All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Evolution Among Organisms for JAMB Exam
Soap box like cell wall is characteristic of :-- a)Archae bacteria
- b)Diatoms
- c)Dinoflagellates
- d)Euglenoids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Soap box like cell wall is characteristic of :-
a)
Archae bacteria
b)
Diatoms
c)
Dinoflagellates
d)
Euglenoids
|
|
Amrita Choudhary answered |
The cell walls construction of diatoms is known as Frustule which consists of two thin overlapping shells fitting into each other just as a soap-box. Their walls are made up of silica. When the diatoms die, the silica in their cell walls gets deposited in the form of diatomaceous earth. This diatomaceous earth is very soft and quite inert. It is used in filtration of oils, sugars, and for other industrial purposes.
Causes of water bloom is :-- a)Green algae
- b)Blue green algae
- c)Bacteria
- d)Hydrilla
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Causes of water bloom is :-
a)
Green algae
b)
Blue green algae
c)
Bacteria
d)
Hydrilla

|
Ambition Institute answered |
These are a result of blue-green algae, which are actually bacteria (cyanobacteria). Some algal blooms are the result of an excess of nutrients (particularly phosphorus and nitrogen) in waters and higher concentrations of these nutrients in water cause increased growth of algae and green plants.
Halophiles, methanogens and thermoacidophils are- a)Cyanobacteria
- b)Eubacteria
- c)Actinomycetes
- d)Archaebacteria
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Halophiles, methanogens and thermoacidophils are
a)
Cyanobacteria
b)
Eubacteria
c)
Actinomycetes
d)
Archaebacteria
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Methanogens , Halophiles , Thermoacidophils , all belong to ARCHAEBACTERIA. They are primitive organisms which means they were the first to inhabit earth . They are often called LIVING FOSSILS. Methanogens are found in Rumen of cattles , Halophiles are found in salt lakes , Thermoacidophils are found in hot sulphur springs and Archaebacteria are found in some of the harsh climatic conditions where no other life form could survive.
The most efficient locomotion in protista is through :-- a)Pseudopodia
- b)Flagella
- c)Cilia
- d)Tentacles
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The most efficient locomotion in protista is through :-
a)
Pseudopodia
b)
Flagella
c)
Cilia
d)
Tentacles
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Cilia are mostly present in hundreds, projecting out of the holes of the pellicle since basal bodies of all cilia are linked to common kinetodesmata. They beat in the coordinated rhythmic manner to produce paddle stroke effect. Due to their occurrence all over the body, they perform the fastest locomotion i.e., 400-2000 micrometer/second. So, they are the most efficient organs of locomotion.
Photosynthetic prokaryotic organism is:-- a)Rhizobium
- b)Nostoc
- c)Pseudomonas
- d)Staphylococcus
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Photosynthetic prokaryotic organism is:-
a)
Rhizobium
b)
Nostoc
c)
Pseudomonas
d)
Staphylococcus
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Nostoc, is genus of blue-green algae with cells arranged in beadlike chains that are grouped together in a gelatinous mass. Like most blue-green algae,Nostoc contains two pigments, blue phycocyanin and red phycoerythrin, as well as chlorophyll, and has the ability to fix nitrogen in specialized cells called heterocysts. This makes them photosynthetic.
Most common method of reproduction in prokaryotes :-
- a) Budding
- b) Binary fission
- c) Transduction
- d) Conjugation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most common method of reproduction in prokaryotes :-
a)
Buddingb)
Binary fissionc)
Transductiond)
Conjugation

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
Binary fission ("division in half") is a kind of asexual reproduction. It is the most common form of reproduction in prokaryotes such as bacteria. It occurs in some single-celled Eukaryotes like the Amoeba and the Paramoecium. In binary fission, DNA replication and segregation occur simultaneously.
Asexual spores in Ascomycetes are called as _______- a)Ascospores
- b)Conidia
- c)Sporangiospores
- d)Aeciospores
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Asexual spores in Ascomycetes are called as _______
a)
Ascospores
b)
Conidia
c)
Sporangiospores
d)
Aeciospores
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
Conidia is a sexual spores in ascomycetes which are produced exogenously on conidiophores :)
The diatoms do not easily decay like most of the other Algae because:-- a)They have water proof cells
- b)Their walls are mucilagenous
- c)They have highly siliceous wall
- d)They are non living
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The diatoms do not easily decay like most of the other Algae because:-
a)
They have water proof cells
b)
Their walls are mucilagenous
c)
They have highly siliceous wall
d)
They are non living
|
|
Suresh Kumar answered |
Their walls are embedded with silica & thus the walls are indestructible...
Armoured algae are :-- a)Dinoflagellates
- b)Euglenoids
- c)Red algae
- d)Cyanobacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Armoured algae are :-
a)
Dinoflagellates
b)
Euglenoids
c)
Red algae
d)
Cyanobacteria
|
|
Megha Desai answered |
The dinoflagellates are a classification subgroup of algae. They are a large group of flagellate eukaryotes that constitute the phylum Dinoflagellata. Most are marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats.
Coenocytic means _______- a)sharing of common cytoplasm
- b)removal of plasma membrane
- c)sharing of common nucleus
- d)sharing of common hyphael wall
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Coenocytic means _______
a)
sharing of common cytoplasm
b)
removal of plasma membrane
c)
sharing of common nucleus
d)
sharing of common hyphael wall
|
|
Srestha Bose answered |
Coenocytic means sharing of common cytoplasm. This term is commonly used to describe a type of cell or organism that does not have distinct cell boundaries or compartments. Instead, coenocytic cells contain multiple nuclei within a single, continuous cytoplasmic mass.
Explanation:
Coenocytic cells are typically found in fungi, algae, and some types of plants. In these organisms, individual cells may fuse together during development to form a single, multinucleate cell. This single cell may then develop into a larger structure or organism, such as a fungus or alga.
Some key characteristics of coenocytic cells include:
- Lack of cell walls: Coenocytic cells do not have distinct cell walls separating them from neighboring cells. Instead, they are connected by a network of cytoplasmic strands.
- Multiple nuclei: Because coenocytic cells contain multiple nuclei within a single cytoplasmic mass, they are often referred to as multinucleate.
- Large size: Without the constraints of cell walls, coenocytic cells can grow to very large sizes. Some fungi, for example, can form structures that are many meters in length.
Overall, the term "coenocytic" refers to a unique type of cell organization that is characterized by the sharing of cytoplasmic material between multiple nuclei.
Explanation:
Coenocytic cells are typically found in fungi, algae, and some types of plants. In these organisms, individual cells may fuse together during development to form a single, multinucleate cell. This single cell may then develop into a larger structure or organism, such as a fungus or alga.
Some key characteristics of coenocytic cells include:
- Lack of cell walls: Coenocytic cells do not have distinct cell walls separating them from neighboring cells. Instead, they are connected by a network of cytoplasmic strands.
- Multiple nuclei: Because coenocytic cells contain multiple nuclei within a single cytoplasmic mass, they are often referred to as multinucleate.
- Large size: Without the constraints of cell walls, coenocytic cells can grow to very large sizes. Some fungi, for example, can form structures that are many meters in length.
Overall, the term "coenocytic" refers to a unique type of cell organization that is characterized by the sharing of cytoplasmic material between multiple nuclei.
Nitrogen fixation in legume roots is performed by:- a)Autotrophic bacteria
- b)Heterotrophic bacteria
- c)Viruses
- d)Protozoa
Correct answer is option 'E'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Autotrophic bacteria
b)
Heterotrophic bacteria
c)
Viruses
d)
Protozoa
|
|
Pranjal Chaudhary answered |
Nitrogen Fixation in Legume Roots
Nitrogen fixation is a crucial biological process that converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3), a form usable by plants. In legumes, this process primarily occurs in symbiotic relationships with specific bacteria.
Key Players in Nitrogen Fixation:
- Rhizobium Bacteria: The primary bacteria involved in nitrogen fixation in legume roots are from the genus Rhizobium. These are heterotrophic bacteria that thrive in the root nodules of legumes.
- Symbiotic Relationship: Legumes, such as peas, beans, and lentils, form nodules on their roots where these bacteria reside. The plant provides carbohydrates and a suitable environment for the bacteria, while the bacteria convert nitrogen gas from the atmosphere into ammonia.
- Mutual Benefits: This mutualistic relationship benefits both partners. The bacteria gain nutrients and a habitat, while legumes receive essential nitrogen, which is vital for their growth and development.
Process of Nitrogen Fixation:
- Root Nodule Formation: When legumes are exposed to Rhizobium, the bacteria invade the root hairs, leading to nodule formation.
- Nitrogen Conversion: Within these nodules, the Rhizobium bacteria utilize the enzyme nitrogenase to convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which the plant can then assimilate.
- Impact on Soil Fertility: This process not only supports the growth of legumes but also enhances soil fertility, benefiting subsequent crops planted in the same soil.
Conclusion:
In summary, nitrogen fixation in legume roots is primarily performed by heterotrophic bacteria, specifically Rhizobium, establishing a vital symbiotic relationship that plays a significant role in agriculture and ecosystem health.
Nitrogen fixation is a crucial biological process that converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into ammonia (NH3), a form usable by plants. In legumes, this process primarily occurs in symbiotic relationships with specific bacteria.
Key Players in Nitrogen Fixation:
- Rhizobium Bacteria: The primary bacteria involved in nitrogen fixation in legume roots are from the genus Rhizobium. These are heterotrophic bacteria that thrive in the root nodules of legumes.
- Symbiotic Relationship: Legumes, such as peas, beans, and lentils, form nodules on their roots where these bacteria reside. The plant provides carbohydrates and a suitable environment for the bacteria, while the bacteria convert nitrogen gas from the atmosphere into ammonia.
- Mutual Benefits: This mutualistic relationship benefits both partners. The bacteria gain nutrients and a habitat, while legumes receive essential nitrogen, which is vital for their growth and development.
Process of Nitrogen Fixation:
- Root Nodule Formation: When legumes are exposed to Rhizobium, the bacteria invade the root hairs, leading to nodule formation.
- Nitrogen Conversion: Within these nodules, the Rhizobium bacteria utilize the enzyme nitrogenase to convert atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia, which the plant can then assimilate.
- Impact on Soil Fertility: This process not only supports the growth of legumes but also enhances soil fertility, benefiting subsequent crops planted in the same soil.
Conclusion:
In summary, nitrogen fixation in legume roots is primarily performed by heterotrophic bacteria, specifically Rhizobium, establishing a vital symbiotic relationship that plays a significant role in agriculture and ecosystem health.
Rhizopus belongs to _________- a)Phycomycetes
- b)Ascomycetes
- c)Basidiomycetes
- d)Deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rhizopus belongs to _________
a)
Phycomycetes
b)
Ascomycetes
c)
Basidiomycetes
d)
Deuteromycetes
|
|
Jaspreet answered |
Rhizopus belongs to Phycomycetes :)
Non-motile spores in Phycomycetes are called as _____- a)Phycospores
- b)Zoospores
- c)Aplanospores
- d)Zygospores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Non-motile spores in Phycomycetes are called as _____
a)
Phycospores
b)
Zoospores
c)
Aplanospores
d)
Zygospores

|
Prahlad Pai answered |
Non motile spore in phycomycetes is aplanospores
Bacteria reproduce by ___________- a)Sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction
- b)Asexual reproduction
- c)Spores
- d)Sexual reproduction
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bacteria reproduce by ___________
a)
Sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction
b)
Asexual reproduction
c)
Spores
d)
Sexual reproduction

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- Bacteria reproduce either by asexual reproduction or sometimes adopt sexual mode of reproduction.
- In sexual reproduction they mainly adopt conjugation in which DNA transfer takes place from one bacterium to other.
- In asexual reproduction they undergo binary fission.
Which of the following is the only group of organisms capable of using inorganic compounds as source of energy :–- a)Eucaryotes
- b)Procaryotes
- c)Both the above
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is the only group of organisms capable of using inorganic compounds as source of energy :–
a)
Eucaryotes
b)
Procaryotes
c)
Both the above
d)
None of the above
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
On the basis of their energy source, organisms are classified as organotrophic and lithotrophs. Most prokaryotes and all non-phototrophic eukaryotes use organic compounds as their energy source and thus, are referred to as organotrophs. They oxidise organic compounds during cellular respiration and the produced oxygen as a byproduct. But some Cyanobacteria and Archaea use inorganic compounds as an electron donor in electron transport chain and are referred to as lithotrophs, none of the eukaryotes falls in this category. Virus act as non-living outside the cell. It becomes active when it enters the host cell and derives the cellular protein from the host.
Which among the following are incorrect about Phycomycetes?- a)Phycomycetes are aseptate fungi and are coenocytic
- b)Phycomycetes are also called as algal fungi
- c)Zygospores are formed due to isogamous fertilization and zoospores are formed due to anisogamous fertilization
- d)Phycomycetes are also called as conjugation fungi
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following are incorrect about Phycomycetes?
a)
Phycomycetes are aseptate fungi and are coenocytic
b)
Phycomycetes are also called as algal fungi
c)
Zygospores are formed due to isogamous fertilization and zoospores are formed due to anisogamous fertilization
d)
Phycomycetes are also called as conjugation fungi
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Zygospores are formed either due to isogamous or anisogamous fertilization. Zoospores and aplanospores are motile and non-motile spores produced due to asexual mode respectively. Phycomycetes are aseptate fungi and are coenocytic. Phycomycetes are also called as algal fungi or conjugation fungi.
The diatomaceous earth is used to insulate boilers and steam pipes because:-- a) The wall of diatoms is deposited with calcium
- b)The diatomaceous earth is cheap
- c)It is a good conductor of heat
- d)The wall of diatoms is made of silica
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The diatomaceous earth is used to insulate boilers and steam pipes because:-
a)
The wall of diatoms is deposited with calcium
b)
The diatomaceous earth is cheap
c)
It is a good conductor of heat
d)
The wall of diatoms is made of silica
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Correct option is d)
Cells of diatoms are surrounded by the cell wall, deposited with silica called as frustules which are composed of two overlapping halves (the epitheca and the hypotheca). Shells of diatoms are highly resistant to decomposition due to the presence of silica and are deposited in ocean beds leading to the formation of the diatomaceous earth. This is used as filters because its silica content makes it chemically inactive and uncompressible during insulation.
Which part of the mushroom is responsible for spore production?- a)Stipe
- b)Cap
- c)Gills
- d)Annulus
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which part of the mushroom is responsible for spore production?
a)
Stipe
b)
Cap
c)
Gills
d)
Annulus
|
|
Adiza Adeleke answered |
Understanding Mushroom Spore Production
Mushrooms, which are the fruiting bodies of fungi, have several key parts, each serving a specific function. Among these, the gills are crucial for spore production.
Key Functions of Mushroom Parts
- Stipe: This is the stem of the mushroom that supports the cap. While it plays a role in elevating the cap for spore dispersal, it is not involved in spore production.
- Cap: The cap is the umbrella-like structure that protects the gills. Although it provides shelter for spore production, it is not the site where spores are generated.
- Gills: Located beneath the cap, the gills are thin, blade-like structures where spore production occurs. They contain specialized cells called basidia, which produce spores through a process known as meiosis. These spores are then released into the environment, allowing for reproduction and the continuation of the fungal life cycle.
- Annulus: This is a ring-like structure found on the stipe, which is a remnant of the partial veil that covers the gills during the mushroom's development. It does not contribute to spore production.
Conclusion
In summary, the gills (option C) are the primary site for spore production in mushrooms. They are integral to the reproductive cycle, ensuring that fungi can spread and thrive in suitable environments. Understanding this anatomy helps in the study of fungi and their ecological roles.
Mushrooms, which are the fruiting bodies of fungi, have several key parts, each serving a specific function. Among these, the gills are crucial for spore production.
Key Functions of Mushroom Parts
- Stipe: This is the stem of the mushroom that supports the cap. While it plays a role in elevating the cap for spore dispersal, it is not involved in spore production.
- Cap: The cap is the umbrella-like structure that protects the gills. Although it provides shelter for spore production, it is not the site where spores are generated.
- Gills: Located beneath the cap, the gills are thin, blade-like structures where spore production occurs. They contain specialized cells called basidia, which produce spores through a process known as meiosis. These spores are then released into the environment, allowing for reproduction and the continuation of the fungal life cycle.
- Annulus: This is a ring-like structure found on the stipe, which is a remnant of the partial veil that covers the gills during the mushroom's development. It does not contribute to spore production.
Conclusion
In summary, the gills (option C) are the primary site for spore production in mushrooms. They are integral to the reproductive cycle, ensuring that fungi can spread and thrive in suitable environments. Understanding this anatomy helps in the study of fungi and their ecological roles.
Select the correct combination of the statements (i-iv) regarding the characteristics of certain organisms.(i) Methanogens are archaebacteria which produce methane in marshy areas.(ii) Nostoc is a filamentous blue-green alga which fixes atmospheric nitrogen.(iii) Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria synthesise cellulose from glucose.(iv) Mycoplasma lack a cell wall and can survive without oxygen.- a)Only (ii) and (iii)
- b)Only (i), (ii) and (iv)
- c)Only (i),(ii) and (iii)
- d)Only (ii), (iii) and (iv)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct combination of the statements (i-iv) regarding the characteristics of certain organisms.
(i) Methanogens are archaebacteria which produce methane in marshy areas.
(ii) Nostoc is a filamentous blue-green alga which fixes atmospheric nitrogen.
(iii) Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria synthesise cellulose from glucose.
(iv) Mycoplasma lack a cell wall and can survive without oxygen.
a)
Only (ii) and (iii)
b)
Only (i), (ii) and (iv)
c)
Only (i),(ii) and (iii)
d)
Only (ii), (iii) and (iv)

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidise various inorganic substances such as nitrates, nitrites and ammonia and use the released energy for their ATP production. They play a great role in recycling nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous, iron and sulphur.
What is the primary role of heterotrophic bacteria in nature?- a)Photosynthesis
- b)Decomposition
- c)Nitrogen fixation
- d)Pollination
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary role of heterotrophic bacteria in nature?
a)
Photosynthesis
b)
Decomposition
c)
Nitrogen fixation
d)
Pollination
|
|
Ananya Chakraborty answered |
Primary Role of Heterotrophic Bacteria
Heterotrophic bacteria play a crucial role in the ecosystem, primarily through the process of decomposition.
What are Heterotrophic Bacteria?
- Heterotrophic bacteria are organisms that obtain their energy and nutrients by consuming organic matter.
- Unlike autotrophic bacteria, which produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, heterotrophs rely on the breakdown of organic materials.
Importance of Decomposition
- Nutrient Recycling: Heterotrophic bacteria break down dead organic matter, such as plant and animal remains. This process returns essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, back into the soil, making them available for other organisms, particularly plants.
- Soil Health: By decomposing organic materials, these bacteria contribute to soil fertility and structure. Healthy soil is vital for agriculture and ecosystem stability.
- Ecosystem Balance: Decomposition helps maintain ecological balance by controlling the accumulation of organic waste. This process prevents the spread of diseases that can occur when organic matter decomposes anaerobically.
Additional Roles
- While decomposition is the primary role, heterotrophic bacteria also participate in nutrient cycling and can influence other processes like fermentation and disease regulation in ecosystems.
In summary, heterotrophic bacteria are essential for decomposing organic matter, recycling nutrients, and maintaining soil health, making them indispensable for ecological balance and sustainability.
Heterotrophic bacteria play a crucial role in the ecosystem, primarily through the process of decomposition.
What are Heterotrophic Bacteria?
- Heterotrophic bacteria are organisms that obtain their energy and nutrients by consuming organic matter.
- Unlike autotrophic bacteria, which produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, heterotrophs rely on the breakdown of organic materials.
Importance of Decomposition
- Nutrient Recycling: Heterotrophic bacteria break down dead organic matter, such as plant and animal remains. This process returns essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon, back into the soil, making them available for other organisms, particularly plants.
- Soil Health: By decomposing organic materials, these bacteria contribute to soil fertility and structure. Healthy soil is vital for agriculture and ecosystem stability.
- Ecosystem Balance: Decomposition helps maintain ecological balance by controlling the accumulation of organic waste. This process prevents the spread of diseases that can occur when organic matter decomposes anaerobically.
Additional Roles
- While decomposition is the primary role, heterotrophic bacteria also participate in nutrient cycling and can influence other processes like fermentation and disease regulation in ecosystems.
In summary, heterotrophic bacteria are essential for decomposing organic matter, recycling nutrients, and maintaining soil health, making them indispensable for ecological balance and sustainability.
In fungi, asexual reproduction takes place by- a) Fission, conidia and ascospores
- b)Conidia, hypnospores and zoospores
- c)Conidia, sporangiospores and zoospores
- d)Sporangiospores, conidia and basidiospores
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In fungi, asexual reproduction takes place by
a)
Fission, conidia and ascospores
b)
Conidia, hypnospores and zoospores
c)
Conidia, sporangiospores and zoospores
d)
Sporangiospores, conidia and basidiospores

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Asexual reproduction is by spores called conidia or sporangiospores or zoospores, and sexual reproduction is by oospores, ascospores and basidiospores
Cyanobacteria do not possess which feature?- a)Unicellular
- b)Colonial or filamentous
- c)Form blooms in polluted water bodies
- d)Only marine algae
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cyanobacteria do not possess which feature?
a)
Unicellular
b)
Colonial or filamentous
c)
Form blooms in polluted water bodies
d)
Only marine algae

|
Poulomi Datta answered |
Unicellular
- Cyanobacteria can be either unicellular or multicellular, depending on the species.
- Some species exist as single cells, while others form colonies or filaments.
Colonial or filamentous
- Cyanobacteria are known to form colonies or filaments, which allows them to thrive in various habitats.
- These colonies or filaments can be seen as slimy masses in water bodies or on surfaces.
Form blooms in polluted water bodies
- Cyanobacteria are notorious for forming blooms in polluted water bodies.
- These blooms can be harmful to the environment and aquatic life due to the toxins they produce.
Only marine algae
- This statement is incorrect, as cyanobacteria are not exclusive to marine environments.
- Cyanobacteria can be found in various habitats, including freshwater, soil, and even extreme environments like hot springs.
Overall, cyanobacteria possess the features of being unicellular or colonial/filamentous, forming blooms in polluted water bodies, and can thrive in a wide range of environments beyond just marine habitats.
- Cyanobacteria can be either unicellular or multicellular, depending on the species.
- Some species exist as single cells, while others form colonies or filaments.
Colonial or filamentous
- Cyanobacteria are known to form colonies or filaments, which allows them to thrive in various habitats.
- These colonies or filaments can be seen as slimy masses in water bodies or on surfaces.
Form blooms in polluted water bodies
- Cyanobacteria are notorious for forming blooms in polluted water bodies.
- These blooms can be harmful to the environment and aquatic life due to the toxins they produce.
Only marine algae
- This statement is incorrect, as cyanobacteria are not exclusive to marine environments.
- Cyanobacteria can be found in various habitats, including freshwater, soil, and even extreme environments like hot springs.
Overall, cyanobacteria possess the features of being unicellular or colonial/filamentous, forming blooms in polluted water bodies, and can thrive in a wide range of environments beyond just marine habitats.
Halophiles, methanogens and thermoacidophils are- a)Cyanobacteria
- b)Eubacteria
- c)Actinomycetes
- d)Archaebacteria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Halophiles, methanogens and thermoacidophils are
a)
Cyanobacteria
b)
Eubacteria
c)
Actinomycetes
d)
Archaebacteria
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Methanogens , Halophiles , Thermoacidophils , all belong to ARCHEBACTERIA
they are the primitive organism means they were the first to inhabit earth , they are often called LIVING FOSSILS
Methanogens are found in Rumen of cattles , Halophiles are found in salt lakes , Thermoacidophils are found in Hot sulphur springs.
Archebacteria are found in some of the harsh climatic conditions where no other life form could survive
Identify the group of fungi that is not correctly matched with all the characters given below:- a)Phycomycetes: Mycelium – aseptate and coenocytic / Asexual reproduction by motile zoospores or by nonmotile aplanospores / spores – endogenously produced in the sporangium
- b)Ascomycetes: Mycelium – unbranched and septate / Asexual spores are conidia / Conidia produced endogenously on conidiophores.
- c)Basidiomycetes: Mycelium–branched and septate / Asexual spores are generally not found.
- d)Deuteromycetes: Only the asexual or vegetative phase of these fungi are known.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the group of fungi that is not correctly matched with all the characters given below:
a)
Phycomycetes: Mycelium – aseptate and coenocytic / Asexual reproduction by motile zoospores or by nonmotile aplanospores / spores – endogenously produced in the sporangium
b)
Ascomycetes: Mycelium – unbranched and septate / Asexual spores are conidia / Conidia produced endogenously on conidiophores.
c)
Basidiomycetes: Mycelium–branched and septate / Asexual spores are generally not found.
d)
Deuteromycetes: Only the asexual or vegetative phase of these fungi are known.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Commonly known as sac-fungi, the ascomycetes are mostly multicellular, e.g., Penicillium, or rarelyunicellular, e.g., yeast (Saccharomyces). They are saprophytic, decomposers, parasitic or coprophilous (growing on dung). is branched and septate. The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of fungi?- a)Chlorophyll pigments
- b)Cellulose cell walls
- c)Autotrophic nutrition
- d)Heterotrophic nutrition
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of fungi?
a)
Chlorophyll pigments
b)
Cellulose cell walls
c)
Autotrophic nutrition
d)
Heterotrophic nutrition
|
|
Amina Garba answered |
Characteristic Features of Fungi
Fungi are a diverse group of organisms with unique characteristics that distinguish them from plants and animals. Among the options provided, heterotrophic nutrition is a key feature.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Fungi cannot produce their own food like plants do.
- They obtain nutrients by absorbing organic matter from their environment.
- This process involves the secretion of enzymes that break down complex substances into simpler compounds, which are then absorbed through their cell walls.
Comparison with Other Options
- Chlorophyll Pigments:
- Fungi do not possess chlorophyll and therefore cannot perform photosynthesis.
- Cellulose Cell Walls:
- While plants have cellulose in their cell walls, fungi have a cell wall made of chitin, which is different from cellulose.
- Autotrophic Nutrition:
- Fungi are not autotrophic; they rely on organic matter for nutrients, as opposed to autotrophs, which create their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Conclusion
Given these points, the correct answer to the characteristic feature of fungi is indeed "heterotrophic nutrition." This feature underscores their role as decomposers in ecosystems, highlighting their importance in nutrient cycling and organic matter breakdown.
Fungi are a diverse group of organisms with unique characteristics that distinguish them from plants and animals. Among the options provided, heterotrophic nutrition is a key feature.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Fungi cannot produce their own food like plants do.
- They obtain nutrients by absorbing organic matter from their environment.
- This process involves the secretion of enzymes that break down complex substances into simpler compounds, which are then absorbed through their cell walls.
Comparison with Other Options
- Chlorophyll Pigments:
- Fungi do not possess chlorophyll and therefore cannot perform photosynthesis.
- Cellulose Cell Walls:
- While plants have cellulose in their cell walls, fungi have a cell wall made of chitin, which is different from cellulose.
- Autotrophic Nutrition:
- Fungi are not autotrophic; they rely on organic matter for nutrients, as opposed to autotrophs, which create their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis.
Conclusion
Given these points, the correct answer to the characteristic feature of fungi is indeed "heterotrophic nutrition." This feature underscores their role as decomposers in ecosystems, highlighting their importance in nutrient cycling and organic matter breakdown.
Where are members of phycomycetes primarily found?- a)In dry desert regions
- b)In high-altitude mountain areas
- c)In aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist places
- d)In arid deserts and sandy soils
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Where are members of phycomycetes primarily found?
a)
In dry desert regions
b)
In high-altitude mountain areas
c)
In aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist places
d)
In arid deserts and sandy soils

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Members of phycomycetes are found in aquatic habitats and on decaying wood in moist and damp places or as obligate parasites on plants.
What do chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidize for their ATP production?- a) Organic compounds
- b) Inorganic substances
- c) Sugars
- d) Fatty acids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What do chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidize for their ATP production?
a)
Organic compounds
b)
Inorganic substances
c)
Sugars
d)
Fatty acids

|
Bs Academy answered |
Chemosynthetic autotrophic bacteria oxidize inorganic substances for their ATP production.
What are the three main steps involved in the sexual cycle in sequence?- a)Karyoogamy→ Plasmogamy→ Meiosis
- b)Plasmogamy→ Meiosis → Karyogamy
- c)Plasmogamy→ Karyogamy → Meiosis
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the three main steps involved in the sexual cycle in sequence?
a)
Karyoogamy→ Plasmogamy→ Meiosis
b)
Plasmogamy→ Meiosis → Karyogamy
c)
Plasmogamy→ Karyogamy → Meiosis
d)
None of these

|
Bs Academy answered |
The sexual cycle involves the following three steps: (i) Fusion of protoplasms between two motile or non-motile gametes called plasmogamy. (ii) Fusion of two nuclei called karyogamy. (iii) Meiosis in zygote resulting in haploid spores
Assertion(A): Deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi.
Reason(R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition .- a)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion(A): Deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi.
Reason(R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition .
Reason(R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition .
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Prasenjit Ghosh answered |
Understanding Deuteromycetes
Deuteromycetes, commonly known as "imperfect fungi," are a group of fungi that do not have a known sexual reproductive stage. Their classification primarily stems from their inability to reproduce sexually, which differentiates them from other fungal groups.
Assertion (A): Deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi.
- This statement is true.
- Deuteromycetes are termed "imperfect" because their sexual reproduction has not been observed, leading to incomplete classification in traditional fungal taxonomy.
Reason (R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition.
- This statement is false.
- Deuteromycetes are primarily heterotrophic, meaning they obtain their nutrition by absorbing organic compounds from their surroundings, unlike autotrophic organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
Conclusion
- Since assertion (A) is true and reason (R) is false, the correct option is (C): (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- The confusion often arises because many people mistakenly associate the term "fungi" with autotrophic characteristics, whereas most fungi, including Deuteromycetes, are heterotrophic.
This analysis clarifies the distinction between the nature of Deuteromycetes and their nutritional mode. Understanding these concepts is crucial for topics related to mycology in exams like NEET.
Deuteromycetes, commonly known as "imperfect fungi," are a group of fungi that do not have a known sexual reproductive stage. Their classification primarily stems from their inability to reproduce sexually, which differentiates them from other fungal groups.
Assertion (A): Deuteromycetes are called imperfect fungi.
- This statement is true.
- Deuteromycetes are termed "imperfect" because their sexual reproduction has not been observed, leading to incomplete classification in traditional fungal taxonomy.
Reason (R): These fungi have autotrophic mode of nutrition.
- This statement is false.
- Deuteromycetes are primarily heterotrophic, meaning they obtain their nutrition by absorbing organic compounds from their surroundings, unlike autotrophic organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis.
Conclusion
- Since assertion (A) is true and reason (R) is false, the correct option is (C): (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- The confusion often arises because many people mistakenly associate the term "fungi" with autotrophic characteristics, whereas most fungi, including Deuteromycetes, are heterotrophic.
This analysis clarifies the distinction between the nature of Deuteromycetes and their nutritional mode. Understanding these concepts is crucial for topics related to mycology in exams like NEET.
Assertion: Mycoplasma is pathogenic both to animaLs and plants
Reason: These organisms lack cell wall and can survive without oxygen - a)Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c)(A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)Both (A) and (R) are false.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion: Mycoplasma is pathogenic both to animaLs and plants
Reason: These organisms lack cell wall and can survive without oxygen
Reason: These organisms lack cell wall and can survive without oxygen
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
Both (A) and (R) are false.

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
(B) - Mycoplasma is pathogenic to both animals and plants.
- These organisms lack cell walls and can survive without oxygen.
- These organisms lack cell walls and can survive without oxygen.
BOTH statements are true but reason is not the correct explaination of assertion
identify the correct statement STATEMENT I : Halophiles are eubacteria living in salty areasSTATEMENT II :Methanogens are abudant in guts of ruminants .STATEMENT III : Thermoacidophiles are bacteria living in hot springs - a)ONLY II
- b)BOTH II AND III
- c)ONLY III
- d)ALL ARE CORRECT
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
identify the correct statement
STATEMENT I : Halophiles are eubacteria living in salty areas
STATEMENT II :Methanogens are abudant in guts of ruminants .
STATEMENT III : Thermoacidophiles are bacteria living in hot springs
a)
ONLY II
b)
BOTH II AND III
c)
ONLY III
d)
ALL ARE CORRECT

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
- Correct Answer: B: BOTH II AND III
- Explanation:
- Explanation:
STATEMENT I : Halophiles are eubacteria living in salty areas - HALOPHILES are archaebacteria not eubacteria
- Statement II: Methanogens are indeed abundant in the guts of ruminants. These are a group of archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of metabolism in the digestive systems of ruminant animals like cows.
- Statement III: Thermoacidophiles are bacteria that thrive in hot, acidic environments like hot springs, demonstrating their ability to survive in extreme conditions.
- Statement II: Methanogens are indeed abundant in the guts of ruminants. These are a group of archaea that produce methane as a byproduct of metabolism in the digestive systems of ruminant animals like cows.
- Statement III: Thermoacidophiles are bacteria that thrive in hot, acidic environments like hot springs, demonstrating their ability to survive in extreme conditions.
Identify distinctive features for kingdom Monera.(a) It includes prokaryotic cells with nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles.
(b) Some of the Monerans are autotrophic and some of them are heterotrophic forms.
(c) Monera have been divided into two domains, archaea and bacteria.
(d) Most bacteria are classified under Monera but Cyanobacteria is classified under Plantae due to its ability to photosynthesize.- a)Only a, b and c
- b)Only b, c and d
- c)Only a, c and d
- d)All are correct.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify distinctive features for kingdom Monera.
(a) It includes prokaryotic cells with nucleus and membrane bound cell organelles.
(b) Some of the Monerans are autotrophic and some of them are heterotrophic forms.
(c) Monera have been divided into two domains, archaea and bacteria.
(d) Most bacteria are classified under Monera but Cyanobacteria is classified under Plantae due to its ability to photosynthesize.
(b) Some of the Monerans are autotrophic and some of them are heterotrophic forms.
(c) Monera have been divided into two domains, archaea and bacteria.
(d) Most bacteria are classified under Monera but Cyanobacteria is classified under Plantae due to its ability to photosynthesize.
a)
Only a, b and c
b)
Only b, c and d
c)
Only a, c and d
d)
All are correct.

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
- Some of the Monerans are autotrophic and some of them are heterotrophic forms.
- Monera have been divided into two domains, archaea and bacteria.
- Most bacteria are classified under Monera, but Cyanobacteria is classified under Plantae due to its ability to photosynthesize.
Assertion(A): Archaebacteria are special bacteria.
Reason(R): They live in harsh habitats.- a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
- b)Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
- c) (A) is true, but (R) is false.
- d)(A) is false, but (R) is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion(A): Archaebacteria are special bacteria.
Reason(R): They live in harsh habitats.
Reason(R): They live in harsh habitats.
a)
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
b)
Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
c)
(A) is true, but (R) is false.
d)
(A) is false, but (R) is true.
|
|
Athira Chauhan answered |
Assertion (A): Archaebacteria are special bacteria.
Archaebacteria are indeed considered special due to their unique characteristics and evolutionary significance. They are distinct from regular bacteria (Eubacteria) and are classified under a separate domain of life.
Reason (R): They live in harsh habitats.
Archaebacteria are known for thriving in extreme environments such as hot springs, salt lakes, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Their ability to survive in these harsh conditions is a defining feature of this group.
Relationship between (A) and (R): Explanation
- Both are true:
- Assertion (A) is true as archaebacteria are indeed special due to their unique genetic and biochemical properties.
- Reason (R) is also true because their survival in extreme conditions is a hallmark of their uniqueness.
- Correct explanation:
- The fact that they live in harsh habitats is a significant reason why they are classified as special. Their adaptations to extreme environments, such as high temperatures, high salinity, and acidic conditions, highlight the evolutionary adaptations that set them apart from other bacteria.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). This relationship emphasizes the special nature of archaebacteria, rooted in their ability to thrive in some of the most inhospitable environments on Earth.
Archaebacteria are indeed considered special due to their unique characteristics and evolutionary significance. They are distinct from regular bacteria (Eubacteria) and are classified under a separate domain of life.
Reason (R): They live in harsh habitats.
Archaebacteria are known for thriving in extreme environments such as hot springs, salt lakes, and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Their ability to survive in these harsh conditions is a defining feature of this group.
Relationship between (A) and (R): Explanation
- Both are true:
- Assertion (A) is true as archaebacteria are indeed special due to their unique genetic and biochemical properties.
- Reason (R) is also true because their survival in extreme conditions is a hallmark of their uniqueness.
- Correct explanation:
- The fact that they live in harsh habitats is a significant reason why they are classified as special. Their adaptations to extreme environments, such as high temperatures, high salinity, and acidic conditions, highlight the evolutionary adaptations that set them apart from other bacteria.
Conclusion
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A': Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). This relationship emphasizes the special nature of archaebacteria, rooted in their ability to thrive in some of the most inhospitable environments on Earth.
Lichens are __________- a)symbiotic existence of blue-green algae and fungi
- b)symbiotic existence of rhizobium bacteria in the roots of leguminous plants
- c)co-existence of coral reef with zooxanthellae
- d)existence of mycorrhiza along with leguminous plants
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Lichens are __________
a)
symbiotic existence of blue-green algae and fungi
b)
symbiotic existence of rhizobium bacteria in the roots of leguminous plants
c)
co-existence of coral reef with zooxanthellae
d)
existence of mycorrhiza along with leguminous plants
|
|
Muhammed Anzal! answered |
No the Correct answer is A. Algal component is called Phycobiont and fungal component is called Mycobiont
Assertion (A): Cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen through specialized cells known as heterocysts.Reason (R): Heterocysts are found in all types of cyanobacteria, including those that do not participate in nitrogen fixation.- a)If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
- b)If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
- c)If Assertion is true but Reason is false
- d)If both Assertion and Reason are false
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Cyanobacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen through specialized cells known as heterocysts.
Reason (R): Heterocysts are found in all types of cyanobacteria, including those that do not participate in nitrogen fixation.
a)
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
b)
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
c)
If Assertion is true but Reason is false
d)
If both Assertion and Reason are false

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Corrected Solution: - The Assertion is true because cyanobacteria, such as Nostoc and Anabaena, are known to have specialized cells called heterocysts that enable them to fix atmospheric nitrogen.
- The Reason is false because heterocysts are not found in all cyanobacteria. Only certain species possess heterocysts specifically for nitrogen fixation, while others may not have this capability.
- Therefore, the Assertion is true, but the Reason is false, as it inaccurately generalizes the presence of heterocysts in all cyanobacteria.
What is the primary function of heterocysts in certain cyanobacteria species?- a) Reproduction
- b) Nitrogen fixation
- c) Photosynthesis
- d) Water storage
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary function of heterocysts in certain cyanobacteria species?
a)
Reproduction
b)
Nitrogen fixation
c)
Photosynthesis
d)
Water storage

|
Bs Academy answered |
Heterocysts in cyanobacteria, such as Nostoc and Anabaena, serve the crucial function of nitrogen fixation. These specialized cells enable the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into a form that can be utilized by the organism. This process is essential for the cyanobacteria to thrive in environments with limited nitrogen availability, contributing to the recycling of nutrients and supporting the overall ecosystem.
According to the three-domain system, how many domains do organisms from the Kingdom Monera belong to?- a)One
- b)Two
- c)Three
- d)Four
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
According to the three-domain system, how many domains do organisms from the Kingdom Monera belong to?
a)
One
b)
Two
c)
Three
d)
Four

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
The three-domain system has also been proposed that divides the Kingdom Monera into two domains, leaving the remaining eukaryotic kingdoms in the third domain and thereby a six kingdom classification
Which group of protozoans includes organisms with an infectious spore-like stage in their life cycle, and is responsible for diseases such as malaria?- a)Flagellated protozoans
- b)Ciliated protozoans
- c)Amoeboid protozoans
- d)Sporozoans
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Flagellated protozoans
b)
Ciliated protozoans
c)
Amoeboid protozoans
d)
Sporozoans

|
Ambition Institute answered |
Sporozoans, such as Plasmodium, have an infectious spore-like stage in their life cycle. Plasmodium causes malaria, which is transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes and has a significant impact on human health.
Which of the following is a commercial use of mushrooms?- a)Food poisoning
- b)Medicine production
- c)Plant pathogens
- d)Water pollution
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a commercial use of mushrooms?
a)
Food poisoning
b)
Medicine production
c)
Plant pathogens
d)
Water pollution
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Mushrooms have various commercial uses, and one of them is medicine production. Certain species of mushrooms are used in the production of various medicines and pharmaceutical products. For example, the mushroom species Agaricus bisporus is commonly used in medicine for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Mushrooms have been studied extensively for their potential health benefits and their ability to produce bioactive compounds.
Rhizopus is commonly known as:- a)Bread mold
- b)Black mold
- c)Green mold
- d)Blue mold
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rhizopus is commonly known as:
a)
Bread mold
b)
Black mold
c)
Green mold
d)
Blue mold
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Rhizopus is commonly referred to as bread mold because it often grows on bread and other food items. It is a fast-growing fungus that thrives in warm and humid conditions. The presence of Rhizopus on bread can lead to spoilage and decay, making it an unwanted contaminant.
A ‘dikaryon’ stage is seen in the members of:- a). Ascomycetes and Phycomycetes
- b)Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
- c)Basidiomycetes and Phycomycetes
- d)Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A ‘dikaryon’ stage is seen in the members of:
a)
. Ascomycetes and Phycomycetes
b)
Ascomycetes and Basidiomycetes
c)
Basidiomycetes and Phycomycetes
d)
Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes

|
EduRev NEET answered |
When a fungus reproduces sexually, two haploid hyphae of compatible mating types come together and fuse. In some fungi the fusion of two haploid cells immediately results in diploid cells (2n). However, in other fungi (ascomycetes and basidiomycetes), an intervening dikaryotic stage (n + n, i.e., two nuclei per cell) occurs; such a condition is called a dikaryon and the phase is called dikaryophase of fungus
Identify the incorrect statement about the diagram of the fungi given below -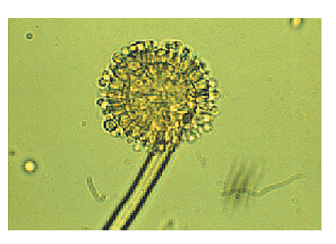
- a)The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores
- b)Sexual spores are called ascospores
- c)Fruiting bodies are called ascocarps.
- d)Fruiting bodies called ascospores.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the incorrect statement about the diagram of the fungi given below -

a)
The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores
b)
Sexual spores are called ascospores
c)
Fruiting bodies are called ascocarps.
d)
Fruiting bodies called ascospores.

|
Bs Academy answered |
Figure mentioned in the question is aspergillus which belong to class ascomycetes.
The asexual spores are conidia produced exogenously on the special mycelium called conidiophores. Conidia on germination produce mycelium. Sexual spores are called ascospores which are produced endogenously in sac like asci (singular ascus). These asci are arranged in different types of fruiting bodies called ascocarps. Some examples are Aspergillus, Claviceps and Neurospora.
What is the term for the long, slender thread-like structures that make up the body of fungi?- a)Spores
- b)Hyphae
- c)Mycorrhizae
- d)Stolons
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the term for the long, slender thread-like structures that make up the body of fungi?
a)
Spores
b)
Hyphae
c)
Mycorrhizae
d)
Stolons

|
Infinity Academy answered |
fungi are filamentous. Their bodies consist of long, slender thread-like structures called hyphae. The network of hyphae is known as mycelium. Some hyphae are continuous tubes filled with multinucleated cytoplasm – these are called coenocytic hyphae. Others have septae or cross walls in their hyphae. The cell walls of fungi are composed of chitin and polysaccharides.
Which of the following is not true regarding the reproduction and life cycle of basidiomycetes?- a)Basidiomycetes reproduce asexually through the formation of basidiospores.
- b)The sex organs are absent in basidiomycetes.
- c)Plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells.
- d)Basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true regarding the reproduction and life cycle of basidiomycetes?
a)
Basidiomycetes reproduce asexually through the formation of basidiospores.
b)
The sex organs are absent in basidiomycetes.
c)
Plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells.
d)
Basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
a) Basidiomycetes reproduce asexually through the formation of basidiospores.
This statement is not true because basidiomycetes primarily reproduce sexually through the formation of basidiospores, which are produced on basidia after plasmogamy and karyogamy. Asexual reproduction is not the primary mode of reproduction in basidiomycetes, though some may produce conidia or other forms of asexual spores in certain circumstances.
The other statements are true:
- b) The sex organs are absent in basidiomycetes. This is true because basidiomycetes do not have distinct male and female sex organs. Sexual reproduction occurs through the fusion of specialized sexual cells.
- c) Plasmogamy is brought about by the fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells. This is true. Plasmogamy involves the fusion of two somatic cells, leading to the formation of a dikaryotic mycelium in basidiomycetes.
- d) Basidia are arranged in fruiting bodies called basidiocarps. This is true. Basidia, which produce basidiospores, are typically found in fruiting bodies known as basidiocarps.
Topic in NCERT: Fungal Reproduction
Line in NCERT: "The sex organs are absent, but plasmogamy is brought about by fusion of two vegetative or somatic cells of different strains or genotypes."
Which structure is responsible for the asexual reproduction in Rhizopus?- a)Conidia
- b)Basidia
- c)Ascocarps
- d)Zygospores
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which structure is responsible for the asexual reproduction in Rhizopus?
a)
Conidia
b)
Basidia
c)
Ascocarps
d)
Zygospores
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Rhizopus reproduces asexually through specialized spore-bearing structures called conidia. Conidia are produced at the tips of specialized hyphae called conidiophores. These asexual spores are dispersed into the environment and can germinate to form new Rhizopus colonies under suitable conditions.
The fusion of hyphae in Rhizopus leads to the formation of:- a)Sporangium
- b)Zygospore
- c)Ascospore
- d)Basidiospore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The fusion of hyphae in Rhizopus leads to the formation of:
a)
Sporangium
b)
Zygospore
c)
Ascospore
d)
Basidiospore
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The fusion of hyphae in Rhizopus results in the formation of a structure called a zygospore. When two compatible hyphae of Rhizopus come into contact, they fuse and undergo sexual reproduction. The fused hyphae form a zygospore, which is a thick-walled structure containing the genetic material of both parent hyphae. The zygospore can survive adverse conditions and germinate to form new Rhizopus colonies when conditions become favorable.
Chapter doubts & questions for Evolution Among Organisms - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Evolution Among Organisms - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily