All Exams >
CUET >
CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Computer Science for CUET Exam
Which of the following is not a type of computer network?- a)Local Area Network (LAN)
- b)Personal Area Network (PAN)
- c)Remote Area Network (RAN)
- d)Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a type of computer network?
a)
Local Area Network (LAN)
b)
Personal Area Network (PAN)
c)
Remote Area Network (RAN)
d)
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
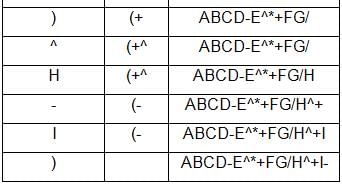
Remote Area Network or RAN was a network method that enabled wireless transfer of data via landline, RS232 serial port, cell phone or satellite connections. The Symax 8030 CRM 560 was a Remote Network Interface Module that used this method of linking IO from field devices to local area and remote area networks. The RAN methodlogy is the basis for transmitting data via radio modems.
What is the output for the given python code?fp = open("sample2.txt", "w")
print(fp.tell())
fp.write('12345678')
print(fp.tell())
fp.close()- a)0
8 - b)0
7 - c)1
8 - d)1
7
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the output for the given python code?
fp = open("sample2.txt", "w")
print(fp.tell())
fp.write('12345678')
print(fp.tell())
fp.close()
print(fp.tell())
fp.write('12345678')
print(fp.tell())
fp.close()
a)
0
8
8
b)
0
7
7
c)
1
8
8
d)
1
7
7
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option A.
Concept:
The given python code is,
tell() method:
This function returns an integer that specifies the current position of the file object in the file. The position so specified is the byte position from the beginning of the file till the current position of the file object.
The syntax of using tell() is:
file_object.tell()
The given code is,
fp = open("sample2.txt", "w")
print(fp.tell())
fp.write('12345678')
print(fp.tell())
fp.close()
The given python code is,
tell() method:
This function returns an integer that specifies the current position of the file object in the file. The position so specified is the byte position from the beginning of the file till the current position of the file object.
The syntax of using tell() is:
file_object.tell()
The given code is,
fp = open("sample2.txt", "w")
print(fp.tell())
fp.write('12345678')
print(fp.tell())
fp.close()
Explanation:
The given sample2.txt opens the file in write mode. If the file already exists, all the contents will be overwritten. If the file doesn’t exist, then a new file will be created.
Here is the file newly created and write the contents. And we will notice the position of the handle before writing and after writing to the Sample2.txt file.
the position of the handle before writing=0
after writing to the Sample2.txt file = 8
Hence the correct answer is
0
8
The given sample2.txt opens the file in write mode. If the file already exists, all the contents will be overwritten. If the file doesn’t exist, then a new file will be created.
Here is the file newly created and write the contents. And we will notice the position of the handle before writing and after writing to the Sample2.txt file.
the position of the handle before writing=0
after writing to the Sample2.txt file = 8
Hence the correct answer is
0
8
Which chart element is utilized to identify data series by its color patterns?- a)Chart title
- b)Marker
- c)Data labels
- d)Legend
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which chart element is utilized to identify data series by its color patterns?
a)
Chart title
b)
Marker
c)
Data labels
d)
Legend
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option D.
Concept:
Legend chart element is utilized to identify data series by their color patterns. Legend depicts the colors, patterns, or symbols assigned to the data series. It helps to differentiate the data.
A legend is a portion that describes the graph's components. There is a method in the matplotlib package called legend() that is used to place a legend on the axes. The property Loc in legend() is used to indicate the legend's placement. loc="best" is the default value (upper left).
Legend chart element is utilized to identify data series by their color patterns. Legend depicts the colors, patterns, or symbols assigned to the data series. It helps to differentiate the data.
A legend is a portion that describes the graph's components. There is a method in the matplotlib package called legend() that is used to place a legend on the axes. The property Loc in legend() is used to indicate the legend's placement. loc="best" is the default value (upper left).
Syntax:
matplotlib.pyplot.legend([“blue”, “green”], bbox_to_anchor=(0.75, 1.15), ncol=2)
Hence the correct answer is Legend.
matplotlib.pyplot.legend([“blue”, “green”], bbox_to_anchor=(0.75, 1.15), ncol=2)
Hence the correct answer is Legend.
Which of the following is not Protocol?- a)File Transfer Protocol
- b)Bluetooth Protocol
- c)Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- d)HyperText Transfer Protocol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not Protocol?
a)
File Transfer Protocol
b)
Bluetooth Protocol
c)
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
d)
HyperText Transfer Protocol
|
|
Sounak Mehra answered |
Bluetooth Protocol is not a Protocol
Protocol Explanation:
File Transfer Protocol (FTP):
- FTP is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another over a TCP-based network.
- It allows users to upload or download files to and from a server.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP):
- SMTP is a communication protocol used for sending email messages between servers.
- It is responsible for sending outgoing mail from a client to a server or between servers.
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP):
- HTTP is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web.
- It defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and how web servers and browsers respond to various commands.
Bluetooth Protocol:
- Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances.
- While Bluetooth itself is not a protocol, it uses various protocols for different types of communication, such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for low-power devices.
Protocol Explanation:
File Transfer Protocol (FTP):
- FTP is a standard network protocol used to transfer files from one host to another over a TCP-based network.
- It allows users to upload or download files to and from a server.
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP):
- SMTP is a communication protocol used for sending email messages between servers.
- It is responsible for sending outgoing mail from a client to a server or between servers.
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP):
- HTTP is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web.
- It defines how messages are formatted and transmitted, and how web servers and browsers respond to various commands.
Bluetooth Protocol:
- Bluetooth is a wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances.
- While Bluetooth itself is not a protocol, it uses various protocols for different types of communication, such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) for low-power devices.
To read the next line of the file from a file object infile, we use ____________.- a)read(2)
- b)infile.read()
- c)readline()
- d)infile.readlines()
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To read the next line of the file from a file object infile, we use ____________.
a)
read(2)
b)
infile.read()
c)
readline()
d)
infile.readlines()
|
|
Milan Das answered |
Explanation:
When working with file objects in Python, we have several methods available to read the contents of a file. One of these methods is `readline()`, which is used to read a single line from the file.
What is `readline()`?
The `readline()` method reads a single line from the file and returns it as a string. It starts reading from the current position of the file pointer and moves it to the next line. If the file pointer is already at the end of the file, it returns an empty string.
Usage of `readline()`:
To read the next line of a file using `readline()`, we need to follow these steps:
1. Open the file using the `open()` function and assign it to a file object (e.g., `infile`).
2. Call the `readline()` method on the file object to read the next line.
The code snippet would look like this:
```
infile = open('filename.txt', 'r')
next_line = infile.readline()
```
Here, `'filename.txt'` should be replaced with the actual filename/path of the file you want to read.
Alternative methods:
- `read(2)`: This method reads a specified number of characters from the file. The parameter `2` specifies that it should read 2 characters. It does not read the next line.
- `infile.read()`: This method reads the entire contents of the file as a single string. It does not read the next line.
- `infile.readlines()`: This method reads all the lines of the file and returns them as a list of strings. It does not read the next line.
Conclusion:
In order to read the next line of a file from a file object, we use the `readline()` method. This method reads a single line from the file and moves the file pointer to the next line. It is important to note that `readline()` only reads one line at a time, so if we want to read multiple lines, we need to call it multiple times.
When working with file objects in Python, we have several methods available to read the contents of a file. One of these methods is `readline()`, which is used to read a single line from the file.
What is `readline()`?
The `readline()` method reads a single line from the file and returns it as a string. It starts reading from the current position of the file pointer and moves it to the next line. If the file pointer is already at the end of the file, it returns an empty string.
Usage of `readline()`:
To read the next line of a file using `readline()`, we need to follow these steps:
1. Open the file using the `open()` function and assign it to a file object (e.g., `infile`).
2. Call the `readline()` method on the file object to read the next line.
The code snippet would look like this:
```
infile = open('filename.txt', 'r')
next_line = infile.readline()
```
Here, `'filename.txt'` should be replaced with the actual filename/path of the file you want to read.
Alternative methods:
- `read(2)`: This method reads a specified number of characters from the file. The parameter `2` specifies that it should read 2 characters. It does not read the next line.
- `infile.read()`: This method reads the entire contents of the file as a single string. It does not read the next line.
- `infile.readlines()`: This method reads all the lines of the file and returns them as a list of strings. It does not read the next line.
Conclusion:
In order to read the next line of a file from a file object, we use the `readline()` method. This method reads a single line from the file and moves the file pointer to the next line. It is important to note that `readline()` only reads one line at a time, so if we want to read multiple lines, we need to call it multiple times.
How many times can a loop in while(0) run?- a)0
- b)1
- c)3
- d)Infinite
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many times can a loop in while(0) run?
a)
0
b)
1
c)
3
d)
Infinite
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
while(0) - It is opposite of while(1). It means condition will always be false and ,thus, the code in 'while' will never get executed.
Which of the following options is not correct?- a)If we try to read a text file that does not exist, an error occurs.
- b)If we try to read a text file that does not exist, the file gets created.
- c)If we try to write on a text file that does not exist, no error occurs.
- d)If we try to write on a text file that does not exist, the file gets created.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following options is not correct?
a)
If we try to read a text file that does not exist, an error occurs.
b)
If we try to read a text file that does not exist, the file gets created.
c)
If we try to write on a text file that does not exist, no error occurs.
d)
If we try to write on a text file that does not exist, the file gets created.
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
If we try to read a text file that does not exist, the file gets created - this is an incorrect statement.
What will be the output of the following code?myobject=open("myfile.txt",'r')
myobject.readline(10)
myobject.close()- a)It prints the first 10 characters of the file opened
- b)It prints the first character of the file 10 times
- c)It prints the first 10 lines of the file
- d)It prints the first 10 characters of the filename
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the output of the following code?
myobject=open("myfile.txt",'r')
myobject.readline(10)
myobject.close()
myobject.readline(10)
myobject.close()
a)
It prints the first 10 characters of the file opened
b)
It prints the first character of the file 10 times
c)
It prints the first 10 lines of the file
d)
It prints the first 10 characters of the filename
|
|
Amita Das answered |
- The readline() function reads the first line until a newline character is found.
- If an argument is passed to the function, it reads that many characters, but stops when a newline character is encountered.
- The function can only read the first line.
Important Point:
Even if the value passed to the function exceeds the number of characters till the newline character, the control does not move on to the next line.
Referential integrity constraint in a relational database is specified with the help of a _________.- a)primary key
- b)secondary key
- c)foreign key
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Referential integrity constraint in a relational database is specified with the help of a _________.
a)
primary key
b)
secondary key
c)
foreign key
d)
none of the above
|
|
Sarthak Joshi answered |
Referential integrity constraint in a relational database is specified with the help of a foreign key.
The referential integrity constraint is a rule that ensures the consistency and accuracy of data in a relational database. It specifies that values in one table's foreign key column must match the values in another table's primary key column. This constraint helps maintain the relationships between tables and prevents inconsistencies or errors in the data.
Foreign Key:
A foreign key is a column or a set of columns in a table that refers to the primary key of another table. It establishes a link between two tables based on a common field. The foreign key acts as a cross-reference between the tables and represents the relationship between them. In other words, it provides a way to connect data from multiple tables in a relational database.
Role of Foreign Key in Referential Integrity Constraint:
When a foreign key is defined in a table, it establishes a relationship between that table (known as the referencing table) and another table (known as the referenced table). The foreign key column in the referencing table contains values that match the primary key values in the referenced table. This relationship is enforced by the referential integrity constraint.
The referential integrity constraint ensures that the values in the foreign key column of the referencing table are always valid and consistent. It prevents the insertion of values that do not exist in the referenced table's primary key column. If an attempt is made to insert such invalid values, the database management system will raise an error and reject the operation.
Similarly, the referential integrity constraint also maintains the integrity of the data during updates and deletions. If a referenced primary key value is modified or deleted, the database management system can automatically update or delete the corresponding foreign key values in the referencing table to maintain consistency.
In summary, the foreign key plays a crucial role in specifying and enforcing the referential integrity constraint in a relational database. It ensures that the relationships between tables are maintained and that the data remains accurate and consistent.
The referential integrity constraint is a rule that ensures the consistency and accuracy of data in a relational database. It specifies that values in one table's foreign key column must match the values in another table's primary key column. This constraint helps maintain the relationships between tables and prevents inconsistencies or errors in the data.
Foreign Key:
A foreign key is a column or a set of columns in a table that refers to the primary key of another table. It establishes a link between two tables based on a common field. The foreign key acts as a cross-reference between the tables and represents the relationship between them. In other words, it provides a way to connect data from multiple tables in a relational database.
Role of Foreign Key in Referential Integrity Constraint:
When a foreign key is defined in a table, it establishes a relationship between that table (known as the referencing table) and another table (known as the referenced table). The foreign key column in the referencing table contains values that match the primary key values in the referenced table. This relationship is enforced by the referential integrity constraint.
The referential integrity constraint ensures that the values in the foreign key column of the referencing table are always valid and consistent. It prevents the insertion of values that do not exist in the referenced table's primary key column. If an attempt is made to insert such invalid values, the database management system will raise an error and reject the operation.
Similarly, the referential integrity constraint also maintains the integrity of the data during updates and deletions. If a referenced primary key value is modified or deleted, the database management system can automatically update or delete the corresponding foreign key values in the referencing table to maintain consistency.
In summary, the foreign key plays a crucial role in specifying and enforcing the referential integrity constraint in a relational database. It ensures that the relationships between tables are maintained and that the data remains accurate and consistent.
Consider the following array a[ ] with n elements and searching element 16 and the linear search is comparing the elements from index n-1.a[6]= {15, 87, 20, 16, 9, 11} Here n=6How many comparisons are required to search a searching element 16 by using linear search?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following array a[ ] with n elements and searching element 16 and the linear search is comparing the elements from index n-1.
a[6]= {15, 87, 20, 16, 9, 11} Here n=6
How many comparisons are required to search a searching element 16 by using linear search?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The correct answer is option C.
Concept:
Linear search:
A linear search, often known as a sequential search, is a technique for locating an element in a list. It systematically verifies each element of the list until a match is discovered or the entire list has been searched.
Algorithm:
linear_search(int a[], int n, int X)
Linear search:
A linear search, often known as a sequential search, is a technique for locating an element in a list. It systematically verifies each element of the list until a match is discovered or the entire list has been searched.
Algorithm:
linear_search(int a[], int n, int X)
{
for (int i = n-1; i=>0; i++)
{
if (a[i] == X)
return i+1;
}
for (int i = n-1; i=>0; i++)
{
if (a[i] == X)
return i+1;
}
}
Explanation:
The given data is,
a[6]= {15, 87, 20, 16, 9, 11} Here n=6
X=16
The linear search is comparing the elements from index n-1.
Comparison 1= (11 == 16)
Comparison 2= (9 == 16)Comparison 3= (16 == 16)
Hence the search is successful. Hence the number of comparisons are= 3.
Hence the correct answer is 3.
The given data is,
a[6]= {15, 87, 20, 16, 9, 11} Here n=6
X=16
The linear search is comparing the elements from index n-1.
Comparison 1= (11 == 16)
Comparison 2= (9 == 16)Comparison 3= (16 == 16)
Hence the search is successful. Hence the number of comparisons are= 3.
Hence the correct answer is 3.
How many swaps are required using bubble sort to sort the list L1?L1: [127,119,223,136,233,134]- a)2
- b)3
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many swaps are required using bubble sort to sort the list L1?
L1: [127,119,223,136,233,134]
a)
2
b)
3
c)
4
d)
5
|
|
Amita Das answered |
In bubble sort, the maximum element will move to the extreme right side of the list.
Applying Bubble sort in L1- [127,119,223,136,233,134] Take 127 to be the bubble element and compare that with the next element, if the next element is greater than the current element then shift the bubble element, if not then swap two elements.
Pass-1:
127 is greater than 119, So, swapping is required. Swap 127 and 119.
Total swap-1
L1- [119,127,223,136,233,134]
Now, compare 127 with 223, No swapping required.
Compare 223 with 136, and swap them.
Total swap - 2
L1- [119,127,136,223,233,134]
Compare 223 with 233, no swapping is required.
Compare 233 and 134,1 Swapping required as 134 is smaller than 233. Pass 1 ends here.
Total swap -3
L1- [119,127,136,223,134,233]
127 is greater than 119, So, swapping is required. Swap 127 and 119.
Total swap-1
L1- [119,127,223,136,233,134]
Now, compare 127 with 223, No swapping required.
Compare 223 with 136, and swap them.
Total swap - 2
L1- [119,127,136,223,233,134]
Compare 223 with 233, no swapping is required.
Compare 233 and 134,1 Swapping required as 134 is smaller than 233. Pass 1 ends here.
Total swap -3
L1- [119,127,136,223,134,233]
Pass-2:
Compare 119 with 127, no swap is required.
Compare 127 with 136 no swap is required.
Compare 136 with 223, no swap is required.
Compare 223 with 134 - 1 swap required as 134 is smaller than 223.
Total swap-4
L1- [119,127,136,134,223,233]
Compare 119 with 127, no swap is required.
Compare 127 with 136 no swap is required.
Compare 136 with 223, no swap is required.
Compare 223 with 134 - 1 swap required as 134 is smaller than 223.
Total swap-4
L1- [119,127,136,134,223,233]
Pass-3:
Now, compare 119 with 127, no swap is required.
Compare 127 with 136, no swap is required.
Compare 136 with 134 and 1 swap is required as 134 is smaller than 136.
Total swap - 5
L1- [119,127,134,136,223,233]
Now, compare 119 with 127, no swap is required.
Compare 127 with 136, no swap is required.
Compare 136 with 134 and 1 swap is required as 134 is smaller than 136.
Total swap - 5
L1- [119,127,134,136,223,233]
Pass-4:
Now compare 119 with 127, no swap is required.
Compare 127 with 134, no swap is required.
So, the list is already sorted.
In total 5 swaps are required to sort the list using bubble sort.
Option 4 will be the answer.
Now compare 119 with 127, no swap is required.
Compare 127 with 134, no swap is required.
So, the list is already sorted.
In total 5 swaps are required to sort the list using bubble sort.
Option 4 will be the answer.
Which of the following is not an SQL commands category?
- a)DDL (Data Definition Language)
- b)DCL (Data Communication Language)
- c)DQL (Data Query Language)
- d)DCL (Data Control Language)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an SQL commands category?
a)
DDL (Data Definition Language)
b)
DCL (Data Communication Language)
c)
DQL (Data Query Language)
d)
DCL (Data Control Language)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Types of SQL Commands:
- DDL (Data Definition Language)
- DML (Data Manipulation Language)
- DQL (Data Query Language)
- DCL (Data Control Language)
- Data administration commands
- Transaction control commands
Which of the following searching technique is to search in which each element is to be visited until we reach the same match?- a)Linear search
- b)Binary search
- c)Not Linear search
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following searching technique is to search in which each element is to be visited until we reach the same match?
a)
Linear search
b)
Binary search
c)
Not Linear search
d)
None of the above
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Concept:
The most fundamental search method is linear search, sometimes referred to as sequential search. In this type of search, we go through the entire list and try to fetch a match for a single element.
If we find a match, then the address of the matching target element is returned.
On the other hand, if the element is not found, then it returns a NULL value.
Algorithm:
linear_search(int a[], int n, int X)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] == X)
return i+1;
}
}
The most fundamental search method is linear search, sometimes referred to as sequential search. In this type of search, we go through the entire list and try to fetch a match for a single element.
If we find a match, then the address of the matching target element is returned.
On the other hand, if the element is not found, then it returns a NULL value.
Algorithm:
linear_search(int a[], int n, int X)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (a[i] == X)
return i+1;
}
}
Worst-case:
In the Linear Search Algorithm, the worst-case scenario happens when the item to be found is at the end of the Array or the element is not present in the array. Hence the linear search compares each element till the end. So it takes maximum time behavior in linear search.
In the Linear Search Algorithm, the worst-case scenario happens when the item to be found is at the end of the Array or the element is not present in the array. Hence the linear search compares each element till the end. So it takes maximum time behavior in linear search.
Best case:
The best case in the Linear Search Algorithm happens when the item to be found is at the beginning of the Array.
The best case in the Linear Search Algorithm happens when the item to be found is at the beginning of the Array.
Average case:
In the Linear Search Algorithm, the average scenario happens when the item to be found is somewhere in the center of the Array.
In the Linear Search Algorithm, the average scenario happens when the item to be found is somewhere in the center of the Array.
Hence the correct answer is Linear search.
The module _________ is used for serializing and de-serializing any Python object structure.- a)Serialize
- b)Pickle
- c)Load
- d)Dump
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The module _________ is used for serializing and de-serializing any Python object structure.
a)
Serialize
b)
Pickle
c)
Load
d)
Dump
|
|
Amita Das answered |
- The Pickle module is used for storing any Python object as a byte stream. When required, the byte stream is reconstructed into an object.
- The dump() and load() are methods of the Pickle module for serializing and de-serializing objects.
Map the following statements with true(T)/false(F) respectively.
S1: SQL query 'SELECT count(distinct *) From EMP' will generate error.
S2: ‘Having’ clause is used to filter groups.- a)TF
- b)FF
- c)FT
- d)TT
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Map the following statements with true(T)/false(F) respectively.
S1: SQL query 'SELECT count(distinct *) From EMP' will generate error.
S2: ‘Having’ clause is used to filter groups.
S1: SQL query 'SELECT count(distinct *) From EMP' will generate error.
S2: ‘Having’ clause is used to filter groups.
a)
TF
b)
FF
c)
FT
d)
TT
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
DISTINCT can be used with aggregates: COUNT, AVG, MAX, etc.
DISTINCT operates on a single column. DISTINCT for multiple columns is not supported.
Having clause is used to filter group.
The HAVING clause was added to SQL because the WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate functions.
The HAVING clause is used to restrict the results returned by the GROUP BY clause.
DISTINCT operates on a single column. DISTINCT for multiple columns is not supported.
Having clause is used to filter group.
The HAVING clause was added to SQL because the WHERE keyword could not be used with aggregate functions.
The HAVING clause is used to restrict the results returned by the GROUP BY clause.
Consider array has n elements and searching element X. What is the minimum and the maximum number of iterations are required to search an element by using binary search?Note: Searching is successful.- a)0, n-1
- b)1, log n
- c)0, n
- d)o, log n
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider array has n elements and searching element X. What is the minimum and the maximum number of iterations are required to search an element by using binary search?
Note: Searching is successful.
a)
0, n-1
b)
1, log n
c)
0, n
d)
o, log n
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Concept:
Binary Search:
A Binary Search is a sorting method used to find a specific member in a sorted array. Because binary search works only on sorted arrays, an array must be sorted before using binary search on it. As the number of iterations in the binary search reduces, it is a superior searching approach to the liner search technique.
Binary Search:
A Binary Search is a sorting method used to find a specific member in a sorted array. Because binary search works only on sorted arrays, an array must be sorted before using binary search on it. As the number of iterations in the binary search reduces, it is a superior searching approach to the liner search technique.
Algorithm:
int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int K)
{
int mid;
if(end >= beg)
{ mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(a[mid] == K)
return mid+1;
else if(a[mid] < K)
return binarySearch(a, mid+1, end, K);
else
return binarySearch(a, beg, mid-1, K);
}
return -1;
}
int binarySearch(int a[], int beg, int end, int K)
{
int mid;
if(end >= beg)
{ mid = (beg + end)/2;
if(a[mid] == K)
return mid+1;
else if(a[mid] < K)
return binarySearch(a, mid+1, end, K);
else
return binarySearch(a, beg, mid-1, K);
}
return -1;
}
Minimum number of iterations:
The given data,
A[4]= {10, 16, 22, 25}
Searching element= K= 16
beg= 0
end = 3
mid = 3/2 = 1
if K with A[mid] and search is successful.
Hence minimum number iterations are =1.
Maximum number of iterations:
The given data,
A[4]= {10, 16, 22, 25}
Searching element= K= 22
beg= 0
end = 3
mid = 3/2 = 1.
Compare 22 with A[1] is not found and K is greater than A[mid]. So call binarySearch(a, 1+1, 3, 2);
beg= 2
end = 3
mid = 5/2 = 2.
Compare 22 with A[2] is found.
The given data,
A[4]= {10, 16, 22, 25}
Searching element= K= 16
beg= 0
end = 3
mid = 3/2 = 1
if K with A[mid] and search is successful.
Hence minimum number iterations are =1.
Maximum number of iterations:
The given data,
A[4]= {10, 16, 22, 25}
Searching element= K= 22
beg= 0
end = 3
mid = 3/2 = 1.
Compare 22 with A[1] is not found and K is greater than A[mid]. So call binarySearch(a, 1+1, 3, 2);
beg= 2
end = 3
mid = 5/2 = 2.
Compare 22 with A[2] is found.
Explanation:
For in each step the array is being cut into two parts, each of the size (n-1)/2, we have a maximum of log2(n-1) steps. This leads to a total of 2*log2(n-1) comparisons, which asymptotically indeed equals O(log(n)).
For in each step the array is being cut into two parts, each of the size (n-1)/2, we have a maximum of log2(n-1) steps. This leads to a total of 2*log2(n-1) comparisons, which asymptotically indeed equals O(log(n)).
Hence the correct answer is 1, log n.
Consider the list of data [56, 80, 39, 41, 29, 61] and the hash function h[i] = i % 7 where i is each element of the list. What will be the index value of the element 39?- a)9
- b)3
- c)2
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the list of data [56, 80, 39, 41, 29, 61] and the hash function h[i] = i % 7 where i is each element of the list. What will be the index value of the element 39?
a)
9
b)
3
c)
2
d)
4
|
|
Amita Das answered |
- The hash function is modulo 7. This means, that each element is divided by 7 and the number is positioned at the index equal to the remainder.
- 39 % 7 = 4 and so the element is located at index position 4.
The domain name is also know as _________ name.- a)Host
- b)Network
- c)Device
- d)Website
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The domain name is also know as _________ name.
a)
Host
b)
Network
c)
Device
d)
Website
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Concept:
Each computer server hosting a website or web resource is given a name against its IP address. These names are called domain names or hostnames.
Each computer server hosting a website or web resource is given a name against its IP address. These names are called domain names or hostnames.
- The Internet is a vast ocean where information is available in the form of millions of websites. Each website is stored on a server that is connected to the internet, which means each server has an IP address.
- Every device connected to the internet has an IP address. To access a website, we need to enter its IP address on our web browser.
- But it is very difficult to remember the IP addresses of different websites as they are in terms of numbers or strings.
- Conversion of the domain name of each web server to its corresponding IP address is called domain name resolution.
Which commands provide definitions for creating table structure, deleting relations and modifying relation schemas?- a)DDL
- b)DML
- c)DCL
- d)DQL
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which commands provide definitions for creating table structure, deleting relations and modifying relation schemas?
a)
DDL
b)
DML
c)
DCL
d)
DQL
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
DDL commands provide definitions for creating table structure, deleting relations and modifying relation schemas.
Which of the following items are present in the function header?- a)Function name
- b)Parameter list
- c)Return value
- d)Both 1 and 2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following items are present in the function header?
a)
Function name
b)
Parameter list
c)
Return value
d)
Both 1 and 2
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Function header consists of function name & parameter list.
In searching, the hash function takes an element from a list and divides it by the size of the hash. This method is known as the __________ method.- a)Hash
- b)Divisior
- c)Dividend
- d)Remainder
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In searching, the hash function takes an element from a list and divides it by the size of the hash. This method is known as the __________ method.
a)
Hash
b)
Divisior
c)
Dividend
d)
Remainder
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Hashing is a searching technique in which we use a hash table and a hash function in the format of h(k) = k mod m, where m is the size or the slot available in the hash table, and k is given the key.
That's the process in which the position of a key is determined in the hash table.
For example - we have a 12-slotted hash table and we want to locate the position of 100 in that table, then
h(k) = 100 mod 12 = 4 (12*8 will be 96 , and 4 as remainder )
h(k) = 100 mod 12 = 4 (12*8 will be 96 , and 4 as remainder )
A simple rule for calculating mod function -
1- if we have m mod n and m>n, then the mod will return only the remainder.
2- and if m=n then it will result in 0.
3- if m<n then it will return m as the answer.
1- if we have m mod n and m>n, then the mod will return only the remainder.
2- and if m=n then it will result in 0.
3- if m<n then it will return m as the answer.
Which of the following device is used to connect similar LAN with same protocols?- a)Gateways
- b)Router
- c)Switches
- d)Bridges
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following device is used to connect similar LAN with same protocols?
a)
Gateways
b)
Router
c)
Switches
d)
Bridges
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Concept:
- The bridge is used to connect similar LANs with the same protocols. A bridge operates at the data link layer. It is also used for interconnecting two LANs working on the same protocol. It has a single input and single output port, thus making it a 2 port device. A bridge must contain addressing and routing capability.
- A bridge is a network device that joins two or more LANs (local area networks) to build a larger LAN. Network bridging is the process of aggregating networks. A bridge joins the various components to make them appear as if they are all part of the same network.
Hence the correct answer is Bridges.
The Programming language Python is named after:- a)A popular BBC comedy show "Monty Python's Flying Circus".
- b)A popular comedy circus "Python's Flying Circus".
- c)A comedy serial "Monty Python"
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The Programming language Python is named after:
a)
A popular BBC comedy show "Monty Python's Flying Circus".
b)
A popular comedy circus "Python's Flying Circus".
c)
A comedy serial "Monty Python"
d)
None of these
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The Programming language Python is named after a popular BBC comedy show "Monty Python's Flying Circus".
Which of the following is not a limitation of the binary search algorithm?- a)It must use a sorted array.
- b)Requirement of sorted array is expensive when a lot of insertion and deletions are needed.
- c)There must be a mechanism to access middle element directly.
- d)Binary search algorithm is not efficient when the data elements are more than 1000.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a limitation of the binary search algorithm?
a)
It must use a sorted array.
b)
Requirement of sorted array is expensive when a lot of insertion and deletions are needed.
c)
There must be a mechanism to access middle element directly.
d)
Binary search algorithm is not efficient when the data elements are more than 1000.
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The major limitation of binary search is that there is a need for the sorted array to perform the binary search operation. If the array is not sorted the output is either not correct or maybe after a long number of steps and according to the data structure, the output should come in a minimum number of steps.
Not a limitation of Binary search :Binary search algorithm is not efficient when the data elements are more than 1000.
Not a limitation of Binary search :Binary search algorithm is not efficient when the data elements are more than 1000.
Assume that the position of the file pointer is at the beginning of 3rd line in a text file. Which of the following option can be used to read all the remaining lines?- a)myfile.read()
- b)myfile.read(n)
- c)myfile.readline()
- d)myfile.readlines()
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assume that the position of the file pointer is at the beginning of 3rd line in a text file. Which of the following option can be used to read all the remaining lines?
a)
myfile.read()
b)
myfile.read(n)
c)
myfile.readline()
d)
myfile.readlines()
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The myfile.readlines() function is used to read the entire files.
To get all the information in a file, readlines() is used. It returns the entire information in the file. The radlines() function gives all data in the file as a collection of strings. When using the readlines() function, all the data in the file is read and it will not be stopped until the entire file ends.
To get all the information in a file, readlines() is used. It returns the entire information in the file. The radlines() function gives all data in the file as a collection of strings. When using the readlines() function, all the data in the file is read and it will not be stopped until the entire file ends.
What is the output of the following program:
print((1, 2) + (3, 4))- a)(1, 2), (3, 4)
- b)(4, 6)
- c)(1, 2, 3, 4)
- d)Invalid Syntax
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the output of the following program:
print((1, 2) + (3, 4))
print((1, 2) + (3, 4))
a)
(1, 2), (3, 4)
b)
(4, 6)
c)
(1, 2, 3, 4)
d)
Invalid Syntax
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The following program, print((1,2) + (3,4)) gives:
For the given program, we have two tuples, and we are printing the concatenation of these tuples.
i.e print((1, 2) + (3, 4))
A collection of Python objects separated by comma is called a Tuple.
In this, we are using the concatenation operator +, to join the two tuples.
So, (1,2,3,4) is the answer.
For the given program, we have two tuples, and we are printing the concatenation of these tuples.
i.e print((1, 2) + (3, 4))
A collection of Python objects separated by comma is called a Tuple.
In this, we are using the concatenation operator +, to join the two tuples.
So, (1,2,3,4) is the answer.
Consider the following array A, and the searching element is X. How many comparisons are required to search an element X in array A.
A[ ]= {25, 45, 87, 21, 18, 49, 13, 115, 83, 65}
X = 83- a)7
- b)8
- c)9
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following array A, and the searching element is X. How many comparisons are required to search an element X in array A.
A[ ]= {25, 45, 87, 21, 18, 49, 13, 115, 83, 65}
X = 83
A[ ]= {25, 45, 87, 21, 18, 49, 13, 115, 83, 65}
X = 83
a)
7
b)
8
c)
9
d)
10
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Concept:
Linear search is a sequential searching strategy in which we start at one end of the list and examine each member until we find the target element. It is the most basic search algorithm.
The given data is,
A[ ]= {25, 45, 87, 21, 18, 49, 13, 115, 83, 65}
X = 83
Linear search is a sequential searching strategy in which we start at one end of the list and examine each member until we find the target element. It is the most basic search algorithm.
The given data is,
A[ ]= {25, 45, 87, 21, 18, 49, 13, 115, 83, 65}
X = 83
Compare element 25 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 45 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 87 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 21 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 18 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 49 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 13 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 115 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 83 with 83.
Hence the search is successful and exits the program.
Total comparsions are=9.
Hence the correct answer is 9.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 45 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 87 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 21 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 18 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 49 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 13 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 115 with 83.
Hence the search is not successful and continues the program.
Compare element 83 with 83.
Hence the search is successful and exits the program.
Total comparsions are=9.
Hence the correct answer is 9.
Which method is used to sets the position of a file pointer?- a)tell()
- b)fseek()
- c)seek()
- d)ftell()
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which method is used to sets the position of a file pointer?
a)
tell()
b)
fseek()
c)
seek()
d)
ftell()
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Concept:
The seek() method :
The seek() method :
This method is used to position the file object at a particular position in a file.
The syntax of seek() is:
file_object.seek(offset [ , reference_point])
In the above syntax, offset is the number of bytes by which the file object is to be moved. reference_point indicates the starting position of the file object. That is, with reference to which position, the offset has to be counted.
- It can have any of the following values:
- 0 - beginning of the file
- 1 - current position of the file
- 2 - end of file
- By default, the value of reference_point is 0, i.e. the offset is counted from the beginning of the file.
Hence the correct answer is seek().
Which function returns the given string after removing leading white space characters?- a)TTRIM(string)
- b)TRIM(string)
- c)LTRIM(string)
- d)RTRIM(string)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which function returns the given string after removing leading white space characters?
a)
TTRIM(string)
b)
TRIM(string)
c)
LTRIM(string)
d)
RTRIM(string)
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The correct option is C
LTRIM(string)
Concept:
LTRIM(string), Returns the given string after removing leading white space characters.
Example: MySQL >SELECT LENGTH (" DELHI" ) LENGTH (LTRIM("DELHI "));
Output: 7 5
LTRIM(string)
Concept:
LTRIM(string), Returns the given string after removing leading white space characters.
Example: MySQL >SELECT LENGTH (" DELHI" ) LENGTH (LTRIM("DELHI "));
Output: 7 5
A ___________ is a request to a database to obtain information in the desired way.- a)Command
- b)Trigger
- c)Query
- d)Statement
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A ___________ is a request to a database to obtain information in the desired way.
a)
Command
b)
Trigger
c)
Query
d)
Statement
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Concept:
A query is a request to a database to obtain information in the desired way. The query can be made to get data from one table or from a combination of tables. For example, " finds names of all those students present on attendance date 20001-01-02" is a query to the database.
A query is a request to a database to obtain information in the desired way. The query can be made to get data from one table or from a combination of tables. For example, " finds names of all those students present on attendance date 20001-01-02" is a query to the database.
- The SQL statement SELECT is used to retrieve data from the tables in a database and is also called a query statement.
- This data may be generated as results returned by Structured Query Language (SQL) or as pictorials, graphs or complex results, and trend analyses from data-mining tools.
- One of several different query languages may be used to perform a range of simple to complex database queries.
- The query database feature is equal to the necessity of data storage capability.
Which of the following statement can be used to display all built in exceptions?- a)print(dir(locals()['__builtins__']))
- b)print(dir(locals()['__annotations__']))
- c)print(dir(locals()['__spec__']))
- d)print(dir(locals()['__doc__']))
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement can be used to display all built in exceptions?
a)
print(dir(locals()['__builtins__']))
b)
print(dir(locals()['__annotations__']))
c)
print(dir(locals()['__spec__']))
d)
print(dir(locals()['__doc__']))
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
CONCEPT:
In Python, there are several built-in exceptions that are raised when errors occur.
To view these built-in exceptions local() function is used which returns a dictionary of the current local symbol table.
dir() is a function that returns a list of the attributes and methods of the object passed to it.
To view these built-in exceptions local() function is used which returns a dictionary of the current local symbol table.
dir() is a function that returns a list of the attributes and methods of the object passed to it.
>>> print(dir(locals()['__builtins__']))
Radha Shah is a programmer, who has recently been given a task to write a python code to perform the following CSV file operations with the help of two user defined functions/modules:
a. CSVOpen() : to create a CSV file called BOOKS.CSV in append mode containing information of books – Title, Author, and Price.
b. CSVRead() : to display the records from the CSV file called BOOKS.CSV where the field title starts with 'R'.
She has succeeded in writing partial code and has missed out certain statements, so she has left certain queries in comment lines.
import csv
def CSVOpen():
with open('books.csv','______',newline='') as csvf:
#Statement-1
cw=______ #Statement-2
______ #Statement-3
cw.writerow(['Rapunzel','Jack',300])
cw.writerow(['Barbie','Doll',900])
cw.writerow(['Johnny','Jane',280])
def CSVRead():
Q. Fill in the appropriate statement to check the field Title starting with 'R' for Statement 3 in the above program.
- a)r[0][0]=='R'
- b)r[1][0]=='R'
- c)r[0][1]=='R'
- d)r[1][1]=='R'
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Radha Shah is a programmer, who has recently been given a task to write a python code to perform the following CSV file operations with the help of two user defined functions/modules:
a. CSVOpen() : to create a CSV file called BOOKS.CSV in append mode containing information of books – Title, Author, and Price.
b. CSVRead() : to display the records from the CSV file called BOOKS.CSV where the field title starts with 'R'.
b. CSVRead() : to display the records from the CSV file called BOOKS.CSV where the field title starts with 'R'.
She has succeeded in writing partial code and has missed out certain statements, so she has left certain queries in comment lines.
import csv
def CSVOpen():
with open('books.csv','______',newline='') as csvf:
#Statement-1
cw=______ #Statement-2
______ #Statement-3
cw.writerow(['Rapunzel','Jack',300])
cw.writerow(['Barbie','Doll',900])
cw.writerow(['Johnny','Jane',280])
def CSVRead():
import csv
def CSVOpen():
with open('books.csv','______',newline='') as csvf:
#Statement-1
cw=______ #Statement-2
______ #Statement-3
cw.writerow(['Rapunzel','Jack',300])
cw.writerow(['Barbie','Doll',900])
cw.writerow(['Johnny','Jane',280])
def CSVRead():
Q. Fill in the appropriate statement to check the field Title starting with 'R' for Statement 3 in the above program.
a)
r[0][0]=='R'
b)
r[1][0]=='R'
c)
r[0][1]=='R'
d)
r[1][1]=='R'
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Title is the first column of CSV file, so its index would be r [0] [0]. Condition to check the field Title starting with 'R' will be r[0][0] = 'R'.
A perfect hash function maps every input key to a unique index in the hash table. If the hash function is perfect, collisions will______.- a)never occur
- b)sometimes occur
- c)depend on the function
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A perfect hash function maps every input key to a unique index in the hash table. If the hash function is perfect, collisions will______.
a)
never occur
b)
sometimes occur
c)
depend on the function
d)
none of these
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
A perfect hash function maps every input key to a unique index in the hash table. If the hash function is perfect, collisions will never occur.
Consider the following relation.
Table: Customers(C_id, C_name, C_age, C_Country)
What is the output for the given SQL Query?
Query:
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD income INT;
What is the degree of the customer relationship?- a)4
- b)5
- c)6
- d)error
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following relation.
Table: Customers(C_id, C_name, C_age, C_Country)
What is the output for the given SQL Query?
Query:
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD income INT;
What is the degree of the customer relationship?
Table: Customers(C_id, C_name, C_age, C_Country)
What is the output for the given SQL Query?
Query:
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD income INT;
What is the degree of the customer relationship?
a)
4
b)
5
c)
6
d)
error
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The correct answer is option B.
Concept:
Add an attribute to an existing table:
Sometimes, we may need to add an additional attribute to a table. It can be done using the syntax given below:
Add an attribute to an existing table:
Sometimes, we may need to add an additional attribute to a table. It can be done using the syntax given below:
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD attribute_name DATATYPE;
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD attribute_name DATATYPE;
DEGREE:
The number of attributes in a relation is called the Degree of the relation.
The number of attributes in a relation is called the Degree of the relation.
Explanation:
The customer relation adds a new attribute to the customer relationship. Now the Customers relation becomes the Customers(C_id, C_name, C_age, C_Country, income)
The customer relation adds a new attribute to the customer relationship. Now the Customers relation becomes the Customers(C_id, C_name, C_age, C_Country, income)
Query:
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD income INT;
Hence the degree of the relation becomes 5.
Hence the correct answer is 5.
ALTER TABLE Customers
ADD income INT;
Hence the degree of the relation becomes 5.
Hence the correct answer is 5.
Statement I: MAC address of a device can change.
Statement II: IP address of a device cannot change.- a)Both I and II are correct
- b)I is correct, II is incorrect
- c)II is correct, I is incorrect
- d)Both I and II are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement I: MAC address of a device can change.
Statement II: IP address of a device cannot change.
Statement II: IP address of a device cannot change.
a)
Both I and II are correct
b)
I is correct, II is incorrect
c)
II is correct, I is incorrect
d)
Both I and II are incorrect
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
- The MAC address is printed on the Ethernet card at the time of manufacturing. When the Ethernet card is placed on a device, the address on the card becomes the MAC address of the device. Thus, the MAC address of a device cannot change.
- The IP address is assigned to a device when it is connected to a network. When the device is connected to a different network, the IP address automatically changes. Thus, the IP address of a device can change.
The elements 9, 5, 7, and 2 are in the queue and are eliminated one by one. The order of elements received is __________?- a)9, 7, 5, and 2
- b)2, 5, 7, and 9
- c)9, 5, 7, and 2
- d)2, 7, 5, and 9
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The elements 9, 5, 7, and 2 are in the queue and are eliminated one by one. The order of elements received is __________?
a)
9, 7, 5, and 2
b)
2, 5, 7, and 9
c)
9, 5, 7, and 2
d)
2, 7, 5, and 9
|
|
Sounak Mehra answered |
Explanation:
Given Elements:
- Queue: 9, 5, 7, 2
Order of Elimination:
- The elements are eliminated one by one from the queue.
Step 1:
- The first element to be eliminated is 9.
- Remaining queue: 5, 7, 2
Step 2:
- The second element to be eliminated is 5.
- Remaining queue: 7, 2
Step 3:
- The third element to be eliminated is 7.
- Remaining queue: 2
Step 4:
- The last element to be eliminated is 2.
Final Order of Elements Received:
- 9, 5, 7, 2
Therefore, the correct order of elements received after eliminating them one by one is 9, 5, 7, and 2.
Given Elements:
- Queue: 9, 5, 7, 2
Order of Elimination:
- The elements are eliminated one by one from the queue.
Step 1:
- The first element to be eliminated is 9.
- Remaining queue: 5, 7, 2
Step 2:
- The second element to be eliminated is 5.
- Remaining queue: 7, 2
Step 3:
- The third element to be eliminated is 7.
- Remaining queue: 2
Step 4:
- The last element to be eliminated is 2.
Final Order of Elements Received:
- 9, 5, 7, 2
Therefore, the correct order of elements received after eliminating them one by one is 9, 5, 7, and 2.
What is the output for the given python program?try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
try:
sum=5/0;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world") - a)Hello world
Hello India - b)Hello world
Hello world - c)Hello India
Hello India - d)Hello India
Hello world
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the output for the given python program?
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
try:
sum=5/0;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
try:
sum=5/0;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
a)
Hello world
Hello India
Hello India
b)
Hello world
Hello world
Hello world
c)
Hello India
Hello India
Hello India
d)
Hello India
Hello world
Hello world
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The correct answer is option A.
Concept:
The given python code is,
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
Concept:
The given python code is,
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
Explanation:
ZeroDivisionError:
It is raised when the denominator in a division operation is zero.
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
ZeroDivisionError:
It is raised when the denominator in a division operation is zero.
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
The above executes and it can not raise the exception and prints the Hello world as output.
try:
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
The above executes and it can raise the exception and print the Hello India as output.
Hence the correct answer is
Hello world
sum=5/2;
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("Hello India")
else:
print("Hello world")
The above executes and it can raise the exception and print the Hello India as output.
Hence the correct answer is
Hello world
Hello India
How many swaps are required to sort the list L2 using selection sort?L2: [54, 23, 12, 44, 18, 22, 14]- a)6
- b)7
- c)5
- d)8
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How many swaps are required to sort the list L2 using selection sort?
L2: [54, 23, 12, 44, 18, 22, 14]
a)
6
b)
7
c)
5
d)
8
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
Selection sort works in the algorithm like we have to pick the smallest element from the unsorted array/list and move that to the beginning of the list. This process can be described as 1 Swap.
Applying Selection sort on the given list -
Pass 1 = {12} {23,54,44,18,22,14} - 1 swap
Pass 2 = {12,14} {54,44,18,22,23} - 2nd swap
Pass 3 = {12,14,18} {44,54,22,23} - 3rd swap
Pass 4 = {12,14,18,22} {44,54,23} - 4th swap
Pass 5 = {12,14,18,22,23} {44,54} - 5th swap
Pass 6 = {12,14,18,22,23,44} {54} - 6th swap
For the last element we do not need any swap, So, in total 6 swap required to sort the list. ( option 1)
Formula - For a n element list , Selection Sort needs (n-1) number of swap. , where n is number of element in a list.
Applying Selection sort on the given list -
Pass 1 = {12} {23,54,44,18,22,14} - 1 swap
Pass 2 = {12,14} {54,44,18,22,23} - 2nd swap
Pass 3 = {12,14,18} {44,54,22,23} - 3rd swap
Pass 4 = {12,14,18,22} {44,54,23} - 4th swap
Pass 5 = {12,14,18,22,23} {44,54} - 5th swap
Pass 6 = {12,14,18,22,23,44} {54} - 6th swap
For the last element we do not need any swap, So, in total 6 swap required to sort the list. ( option 1)
Formula - For a n element list , Selection Sort needs (n-1) number of swap. , where n is number of element in a list.
What will be the output for the following python code statements, respectively?print("Hello world")
print('Hello world')
print('\"Hello world')- a)"Hello world"
Hello world
"Hello world - b)Hello world
Hello world
Hello world - c)Hello world
Hello world
"Hello world - d)Hello world
Hello world
SyntaxError
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the output for the following python code statements, respectively?
print("Hello world")
print('Hello world')
print('\"Hello world')
print('Hello world')
print('\"Hello world')
a)
"Hello world"
Hello world
"Hello world
Hello world
"Hello world
b)
Hello world
Hello world
Hello world
Hello world
Hello world
c)
Hello world
Hello world
"Hello world
Hello world
"Hello world
d)
Hello world
Hello world
SyntaxError
Hello world
SyntaxError
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The correct answer is option 3.
Concept:
print() method:
The print() method outputs the message supplied to the screen or another standard output device. The message can be a string or any other object, which will be transformed into a string before being displayed on the screen.
print() method:
The print() method outputs the message supplied to the screen or another standard output device. The message can be a string or any other object, which will be transformed into a string before being displayed on the screen.
Syntax:
print(object(s), sep=separator, end=end, file=file, flush=flush)
print(object(s), sep=separator, end=end, file=file, flush=flush)
Explanation:
The given python code is,
print("Hello world"):
The print function prints the data which are there in double-quotes and give the output is Hello world.
print('Hello world'):
The print function prints the data which are there in single quotes and gives the output is Hello world. And python accepts either double quotes or single quotes.
print('\"Hello world'):
The print function prints the data which are there in single quotes and gives the output as "Hello world. \ back ward slash emits after the single or double quotes in the print function.
Hence the correct answer is
Hello world
Hello world
"Hello world
The given python code is,
print("Hello world"):
The print function prints the data which are there in double-quotes and give the output is Hello world.
print('Hello world'):
The print function prints the data which are there in single quotes and gives the output is Hello world. And python accepts either double quotes or single quotes.
print('\"Hello world'):
The print function prints the data which are there in single quotes and gives the output as "Hello world. \ back ward slash emits after the single or double quotes in the print function.
Hence the correct answer is
Hello world
Hello world
"Hello world
The given array is a = {7,8,9,6,5}. The number of iterations in selection sort and bubble sort respectively are __________.- a)4 and 4.
- b)5 and 4.
- c)3 and 5
- d)5 and 5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The given array is a = {7,8,9,6,5}. The number of iterations in selection sort and bubble sort respectively are __________.
a)
4 and 4.
b)
5 and 4.
c)
3 and 5
d)
5 and 5
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element from the unsorted part and putting it at the beginning.So, Every pass 1 swap minimum is required.
The selection sort is good for swapping purposes.
The selection sort is good for swapping purposes.
According to the question , the array is {7,8,9,6,5}
Applying selection sort :
1st pass - 5 {7,8,9,6}
2nd pass - 5, 6 {7,8,9}
Applying selection sort :
1st pass - 5 {7,8,9,6}
2nd pass - 5, 6 {7,8,9}
3rd pass - 5, 6, 7 {8,9}
4th pass - 5,6,7,8 {9} ( array sorted)
So, we need 4 passes/iterations to sort the array using selection sort.
So, we need 4 passes/iterations to sort the array using selection sort.
Bubble sort work by the principle of finding the max element from the array and pushing it to the end.
Applying bubble sort on {7,8,9,6,5}
1st pass- {7,8,6,5} 9
2nd pass - {7,6,5} 8, 9
3rd pass- {6,5} 7, 8, 9
4th pass - {5} 6, 7, 8, 9 ( array sorted )
So, we need 4 passes to sort the array using bubble sort.
Both selection and bubble sort takes (n-1) passes / iteration to sort the array.
Consider the array L = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. Suppose you’re searching for the value 3 using binary search method. What is the value of the variable last after two iterations?- a)14
- b)2
- c)6
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the array L = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15]. Suppose you’re searching for the value 3 using binary search method. What is the value of the variable last after two iterations?
a)
14
b)
2
c)
6
d)
3
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
The starting values of first and last are 0 and 14 respectively.
The iterations are shown below:
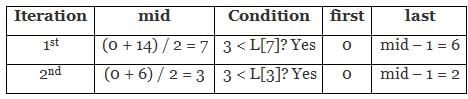
Therefore, the value of the variable last is 2 after the first two iterations.
The iterations are shown below:

Therefore, the value of the variable last is 2 after the first two iterations.
A text file student.txt is stored in the storage device. Identify the correct option out of the following options to open the file in read mode.
(i) myfile = open('student.txt','rb')
(ii) myfile = open('student.txt','w')
(iii) myfile = open('student.txt','r')
(iv) myfile = open('student.txt')- a)Only i
- b)Both i and iv
- c)Both iii and iv
- d)Both i and iii
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A text file student.txt is stored in the storage device. Identify the correct option out of the following options to open the file in read mode.
(i) myfile = open('student.txt','rb')
(ii) myfile = open('student.txt','w')
(iii) myfile = open('student.txt','r')
(iv) myfile = open('student.txt')
(i) myfile = open('student.txt','rb')
(ii) myfile = open('student.txt','w')
(iii) myfile = open('student.txt','r')
(iv) myfile = open('student.txt')
a)
Only i
b)
Both i and iv
c)
Both iii and iv
d)
Both i and iii
|
|
Amita Das answered |
- There are some codes to handle a file in a programming language.
- myfile=open('student. txt', 'w') is the mode that allows opening a file in write mode.
- myfile=open('student.txt', 'r') is the mode that open file in only read mode.
- myfile= open ('student.txt') is also allowed to open in reading mode.
In which case is the NameError exception raised in Python?- a)When a requested module definition is not found
- b)When a keyword is used as a variable name
- c)When a variable name cannot be found
- d)When a file to be opened cannot be found
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which case is the NameError exception raised in Python?
a)
When a requested module definition is not found
b)
When a keyword is used as a variable name
c)
When a variable name cannot be found
d)
When a file to be opened cannot be found
|
|
Amita Das answered |
- When a requested module definition is not found, the ImportError exception is raised.
- When a keyword or a reserved word is used as a variable name, it leads to a syntax error.
- When a statement accessed a variable that is not found in the local or global scope, then the program raises a NameError.
- When a specified file cannot be opened by a program, it causes an exception of IOError type.
What is the significance of the tell() method?- a)It tells the path of file.
- b)It tells the current position of the file pointer within the file.
- c)It tells the end position within the file.
- d)It checks the existence of a file at the desired location.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the significance of the tell() method?
a)
It tells the path of file.
b)
It tells the current position of the file pointer within the file.
c)
It tells the end position within the file.
d)
It checks the existence of a file at the desired location.
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The tell() method returns the current position of file object. This method takes no parameters and returns an integer value. Initially file pointer points to the beginning of the file (if not opened in append mode). So, the initial value of tell() is zero.
Syntax of seek function in Python is myfile.seek(offset, reference_point) where myfile is the file object. What is the default value of reference_point?- a)0
- b)1
- c)2
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Syntax of seek function in Python is myfile.seek(offset, reference_point) where myfile is the file object. What is the default value of reference_point?
a)
0
b)
1
c)
2
d)
3
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The reference_point is selected by the from_what argument. It accepts three values:
0: sets the reference_point at the beginning of the file.
1: sets the reference_point at the current file position.
2: sets the reference_point at the end of the file.
By default from_what argument is set to 0.
0: sets the reference_point at the beginning of the file.
1: sets the reference_point at the current file position.
2: sets the reference_point at the end of the file.
By default from_what argument is set to 0.
Consider a list of 10 elements:
Array = [7, 11, 3, 10, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5]
Determine the partially sorted list after three complete passes of insertion sort, in descending order.- a)11, 10, 7, 3, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5
- b)11, 17, 23, 10, 7, 21, 5, 4, 3, 1
- c)3, 7, 11, 10, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5
- d)23, 21, 17, 10, 3, 7, 1, 4, 11, 5
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider a list of 10 elements:
Array = [7, 11, 3, 10, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5]
Determine the partially sorted list after three complete passes of insertion sort, in descending order.
Array = [7, 11, 3, 10, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5]
Determine the partially sorted list after three complete passes of insertion sort, in descending order.
a)
11, 10, 7, 3, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5
b)
11, 17, 23, 10, 7, 21, 5, 4, 3, 1
c)
3, 7, 11, 10, 17, 23, 1, 4, 21, 5
d)
23, 21, 17, 10, 3, 7, 1, 4, 11, 5
|
|
Amita Das answered |
- In insertion sort, the first element is considered as the sorted list, and the remaining list is the unsorted part.
- At each iteration, the first element of the unsorted list is placed into the appropriate position in the sorted list. The checking is done backwards in the sorted list.
- In the first pass over this list, the element 11 is greater than 7 so it is moved to the left of 7 as the sorting is being done in descending order.
- The second passes places the value 3 into the sorted list. It remains where it is because 3 is already to the right of 7.
- In the third pass, 10 is placed between 11 and 7.
Which of the following File open modes is used for Opens the file in append mode?Note: If the file doesn’t exist, then a new file will be created.- a)<r>
- b)<rb>
- c)<w>
- d)<a>
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following File open modes is used for Opens the file in append mode?
Note: If the file doesn’t exist, then a new file will be created.
a)
<r>
b)
<rb>
c)
<w>
d)
<a>
|
|
Amita Das answered |
The correct answer is option 4.
Concept:
To open a file in Python:
we use the open() function. The syntax of open() is as follows:
file_object= open(file_name, access_mode)
The access_mode is an optional argument that represents the mode in which the file has to be accessed by the program. It is also referred to as processing mode.
To open a file in Python:
we use the open() function. The syntax of open() is as follows:
file_object= open(file_name, access_mode)
The access_mode is an optional argument that represents the mode in which the file has to be accessed by the program. It is also referred to as processing mode.
Different File open modes:
- <r> Opens the file in read-only mode.
- <rb> Opens the file in binary and read-only mode.
- <w> Opens the file in write mode. If the file already exists, all the contents will be overwritten. If the file doesn’t exist, then a new file will be created.
- <a> Opens the file in append mode. If the file doesn’t exist, then a new file will be created.
Hence the correct answer is <a>.
What is the output of the following if statementa, b = 12, 5
if a + b:
print('True')
else:
print('False')- a)False
- b)True
- c)Can't say
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the output of the following if statement
a, b = 12, 5
if a + b:
print('True')
else:
print('False')
if a + b:
print('True')
else:
print('False')
a)
False
b)
True
c)
Can't say
d)
None of these
|
|
Amita Das answered |
In Python, any non-zero value is considered True. So, it will evaluate to true.
Statement 1: A program cannot be executed until all errors are rectified.
Statement 2: A program cannot be executed until all exceptions are handled.- a)Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true.
- b)Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false.
- c)Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true.
- d)Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement 1: A program cannot be executed until all errors are rectified.
Statement 2: A program cannot be executed until all exceptions are handled.
Statement 2: A program cannot be executed until all exceptions are handled.
a)
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is true.
b)
Statement 1 is true, statement 2 is false.
c)
Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is true.
d)
Statement 1 is false, statement 2 is false.
|
|
Amita Das answered |
Explanation:
- In Python, mistakes in the syntax are known as errors. Unless and until the errors are rectified, the program cannot be compiled and executed.
- Exceptions are those errors which terminate the program abnormally. However, exceptions can only be encountered at runtime. So, a program with exceptions can be executed.
Important Point:
- Even though a syntax error is a type of exception, but it is different from other exceptions because a program with syntax error cannot be executed.
Chapter doubts & questions for Computer Science - CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 2025 is part of CUET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the CUET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for CUET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Computer Science - CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of CUET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for CUET Exam by signing up for free.
CUET UG Mock Test Series 2026
39 docs|145 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup