All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
History for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Economic & Social Life, Education And Religious Belief [8-12 Century] for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
Who of the following destroyed the Pala supremacy in Bengal?- a)Dhruva
- b)Vijayasena
- c)Govinda III
- d)Rajendra Chola I
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who of the following destroyed the Pala supremacy in Bengal?
a)
Dhruva
b)
Vijayasena
c)
Govinda III
d)
Rajendra Chola I
|
|
Aruna Singh answered |
Vijayasena destroyed the Pala supremacy in Bengal. The Pala dynasty was a royal dynasty that ruled over the region of Bengal in India from the 8th to the 12th centuries. Vijayasena was a king of the Sena dynasty, which was a rival of the Pala dynasty. He is credited with defeating the Pala king Mahipala I and establishing the Sena dynasty as the dominant power in Bengal. Rajendra Chola I was a ruler of the Chola dynasty in South India and was not involved in the destruction of the Pala dynasty in Bengal. Similarly, Dhruva and Govinda III were not involved in the destruction of the Pala dynasty in Bengal.
Which one of the following was the second Pratihara king to defeat Dharmapala and drive away his protege from Kanauj?- a)Rambhadra
- b)Vatsaraja
- c)Bhoja I
- d)Nagabhatta I
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following was the second Pratihara king to defeat Dharmapala and drive away his protege from Kanauj?
a)
Rambhadra
b)
Vatsaraja
c)
Bhoja I
d)
Nagabhatta I

|
Capstone Ias Learning answered |
The second Pratihara king who defeated Dharmapala and removed his protege from Kanauj was Nagabhatta II.
- Nagabhatta II was a significant ruler of the Pratihara dynasty.
- He played a crucial role in strengthening the dynasty's power.
- His victory over Dharmapala marked an important event in the history of North India.
Therefore, Correct Answer - Option D
When Mahmud of Ghazni attacked Somnath, the Chalukya or Solanki ruler of Gujarat was- a)Kumarpala
- b)Somesvara
- c)Bhima
- d)Jayasimha Siddharaja
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When Mahmud of Ghazni attacked Somnath, the Chalukya or Solanki ruler of Gujarat was
a)
Kumarpala
b)
Somesvara
c)
Bhima
d)
Jayasimha Siddharaja
|
|
Saranya Gupta answered |
Historical Context of Mahmud of Ghazni's Invasion
Mahmud of Ghazni, a prominent ruler of the Ghaznavid Empire, is well-known for his invasions of India in the early 11th century. One of his most famous attacks was on the temple of Somnath in Gujarat, which occurred in 1025 CE.
The Ruler of Gujarat during the Attack
At the time of Mahmud's invasion, the Chalukya or Solanki ruler of Gujarat was Bhima I. He was a significant figure known for his efforts to consolidate power and defend his territory against external threats.
Why Bhima I?
- Chronological Accuracy:
- Bhima I ruled from approximately 1022 to 1064 CE, making him the contemporary ruler during Mahmud's attack in 1025 CE.
- Historical Accounts:
- Various historical texts, including accounts from travelers and historians of that era, confirm Bhima I's reign coinciding with this pivotal event.
- Defense and Resistance:
- Bhima I is noted for his attempts to protect his kingdom and the important religious site of Somnath from invaders.
Conclusion
The significance of this event lies not only in the military confrontation but also in the cultural and religious implications for the region. Bhima I's reign marked a critical point in the resistance against invasions, shaping the future of the Gujarat region and its historical narrative. Thus, the correct answer to the question about the ruler of Gujarat during Mahmud of Ghazni's attack on Somnath is indeed option 'C', Bhima I.
Mahmud of Ghazni, a prominent ruler of the Ghaznavid Empire, is well-known for his invasions of India in the early 11th century. One of his most famous attacks was on the temple of Somnath in Gujarat, which occurred in 1025 CE.
The Ruler of Gujarat during the Attack
At the time of Mahmud's invasion, the Chalukya or Solanki ruler of Gujarat was Bhima I. He was a significant figure known for his efforts to consolidate power and defend his territory against external threats.
Why Bhima I?
- Chronological Accuracy:
- Bhima I ruled from approximately 1022 to 1064 CE, making him the contemporary ruler during Mahmud's attack in 1025 CE.
- Historical Accounts:
- Various historical texts, including accounts from travelers and historians of that era, confirm Bhima I's reign coinciding with this pivotal event.
- Defense and Resistance:
- Bhima I is noted for his attempts to protect his kingdom and the important religious site of Somnath from invaders.
Conclusion
The significance of this event lies not only in the military confrontation but also in the cultural and religious implications for the region. Bhima I's reign marked a critical point in the resistance against invasions, shaping the future of the Gujarat region and its historical narrative. Thus, the correct answer to the question about the ruler of Gujarat during Mahmud of Ghazni's attack on Somnath is indeed option 'C', Bhima I.
Whose kingdom was visited by Al-Masudi, an Arab traveller of the early 10th century A.D.?- a)Indra-III
- b)Dharmapala
- c)Mihira Bhoja
- d)Lakshmana Sena
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Whose kingdom was visited by Al-Masudi, an Arab traveller of the early 10th century A.D.?
a)
Indra-III
b)
Dharmapala
c)
Mihira Bhoja
d)
Lakshmana Sena
|
|
Ravi Sharma answered |
A is the correct option.The Arab traveller, al Masudi, visited Kannauj in the early tenth century and wrote that "the king of Kannauj was the natural enemy of the king of the Deccan : that he kept a large army and was surrounded by smaller kings always ready to go to war."
What was the name of the Pratihara king who was defeated by Dhruva II of the Rashtrakuta dynasty?- a)Mihira Bhoja
- b)Mahipala
- c)Nagabhatta II
- d)Vijayapala
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What was the name of the Pratihara king who was defeated by Dhruva II of the Rashtrakuta dynasty?
a)
Mihira Bhoja
b)
Mahipala
c)
Nagabhatta II
d)
Vijayapala
|
|
Diya Singh answered |
King Mahipala of the Pratihara dynasty was defeated by Dhruva II of the Rashtrakuta dynasty. The defeat of Mahipala marked the end of the Pratihara dynasty's dominance in North India.
Background:
- The Pratihara dynasty was a Rajput clan that ruled much of North India from the 6th to the 11th century.
- The Rashtrakuta dynasty was a royal Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of India from the 6th to the 10th century.
The Battle:
- The battle between the two kingdoms took place in the early 9th century.
- Dhruva II, the ruler of the Rashtrakuta dynasty, launched an attack on the Pratihara kingdom.
- Mahipala, the Pratihara king, was defeated in this battle.
- After this defeat, the Rashtrakuta dynasty became the dominant power in North India.
Impact:
- The defeat of Mahipala marked the end of the Pratihara dynasty's dominance in North India.
- The Rashtrakuta dynasty continued to expand its territory and influence in North India.
- The defeat of the Pratihara dynasty also paved the way for the emergence of other regional powers in North India.
Conclusion:
The defeat of Mahipala by Dhruva II was a significant event in the history of North India. It marked the end of the Pratihara dynasty's dominance and the rise of the Rashtrakuta dynasty as the dominant power in the region.
Background:
- The Pratihara dynasty was a Rajput clan that ruled much of North India from the 6th to the 11th century.
- The Rashtrakuta dynasty was a royal Indian dynasty that ruled large parts of India from the 6th to the 10th century.
The Battle:
- The battle between the two kingdoms took place in the early 9th century.
- Dhruva II, the ruler of the Rashtrakuta dynasty, launched an attack on the Pratihara kingdom.
- Mahipala, the Pratihara king, was defeated in this battle.
- After this defeat, the Rashtrakuta dynasty became the dominant power in North India.
Impact:
- The defeat of Mahipala marked the end of the Pratihara dynasty's dominance in North India.
- The Rashtrakuta dynasty continued to expand its territory and influence in North India.
- The defeat of the Pratihara dynasty also paved the way for the emergence of other regional powers in North India.
Conclusion:
The defeat of Mahipala by Dhruva II was a significant event in the history of North India. It marked the end of the Pratihara dynasty's dominance and the rise of the Rashtrakuta dynasty as the dominant power in the region.
Which one of the following was the first to wrest the control of Kanauj from Dharmapala?- a)Pratihara ruler Vatsaraja
- b)Rashtrakuta ruler Govinda III
- c)Rashtrakuta king Dhurva
- d)Pratihara king Nagabhatta III
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following was the first to wrest the control of Kanauj from Dharmapala?
a)
Pratihara ruler Vatsaraja
b)
Rashtrakuta ruler Govinda III
c)
Rashtrakuta king Dhurva
d)
Pratihara king Nagabhatta III
|
|
Ravi Sharma answered |
A is the correct option. Undiyejeral was called “Imayavaramban”, he who had the Himalayas as his boundary'. Lord Venkateswara(Maha Vishnu) is the presiding deity of Tirumala Venkateswara Temple located in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, India. Eripatti, Land, revenue from which was set apart for the maintenance of the village tank.
Where was the capital of Hindu Shahi kingdom located at the time of Mahmud’s attack?- a)Udabhanda or Und
- b)Attock
- c)Kabul
- d)Peshawar
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Where was the capital of Hindu Shahi kingdom located at the time of Mahmud’s attack?
a)
Udabhanda or Und
b)
Attock
c)
Kabul
d)
Peshawar
|
|
Aarya Nambiar answered |
Capital of the Hindu Shahi Kingdom
The Hindu Shahi kingdom, which thrived in the North-Western region of the Indian subcontinent, had its capital located at Udabhanda, also known as Uddiyana. This location was significant during the time of Mahmud of Ghazni's attacks in the early 11th century.
Geographical Significance
- Udabhanda was strategically situated near the ancient trade routes that linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent.
- Its proximity to major rivers and fertile lands made it a thriving center of commerce and culture.
Historical Context
- The Hindu Shahi dynasty ruled over parts of present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, holding power against various invasions.
- Mahmud of Ghazni, an invader from the region of modern-day Afghanistan, targeted the Hindu Shahi kingdom for its wealth and strategic importance.
Mahmud’s Attacks
- Mahmud launched multiple raids into the Indian subcontinent, with Udabhanda being one of the key targets due to its status as the capital.
- His attacks were not only military in nature but also aimed at looting the rich temples and resources of the Hindu Shahi domain.
Conclusion
In summary, the capital of the Hindu Shahi kingdom at the time of Mahmud's attack was Udabhanda. This location played a crucial role in the historical dynamics of power during the turbulent times of the early medieval period in South Asia.
The Hindu Shahi kingdom, which thrived in the North-Western region of the Indian subcontinent, had its capital located at Udabhanda, also known as Uddiyana. This location was significant during the time of Mahmud of Ghazni's attacks in the early 11th century.
Geographical Significance
- Udabhanda was strategically situated near the ancient trade routes that linked Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent.
- Its proximity to major rivers and fertile lands made it a thriving center of commerce and culture.
Historical Context
- The Hindu Shahi dynasty ruled over parts of present-day Pakistan and Afghanistan, holding power against various invasions.
- Mahmud of Ghazni, an invader from the region of modern-day Afghanistan, targeted the Hindu Shahi kingdom for its wealth and strategic importance.
Mahmud’s Attacks
- Mahmud launched multiple raids into the Indian subcontinent, with Udabhanda being one of the key targets due to its status as the capital.
- His attacks were not only military in nature but also aimed at looting the rich temples and resources of the Hindu Shahi domain.
Conclusion
In summary, the capital of the Hindu Shahi kingdom at the time of Mahmud's attack was Udabhanda. This location played a crucial role in the historical dynamics of power during the turbulent times of the early medieval period in South Asia.
Which of the following was not one of the three Chalukya feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani when it split up towards the end of the twelfth century?- a)Yadavas of Devagiri
- b)Hoyasalas of Dorasamudra
- c)Kakatiyas of Warangal
- d)Pandyas of Madurai
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following was not one of the three Chalukya feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani when it split up towards the end of the twelfth century?
a)
Yadavas of Devagiri
b)
Hoyasalas of Dorasamudra
c)
Kakatiyas of Warangal
d)
Pandyas of Madurai
|
|
Simran Mehta answered |
Explanation:
The Chalukya dynasty was a powerful dynasty that ruled over a large part of southern and central India from the 6th century to the 12th century. Towards the end of the 12th century, the Chalukya empire of Kalyani split up into three feudatories, each ruled by a different dynasty.
Feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani:
1. Yadavas of Devagiri: The Yadavas of Devagiri, also known as the Seuna dynasty, were one of the feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani. They ruled over the region of present-day Maharashtra and parts of Madhya Pradesh. The Yadavas were known for their patronage of arts and literature.
2. Hoysalas of Dorasamudra: The Hoysalas of Dorasamudra, also known as the Hoysala dynasty, were another feudatory who shared the empire of Kalyani. They ruled over the region of present-day Karnataka. The Hoysalas were known for their architectural prowess, and their temples and sculptures are considered to be masterpieces of Indian art.
3. Kakatiyas of Warangal: The Kakatiyas of Warangal, also known as the Kakatiya dynasty, were the third feudatory who shared the empire of Kalyani. They ruled over the region of present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. The Kakatiyas were known for their military strength and architectural achievements, most notably the famous Warangal Fort and the Thousand Pillar Temple.
Pandyas of Madurai:
The Pandyas of Madurai, also known as the Pandyan dynasty, were not one of the three feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani. The Pandyas were a Tamil dynasty that ruled over the region of present-day Tamil Nadu. They had a long and illustrious history, with their rule often marked by trade and cultural exchanges with the Roman Empire and Southeast Asia.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D - Pandyas of Madurai. They were not one of the three Chalukya feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani when it split up towards the end of the twelfth century.
The Chalukya dynasty was a powerful dynasty that ruled over a large part of southern and central India from the 6th century to the 12th century. Towards the end of the 12th century, the Chalukya empire of Kalyani split up into three feudatories, each ruled by a different dynasty.
Feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani:
1. Yadavas of Devagiri: The Yadavas of Devagiri, also known as the Seuna dynasty, were one of the feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani. They ruled over the region of present-day Maharashtra and parts of Madhya Pradesh. The Yadavas were known for their patronage of arts and literature.
2. Hoysalas of Dorasamudra: The Hoysalas of Dorasamudra, also known as the Hoysala dynasty, were another feudatory who shared the empire of Kalyani. They ruled over the region of present-day Karnataka. The Hoysalas were known for their architectural prowess, and their temples and sculptures are considered to be masterpieces of Indian art.
3. Kakatiyas of Warangal: The Kakatiyas of Warangal, also known as the Kakatiya dynasty, were the third feudatory who shared the empire of Kalyani. They ruled over the region of present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. The Kakatiyas were known for their military strength and architectural achievements, most notably the famous Warangal Fort and the Thousand Pillar Temple.
Pandyas of Madurai:
The Pandyas of Madurai, also known as the Pandyan dynasty, were not one of the three feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani. The Pandyas were a Tamil dynasty that ruled over the region of present-day Tamil Nadu. They had a long and illustrious history, with their rule often marked by trade and cultural exchanges with the Roman Empire and Southeast Asia.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D - Pandyas of Madurai. They were not one of the three Chalukya feudatories who shared the empire of Kalyani when it split up towards the end of the twelfth century.
Match the early medieval Indian rulers with their ruling dynasties:
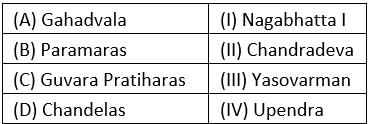
- a)(A-I) (B-II) (C-III) (D-IV)
- b)(A-II) (B-IV) (C-I) (D-III)
- c)(A-IV) (B-I) (C-II) (D-III)
- d)(A-III) (B-II) (C-I) (D-IV)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the early medieval Indian rulers with their ruling dynasties:


a)
(A-I) (B-II) (C-III) (D-IV)
b)
(A-II) (B-IV) (C-I) (D-III)
c)
(A-IV) (B-I) (C-II) (D-III)
d)
(A-III) (B-II) (C-I) (D-IV)
|
|
Ravi Sharma answered |
a) Chandradeva, who belonged to the Rathore clan of Rajput warriors, established the Gahadavala dynasty. He was the founder of the Gahadwala dynasty at Kannauj.
b) The Paramara Dynasty was founded by a chief called Upendra (Krishanaraja) at the beginning of the 9th century. The capital of Paramaras initially was Ujjain which later was replaced by Dhara. They were able to rule till 1305 when Malwa was conquered finally by Alauddin Khilji.
c) The Gurjara Pratihara dynasty (or Pratihara Dynasty) was founded by Nagabhata I who was the ruler of the kingdom of Avanti between 730-760 AD. His capital was Ujjain. He defeated an invasion by the Arabs from Sindh and captured Kathiawar, Malwa, Gujarat, and many parts of Rajputana.
d) The Chandelas initially ruled as feudatories of the Gurjara-Pratiharas of Kanyakubja (Kannauj). The 10th century Chandela ruler Yashovarman became practically independent, although he continued to acknowledge the Pratihara suzerainty. By the time of his successor Dhanga, the Chandelas had become a sovereign power.
b) The Paramara Dynasty was founded by a chief called Upendra (Krishanaraja) at the beginning of the 9th century. The capital of Paramaras initially was Ujjain which later was replaced by Dhara. They were able to rule till 1305 when Malwa was conquered finally by Alauddin Khilji.
c) The Gurjara Pratihara dynasty (or Pratihara Dynasty) was founded by Nagabhata I who was the ruler of the kingdom of Avanti between 730-760 AD. His capital was Ujjain. He defeated an invasion by the Arabs from Sindh and captured Kathiawar, Malwa, Gujarat, and many parts of Rajputana.
d) The Chandelas initially ruled as feudatories of the Gurjara-Pratiharas of Kanyakubja (Kannauj). The 10th century Chandela ruler Yashovarman became practically independent, although he continued to acknowledge the Pratihara suzerainty. By the time of his successor Dhanga, the Chandelas had become a sovereign power.
Chapter doubts & questions for Economic & Social Life, Education And Religious Belief [8-12 Century] - History for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Economic & Social Life, Education And Religious Belief [8-12 Century] - History for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
History for State PSC Exams
125 videos|773 docs|270 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










