All Exams >
Commerce >
Online MCQ Tests for Commerce >
All Questions
All questions of Part C - Introductory Microeconomics for Commerce Exam
Calculate Purchase on Investment. The information is Opening balance of Investment – Rs. 2,50,000, closing balance Investment – Rs. 5,00,000, Sale – Rs.1,37,500, Profit on sale – Rs.12,500.- a)Rs. 3,75,000
- b)Rs. 2,75,000
- c)Rs. 3,50,000
- d)Rs. 2,50,000
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate Purchase on Investment. The information is Opening balance of Investment – Rs. 2,50,000, closing balance Investment – Rs. 5,00,000, Sale – Rs.1,37,500, Profit on sale – Rs.12,500.
a)
Rs. 3,75,000
b)
Rs. 2,75,000
c)
Rs. 3,50,000
d)
Rs. 2,50,000

|
Rithika Khanna answered |
Purchase of investment during the year Rs.3,75,000 i.e. 5,00,000 + 1,37,500 – 2,50,000 – 12,500 = 3,75,000
What is the other name for opportunity cost in economics- a)Total Cost
- b)Marginal cost
- c)Economic cost
- d)Economic problem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the other name for opportunity cost in economics
a)
Total Cost
b)
Marginal cost
c)
Economic cost
d)
Economic problem
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Economic cost is the combination of losses of any goods that have a value attached to them by any one individual. Economic cost is used mainly by economists as means to compare the prudence of one course of action with that of another.
An economy always produces on, but not inside a PPC.
- a)True
- b)False
- c)Occasionally
- d)Can’t say
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An economy always produces on, but not inside a PPC.
a)
True
b)
False
c)
Occasionally
d)
Can’t say
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
An economy does not always on a ppc . when an economy produces on ppc it mean there is no unemployment and all the resources are fully and being used efficiently but practically these 2 conditions may not apply . if there is unemployment or inefficent use of resources an ecnmy will opreate inside the ppc therefor the above given statement is refuted .
A budget constraint line is a result of?- a)Market price of commodity X
- b)Market price of commodity Y
- c)Income of the consumer
- d)All of above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A budget constraint line is a result of?
a)
Market price of commodity X
b)
Market price of commodity Y
c)
Income of the consumer
d)
All of above
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
A budget constraint represents all the combinations of goods and services that a consumer may purchase given current prices within his or her given income. Consumer theory uses the concepts of a budget constraint and a preference map to analyze consumer choices.
One factor that causes a leftward shift of the demand curve out of the following is- a) Rise in income
- b) Fall in the price of substitute goods
- c) Rise in the price of complementary goods
- d) Fall in income
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One factor that causes a leftward shift of the demand curve out of the following is
a)
Rise in income
b)
Fall in the price of substitute goods
c)
Rise in the price of complementary goods
d)
Fall in income
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
A leftward shift in the demand curve indicates a decrease in demand because consumers are purchasing fewer products for the same price.
The want satisfying power of a commodity is known as:- a)Utility
- b)Consumption
- c)Supply
- d)Demand
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The want satisfying power of a commodity is known as:
a)
Utility
b)
Consumption
c)
Supply
d)
Demand
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
The want satisfying power of a commodity is called utility. It is a quality possessed by a commodity or service to satisfy human wants. Utility can also be defined as value-in-use of a commodity because the satisfaction which we get from the consumption of a commodity is its value-in-use.
A tutor earns Rs. 1000 per hour teaching economics. If he joins a school, he would earn on an average Rs. 300 per hour. What is the opportunity cost of teaching in school?- a) Rs. 300
- b)Rs. 700
- c)Rs. 1000
- d)Rs. 1300
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A tutor earns Rs. 1000 per hour teaching economics. If he joins a school, he would earn on an average Rs. 300 per hour. What is the opportunity cost of teaching in school?
a)
Rs. 300
b)
Rs. 700
c)
Rs. 1000
d)
Rs. 1300
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Opportunity cost is the profit lost when one alternative is selected over another. The concept is useful simply as a reminder to examine all reasonable alternatives before making a decision.
The basic economic activities put in order are- a)Consumption, exchange and production
- b) Production, Exchange and consumption
- c) Production, consumption and exchange
- d) Exchange, production and consumption
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic economic activities put in order are
a)
Consumption, exchange and production
b)
Production, Exchange and consumption
c)
Production, consumption and exchange
d)
Exchange, production and consumption
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Production, consumption and capital formation are called the basic economic activities of an economy. Scarce resources are used in the production of goods and services with the objective of satisfying our needs and wants.
A firm can sell as much as it wants at the market price. The situation is related to?- a)Monopoly
- b)Monopolistic competition
- c)Perfect competition
- d)Oligopoly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A firm can sell as much as it wants at the market price. The situation is related to?
a)
Monopoly
b)
Monopolistic competition
c)
Perfect competition
d)
Oligopoly

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which the following criteria are met:
- All firms sell an identical product (the product is a "commodity" or "homogeneous").
- All firms are price takers (they cannot influence the market price of their product). Market share has no influence on prices.
The subject of a Microeconomic study is- a) Individual economy
- b) Mixed economies
- c) Individual economic unit
- d) Planned economies
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The subject of a Microeconomic study is
a)
Individual economy
b)
Mixed economies
c)
Individual economic unit
d)
Planned economies

|
Arjun Saini answered |
Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, _________?- a)Additional consumption always yields extra utility
- b)Additional consumption leads to lower average total utility
- c)Additional consumption always yields negative utility
- d)After a point any addition in the consumption causes a reduction in total utility.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility, _________?
a)
Additional consumption always yields extra utility
b)
Additional consumption leads to lower average total utility
c)
Additional consumption always yields negative utility
d)
After a point any addition in the consumption causes a reduction in total utility.
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
According to the Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, marginal utility of a good diminishes as an individual consumes more units of a good. In other words, as a consumer takes more units of a good, the extra utility or satisfaction that he derives from an extra unit of the good goes on falling.
It should be carefully noted that is the marginal utility and not the total utility than declines with the increase in the consumption of a good. The law of diminishing marginal utility means that the total utility increases but at a decreasing rate.
When AR=Rs. 10 and AC=Rs. 8, the firm makes?- a)Gross profit
- b)Supernormal profit
- c)Normal profit
- d)Net profit
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When AR=Rs. 10 and AC=Rs. 8, the firm makes?
a)
Gross profit
b)
Supernormal profit
c)
Normal profit
d)
Net profit
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
Supernormal profit is defined as extra profit above that level of normal profit.
Here the firm earns profit of Rs. 2 over the cost occurred.
Here the firm earns profit of Rs. 2 over the cost occurred.
A PPC can shift its position if and only if- a) If technology improves
- b) If resources remain constant
- c) None of these
- d) If technology remains constant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A PPC can shift its position if and only if
a)
If technology improves
b)
If resources remain constant
c)
None of these
d)
If technology remains constant

|
Rhea Choudhary answered |
The most common reason a PPF would shift is because of a change in technology, or because of economic growth.
All unattainable combinations will lie- a)Under the PPC only
- b)On and under the PPC
- c)On the PPC only
- d) Above the PPC only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
All unattainable combinations will lie
a)
Under the PPC only
b)
On and under the PPC
c)
On the PPC only
d)
Above the PPC only

|
Muskaan Mishra answered |
Points outside the PPF are unattainable production points given current resources and technologies. It is impossible for an economy to produce outside its PPF. The PPF can change, however, with changes in resources or technology.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Indifference curve represents?
- A:
Four commodities
- B:
Less than two commodities
- C:
Only two commodities
- D:
More than two commodities
The answer is C.
Indifference curve represents?
Four commodities
Less than two commodities
Only two commodities
More than two commodities
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
An indifference curve is a graph showing combination of two goods that give the consumer equal satisfaction and utility. Each point on an indifference curve indicates that a consumer is indifferent between the two and all points give him the same utility.
____________ is an ideal market?- a)Monopolistic competition
- b)Oligopoly
- c)Perfect competition
- d)Monopoly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
____________ is an ideal market?
a)
Monopolistic competition
b)
Oligopoly
c)
Perfect competition
d)
Monopoly
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
Pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which the following criteria are met: All firms sell an identical product (the product is a "commodity" or "homogeneous"). All firms are price takers (they cannot influence the market price of their product). Market share has no influence on prices.
Which of the following curve has a negative slope and cannot interest each other?- a)Isoquants
- b)Demand and supply curves
- c)Indifference curves
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following curve has a negative slope and cannot interest each other?
a)
Isoquants
b)
Demand and supply curves
c)
Indifference curves
d)
None of above
|
|
Vikas Kapoor answered |
An indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is indifferent. Along the curve, the consumer has no preference for either combination of goods because both goods provide the same level of utility.
Each indifference curve is convex to the origin, and no two indifference curves ever intersect.
Each indifference curve is convex to the origin, and no two indifference curves ever intersect.
The coefficient of price elasticity of demand is always- a)Zero
- b)Undefined
- c)Positive
- d)Negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The coefficient of price elasticity of demand is always
a)
Zero
b)
Undefined
c)
Positive
d)
Negative
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
This ratio is often called the elasticity c
Microeconomics studies the behaviour of - a)Individual economic unit
- b) Mixed economies
- c) Individual economy
- d)Planned economies
Correct answer is 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Microeconomics studies the behaviour of
a)
Individual economic unit
b)
Mixed economies
c)
Individual economy
d)
Planned economies
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
I. The term Micro Economics is derived from the Greek work “Mikros” which means “Small”. Micro economics gives a detailed analysis of one part of the economy or society. It studies the behaviour of individual units of the economy, such as households, firms, industries and markets.ii. Micro economics is concerned with the study of behaviour of individual element(s) of an economy, whereas, macro economies concerned with the study of behaviours of an economy as whole.iii. Micro-economics gives a microscopic picture of the economy. The activities of numerous economic units and their inter-relationship are studied and analysed minutely through this method.
Opportunity cost is the- a)Next best alternative sacrificed
- b)Next best alternative chosen
- c)Next best alternative available
- d)Next best alternative produced
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Opportunity cost is the
a)
Next best alternative sacrificed
b)
Next best alternative chosen
c)
Next best alternative available
d)
Next best alternative produced

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
“Opportunity cost” of a resource, means the value of the next-highest-valued alternative use of that resource.
E.g. you spend time and money going to a movie, you cannot spend that time at home playing video games, and you cannot spend the money on something else. If your next-best alternative to seeing the movie is playing video games at home, then the opportunity cost of seeing the movie is the money spent plus the pleasure you forgo by not playing videos game at home.
E.g. you spend time and money going to a movie, you cannot spend that time at home playing video games, and you cannot spend the money on something else. If your next-best alternative to seeing the movie is playing video games at home, then the opportunity cost of seeing the movie is the money spent plus the pleasure you forgo by not playing videos game at home.
In the long run TPP changes with the change in which of the following factors- a)Fixed factors
- b)Variable factors
- c)Economic cost
- d)All the factors
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the long run TPP changes with the change in which of the following factors
a)
Fixed factors
b)
Variable factors
c)
Economic cost
d)
All the factors
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
In the long run TPP changes with the change in all the factors is the right option because total product can be change in long run production function. After change every situation because in long run production more time should be taken by performer.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - Theory of Consumer Behaviour of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?
- A:
It helps consumers to make choices.
- B:
Utility is always measurable.
- C:
It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
- D:
It is purely a subjective entity.
The answer is B.
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 2 - Theory of Consumer Behaviour of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?
It helps consumers to make choices.
Utility is always measurable.
It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
It is purely a subjective entity.

|
Priyanka Ravichandran answered |
B is the correct answer because utility is nothing but human satisfaction so it can't be measured
The positive economic analysis deals with the variables- a) As they should be
- b) As they are
- c) As they are expected
- d) As they seem to be
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The positive economic analysis deals with the variables
a)
As they should be
b)
As they are
c)
As they are expected
d)
As they seem to be
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Positive economics is the branch of economics that concerns the description and explanation of economic phenomena. It focuses on facts and cause-and-effect behavioral relationships and includes the development and testing of economics theories.
Positive economics states- a)Central problems of an economy be
- b)What will
- c)What is
- d)What is supposed to be
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Positive economics states
a)
Central problems of an economy be
b)
What will
c)
What is
d)
What is supposed to be
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Positive economics is objective and fact based, while normative economics is subjective and value based. Positive economic statements must be able to be tested and proved or disproved. Normative economic statements are opinion based, so they cannot be proved or disproved.
At what point does total utility starts diminishing?- a)When marginal utility is negative
- b)When marginal utility remains constant
- c)When marginal utility is increasing
- d)When marginal utility is postive
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
At what point does total utility starts diminishing?
a)
When marginal utility is negative
b)
When marginal utility remains constant
c)
When marginal utility is increasing
d)
When marginal utility is postive

|
Arya Reddy answered |
MU is addition to TU when an MU becomes -ive TU falls.
Which central problem explains ‘who gets more and who gets less’? - a)Scarcity of resources
- b) What to produce
- c)For whom to produce
- d)How to produce
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which central problem explains ‘who gets more and who gets less’?
a)
Scarcity of resources
b)
What to produce
c)
For whom to produce
d)
How to produce

|
Rahul Chaudhary answered |
This problem refers to selection of the category of people who will ultimately consume the goods, i.e. whether to produce goods for more poor and less rich or more rich and less poor. Since resources are scarce in every economy, no society can satisfy all the wants of its people. Thus, a problem of choice arises.
Utility is measured in terms of?- a)Centimeter
- b)Seconds
- c)Gram
- d)Utils
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Utility is measured in terms of?
a)
Centimeter
b)
Seconds
c)
Gram
d)
Utils
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
It can be seen that utility is measured in numbers that are purely cardinal, rather than ordinal. The numbers used to measure utility (often in a unit called the "util") is useful only for comparison.
Total utility curve:- a)First falls and then rises
- b)Always falls
- c)Always rises
- d)First rises at an increasing rate, then rises at a decreasing rate and falls after reaching its maximum.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Total utility curve:
a)
First falls and then rises
b)
Always falls
c)
Always rises
d)
First rises at an increasing rate, then rises at a decreasing rate and falls after reaching its maximum.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
MU decrease then TU increases at decreasing rate till MU becomes zero. when MU zero then TU maximum and when MU gets negative TU starts fall
Which of the following utility approach is based on the theory of Alfred Marshall?- a)None of these
- b) Ordinal utility approach
- c) Independent variable approach
- d) Cardinal utility approach
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following utility approach is based on the theory of Alfred Marshall?
a)
None of these
b)
Ordinal utility approach
c)
Independent variable approach
d)
Cardinal utility approach
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Alfred Marshall was the dominant figure in British economics from about 1890 until his death in 1924.His specialty was microeconomics—the study of individual markets and industries, as opposed to the study of the whole economy.
It was Alfred Marshall who first discussed the role played by the theory of utility in the theory of value. In Marshall's theory, the concept of utility is cardinal.
It was Alfred Marshall who first discussed the role played by the theory of utility in the theory of value. In Marshall's theory, the concept of utility is cardinal.
Does production takes place only on PPC?
- a) No
- b)Sometimes
- c)Yes
- d)Can’t say
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Does production takes place only on PPC?
a)
No
b)
Sometimes
c)
Yes
d)
Can’t say

|
Subham Roy answered |
When all resources are employed on ideal situation, production can take place on PPC
_____________ is defined as the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay for a product and what he actually pays?- a)Consumer surplus
- b)Price gap
- c)Consumer burden
- d)Optimum price
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
_____________ is defined as the difference between what the consumer is willing to pay for a product and what he actually pays?
a)
Consumer surplus
b)
Price gap
c)
Consumer burden
d)
Optimum price

|
Devansh Goyal answered |
The consumer surplus is the difference between the highest price a consumer is willing to pay and the actual market price of the good. The producer surplus is the difference between the market price and the lowest price a producer would be willing to accept. For producers, a surplus can be thought of as profit, because producers usually don't want to produce at a loss. The two together create an economic surplus.
Which of the following utility approach is based on the theory of Alfred Marshall?- a)Independent variable approach
- b)Cardinal utility approach
- c)Ordinal utility approach
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following utility approach is based on the theory of Alfred Marshall?
a)
Independent variable approach
b)
Cardinal utility approach
c)
Ordinal utility approach
d)
None of these
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The Cardinal Utility approach is propounded by neo-classical economists, who believe that utility is measurable, and the customer can express his satisfaction in cardinal or quantitative numbers, such as 1,2,3, and so on. Here, one Util is equivalent to one rupee and the utility of money remains constant.
The concept of marginal utility was developed by?- a)Paul Samuelson
- b)Alfred Marshall
- c)Hicks & Allen
- d)Robbins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The concept of marginal utility was developed by?
a)
Paul Samuelson
b)
Alfred Marshall
c)
Hicks & Allen
d)
Robbins
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
The concept of marginal utility grew out of attempts by economists to explain the determination of price. The term “marginal utility”, credited to the Austrian economist Friedrich von Wieser by Alfred Marshall, was a translation of Wieser's term “Grenznutzen” (border-use).
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 4 - Theory of Firm Under Perfect Competition of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinationsQ Condition for producer equilibrium is:- a)TC=TSC
- b)MC=MR
- c)TR=TVC
- d)None of above
Correct answer is 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 4 - Theory of Firm Under Perfect Competition of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q Condition for producer equilibrium is:
a)
TC=TSC
b)
MC=MR
c)
TR=TVC
d)
None of above

|
Puja Nambiar answered |
Condition for Producer Equilibrium
The producer equilibrium is a situation where a firm is maximizing its profits by producing a level of output where marginal cost (MC) is equal to marginal revenue (MR). In other words, the producer equilibrium is reached when a firm is producing at the point where it is making the highest possible economic profit.
The condition for producer equilibrium is as follows:
MC = MR
Explanation
Marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output. Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned by selling one more unit of output. In perfect competition, a firm is a price taker, meaning it cannot influence the market price of the product it sells. Therefore, the price of the product remains constant for the firm.
In perfect competition, the firm's marginal revenue (MR) is equal to the price of the product. Therefore, the condition for producer equilibrium can be rephrased as:
MC = P
where P is the price of the product.
If a firm produces at a level where MC is less than MR, it means that the firm can increase its profits by producing more units of output. Similarly, if a firm produces at a level where MC is greater than MR, it means that the firm can increase its profits by producing fewer units of output. So, the producer equilibrium is reached only when MC is equal to MR, where the firm is producing the level of output that maximizes its profits.
Conclusion
The condition for producer equilibrium is MC = MR, where a firm is producing the level of output that maximizes its profits. In perfect competition, where a firm is a price taker, the condition can be rephrased as MC = P.
The producer equilibrium is a situation where a firm is maximizing its profits by producing a level of output where marginal cost (MC) is equal to marginal revenue (MR). In other words, the producer equilibrium is reached when a firm is producing at the point where it is making the highest possible economic profit.
The condition for producer equilibrium is as follows:
MC = MR
Explanation
Marginal cost (MC) is the additional cost of producing one more unit of output. Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue earned by selling one more unit of output. In perfect competition, a firm is a price taker, meaning it cannot influence the market price of the product it sells. Therefore, the price of the product remains constant for the firm.
In perfect competition, the firm's marginal revenue (MR) is equal to the price of the product. Therefore, the condition for producer equilibrium can be rephrased as:
MC = P
where P is the price of the product.
If a firm produces at a level where MC is less than MR, it means that the firm can increase its profits by producing more units of output. Similarly, if a firm produces at a level where MC is greater than MR, it means that the firm can increase its profits by producing fewer units of output. So, the producer equilibrium is reached only when MC is equal to MR, where the firm is producing the level of output that maximizes its profits.
Conclusion
The condition for producer equilibrium is MC = MR, where a firm is producing the level of output that maximizes its profits. In perfect competition, where a firm is a price taker, the condition can be rephrased as MC = P.
Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?- a)Utility is always measurable.
- b) It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
- c) It helps consumers to make choices.
- d) It is purely a subjective entity.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding utility is not true?
a)
Utility is always measurable.
b)
It is a satisfying power of a commodity.
c)
It helps consumers to make choices.
d)
It is purely a subjective entity.
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
Utility is a subjective concept and varies from person to person, at different times and at different places. There cannot be a standardised measure for utility. Therefore, the point that utility always measurable is not true.
At what point does total utility starts diminishing?- a)When marginal utility remains constant
- b)When marginal utility is increasing
- c) When marginal utility is negative
- d)When marginal utility is negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
At what point does total utility starts diminishing?
a)
When marginal utility remains constant
b)
When marginal utility is increasing
c)
When marginal utility is negative
d)
When marginal utility is negative
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
The law of diminishing marginal utility is a law of economics stating that as a person in creases consumption of a products while keeping consumption of other product costant , there is a decline in the marginal utility that persob derives from consuming each additional unit of product.
Consumer’s surplus is also known as?- a)Buyer’s surplus
- b)Elasticity of demand
- c)Differential surplus
- d) Indifference surplus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consumer’s surplus is also known as?
a)
Buyer’s surplus
b)
Elasticity of demand
c)
Differential surplus
d)
Indifference surplus
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Consumer surplus is defined as the difference between the total amount that consumers are willing and able to pay for a good or service (indicated by the demand curve) and the total amount that they actually do pay (i.e. the market price) it is also known as buyer 's surplus.
The slope of price line throughout its length?- a)Remains the same
- b)Is equal on the other side of the mid points
- c)Differs from point to point
- d)None of above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The slope of price line throughout its length?
a)
Remains the same
b)
Is equal on the other side of the mid points
c)
Differs from point to point
d)
None of above
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
This is because in perfect competition , price line is a straight line. And the ratio (∆TR/∆Q )That is change in total revenue and change in output is constant.{MR=AR}So slope of a straight line is always constant.
Which of the following is the correct expression of Marginal Rate of Transformation?- a) 2Y for 1X
- b) 1:2
- c) 2:1
- d) 2Y
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the correct expression of Marginal Rate of Transformation?
a)
2Y for 1X
b)
1:2
c)
2:1
d)
2Y
|
|
Alok Mehta answered |
Marginal rate of transformation
The marginal rate of transformation (MRT) can be defined as how many units of good x have to stop being produced in order to produce an extra unit of good y, while keeping constant the use of production factors and the technology being used. It involves the relation between the production of different outputs, while maintaining constant the same level of production factors. It can be determined using the following formula:
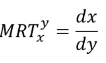
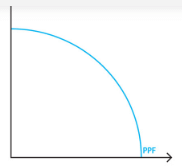
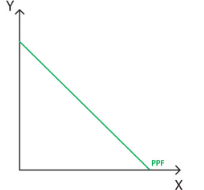
The MRT is related to the production possibility frontier (PPF). The slope of the curves shows how a reallocation of the production can end with a different bundle of production, using the same quantity of inputs. Two of the most commonly used PPFs are depicted in the adjacent figure.
In the first graph, the MRT will change along the curve.
The second graph, which portrays the case of perfect substitutes output, that is the slope has an angle of 45DEG with each axis and therefore we have MRT = 1. When considering different substitutes goods, the slope will be different and the MRT can be defined as a fraction, such as 1/2 ,1/3, and so on. For perfect substitutes, the MRT will remain constant.
Which of the following curve has a negative slope and cannot interest each other?- a)None of above
- b)Indifference curves
- c)Demand and supply curves
- d)Isoquants
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following curve has a negative slope and cannot interest each other?
a)
None of above
b)
Indifference curves
c)
Demand and supply curves
d)
Isoquants
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
IC slopes downward because as the consumer increases the consumption of one commodity, he has to give up certain units of other commodity in order to maintain the same level of satisfaction.
two indifference curves represent two different levels of satisfaction. If these indifference curves intersect each other, the intersection will represent same level of satisfaction, which is impossible.
Which of the following will have inelastic demand?- a)Fruits
- b)ice-cream
- c)petrol
- d)Medicine
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will have inelastic demand?
a)
Fruits
b)
ice-cream
c)
petrol
d)
Medicine

|
Arpita Nambiar answered |
Demand for medicine is in-elastic as it falls in category of a necessity good.
The basic factors of production are land, labour, capital and______ - a)Resources
- b)Machinery
- c)Investment
- d)Entrepreneurship
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The basic factors of production are land, labour, capital and______
a)
Resources
b)
Machinery
c)
Investment
d)
Entrepreneurship

|
Aditya Kumar The Best answered |
Factors of production is an economic term that describes the inputs that are used in the production of goods or services in order to make an economic profit. This include land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship.
When the total utility is increasing at an increasing rate, marginal utility is___________?- a)Increasing
- b)Constant
- c)Negative
- d)Decreasing
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the total utility is increasing at an increasing rate, marginal utility is___________?
a)
Increasing
b)
Constant
c)
Negative
d)
Decreasing
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
The correct option is D.
Total utility refers to the total satisfaction obtained from the consumption of all possible units of a commodity. Marginal utility is the additional utility derived from the consumption of one more unit of the given commodity. MU=TUn-TUn-1.So when TU is increasing at an increases this means utility derived from each unit is increasing. This means marginal utility is increasing.
One of the characteristics of economic resource is scarcity. Which is the other?- a)They have alternate uses
- b)They are available in limited quantity
- c)They are in abundance
- d)They are not marketable
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the characteristics of economic resource is scarcity. Which is the other?
a)
They have alternate uses
b)
They are available in limited quantity
c)
They are in abundance
d)
They are not marketable

|
Priyanka Ravichandran answered |
Economics is scracity because they have alternative uses... It is the important characteristics of economy
Under which market condition firms make only Normal Profit in the long run?- a)Oligopoly
- b)Monopoly
- c)Monopolistic competition
- d)Duopoly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Under which market condition firms make only Normal Profit in the long run?
a)
Oligopoly
b)
Monopoly
c)
Monopolistic competition
d)
Duopoly
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
In the long-run, the demand curve of a firm in a m... moreonopolistic competitive
Other name by which average revenue curve known:- a)Indifference curve
- b)Profit curve
- c)Average cost curve
- d)Demand curve
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Other name by which average revenue curve known:
a)
Indifference curve
b)
Profit curve
c)
Average cost curve
d)
Demand curve
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
Average revenue curve is often called the demand curve due to its representation of the product's demand in the market. Each point on the curve represents the price of the product in the market. Price determines the demand for a product, hence Average revenue curve is also demand curve.
Assuming it is a perfect competitive market.
Assuming it is a perfect competitive market.
Who gets how much in an economy is best described by which of the following central problems?
- a)What to produce
- b) For whom to produce
- c) How to produce
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Who gets how much in an economy is best described by which of the following central problems?
a)
What to produce
b)
For whom to produce
c)
How to produce
d)
None of these

|
Anuj Choudhury answered |
For whom to produce refers to selection of the category of people who will ultimately consume the goods, i.e. whether to produce goods for more poor and less rich or more rich and less poor. Since resources are scarce in every economy, no society can satisfy all the wants of its people.
Chapter doubts & questions for Part C - Introductory Microeconomics - Online MCQ Tests for Commerce 2025 is part of Commerce exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Commerce 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Part C - Introductory Microeconomics - Online MCQ Tests for Commerce in English & Hindi are available as part of Commerce exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup













