remineralizing it in acidic conditions.
Explanation:
1. Composition of Tooth Enamel:
Tooth enamel is the hard, outermost layer of the tooth that covers and protects the underlying dentin and pulp. It is primarily composed of hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline form of calcium phosphate. Hydroxyapatite is a mineral that gives tooth enamel its strength and hardness.
2. Nature of Calcium Phosphate:
Calcium phosphate is an inorganic compound that contains calcium ions (Ca2+) and phosphate ions (PO43-). It is classified as a basic compound because it can accept protons (H+) and increase the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution.
3. Acid-Base Properties:
Acidic compounds are substances that release hydrogen ions (H+) in solution, while basic compounds release hydroxide ions (OH-). Neutral compounds have an equal concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). Amphoteric compounds can act as both acids and bases depending on the pH of the solution.
4. Tooth Enamel and pH:
Tooth enamel is constantly exposed to various acids produced by bacteria in the mouth, as well as acidic foods and drinks. The acids can demineralize the enamel, leading to tooth decay and cavities. However, tooth enamel also has the ability to remineralize itself to some extent through the uptake of minerals like calcium and phosphate ions.
5. Role of Calcium Phosphate:
Calcium phosphate plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and strength of tooth enamel. When the pH in the mouth becomes acidic, calcium phosphate in the enamel can release calcium ions and phosphate ions. These ions can combine with hydroxide ions (OH-) from saliva to form hydroxyapatite crystals, which remineralize the enamel and restore its hardness.
6. Conclusion:
In conclusion, calcium phosphate is present in tooth enamel and its nature is basic. It plays a vital role in maintaining the strength and integrity of tooth enamel by remineralizing it in acidic conditions.
A sample of soil is mixed with water and allowed to settle. The clear supernatant solution turns the pH paper yellowish – orange. Which of the following would change the colour of this pH paper to greenish blue- a)Common salt
- b)Vinegar
- c)An antacid
- d)Lemmon juice
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sample of soil is mixed with water and allowed to settle. The clear supernatant solution turns the pH paper yellowish – orange. Which of the following would change the colour of this pH paper to greenish blue
a)
Common salt
b)
Vinegar
c)
An antacid
d)
Lemmon juice
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Turning of the pH paper yellowish – orange shows that the solution is acidic (pH ≈ 5) . To change it to greens blue means we want to change it to basic (pH ≈ 8) This can be done by adding an antacid [like Mg(OH)2)]
Solutions A, B, C and D have pH 3, 4, 6 and 8. The solution with highest acidic strength is- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Solutions A, B, C and D have pH 3, 4, 6 and 8. The solution with highest acidic strength is
a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Divya shukla answered |
Acidic Strength of Solutions
Introduction:
The pH scale is used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic, and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic.
Given Information:
- Solution A has a pH of 3.
- Solution B has a pH of 4.
- Solution C has a pH of 6.
- Solution D has a pH of 8.
Determining the Most Acidic Solution:
To determine the most acidic solution among A, B, C, and D, we need to compare their pH values. The lower the pH value, the more acidic the solution is.
- Solution A has a pH of 3.
- Solution B has a pH of 4.
- Solution C has a pH of 6.
- Solution D has a pH of 8.
Comparison:
- Solution A has the lowest pH value of 3, making it the most acidic solution among the given options.
- Solution B has a pH of 4, making it less acidic than solution A.
- Solution C has a pH of 6, making it less acidic than solutions A and B.
- Solution D has the highest pH value of 8, making it the least acidic solution among the given options.
Conclusion:
Based on the pH values provided, solution A with a pH of 3 has the highest acidic strength among solutions A, B, C, and D.
Introduction:
The pH scale is used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It ranges from 0 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic, and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic.
Given Information:
- Solution A has a pH of 3.
- Solution B has a pH of 4.
- Solution C has a pH of 6.
- Solution D has a pH of 8.
Determining the Most Acidic Solution:
To determine the most acidic solution among A, B, C, and D, we need to compare their pH values. The lower the pH value, the more acidic the solution is.
- Solution A has a pH of 3.
- Solution B has a pH of 4.
- Solution C has a pH of 6.
- Solution D has a pH of 8.
Comparison:
- Solution A has the lowest pH value of 3, making it the most acidic solution among the given options.
- Solution B has a pH of 4, making it less acidic than solution A.
- Solution C has a pH of 6, making it less acidic than solutions A and B.
- Solution D has the highest pH value of 8, making it the least acidic solution among the given options.
Conclusion:
Based on the pH values provided, solution A with a pH of 3 has the highest acidic strength among solutions A, B, C, and D.
Which of the following statements is not correct ?- a)All metal carbonates react with acid to give a salt, water and carbon dioxide
- b)Some metal react with acids to give salt, water and hydrogen
- c)All metal oxides react with water to give a salt and acid
- d)Some non-metal oxides react with water to form an acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is not correct ?
a)
All metal carbonates react with acid to give a salt, water and carbon dioxide
b)
Some metal react with acids to give salt, water and hydrogen
c)
All metal oxides react with water to give a salt and acid
d)
Some non-metal oxides react with water to form an acid
|
|
Shiladitya shah answered |
**Explanation:**
The statement that is not correct is option C: All metal oxides react with water to give a salt and acid.
**Metal Oxides and Water:**
Metal oxides are compounds formed by the reaction of metals with oxygen. When metal oxides react with water, they generally form metal hydroxides.
For example:
- Sodium oxide (Na2O) reacts with water (H2O) to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
- Magnesium oxide (MgO) reacts with water (H2O) to form magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2):
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
**Acid-Base Reactions:**
Acid-base reactions occur when an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. Metal oxides can react with acids to form salts and water, but not the other way around. Metal oxides are considered basic in nature.
For example:
- Calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water:
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
**Correct Statements:**
a) All metal carbonates react with acid to give a salt, water, and carbon dioxide.
- This statement is correct. When metal carbonates react with acids, they produce a salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas. For example, when calcium carbonate (CaCO3) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms calcium chloride (CaCl2), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2):
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
b) Some metals react with acids to give salt, water, and hydrogen.
- This statement is correct. Some metals, such as magnesium and zinc, react with acids to produce a salt, water, and hydrogen gas. For example, when magnesium (Mg) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms magnesium chloride (MgCl2), water (H2O), and hydrogen gas (H2):
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
d) Some non-metal oxides react with water to form an acid.
- This statement is correct. Non-metal oxides, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), can react with water to form acidic solutions. For example, when sulfur dioxide (SO2) dissolves in water, it forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3):
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
The statement that is not correct is option C: All metal oxides react with water to give a salt and acid.
**Metal Oxides and Water:**
Metal oxides are compounds formed by the reaction of metals with oxygen. When metal oxides react with water, they generally form metal hydroxides.
For example:
- Sodium oxide (Na2O) reacts with water (H2O) to form sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
Na2O + H2O → 2NaOH
- Magnesium oxide (MgO) reacts with water (H2O) to form magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2):
MgO + H2O → Mg(OH)2
**Acid-Base Reactions:**
Acid-base reactions occur when an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. Metal oxides can react with acids to form salts and water, but not the other way around. Metal oxides are considered basic in nature.
For example:
- Calcium oxide (CaO) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl) to form calcium chloride (CaCl2) and water:
CaO + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O
**Correct Statements:**
a) All metal carbonates react with acid to give a salt, water, and carbon dioxide.
- This statement is correct. When metal carbonates react with acids, they produce a salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas. For example, when calcium carbonate (CaCO3) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms calcium chloride (CaCl2), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2):
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
b) Some metals react with acids to give salt, water, and hydrogen.
- This statement is correct. Some metals, such as magnesium and zinc, react with acids to produce a salt, water, and hydrogen gas. For example, when magnesium (Mg) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), it forms magnesium chloride (MgCl2), water (H2O), and hydrogen gas (H2):
Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2
d) Some non-metal oxides react with water to form an acid.
- This statement is correct. Non-metal oxides, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), can react with water to form acidic solutions. For example, when sulfur dioxide (SO2) dissolves in water, it forms sulfurous acid (H2SO3):
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
When dilute hydrochloric acid is poured over powdered calcium carbonate, efflorescence are formed, it is because- a)Acids are corrosive
- b)Calcium oxide is formed
- c)Carbon dioxide is evolved
- d)Calcium carbonate is very reactive
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When dilute hydrochloric acid is poured over powdered calcium carbonate, efflorescence are formed, it is because
a)
Acids are corrosive
b)
Calcium oxide is formed
c)
Carbon dioxide is evolved
d)
Calcium carbonate is very reactive

|
Neha Sharma answered |
Effervescence Formation when Hydrochloric Acid is Poured over Calcium Carbonate
Effervescence refers to the formation of gas bubbles when a chemical reaction occurs. In the case of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate, the reaction produces carbon dioxide gas, which is responsible for the effervescence.
Acid-Base Reaction
When hydrochloric acid (HCl) is poured over powdered calcium carbonate (CaCO3), an acid-base reaction takes place. The acid (HCl) reacts with the base (CaCO3) to form a salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
Chemical Equation
The chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
HCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Explanation
- Acids are corrosive: While acids are generally corrosive, their corrosive nature is not directly related to the formation of effervescence. Therefore, option 'a' is incorrect.
- Calcium oxide is formed: Calcium oxide (CaO) is not formed in this reaction. Therefore, option 'b' is incorrect.
- Carbon dioxide is evolved: When hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium carbonate, carbon dioxide gas (CO2) is released. This gas escapes as bubbles, leading to the formation of effervescence. Therefore, option 'c' is correct.
- Calcium carbonate is very reactive: While calcium carbonate is reactive, its reactivity is not the primary reason for the formation of effervescence. Therefore, option 'd' is incorrect.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'c' - Carbon dioxide is evolved. When dilute hydrochloric acid is poured over powdered calcium carbonate, an acid-base reaction occurs, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide gas. This gas escapes as bubbles, leading to the formation of effervescence.
Effervescence refers to the formation of gas bubbles when a chemical reaction occurs. In the case of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate, the reaction produces carbon dioxide gas, which is responsible for the effervescence.
Acid-Base Reaction
When hydrochloric acid (HCl) is poured over powdered calcium carbonate (CaCO3), an acid-base reaction takes place. The acid (HCl) reacts with the base (CaCO3) to form a salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
Chemical Equation
The chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
HCl + CaCO3 → CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Explanation
- Acids are corrosive: While acids are generally corrosive, their corrosive nature is not directly related to the formation of effervescence. Therefore, option 'a' is incorrect.
- Calcium oxide is formed: Calcium oxide (CaO) is not formed in this reaction. Therefore, option 'b' is incorrect.
- Carbon dioxide is evolved: When hydrochloric acid reacts with calcium carbonate, carbon dioxide gas (CO2) is released. This gas escapes as bubbles, leading to the formation of effervescence. Therefore, option 'c' is correct.
- Calcium carbonate is very reactive: While calcium carbonate is reactive, its reactivity is not the primary reason for the formation of effervescence. Therefore, option 'd' is incorrect.
Conclusion
The correct answer is option 'c' - Carbon dioxide is evolved. When dilute hydrochloric acid is poured over powdered calcium carbonate, an acid-base reaction occurs, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide gas. This gas escapes as bubbles, leading to the formation of effervescence.
What will be pH of solution when 0.02 mole of hydrochloric acid in 2 litres of the solution- a)2
- b)1
- c)– 2
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be pH of solution when 0.02 mole of hydrochloric acid in 2 litres of the solution
a)
2
b)
1
c)
– 2
d)
10
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Molar concentration of HCl acid solution = 0.02/2L = 0.01 mol L–1
= 10–2 mol L–1
pH = – log [H+]
pH = – log (10–2)
pH = 2 log 10
pH = 2
= 10–2 mol L–1
pH = – log [H+]
pH = – log (10–2)
pH = 2 log 10
pH = 2
Which of the following phenomenon occur, when a small amount of acid is added to water?
(i) Ionisation
(ii) Neutralization
(iii) Dilution
(iv) Salt formation- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(iii) and (iv)
- d)(i) and (iii)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following phenomenon occur, when a small amount of acid is added to water?
(i) Ionisation
(ii) Neutralization
(iii) Dilution
(iv) Salt formation
(i) Ionisation
(ii) Neutralization
(iii) Dilution
(iv) Salt formation
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(iii) and (iv)
d)
(i) and (iii)
|
|
Maitri Daga answered |
C option dilution because it is a process in which less concentration of water is added into an acid.
Each volumes of solutions with pH = 4 and pH = 10 are mixed. What is the pH of the resulting solution ?- a)4
- b)10
- c)7
- d)14
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Each volumes of solutions with pH = 4 and pH = 10 are mixed. What is the pH of the resulting solution ?
a)
4
b)
10
c)
7
d)
14
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
pH = 4 means [H+] = 10–4 M. pH = 10 means (H+) = 10–10 M or [H–] = 10–4 M
Thus, one solution is acidic and the other is basic. Further, they have same molarity. On mxing equal volumes, then will neutralize each other completely. The resulting solution will be neutral with pH = 7.0
Thus, one solution is acidic and the other is basic. Further, they have same molarity. On mxing equal volumes, then will neutralize each other completely. The resulting solution will be neutral with pH = 7.0
The water of crystallization of green vitriol is- a)10
- b)9
- c)7
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The water of crystallization of green vitriol is
a)
10
b)
9
c)
7
d)
5

|
Rajeev Ghosh answered |
Water of Crystallization of Green Vitriol
Green vitriol, also known as ferrous sulfate, has a chemical formula of FeSO4·7H2O. This formula indicates that green vitriol contains 7 molecules of water of crystallization.
Explanation:
- Water of Crystallization: Water of crystallization refers to water molecules that are present in a definite and fixed ratio in a crystalline compound.
- Green Vitriol: Green vitriol is a hydrated form of ferrous sulfate, which means it contains water molecules in its crystal structure.
- Chemical Formula: The chemical formula of green vitriol is FeSO4·7H2O, which indicates that for every molecule of ferrous sulfate, there are 7 molecules of water of crystallization.
- Significance: Water of crystallization plays a crucial role in the physical and chemical properties of a compound. In the case of green vitriol, the presence of water molecules affects its color, solubility, and crystal structure.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'C' - 7 molecules of water of crystallization in green vitriol.
Which among the following is not a base ?- a)NaOH
- b)NH4OH
- c)C2H5OH
- d)KOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is not a base ?
a)
NaOH
b)
NH4OH
c)
C2H5OH
d)
KOH
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
C2H5OH is ethyl alcohol which does not give OH– ions in the solution. Hence, it is not base.
Which of the following substances will not give carbon dioxide on treatment with dilute acid ?- a)Lime
- b)Limestone
- c)Marble
- d)Baking soda
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following substances will not give carbon dioxide on treatment with dilute acid ?
a)
Lime
b)
Limestone
c)
Marble
d)
Baking soda
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Line (CaO) reacts with HCl acid to form CaCl2 and H2O. NO CO2 is produced.
The acid used for washing eyes is- a)Boric acid
- b)Acetic acid
- c)Oxalic acid
- d)Carbonic acid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The acid used for washing eyes is
a)
Boric acid
b)
Acetic acid
c)
Oxalic acid
d)
Carbonic acid
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
- The acid used in eye wash is boric acid.
- Boric acid is a mild antiseptic, insecticide and its chemical formula is H3BO3.
- It has antibiotic properties against bacterial infection.
- It is used as a cleanser for the eyes.
What is pH of a solution whose hydrogen ion concentration is 1 × 10–3 M?
- a)2
- b)-3
- c)3
- d)= 7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is pH of a solution whose hydrogen ion concentration is 1 × 10–3 M?
a)
2
b)
-3
c)
3
d)
= 7
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
pH = – log [H+]
pH = – log (1 × 10–3] = – (– 3) log10
pH = 3
pH = – log (1 × 10–3] = – (– 3) log10
pH = 3
What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube ?
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution decreases
(iii) The temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place- a)(i) only
- b)(i) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iii)
- d)(i) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when a solution of an acid is mixed with a solution of a base in a test tube ?
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution decreases
(iii) The temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
(i) The temperature of the solution increases
(ii) The temperature of the solution decreases
(iii) The temperature of the solution remains the same
(iv) Salt formation takes place
a)
(i) only
b)
(i) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iii)
d)
(i) and (iv)
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Mixing of solution of an acid with the solution of base (neutralization) is exothermic i.e. temperature increase and salt formation takes place.
In an attempt to demonstrate electrical conductivity through an electrolyte, the following apparatus was set up
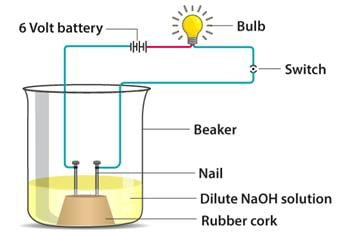
Which among the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Bulb will not glow because electrolyte is not acidic
(ii) Bulb will not glow because NaOH is a strong base and furnishes ions for conduction
(iii) Bulb will not glow because circuit is incomplete
(iv) Bulb will not glow because it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution
- a)(i) and (iii)
- b)(ii) and (iv)
- c)(ii) only
- d)(iv) Only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an attempt to demonstrate electrical conductivity through an electrolyte, the following apparatus was set up

Which among the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Bulb will not glow because electrolyte is not acidic
(ii) Bulb will not glow because NaOH is a strong base and furnishes ions for conduction
(iii) Bulb will not glow because circuit is incomplete
(iv) Bulb will not glow because it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution

Which among the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Bulb will not glow because electrolyte is not acidic
(ii) Bulb will not glow because NaOH is a strong base and furnishes ions for conduction
(iii) Bulb will not glow because circuit is incomplete
(iv) Bulb will not glow because it depends upon the type of electrolytic solution
a)
(i) and (iii)
b)
(ii) and (iv)
c)
(ii) only
d)
(iv) Only
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
- A channel through which electrons travel from a voltage or current source is known as an electric circuit.
- Electric current flows in a closed circuit. Because NaOH is such a strong base, it produces OH- and Na+ ions, which are responsible for electrical conductivity.
- Sodium hydroxide conducts electrons as sodium cations and hydroxyl anions.
- The particles travel towards the two iron nails in the arrangement, one serving as a cathode (-) for cations and the other as an anode (+) for anions.
Glauber’s salt is- a)Sodium sulphate
- b)Sodium sulphate decahydrate
- c)Sodium carbonate decahydrate
- d)Sodium carbonate monohydrate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Glauber’s salt is
a)
Sodium sulphate
b)
Sodium sulphate decahydrate
c)
Sodium carbonate decahydrate
d)
Sodium carbonate monohydrate
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Glauber’s salt is sodium sulphate decahydrate Na2SO4.10H2O
Which of the following is not a mineral acid ?- a)Hydrochloric acid
- b)Nitric acid
- c)Citric acid
- d)Sulphuric acid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a mineral acid ?
a)
Hydrochloric acid
b)
Nitric acid
c)
Citric acid
d)
Sulphuric acid
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Citric acid is not a mineral acid but an organic acid present in citrus fruits
Which of the following statements is true for acids ?- a)Bitter and change blue litmus to red
- b)Sour and change blue litmus to red
- c)Bitter and change red litmus to blue
- d)Sour and change red litmus to blue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true for acids ?
a)
Bitter and change blue litmus to red
b)
Sour and change blue litmus to red
c)
Bitter and change red litmus to blue
d)
Sour and change red litmus to blue
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Acids change the colour of the litmus solution from blue to red. They have a sour, vinegar-like flavour and are sticky to the touch. Bases, on the other hand, change the colour of the red litmus solution to blue. They have a bitter taste, similar to baking soda, and are slippery to the touch.
Chapter doubts & questions for Acids, Bases and Salts - Science Olympiad for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Acids, Bases and Salts - Science Olympiad for Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









