All Exams >
UPSC >
Lucent For GK >
All Questions
All questions of Unit for UPSC CSE Exam
The mass of a body is equivalent to the ratio of the force acting on it to the acceleration it generates.- a)the gravitational mass
- b)the mass of the electromagnetic field
- c)the mass of the internal organs
- d)the mass of inertia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The mass of a body is equivalent to the ratio of the force acting on it to the acceleration it generates.
a)
the gravitational mass
b)
the mass of the electromagnetic field
c)
the mass of the internal organs
d)
the mass of inertia
|
|
Catalyst Learningacademy answered |
The statement describes the concept of inertia, which is an inherent property of matter. The mass of a body determines its resistance to changes in motion and is measured by the amount of inertia it possesses. The ratio of the force acting on an object to the acceleration it produces is known as its mass of inertia or simply inertia. This concept is fundamental to Newton's second law of motion, which states that the force acting on an object is directly proportional to its mass and the acceleration it experiences. Gravitational mass, the mass of the electromagnetic field, and the mass of internal organs are not relevant to the given statement.
If the force applied to a body is doubled and the mass is cut in half, What would be the accelerations’ ratio?- a)1:2
- b)2:1
- c)1:4
- d)4:1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the force applied to a body is doubled and the mass is cut in half, What would be the accelerations’ ratio?
a)
1:2
b)
2:1
c)
1:4
d)
4:1
|
|
Paradigm Institute answered |
The ratio of accelerations will be calculated as: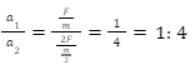
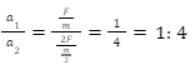
What is the mass of a body that accelerates at a rate of 2.6 m/s2 with a force of 90 N?- a)44.6 kg
- b)34.6 kg
- c)54.6 kg
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the mass of a body that accelerates at a rate of 2.6 m/s2 with a force of 90 N?
a)
44.6 kg
b)
34.6 kg
c)
54.6 kg
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Paradigm Institute answered |
To determine the mass of a body, we can use Newton's second law of motion, which states that force (F) is equal to mass (m) multiplied by acceleration (a), or F = ma.
Given: Force (F) = 90 N Acceleration (a) = 2.6 m/s²
Using the formula F = ma, we can rearrange it to solve for mass: m = F / a
Substituting the given values: m = 90 N / 2.6 m/s² ≈ 34.6 kg
Therefore, the mass of the body is approximately 34.6 kg.
The correct answer is b) 34.6 kg.
What are the components required to calculate the momentum of a body?- a)Mass and acceleration
- b)Velocity and mass
- c)Displacement and mass
- d)None of the mentioned
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the components required to calculate the momentum of a body?
a)
Mass and acceleration
b)
Velocity and mass
c)
Displacement and mass
d)
None of the mentioned
|
|
Maya Pillai answered |
Momentum:
Momentum is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the motion of an object. It is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. Mathematically, momentum (p) is calculated using the equation:
p = m * v
Where:
p = momentum
m = mass of the object
v = velocity of the object
Components required to calculate momentum:
To calculate the momentum of a body, we need two components:
1. Mass:
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity and is usually measured in kilograms (kg). The mass of an object determines how difficult it is to change its state of motion, and it is an important factor in calculating momentum.
2. Velocity:
Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the speed and direction of an object's motion. It is the rate at which an object changes its position. Velocity is usually measured in meters per second (m/s). In the context of calculating momentum, we need to consider the velocity of the object.
Explanation of the correct answer:
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that velocity and mass are the components required to calculate the momentum of a body. This is because velocity and mass are the two fundamental quantities that directly affect and determine the momentum of an object.
- Mass is a scalar quantity that represents the amount of matter in an object. It determines the inertia and resistance to changes in motion. The greater the mass, the greater the momentum of the object for a given velocity.
- Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that describes the speed and direction of an object's motion. It determines how fast an object is moving and in which direction. The velocity of an object affects its momentum, and a greater velocity results in a greater momentum for a given mass.
By multiplying the mass and velocity of an object, we obtain the momentum of the object. Therefore, to calculate the momentum, we need both the mass and velocity of the object.
In conclusion, the correct components required to calculate the momentum of a body are the mass and velocity of the object. These two quantities are necessary to determine the momentum of an object accurately.
Momentum is a fundamental concept in physics that describes the motion of an object. It is defined as the product of an object's mass and its velocity. Mathematically, momentum (p) is calculated using the equation:
p = m * v
Where:
p = momentum
m = mass of the object
v = velocity of the object
Components required to calculate momentum:
To calculate the momentum of a body, we need two components:
1. Mass:
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It is a scalar quantity and is usually measured in kilograms (kg). The mass of an object determines how difficult it is to change its state of motion, and it is an important factor in calculating momentum.
2. Velocity:
Velocity is a vector quantity that describes the speed and direction of an object's motion. It is the rate at which an object changes its position. Velocity is usually measured in meters per second (m/s). In the context of calculating momentum, we need to consider the velocity of the object.
Explanation of the correct answer:
The correct answer is option 'B' which states that velocity and mass are the components required to calculate the momentum of a body. This is because velocity and mass are the two fundamental quantities that directly affect and determine the momentum of an object.
- Mass is a scalar quantity that represents the amount of matter in an object. It determines the inertia and resistance to changes in motion. The greater the mass, the greater the momentum of the object for a given velocity.
- Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that describes the speed and direction of an object's motion. It determines how fast an object is moving and in which direction. The velocity of an object affects its momentum, and a greater velocity results in a greater momentum for a given mass.
By multiplying the mass and velocity of an object, we obtain the momentum of the object. Therefore, to calculate the momentum, we need both the mass and velocity of the object.
In conclusion, the correct components required to calculate the momentum of a body are the mass and velocity of the object. These two quantities are necessary to determine the momentum of an object accurately.
When a passenger on a bus travelling at a constant speed is pushed backward, the bus accelerates forward) This force is referred to as- a)gravitational force
- b)real force.
- c)fictitious or pseudo force
- d)Frictional force
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When a passenger on a bus travelling at a constant speed is pushed backward, the bus accelerates forward) This force is referred to as
a)
gravitational force
b)
real force.
c)
fictitious or pseudo force
d)
Frictional force

|
KS Coaching Center answered |
When a passenger on a bus traveling at a constant speed is pushed backward, the bus accelerates forward due to an external force. This force is referred to as a fictitious or pseudo force.
Fictitious or pseudo forces are forces that appear to act on objects in non-inertial frames of reference, such as accelerating or rotating frames. In this case, when the passenger is pushed backward, their inertia tends to keep them at rest or in uniform motion. However, because the bus is accelerating forward, a fictitious force is experienced by the passenger, pushing them backward.
This force is not a real force in the sense that it does not arise from a physical interaction between objects. It is a result of the frame of reference being non-inertial, and it is necessary to explain the observed motion within that frame.
On a flat surface, a block of wood is placed) To move the body, a force is provided parallel to the surface. The frictional force develops in the following directions:- a)normal to the surface upwards
- b)normal to the surface downwards
- c)along the applied force’s direction
- d)opposite to the applied force’s direction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On a flat surface, a block of wood is placed) To move the body, a force is provided parallel to the surface. The frictional force develops in the following directions:
a)
normal to the surface upwards
b)
normal to the surface downwards
c)
along the applied force’s direction
d)
opposite to the applied force’s direction
|
|
Catalyst Learningacademy answered |
When a force is applied to move a block of wood on a flat surface, the frictional force develops in the direction opposite to the applied force. This frictional force is known as the static frictional force, which acts to oppose the motion or tendency of motion between the block and the surface.
The normal force (a force perpendicular to the surface) acts upwards to balance the weight of the block. The frictional force acts in the opposite direction of the applied force to prevent the block from sliding freely and to provide the necessary force to move the block.
Therefore, the correct answer is d) opposite to the applied force's direction.
Unless driven to act otherwise by an external force, every body remains in its condition of rest or uniform motion along a straight line. This is the
- a)Newton’s second law
- b)Newton’s third law
- c)Newton’s first law
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Unless driven to act otherwise by an external force, every body remains in its condition of rest or uniform motion along a straight line. This is the
a)
Newton’s second law
b)
Newton’s third law
c)
Newton’s first law
d)
None of the above
|
|
Harsh Goyal answered |
Understanding the Concept
The statement provided refers to the fundamental principle of motion in classical mechanics, commonly known as Newton's First Law of Motion. This law articulates the behavior of objects in the absence of external forces.
Key Points of Newton’s First Law
- **Inertia**: The term "inertia" describes the property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its state of motion. An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
- **Rest and Uniform Motion**: The law specifies that bodies remain in their current state—whether at rest or moving uniformly in a straight line—until a force intervenes. This establishes a clear understanding of how forces influence motion.
Terminology
- **Inertia Law**: While often referred to as the "Inertia Law," it is more accurately a description of the behavior of objects under the influence of forces. However, this term is commonly used interchangeably with Newton’s First Law.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is indeed option 'C', as both terms "Inertia Law" and "Newton’s first law" describe the same principle. Understanding this law is essential for grasping the foundational concepts of physics, particularly in mechanics. Recognizing how objects behave in the absence of external forces is crucial for studying motion and the effects of forces.
The statement provided refers to the fundamental principle of motion in classical mechanics, commonly known as Newton's First Law of Motion. This law articulates the behavior of objects in the absence of external forces.
Key Points of Newton’s First Law
- **Inertia**: The term "inertia" describes the property of matter that causes it to resist changes in its state of motion. An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by an external force.
- **Rest and Uniform Motion**: The law specifies that bodies remain in their current state—whether at rest or moving uniformly in a straight line—until a force intervenes. This establishes a clear understanding of how forces influence motion.
Terminology
- **Inertia Law**: While often referred to as the "Inertia Law," it is more accurately a description of the behavior of objects under the influence of forces. However, this term is commonly used interchangeably with Newton’s First Law.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the correct answer to the question is indeed option 'C', as both terms "Inertia Law" and "Newton’s first law" describe the same principle. Understanding this law is essential for grasping the foundational concepts of physics, particularly in mechanics. Recognizing how objects behave in the absence of external forces is crucial for studying motion and the effects of forces.
In 5 seconds, an automobile speeds from 18 km/h to 36 km/h. What is the acceleration of the automobile in m/s?- a)0.5 m/s²
- b)3 m/s²
- c)1 m/s²
- d)2 m/s²
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In 5 seconds, an automobile speeds from 18 km/h to 36 km/h. What is the acceleration of the automobile in m/s?
a)
0.5 m/s²
b)
3 m/s²
c)
1 m/s²
d)
2 m/s²

|
Pallavi Chakraborty answered |
Understanding the Problem
To find the acceleration of the automobile, we need to determine the change in velocity over time. The initial velocity is 18 km/h, and the final velocity is 36 km/h.
Step 1: Convert velocities from km/h to m/s
- 1 km/h is equal to 1/3.6 m/s.
- Initial velocity (u) = 18 km/h = 18 / 3.6 = 5 m/s.
- Final velocity (v) = 36 km/h = 36 / 3.6 = 10 m/s.
Step 2: Calculate the change in velocity
- Change in velocity (Δv) = Final velocity (v) - Initial velocity (u)
- Δv = 10 m/s - 5 m/s = 5 m/s.
Step 3: Calculate the time taken
- The time interval (t) is given as 5 seconds.
Step 4: Calculate acceleration
- Acceleration (a) is given by the formula: a = Δv / t.
- Substituting the values: a = 5 m/s / 5 s = 1 m/s².
Conclusion
Hence, the acceleration of the automobile is 1 m/s², which corresponds to option 'C'.
This calculation illustrates how to convert units and use the formula for acceleration effectively.
To find the acceleration of the automobile, we need to determine the change in velocity over time. The initial velocity is 18 km/h, and the final velocity is 36 km/h.
Step 1: Convert velocities from km/h to m/s
- 1 km/h is equal to 1/3.6 m/s.
- Initial velocity (u) = 18 km/h = 18 / 3.6 = 5 m/s.
- Final velocity (v) = 36 km/h = 36 / 3.6 = 10 m/s.
Step 2: Calculate the change in velocity
- Change in velocity (Δv) = Final velocity (v) - Initial velocity (u)
- Δv = 10 m/s - 5 m/s = 5 m/s.
Step 3: Calculate the time taken
- The time interval (t) is given as 5 seconds.
Step 4: Calculate acceleration
- Acceleration (a) is given by the formula: a = Δv / t.
- Substituting the values: a = 5 m/s / 5 s = 1 m/s².
Conclusion
Hence, the acceleration of the automobile is 1 m/s², which corresponds to option 'C'.
This calculation illustrates how to convert units and use the formula for acceleration effectively.
On the roof of a train travelling on horizontal rails, a simple pendulum swing. If the pendulum’s string is pointing towards the front, the train is-- a)Moving at a steady speed
- b)Moving with acceleration
- c)Moving with retardation
- d)At rest
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On the roof of a train travelling on horizontal rails, a simple pendulum swing. If the pendulum’s string is pointing towards the front, the train is-
a)
Moving at a steady speed
b)
Moving with acceleration
c)
Moving with retardation
d)
At rest
|
|
Paradigm Institute answered |
The correct answer is:
c) Moving with retardation.
Here’s why:
- If the pendulum's string points towards the front of the train, it suggests that the train is slowing down (decelerating or undergoing retardation). This happens because, due to inertia, the pendulum tends to keep moving forward even when the train is slowing down. As a result, the string appears to tilt towards the front of the train.
- If the train were accelerating, the pendulum would swing backward relative to the train, and its string would point toward the rear of the train.
Thus, the string pointing towards the front indicates that the train is moving with retardation (deceleration).
Which of the following has the greatest inertia?- a)A single atom
- b)a molecule
- c)A one-rupee coin
- d)a cricket ball
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following has the greatest inertia?
a)
A single atom
b)
a molecule
c)
A one-rupee coin
d)
a cricket ball
|
|
Catalyst Learningacademy answered |
Inertia is the resistance of an object to changes in its state of motion. It depends on the mass of the object. Generally, objects with greater mass have greater inertia.
Comparing the given options:
a) A single atom: Atoms are extremely small and have very low mass compared to other objects. Therefore, a single atom has the lowest inertia among the given options.
b) A molecule: Molecules consist of multiple atoms bonded together. The mass of a molecule depends on the types and number of atoms it contains. It can vary significantly, but generally, molecules have more mass than a single atom. Therefore, a molecule has greater inertia compared to a single atom.
c) A one-rupee coin: A one-rupee coin typically has a mass greater than that of a molecule. It is composed of metal and has a significant size compared to atoms or molecules. Thus, a one-rupee coin has greater inertia than both a single atom and a molecule.
d) A cricket ball: A cricket ball is much larger and heavier than a one-rupee coin. It has a mass greater than all the previous options. Consequently, a cricket ball has the greatest inertia among the given options.
Therefore, the cricket ball (option d) has the greatest inertia.
Chapter doubts & questions for Unit - Lucent For GK 2025 is part of UPSC CSE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the UPSC CSE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for UPSC CSE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Unit - Lucent For GK in English & Hindi are available as part of UPSC CSE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC CSE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









