All Exams >
Grade 4 >
Science for Grade 4 >
All Questions
All questions of Speed and Energy for Grade 4 Exam
In a battery cell, energy is stored in the form of- a)electrical energy.
- b)muscular energy.
- c)chemical energy.
- d)solar energy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a battery cell, energy is stored in the form of
a)
electrical energy.
b)
muscular energy.
c)
chemical energy.
d)
solar energy.
|
|
Edu Impact answered |
In a battery cell, energy stored is in the form of chemical energy.

Which of the following statements is NOT true?- a)Machines make work easy.
- b)Machines increase the speed of doing work.
- c)Machines change the direction of force
- d)Machines produce energy.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
a)
Machines make work easy.
b)
Machines increase the speed of doing work.
c)
Machines change the direction of force
d)
Machines produce energy.
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Machines work when energy is provided to them and it does not produce energy.
Radha pushed a heavy table but failed to move it. Which of the following is TRUE of the above statement?- a)Energy is not spent but work is done.
- b)Energy is spent but work is not done.
- c)Energy is not spent and work is not done.
- d)Energy is spent and work is done.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Radha pushed a heavy table but failed to move it. Which of the following is TRUE of the above statement?
a)
Energy is not spent but work is done.
b)
Energy is spent but work is not done.
c)
Energy is not spent and work is not done.
d)
Energy is spent and work is done.
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Work is said to be done when an object is displaced or moved from one place to another by the application of force.
The ultimate source of our energy is- a)the sun.
- b)coal.
- c)wind.
- d)plants.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ultimate source of our energy is
a)
the sun.
b)
coal.
c)
wind.
d)
plants.
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
The ultimate source of energy is the sun.
To do work, we need- a)force.
- b)energy.
- c)hands.
- d)muscles.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
To do work, we need
a)
force.
b)
energy.
c)
hands.
d)
muscles.
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
We need energy to do work.
When we throw a ball into air, it falls back. The force responsible for this is- a)Muscular force.
- b)Gravitational force.
- c)Mechanical force.
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When we throw a ball into air, it falls back. The force responsible for this is
a)
Muscular force.
b)
Gravitational force.
c)
Mechanical force.
d)
none of these
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
The gravitational force of the earth pulls objects towards it.
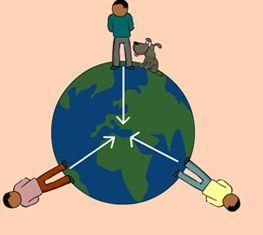
As defined in physics, work is done:- a)When an object moves
- b)When an object is stationary
- c)When an object stops
- d)A and C both
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
As defined in physics, work is done:
a)
When an object moves
b)
When an object is stationary
c)
When an object stops
d)
A and C both
|
|
Raj Majumdar answered |
Work is done when an object moves or stops
Work is a concept in physics that refers to the transfer of energy from one object to another. It is done when a force is applied to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force. However, work is also considered to be done when an object stops moving.
Definition of work
In physics, work is defined as the product of the force applied to an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force. Mathematically, work (W) is calculated using the formula:
W = F * d * cos(theta)
where F is the applied force, d is the displacement of the object, and theta is the angle between the force and the displacement vectors.
Explanation of the options
a) When an object moves: When a force is applied to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is done. This is because the force is causing a displacement in the object.
b) When an object is stationary: When an object is stationary, there is no displacement. Therefore, work is not done on the object in this case.
c) When an object stops: When an object is in motion and comes to a stop, work is considered to be done. This is because a force is applied to the object to bring it to a stop, causing a displacement in the opposite direction of the force.
d) A and C both: Both options A and C are correct. Work is done when an object moves and when an object stops. In both cases, there is a force applied to the object that results in a displacement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, work is done when an object moves in the direction of a force and when an object stops due to an applied force. Both scenarios involve a force causing a displacement, which is the key requirement for work to be done.
Work is a concept in physics that refers to the transfer of energy from one object to another. It is done when a force is applied to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force. However, work is also considered to be done when an object stops moving.
Definition of work
In physics, work is defined as the product of the force applied to an object and the displacement of the object in the direction of the force. Mathematically, work (W) is calculated using the formula:
W = F * d * cos(theta)
where F is the applied force, d is the displacement of the object, and theta is the angle between the force and the displacement vectors.
Explanation of the options
a) When an object moves: When a force is applied to an object and the object moves in the direction of the force, work is done. This is because the force is causing a displacement in the object.
b) When an object is stationary: When an object is stationary, there is no displacement. Therefore, work is not done on the object in this case.
c) When an object stops: When an object is in motion and comes to a stop, work is considered to be done. This is because a force is applied to the object to bring it to a stop, causing a displacement in the opposite direction of the force.
d) A and C both: Both options A and C are correct. Work is done when an object moves and when an object stops. In both cases, there is a force applied to the object that results in a displacement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, work is done when an object moves in the direction of a force and when an object stops due to an applied force. Both scenarios involve a force causing a displacement, which is the key requirement for work to be done.
If Ravi is able to move the table through a distance, then ____ is said to be done.- a)work
- b)force
- c)energy
- d)muscles
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If Ravi is able to move the table through a distance, then ____ is said to be done.
a)
work
b)
force
c)
energy
d)
muscles
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Work is said to be done only when a push or pull moves something that has weight, through a distance.
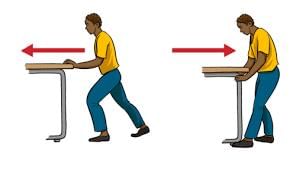
Choose the wrong statement among followings- a)Sounds vary in three ways: volume (loud or soft), pitch (high or low), and timbre (quality)
- b)The loudness of sound is measured in decibels (dB)
- c)Acoustics is the science and technology of energy
- d)All of the above statements are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the wrong statement among followings
a)
Sounds vary in three ways: volume (loud or soft), pitch (high or low), and timbre (quality)
b)
The loudness of sound is measured in decibels (dB)
c)
Acoustics is the science and technology of energy
d)
All of the above statements are incorrect
|
|
Sounak Kulkarni answered |
Acoustics is the interdisciplinary science that deals with the study of all mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound.
In which of the following situations no work is done?
- a)A spaceship moves at constant velocity
- b)You push on a heavy box but cannot move it
- c)A child slides down a playground slide
- d)You slam on the brakes and your car stops quickly
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following situations no work is done?
a)
A spaceship moves at constant velocity
b)
You push on a heavy box but cannot move it
c)
A child slides down a playground slide
d)
You slam on the brakes and your car stops quickly
|
|
Swara Roy answered |
Explanation:
When we talk about work, we are talking about the energy transferred when a force is applied over a distance. In other words, work is only done when a force causes an object to move. With that in mind, let's look at the given situations:
a) A spaceship moves at constant velocity:
- If a spaceship is moving at a constant velocity, then there is no acceleration, and no net force acting upon it. Therefore, no work is being done.
b) You push on a heavy box but cannot move it:
- In this situation, you are applying a force to the box, but the box is not moving. Since there is no displacement, no work is being done.
c) A child slides down a playground slide:
- In this situation, the force of gravity is causing the child to slide down the slide. Work is being done by gravity as it is causing the child to move a certain distance.
d) You slam on the brakes and your car stops quickly:
- When you slam on the brakes of your car, the brakes are applying a force to the wheels, which in turn apply a force to the car. This force causes the car to slow down and stop. Work is being done by the brakes because they are causing the car to move a certain distance.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', where no work is done when you push on a heavy box but cannot move it.
When we talk about work, we are talking about the energy transferred when a force is applied over a distance. In other words, work is only done when a force causes an object to move. With that in mind, let's look at the given situations:
a) A spaceship moves at constant velocity:
- If a spaceship is moving at a constant velocity, then there is no acceleration, and no net force acting upon it. Therefore, no work is being done.
b) You push on a heavy box but cannot move it:
- In this situation, you are applying a force to the box, but the box is not moving. Since there is no displacement, no work is being done.
c) A child slides down a playground slide:
- In this situation, the force of gravity is causing the child to slide down the slide. Work is being done by gravity as it is causing the child to move a certain distance.
d) You slam on the brakes and your car stops quickly:
- When you slam on the brakes of your car, the brakes are applying a force to the wheels, which in turn apply a force to the car. This force causes the car to slow down and stop. Work is being done by the brakes because they are causing the car to move a certain distance.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B', where no work is done when you push on a heavy box but cannot move it.
Which of these contain(s) an electromagnet?
- a)Lamp
- b)Electric stove
- c)Compass
- d)Headphones
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these contain(s) an electromagnet?
a)
Lamp
b)
Electric stove
c)
Compass
d)
Headphones
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
4. Headphones
Headphones use electromagnets to convert electrical signals into sound. When an electric current passes through the coils of wire in the headphones, it creates a magnetic field that moves the diaphragm to produce sound.
- Lamp: Typically uses an incandescent bulb or LED, not an electromagnet.
- Electric stove: Uses heating elements rather than electromagnets.
- Compass: Uses a permanent magnet, not an electromagnet.
So, the correct answer is:
4. Headphones
The _______________ works by using fuel derived from living and dead biological organisms.- a)Wind Energy
- b)Solar Energy
- c)Hydroelectric
- d)Biofuel
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The _______________ works by using fuel derived from living and dead biological organisms.
a)
Wind Energy
b)
Solar Energy
c)
Hydroelectric
d)
Biofuel
|
|
Ajay sethi answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option 'D' - Biofuel. Biofuel is a type of fuel that is derived from living and dead biological organisms. It is a renewable source of energy as it is made from organic matter which can be replenished.
Here is a detailed explanation of biofuel:
Definition of Biofuel:
Biofuel is a type of fuel that is produced from organic matter, such as plants, algae, and even animal waste. It is considered a renewable source of energy because the organic matter used to make biofuel can be grown and harvested repeatedly.
Types of Biofuel:
There are several types of biofuels, including:
1. Ethanol: Ethanol is a biofuel that is made from crops such as corn, sugarcane, and wheat. These crops undergo a fermentation process to convert their sugars into ethanol. Ethanol can be used as a fuel additive or as a complete replacement for gasoline in vehicles.
2. Biodiesel: Biodiesel is a biofuel that is made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking grease. These feedstocks undergo a chemical process called transesterification to convert them into biodiesel. Biodiesel can be used as a replacement for diesel fuel in vehicles.
3. Biogas: Biogas is a biofuel that is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter, such as agricultural waste, food waste, and sewage. The organic matter is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be used as a fuel for heating, electricity generation, and even as a vehicle fuel.
Advantages of Biofuel:
- Renewable: Biofuel is derived from organic matter, which can be grown and harvested repeatedly.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biofuel produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Energy independence: Biofuel can be produced locally, reducing dependence on foreign oil imports.
- Job creation: The biofuel industry can create jobs in agriculture, manufacturing, and research.
Conclusion:
Biofuel is an important source of renewable energy that is derived from living and dead biological organisms. It can be produced from a variety of feedstocks and has several advantages over fossil fuels. By using biofuel, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote energy independence, and create jobs in the biofuel industry.
The correct answer is option 'D' - Biofuel. Biofuel is a type of fuel that is derived from living and dead biological organisms. It is a renewable source of energy as it is made from organic matter which can be replenished.
Here is a detailed explanation of biofuel:
Definition of Biofuel:
Biofuel is a type of fuel that is produced from organic matter, such as plants, algae, and even animal waste. It is considered a renewable source of energy because the organic matter used to make biofuel can be grown and harvested repeatedly.
Types of Biofuel:
There are several types of biofuels, including:
1. Ethanol: Ethanol is a biofuel that is made from crops such as corn, sugarcane, and wheat. These crops undergo a fermentation process to convert their sugars into ethanol. Ethanol can be used as a fuel additive or as a complete replacement for gasoline in vehicles.
2. Biodiesel: Biodiesel is a biofuel that is made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking grease. These feedstocks undergo a chemical process called transesterification to convert them into biodiesel. Biodiesel can be used as a replacement for diesel fuel in vehicles.
3. Biogas: Biogas is a biofuel that is produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter, such as agricultural waste, food waste, and sewage. The organic matter is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing a mixture of methane and carbon dioxide. Biogas can be used as a fuel for heating, electricity generation, and even as a vehicle fuel.
Advantages of Biofuel:
- Renewable: Biofuel is derived from organic matter, which can be grown and harvested repeatedly.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biofuel produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Energy independence: Biofuel can be produced locally, reducing dependence on foreign oil imports.
- Job creation: The biofuel industry can create jobs in agriculture, manufacturing, and research.
Conclusion:
Biofuel is an important source of renewable energy that is derived from living and dead biological organisms. It can be produced from a variety of feedstocks and has several advantages over fossil fuels. By using biofuel, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, promote energy independence, and create jobs in the biofuel industry.
While walking, some or all of the following types of energy and work are involved:- a)Mechanical and kinetic energies
- b)Potential energy and the work done by the force that moves the body
- c)Kinetic energy, potential energy, work done by forces excluding the body´s weight and work lost through friction
- d)Kinetic energy, potential energy and work done by the body´s weight
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
While walking, some or all of the following types of energy and work are involved:
a)
Mechanical and kinetic energies
b)
Potential energy and the work done by the force that moves the body
c)
Kinetic energy, potential energy, work done by forces excluding the body´s weight and work lost through friction
d)
Kinetic energy, potential energy and work done by the body´s weight
|
|
Kavya Desai answered |
Understanding the Energy and Work Involved in Walking
Walking involves various forms of energy and work, primarily linked to the motion and position of the body. The correct answer is option 'D' because it encompasses the essential energies and work done by the body's weight.
1. Kinetic Energy
- Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
- When walking, the legs and body are in constant movement, which means kinetic energy is being generated.
2. Potential Energy
- Potential energy is the energy stored due to an object's position.
- When walking uphill, for example, the body gains potential energy, which is related to its height above the ground.
3. Work Done by the Body's Weight
- The weight of the body (mass multiplied by the gravitational force) plays a significant role in walking.
- As you walk, gravitational forces act on your body, contributing to the work done against gravity when moving up or down slopes.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option A mentions mechanical energy but lacks specificity on work done by gravity.
- Option B incorrectly includes work done by external forces, which isn’t solely dependent on the body.
- Option C excludes the work done by the body's weight, which is crucial in walking dynamics.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'D' accurately captures the essential energy types and work involved in walking: kinetic energy from movement, potential energy from height changes, and work done by the body's weight against gravity. Understanding these concepts is vital for comprehending the physics of movement.
Walking involves various forms of energy and work, primarily linked to the motion and position of the body. The correct answer is option 'D' because it encompasses the essential energies and work done by the body's weight.
1. Kinetic Energy
- Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
- When walking, the legs and body are in constant movement, which means kinetic energy is being generated.
2. Potential Energy
- Potential energy is the energy stored due to an object's position.
- When walking uphill, for example, the body gains potential energy, which is related to its height above the ground.
3. Work Done by the Body's Weight
- The weight of the body (mass multiplied by the gravitational force) plays a significant role in walking.
- As you walk, gravitational forces act on your body, contributing to the work done against gravity when moving up or down slopes.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect
- Option A mentions mechanical energy but lacks specificity on work done by gravity.
- Option B incorrectly includes work done by external forces, which isn’t solely dependent on the body.
- Option C excludes the work done by the body's weight, which is crucial in walking dynamics.
Conclusion
In summary, option 'D' accurately captures the essential energy types and work involved in walking: kinetic energy from movement, potential energy from height changes, and work done by the body's weight against gravity. Understanding these concepts is vital for comprehending the physics of movement.
If the resultant force acting on a body of constant mass is zero, the body’s momentum is:- a)Increasing
- b)Decreasing
- c)Always zero
- d)Constant
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the resultant force acting on a body of constant mass is zero, the body’s momentum is:
a)
Increasing
b)
Decreasing
c)
Always zero
d)
Constant
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Since the acceleration is 0, the velocity must be constant. therefore the momentum of the body will also be constant.
A calorimeter is used to:
- a)Determine the heat of a reaction
- b)Determine the heat given off/absorbed during some process
- c)Store the heat from a chemical reaction
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A calorimeter is used to:
a)
Determine the heat of a reaction
b)
Determine the heat given off/absorbed during some process
c)
Store the heat from a chemical reaction
d)
None of these
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
A calorimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the heat released or absorbed during a chemical or physical process. It helps in determining the energy content of a substance by measuring the temperature change that occurs when the substance undergoes a chemical reaction or experiences a physical change.
Look at the following picture carefully. First identify the picture. The below machine is a combination two simple machines. Which simple machines combine to make it?

- a)Pulley and lever
- b)Lever and gears
- c)Wheel, axle and gears
- d)Gears
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Look at the following picture carefully. First identify the picture. The below machine is a combination two simple machines. Which simple machines combine to make it?


a)
Pulley and lever
b)
Lever and gears
c)
Wheel, axle and gears
d)
Gears
|
|
Mehala Selvam answered |
Wheel, axle and gears is the correct answer.
What happens to the energy of an object when it is lifted to a higher position?- a)The energy decreases.
- b)The energy remains the same.
- c)The energy increases as potential energy.
- d)The energy changes into chemical energy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
The energy decreases.
b)
The energy remains the same.
c)
The energy increases as potential energy.
d)
The energy changes into chemical energy.
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
When an object is lifted to a higher position, its potential energy increases. This is because it has the potential to do more work due to its elevated position.
What is the role of energy in a moving car?- a)It keeps the car stationary.
- b)It allows the car to remain in a fixed position.
- c)It is converted into kinetic energy to move the car.
- d)It prevents the car from moving.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It keeps the car stationary.
b)
It allows the car to remain in a fixed position.
c)
It is converted into kinetic energy to move the car.
d)
It prevents the car from moving.
|
|
Hiral Sengupta answered |
Understanding Energy in a Moving Car
Energy plays a crucial role in the operation of a moving car. Here’s how it works:
1. Energy Types in a Car
- Cars primarily use chemical energy stored in fuel (like gasoline or diesel).
- This energy is released through combustion in the engine, converting it into other forms of energy.
2. Conversion to Kinetic Energy
- The chemical energy from the fuel is transformed into mechanical energy.
- This mechanical energy is used to turn the car’s wheels, which results in movement.
3. Kinetic Energy Explained
- When a car is in motion, it possesses kinetic energy.
- Kinetic energy is the energy of an object due to its motion, which increases with the speed of the car.
4. Why Option C is Correct
- Option C states: "It is converted into kinetic energy to move the car."
- This is correct because the energy from the fuel is not just there; it actively transforms to create motion.
5. Other Options Explained
- Option A: Energy does not keep the car stationary.
- Option B: Energy does not allow the car to remain in a fixed position.
- Option D: Energy is essential for movement, not for prevention.
Conclusion
In summary, energy is vital for a moving car as it is converted into kinetic energy, enabling the car to travel from one place to another efficiently. Understanding this process highlights the importance of energy in everyday vehicles.
Energy plays a crucial role in the operation of a moving car. Here’s how it works:
1. Energy Types in a Car
- Cars primarily use chemical energy stored in fuel (like gasoline or diesel).
- This energy is released through combustion in the engine, converting it into other forms of energy.
2. Conversion to Kinetic Energy
- The chemical energy from the fuel is transformed into mechanical energy.
- This mechanical energy is used to turn the car’s wheels, which results in movement.
3. Kinetic Energy Explained
- When a car is in motion, it possesses kinetic energy.
- Kinetic energy is the energy of an object due to its motion, which increases with the speed of the car.
4. Why Option C is Correct
- Option C states: "It is converted into kinetic energy to move the car."
- This is correct because the energy from the fuel is not just there; it actively transforms to create motion.
5. Other Options Explained
- Option A: Energy does not keep the car stationary.
- Option B: Energy does not allow the car to remain in a fixed position.
- Option D: Energy is essential for movement, not for prevention.
Conclusion
In summary, energy is vital for a moving car as it is converted into kinetic energy, enabling the car to travel from one place to another efficiently. Understanding this process highlights the importance of energy in everyday vehicles.
How does friction help in daily activities?- a)It allows objects to slide easily without resistance.
- b)It helps us grip surfaces and move effectively.
- c)It increases the speed of objects.
- d)It reduces the force required to push objects.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
It allows objects to slide easily without resistance.
b)
It helps us grip surfaces and move effectively.
c)
It increases the speed of objects.
d)
It reduces the force required to push objects.

|
Bespoke Classes answered |
Friction helps in gripping surfaces and moving effectively. It provides the necessary resistance to prevent slipping and enables control during movement.
Which force makes objects fall to the ground?- a)Magnetic force
- b)Muscular force
- c)Gravitational force
- d)Frictional force
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Magnetic force
b)
Muscular force
c)
Gravitational force
d)
Frictional force
|
|
Subset Academy answered |
Gravitational force is responsible for making objects fall to the ground. Gravity pulls everything towards the center of the Earth. Fun fact: On the Moon, gravity is much weaker, so you would weigh less there!
Energy can be defined as- a)the capacity to do work.
- b)work done in unit time.
- c)a push or a pull.
- d)attraction between two oppositely charged particles.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Energy can be defined as
a)
the capacity to do work.
b)
work done in unit time.
c)
a push or a pull.
d)
attraction between two oppositely charged particles.
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Energy can be defined as the capacity to do work.
Air pressure is measured with a(n)- a)Thermometer
- b)Barometer
- c)Anemometer
- d)Psychrometer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Air pressure is measured with a(n)
a)
Thermometer
b)
Barometer
c)
Anemometer
d)
Psychrometer
|
|
Eshaan B Raj answered |
Barometer , Anemometer can't be because it is used to calculate wind speed.
The part of a nuclear power plant that prevents thermal pollution of lakes or rivers is the:- a)Reactor
- b)Coolant/moderator
- c)Cooling tower
- d)Control rod
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The part of a nuclear power plant that prevents thermal pollution of lakes or rivers is the:
a)
Reactor
b)
Coolant/moderator
c)
Cooling tower
d)
Control rod
|
|
Maheshwar Patel answered |
Introduction:
In a nuclear power plant, thermal pollution refers to the excessive heating of water bodies like lakes or rivers due to the release of heated water from the plant. This increase in water temperature can have detrimental effects on aquatic life. Therefore, it is crucial to prevent thermal pollution to maintain the ecological balance of the surrounding environment.
Cooling Tower:
The part of a nuclear power plant that prevents thermal pollution of lakes or rivers is the cooling tower. The cooling tower is responsible for removing excess heat from the power plant's cooling system by transferring it to the atmosphere. It accomplishes this through the process of evaporation.
How Cooling Towers Work:
1. Heat Exchange: The cooling tower receives hot water from the power plant's cooling system, which contains excess heat.
2. Water Distribution: The hot water is distributed over the fill surfaces of the cooling tower. The fill surfaces provide a large surface area for the water to come into contact with air.
3. Airflow: Air is drawn into the cooling tower through the lower part and flows upward. As the hot water trickles down the fill surfaces, it comes into contact with the incoming air.
4. Evaporation: As the hot water is exposed to the air, a portion of it evaporates, taking away heat in the process. This evaporation causes a cooling effect on the remaining water.
5. Exhaust: The heated air, now saturated with moisture, is expelled from the cooling tower through the top, while the cooled water collects at the bottom and is returned to its source.
Benefits of Cooling Towers:
- Thermal Pollution Prevention: By continuously removing heat from the power plant's cooling system, cooling towers help regulate the temperature of the water bodies where the heated water is discharged. This prevents thermal pollution and minimizes the impact on aquatic ecosystems.
- Energy Efficiency: Cooling towers facilitate the reuse of water within the power plant's cooling system, reducing the need for fresh water intake. This conserves water resources and improves the overall energy efficiency of the plant.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cooling towers are a cost-effective solution for managing the excess heat generated by power plants. They provide an efficient means of heat dissipation without relying on large quantities of water or other resources.
Conclusion:
In a nuclear power plant, the cooling tower plays a vital role in preventing thermal pollution of lakes or rivers. By removing excess heat from the plant's cooling system through evaporation, cooling towers ensure that the discharged water does not excessively raise the temperature of surrounding water bodies. This helps maintain the ecological balance and protect aquatic life in the vicinity of the power plant.
In a nuclear power plant, thermal pollution refers to the excessive heating of water bodies like lakes or rivers due to the release of heated water from the plant. This increase in water temperature can have detrimental effects on aquatic life. Therefore, it is crucial to prevent thermal pollution to maintain the ecological balance of the surrounding environment.
Cooling Tower:
The part of a nuclear power plant that prevents thermal pollution of lakes or rivers is the cooling tower. The cooling tower is responsible for removing excess heat from the power plant's cooling system by transferring it to the atmosphere. It accomplishes this through the process of evaporation.
How Cooling Towers Work:
1. Heat Exchange: The cooling tower receives hot water from the power plant's cooling system, which contains excess heat.
2. Water Distribution: The hot water is distributed over the fill surfaces of the cooling tower. The fill surfaces provide a large surface area for the water to come into contact with air.
3. Airflow: Air is drawn into the cooling tower through the lower part and flows upward. As the hot water trickles down the fill surfaces, it comes into contact with the incoming air.
4. Evaporation: As the hot water is exposed to the air, a portion of it evaporates, taking away heat in the process. This evaporation causes a cooling effect on the remaining water.
5. Exhaust: The heated air, now saturated with moisture, is expelled from the cooling tower through the top, while the cooled water collects at the bottom and is returned to its source.
Benefits of Cooling Towers:
- Thermal Pollution Prevention: By continuously removing heat from the power plant's cooling system, cooling towers help regulate the temperature of the water bodies where the heated water is discharged. This prevents thermal pollution and minimizes the impact on aquatic ecosystems.
- Energy Efficiency: Cooling towers facilitate the reuse of water within the power plant's cooling system, reducing the need for fresh water intake. This conserves water resources and improves the overall energy efficiency of the plant.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cooling towers are a cost-effective solution for managing the excess heat generated by power plants. They provide an efficient means of heat dissipation without relying on large quantities of water or other resources.
Conclusion:
In a nuclear power plant, the cooling tower plays a vital role in preventing thermal pollution of lakes or rivers. By removing excess heat from the plant's cooling system through evaporation, cooling towers ensure that the discharged water does not excessively raise the temperature of surrounding water bodies. This helps maintain the ecological balance and protect aquatic life in the vicinity of the power plant.
In which of the following activities is force used for pulling?- a)Blowing air into a balloon
- b)Cycling
- c)Stretching a rubber band
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following activities is force used for pulling?
a)
Blowing air into a balloon
b)
Cycling
c)
Stretching a rubber band
d)
All of the above
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Stretching of a rubber band is an example of a pulling force.

When a pin wheel is placed against wind, it begins to spin. This proves that- a)moving air has energy
- b)pin wheel has life
- c)pin has energy
- d)moving air has no energy.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When a pin wheel is placed against wind, it begins to spin. This proves that
a)
moving air has energy
b)
pin wheel has life
c)
pin has energy
d)
moving air has no energy.
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
Moving air has energy. Since moving air can make a pin-wheel move, it has energy.
What is a force?- a)A push or pull applied to an object
- b)A tool used to lift objects
- c)A type of machine
- d)A type of energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
A push or pull applied to an object
b)
A tool used to lift objects
c)
A type of machine
d)
A type of energy
|
|
Pranab Choudhury answered |
What is Force?
Force is a fundamental concept in physics that describes an interaction that can change the motion of an object. It is primarily defined as:
Understanding Force
Force can be understood through its various characteristics:
Types of Force
There are various types of forces, which can be categorized as:
Real-Life Examples
To grasp the concept of force better, consider these examples:
In summary, understanding force is essential as it lays the foundation for studying motion and mechanics in everyday life.
Force is a fundamental concept in physics that describes an interaction that can change the motion of an object. It is primarily defined as:
- A push or pull applied to an object
Understanding Force
Force can be understood through its various characteristics:
- Push or Pull: When you push a door to open it, you apply a force. Similarly, pulling a drawer involves exerting a force in the opposite direction.
- Effect on Motion: Force can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. For instance, kicking a soccer ball applies a force that moves the ball forward.
- Measured in Newtons: The standard unit of force is called a Newton (N). This helps quantify the amount of force applied.
Types of Force
There are various types of forces, which can be categorized as:
- Contact Forces: Forces that occur when objects physically touch each other, such as friction and tension.
- Non-contact Forces: Forces that act at a distance, such as gravitational force and magnetic force.
Real-Life Examples
To grasp the concept of force better, consider these examples:
- Gravity: The force that pulls objects toward the Earth.
- Friction: The force that opposes the motion of objects sliding against each other.
In summary, understanding force is essential as it lays the foundation for studying motion and mechanics in everyday life.
Which simple machine consists of a wheel attached to a rod called an axle?- a)Lever
- b)Pulley
- c)Wheel and axle
- d)Screw
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Lever
b)
Pulley
c)
Wheel and axle
d)
Screw
|
|
Pranab Choudhury answered |
Understanding the Wheel and Axle
The wheel and axle is a fundamental simple machine that plays a crucial role in various mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how it works:
Definition
- The wheel and axle consists of two circular objects: a larger wheel and a smaller cylindrical rod called the axle.
- These two components are connected so that they rotate together.
How It Works
- When force is applied to the wheel, it turns the axle, allowing for movement.
- This mechanism reduces friction, making it easier to move heavy loads.
- The wheel's larger radius allows for a greater distance to be covered with less effort compared to directly lifting an object.
Applications
- The wheel and axle is found in various everyday items, such as:
- Cars (where wheels rotate around axles)
- Bicycles (wheels attached to axles)
- Rolling carts (helping in transportation)
Advantages
- Enhances efficiency in moving objects.
- Reduces the amount of force needed to lift or move a load.
- Allows for smoother and easier transportation.
Conclusion
- The wheel and axle is a simple yet powerful machine that serves as the foundation for many technologies we use today.
- Its design demonstrates how basic principles of physics can be applied to improve our daily lives.
Understanding this machine's mechanics is essential for grasping the concepts of simple machines in physics.
The wheel and axle is a fundamental simple machine that plays a crucial role in various mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how it works:
Definition
- The wheel and axle consists of two circular objects: a larger wheel and a smaller cylindrical rod called the axle.
- These two components are connected so that they rotate together.
How It Works
- When force is applied to the wheel, it turns the axle, allowing for movement.
- This mechanism reduces friction, making it easier to move heavy loads.
- The wheel's larger radius allows for a greater distance to be covered with less effort compared to directly lifting an object.
Applications
- The wheel and axle is found in various everyday items, such as:
- Cars (where wheels rotate around axles)
- Bicycles (wheels attached to axles)
- Rolling carts (helping in transportation)
Advantages
- Enhances efficiency in moving objects.
- Reduces the amount of force needed to lift or move a load.
- Allows for smoother and easier transportation.
Conclusion
- The wheel and axle is a simple yet powerful machine that serves as the foundation for many technologies we use today.
- Its design demonstrates how basic principles of physics can be applied to improve our daily lives.
Understanding this machine's mechanics is essential for grasping the concepts of simple machines in physics.
Two girls playing table tennis. First girl hit the ball over the net and at a Point say ‘T’, the other girl hit it back with a lot of force.
What would happen at point ‘T’?
1. The force caused a change in the size of the ball.
2. The force caused a change in the direction of the ball.
3. The force caused the ball to stop moving.- a)1
- b)2
- c)1 and 2 both
- d)1 and 3 both
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two girls playing table tennis. First girl hit the ball over the net and at a Point say ‘T’, the other girl hit it back with a lot of force.
What would happen at point ‘T’?
1. The force caused a change in the size of the ball.
2. The force caused a change in the direction of the ball.
3. The force caused the ball to stop moving.
What would happen at point ‘T’?
1. The force caused a change in the size of the ball.
2. The force caused a change in the direction of the ball.
3. The force caused the ball to stop moving.
a)
1
b)
2
c)
1 and 2 both
d)
1 and 3 both
|
|
Surbhi Saha answered |
"Nice shot!"
X enables work to be done. There are many forms of X. What is X?- a)Energy
- b)The Sun
- c)Heat
- d)Sound
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
X enables work to be done. There are many forms of X. What is X?
a)
Energy
b)
The Sun
c)
Heat
d)
Sound
|
|
Sudhir Mehta answered |
The capacity to do work is called energy. Energy is available in different forms such as heat energy, light energy etc.
Which of the following is NOT an SI unit of measure?
- a)Watt
- b)Newton
- c)Joule
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is NOT an SI unit of measure?
a)
Watt
b)
Newton
c)
Joule
d)
none
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
All the options provided are indeed SI units of measure. Here's an explanation for each:
- Watt (W): The SI unit of power, representing the rate of energy transfer. It is defined as one joule per second (1 W = 1 J/s).
- Newton (N): The SI unit of force. It is defined as the force required to accelerate a one-kilogram mass by one meter per second squared (1 N = 1 kg·m/s²).
- Joule (J): The SI unit of energy. It is defined as the amount of energy transferred when a force of one newton is applied over a distance of one meter (1 J = 1 N·m).
Since all of these units are part of the International System of Units (SI), the correct answer to the question of which is NOT an SI unit of measure is:
4. None
Which type of force opposes the motion of objects and slows them down?- a)Gravitational force
- b)Magnetic force
- c)Frictional force
- d)Muscular force
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Gravitational force
b)
Magnetic force
c)
Frictional force
d)
Muscular force
|
|
Stoneridge Institute answered |
Frictional force opposes the motion of objects and slows them down when they are in contact with a surface. Fun fact: Without friction, we wouldn’t be able to walk properly because our feet would keep slipping!
Which of the following is an example of a class 1 lever?- a)Scissors
- b)Bottle opener
- c)Stapler
- d)Wheelbarrow
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Scissors
b)
Bottle opener
c)
Stapler
d)
Wheelbarrow
|
|
Stoneridge Institute answered |
Scissors are an example of a class 1 lever, where the fulcrum is located between the load and the effort. The same principle applies to seesaws. Fun fact: Class 1 levers can increase force or speed, depending on the design.
Which of these is a source of mechanical energy?- a)Sunlight
- b)A moving car
- c)A light bulb
- d)A television
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Sunlight
b)
A moving car
c)
A light bulb
d)
A television

|
Learning Education answered |
A moving car possesses mechanical energy, as it has both potential and kinetic energy. Fun fact: The faster the car moves, the more kinetic energy it has!
What is the primary difference between work and energy?- a)Work is the transfer of energy, while energy is the ability to do work.
- b)Work and energy are the same thing.
- c)Energy is a measure of distance, while work is a measure of force.
- d)Work is the power required to do a task, while energy is the speed of the task.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Work is the transfer of energy, while energy is the ability to do work.
b)
Work and energy are the same thing.
c)
Energy is a measure of distance, while work is a measure of force.
d)
Work is the power required to do a task, while energy is the speed of the task.
|
|
Prasad Joshi answered |
Understanding the Difference Between Work and Energy
The concepts of work and energy are fundamental in physics and are closely related but distinct.
Definition of Work
- Work is defined as the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied to an object, causing it to move.
- The formula for work is: Work = Force × Distance × cos(θ), where θ is the angle between the force and the direction of movement.
Definition of Energy
- Energy is the ability or capacity to do work. It exists in various forms, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, and more.
- Energy can be stored or transferred, and it is conserved in a closed system.
Relationship Between Work and Energy
- When work is done on an object, energy is transferred to that object, allowing it to change its state or position. For example, lifting a book off the ground requires work, which transfers energy to the book as gravitational potential energy.
- Conversely, when an object does work (like a falling object hitting the ground), it transfers energy away.
Why Option A is Correct
- Option A clearly states that "Work is the transfer of energy, while energy is the ability to do work." This statement accurately captures the essence of both concepts.
- The other options incorrectly define or confuse the terms, making option A the only accurate choice.
Understanding these differences helps in grasping how forces and movements interact in our physical world.
The concepts of work and energy are fundamental in physics and are closely related but distinct.
Definition of Work
- Work is defined as the transfer of energy that occurs when a force is applied to an object, causing it to move.
- The formula for work is: Work = Force × Distance × cos(θ), where θ is the angle between the force and the direction of movement.
Definition of Energy
- Energy is the ability or capacity to do work. It exists in various forms, such as kinetic, potential, thermal, and more.
- Energy can be stored or transferred, and it is conserved in a closed system.
Relationship Between Work and Energy
- When work is done on an object, energy is transferred to that object, allowing it to change its state or position. For example, lifting a book off the ground requires work, which transfers energy to the book as gravitational potential energy.
- Conversely, when an object does work (like a falling object hitting the ground), it transfers energy away.
Why Option A is Correct
- Option A clearly states that "Work is the transfer of energy, while energy is the ability to do work." This statement accurately captures the essence of both concepts.
- The other options incorrectly define or confuse the terms, making option A the only accurate choice.
Understanding these differences helps in grasping how forces and movements interact in our physical world.
Which of the following gadget is used to measure temperature?- a)Stop watch
- b)Scale
- c)Measuring jar
- d)Thermometer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following gadget is used to measure temperature?
a)
Stop watch
b)
Scale
c)
Measuring jar
d)
Thermometer
|
|
Arri Rap answered |
Answer is d)thermometer
Stop watch is used to measure time.
Scale to measure length.
Measuring jar used to measure quantity of water.
Thermometer to measure temperature.
Fun fact about thermometer:
There are two kinds of thermometer clinical thermometer and labatory thermometer.
Now there are many kinds for example digital thermometer.
What should you do to stay safe when using sharp tools like scissors?- a)Wave them around
- b)Hold them by the sharp end
- c)Carry them with the pointed edge downward
- d)Leave them lying on the floor
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Wave them around
b)
Hold them by the sharp end
c)
Carry them with the pointed edge downward
d)
Leave them lying on the floor
|
|
Edu Impact answered |
To stay safe when using sharp tools like scissors, always carry them with the pointed edge downward to avoid accidents. Fun fact: Sharp objects should always be stored in a tool box to prevent injury!
What type of energy helps us to see things?- a)Heat energy
- b)Electrical energy
- c)Mechanical energy
- d)Light energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Heat energy
b)
Electrical energy
c)
Mechanical energy
d)
Light energy
|
|
Edu Impact answered |
Light energy helps us to see things. It comes from sources like the Sun, bulbs, and candles. Fun fact: Light from the Sun takes about 8 minutes to reach the Earth!
Which part of a lever is the fixed point around which it moves?- a)Load
- b)Effort
- c)Fulcrum
- d)Wheel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Load
b)
Effort
c)
Fulcrum
d)
Wheel

|
Tutorpedia Coaching answered |
The fulcrum is the fixed point around which a lever moves. Depending on the position of the fulcrum, levers can be classified into different types. Fun fact: Your elbow acts as a fulcrum when you bend your arm!
The following is a diagram of a simple electromagnet.
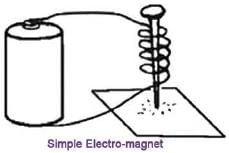
Q. How could this electromagnet be made stronger?- a)Remove all the coils and the nail
- b)Add more coils of wire to the nail
- c)Use a smaller battery
- d)Reverse the poles of the magnet
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The following is a diagram of a simple electromagnet.

Q. How could this electromagnet be made stronger?

Q. How could this electromagnet be made stronger?
a)
Remove all the coils and the nail
b)
Add more coils of wire to the nail
c)
Use a smaller battery
d)
Reverse the poles of the magnet

|
Satyaprakash Pogula Pogu answered |
The current from the battery going around the iron nail turns iron nail into a magnet.
More coil around nail more current around nail results in more magnetism which means more powerful magnet.
More coil around nail more current around nail results in more magnetism which means more powerful magnet.
Electricity traveling through a wire is an example of- a)A force applied by a simple machine
- b)Energy flowing through the water cycle
- c)Earth’s gravitational pull on an object
- d)Energy being transferred from place to place
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Electricity traveling through a wire is an example of
a)
A force applied by a simple machine
b)
Energy flowing through the water cycle
c)
Earth’s gravitational pull on an object
d)
Energy being transferred from place to place
|
|
Milind ghosh answered |
Electricity traveling through a wire is an example of electricity flowing through a conductor.
What can happen if you walk on a smooth tiled floor where water has been spilled?- a)You can jump higher
- b)You can slide easily
- c)You can run faster
- d)You can feel warmer
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What can happen if you walk on a smooth tiled floor where water has been spilled?
a)
You can jump higher
b)
You can slide easily
c)
You can run faster
d)
You can feel warmer
|
|
Glitz Classes answered |
When you walk on a smooth tiled floor with water on it, you might slip and slide easily. This is because the smooth surface combined with water makes it very slippery, so it's important to be careful and not run on such a floor to avoid falling down.
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The sun is the greatest source of energy on Earth.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether the following statement is True or False:
The sun is the greatest source of energy on Earth.
The sun is the greatest source of energy on Earth.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
- The sun is like a big ball of fire in the sky. It gives us light and warmth every day.
- Plants use the light from the sun to make food, and this food gives us energy to do things like play and learn.
- So, the sun is a very important source of energy for us.
- It's like a big battery in the sky that keeps everything on Earth alive and moving.
Friction is not always bad. We are able to walk because of friction between our feet and the ______.- a)air
- b)water
- c)ground
- d)fire
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Friction is not always bad. We are able to walk because of friction between our feet and the ______.
a)
air
b)
water
c)
ground
d)
fire

|
Learning Enablers answered |
Friction helps us walk by providing grip between our feet and the ground. Without this grip from friction, we would slip and fall. So, friction between our feet and the ground is important for walking safely.
What type of simple machine is a ramp?- a)Lever
- b)Pulley
- c)Wheel and axle
- d)Inclined plane
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Lever
b)
Pulley
c)
Wheel and axle
d)
Inclined plane

|
Tutorpedia Coaching answered |
A ramp is an inclined plane, which helps to move heavy objects with less effort. It reduces the amount of force needed to lift an object. Fun fact: The ancient Egyptians used inclined planes to build the pyramids!
What force pulls everything towards the earth?- a)Muscular Force
- b)Gravitational Force
- c)Magnetic Force
- d)Friction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What force pulls everything towards the earth?
a)
Muscular Force
b)
Gravitational Force
c)
Magnetic Force
d)
Friction
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
- Gravitational force is the force that pulls everything towards the earth.
- Imagine the earth is like a big magnet that pulls everything down towards it.
- This force is why things fall to the ground instead of floating in the air.
- So, when you drop something, like a ball, it comes down because of this gravitational force.
What happens to the total energy of a moving object if all the applied forces are conserved?- a)It increases
- b)It decreases
- c)It remains constant
- d)The velocity is required to answer this question
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens to the total energy of a moving object if all the applied forces are conserved?
a)
It increases
b)
It decreases
c)
It remains constant
d)
The velocity is required to answer this question
|
|
Stuti Chauhan answered |
Understanding Total Energy and Applied Forces
When discussing the total energy of a moving object, it is essential to understand the role of applied forces and how they relate to energy conservation.
What is Total Energy?
- Total energy of an object includes its kinetic energy (energy of motion) and potential energy (stored energy based on position).
Conservation of Energy Principle
- The principle of conservation of energy states that in a closed system, energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms.
Applied Forces and Energy
- If all applied forces are conservative, they do not dissipate energy through non-conservative forces like friction or air resistance.
- Examples of conservative forces include gravitational force and spring force.
Implications of Conservative Forces
- When only conservative forces are acting, the total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of the object remains constant.
- The work done by these forces merely converts energy from one form to another (e.g., kinetic energy to potential energy and vice versa) without changing the total energy quantity.
Conclusion
- Since the total energy remains unchanged when all applied forces are conservative, the correct answer is option 'C': it remains constant.
- Understanding this concept helps in analyzing motion in physics, especially in fields like mechanics and dynamics.
When discussing the total energy of a moving object, it is essential to understand the role of applied forces and how they relate to energy conservation.
What is Total Energy?
- Total energy of an object includes its kinetic energy (energy of motion) and potential energy (stored energy based on position).
Conservation of Energy Principle
- The principle of conservation of energy states that in a closed system, energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms.
Applied Forces and Energy
- If all applied forces are conservative, they do not dissipate energy through non-conservative forces like friction or air resistance.
- Examples of conservative forces include gravitational force and spring force.
Implications of Conservative Forces
- When only conservative forces are acting, the total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of the object remains constant.
- The work done by these forces merely converts energy from one form to another (e.g., kinetic energy to potential energy and vice versa) without changing the total energy quantity.
Conclusion
- Since the total energy remains unchanged when all applied forces are conservative, the correct answer is option 'C': it remains constant.
- Understanding this concept helps in analyzing motion in physics, especially in fields like mechanics and dynamics.
State whether the following statement is True or False:Muscular force is the force that uses the power of our muscles when we push or pull something.- a)True
- b)False
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
State whether the following statement is True or False:
Muscular force is the force that uses the power of our muscles when we push or pull something.
a)
True
b)
False
|
|
Riya Singh answered |
- Muscular force is the force that helps us move things by using our muscles.
- When you push a heavy box, you are using muscular force from your arms.
- This force comes from the strength of your muscles.
- So, when you push or pull something, you are using your muscles to apply force.
- Isn't it cool how our muscles help us do so many things?
Mark the action in which work is being done:- a)Carrying a rucksack to school
- b)A vehicle warming up its motor
- c)A computer running a program
- d)A man trying to open the door
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mark the action in which work is being done:
a)
Carrying a rucksack to school
b)
A vehicle warming up its motor
c)
A computer running a program
d)
A man trying to open the door
|
|
Stuti Chauhan answered |
Understanding Work in Physics
In physics, work is defined as the transfer of energy that occurs when an object is moved over a distance by an external force. To determine if work is being done, we need to consider two essential factors:
- Force: There must be a force acting on the object.
- Displacement: The object must move in the direction of the force applied.
Analysis of Each Option
- Carrying a rucksack to school
- When you carry a rucksack, you exert an upward force against gravity.
- As you walk, the rucksack moves in the direction of the force you apply.
- Therefore, work is being done here.
- A vehicle warming up its motor
- While the engine generates heat and runs, there is no displacement of the vehicle.
- The key point is that the vehicle is not moving in the direction of any applied force, so no work is done.
- A computer running a program
- The computer processes data, but it does not move any object in a physical sense.
- Since there is no displacement of a physical object, work is not being done in the physics context.
- A man trying to open the door
- Although the man applies force to the door, if the door does not move, then no work is done.
- Work requires movement as a result of the applied force.
Conclusion
In summary, the only action in which work is clearly being done is option A: carrying a rucksack to school. This involves both a force and a displacement, meeting the criteria for work in physics.
In physics, work is defined as the transfer of energy that occurs when an object is moved over a distance by an external force. To determine if work is being done, we need to consider two essential factors:
- Force: There must be a force acting on the object.
- Displacement: The object must move in the direction of the force applied.
Analysis of Each Option
- Carrying a rucksack to school
- When you carry a rucksack, you exert an upward force against gravity.
- As you walk, the rucksack moves in the direction of the force you apply.
- Therefore, work is being done here.
- A vehicle warming up its motor
- While the engine generates heat and runs, there is no displacement of the vehicle.
- The key point is that the vehicle is not moving in the direction of any applied force, so no work is done.
- A computer running a program
- The computer processes data, but it does not move any object in a physical sense.
- Since there is no displacement of a physical object, work is not being done in the physics context.
- A man trying to open the door
- Although the man applies force to the door, if the door does not move, then no work is done.
- Work requires movement as a result of the applied force.
Conclusion
In summary, the only action in which work is clearly being done is option A: carrying a rucksack to school. This involves both a force and a displacement, meeting the criteria for work in physics.
Chapter doubts & questions for Speed and Energy - Science for Grade 4 2025 is part of Grade 4 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 4 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 4 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Speed and Energy - Science for Grade 4 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 4 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 4 Exam by signing up for free.
Science for Grade 4
26 videos|122 docs|37 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup










