All Exams >
JAMB >
Physics for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Friction for JAMB Exam
A particle moves in a circle with a constant speed of 6m /s. Its centripetal acceleration is 120 m/s2, The radius of the circle is- a)20 cm
- b)200 cm
- c)300 cm
- d)30 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves in a circle with a constant speed of 6m /s. Its centripetal acceleration is 120 m/s2, The radius of the circle is
a)
20 cm
b)
200 cm
c)
300 cm
d)
30 cm
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
a = v^2 /r
or, r = v^2 /a = 36 /120 = 0.3 m = 30 cm
A block of mass 1kg is placed on the floor. The coefficient of static friction is 0.2. If a force of 1N is applied to the block, the force of friction is- a)0
- b)2 N
- c)1 N
- d)varies with the area of contact of the block
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass 1kg is placed on the floor. The coefficient of static friction is 0.2. If a force of 1N is applied to the block, the force of friction is
a)
0
b)
2 N
c)
1 N
d)
varies with the area of contact of the block

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
The applied force is less than the maximum value of static friction which will be (0.2)(1kg)(10) = 2N. So the force of friction is equal to the applied force.
After the body starts moving, the friction involved with motion is- a)Static Friction
- b)Rolling Friction
- c)Sliding Friction
- d)Kinetic Friction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
After the body starts moving, the friction involved with motion is
a)
Static Friction
b)
Rolling Friction
c)
Sliding Friction
d)
Kinetic Friction
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
When the body is in rest it is under static friction but when it starts moving (neither rolling nor sliding), the static friction slowly chngs to kinetic friction as the coefficient of static friction start decreasing and that of kinetic friction starts increasing. In case it starts rolling motion then the friction is rolling friction & if it slides then sliding fiction.
A particle moves in a circle of radius 0.30m with a constant speed of 6m/s. Its centripetal acceleration is- a)20 m/s2
- b)zero
- c)12 m/s2
- d)120 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A particle moves in a circle of radius 0.30m with a constant speed of 6m/s. Its centripetal acceleration is
a)
20 m/s2
b)
zero
c)
12 m/s2
d)
120 m/s2

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
We know that centripetal acceleration, a = v x v /r
Here v = 6m/s and r = 0.3m
Thus a = 36 / 0.3 m/s2
= 120 m/s2
Here v = 6m/s and r = 0.3m
Thus a = 36 / 0.3 m/s2
= 120 m/s2
Impending motion of a body is opposed by- a)sliding friction
- b)rolling friction
- c)static friction
- d)kinetic friction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Impending motion of a body is opposed by
a)
sliding friction
b)
rolling friction
c)
static friction
d)
kinetic friction
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
When the motion is not impending, b) Impending motion is the moment where the body is on the verge of slipping. Static friction force reaches the max value. For a given pair of mating surfaces, . c) Motion The body starts moving in the direction of the applied force.
When a wheel rolls on a level road, the direction of frictional force at the point of contact of wheel and ground is:
- a)along the tangent to the wheel
- b)forward direction
- c)along the centre of the wheel
- d)backward direction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a wheel rolls on a level road, the direction of frictional force at the point of contact of wheel and ground is:
a)
along the tangent to the wheel
b)
forward direction
c)
along the centre of the wheel
d)
backward direction

|
Advait Ghoshal answered |
Frictional force is the opposing force which plays between two surfaces and it destroys the relative motion between them. Frictional force is a non-conservative force. The force produced by two surfaces that contact and slide against each other, that force is called the frictional force. These forces are affected by the nature of the surface and amount of force acting on them.
In case of a bicycle, the front wheel of the bicycle is connected to a rod passing through its centre. The force acting on the wheel about its central axis by the force coming from the rest of the bicycle is zero. Front wheel obtains linear velocity by pedalling but it cannot rotate it.
Wheel or ball can also be rolled by pushing on it. The frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding forward at the point of contact. Here, the frictional force prevents the wheel from sliding forward and it is in the opposite direction.
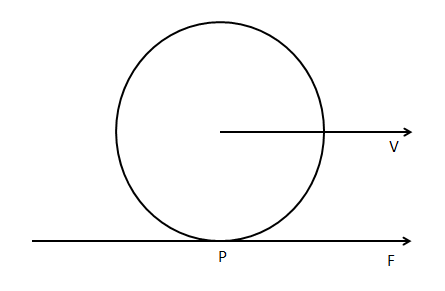
So, in the case of the wheel, the point P which is in contact with the ground tries to go backward due to rotation. Frictional force will oppose this motion. Hence it will move forward.
Hence the direction of frictional force at the point P of the wheel is in forward direction.
Note: Frictional force opposes the motion. Here static friction holds a wheel or a ball on the surface. Frictional force is equal and opposite in direction to the applied force parallel to the contacting surfaces. The resistance due to the rolling body on a surface is called rolling friction. Torque is a force that acts on a body that is undergoing rotation.
A block of mass 2kg rests on a plane inclined at an angle of 30o with the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is 0.7. The frictional force acting on the block is
- a)9.8N
- b)0.7×9.8×3–√N
- c)12.5 N
- d)0.7×9.8N
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A block of mass 2kg rests on a plane inclined at an angle of 30o with the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is 0.7. The frictional force acting on the block is
a)
9.8N
b)
0.7×9.8×3–√N
c)
12.5 N
d)
0.7×9.8N
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Since the frictional force is self adjusting, the weight component acting down the inclined plane is mgsin?, which comes out to be 2 x 10 sin 30 = 10 N. So the frictional force balancing this downward force will also be 10 N acting up the plane.
A body rests on an inclined plane and the angle of inclination is varied till the body just begins to slide down. The coefficient of friction is 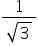 . What is the angle of inclination?
. What is the angle of inclination?- a)45o
- b)60o
- c)15o
- d)30o
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A body rests on an inclined plane and the angle of inclination is varied till the body just begins to slide down. The coefficient of friction is 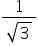 . What is the angle of inclination?
. What is the angle of inclination?
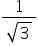 . What is the angle of inclination?
. What is the angle of inclination?a)
45o
b)
60o
c)
15o
d)
30o
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
At the time when the block just starts to move, we get that net force acting upon it is 0, thus we get, f - mg.sin a = 0
Where f is friction force and a is angle of incline.
We also know that f = 1√3 x N
= 1√3 x mg.cos a
Thus we get 1√3 x mg.cos a = mg.sin a
Thus we get tan a = 1√3
And a = 30
Where f is friction force and a is angle of incline.
We also know that f = 1√3 x N
= 1√3 x mg.cos a
Thus we get 1√3 x mg.cos a = mg.sin a
Thus we get tan a = 1√3
And a = 30
Complete the sentence.Friction always ____________- a)helps the motion
- b)opposes the relative motion
- c)both of these
- d)none of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Complete the sentence.
Friction always ____________
a)
helps the motion
b)
opposes the relative motion
c)
both of these
d)
none of these
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Frictional forces act over the common surfaces of the two bodies to avoid and restrict relative moment between those two surfaces.
If the viscosity of a fluid decreases while all other factors remain constant, how will it affect the terminal velocity of an object falling through the fluid?- a)The terminal velocity will decrease
- b)The terminal velocity will increase
- c)The terminal velocity will remain the same
- d)The terminal velocity will become zero
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the viscosity of a fluid decreases while all other factors remain constant, how will it affect the terminal velocity of an object falling through the fluid?
a)
The terminal velocity will decrease
b)
The terminal velocity will increase
c)
The terminal velocity will remain the same
d)
The terminal velocity will become zero
|
|
Bolaji Afolabi answered |
Effect of Decreased Viscosity on Terminal Velocity of an Object Falling through a Fluid
When the viscosity of a fluid decreases while all other factors remain constant, the terminal velocity of an object falling through the fluid will increase. This can be understood by considering the factors that affect terminal velocity.
Terminal Velocity:
Terminal velocity is the constant velocity that a freely falling object eventually reaches when the resistance from the fluid through which it is falling equals the force of gravity acting on it. At terminal velocity, the net force on the object is zero, resulting in a constant velocity.
Viscosity:
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is a property that determines the internal frictional forces within a fluid as it flows. When the viscosity of a fluid decreases, it means that the fluid becomes less resistant to flow and flows more easily.
Factors Affecting Terminal Velocity:
Terminal velocity is determined by the balance between the gravitational force pulling the object downward and the resistance force exerted by the fluid. The resistance force is dependent on several factors, including the shape, size, and density of the object, as well as the viscosity of the fluid.
Explanation:
When the viscosity of a fluid decreases, the resistance force exerted by the fluid on the falling object decreases. This decrease in resistance force allows the object to fall more easily through the fluid, resulting in an increase in its terminal velocity.
Key Points:
- Terminal velocity is the constant velocity a falling object reaches when the resistance force equals the force of gravity.
- Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow.
- When the viscosity of a fluid decreases, the resistance force exerted by the fluid on the object decreases.
- With decreased viscosity, the object experiences less resistance and can fall more easily through the fluid.
- Consequently, the terminal velocity of the object increases.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - the terminal velocity will increase.
When the viscosity of a fluid decreases while all other factors remain constant, the terminal velocity of an object falling through the fluid will increase. This can be understood by considering the factors that affect terminal velocity.
Terminal Velocity:
Terminal velocity is the constant velocity that a freely falling object eventually reaches when the resistance from the fluid through which it is falling equals the force of gravity acting on it. At terminal velocity, the net force on the object is zero, resulting in a constant velocity.
Viscosity:
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It is a property that determines the internal frictional forces within a fluid as it flows. When the viscosity of a fluid decreases, it means that the fluid becomes less resistant to flow and flows more easily.
Factors Affecting Terminal Velocity:
Terminal velocity is determined by the balance between the gravitational force pulling the object downward and the resistance force exerted by the fluid. The resistance force is dependent on several factors, including the shape, size, and density of the object, as well as the viscosity of the fluid.
Explanation:
When the viscosity of a fluid decreases, the resistance force exerted by the fluid on the falling object decreases. This decrease in resistance force allows the object to fall more easily through the fluid, resulting in an increase in its terminal velocity.
Key Points:
- Terminal velocity is the constant velocity a falling object reaches when the resistance force equals the force of gravity.
- Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow.
- When the viscosity of a fluid decreases, the resistance force exerted by the fluid on the object decreases.
- With decreased viscosity, the object experiences less resistance and can fall more easily through the fluid.
- Consequently, the terminal velocity of the object increases.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - the terminal velocity will increase.
Which of the following fluids would offer the least resistance to the motion of an object passing through it?- a)Honey
- b)Water
- c)Air
- d)Motor oil
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following fluids would offer the least resistance to the motion of an object passing through it?
a)
Honey
b)
Water
c)
Air
d)
Motor oil
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Among the given options, air offers the least resistance to the motion of an object passing through it.
Which of the following factors affects the terminal velocity of an object falling through a fluid?- a)Mass of the object
- b)Density of the fluid
- c)Viscosity of the fluid
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors affects the terminal velocity of an object falling through a fluid?
a)
Mass of the object
b)
Density of the fluid
c)
Viscosity of the fluid
d)
All of the above
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The terminal velocity of an object falling through a fluid is affected by factors such as its mass, the density of the fluid, and the viscosity of the fluid.
Which of the following factors affects the viscosity of a fluid?- a)Temperature
- b)Pressure
- c)Density
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors affects the viscosity of a fluid?
a)
Temperature
b)
Pressure
c)
Density
d)
All of the above
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Factors such as temperature, pressure, and density affect the viscosity of a fluid.
According to Stoke's law, the terminal velocity of a spherical object falling through a fluid is directly proportional to its:- a)Mass
- b)Volume
- c)Surface area
- d)Density
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Stoke's law, the terminal velocity of a spherical object falling through a fluid is directly proportional to its:
a)
Mass
b)
Volume
c)
Surface area
d)
Density
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
According to Stoke's law, the terminal velocity of a spherical object falling through a fluid is directly proportional to its surface area.
Which of the following statements is true regarding the relationship between viscosity and terminal velocity?- a)Higher viscosity leads to higher terminal velocity
- b)Higher viscosity leads to lower terminal velocity
- c)Viscosity and terminal velocity are not related
- d)Terminal velocity remains constant regardless of viscosity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the relationship between viscosity and terminal velocity?
a)
Higher viscosity leads to higher terminal velocity
b)
Higher viscosity leads to lower terminal velocity
c)
Viscosity and terminal velocity are not related
d)
Terminal velocity remains constant regardless of viscosity
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Higher viscosity leads to lower terminal velocity because a more viscous fluid offers greater resistance to the motion of an object.
In Stoke's law, the drag force acting on an object is directly proportional to:- a)The object's velocity
- b)The object's acceleration
- c)The object's mass
- d)The object's surface area
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In Stoke's law, the drag force acting on an object is directly proportional to:
a)
The object's velocity
b)
The object's acceleration
c)
The object's mass
d)
The object's surface area
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
In Stoke's law, the drag force acting on an object is directly proportional to the object's surface area.
If the radius of a spherical object falling through a fluid is doubled while its density and viscosity remain constant, how will its terminal velocity change?- a)It will remain the same
- b)It will be halved
- c)It will be doubled
- d)It will be quadrupled
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the radius of a spherical object falling through a fluid is doubled while its density and viscosity remain constant, how will its terminal velocity change?
a)
It will remain the same
b)
It will be halved
c)
It will be doubled
d)
It will be quadrupled
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The terminal velocity of an object falling through a fluid depends on factors such as the density and viscosity of the fluid but is independent of the object's size.
In the context of viscosity, what does it mean when a fluid is described as "thick"?- a)The fluid is highly viscous
- b)The fluid has low viscosity
- c)The fluid is dense
- d)The fluid is incompressible
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the context of viscosity, what does it mean when a fluid is described as "thick"?
a)
The fluid is highly viscous
b)
The fluid has low viscosity
c)
The fluid is dense
d)
The fluid is incompressible
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
When a fluid is described as "thick" in the context of viscosity, it means that the fluid is highly viscous.
Chapter doubts & questions for Friction - Physics for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Friction - Physics for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for JAMB
259 videos|253 docs|230 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup