All Exams >
BPSC (Bihar) >
Science & Technology for State PSC Exams >
All Questions
All questions of Physics for BPSC (Bihar) Exam
Food gets cooked faster in a pressure cooker because- a)water starts boiling at a lower temperature due to high pressure
- b)water starts boiling at a higher temperature due to high pressure
- c)water boils only at 100°C but the heat content is higher at high pressure
- d)convection currents are set inside the cooker
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Food gets cooked faster in a pressure cooker because
a)
water starts boiling at a lower temperature due to high pressure
b)
water starts boiling at a higher temperature due to high pressure
c)
water boils only at 100°C but the heat content is higher at high pressure
d)
convection currents are set inside the cooker

|
Anjana Choudhary answered |
Because water starts boiling at a lower temperature due to high pressure. According to Gay-Lussac’s law ρ ∝ T.
A piece of ice is floating in a beaker containing water. When whole of the ice melts- a)the level of water will come down.
- b)the level of water will come up.
- c)the level of water will first rise and then fall.
- d)the level of water will remain the same
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A piece of ice is floating in a beaker containing water. When whole of the ice melts
a)
the level of water will come down.
b)
the level of water will come up.
c)
the level of water will first rise and then fall.
d)
the level of water will remain the same

|
Surbhi Rane answered |
After the melting of ice, the level of water remains the same because the total volume of the melted ice is equal to the volume of floating ice.
Which one of the following statements is not true for a person suffering from hypermetropia?- a)The person can see far objects distinctly.
- b)The focal length of the lens is large.
- c)The image of the close object is focussed behind the retina.
- d)A concave lens is used to correct this defect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is not true for a person suffering from hypermetropia?
a)
The person can see far objects distinctly.
b)
The focal length of the lens is large.
c)
The image of the close object is focussed behind the retina.
d)
A concave lens is used to correct this defect.

|
Janhavi Dey answered |
Hypermetropia is corrected by using a concave lens. Myopia is corrected by convex lens.
An iron needle sinks in water whereas a ship made of iron floats on it because- a)the edge of the needle is pointed
- b)the ship is flat
- c)the ship is driven by powerful engine
- d)specific gravity of the needle is greater than that of water displaced by it.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An iron needle sinks in water whereas a ship made of iron floats on it because
a)
the edge of the needle is pointed
b)
the ship is flat
c)
the ship is driven by powerful engine
d)
specific gravity of the needle is greater than that of water displaced by it.

|
Kajal Shah answered |
Because the specific gravity of the needle is greater than that of water displaced by it. Specific gravity (or relative density) = Density of the substance / Density of the water at 4°C The average density of iron needle is greater than water, therefore, it sinks.
A fluorescent tube is preferred to an electric bulb because- a)it has a larger light emitting surface.
- b)voltage fluctuations do not affect it.
- c)in a tube electrical energy is almost converted into light.
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A fluorescent tube is preferred to an electric bulb because
a)
it has a larger light emitting surface.
b)
voltage fluctuations do not affect it.
c)
in a tube electrical energy is almost converted into light.
d)
None of these

|
Simran Sarkar answered |
In a fluorescent tube, electrical energy is almost converted into light. The inner wall of the fluorescent tube is coated with phosphorus which immediately transformed into bright light.
Consider the following natural phenomena:
1. Terrestrial heating
2. Reflection of light
3. Refraction of light
4. Diffraction of light
Q. Due to which of these phenomena is mirage formed?- a)1 and 2
- b)2, 3 and 4
- c)2 and 3
- d)4 only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following natural phenomena:
1. Terrestrial heating
2. Reflection of light
3. Refraction of light
4. Diffraction of light
Q. Due to which of these phenomena is mirage formed?
1. Terrestrial heating
2. Reflection of light
3. Refraction of light
4. Diffraction of light
Q. Due to which of these phenomena is mirage formed?
a)
1 and 2
b)
2, 3 and 4
c)
2 and 3
d)
4 only

|
Rinu Joseph answered |
There refraction and total internal reflection takes place. The ground will be hot and the air will be cool comparatively. Hence the layer just above the ground would also be hot. when the light enters from cool air to hot air, the refraction takes place and then total internal reflection happens. As a result it looks like a bend one like mirage.
A hydrogen-inflated polythene balloon is released from the surface of the earth. As the balloon rises to an altitude up in the atmosphere, it will
- a)decrease in size
- b)flatten into a disc-like shape
- c)maintain the same size and shape
- d)increase in size
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A hydrogen-inflated polythene balloon is released from the surface of the earth. As the balloon rises to an altitude up in the atmosphere, it will
a)
decrease in size
b)
flatten into a disc-like shape
c)
maintain the same size and shape
d)
increase in size

|
Arshiya Patel answered |
As a hydrogen-inflated polythene balloon rises to an altitude in the atmosphere, it will increase in size. This is because the atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing altitude. As the balloon ascends, the external pressure decreases while the pressure inside the balloon remains relatively constant
A man is standing on a boat in still water. If he walks towards the shore, the boat will- a)move towards the shore
- b)move away from the shore
- c)remain stationary
- d)sink
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A man is standing on a boat in still water. If he walks towards the shore, the boat will
a)
move towards the shore
b)
move away from the shore
c)
remain stationary
d)
sink

|
Juhi Patel answered |
Aman is standing on a boat in still water. If he walks towards the shore, the boat will move away from the shore. This is according to Newton’s third law of motion — to every action there is equal and opposite reaction.
The cloudy nights are warmer than clear nights because- a)clouds prevent escape of radiation of heat from the ground and the air.
- b)absorb sunlight in the day and radiate the same in night.
- c)clouds make the atmosphere damp and generate heat.
- d)clouds obstruct the movement of air which creates heat.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The cloudy nights are warmer than clear nights because
a)
clouds prevent escape of radiation of heat from the ground and the air.
b)
absorb sunlight in the day and radiate the same in night.
c)
clouds make the atmosphere damp and generate heat.
d)
clouds obstruct the movement of air which creates heat.
|
|
Jatin Ghosh answered |
The cloudy nights are warmer because clouds prevent escape of radiation of heat from the ground and the air.
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the phenomenon of- a)nuclear magnetic resonance
- b)electron spin resonance
- c)electron paramagnetic resonance
- d)diamagnetism of human tissues
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the phenomenon of
a)
nuclear magnetic resonance
b)
electron spin resonance
c)
electron paramagnetic resonance
d)
diamagnetism of human tissues

|
Arshiya Patel answered |
Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the phenomenon nuclear magnetic resonance.
If a rock is brought from the surface of the moon to the earth, then- a)its mass will change.
- b)its weight will change but not its mass.
- c)both mass and weight will change.
- d)both mass and weight will remain the same.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a rock is brought from the surface of the moon to the earth, then
a)
its mass will change.
b)
its weight will change but not its mass.
c)
both mass and weight will change.
d)
both mass and weight will remain the same.

|
Anjana Choudhary answered |
If a rock is brought from the surface of the moon to the earth, its weight will change but not its mass. Mass is a invariant physical quantity whereas weight of a body (w = mg) is variable as the value of acceleration due to gravity (g) changes.
A man inside a moving train tosses a coin, the coin falls behind him. The train is moving- a)forward with a uniform speed
- b)backward with a uniform speed
- c)forward with deceleration
- d)forward with acceleration
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A man inside a moving train tosses a coin, the coin falls behind him. The train is moving
a)
forward with a uniform speed
b)
backward with a uniform speed
c)
forward with deceleration
d)
forward with acceleration

|
Avi Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Train's Direction and Coin's Motion:
When the man tosses the coin inside a moving train, the coin falls behind him. This indicates that the train is accelerating forward.
Reasoning:
- If the train was moving forward with a uniform speed, the coin would fall straight down vertically relative to the train.
- If the train was moving backward with a uniform speed, the coin would fall forward relative to the train.
- If the train was moving forward with deceleration, the coin would fall forward but at a slower rate than the train's motion.
Acceleration of the Train:
- Since the coin falls behind the man, it means that the train is accelerating forward, causing the coin to lag behind due to inertia.
- The acceleration of the train causes the coin to fall at a position behind the man where it was released.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - forward with acceleration.
Train's Direction and Coin's Motion:
When the man tosses the coin inside a moving train, the coin falls behind him. This indicates that the train is accelerating forward.
Reasoning:
- If the train was moving forward with a uniform speed, the coin would fall straight down vertically relative to the train.
- If the train was moving backward with a uniform speed, the coin would fall forward relative to the train.
- If the train was moving forward with deceleration, the coin would fall forward but at a slower rate than the train's motion.
Acceleration of the Train:
- Since the coin falls behind the man, it means that the train is accelerating forward, causing the coin to lag behind due to inertia.
- The acceleration of the train causes the coin to fall at a position behind the man where it was released.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' - forward with acceleration.
What were the majority of atoms produced during the Big Bang?- a)Hydrogen
- b)Helium
- c)Oxygen
- d)Carbon
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What were the majority of atoms produced during the Big Bang?
a)
Hydrogen
b)
Helium
c)
Oxygen
d)
Carbon
|
|
Rashi Mukherjee answered |
Overview of Big Bang Nucleosynthesis
The Big Bang theory explains the formation of the universe and the primary elements produced in its early moments, known as Big Bang nucleosynthesis. This process occurred within the first few minutes after the Big Bang when the universe was hot and dense.
Production of Light Elements
During this initial phase, the extreme temperatures and pressures facilitated nuclear reactions, leading to the formation of the lightest elements. The predominant atoms produced were:
Why Hydrogen Dominates
The dominance of hydrogen is due to several factors:
Conclusion
In summary, while helium was also produced in significant quantities, the overwhelming majority of atoms formed during the Big Bang were hydrogen. This abundance laid the foundation for later star formation and the synthesis of heavier elements in stellar processes.
The Big Bang theory explains the formation of the universe and the primary elements produced in its early moments, known as Big Bang nucleosynthesis. This process occurred within the first few minutes after the Big Bang when the universe was hot and dense.
Production of Light Elements
During this initial phase, the extreme temperatures and pressures facilitated nuclear reactions, leading to the formation of the lightest elements. The predominant atoms produced were:
- Hydrogen: Approximately 75% of the universe's baryonic mass is composed of hydrogen. Protons were formed from quarks, and these protons became the basic building blocks of hydrogen.
- Helium: Roughly 25% of the mass was converted into helium, primarily in the form of helium-4 nuclei, as nuclear fusion occurred among protons and neutrons.
- Trace Elements: Minor amounts of lithium and beryllium were formed, but the quantities were significantly less than hydrogen and helium.
Why Hydrogen Dominates
The dominance of hydrogen is due to several factors:
- Simple Structure: Hydrogen, being the simplest element, requires the least energy to form. The fusion process favored its production over heavier elements.
- Stability: Hydrogen nuclei (protons) are stable and do not undergo further fusion under the conditions present at the time, allowing them to remain abundant.
Conclusion
In summary, while helium was also produced in significant quantities, the overwhelming majority of atoms formed during the Big Bang were hydrogen. This abundance laid the foundation for later star formation and the synthesis of heavier elements in stellar processes.
What is the significance of studying the Cosmic Background Radiation?- a)To understand the expansion of galaxies.
- b)To learn about dark matter's properties.
- c)To gain insights into the early stages of the Universe.
- d)To study the formation of planets.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the significance of studying the Cosmic Background Radiation?
a)
To understand the expansion of galaxies.
b)
To learn about dark matter's properties.
c)
To gain insights into the early stages of the Universe.
d)
To study the formation of planets.
|
|
Kavita Shah answered |
Studying the Cosmic Background Radiation provides valuable insights into the early stages of the Universe and its evolution.
What did the early Universe contain before the formation of atoms?- a)Galaxies
- b)Photons and free electrons
- c)Dark matter
- d)Planets
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What did the early Universe contain before the formation of atoms?
a)
Galaxies
b)
Photons and free electrons
c)
Dark matter
d)
Planets
|
|
Kavita Shah answered |
The early Universe contained photons (light) as elementary particles and free electrons.
The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall because- a)it is tappered at the top.
- b)it covers a large base area.
- c)its centre of gravity remains at the lowest position.
- d)the vertical line through the centre of gravity of the tower falls within the base.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall because
a)
it is tappered at the top.
b)
it covers a large base area.
c)
its centre of gravity remains at the lowest position.
d)
the vertical line through the centre of gravity of the tower falls within the base.
|
|
Gargi Kumar answered |
The Leaning Tower of Pisa does not fall because:
Explanation:
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is famous for its unintended tilt, which has been attracting tourists from all over the world. Despite its significant lean, the tower has managed to remain standing for centuries. The correct answer to why the tower does not fall is option 'D', which states that the vertical line through the center of gravity of the tower falls within the base. Let's explore this answer in more detail:
Center of Gravity:
The center of gravity is the point through which the entire weight of an object can be considered to act. In a symmetrical object, the center of gravity lies at the geometrical center. However, in an asymmetrical object like the Leaning Tower of Pisa, the center of gravity is shifted due to its tilt.
Effect of Tapering at the Top:
The tower is tapered at the top, which means it becomes narrower as it goes higher. This tapering helps in distributing the weight of the tower more evenly, reducing the stress on the lower parts. It prevents the tower from toppling over due to excessive weight at the higher levels.
Large Base Area:
The tower has a large base area, which provides stability and prevents it from tipping over. The weight of the tower is distributed over a larger surface area, reducing the pressure on the ground and maintaining its equilibrium.
Center of Gravity within the Base:
The most crucial factor that prevents the tower from falling is that the vertical line through the center of gravity of the tower falls within the base. This means that the imaginary line passing through the center of gravity always remains inside the footprint of the tower, ensuring its stability. If the center of gravity were to fall outside the base, the tower would lose its balance and topple over.
Conclusion:
The Leaning Tower of Pisa remains standing due to a combination of factors, including its tapered structure, large base area, and most importantly, the positioning of the center of gravity within the base. These factors work together to maintain the tower's equilibrium and prevent it from falling.
Explanation:
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is famous for its unintended tilt, which has been attracting tourists from all over the world. Despite its significant lean, the tower has managed to remain standing for centuries. The correct answer to why the tower does not fall is option 'D', which states that the vertical line through the center of gravity of the tower falls within the base. Let's explore this answer in more detail:
Center of Gravity:
The center of gravity is the point through which the entire weight of an object can be considered to act. In a symmetrical object, the center of gravity lies at the geometrical center. However, in an asymmetrical object like the Leaning Tower of Pisa, the center of gravity is shifted due to its tilt.
Effect of Tapering at the Top:
The tower is tapered at the top, which means it becomes narrower as it goes higher. This tapering helps in distributing the weight of the tower more evenly, reducing the stress on the lower parts. It prevents the tower from toppling over due to excessive weight at the higher levels.
Large Base Area:
The tower has a large base area, which provides stability and prevents it from tipping over. The weight of the tower is distributed over a larger surface area, reducing the pressure on the ground and maintaining its equilibrium.
Center of Gravity within the Base:
The most crucial factor that prevents the tower from falling is that the vertical line through the center of gravity of the tower falls within the base. This means that the imaginary line passing through the center of gravity always remains inside the footprint of the tower, ensuring its stability. If the center of gravity were to fall outside the base, the tower would lose its balance and topple over.
Conclusion:
The Leaning Tower of Pisa remains standing due to a combination of factors, including its tapered structure, large base area, and most importantly, the positioning of the center of gravity within the base. These factors work together to maintain the tower's equilibrium and prevent it from falling.
A fan produces a feeling of comfort during hot weather because- a)fan supplies cool air
- b)our body radiates more heat in air
- c)conductivity of air increases
- d)our perspiration evaporates rapidly
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A fan produces a feeling of comfort during hot weather because
a)
fan supplies cool air
b)
our body radiates more heat in air
c)
conductivity of air increases
d)
our perspiration evaporates rapidly

|
Puja Menon answered |
A fan produces a feeling of comfort during hot weather because our perspiration evaporates rapidly. Evaporation process takes surroundings temperature.
If the doors of a refrigerator are left open for a few hours, the room temperature will- a)decrease
- b)increase
- c)remain the same
- d)decrease only in the area in the vicinity of the refrigerator
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the doors of a refrigerator are left open for a few hours, the room temperature will
a)
decrease
b)
increase
c)
remain the same
d)
decrease only in the area in the vicinity of the refrigerator

|
Pallavi Chakraborty answered |
If the doors of a refrigerator are left open for a few hours, the room temperature will increase as the system release heat to the surroundings.
Consider the following statements and select the correct code.
Assertion (A): A piece of copper and a piece of glass are heated to the same temperature. When touched, thereafter, the copper piece appears hotter than the glass piece.
Reason (R): The density of copper is more than that of glass.- a)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct code.
Assertion (A): A piece of copper and a piece of glass are heated to the same temperature. When touched, thereafter, the copper piece appears hotter than the glass piece.
Reason (R): The density of copper is more than that of glass.
Assertion (A): A piece of copper and a piece of glass are heated to the same temperature. When touched, thereafter, the copper piece appears hotter than the glass piece.
Reason (R): The density of copper is more than that of glass.
a)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Devanshi Reddy answered |
Assertion (A): A piece of copper and a piece of glass are heated to the same temperature. When touched, thereafter, the copper piece appears hotter than the glass piece.
Reason (R): The density of copper is more than that of glass.
The correct answer is option B: Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Difference in Heat Transfer:
When two objects at the same temperature are touched, heat flows from the hotter object to the cooler object. The rate of heat transfer depends on various factors including the thermal conductivity of the materials.
Thermal Conductivity:
The thermal conductivity of a material determines how well it conducts heat. Copper has a higher thermal conductivity compared to glass. This means that copper can transfer heat more efficiently than glass.
Rate of Heat Transfer:
When the copper and glass pieces are heated to the same temperature and then touched, the copper piece will transfer heat to our skin more effectively due to its higher thermal conductivity. As a result, it will feel hotter to the touch compared to the glass piece.
Density:
Density, on the other hand, is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume. It is not directly related to the sensation of heat. The density of copper is indeed higher than that of glass, but this difference in density does not directly contribute to the perceived temperature difference when the objects are touched.
Explanation of the Answer:
Both the assertion and the reason are true. When two objects at the same temperature are touched, the object with higher thermal conductivity (in this case, copper) will transfer heat more effectively and feel hotter to the touch. However, the reason provided (density) does not directly explain why the copper piece feels hotter. Density is not a factor in the sensation of temperature. Therefore, option B is the correct answer as it states that both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Reason (R): The density of copper is more than that of glass.
The correct answer is option B: Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation:
Difference in Heat Transfer:
When two objects at the same temperature are touched, heat flows from the hotter object to the cooler object. The rate of heat transfer depends on various factors including the thermal conductivity of the materials.
Thermal Conductivity:
The thermal conductivity of a material determines how well it conducts heat. Copper has a higher thermal conductivity compared to glass. This means that copper can transfer heat more efficiently than glass.
Rate of Heat Transfer:
When the copper and glass pieces are heated to the same temperature and then touched, the copper piece will transfer heat to our skin more effectively due to its higher thermal conductivity. As a result, it will feel hotter to the touch compared to the glass piece.
Density:
Density, on the other hand, is a measure of how much mass is packed into a given volume. It is not directly related to the sensation of heat. The density of copper is indeed higher than that of glass, but this difference in density does not directly contribute to the perceived temperature difference when the objects are touched.
Explanation of the Answer:
Both the assertion and the reason are true. When two objects at the same temperature are touched, the object with higher thermal conductivity (in this case, copper) will transfer heat more effectively and feel hotter to the touch. However, the reason provided (density) does not directly explain why the copper piece feels hotter. Density is not a factor in the sensation of temperature. Therefore, option B is the correct answer as it states that both the assertion and the reason are true, but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
An endoscopic process is based on the principle of
- a)refraction of light
- b)reflection of light
- c)total internal reflection of light
- d)dispersion of light
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An endoscopic process is based on the principle of
a)
refraction of light
b)
reflection of light
c)
total internal reflection of light
d)
dispersion of light
|
|
Pritam Chaudhary answered |
Understanding Endoscopic Processes
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that allows doctors to view the inside of a patient's body using a flexible tube with a camera and light source. The principle that enables this visualization is based on total internal reflection of light.
What is Total Internal Reflection?
- Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a denser medium to a less dense medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.
- In endoscopes, this principle is utilized to transmit light and images through optical fibers.
How It Works in Endoscopy
- Light Transmission: The endoscope contains numerous optical fibers that guide light. When light is sent through these fibers, it reflects internally, allowing it to bend around corners and maintain brightness.
- Image Capture: The camera at the end of the endoscope captures the light reflected from the tissue, creating a clear image for the physician to analyze.
Advantages of Using Total Internal Reflection
- Minimally Invasive: Endoscopy provides a less invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods, leading to quicker recovery times.
- High-Quality Images: The use of optical fibers ensures high-resolution images, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
In summary, the effectiveness of endoscopic procedures is largely due to the principle of total internal reflection, allowing for effective light transmission and high-quality imaging within the human body. This technology has revolutionized diagnostic and surgical techniques in medicine.
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that allows doctors to view the inside of a patient's body using a flexible tube with a camera and light source. The principle that enables this visualization is based on total internal reflection of light.
What is Total Internal Reflection?
- Total internal reflection occurs when light travels from a denser medium to a less dense medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.
- In endoscopes, this principle is utilized to transmit light and images through optical fibers.
How It Works in Endoscopy
- Light Transmission: The endoscope contains numerous optical fibers that guide light. When light is sent through these fibers, it reflects internally, allowing it to bend around corners and maintain brightness.
- Image Capture: The camera at the end of the endoscope captures the light reflected from the tissue, creating a clear image for the physician to analyze.
Advantages of Using Total Internal Reflection
- Minimally Invasive: Endoscopy provides a less invasive alternative to traditional surgical methods, leading to quicker recovery times.
- High-Quality Images: The use of optical fibers ensures high-resolution images, which are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Conclusion
In summary, the effectiveness of endoscopic procedures is largely due to the principle of total internal reflection, allowing for effective light transmission and high-quality imaging within the human body. This technology has revolutionized diagnostic and surgical techniques in medicine.
Consider the following statements and select the correct code.
Assertion (A): The temperature of a metal wire rises when an electric current is passed through it.
Reason (R): Collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy.
- a)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct code.
Assertion (A): The temperature of a metal wire rises when an electric current is passed through it.
Reason (R): Collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy.
Assertion (A): The temperature of a metal wire rises when an electric current is passed through it.
Reason (R): Collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy.
a)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Dishani Dasgupta answered |
Assertion: The temperature of a metal wire rises when an electric current is passed through it.
Reason: Collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy.
The correct code for the given statements is option A, which states that both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation:
When an electric current is passed through a metal wire, the temperature of the wire rises. This phenomenon is known as the Joule heating effect or resistive heating. It can be understood through the following explanation:
1. Joule Heating Effect:
When an electric current flows through a conductor, such as a metal wire, it encounters resistance. This resistance causes the collision of free electrons with metal atoms in the wire. The collision transfers energy to the metal atoms in the form of kinetic energy, which leads to an increase in their random motion. This increased random motion of metal atoms results in an increase in the temperature of the wire.
2. Collision of Metal Atoms:
The reason behind the rise in temperature during the flow of electric current is the collision of metal atoms with each other. These collisions release heat energy due to the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy. The energy transferred during collisions is responsible for the rise in temperature of the metal wire.
3. Explanation of Assertion and Reason:
The assertion is true as the temperature of a metal wire does rise when an electric current is passed through it. This is a well-established phenomenon known as the Joule heating effect. The reason provided is also true as the collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy, which is responsible for the rise in temperature. Therefore, the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it can be concluded that both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Hence, option A is the correct code for the given statements.
Reason: Collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy.
The correct code for the given statements is option A, which states that both the assertion and reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation:
When an electric current is passed through a metal wire, the temperature of the wire rises. This phenomenon is known as the Joule heating effect or resistive heating. It can be understood through the following explanation:
1. Joule Heating Effect:
When an electric current flows through a conductor, such as a metal wire, it encounters resistance. This resistance causes the collision of free electrons with metal atoms in the wire. The collision transfers energy to the metal atoms in the form of kinetic energy, which leads to an increase in their random motion. This increased random motion of metal atoms results in an increase in the temperature of the wire.
2. Collision of Metal Atoms:
The reason behind the rise in temperature during the flow of electric current is the collision of metal atoms with each other. These collisions release heat energy due to the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy. The energy transferred during collisions is responsible for the rise in temperature of the metal wire.
3. Explanation of Assertion and Reason:
The assertion is true as the temperature of a metal wire does rise when an electric current is passed through it. This is a well-established phenomenon known as the Joule heating effect. The reason provided is also true as the collision of metal atoms with each other releases heat energy, which is responsible for the rise in temperature. Therefore, the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it can be concluded that both the assertion and reason are true, and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion. Hence, option A is the correct code for the given statements.
What is the overall shape of the Universe according to scientific observations?- a)Spherical
- b)Cylindrical
- c)Flat
- d)Conical
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the overall shape of the Universe according to scientific observations?
a)
Spherical
b)
Cylindrical
c)
Flat
d)
Conical
|
|
Maheshwar Jain answered |
Flat Shape of the Universe:
The overall shape of the Universe according to scientific observations is considered to be flat. This conclusion is based on a variety of observations and measurements made by astronomers and cosmologists.
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation:
One of the key pieces of evidence supporting the flat shape of the Universe comes from the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMB). The fluctuations in the CMB provide valuable information about the geometry of the Universe, and the data collected indicates that the Universe is flat.
Measurements of Large-Scale Structure:
Observations of the large-scale structure of the Universe, including the distribution of galaxies and galaxy clusters, also support the idea that the Universe is flat. These measurements suggest that the overall geometry of the Universe is consistent with a flat shape.
General Relativity:
The theory of General Relativity, proposed by Albert Einstein, also supports the idea of a flat Universe. According to General Relativity, the geometry of the Universe is determined by the distribution of matter and energy, and in a flat Universe, the total energy density is equal to the critical density.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, based on observations of the CMB, measurements of the large-scale structure of the Universe, and the predictions of General Relativity, scientists have determined that the overall shape of the Universe is flat. This has significant implications for our understanding of the cosmos and the fundamental nature of the Universe.
What is the Big Bang Theory?- a)A theory proposing the existence of multiple universes.
- b)A theory explaining the origin of the universe through a massive explosion.
- c)A theory suggesting that the universe has always existed in its current state.
- d)A theory explaining the formation of stars and galaxies.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the Big Bang Theory?
a)
A theory proposing the existence of multiple universes.
b)
A theory explaining the origin of the universe through a massive explosion.
c)
A theory suggesting that the universe has always existed in its current state.
d)
A theory explaining the formation of stars and galaxies.
|
|
Sanjay Rana answered |
The Big Bang Theory is a scientific model that explains the origin of the universe through a massive explosion approximately 13.7 billion years ago.
What do we call the afterglow of the Big Bang?- a)Cosmic Background Radiation
- b)Galactic Glow
- c)Celestial Aftermath
- d)Stellar Residue
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What do we call the afterglow of the Big Bang?
a)
Cosmic Background Radiation
b)
Galactic Glow
c)
Celestial Aftermath
d)
Stellar Residue

|
Ashwini Mehta answered |
Understanding the Cosmic Background Radiation
The afterglow of the Big Bang, known as Cosmic Background Radiation (CBR), is a crucial concept in cosmology. It represents the remnant heat from the early universe, providing insights into its origins and evolution.
What is Cosmic Background Radiation?
- CBR is the faint microwave radiation that fills the universe.
- It originated about 380,000 years after the Big Bang, when the universe cooled enough for protons and electrons to combine and form hydrogen atoms.
Significance of CBR
- Evidence of the Big Bang: CBR supports the Big Bang theory by confirming that the universe was once in a hot, dense state.
- Uniformity: The radiation is remarkably uniform across the sky, indicating that the early universe was homogeneous.
- Temperature: The temperature of CBR is approximately 2.7 Kelvin, which is consistent across the observable universe.
Discovery and Impact
- CBR was discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, leading to a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1978.
- Its discovery provided strong evidence for the Big Bang theory over alternative models, such as steady-state theories.
Conclusion
Cosmic Background Radiation is a fundamental aspect of our understanding of the universe, acting as a snapshot of the cosmos shortly after its inception. It not only supports the Big Bang theory but also offers a wealth of information about the universe's structure and evolution.
The afterglow of the Big Bang, known as Cosmic Background Radiation (CBR), is a crucial concept in cosmology. It represents the remnant heat from the early universe, providing insights into its origins and evolution.
What is Cosmic Background Radiation?
- CBR is the faint microwave radiation that fills the universe.
- It originated about 380,000 years after the Big Bang, when the universe cooled enough for protons and electrons to combine and form hydrogen atoms.
Significance of CBR
- Evidence of the Big Bang: CBR supports the Big Bang theory by confirming that the universe was once in a hot, dense state.
- Uniformity: The radiation is remarkably uniform across the sky, indicating that the early universe was homogeneous.
- Temperature: The temperature of CBR is approximately 2.7 Kelvin, which is consistent across the observable universe.
Discovery and Impact
- CBR was discovered in 1965 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, leading to a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1978.
- Its discovery provided strong evidence for the Big Bang theory over alternative models, such as steady-state theories.
Conclusion
Cosmic Background Radiation is a fundamental aspect of our understanding of the universe, acting as a snapshot of the cosmos shortly after its inception. It not only supports the Big Bang theory but also offers a wealth of information about the universe's structure and evolution.
Why is hydrogen's presence essential during the Big Bang?- a)Hydrogen is crucial for the formation of stars and galaxies.
- b)Without hydrogen, there would be no planets in the universe.
- c)Hydrogen is the primary building block for water, vital for life's sustenance.
- d)Hydrogen helps maintain the equilibrium of the expanding universe.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Why is hydrogen's presence essential during the Big Bang?
a)
Hydrogen is crucial for the formation of stars and galaxies.
b)
Without hydrogen, there would be no planets in the universe.
c)
Hydrogen is the primary building block for water, vital for life's sustenance.
d)
Hydrogen helps maintain the equilibrium of the expanding universe.
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Hydrogen is a primary building block for water, and without it, there would be no water, which is vital for life's sustenance.
Pendulum clocks become slow in summer because- a)days in summer are large.
- b)of the friction in the coil.
- c)the length of the pendulum increases.
- d)the weight of the pendulum changes.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Pendulum clocks become slow in summer because
a)
days in summer are large.
b)
of the friction in the coil.
c)
the length of the pendulum increases.
d)
the weight of the pendulum changes.

|
Janhavi Dey answered |
Pendulum clocks become slow in summer because the length of the pendulum increases. Increase in length ∆l = lo α ∆T where lo = original length, α = coefficient of linear expansion and ∆T = change in temperature.
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Assertion (A): If ice collects on the freezer, the cooling in the refrigerator is affected adversely.
Reason (R): Ice is a poor conductor.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
Assertion (A): If ice collects on the freezer, the cooling in the refrigerator is affected adversely.
Reason (R): Ice is a poor conductor.
Assertion (A): If ice collects on the freezer, the cooling in the refrigerator is affected adversely.
Reason (R): Ice is a poor conductor.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Aniket Mehra answered |
If ice collects on the freezer, the cooling in the refrigerator is affected adversely because ice is a poor conductor of heat.
An oil tanker is partially filled with oil and moves forward on a level road with uniform acceleration. The free surface of oil then- a)remains horizontal.
- b)is inclined to the horizontal with smaller depth at the rear end.
- c)is inclined to the horizontal with larger depth at the rear end.
- d)assumes parabolic curves.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An oil tanker is partially filled with oil and moves forward on a level road with uniform acceleration. The free surface of oil then
a)
remains horizontal.
b)
is inclined to the horizontal with smaller depth at the rear end.
c)
is inclined to the horizontal with larger depth at the rear end.
d)
assumes parabolic curves.

|
Shivam Verma answered |
The free surface of oil is inclined to the horizontal with larger depth at the rear end as the oil tanker is moving forward with uniform acceleration.
What happened during the Big Bang?- a)All matter and energy in the universe were concentrated into an incredibly small, dense point.
- b)The universe reached a state of equilibrium.
- c)The universe expanded, leading to the formation of galaxies.
- d)All planets and stars were formed.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What happened during the Big Bang?
a)
All matter and energy in the universe were concentrated into an incredibly small, dense point.
b)
The universe reached a state of equilibrium.
c)
The universe expanded, leading to the formation of galaxies.
d)
All planets and stars were formed.
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
During the Big Bang, all matter and energy in the cosmos were concentrated into an incredibly small, dense point, much smaller than an atom.
What is the prevailing theory about the universe just before the Big Bang?- a)The universe was filled with stars and galaxies.
- b)The universe was an empty void with no matter or energy.
- c)The universe was filled with an intensely concentrated and unstable form of energy.
- d)The universe existed in a steady state.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the prevailing theory about the universe just before the Big Bang?
a)
The universe was filled with stars and galaxies.
b)
The universe was an empty void with no matter or energy.
c)
The universe was filled with an intensely concentrated and unstable form of energy.
d)
The universe existed in a steady state.
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
The prevailing theory is that the universe just before the Big Bang was filled with an intensely concentrated and unstable form of energy.
What force is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the Universe?- a)Gravitational pull of matter
- b)Dark energy
- c)Electromagnetic force
- d)Nuclear force
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What force is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the Universe?
a)
Gravitational pull of matter
b)
Dark energy
c)
Electromagnetic force
d)
Nuclear force
|
|
Kavita Shah answered |
Dark energy is the force responsible for the accelerated expansion of the Universe.
The minimum height of a plane mirror to see the full size image of a person is equal to- a)the height of the person
- b)half the height of the person
- c)one-fourth the height of the person
- d)double the height of the person
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum height of a plane mirror to see the full size image of a person is equal to
a)
the height of the person
b)
half the height of the person
c)
one-fourth the height of the person
d)
double the height of the person

|
Avi Sengupta answered |
Explanation:
Height of the Mirror:
- When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, the image formed is virtual and erect.
- In order to see the full size image of the person, the mirror needs to be positioned in such a way that the top of the person's head is at the same level as the top of the mirror.
Height Requirement:
- The minimum height of the mirror should be half the height of the person to ensure that the entire image of the person is visible in the mirror.
- This is because the bottom half of the person's body will be reflected from the top half of the mirror, and the top half of the person's body will be reflected from the bottom half of the mirror.
- Therefore, half the height of the person is sufficient for the mirror to display the full-size image.
Conclusion:
- In conclusion, the minimum height of a plane mirror to see the full size image of a person is half the height of the person.
- This ensures that both the top and bottom halves of the person are reflected in the mirror, allowing for a complete and accurate representation of the person's image.
Height of the Mirror:
- When a person stands in front of a plane mirror, the image formed is virtual and erect.
- In order to see the full size image of the person, the mirror needs to be positioned in such a way that the top of the person's head is at the same level as the top of the mirror.
Height Requirement:
- The minimum height of the mirror should be half the height of the person to ensure that the entire image of the person is visible in the mirror.
- This is because the bottom half of the person's body will be reflected from the top half of the mirror, and the top half of the person's body will be reflected from the bottom half of the mirror.
- Therefore, half the height of the person is sufficient for the mirror to display the full-size image.
Conclusion:
- In conclusion, the minimum height of a plane mirror to see the full size image of a person is half the height of the person.
- This ensures that both the top and bottom halves of the person are reflected in the mirror, allowing for a complete and accurate representation of the person's image.
Consider the following statements in respect of a jet engine and a rocket:
1. A jet engine uses the surrounding air for its oxygen supply and so is unsuitable for motion in space.
2. A rocket carries its own supply of oxygen in the gas form as a fuel.
Q. Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?- a)1 only
- b)2 only
- c)Both 1 and 2
- d)Neither 1 nor 2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements in respect of a jet engine and a rocket:
1. A jet engine uses the surrounding air for its oxygen supply and so is unsuitable for motion in space.
2. A rocket carries its own supply of oxygen in the gas form as a fuel.
Q. Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
1. A jet engine uses the surrounding air for its oxygen supply and so is unsuitable for motion in space.
2. A rocket carries its own supply of oxygen in the gas form as a fuel.
Q. Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
a)
1 only
b)
2 only
c)
Both 1 and 2
d)
Neither 1 nor 2

|
Saumya Bose answered |
In respect of a jet engine and a rocket, both the given statements are correct.
Consider the following statements and select the correct code:
Assertion (A): A piece of ice added to the drink cools it.
Reason (R): Ice takes latent heat from the drink for melting resulting in the cooling of the drink.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct code:
Assertion (A): A piece of ice added to the drink cools it.
Reason (R): Ice takes latent heat from the drink for melting resulting in the cooling of the drink.
Assertion (A): A piece of ice added to the drink cools it.
Reason (R): Ice takes latent heat from the drink for melting resulting in the cooling of the drink.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Baishali Patel answered |
A piece of ice added to the drink cool it because ice takes latent heat from the drink for melting resulting in the cooling of the drink.
Consider the following statements:
1. Light of longer wavelength is scattered much more than the light of shorter wavelength.
2. The speed of visible light in water is 0.95 times the speed in vacuum.
3. Radio waves are produced by rapidly oscillating electrical currents.
4. To detect the overspeeding of vehicles, police use the Doppler effect to reflected short radio waves.
Q. Which of these statements are correct?- a)1 and 2
- b)1 and 3
- c)2 and 4
- d)3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Light of longer wavelength is scattered much more than the light of shorter wavelength.
2. The speed of visible light in water is 0.95 times the speed in vacuum.
3. Radio waves are produced by rapidly oscillating electrical currents.
4. To detect the overspeeding of vehicles, police use the Doppler effect to reflected short radio waves.
Q. Which of these statements are correct?
1. Light of longer wavelength is scattered much more than the light of shorter wavelength.
2. The speed of visible light in water is 0.95 times the speed in vacuum.
3. Radio waves are produced by rapidly oscillating electrical currents.
4. To detect the overspeeding of vehicles, police use the Doppler effect to reflected short radio waves.
Q. Which of these statements are correct?
a)
1 and 2
b)
1 and 3
c)
2 and 4
d)
3 and 4

|
Puja Menon answered |
Radio waves are produced by rapidly oscillating electrical currents. For detecting over speeding of vehicles, police use the Doppler effect to reflected short radio waves.
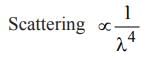
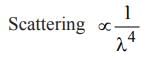
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct?- a)The velocity of sound in air increases with the increase of temperature.
- b)The velocity of sound in air is independent of pressure.
- c)The velocity of sound in air decreases as the humidity increases.
- d)The velocity of sound in air is not affected by the change in amplitude and frequency.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
a)
The velocity of sound in air increases with the increase of temperature.
b)
The velocity of sound in air is independent of pressure.
c)
The velocity of sound in air decreases as the humidity increases.
d)
The velocity of sound in air is not affected by the change in amplitude and frequency.

|
Surbhi Rane answered |
The velocity of sound in air increases as the humidity increases.
Consider the following statements and select the correct code.
Assertion (A): A diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation cut to the same shape.
Reason (R): The refractive index of diamond is less than that of glass.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements and select the correct code.
Assertion (A): A diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation cut to the same shape.
Reason (R): The refractive index of diamond is less than that of glass.
Assertion (A): A diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation cut to the same shape.
Reason (R): The refractive index of diamond is less than that of glass.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Gargi Saha answered |
A diamond sparkles more than a glass imitation cut to the same shape is only the true statement. The refractive index of diamond 2.42 > glass 1.5.
Consider the following statements:
1. Two persons on the surface of moon cannot talk to each other.
2. Sound waves cannot travel through vacuum.
3. Speed of sound is greater in solid medium than in liquid or gas medium. - a)3 alone is correct
- b)1 and 2 are correct
- c)1 and 3 are correct
- d)1, 2 and 3 are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following statements:
1. Two persons on the surface of moon cannot talk to each other.
2. Sound waves cannot travel through vacuum.
3. Speed of sound is greater in solid medium than in liquid or gas medium.
1. Two persons on the surface of moon cannot talk to each other.
2. Sound waves cannot travel through vacuum.
3. Speed of sound is greater in solid medium than in liquid or gas medium.
a)
3 alone is correct
b)
1 and 2 are correct
c)
1 and 3 are correct
d)
1, 2 and 3 are correct

|
Arshiya Patel answered |
Sound waves require material medium to travel. On the surface of the moon, there is no atmosphere. The speed of sound is maximum in solids and minimum in gas medium.
Rainbow is formed due to a combination of- a)refraction and absorption
- b)dispersion and total internal reflection
- c)refraction and scattering
- d)dispersion and diffraction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Rainbow is formed due to a combination of
a)
refraction and absorption
b)
dispersion and total internal reflection
c)
refraction and scattering
d)
dispersion and diffraction

|
Gauri Bose answered |
A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection, refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun.
What did the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) mission study?- a)Formation of stars and galaxies.
- b)Cosmic Background Radiation.
- c)The expansion of the universe.
- d)The dark energy accelerating the universe's expansion.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What did the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) mission study?
a)
Formation of stars and galaxies.
b)
Cosmic Background Radiation.
c)
The expansion of the universe.
d)
The dark energy accelerating the universe's expansion.
|
|
Disha Yadav answered |
Study of Cosmic Background Radiation by WMAP:
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) mission primarily studied the Cosmic Background Radiation, also known as the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) radiation.
Understanding the CMB:
- The CMB is the radiation left over from the Big Bang, which occurred approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
- It is one of the most important pieces of evidence for the Big Bang theory, providing insights into the early universe.
Mapping the CMB:
- WMAP was designed to map the temperature fluctuations in the CMB across the entire sky with high precision.
- By studying these fluctuations, scientists can learn about the distribution of matter and energy in the early universe.
Key Discoveries:
- WMAP provided crucial data on the age, composition, and geometry of the universe.
- It helped determine the universe's density, which has implications for its ultimate fate (expansion or contraction).
Implications for Cosmology:
- The precise measurements of the CMB by WMAP have significantly advanced our understanding of the universe's origins and evolution.
- It has provided valuable insights into the structure and content of the universe, supporting the current cosmological model.
In conclusion, the WMAP mission's study of the Cosmic Background Radiation has been instrumental in shaping our understanding of the universe's early history and evolution.
What is the potential fate of the universe according to some scientists?- a)The universe will continue to expand indefinitely.
- b)The universe will contract back on itself in a phase called the "Big Crunch."
- c)The universe will stabilize and remain in its current state.
- d)The universe will fragment into multiple smaller universes.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the potential fate of the universe according to some scientists?
a)
The universe will continue to expand indefinitely.
b)
The universe will contract back on itself in a phase called the "Big Crunch."
c)
The universe will stabilize and remain in its current state.
d)
The universe will fragment into multiple smaller universes.
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Some scientists believe that the expansion of the universe is finite and will eventually slow down, leading to a contraction phase known as the "Big Crunch."
Of the two bulbs in a house, one glows brighter than the other. Which of the following statements is correct?- a)The brightness does not depend on resistance.
- b)Both the bulbs have the same resistance.
- c)The brighter bulb has larger resistance.
- d)The dimmer bulb has larger resistance.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Of the two bulbs in a house, one glows brighter than the other. Which of the following statements is correct?
a)
The brightness does not depend on resistance.
b)
Both the bulbs have the same resistance.
c)
The brighter bulb has larger resistance.
d)
The dimmer bulb has larger resistance.

|
Gauri Menon answered |
The dimmer bulb has larger resistance than the brighter one. Power of the bulb ∝ 1 / Resistance Resistance is the obstruction offer to the flow of current.
Electronic motors operating at low voltages tend to burn out because- a)they draw more current which is inversely proportional to the voltage.
- b)they draw more current which is inversely proportional to the square root of the voltage.
- c)they draw heat proportional to V2.
- d)low voltage sets in electrical discharge.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electronic motors operating at low voltages tend to burn out because
a)
they draw more current which is inversely proportional to the voltage.
b)
they draw more current which is inversely proportional to the square root of the voltage.
c)
they draw heat proportional to V2.
d)
low voltage sets in electrical discharge.

|
Akshara Chavan answered |
Electronic motors draw more current which is inversely proportional to the voltage, therefore, more heat H = I2Rt is generated.
Which one of the following statements is not true about cosmic rays?- a)They have very high frequency.
- b)They have very high wavelength.
- c)They are made of highly energetic charged particles.
- d)They originate from the sun.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is not true about cosmic rays?
a)
They have very high frequency.
b)
They have very high wavelength.
c)
They are made of highly energetic charged particles.
d)
They originate from the sun.

|
Future Foundation Institute answered |
Cosmic rays have very high frequency >1023 Hz and wavelength <10–24 m.
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:


a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D

|
Amrutha Kapoor answered |
Revolver was discovered by Colt. Dynamite was discovered by Alfred Nobel. Law of cooling was discovered by Newton and law of pressure by Pascal.
What caused the Universe to become transparent?- a)The formation of galaxies.
- b)The cooling down of the Universe.
- c)The disappearance of dark energy.
- d)The formation of neutral atoms during recombination.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What caused the Universe to become transparent?
a)
The formation of galaxies.
b)
The cooling down of the Universe.
c)
The disappearance of dark energy.
d)
The formation of neutral atoms during recombination.
|
|
Kavita Shah answered |
The Universe became transparent when neutral atoms were formed during recombination, causing the scattering of photons to cease.
Why did the Universe appear opaque during its early stages?- a)Due to the absence of photons.
- b)Due to the scattering of photons by free electrons.
- c)Due to the presence of dark energy.
- d)Due to the formation of galaxies.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Why did the Universe appear opaque during its early stages?
a)
Due to the absence of photons.
b)
Due to the scattering of photons by free electrons.
c)
Due to the presence of dark energy.
d)
Due to the formation of galaxies.
|
|
Kavita Shah answered |
The Universe appeared opaque during its early stages because photons were scattered by free electrons, making it difficult for light to travel freely.
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:

- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:


a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D

|
Baishali Patel answered |
Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs and 1 angstrom = 10–10m, joule is the unit of energy. Intensity of sound is measured in decibel. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz).
It is more comfortable to wear white cloths in summer because- a)they reflect heat falling on them.
- b)they radiate heat tansferred from the body.
- c)they absorb perspiration.
- d)they are soothing to the eye.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
It is more comfortable to wear white cloths in summer because
a)
they reflect heat falling on them.
b)
they radiate heat tansferred from the body.
c)
they absorb perspiration.
d)
they are soothing to the eye.

|
Shraddha Mukherjee answered |
The white clothes reflect heat falling on them in summer and they absorb the least from the sun.
Chapter doubts & questions for Physics - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams 2025 is part of BPSC (Bihar) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for BPSC (Bihar) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Physics - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams in English & Hindi are available as part of BPSC (Bihar) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Science & Technology for State PSC Exams
113 videos|527 docs|217 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










