All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
Indian Economy for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Nature of Indian Economy for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
Consider the following statements regarding the sectors of Indian economy.
1. Agriculture provides direct employment to more than 50 % people of the country.
2. The service sector is the biggest contributor to India’s economy.
3. Manufacturing activities contribute more to Indian economy than the primary sector.
4. Mining comes under primary sector.
Which of the above given statements is/ are correct?
- a)1 and 2
- b)2 and 4
- c)2 ,3 and 4
- d)1 , 2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements regarding the sectors of Indian economy.
1. Agriculture provides direct employment to more than 50 % people of the country.
2. The service sector is the biggest contributor to India’s economy.
3. Manufacturing activities contribute more to Indian economy than the primary sector.
4. Mining comes under primary sector.
Which of the above given statements is/ are correct?
1. Agriculture provides direct employment to more than 50 % people of the country.
2. The service sector is the biggest contributor to India’s economy.
3. Manufacturing activities contribute more to Indian economy than the primary sector.
4. Mining comes under primary sector.
Which of the above given statements is/ are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 and 4
c)
2 ,3 and 4
d)
1 , 2 and 4
|
|
Sahil Khanna answered |
Correct Answer:- B (2,4)
Explanation: The economy is divided into three broad categories—agriculture (which includes broader activities such as mining, utilities, and construction), manufacturing, and services. Services has been, by far, the biggest contributor to GDP, accounting for over 68 percent in 2018.
The Primary sector of the economy includes any industry involved in the extraction and production of raw materials, such as farming, logging, hunting, fishing, and mining. The primary sector tends to make up a larger portion of the economy in developing countries than it does in developed countries.
Which of the following is not a feature of capitalism?
1. Limited role of the government in economic activities.
2. Freedom of competition
3. Efficiency, innovation and creativity
4. Classless society- a)2 and 3
- b)1 and 4
- c)0nly 3
- d)Only 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a feature of capitalism?
1. Limited role of the government in economic activities.
2. Freedom of competition
3. Efficiency, innovation and creativity
4. Classless society
1. Limited role of the government in economic activities.
2. Freedom of competition
3. Efficiency, innovation and creativity
4. Classless society
a)
2 and 3
b)
1 and 4
c)
0nly 3
d)
Only 4
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Achieving a classless society is a feature of command economy.
Arrange the following countries in an ascending order according to their HDI ranking -2019.
1. China
2. Sri Lanka
3. Bhutan
4. Pakistan
5. Myanmar
6. Nepal - a)6-5-4-3-2-1
- b)4-6-5-3-1-2
- c)4-5-3-6-2-1
- d)6-4-5-2-3-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following countries in an ascending order according to their HDI ranking -2019.
1. China
2. Sri Lanka
3. Bhutan
4. Pakistan
5. Myanmar
6. Nepal
1. China
2. Sri Lanka
3. Bhutan
4. Pakistan
5. Myanmar
6. Nepal
a)
6-5-4-3-2-1
b)
4-6-5-3-1-2
c)
4-5-3-6-2-1
d)
6-4-5-2-3-1
|
|
Nidhi Solanki answered |
Ascending order of countries of HDI ranking 2019 are as follows:
Pakistan(152 rank)-Nepal(147 rank)-Myanmar(145rank)-Bhutan(134rank)-China(85rank)-Sri Lanka(71 rank)
Pakistan(152 rank)-Nepal(147 rank)-Myanmar(145rank)-Bhutan(134rank)-China(85rank)-Sri Lanka(71 rank)
Which of the following is true with regard to food security?- a)Food security exists when government maintains buffer stock of grains for next five years.
- b)Government imposes ban on grains exports for maintaining sufficient stock.
- c)Government encourges to produce organic foods for better and secure health.
- d)Food security exists when all people, at all time have access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is true with regard to food security?
a)
Food security exists when government maintains buffer stock of grains for next five years.
b)
Government imposes ban on grains exports for maintaining sufficient stock.
c)
Government encourges to produce organic foods for better and secure health.
d)
Food security exists when all people, at all time have access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food.

|
Education Mature answered |
Correct option d hai toh mera test mai wrong kyu kiya....?
Which of the following is/are not included in the GDP?
1. Pensions
2. Scholarships
3. Subsidies
4. Remittances
Select the correct answer from the options given below:- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1, 2 and 4
- d)1, 2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not included in the GDP?
1. Pensions
2. Scholarships
3. Subsidies
4. Remittances
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
1. Pensions
2. Scholarships
3. Subsidies
4. Remittances
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1, 2 and 4
d)
1, 2, 3 and 4
|
|
Sandeep Iyer answered |
Transfer payments such as pensions, scholarships, subsidies etc are excluded from GDP calculations because there is no production of any goods or services in exchange of such payments. Remittances (Money sent home from emigrants working abroad) are also not included in the GDP. This is because, in GDP estimations, only those goods and services produced within a country are included.
Identify the incorrect statement/s
1. Capitalism allows private property
2. Communism allows for free market
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship
Options:
- a)Only 3
- b)2 and 4 only
- c)2 , 3 and 4
- d)Only 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement/s
1. Capitalism allows private property
2. Communism allows for free market
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship
Options:
1. Capitalism allows private property
2. Communism allows for free market
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship
Options:
a)
Only 3
b)
2 and 4 only
c)
2 , 3 and 4
d)
Only 4
|
|
Manoj Nair answered |
Incorrect Statements about Capitalism and Communism
Capitalism and communism are two different economic systems that have been widely debated and compared. They have different principles and objectives that affect the way businesses and individuals operate within the economy. The incorrect statements about capitalism and communism are:
2. Communism allows for free market
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship
Explanation:
1. Capitalism allows private property:
- Private property is the foundation of capitalism. In a capitalist economy, individuals have the right to own and control property, including businesses, factories, and land. This right to private property is protected by law and is essential for the functioning of a market economy.
2. Communism allows for free market:
- This statement is incorrect. Communism is a type of economic system where the government owns and controls all property and resources. There is no private ownership, and the government decides what gets produced and how it is distributed. There is no free market in communism.
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly:
- This statement is incorrect. Capitalism is based on the principle of individualism, where the pursuit of self-interest drives economic activity. While capitalism can generate wealth, it does not guarantee that this wealth will be distributed evenly. In fact, capitalism often results in income inequality, where a small percentage of the population holds a significant portion of the wealth.
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship:
- This statement is incorrect. In communism, the government controls all economic activity, including entrepreneurship. There is no incentive for individuals to start their own businesses or innovate since the government controls all resources and production.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while capitalism and communism are two different economic systems, they both have their strengths and weaknesses. It is essential to understand the fundamental principles of both systems to make informed decisions about economic policies and strategies.
Capitalism and communism are two different economic systems that have been widely debated and compared. They have different principles and objectives that affect the way businesses and individuals operate within the economy. The incorrect statements about capitalism and communism are:
2. Communism allows for free market
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship
Explanation:
1. Capitalism allows private property:
- Private property is the foundation of capitalism. In a capitalist economy, individuals have the right to own and control property, including businesses, factories, and land. This right to private property is protected by law and is essential for the functioning of a market economy.
2. Communism allows for free market:
- This statement is incorrect. Communism is a type of economic system where the government owns and controls all property and resources. There is no private ownership, and the government decides what gets produced and how it is distributed. There is no free market in communism.
3. Capitalism, in theory, spreads wealth evenly:
- This statement is incorrect. Capitalism is based on the principle of individualism, where the pursuit of self-interest drives economic activity. While capitalism can generate wealth, it does not guarantee that this wealth will be distributed evenly. In fact, capitalism often results in income inequality, where a small percentage of the population holds a significant portion of the wealth.
4. Communism encourages entrepreneurship:
- This statement is incorrect. In communism, the government controls all economic activity, including entrepreneurship. There is no incentive for individuals to start their own businesses or innovate since the government controls all resources and production.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, while capitalism and communism are two different economic systems, they both have their strengths and weaknesses. It is essential to understand the fundamental principles of both systems to make informed decisions about economic policies and strategies.
Arrange the following countries in a descending order according to their GDP
1. India
2. U.S.A
3. China
4. Germany
5. Japan
- a)2-3-4-5-1
- b)2-3-5-4-1
- c)1-4-5-3-2
- d)2-5-2-3-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Arrange the following countries in a descending order according to their GDP
1. India
2. U.S.A
3. China
4. Germany
5. Japan
1. India
2. U.S.A
3. China
4. Germany
5. Japan
a)
2-3-4-5-1
b)
2-3-5-4-1
c)
1-4-5-3-2
d)
2-5-2-3-1
|
|
Devansh Yadav answered |
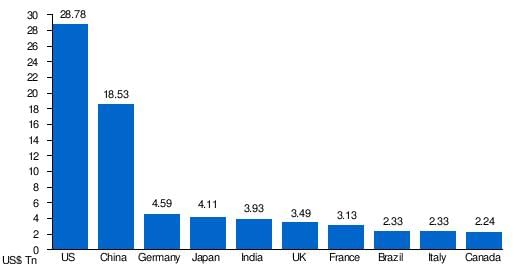
The top 5 biggest GDPs in the world are USA, China, Germany,Japan, India

Which method is usually used for calculating the purchasing power parity by the IMF?
- a)Gross Domestic Product
- b)Net domestic product
- c)Net National Product
- d)Gross National Product
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which method is usually used for calculating the purchasing power parity by the IMF?
a)
Gross Domestic Product
b)
Net domestic product
c)
Net National Product
d)
Gross National Product
|
|
Deepa Iyer answered |
- GNP is the 'national income' according to which the IMF ranks the nations of the world in terms of the volumes—at purchasing power parity (PPP).
- India is ranked as the 3rd largest economy of the world (after China and the USA), while as per the nominal/ prevailing exchange rate of the rupee, India is the 7th largest economy (IMF, April 2016). Now such comparisons are done using the GDP, too.
Consider the following statements.
1. The concept of economic growth is quantitative whereas economic development is qualitative.
2. The concept of inclusive growth is associated with economic development.
Identify the correct statement/s.- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Both
- d)Neither
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements.
1. The concept of economic growth is quantitative whereas economic development is qualitative.
2. The concept of inclusive growth is associated with economic development.
Identify the correct statement/s.
1. The concept of economic growth is quantitative whereas economic development is qualitative.
2. The concept of inclusive growth is associated with economic development.
Identify the correct statement/s.
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both
d)
Neither
|
|
Kalyan Kulkarni answered |
C is the correct option. Both Are correct.
- Growth is the expansion of some object, institution or population which is measurable and is always quantitative whereas development is related to qualitative improvement,” said the Reader of the department of Economics, Mangalore University Prof Shripathi Kalluraya.
- Inclusive growth is a concept that advances equitable opportunities for economic participants during economic growth with benefits incurred by every section of society. The definition of inclusive growth implies direct links between the macroeconomic and microeconomic determinants of the economy and economic growth.
Consider the following statements.
1. Factor income from abroad is included in the GDP.
2. GDP gives importance to who produces goods and services rather than where it is produced.
3. Negative externalities are taken in to consideration while calculating GDP.
4. Care economy is excluded from GDP.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?- a)1, 2 and 3
- b)3 and 4
- c)2 and 4
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements.
1. Factor income from abroad is included in the GDP.
2. GDP gives importance to who produces goods and services rather than where it is produced.
3. Negative externalities are taken in to consideration while calculating GDP.
4. Care economy is excluded from GDP.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?
1. Factor income from abroad is included in the GDP.
2. GDP gives importance to who produces goods and services rather than where it is produced.
3. Negative externalities are taken in to consideration while calculating GDP.
4. Care economy is excluded from GDP.
Which of the above statements is/are not correct?
a)
1, 2 and 3
b)
3 and 4
c)
2 and 4
d)
All of the above
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Net factor income from abroad is included in GNP
GDP gives importance to where goods and services are produced.
Negative externalities such as environmental pollution are not considered while calculating GDP
GDP gives importance to where goods and services are produced.
Negative externalities such as environmental pollution are not considered while calculating GDP
Which of the following statement/s about Gender Inequality Index is not true? - a)It was introduced in 2010.
- b)It measures gender inequalities in three important aspects of human Development namely, reproductive health, empowerment, economic status.
- c)India’s rank is 122 out of 162 countries in the 2019 GII.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statement/s about Gender Inequality Index is not true?
a)
It was introduced in 2010.
b)
It measures gender inequalities in three important aspects of human Development namely, reproductive health, empowerment, economic status.
c)
India’s rank is 122 out of 162 countries in the 2019 GII.
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kaavya Tiwari answered |
D is the correct option. None of the statements are true.The GII is built on the same framework as the IHDI—to better expose differences in the distribution of achievements between women and men. It measures the human development costs of gender inequality. Thus the higher the GII value the more disparities between females and males and the more loss to human development.
Consider the following pairs:1. Lionel Robbins: Defined economics as the study of managing limited resources.2. Economics: Often called the "dismal science."3. Economic activities: Only involve non-monetary transactions.4. Humanities: Economics is interconnected with other disciplines within humanities.How many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Lionel Robbins: Defined economics as the study of managing limited resources.
2. Economics: Often called the "dismal science."
3. Economic activities: Only involve non-monetary transactions.
4. Humanities: Economics is interconnected with other disciplines within humanities.
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Understanding the Pairs
Let's analyze each of the pairs given:
1. Lionel Robbins: Defined economics as the study of managing limited resources.
- This statement is correct. Lionel Robbins indeed defined economics in terms of scarcity and choice, emphasizing the management of limited resources to meet unlimited wants.
2. Economics: Often called the "dismal science."
- This is also correct. The term "dismal science" is often attributed to economics due to its focus on the limitations and challenges posed by scarcity and choice, as well as its often pessimistic outlook on human behavior and economic outcomes.
3. Economic activities: Only involve non-monetary transactions.
- This statement is incorrect. Economic activities encompass both monetary and non-monetary transactions. While some economic activities may not involve money directly (like barter), many do involve monetary exchanges.
4. Humanities: Economics is interconnected with other disciplines within humanities.
- This is correct. Economics intersects with various fields within the humanities, such as sociology, psychology, and political science, influencing and being influenced by these disciplines.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct pairs are 1, 2, and 4. Thus, three pairs are accurately matched.
Correct Answer: Only three pairs
This aligns with option 'C'.
Let's analyze each of the pairs given:
1. Lionel Robbins: Defined economics as the study of managing limited resources.
- This statement is correct. Lionel Robbins indeed defined economics in terms of scarcity and choice, emphasizing the management of limited resources to meet unlimited wants.
2. Economics: Often called the "dismal science."
- This is also correct. The term "dismal science" is often attributed to economics due to its focus on the limitations and challenges posed by scarcity and choice, as well as its often pessimistic outlook on human behavior and economic outcomes.
3. Economic activities: Only involve non-monetary transactions.
- This statement is incorrect. Economic activities encompass both monetary and non-monetary transactions. While some economic activities may not involve money directly (like barter), many do involve monetary exchanges.
4. Humanities: Economics is interconnected with other disciplines within humanities.
- This is correct. Economics intersects with various fields within the humanities, such as sociology, psychology, and political science, influencing and being influenced by these disciplines.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct pairs are 1, 2, and 4. Thus, three pairs are accurately matched.
Correct Answer: Only three pairs
This aligns with option 'C'.
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
Economics is the study of how societies use resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people.Statement-II:
Economics studies how individuals, firms, governments, and organizations make choices that determine a society's resource utilization.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c) Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d) Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
Economics is the study of how societies use resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people.
Economics is the study of how societies use resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people.
Statement-II:
Economics studies how individuals, firms, governments, and organizations make choices that determine a society's resource utilization.
Economics studies how individuals, firms, governments, and organizations make choices that determine a society's resource utilization.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Shivani Singh answered |
Explanation:
Statement Analysis:
- Statement-I: Economics is the study of how societies use resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people.
- Statement-II: Economics studies how individuals, firms, governments, and organizations make choices that determine a society's resource utilization.
Correct Answer Justification:
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct as they both provide accurate definitions of economics.
- Statement-II explains Statement-I as it further elaborates on the idea of resource allocation and decision-making within economics.
- Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer as it states that both statements are correct, and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
In conclusion, economics is indeed the study of resource allocation, production, distribution, and decision-making within societies, making both statements accurate and interconnected.
Statement Analysis:
- Statement-I: Economics is the study of how societies use resources to produce valuable commodities and distribute them among different people.
- Statement-II: Economics studies how individuals, firms, governments, and organizations make choices that determine a society's resource utilization.
Correct Answer Justification:
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct as they both provide accurate definitions of economics.
- Statement-II explains Statement-I as it further elaborates on the idea of resource allocation and decision-making within economics.
- Therefore, option 'A' is the correct answer as it states that both statements are correct, and Statement-II explains Statement-I.
In conclusion, economics is indeed the study of resource allocation, production, distribution, and decision-making within societies, making both statements accurate and interconnected.
Which type of economy is also called ‘dual economy’?- a)Free market economy
- b)Socialist economy
- c)Communist economy
- d)Mixed economy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of economy is also called ‘dual economy’?
a)
Free market economy
b)
Socialist economy
c)
Communist economy
d)
Mixed economy
|
|
Alok Sengupta answered |
A dual economy refers to the existence of two distinct types of economic segments within an economy.
Mixed Economy = Market economy + Command economy.
Mixed Economy = Market economy + Command economy.
Consider the following:
1. Depreciation is the reduction in the value of capital assets due to wear and tear.
2. Different capital assets have different depreciation rates.
3. Depreciation rates of similar capital assets are same in different countries.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct? - a)1 and 2
- b)2 only
- c)3 only
- d)1,2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following:
1. Depreciation is the reduction in the value of capital assets due to wear and tear.
2. Different capital assets have different depreciation rates.
3. Depreciation rates of similar capital assets are same in different countries.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
1. Depreciation is the reduction in the value of capital assets due to wear and tear.
2. Different capital assets have different depreciation rates.
3. Depreciation rates of similar capital assets are same in different countries.
Which of the above given statements is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
2 only
c)
3 only
d)
1,2 and 3
|
|
Kavita Mehta answered |
Every asset undergoes depreciation. Government (Ministry of commerce and industry) announces the rates by which assets depreciate. Different rate of depreciation is set by different countries depending on their geography, climate, economic conditions etc.
Consider the following statements:1. The Market Economy, as discussed by Adam Smith, operates primarily through government regulations.2. In a Socialist model, the state controls natural resources but not labor.3. The Non-Market Economy is also known as a command economy or centrally planned economy.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)2 and 3 Only
- d)3 Only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. The Market Economy, as discussed by Adam Smith, operates primarily through government regulations.
2. In a Socialist model, the state controls natural resources but not labor.
3. The Non-Market Economy is also known as a command economy or centrally planned economy.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
2 and 3 Only
d)
3 Only
|
|
Mrinalini Patel answered |
Explanation:
1. The Market Economy:
- The Market Economy, as discussed by Adam Smith, operates primarily through the mechanism of supply and demand, with minimal government intervention.
- Adam Smith, known as the father of modern economics, believed that individuals pursuing their self-interest in a competitive market would lead to the best outcomes for society.
2. Socialist Model:
- In a Socialist model, the state does control natural resources, as they are considered the property of the people.
- However, in a Socialist system, labor is not necessarily controlled by the state. Instead, the emphasis is on collective ownership and decision-making.
3. Non-Market Economy:
- The Non-Market Economy, also known as a command economy or centrally planned economy, is characterized by government control over the allocation of resources and production decisions.
- In this type of economy, the government determines what goods and services are produced, how they are produced, and for whom they are produced.
Therefore, out of the given statements:
- Statement 1 is incorrect as the Market Economy operates primarily through free market mechanisms without significant government regulations.
- Statement 2 is incorrect as in a Socialist model, the state does control labor to some extent, along with natural resources.
- Statement 3 is correct as the Non-Market Economy is indeed known as a command economy or centrally planned economy.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'D' - 3 Only.
1. The Market Economy:
- The Market Economy, as discussed by Adam Smith, operates primarily through the mechanism of supply and demand, with minimal government intervention.
- Adam Smith, known as the father of modern economics, believed that individuals pursuing their self-interest in a competitive market would lead to the best outcomes for society.
2. Socialist Model:
- In a Socialist model, the state does control natural resources, as they are considered the property of the people.
- However, in a Socialist system, labor is not necessarily controlled by the state. Instead, the emphasis is on collective ownership and decision-making.
3. Non-Market Economy:
- The Non-Market Economy, also known as a command economy or centrally planned economy, is characterized by government control over the allocation of resources and production decisions.
- In this type of economy, the government determines what goods and services are produced, how they are produced, and for whom they are produced.
Therefore, out of the given statements:
- Statement 1 is incorrect as the Market Economy operates primarily through free market mechanisms without significant government regulations.
- Statement 2 is incorrect as in a Socialist model, the state does control labor to some extent, along with natural resources.
- Statement 3 is correct as the Non-Market Economy is indeed known as a command economy or centrally planned economy.
Thus, the correct answer is option 'D' - 3 Only.
Gross National Product (GNP) is- a)GDP – Net factor income from abroad
- b)GDP + Net factor income from abroad
- c)GDP + depreciation
- d)GDP – depreciation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gross National Product (GNP) is
a)
GDP – Net factor income from abroad
b)
GDP + Net factor income from abroad
c)
GDP + depreciation
d)
GDP – depreciation
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
Gross National Product (GNP) is the total value of goods and services produced by the people of a country in a given year. It is not territory specific.
GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA)
GNP = GDP + Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA)
In terms of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), India is the ______ largest economy in the world.- a)Fifth
- b)Sixth
- c)Third
- d)Fourth
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In terms of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP), India is the ______ largest economy in the world.
a)
Fifth
b)
Sixth
c)
Third
d)
Fourth
|
|
Anand Kulkarni answered |
In terms of Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) terms, India is the third largest economy in the world behind US and China.
Which of the following is/are not included in GDP calculation?
1. Foods and services provided free of cost by a NGO
2. Housewives' works
3. A doctor treating his own children
4. Goods in the inventory - a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 ,2 and 3
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1,2,3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are not included in GDP calculation?
1. Foods and services provided free of cost by a NGO
2. Housewives' works
3. A doctor treating his own children
4. Goods in the inventory
1. Foods and services provided free of cost by a NGO
2. Housewives' works
3. A doctor treating his own children
4. Goods in the inventory
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 ,2 and 3
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1,2,3 and 4
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Only those goods and services which have a monetary value affixed to them are considered while calculating GDP.
Which of the following comes under Macroeconomics?
1. Gross Domestic product
2. National income
3. Inflation
4. Profits of a firm
5. Demand and supply
Select the correct answer from the options given below: - a)1 and 3
- b)1, 2 and 5
- c)1, 2 and 3
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following comes under Macroeconomics?
1. Gross Domestic product
2. National income
3. Inflation
4. Profits of a firm
5. Demand and supply
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
1. Gross Domestic product
2. National income
3. Inflation
4. Profits of a firm
5. Demand and supply
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
1 and 3
b)
1, 2 and 5
c)
1, 2 and 3
d)
All of the above
|
|
Prasad Chatterjee answered |
Macroeconomics studies larger phenomena such as inflation, price levels, rate of economic growth, national income, gross domestic product (GDP), and changes in unemployment etc.
Microeconomics: Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individual units in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individual units.
Microeconomics: Microeconomics is a branch of economics that studies the behavior of individual units in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individual units.
Consider the following pairs:1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period.2. Net Domestic Product (NDP): GDP minus income from abroad.3. Gross National Product (GNP): GDP adjusted for depreciation.4. Net National Product (NNP): GNP minus depreciation.How many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only two pair
- b)Only one pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period.
2. Net Domestic Product (NDP): GDP minus income from abroad.
3. Gross National Product (GNP): GDP adjusted for depreciation.
4. Net National Product (NNP): GNP minus depreciation.
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only two pair
b)
Only one pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs

|
Upsc Toppers answered |
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Correctly matched. GDP is indeed the total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period.
2. Net Domestic Product (NDP): Incorrectly matched. NDP is actually GDP minus depreciation, not income from abroad.
3. Gross National Product (GNP): Incorrectly matched. GNP is GDP plus income from abroad, not adjusted for depreciation.
4. Net National Product (NNP): correctly matched.
Alternatively, NNP can be calculated as:
NNP=Gross National Product−DepreciationNNP=Gross National Product−Depreciation
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
A mixed economic system emerged in the late 1930s with market economies adopting policies from non-market economies to recover from the Depression.Statement-II:
The World Bank recognized the necessity of state intervention in the economy, deviating from its previous stance in support of free market principles.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
A mixed economic system emerged in the late 1930s with market economies adopting policies from non-market economies to recover from the Depression.
A mixed economic system emerged in the late 1930s with market economies adopting policies from non-market economies to recover from the Depression.
Statement-II:
The World Bank recognized the necessity of state intervention in the economy, deviating from its previous stance in support of free market principles.
The World Bank recognized the necessity of state intervention in the economy, deviating from its previous stance in support of free market principles.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Aurora Knowledge answered |
Statement-I correctly outlines the emergence of the mixed economic system in the late 1930s, where market economies integrated policies from non-market economies to recover from economic downturns like the Great Depression. This is historically accurate.
Statement-II accurately reflects the shift in the World Bank's stance towards recognizing the importance of state intervention in the economy, departing from its previous emphasis on free market principles. The World Bank's acknowledgment of the necessity of state involvement aligns with the evolution of economic systems towards a blend of market and non-market principles, as seen in mixed economies.
Therefore, both statements are correct, and Statement-II logically complements and explains the emergence of mixed economies following the Depression.
Which economic system led to increase in inequality, class conflicts and economic depressions?- a)Capitalism
- b)Communism
- c)Mixed economy
- d)Both a and b
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which economic system led to increase in inequality, class conflicts and economic depressions?
a)
Capitalism
b)
Communism
c)
Mixed economy
d)
Both a and b
|
|
Preethi Chauhan answered |
Capitalism is the economic system that led to an increase in inequality, class conflicts, and economic depressions.
Explanation:
Capitalism is an economic system in which private individuals or businesses own and control the means of production and distribution of goods and services. The main goal of capitalism is to maximize profits and accumulate wealth. This system has been criticized for its negative effects on society, including the following:
1. Inequality: Capitalism often leads to a widening gap between the rich and the poor. The wealthy individuals or businesses have more resources and opportunities to accumulate wealth, while the poor struggle to make ends meet. This results in unequal access to resources, education, healthcare, and other basic needs.
2. Class conflicts: The unequal distribution of wealth and resources often leads to class conflicts between the rich and the poor. The rich use their power and influence to maintain their position and protect their interests, while the poor struggle to gain equal rights and opportunities.
3. Economic depressions: Capitalism is prone to economic cycles of growth and recession. During economic booms, businesses and individuals accumulate wealth and invest in new projects. However, during economic downturns, businesses may fail, jobs may be lost, and the economy may contract. This results in economic depressions that can have severe impacts on society.
In conclusion, capitalism is an economic system that has led to an increase in inequality, class conflicts, and economic depressions. While it has some benefits, such as promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, it also has negative effects on society that need to be addressed.
Explanation:
Capitalism is an economic system in which private individuals or businesses own and control the means of production and distribution of goods and services. The main goal of capitalism is to maximize profits and accumulate wealth. This system has been criticized for its negative effects on society, including the following:
1. Inequality: Capitalism often leads to a widening gap between the rich and the poor. The wealthy individuals or businesses have more resources and opportunities to accumulate wealth, while the poor struggle to make ends meet. This results in unequal access to resources, education, healthcare, and other basic needs.
2. Class conflicts: The unequal distribution of wealth and resources often leads to class conflicts between the rich and the poor. The rich use their power and influence to maintain their position and protect their interests, while the poor struggle to gain equal rights and opportunities.
3. Economic depressions: Capitalism is prone to economic cycles of growth and recession. During economic booms, businesses and individuals accumulate wealth and invest in new projects. However, during economic downturns, businesses may fail, jobs may be lost, and the economy may contract. This results in economic depressions that can have severe impacts on society.
In conclusion, capitalism is an economic system that has led to an increase in inequality, class conflicts, and economic depressions. While it has some benefits, such as promoting innovation and entrepreneurship, it also has negative effects on society that need to be addressed.
Consider the following pairs:1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) : Total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period2. Net Domestic Product (NDP) : GDP adjusted for exports and imports3. Gross National Product (GNP) : GDP plus net factor income from abroad4. Net National Product (NNP) : GNP minus depreciationHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) : Total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period
2. Net Domestic Product (NDP) : GDP adjusted for exports and imports
3. Gross National Product (GNP) : GDP plus net factor income from abroad
4. Net National Product (NNP) : GNP minus depreciation
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Bhaskar Roy answered |
Understanding the Economic Terms
To evaluate the correctness of the pairs, we need to define each economic term accurately.
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Correct Definition: Total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period.
- This pair is correctly matched.
2. Net Domestic Product (NDP)
- Incorrect Definition: NDP is actually GDP adjusted for depreciation, not exports and imports.
- This pair is incorrectly matched.
3. Gross National Product (GNP)
- Correct Definition: GNP is GDP plus net factor income from abroad, which includes income earned by residents from overseas investments minus income earned by foreign residents from domestic investments.
- This pair is correctly matched.
4. Net National Product (NNP)
- Correct Definition: NNP is GNP minus depreciation.
- This pair is correctly matched.
Summary of Correct Matches
- Correctly Matched:
- GDP
- GNP
- NNP
- Incorrectly Matched:
- NDP
Conclusion
Out of the four pairs provided, three are correctly matched (GDP, GNP, and NNP), while only one is incorrect (NDP). Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that only three pairs are correctly matched.
To evaluate the correctness of the pairs, we need to define each economic term accurately.
1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Correct Definition: Total value of all final goods and services produced within a nation's boundaries during a one-year period.
- This pair is correctly matched.
2. Net Domestic Product (NDP)
- Incorrect Definition: NDP is actually GDP adjusted for depreciation, not exports and imports.
- This pair is incorrectly matched.
3. Gross National Product (GNP)
- Correct Definition: GNP is GDP plus net factor income from abroad, which includes income earned by residents from overseas investments minus income earned by foreign residents from domestic investments.
- This pair is correctly matched.
4. Net National Product (NNP)
- Correct Definition: NNP is GNP minus depreciation.
- This pair is correctly matched.
Summary of Correct Matches
- Correctly Matched:
- GDP
- GNP
- NNP
- Incorrectly Matched:
- NDP
Conclusion
Out of the four pairs provided, three are correctly matched (GDP, GNP, and NNP), while only one is incorrect (NDP). Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', which states that only three pairs are correctly matched.
The Economist who developed Human Development Index (HDI) is- a)Simon Kuznets
- b)David Ricardo
- c)Joseph Schumpeter
- d)Mahbub Ul Haq
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The Economist who developed Human Development Index (HDI) is
a)
Simon Kuznets
b)
David Ricardo
c)
Joseph Schumpeter
d)
Mahbub Ul Haq
|
|
Debolina Chakraborty answered |
The Economist who developed Human Development Index (HDI) is Mahbub Ul Haq.
Mahbub Ul Haq was a Pakistani economist who served as the Finance Minister of Pakistan in the 1980s. He was a strong advocate of human development and believed that GDP alone was not a sufficient measure of development. He developed the Human Development Index (HDI) in collaboration with Amartya Sen, an Indian economist, in 1990.
What is Human Development Index (HDI)?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which are used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. It was developed as an alternative to the traditional economic measures of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross National Product (GNP), which only measure economic progress and do not take into account the social and human aspects of development.
How is HDI calculated?
The HDI is calculated using three dimensions of human development: health, education, and income. It takes into account the following indicators:
1. Life expectancy at birth
2. Mean years of schooling
3. Expected years of schooling
4. Gross national income (GNI) per capita
These indicators are combined to create a single index value ranging from 0 to 1, with a higher value indicating higher human development.
Conclusion:
Mahbub Ul Haq's contribution to the field of economics and development is significant. His work on human development and the creation of HDI has helped shift the focus of development policies from economic growth to a more holistic approach that considers the social and human aspects of development. The HDI is now widely used by governments, international organizations, and researchers as a measure of development and progress.
Mahbub Ul Haq was a Pakistani economist who served as the Finance Minister of Pakistan in the 1980s. He was a strong advocate of human development and believed that GDP alone was not a sufficient measure of development. He developed the Human Development Index (HDI) in collaboration with Amartya Sen, an Indian economist, in 1990.
What is Human Development Index (HDI)?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic of life expectancy, education, and per capita income indicators, which are used to rank countries into four tiers of human development. It was developed as an alternative to the traditional economic measures of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Gross National Product (GNP), which only measure economic progress and do not take into account the social and human aspects of development.
How is HDI calculated?
The HDI is calculated using three dimensions of human development: health, education, and income. It takes into account the following indicators:
1. Life expectancy at birth
2. Mean years of schooling
3. Expected years of schooling
4. Gross national income (GNI) per capita
These indicators are combined to create a single index value ranging from 0 to 1, with a higher value indicating higher human development.
Conclusion:
Mahbub Ul Haq's contribution to the field of economics and development is significant. His work on human development and the creation of HDI has helped shift the focus of development policies from economic growth to a more holistic approach that considers the social and human aspects of development. The HDI is now widely used by governments, international organizations, and researchers as a measure of development and progress.
Which of the following is/are included in the expenditure method of GDP calculation?
1. Private consumption
2. Government Consumption
3. Net exports
4. Investments
5. Firm profits- a)1, 2 and 5
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)1, 2, 3 and 4
- d)1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are included in the expenditure method of GDP calculation?
1. Private consumption
2. Government Consumption
3. Net exports
4. Investments
5. Firm profits
1. Private consumption
2. Government Consumption
3. Net exports
4. Investments
5. Firm profits
a)
1, 2 and 5
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
1, 2, 3 and 4
d)
1, 2, 3, 4, and 5
|
|
Eshaan Kapoor answered |
The correct option is Option C.
There are four main aggregate expenses to measure GDP: household consumption, corporate investment, government spending on goods and services, and net exports, which are equivalent to exports minus imports of goods and services.
Consider the following statements about HDI rankings of 2019.
1. The HDI rank of India has slightly improved in 2019.
2. India is the best performing country in the south Asian region.
3. African nation Niger is the worst performing country in 2019.
4. India is the worst performing country among BRICS grouping.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?- a)1 and 2 only
- b)1 ,3 and 4
- c)2 and 3 only
- d)1 ,2 and 4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements about HDI rankings of 2019.
1. The HDI rank of India has slightly improved in 2019.
2. India is the best performing country in the south Asian region.
3. African nation Niger is the worst performing country in 2019.
4. India is the worst performing country among BRICS grouping.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
1. The HDI rank of India has slightly improved in 2019.
2. India is the best performing country in the south Asian region.
3. African nation Niger is the worst performing country in 2019.
4. India is the worst performing country among BRICS grouping.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
a)
1 and 2 only
b)
1 ,3 and 4
c)
2 and 3 only
d)
1 ,2 and 4
|
|
Shivani Dey answered |
India is ranked 129 out of 189 countries on the 2019 Human Development Index (HDI) improving from the 130th position in 2018.
Sri Lanka (71) is the best performing country in South Asian region.
Niger is ranked 189th (Last ranked country)
Position of BRICS countries in the HDI 2019:
Brazil -79.
Russia- 49.
China-85
South Africa- 113
India-129
Sri Lanka (71) is the best performing country in South Asian region.
Niger is ranked 189th (Last ranked country)
Position of BRICS countries in the HDI 2019:
Brazil -79.
Russia- 49.
China-85
South Africa- 113
India-129
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
External Grants in recent times indicate that India has been a net giver rather than a receiver, showcasing its increased participation in international economic diplomacy.Statement-II:
India's GNP is consistently lower than GDP due to the negative balance in Income from Abroad, reflecting the nation's dependence on global markets.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
External Grants in recent times indicate that India has been a net giver rather than a receiver, showcasing its increased participation in international economic diplomacy.
External Grants in recent times indicate that India has been a net giver rather than a receiver, showcasing its increased participation in international economic diplomacy.
Statement-II:
India's GNP is consistently lower than GDP due to the negative balance in Income from Abroad, reflecting the nation's dependence on global markets.
India's GNP is consistently lower than GDP due to the negative balance in Income from Abroad, reflecting the nation's dependence on global markets.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Prashanth Malik answered |
Analysis of Statement-I
- Statement-I suggests that India has become a net giver in external grants, indicating a shift in its role in international economic diplomacy.
- This statement is correct as India has indeed increased its contributions to global development initiatives and has been actively participating in various international forums.
Analysis of Statement-II
- Statement-II asserts that India's GNP is consistently lower than its GDP due to a negative balance in income from abroad.
- This statement is also correct; GNP (Gross National Product) measures the economic output of residents, including income earned abroad, while GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures output within the country.
- A negative balance in income from abroad implies that India is paying more to foreign entities than it is earning from them, which leads to GNP being lower than GDP.
Relation Between Statements
- Although both statements are correct, Statement-II does not explain Statement-I.
- The first statement focuses on India’s role in international economic diplomacy and its contributions, while the second addresses the economic metrics of GNP and GDP, which are not directly related to India's diplomatic activities.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C': Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect in explaining Statement-I.
- Statement-I suggests that India has become a net giver in external grants, indicating a shift in its role in international economic diplomacy.
- This statement is correct as India has indeed increased its contributions to global development initiatives and has been actively participating in various international forums.
Analysis of Statement-II
- Statement-II asserts that India's GNP is consistently lower than its GDP due to a negative balance in income from abroad.
- This statement is also correct; GNP (Gross National Product) measures the economic output of residents, including income earned abroad, while GDP (Gross Domestic Product) measures output within the country.
- A negative balance in income from abroad implies that India is paying more to foreign entities than it is earning from them, which leads to GNP being lower than GDP.
Relation Between Statements
- Although both statements are correct, Statement-II does not explain Statement-I.
- The first statement focuses on India’s role in international economic diplomacy and its contributions, while the second addresses the economic metrics of GNP and GDP, which are not directly related to India's diplomatic activities.
Conclusion
- Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C': Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect in explaining Statement-I.
Consider the following statements about GDP at market cost
1. GDP at market cost will increase if the government increases indirect taxes on goods and services.
2. GDP at market cost will increase if the government decreases indirect taxes on goods and services.
3. GDP at market cost will be constant irrespective of changes in indirect tax rates.
Identify the correct answer from the options given below:- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)All of the above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements about GDP at market cost
1. GDP at market cost will increase if the government increases indirect taxes on goods and services.
2. GDP at market cost will increase if the government decreases indirect taxes on goods and services.
3. GDP at market cost will be constant irrespective of changes in indirect tax rates.
Identify the correct answer from the options given below:
1. GDP at market cost will increase if the government increases indirect taxes on goods and services.
2. GDP at market cost will increase if the government decreases indirect taxes on goods and services.
3. GDP at market cost will be constant irrespective of changes in indirect tax rates.
Identify the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
All of the above
d)
None of the above
|
|
Debanshi Desai answered |
Understanding GDP at Market Cost
GDP at market cost refers to the total economic output of a country, adjusted for indirect taxes and subsidies. It reflects the market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation.
Statement Analysis
1. GDP at market cost will increase if the government increases indirect taxes on goods and services.
- Explanation: When indirect taxes (such as sales tax and VAT) are increased, the prices of goods and services rise. This inflationary effect increases the market value of GDP, leading to a higher calculation of GDP at market cost. Thus, this statement is correct.
2. GDP at market cost will increase if the government decreases indirect taxes on goods and services.
- Explanation: A decrease in indirect taxes generally leads to lower prices for goods and services. This would reduce the market value of GDP, not increase it. Hence, this statement is incorrect.
3. GDP at market cost will be constant irrespective of changes in indirect tax rates.
- Explanation: This statement suggests that GDP at market cost remains unaffected by any changes in tax rates, which is misleading. Changes in indirect tax rates directly influence the market prices of goods and services, thereby affecting GDP at market cost. Thus, this statement is also incorrect.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis, only the first statement is true. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - only statement 1 is correct.
This highlights the significant role that indirect taxes play in the calculation of GDP at market cost, influencing economic indicators and policymaking.
GDP at market cost refers to the total economic output of a country, adjusted for indirect taxes and subsidies. It reflects the market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation.
Statement Analysis
1. GDP at market cost will increase if the government increases indirect taxes on goods and services.
- Explanation: When indirect taxes (such as sales tax and VAT) are increased, the prices of goods and services rise. This inflationary effect increases the market value of GDP, leading to a higher calculation of GDP at market cost. Thus, this statement is correct.
2. GDP at market cost will increase if the government decreases indirect taxes on goods and services.
- Explanation: A decrease in indirect taxes generally leads to lower prices for goods and services. This would reduce the market value of GDP, not increase it. Hence, this statement is incorrect.
3. GDP at market cost will be constant irrespective of changes in indirect tax rates.
- Explanation: This statement suggests that GDP at market cost remains unaffected by any changes in tax rates, which is misleading. Changes in indirect tax rates directly influence the market prices of goods and services, thereby affecting GDP at market cost. Thus, this statement is also incorrect.
Conclusion
Based on the analysis, only the first statement is true. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - only statement 1 is correct.
This highlights the significant role that indirect taxes play in the calculation of GDP at market cost, influencing economic indicators and policymaking.
Consider the following two statements:Statement-I: GDP serves as a widely-used metric for comparing global economies, with the IMF ranking nations based on GDP sizes.Statement-II: India presently ranks as the world's fifth-largest economy at exchange rates and third-largest at purchasing power parity (PPP).Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)a. Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)b. Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c)c. Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)d. Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following two statements:
Statement-I: GDP serves as a widely-used metric for comparing global economies, with the IMF ranking nations based on GDP sizes.
Statement-II: India presently ranks as the world's fifth-largest economy at exchange rates and third-largest at purchasing power parity (PPP).
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
a. Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
b. Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
c. Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
d. Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Aurora Knowledge answered |
- Statement-I: GDP is indeed a widely-used metric for comparing global economies, and the IMF ranks nations based on their GDP sizes. This is a correct statement.
- Statement-II: India's ranking as the world's fifth-largest economy at exchange rates and third-largest at purchasing power parity (PPP) is also accurate. However, this statement does not directly explain the significance or use of GDP in global comparisons, hence it does not explain Statement-I.
Therefore, both statements are individually correct, but Statement-II does not provide an explanation for Statement-I.
What does the Beijing Consensus propose as an alternative to the policies advocated by the Washington Consensus?- a)Constant experimentation and innovation
- b)Reduced state intervention in economies
- c)Imposition of neoliberal policies on nations
- d)Market fundamentalism and globalization
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What does the Beijing Consensus propose as an alternative to the policies advocated by the Washington Consensus?
a)
Constant experimentation and innovation
b)
Reduced state intervention in economies
c)
Imposition of neoliberal policies on nations
d)
Market fundamentalism and globalization

|
K.L Institute answered |
The Beijing Consensus, introduced as an alternative to the Washington Consensus, emphasizes constant experimentation and innovation as one of its core pillars. This approach contrasts with the Washington Consensus's focus on neoliberal policies and market fundamentalism. The Beijing Consensus advocates for gradual reforms, peaceful distributive growth, and selective incorporation of foreign ideas, offering a different perspective on economic development and governance.
The concept of ‘invisible hand’ propagated by Adam Smith means- a)Every person, by looking out for themselves, inadvertently helps to create the best outcome for all.
- b)A wealthy nation is one that is populated with citizens working productively.
- c)An institutional framework is necessary to steer humans toward productive pursuits that are beneficial to society.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The concept of ‘invisible hand’ propagated by Adam Smith means
a)
Every person, by looking out for themselves, inadvertently helps to create the best outcome for all.
b)
A wealthy nation is one that is populated with citizens working productively.
c)
An institutional framework is necessary to steer humans toward productive pursuits that are beneficial to society.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Harshitha Gupta answered |
The phrase invisible hand was introduced by Adam Smith in his book 'The Wealth of Nations'. He assumed that an economy can work well in a free market scenario where everyone will work for his/her own interest.
He explained that an economy will comparatively work and function well if the government will leave people alone to buy and sell freely among themselves. He suggested that if people were allowed to trade freely, self-interested traders present in the market would compete with each other, leading markets towards the positive output with the help of an invisible hand.
The unobservable market force that helps the demand and supply of goods in a free market to reach equilibrium automatically is the invisible hand.
He explained that an economy will comparatively work and function well if the government will leave people alone to buy and sell freely among themselves. He suggested that if people were allowed to trade freely, self-interested traders present in the market would compete with each other, leading markets towards the positive output with the help of an invisible hand.
The unobservable market force that helps the demand and supply of goods in a free market to reach equilibrium automatically is the invisible hand.
Consider the following statements:Statement-I:
Market Economy emerged as the first formal economic system post traditional economies.
Statement-II:
Non-Market Economy is rooted in Karl Marx's ideas and had socialist and communist variants.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- c)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I:
Market Economy emerged as the first formal economic system post traditional economies.
Statement-II:
Non-Market Economy is rooted in Karl Marx's ideas and had socialist and communist variants.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
Market Economy emerged as the first formal economic system post traditional economies.
Statement-II:
Non-Market Economy is rooted in Karl Marx's ideas and had socialist and communist variants.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
c)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Aurora Knowledge answered |
Statement-I correctly identifies the emergence of Market Economy as the first formal economic system post traditional economies, tracing back to Adam Smith's work in 1776. Statement-II correctly links Non-Market Economy to Karl Marx's ideas, highlighting the socialist and communist variants of this economic system. The socialist model controlled natural resources, while the communist model controlled labor and resources, aligning with Marx's ideologies. Hence, both statements are accurate, and Statement-II effectively provides additional context that complements Statement-I.
The concept of ‘collective ownership ‘of means of production is associated with which of the following? - a)Only communism
- b)Only socialism
- c)Both a and b
- d)Neither
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The concept of ‘collective ownership ‘of means of production is associated with which of the following?
a)
Only communism
b)
Only socialism
c)
Both a and b
d)
Neither
|
|
Isha Tiwari answered |
"concept" refers to a general idea or understanding of something, often in the form of an abstract or mental construct. It can be a theoretical or practical notion that helps people to categorize, understand, or explain different aspects of the world around them. Concepts can be used to create models, theories, or frameworks that describe the relationships among different phenomena or objects. They can be applied in various fields such as philosophy, psychology, linguistics, biology, mathematics, and many others. Overall, the concept of "concept" plays a crucial role in human cognition and communication by providing a shared language and understanding of the world.
How many countries are covered in the Human Development Index (HDI) of 2019?- a)154
- b)178
- c)189
- d)193
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many countries are covered in the Human Development Index (HDI) of 2019?
a)
154
b)
178
c)
189
d)
193
|
|
Shalini Datta answered |
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite index developed by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). It measures the average achievements of countries in three dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, access to education, and a decent standard of living. The HDI is released annually, with the latest report being the 2019 edition.
The number of countries covered in the HDI of 2019 is 189. This means that the HDI covers a vast majority of the world's nations. The report provides a snapshot of the state of human development across the globe and highlights areas where progress has been made and where more work is needed.
The HDI is a valuable tool for policymakers, researchers, and development practitioners as it provides insights into the factors that contribute to human development and helps identify areas where interventions can be most effective. The index also serves as a benchmark against which countries can measure their progress over time.
In conclusion, the HDI of 2019 covers 189 countries and provides a comprehensive picture of human development across the globe. It is an important tool for shaping policies and interventions aimed at improving the lives of people around the world.
The number of countries covered in the HDI of 2019 is 189. This means that the HDI covers a vast majority of the world's nations. The report provides a snapshot of the state of human development across the globe and highlights areas where progress has been made and where more work is needed.
The HDI is a valuable tool for policymakers, researchers, and development practitioners as it provides insights into the factors that contribute to human development and helps identify areas where interventions can be most effective. The index also serves as a benchmark against which countries can measure their progress over time.
In conclusion, the HDI of 2019 covers 189 countries and provides a comprehensive picture of human development across the globe. It is an important tool for shaping policies and interventions aimed at improving the lives of people around the world.
The Gross National Product (GNP) of India is less than its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) because- a)Indians earn very less salaries and wages abroad
- b)Indian companies are inefficient
- c)Foreigners earn more in India than what Indians earn abroad
- d)Lack of government support to Indian companies abroad
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The Gross National Product (GNP) of India is less than its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) because
a)
Indians earn very less salaries and wages abroad
b)
Indian companies are inefficient
c)
Foreigners earn more in India than what Indians earn abroad
d)
Lack of government support to Indian companies abroad
|
|
Sahana Patel answered |
The correct answer is option C: Foreigners earn more in India than what Indians earn abroad. Let's explore why this is the case in more detail.
Explanation:
Definition of GNP and GDP:
1. Gross National Product (GNP) is the total value of goods and services produced by the residents of a country, both domestically and abroad, in a given time period.
2. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country in a given time period.
Factors affecting GNP and GDP:
1. Income from abroad: GNP takes into account the income earned by the residents of a country from their economic activities abroad. This includes wages, salaries, profits, and dividends earned by Indian citizens working or investing in other countries. Conversely, it also includes the income earned by foreign citizens working or investing in India.
Reasons for GNP being less than GDP in India:
1. Lower income of Indians abroad: Indians working abroad, particularly in low-skilled and low-paying jobs, tend to earn relatively lower salaries and wages compared to their counterparts in developed countries. This reduces the income earned by Indians abroad, leading to a lower GNP.
2. Higher income of foreigners in India: On the other hand, due to factors such as exchange rate differences and differences in the cost of living, foreigners working or investing in India may earn higher salaries and wages compared to what Indians earn abroad. This increases the income earned by foreigners in India, contributing to a higher GDP.
Impact on GNP and GDP:
1. GNP is typically lower than GDP in countries where residents earn relatively lower incomes abroad compared to the income earned by foreigners in the country. This is the case in India, where a significant number of Indian citizens work in low-skilled jobs abroad, resulting in lower income generation.
2. GDP, on the other hand, reflects the total economic activity within the country's borders, including the income generated by both residents and non-residents. As a result, GDP is often higher than GNP in countries like India.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Gross National Product (GNP) of India is less than its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) because foreigners working or investing in India tend to earn more than what Indians earn abroad. This difference in income levels contributes to the disparity between GNP and GDP figures.
Explanation:
Definition of GNP and GDP:
1. Gross National Product (GNP) is the total value of goods and services produced by the residents of a country, both domestically and abroad, in a given time period.
2. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total value of goods and services produced within the borders of a country in a given time period.
Factors affecting GNP and GDP:
1. Income from abroad: GNP takes into account the income earned by the residents of a country from their economic activities abroad. This includes wages, salaries, profits, and dividends earned by Indian citizens working or investing in other countries. Conversely, it also includes the income earned by foreign citizens working or investing in India.
Reasons for GNP being less than GDP in India:
1. Lower income of Indians abroad: Indians working abroad, particularly in low-skilled and low-paying jobs, tend to earn relatively lower salaries and wages compared to their counterparts in developed countries. This reduces the income earned by Indians abroad, leading to a lower GNP.
2. Higher income of foreigners in India: On the other hand, due to factors such as exchange rate differences and differences in the cost of living, foreigners working or investing in India may earn higher salaries and wages compared to what Indians earn abroad. This increases the income earned by foreigners in India, contributing to a higher GDP.
Impact on GNP and GDP:
1. GNP is typically lower than GDP in countries where residents earn relatively lower incomes abroad compared to the income earned by foreigners in the country. This is the case in India, where a significant number of Indian citizens work in low-skilled jobs abroad, resulting in lower income generation.
2. GDP, on the other hand, reflects the total economic activity within the country's borders, including the income generated by both residents and non-residents. As a result, GDP is often higher than GNP in countries like India.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Gross National Product (GNP) of India is less than its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) because foreigners working or investing in India tend to earn more than what Indians earn abroad. This difference in income levels contributes to the disparity between GNP and GDP figures.
Which is considered as the official GDP of India?- a)GDP at factor cost in constant prices
- b)GDP at factor cost in current prices
- c)GDP at market cost in constant prices
- d)GDP at market cost in current prices
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is considered as the official GDP of India?
a)
GDP at factor cost in constant prices
b)
GDP at factor cost in current prices
c)
GDP at market cost in constant prices
d)
GDP at market cost in current prices
|
|
Disha Yadav answered |
GDP at market cost in constant prices is considered as the official GDP of India
Explanation:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total value of all final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country in a given period of time. GDP is an important indicator of the economic health of a country. In India, the Central Statistical Office (CSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI) is responsible for estimating GDP.
There are two methods of calculating GDP - the factor cost method and the market cost method. The factor cost method measures the value of goods and services at the production stage, while the market cost method measures the value of goods and services at the market prices.
In India, the official GDP is calculated using the market cost method in constant prices. Constant prices refer to a base year, against which the prices of goods and services in the current year are compared. This is done to remove the effect of inflation on GDP.
The use of market cost method in constant prices gives a more accurate picture of the real growth of the economy, as it takes into account the changes in both prices and production levels. This method also allows for international comparisons of GDP, as it provides a standard measure of economic output across countries.
In conclusion, the official GDP of India is calculated using the market cost method in constant prices. This method provides a more accurate picture of the real growth of the economy and allows for international comparisons of GDP.
Explanation:
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total value of all final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country in a given period of time. GDP is an important indicator of the economic health of a country. In India, the Central Statistical Office (CSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MOSPI) is responsible for estimating GDP.
There are two methods of calculating GDP - the factor cost method and the market cost method. The factor cost method measures the value of goods and services at the production stage, while the market cost method measures the value of goods and services at the market prices.
In India, the official GDP is calculated using the market cost method in constant prices. Constant prices refer to a base year, against which the prices of goods and services in the current year are compared. This is done to remove the effect of inflation on GDP.
The use of market cost method in constant prices gives a more accurate picture of the real growth of the economy, as it takes into account the changes in both prices and production levels. This method also allows for international comparisons of GDP, as it provides a standard measure of economic output across countries.
In conclusion, the official GDP of India is calculated using the market cost method in constant prices. This method provides a more accurate picture of the real growth of the economy and allows for international comparisons of GDP.
Gross value added (GVA) at basic prices- a)Includes production taxes and excludes production subsidies
- b)Includes product taxes and excludes product subsidies
- c)Includes only production taxes and product taxes
- d)Includes only production subsides and product subsidies
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gross value added (GVA) at basic prices
a)
Includes production taxes and excludes production subsidies
b)
Includes product taxes and excludes product subsidies
c)
Includes only production taxes and product taxes
d)
Includes only production subsides and product subsidies
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
GVA at basic prices = factor cost + (Production taxes - Production subsidies)
Examples of production taxes are land revenues, stamps and registration fees and tax on profession. Examples of production subsidies include, input subsidies to farmers, subsidies to village and small industries, administrative subsidies to corporations or cooperatives, etc Some examples of product taxes are excise tax, sales tax, service tax and import and export duties. Product subsidies include food, petroleum and fertilizer subsidies, interest subsidies given to farmers, households, etc.
Examples of production taxes are land revenues, stamps and registration fees and tax on profession. Examples of production subsidies include, input subsidies to farmers, subsidies to village and small industries, administrative subsidies to corporations or cooperatives, etc Some examples of product taxes are excise tax, sales tax, service tax and import and export duties. Product subsidies include food, petroleum and fertilizer subsidies, interest subsidies given to farmers, households, etc.
Consider the following statements:
1. If the national income is being derived at ‘Factor Cost', the indirect taxes do not need to be deducted from it.
2. In this case, the government does not have to add their income accruing from indirect taxes to the national income.
Which of these statements is/ are correct?
- a)1 Only
- b)Both 1 and 2
- c)2 Only
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. If the national income is being derived at ‘Factor Cost', the indirect taxes do not need to be deducted from it.
2. In this case, the government does not have to add their income accruing from indirect taxes to the national income.
Which of these statements is/ are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
Both 1 and 2
c)
2 Only
d)
None of the above
|
|
Kabir Verma answered |
- If the national income is being derived at ‘market cost, the indirect taxes do not need to be deducted from it.
- In this case, the government does not have to add their income accruing from indirect taxes to the national income. It means that the confusion in the case of national income accounting at factor cost is only related to indirect taxes.
Which statements about Gross Domestic Product (GDP) are /are correct?
1. GDP is the total value of all final goods and services that are sold in a given year.
2. In GDP estimates, the value of intermediary goods is not included at all.
3. GDP is a quantitative concept.
4. GDP measures growth but not progress.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
- a)1 and 4 only
- b)1, 2 and 3 only
- c)2, 3 and 4 only
- d)1, 2, 3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which statements about Gross Domestic Product (GDP) are /are correct?
1. GDP is the total value of all final goods and services that are sold in a given year.
2. In GDP estimates, the value of intermediary goods is not included at all.
3. GDP is a quantitative concept.
4. GDP measures growth but not progress.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
1. GDP is the total value of all final goods and services that are sold in a given year.
2. In GDP estimates, the value of intermediary goods is not included at all.
3. GDP is a quantitative concept.
4. GDP measures growth but not progress.
Select the correct answer from the options given below:
a)
1 and 4 only
b)
1, 2 and 3 only
c)
2, 3 and 4 only
d)
1, 2, 3 and 4
|
|
Nisha Tiwari answered |
GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given year irrespective of them being sold or not.
Intermediate goods are not included in the calculation of a country's GDP. The reason for not including them in the GDP is because it will lead to counting the value of the goods twice, and the norm is to count the price of final goods only once.
GDP is a measure of growth and not progress: GDP indicates growth that is quantitative. Qualitative aspects such as development, progress and well being are not taken in to account.
Intermediate goods are not included in the calculation of a country's GDP. The reason for not including them in the GDP is because it will lead to counting the value of the goods twice, and the norm is to count the price of final goods only once.
GDP is a measure of growth and not progress: GDP indicates growth that is quantitative. Qualitative aspects such as development, progress and well being are not taken in to account.
What is the core purpose of economics?- a)To study the economic activities of human beings.
- b)To understand the production, allocation, and consumption of goods and services.
- c)To improve the world through the application of economic concepts.
- d)To manage limited resources in the face of perpetual scarcity.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the core purpose of economics?
a)
To study the economic activities of human beings.
b)
To understand the production, allocation, and consumption of goods and services.
c)
To improve the world through the application of economic concepts.
d)
To manage limited resources in the face of perpetual scarcity.
|
|
Roshni Shah answered |
Core Purpose of Economics
The core purpose of economics revolves around the fundamental issue of scarcity and the management of limited resources. This concept is essential in understanding how societies function and make decisions.
Scarcity and Limited Resources
- Economic resources, such as land, labor, and capital, are finite.
- Human wants and needs, on the other hand, are virtually unlimited.
- This disparity creates a need for effective management of resources to satisfy as many needs as possible.
Allocation of Resources
- Economics focuses on how resources are allocated among competing uses.
- It studies mechanisms such as markets, government policies, and social norms that influence this allocation.
- Different economic systems (capitalism, socialism, etc.) reflect various approaches to resource management.
Production and Consumption
- Understanding how goods and services are produced efficiently is vital.
- Economics examines production techniques, technology, and labor input to optimize output.
- It also looks at consumption patterns to gauge demand and improve welfare.
Decision Making
- Economics aids in decision-making for individuals, businesses, and governments.
- By analyzing costs and benefits, economic principles guide choices that maximize utility.
- This strategic approach is crucial for sustainable development and societal progress.
Conclusion
In summary, the core purpose of economics is to manage limited resources amidst perpetual scarcity. This fundamental principle drives the study of production, allocation, and consumption, ultimately aiming for an efficient and fair distribution of resources in society.
The core purpose of economics revolves around the fundamental issue of scarcity and the management of limited resources. This concept is essential in understanding how societies function and make decisions.
Scarcity and Limited Resources
- Economic resources, such as land, labor, and capital, are finite.
- Human wants and needs, on the other hand, are virtually unlimited.
- This disparity creates a need for effective management of resources to satisfy as many needs as possible.
Allocation of Resources
- Economics focuses on how resources are allocated among competing uses.
- It studies mechanisms such as markets, government policies, and social norms that influence this allocation.
- Different economic systems (capitalism, socialism, etc.) reflect various approaches to resource management.
Production and Consumption
- Understanding how goods and services are produced efficiently is vital.
- Economics examines production techniques, technology, and labor input to optimize output.
- It also looks at consumption patterns to gauge demand and improve welfare.
Decision Making
- Economics aids in decision-making for individuals, businesses, and governments.
- By analyzing costs and benefits, economic principles guide choices that maximize utility.
- This strategic approach is crucial for sustainable development and societal progress.
Conclusion
In summary, the core purpose of economics is to manage limited resources amidst perpetual scarcity. This fundamental principle drives the study of production, allocation, and consumption, ultimately aiming for an efficient and fair distribution of resources in society.
Consider the following statements:Statement-I: India switched to calculating national income at market price in January 2015.Statement-II: The transition to market price calculation was facilitated by GST implementation.Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?- a)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
- b)Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
- c)Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
- d)Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: India switched to calculating national income at market price in January 2015.
Statement-II: The transition to market price calculation was facilitated by GST implementation.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
a)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II explains Statement-I
b)
Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect
c)
Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct, but Statement-II does not explain Statement-I
d)
Statement-I is incorrect, but Statement-II is correct
|
|
Saptarshi Majumdar answered |
Understanding the Statements
The question revolves around two statements regarding India's national income calculation methodology and the impact of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
Statement-I: India switched to calculating national income at market price in January 2015.
- This statement is incorrect.
- India has been using market prices to calculate national income for several years prior to 2015. The shift in methodology in 2015 was more about revising the base year for GDP calculations and adopting a new series based on the 2011-12 base year.
Statement-II: The transition to market price calculation was facilitated by GST implementation.
- This statement is also incorrect in the context provided.
- While the GST, implemented in July 2017, aimed to streamline the taxation system and improve revenue collection, it did not directly facilitate a switch to market price calculation for national income.
Correct Answer Explanation
- Since Statement-I is incorrect, and Statement-II, while partially related to economic reforms, does not accurately explain or relate to the transition mentioned in Statement-I, the correct answer is option B: "Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect."
Conclusion
- In summary, the confusion stems from the timing and nature of the calculations. India's national income calculations have been based on market prices long before 2015, and while GST is an important reform, it did not trigger a change in the national income calculation methodology. Therefore, the option stating that Statement-I is correct and Statement-II is incorrect is the most accurate.
The question revolves around two statements regarding India's national income calculation methodology and the impact of the Goods and Services Tax (GST).
Statement-I: India switched to calculating national income at market price in January 2015.
- This statement is incorrect.
- India has been using market prices to calculate national income for several years prior to 2015. The shift in methodology in 2015 was more about revising the base year for GDP calculations and adopting a new series based on the 2011-12 base year.
Statement-II: The transition to market price calculation was facilitated by GST implementation.
- This statement is also incorrect in the context provided.
- While the GST, implemented in July 2017, aimed to streamline the taxation system and improve revenue collection, it did not directly facilitate a switch to market price calculation for national income.
Correct Answer Explanation
- Since Statement-I is incorrect, and Statement-II, while partially related to economic reforms, does not accurately explain or relate to the transition mentioned in Statement-I, the correct answer is option B: "Statement-I is correct, but Statement-II is incorrect."
Conclusion
- In summary, the confusion stems from the timing and nature of the calculations. India's national income calculations have been based on market prices long before 2015, and while GST is an important reform, it did not trigger a change in the national income calculation methodology. Therefore, the option stating that Statement-I is correct and Statement-II is incorrect is the most accurate.
Consider the following pairs:1. Market Economy - Laissez-faire policy2. Non-Market Economy - Emphasis on wealth exchange3. Socialist Model - State control of natural resources4. Communist Model - State control of labor and resourcesHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. Market Economy - Laissez-faire policy
2. Non-Market Economy - Emphasis on wealth exchange
3. Socialist Model - State control of natural resources
4. Communist Model - State control of labor and resources
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs
|
|
Aurora Knowledge answered |
1. Market Economy - Laissez-faire policy: Correct. A market economy operates on the principles of laissez-faire, emphasizing minimal government intervention and relying on market forces to regulate economic activities.
2. Non-Market Economy - Emphasis on wealth exchange: Incorrect. A non-market economy, such as socialism or communism, does not emphasize wealth exchange. Instead, it focuses on state control of resources and production, aiming for the well-being of all citizens and preventing economic inequality through state ownership and planning.
3. Socialist Model - State control of natural resources: Correct. In a socialist model, the state controls natural resources, which are utilized for the benefit of society as a whole.
4. Communist Model - State control of labor and resources: Correct. In a communist model, the state controls both labor and resources, ensuring that production and distribution are managed centrally by the state to achieve a classless society.
Thus, three pairs are correctly matched: 1, 3, and 4.
‘Remittances’ are included in- a)G.N.P and G.D.P
- b)G.N.P only
- c)G.D.P only
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
‘Remittances’ are included in
a)
G.N.P and G.D.P
b)
G.N.P only
c)
G.D.P only
d)
None of the above
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
Remittances are money sent home from emigrants working abroad. It is included in GNP and not GDP because GDP takes in to account the value of only those goods and services which are produced within the country.
The concept of Gross National Happiness (GNH) was first introduced in- a)Bhutan
- b)Tibet
- c)Nepal
- d)India
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The concept of Gross National Happiness (GNH) was first introduced in
a)
Bhutan
b)
Tibet
c)
Nepal
d)
India
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
The phrase ‘gross national happiness’ was first coined by the 4th King of Bhutan, King Jigme Singye Wangchuck, in 1972 when he declared, “Gross National Happiness is more important than Gross Domestic Product.”
The following 4 parameters are used to measure the happiness,
1. Higher per capita income
2. Good Governance
3. Environmental protection
4. Cultural promotion (i.e., inculcation of ethics and spiritual values in life without which, progress may become curse rather than a blessing).
The following 4 parameters are used to measure the happiness,
1. Higher per capita income
2. Good Governance
3. Environmental protection
4. Cultural promotion (i.e., inculcation of ethics and spiritual values in life without which, progress may become curse rather than a blessing).
Consider the following pairs:1. GNP Calculation: GDP - Depreciation2. NNP Calculation: GDP + Income from Abroad3. GVA Calculation: GDP + taxes on products – taxes on subsidies4. Market Cost Calculation: Factor cost + Indirect taxesHow many pairs given above are correctly matched?- a)Only one pair
- b)Only two pairs
- c)Only three pairs
- d)All four pairs
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following pairs:
1. GNP Calculation: GDP - Depreciation
2. NNP Calculation: GDP + Income from Abroad
3. GVA Calculation: GDP + taxes on products – taxes on subsidies
4. Market Cost Calculation: Factor cost + Indirect taxes
How many pairs given above are correctly matched?
a)
Only one pair
b)
Only two pairs
c)
Only three pairs
d)
All four pairs

|
Innovative Classes answered |
1. GNP Calculation: GDP - Depreciation
This is incorrect. The correct formula for GNP is GDP + Income from Abroad. Depreciation is not used in calculating GNP.
This is incorrect. The correct formula for GNP is GDP + Income from Abroad. Depreciation is not used in calculating GNP.
2. NNP Calculation: GDP + Income from Abroad
This is incorrect. NNP is calculated by taking GNP and subtracting depreciation, and GNP itself is GDP + Income from Abroad.
This is incorrect. NNP is calculated by taking GNP and subtracting depreciation, and GNP itself is GDP + Income from Abroad.
3. GVA Calculation: GDP at basic prices + Product taxes - Production subsidies
This is incorrect. GVA is calculated at basic prices, not directly from GDP. It includes product taxes and excludes production subsidies.
This is incorrect. GVA is calculated at basic prices, not directly from GDP. It includes product taxes and excludes production subsidies.
4. Market Cost Calculation: Factor cost + Indirect taxes
This is correct. Market cost is calculated by adding indirect taxes to the factor cost.
This is correct. Market cost is calculated by adding indirect taxes to the factor cost.
Thus, only pair 4 is correctly matched. Hence, the answer is Option A: Only one pair.
Consider the following statements:1. In recent times, India has been more of a giver than a receiver of external grants.2. Net National Product (NNP) is derived by subtracting depreciation from Gross Domestic Product (GDP).3. The Central Statistics Office (CSO) revised the base year for calculating national accounts from 2004-05 to 2011-12 in January 2015.Which of the statements given above is/are correct?- a)1 Only
- b)1 and 2 Only
- c)1 and 3 Only
- d)1, 2 and 3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. In recent times, India has been more of a giver than a receiver of external grants.
2. Net National Product (NNP) is derived by subtracting depreciation from Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
3. The Central Statistics Office (CSO) revised the base year for calculating national accounts from 2004-05 to 2011-12 in January 2015.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a)
1 Only
b)
1 and 2 Only
c)
1 and 3 Only
d)
1, 2 and 3

|
BT Educators answered |
1. Statement 1: This statement is correct. The text mentions that India has become more of a giver than a receiver of external grants, aligning with its increased participation in international economic diplomacy and commitment to developmental and humanitarian assistance.
2. Statement 2: This statement is incorrect. Net National Product (NNP) is derived by subtracting depreciation from Gross National Product (GNP), not from GDP. The correct formula for NNP is NNP = GNP - Depreciation.
3. Statement 3: This statement is correct. The Central Statistics Office (CSO) indeed revised the base year for calculating national accounts from 2004-05 to 2011-12 in January 2015 following the recommendation of the National Statistical Commission (NSC).
Given the above analysis, the correct answer is Option C.
Which of the following is not an intermediate good?- a)Flour used to make cake
- b)Wood used to make a chair
- c)Steel used in manufacturing a car
- d)Car tyre sold in a retail showroom
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not an intermediate good?
a)
Flour used to make cake
b)
Wood used to make a chair
c)
Steel used in manufacturing a car
d)
Car tyre sold in a retail showroom
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Intermediate goods refer to those goods which are used either for resale or for further production. Final goods refer to those goods which are used for final consumption.
Options a, b and c are intermediate goods where as option d is a final good as it is directly consumed by the user.
Options a, b and c are intermediate goods where as option d is a final good as it is directly consumed by the user.
HDI measures human development in a country using which of the following indicators?
1. Life expectancy
2. Education
3. Per capital income
4. Gender empowerment
5. Research and development- a)1, 2 and 3 Only
- b)2, 3 and 4 only
- c)1, 2, 3 and 4
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
HDI measures human development in a country using which of the following indicators?
1. Life expectancy
2. Education
3. Per capital income
4. Gender empowerment
5. Research and development
1. Life expectancy
2. Education
3. Per capital income
4. Gender empowerment
5. Research and development
a)
1, 2 and 3 Only
b)
2, 3 and 4 only
c)
1, 2, 3 and 4
d)
All of the above
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
HDI measures human development in a country using 3 indicators,
Health: The health component is measured using the life expectancy at birth in the country.
Education: Education component is measured using a. Expected years of schooling for children of school entering age b. Mean years of schooling for adults aged 25 years and above.
Standard of living: This component is measured using per capita income (in US dollars).
Health: The health component is measured using the life expectancy at birth in the country.
Education: Education component is measured using a. Expected years of schooling for children of school entering age b. Mean years of schooling for adults aged 25 years and above.
Standard of living: This component is measured using per capita income (in US dollars).
Chapter doubts & questions for Nature of Indian Economy - Indian Economy for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Nature of Indian Economy - Indian Economy for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Indian Economy for State PSC Exams
113 videos|387 docs|113 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









