All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Animal Kingdom for JAMB Exam
The cross-section of the body of an invertebrate is given below. Identify the animal which has this body plan.
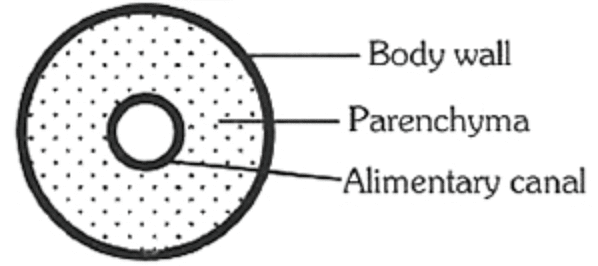
- a)Cockroach
- b)Earthworm
- c)Roundworm
- d)Planaria
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cross-section of the body of an invertebrate is given below. Identify the animal which has this body plan.

a)
Cockroach
b)
Earthworm
c)
Roundworm
d)
Planaria

|
Stepway Academy answered |
- It has three-layered body wall which includes ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm.
- Acoelomates lack a body cavity, and instead the space between the body wall and the digestive tract is filled with muscle fibres and loose tissue called parenchyma.
- It acts as a skeletal support, nutrient storage, motility, reserves of regenerative cells and transporting materials.
- Planaria belongs to phylum Platyhelminthes.
- These are flatworms and has acoelomate body plan.
Hence, the correct option is D.
NCERT Reference: Topic Phylum – Platyhelminthes” of chapter Animal Kingdom
Which phylum is a coelom and triploblastic animals?- a)Phylum Ctenophora
- b)Phylum Annelida
- c)Phylum Coelenterata
- d)Phylum Porifera
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum is a coelom and triploblastic animals?
a)
Phylum Ctenophora
b)
Phylum Annelida
c)
Phylum Coelenterata
d)
Phylum Porifera
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Annelida are aquatic (marine and freshwater) or terrestrial, free-living, and sometimes parasitic. They are bilateral symmetric and triploblastic.
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
- a) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- b)A is true, but R is false.
- c)A is false, but R is true.
- d)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Nematodes are pseudocoelomates.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
Reason (R): Pseudocoelomates have a body cavity that is not fully lined with mesoderm.
a)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
b)
A is true, but R is false.
c)
A is false, but R is true.
d)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Nematodes, or roundworms, are indeed classified as pseudocoelomates because they possess a body cavity, known as a pseudocoel, which is not completely lined by tissue derived from mesoderm.
Which among the following is a gregarious pest?- a)Locusta
- b)Apis
- c)Laccifer
- d)Bombyx
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is a gregarious pest?
a)
Locusta
b)
Apis
c)
Laccifer
d)
Bombyx
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Locust (Locusta) is a gregarious pest belonging to phylum Arthropoda.

Fig: Image of Locust
A reptile having four chambered heart isa)Snakeb)Salamanderc)Crocodiled)LizardsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Prakhar Maheshwari answered |
Except for crocodilians, which have a four-chambered heart, all reptiles have a three-chambered heart consisting of two atria and one ventricle.
What is the main excretory organ in insects?- a)Proboscis gland
- b)Malphighian tubules
- c)Gills
- d)Excretory pore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main excretory organ in insects?
a)
Proboscis gland
b)
Malphighian tubules
c)
Gills
d)
Excretory pore
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Malpighian tubule
The Malpighian tubule system is a type of excretory and osmoregulatory system found in some insects, myriapods, arachnids, and tardigrades. The system consists of branching tubules extending from the alimentary canal that absorbs solutes, water, and wastes from the surrounding hemolymph.
Which among the following is oviparous?- a)Platypus
- b)Flying fox
- c)Common dolphin
- d)lephant
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is oviparous?
a)
Platypus
b)
Flying fox
c)
Common dolphin
d)
lephant
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Platypus is oviparous as it is an egg-laying mammal
Rest three are viviparous mammals.
Species going to extinct due to low reproductive rate is- a)Island sps
- b)Bald eagle
- c)Lion
- d)Giant panda
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Species going to extinct due to low reproductive rate is
a)
Island sps
b)
Bald eagle
c)
Lion
d)
Giant panda

|
Rajesh Datta answered |
Giant panda is going to extinct due to low reproductively rate. They live in mountain ranges in central china. There reproductively rate is varyless due to climatic conditions.
Which one of the following group of animals is correctly matched with its characteristics without any exception?- a)Reptila possess 3-chambered heart with incompletely divided ventricle
- b)Mammalia give birth to young ones
- c)Chordates possess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw
- d)Chondrichthyes possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following group of animals is correctly matched with its characteristics without any exception?
a)
Reptila possess 3-chambered heart with incompletely divided ventricle
b)
Mammalia give birth to young ones
c)
Chordates possess a mouth with an upper and lower jaw
d)
Chondrichthyes possess cartilaginous endoskeleton
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
The members of the class - Chondrichthyes are marine animals with a streamlined body and have a cartilaginous endoskeleton.
The excretory organ of Saccoglossus is- a)Malphighian tubules
- b)Proboscis gland
- c)Gills
- d)Excretory pore
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The excretory organ of Saccoglossus is
a)
Malphighian tubules
b)
Proboscis gland
c)
Gills
d)
Excretory pore
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A proboscis is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouth parts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elongated nose or snout.
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called- a)Segmentation
- b)Metagenesis
- c)Metamerism
- d)Metamorphosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In some animal groups, the body is found divided into compartments with serial repetition of at least some organs. This characteristic feature is called
a)
Segmentation
b)
Metagenesis
c)
Metamerism
d)
Metamorphosis
|
|
Santunu Pradhan answered |
Metamerism
How many chambers are there in camel’s stomach?Identify the animal given below. Mention its phylum.
- a)1 chamber, Ascidia and phylum Chordata
- b)3 Chamber, Spongilla and phylum Porifera
- c)3 chambers, Euspongia and phylum Porifera
- d)4 chamber, Aurelia and phylum Coelenterata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many chambers are there in camel’s stomach?Identify the animal given below. Mention its phylum.
a)
1 chamber, Ascidia and phylum Chordata
b)
3 Chamber, Spongilla and phylum Porifera
c)
3 chambers, Euspongia and phylum Porifera
d)
4 chamber, Aurelia and phylum Coelenterata

|
Shiksha Academy answered |
Euspongia, which belongs to the phylum Porifera, is commonly known as a sponge. Sponges are some of the simplest and most primitive animals in the animal kingdom.
Hence, the correct option is C.
NCERT Reference: Topic: Phylum – Porifera” of chapter Animal Kingdom
NCERT Reference: Topic: Phylum – Porifera” of chapter Animal Kingdom
Which group of chordates possesses sucking and circular mouth without jaws?- a)ClassChondrichthyes
- b)Class Cyclostomata
- c)Class Osteichthyes
- d)Both (b) and (c)
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which group of chordates possesses sucking and circular mouth without jaws?
a)
ClassChondrichthyes
b)
Class Cyclostomata
c)
Class Osteichthyes
d)
Both (b) and (c)
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
Class-Cyclostomata is comprised of, the living jawless fishes. Their mouth is circular and lack jaws, hence they are also called agnathans. It is surrounded by tentacles (e.g., lampreys and hellish). These also presses retractable teeth.
Animals which possess cleidoic egg exhibit- a)External fertilisation and external development
- b)External fertilisation and internal development
- c)Internal fertilisation and internal development
- d)Internal fertilisation and external development
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Animals which possess cleidoic egg exhibit
a)
External fertilisation and external development
b)
External fertilisation and internal development
c)
Internal fertilisation and internal development
d)
Internal fertilisation and external development
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Cleidoic eggs are laid by reptiles & birds. These eggs have protective shell which is porous to air and may be flexible or calcareous (hard). Birds and reptiles exhibit internal fertilization and laid eggs contain all the food the embryo needs for external development.
Silk produced by Antheraea Mylitta is called- a)Eri silk
- b)Muga silk
- c)Mysore silk
- d)Tasar silk
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Silk produced by Antheraea Mylitta is called
a)
Eri silk
b)
Muga silk
c)
Mysore silk
d)
Tasar silk
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Tropical Tasar: Tasar (Tussah) is copperish colour, coarse silk mainly used for furnishings and interiors. It is less lustrous than mulberry silk, but has its own feel and appeal. Tasar silk is generated by the silkworm, Antheraea mylitta which mainly thrive on the food plants Asan and Arjun.
Air bladder is absent in- a)Sea horse
- b)Shark
- c)Flying fish
- d)All of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Air bladder is absent in
a)
Sea horse
b)
Shark
c)
Flying fish
d)
All of the above
|
|
Roshni Tiwari answered |
Explanation:
Air bladder is a gas-filled sac that helps fish to maintain buoyancy in water. However, not all fish have air bladders. The correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., shark, as sharks do not have air bladders.
Reasons why sharks do not have an air bladder are:
1. Buoyancy control: Sharks have a special organ called the liver that is filled with oil. This oil is less dense than water and provides buoyancy to the shark, allowing it to stay afloat.
2. Depth control: Unlike bony fish that have a swim bladder to adjust their depth in water, sharks are able to control their depth by swimming. They can swim at different angles to adjust their depth in water.
3. Adaptation to environment: Sharks have evolved to live in their environment, and their body shape and buoyancy control mechanisms have adapted to suit their needs.
Therefore, it can be concluded that while some fish have air bladders to maintain buoyancy in water, sharks have evolved different mechanisms to control their buoyancy and depth in water.
Air bladder is a gas-filled sac that helps fish to maintain buoyancy in water. However, not all fish have air bladders. The correct answer to the given question is option B, i.e., shark, as sharks do not have air bladders.
Reasons why sharks do not have an air bladder are:
1. Buoyancy control: Sharks have a special organ called the liver that is filled with oil. This oil is less dense than water and provides buoyancy to the shark, allowing it to stay afloat.
2. Depth control: Unlike bony fish that have a swim bladder to adjust their depth in water, sharks are able to control their depth by swimming. They can swim at different angles to adjust their depth in water.
3. Adaptation to environment: Sharks have evolved to live in their environment, and their body shape and buoyancy control mechanisms have adapted to suit their needs.
Therefore, it can be concluded that while some fish have air bladders to maintain buoyancy in water, sharks have evolved different mechanisms to control their buoyancy and depth in water.
The scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito- a)Aedes aegypti
- b)Aedes albolineatus
- c)Aedes taeniorhynchus
- d)Aedes albopictus
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The scientific name of Asian tiger mosquito
a)
Aedes aegypti
b)
Aedes albolineatus
c)
Aedes taeniorhynchus
d)
Aedes albopictus
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is a small black and white mosquito, about 1/4-inch long.
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Echinodermata
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Aschelminthes
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phylum in which adults exhibit radial symmetry and larva exhibit bilateral symmetry is
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Echinodermata
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Aschelminthes
|
|
Jyoti Kapoor answered |
Symmetry is an attribute of an organism showing regularity in body parts on a plane or around an axis. In Phylum Echinodermata, the adult echinoderms are radially symmetrical but the larvae are bilaterally symmetrical.
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe- a)the number of in vaginations during embryonic development
- b)the number of heads during embryonic development
- c)the number of germinal layers during embryonic development
- d)the number of cell types during development
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Diploblastic and triplo blastic are terms that describe
a)
the number of in vaginations during embryonic development
b)
the number of heads during embryonic development
c)
the number of germinal layers during embryonic development
d)
the number of cell types during development
|
|
Pooja Mukherjee answered |
Germinal Layers in Embryonic Development and Diploblastic/Triploblastic Classification
Embryonic development is a complex process that involves the formation of various tissues and organs from a single cell. During this process, the embryo undergoes several stages of development that are marked by the formation of germinal layers. Germinal layers are the layers of cells that differentiate into specific tissues and organs during embryonic development. These layers form the basis of the body plan of an organism and are classified as either diploblastic or triploblastic.
Diploblastic Organisms
Diploblastic organisms are those that have only two germinal layers: the ectoderm and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, which is the process by which the embryo folds in on itself to form a hollow ball of cells called the gastrula. In diploblastic organisms, the ectoderm gives rise to the outer layer of the body and the nervous system, while the endoderm gives rise to the inner layer of the body.
Examples of diploblastic organisms include cnidarians (e.g. jellyfish, corals, sea anemones) and ctenophores (comb jellies).
Triploblastic Organisms
Triploblastic organisms are those that have three germinal layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, but unlike in diploblastic organisms, the mesoderm layer is also formed. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, circulatory system, and other internal organs.
Examples of triploblastic organisms include most animals, including humans.
Conclusion
The diploblastic/triploblastic classification is based on the number of germinal layers that are present during embryonic development. Diploblastic organisms have two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm), while triploblastic organisms have three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). This classification is important for understanding the basic body plan of organisms and how different tissues and organs are formed during embryonic development.
Embryonic development is a complex process that involves the formation of various tissues and organs from a single cell. During this process, the embryo undergoes several stages of development that are marked by the formation of germinal layers. Germinal layers are the layers of cells that differentiate into specific tissues and organs during embryonic development. These layers form the basis of the body plan of an organism and are classified as either diploblastic or triploblastic.
Diploblastic Organisms
Diploblastic organisms are those that have only two germinal layers: the ectoderm and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, which is the process by which the embryo folds in on itself to form a hollow ball of cells called the gastrula. In diploblastic organisms, the ectoderm gives rise to the outer layer of the body and the nervous system, while the endoderm gives rise to the inner layer of the body.
Examples of diploblastic organisms include cnidarians (e.g. jellyfish, corals, sea anemones) and ctenophores (comb jellies).
Triploblastic Organisms
Triploblastic organisms are those that have three germinal layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. These layers are formed during gastrulation, but unlike in diploblastic organisms, the mesoderm layer is also formed. The mesoderm gives rise to the muscles, circulatory system, and other internal organs.
Examples of triploblastic organisms include most animals, including humans.
Conclusion
The diploblastic/triploblastic classification is based on the number of germinal layers that are present during embryonic development. Diploblastic organisms have two germinal layers (ectoderm and endoderm), while triploblastic organisms have three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). This classification is important for understanding the basic body plan of organisms and how different tissues and organs are formed during embryonic development.
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
- a)Body can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane only.
- b)The organisms that show bilateral symmetry have paired body organs that occur on the two sides of a central axis.
- c)It is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates.
- d)Spider and crab show bilateral symmetry.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is incorrect with regard to bilateral symmetry?
a)
Body can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane only.
b)
The organisms that show bilateral symmetry have paired body organs that occur on the two sides of a central axis.
c)
It is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates.
d)
Spider and crab show bilateral symmetry.
|
|
Poulomi Roy answered |
Bilateral Symmetry
Bilateral symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts in such a way that an organism can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane passing through the central axis of the body. This type of symmetry is found in many animals, especially invertebrates and some vertebrates.
Incorrect statement
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that bilateral symmetry is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates. This statement is incorrect because bilateral symmetry is actually found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. Almost all animals belonging to the phyla Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Examples of animals with bilateral symmetry
- Invertebrates like insects, crustaceans, spiders, and worms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
- Vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Advantages of bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry provides several advantages to animals:
- It allows for more efficient movement and coordination since paired limbs and muscles can work together to produce more precise movements.
- It facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, such as eyes and ears, that are paired and located on opposite sides of the body.
- It enables animals to have directional movement, since paired limbs can be used to move forward or backward, up or down, and left or right.
Conclusion
Bilateral symmetry is a common type of symmetry found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. It allows for more efficient movement and coordination, facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, and enables directional movement.
Bilateral symmetry refers to the arrangement of body parts in such a way that an organism can be divided into two equal halves by a single plane passing through the central axis of the body. This type of symmetry is found in many animals, especially invertebrates and some vertebrates.
Incorrect statement
The incorrect statement is option C, which states that bilateral symmetry is found in all invertebrates and few vertebrates. This statement is incorrect because bilateral symmetry is actually found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. Almost all animals belonging to the phyla Chordata, Arthropoda, Mollusca, and Annelida exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Examples of animals with bilateral symmetry
- Invertebrates like insects, crustaceans, spiders, and worms exhibit bilateral symmetry.
- Vertebrates like fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals exhibit bilateral symmetry.
Advantages of bilateral symmetry
Bilateral symmetry provides several advantages to animals:
- It allows for more efficient movement and coordination since paired limbs and muscles can work together to produce more precise movements.
- It facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, such as eyes and ears, that are paired and located on opposite sides of the body.
- It enables animals to have directional movement, since paired limbs can be used to move forward or backward, up or down, and left or right.
Conclusion
Bilateral symmetry is a common type of symmetry found in the majority of animals, both invertebrates, and vertebrates. It allows for more efficient movement and coordination, facilitates the development of specialized organs and structures, and enables directional movement.
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
- a)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
- c)Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the given statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
Statement 1: All triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
Statement 2: They have a false coelom.
a)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct and statement 2 is the correct explanation of statement 1.
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct but statement 2 is not the correct explanation of statement 1.
c)
Statement 1 is correct and statement 2 is incorrect.
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect.
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
- Animals that belong to the phylum Platyhelminthes to Chordata are all triploblastic.
- But Platyhelminthes and aschelminthes belong to pseudocoelomates.
- Annelids, arthropods, echinoderms and chordates are under eucoelomates. This means not all triploblastic animals are eucoelomates.
- Pseudocoelomates have false coelom while eucoelomate animals only have the true coelom.
Hence, both statement 1 and statement 2 are incorrect.
Read the following statements:
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eye
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them.
iii) All animals having true coelom are characterized by the presence of bilateral symmetry usually, tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm and true segmentation
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have originated from colonial protozoans.
Which of the above statements are correct?- a)i, ii, iv
- b)iii, iv
- c)i, iii
- d)ii, iii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements:
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eye
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them.
iii) All animals having true coelom are characterized by the presence of bilateral symmetry usually, tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm and true segmentation
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have originated from colonial protozoans.
Which of the above statements are correct?
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eye
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them.
iii) All animals having true coelom are characterized by the presence of bilateral symmetry usually, tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm and true segmentation
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have originated from colonial protozoans.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
i, ii, iv
b)
iii, iv
c)
i, iii
d)
ii, iii

|
Stepway Academy answered |
i) Spider and mosquito possess compound eyes. The eyes of most insects, which are composed of many light-sensitive elements, each having its own reflective system and each forming a portion of an image.
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them. Cnidoblasts are features of Coelenterata (Cnidaria) and comb-jellies come under the phylum Ctenophora.
iii) All animals with a true coelom usually exhibit bilateral symmetry, a tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm, and true segmentation.
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have indeed originated from colonial protozoans.
Thus, the correct statements are i, ii, and iv. The answer is Option A.
ii) Jelly fishes possess cnidoblasts but comb-jellies lack them. Cnidoblasts are features of Coelenterata (Cnidaria) and comb-jellies come under the phylum Ctenophora.
iii) All animals with a true coelom usually exhibit bilateral symmetry, a tube-within-tube body plan, presence of mesoderm, and true segmentation.
iv) The animals of the phylum Porifera have indeed originated from colonial protozoans.
Thus, the correct statements are i, ii, and iv. The answer is Option A.
Select the correct matching of animals, their symmetry, organisation and coelom type.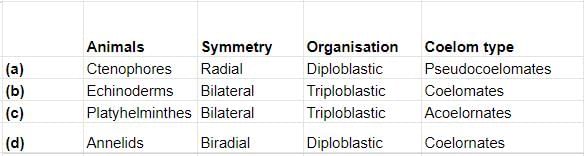
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct matching of animals, their symmetry, organisation and coelom type.

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Yashvi Khanna answered |
Correct Matching Explained
The correct answer is option 'C', as it accurately matches the animals with their corresponding symmetry, organization, and coelom type.
Animal Categories and Their Characteristics
- Ctenophores
- Symmetry: Radial
- Organisation: Diploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Pseudocoelomates)
- Echinoderms
- Symmetry: Bilateral (larval stage) and Radial (adult stage)
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates
- Platyhelminthes
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Acoelomates
- Annelids
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Diploblastic)
Detailed Breakdown of Option 'C'
- Platyhelminthes
- These organisms, commonly known as flatworms, exhibit bilateral symmetry which allows for more complex movement and organization.
- They are triploblastic, meaning they have three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- Importantly, they are classified as acoelomates, lacking a true coelom, which differentiates them from other triploblastic groups.
Conclusion
The other options provided contain inaccuracies regarding the animals' symmetry, organization, or coelom type. Thus, option 'C' is indeed the correct choice, effectively aligning Platyhelminthes with bilateral symmetry, triploblastic organization, and acoelomate structure.
The correct answer is option 'C', as it accurately matches the animals with their corresponding symmetry, organization, and coelom type.
Animal Categories and Their Characteristics
- Ctenophores
- Symmetry: Radial
- Organisation: Diploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Pseudocoelomates)
- Echinoderms
- Symmetry: Bilateral (larval stage) and Radial (adult stage)
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates
- Platyhelminthes
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Acoelomates
- Annelids
- Symmetry: Bilateral
- Organisation: Triploblastic
- Coelom Type: Coelomates (not Diploblastic)
Detailed Breakdown of Option 'C'
- Platyhelminthes
- These organisms, commonly known as flatworms, exhibit bilateral symmetry which allows for more complex movement and organization.
- They are triploblastic, meaning they have three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- Importantly, they are classified as acoelomates, lacking a true coelom, which differentiates them from other triploblastic groups.
Conclusion
The other options provided contain inaccuracies regarding the animals' symmetry, organization, or coelom type. Thus, option 'C' is indeed the correct choice, effectively aligning Platyhelminthes with bilateral symmetry, triploblastic organization, and acoelomate structure.
Match each item in Column I with one item in Column II and choose your answer from the codes given below.
Column I | Column II
I. Placoid Scales | 1. Chondrichthyes
II. Ctenoid scales | 2. Osteichthyes
III. Ectoparasites | 3. Hemichordata
IV. Proboscis gland | 4. Cyclostomata
Codes:- a)1 2 3 4
- b)2 1 4 3
- c)2 1 3 4
- d)1 2 4 3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Column I | Column II
I. Placoid Scales | 1. Chondrichthyes
II. Ctenoid scales | 2. Osteichthyes
III. Ectoparasites | 3. Hemichordata
IV. Proboscis gland | 4. Cyclostomata
Codes:
a)
1 2 3 4
b)
2 1 4 3
c)
2 1 3 4
d)
1 2 4 3
|
|
Sinjini Choudhury answered |
Understanding the Matchings
In this question, we need to match items from Column I with their respective classifications or characteristics from Column II. Here’s an explanation of each item:
Placoid Scales
- These are the scales found in Chondrichthyes, which include sharks and rays.
- Placoid scales are tooth-like structures that provide protection and help reduce turbulence while swimming.
Ctenoid Scales
- These scales are characteristic of Osteichthyes, or bony fish.
- Ctenoid scales have a comb-like edge and are more flexible compared to other types of scales, providing better movement in water.
Ectoparasites
- Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the outside of a host, often feeding on its blood or tissues.
- An example of ectoparasites includes certain species of leeches and lice, which are commonly associated with Hemichordata and other marine organisms.
Proboscis Gland
- This gland is primarily found in Cyclostomata, which includes lampreys and hagfish.
- The proboscis gland is used for feeding and attachment to hosts, particularly in parasitic species.
Matching Codes
- Based on the definitions and classifications:
- I. Placoid Scales → 1. Chondrichthyes
- II. Ctenoid Scales → 2. Osteichthyes
- III. Ectoparasites → 4. Cyclostomata
- IV. Proboscis Gland → 3. Hemichordata
Correct Answer Explanation
The correct matching is represented by option D (1 2 4 3), indicating:
- Placoid Scales are associated with Chondrichthyes (1).
- Ctenoid Scales are associated with Osteichthyes (2).
- Ectoparasites are linked to Cyclostomata (4).
- Proboscis Gland corresponds with Hemichordata (3).
Thus, option D accurately matches each item from Column I to Column II.
In this question, we need to match items from Column I with their respective classifications or characteristics from Column II. Here’s an explanation of each item:
Placoid Scales
- These are the scales found in Chondrichthyes, which include sharks and rays.
- Placoid scales are tooth-like structures that provide protection and help reduce turbulence while swimming.
Ctenoid Scales
- These scales are characteristic of Osteichthyes, or bony fish.
- Ctenoid scales have a comb-like edge and are more flexible compared to other types of scales, providing better movement in water.
Ectoparasites
- Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the outside of a host, often feeding on its blood or tissues.
- An example of ectoparasites includes certain species of leeches and lice, which are commonly associated with Hemichordata and other marine organisms.
Proboscis Gland
- This gland is primarily found in Cyclostomata, which includes lampreys and hagfish.
- The proboscis gland is used for feeding and attachment to hosts, particularly in parasitic species.
Matching Codes
- Based on the definitions and classifications:
- I. Placoid Scales → 1. Chondrichthyes
- II. Ctenoid Scales → 2. Osteichthyes
- III. Ectoparasites → 4. Cyclostomata
- IV. Proboscis Gland → 3. Hemichordata
Correct Answer Explanation
The correct matching is represented by option D (1 2 4 3), indicating:
- Placoid Scales are associated with Chondrichthyes (1).
- Ctenoid Scales are associated with Osteichthyes (2).
- Ectoparasites are linked to Cyclostomata (4).
- Proboscis Gland corresponds with Hemichordata (3).
Thus, option D accurately matches each item from Column I to Column II.
Which phylum includes organisms such as spiders, insects, and crustaceans?- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Mollusca
- c)Phylum Echinodermata
- d)Phylum Porifera
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum includes organisms such as spiders, insects, and crustaceans?
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Mollusca
c)
Phylum Echinodermata
d)
Phylum Porifera
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phylum Arthropoda includes organisms such as spiders, insects, and crustaceans. Arthropods are the largest phylum in the animal kingdom and exhibit a wide range of diversity in terms of species and habitats.
Which of the following is correctly matched?- a)Radial symmetry - Coelenterates
- b)Coelomates - Aschelminthes
- c)Metamerism - Molluscs
- d)Triploblastic - Sponges
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is correctly matched?
a)
Radial symmetry - Coelenterates
b)
Coelomates - Aschelminthes
c)
Metamerism - Molluscs
d)
Triploblastic - Sponges
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Coelenterates have radial symmetry. Aschelminth are pseudocoelomates. Molluscs do not show metamerit Sponges are diploblastic.
Metagenesis refers to?
Options:- a)The presence of different morphic forms
- b)Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
- c)Occurrence of a drastic change in the form during post-embryonic development
- d)Presence of a segmented body and parthenogenic mode of reproduction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Options:
a)
The presence of different morphic forms
b)
Alternation of generation between asexual and sexual phases of an organism
c)
Occurrence of a drastic change in the form during post-embryonic development
d)
Presence of a segmented body and parthenogenic mode of reproduction

|
Infinity Academy answered |
Metagenesis refers to the alternation of generations between asexual and sexual phases of an organism, commonly observed in cnidarians like jellyfish.
Option A: The presence of different morphic forms could refer to polymorphism, not specifically metagenesis.
Option C: This describes metamorphosis, not metagenesis.
Option D: This refers to characteristics unrelated to metagenesis.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B.
Option A: The presence of different morphic forms could refer to polymorphism, not specifically metagenesis.
Option C: This describes metamorphosis, not metagenesis.
Option D: This refers to characteristics unrelated to metagenesis.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B.
Which of the following statements correctly describes the presence of the notochord in Urochordata and Cephalochordata?- a)In Urochordata, the notochord is present throughout the life and extends from head to tail, while in Cephalochordata, it is present only in the larval tail.
- b)In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
- c)In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail.
- d)In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord extends from head to tail and is persistent throughout their life.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements correctly describes the presence of the notochord in Urochordata and Cephalochordata?
a)
In Urochordata, the notochord is present throughout the life and extends from head to tail, while in Cephalochordata, it is present only in the larval tail.
b)
In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
c)
In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail.
d)
In both Urochordata and Cephalochordata, the notochord extends from head to tail and is persistent throughout their life.

|
Bs Academy answered |
In Urochordata, the notochord is present only in the larval tail, while in Cephalochordata, it extends from head to tail region and is persistent throughout their life.
Read the following statements:
(a) Metagenesis is observed in Helminths.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms.
Options:- a)(a), (d) and (e) are correct
- b)(b), (c) and (e) are correct
- c)(c), (d) and (e) are correct
- d)(a), (b) and (c) are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
(a) Metagenesis is observed in Helminths.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms.
Options:
a)
(a), (d) and (e) are correct
b)
(b), (c) and (e) are correct
c)
(c), (d) and (e) are correct
d)
(a), (b) and (c) are correct

|
EduRev NEET answered |
(a) Metagenesis is observed in Helminths: Incorrect. Metagenesis refers to the alternation of generations between asexual and sexual phases, observed in cnidarians, not in helminths.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals: Correct. Echinoderms have three germ layers (triploblastic) and a true coelom.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization: Correct. Roundworms (nematodes) have an organ-system level of organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion: Incorrect. Comb plates (ctenes) in ctenophores are used for locomotion, not digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms: Correct. The water vascular system is a unique feature of echinoderms.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B.
(b) Echinoderms are triploblastic and coelomate animals: Correct. Echinoderms have three germ layers (triploblastic) and a true coelom.
(c) Round worms have organ-system level of body organization: Correct. Roundworms (nematodes) have an organ-system level of organization.
(d) Comb plates present in ctenophores help in digestion: Incorrect. Comb plates (ctenes) in ctenophores are used for locomotion, not digestion.
(e) Water vascular system is characteristic of Echinoderms: Correct. The water vascular system is a unique feature of echinoderms.
Thus, the correct answer is Option B.
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of vertebrates?- a)Bilateral symmetry
- b)Well-developed nervous system
- c)Endoskeleton
- d)Segmented body
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a characteristic feature of vertebrates?
a)
Bilateral symmetry
b)
Well-developed nervous system
c)
Endoskeleton
d)
Segmented body
|
|
Ijeoma Nwosu answered |
The correct answer is option D: Segmented body.
Explanation:
Vertebrates are a group of animals that possess a backbone or spine. They are characterized by several distinct features that set them apart from other animals. Let's discuss the characteristics of vertebrates and why a segmented body is not one of them.
1. Bilateral symmetry:
Vertebrates exhibit bilateral symmetry, which means their bodies can be divided into two similar halves along a vertical plane. This symmetry allows for efficient movement and organization of body structures.
2. Well-developed nervous system:
Vertebrates have a highly developed nervous system, including a brain and a spinal cord. This complex nervous system enables them to process information, respond to stimuli, and exhibit complex behaviors.
3. Endoskeleton:
One of the defining features of vertebrates is their possession of an endoskeleton. An endoskeleton is an internal framework of bones or cartilage that provides support, protection, and attachment points for muscles. This internal skeleton allows for greater size, mobility, and protection compared to animals with exoskeletons or no skeleton at all.
4. Segmented body:
Unlike invertebrates, vertebrates do not typically possess a segmented body. Segmentation refers to the division of an organism's body into repetitive segments or units. While some invertebrates, such as arthropods, exhibit segmentation, vertebrates have a more integrated body structure without distinct segments.
In conclusion, the characteristic feature of vertebrates that is not present in the given options is a segmented body. Vertebrates have bilateral symmetry, a well-developed nervous system, and an endoskeleton.
Explanation:
Vertebrates are a group of animals that possess a backbone or spine. They are characterized by several distinct features that set them apart from other animals. Let's discuss the characteristics of vertebrates and why a segmented body is not one of them.
1. Bilateral symmetry:
Vertebrates exhibit bilateral symmetry, which means their bodies can be divided into two similar halves along a vertical plane. This symmetry allows for efficient movement and organization of body structures.
2. Well-developed nervous system:
Vertebrates have a highly developed nervous system, including a brain and a spinal cord. This complex nervous system enables them to process information, respond to stimuli, and exhibit complex behaviors.
3. Endoskeleton:
One of the defining features of vertebrates is their possession of an endoskeleton. An endoskeleton is an internal framework of bones or cartilage that provides support, protection, and attachment points for muscles. This internal skeleton allows for greater size, mobility, and protection compared to animals with exoskeletons or no skeleton at all.
4. Segmented body:
Unlike invertebrates, vertebrates do not typically possess a segmented body. Segmentation refers to the division of an organism's body into repetitive segments or units. While some invertebrates, such as arthropods, exhibit segmentation, vertebrates have a more integrated body structure without distinct segments.
In conclusion, the characteristic feature of vertebrates that is not present in the given options is a segmented body. Vertebrates have bilateral symmetry, a well-developed nervous system, and an endoskeleton.
Mark the incorrect statement:- a)Radial symmetry is advantageous to sedentary mode of life
- b)Notochord is mesodermal in origin placed between dorsal hollow nerve cord and alimentary canal in some animals
- c)Pseudocoel (false coelom) derived from blastocoel of the embryo and is bounded by ectoderm and mesoderm
- d)Cephalization is the concentration of sense organs, nervous tissue (brain), and food capturing organs at the anterior end
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
Radial symmetry is advantageous to sedentary mode of life
b)
Notochord is mesodermal in origin placed between dorsal hollow nerve cord and alimentary canal in some animals
c)
Pseudocoel (false coelom) derived from blastocoel of the embryo and is bounded by ectoderm and mesoderm
d)
Cephalization is the concentration of sense organs, nervous tissue (brain), and food capturing organs at the anterior end
|
|
Arnav Unni answered |
Incorrect Statement Explanation:
Explanation of Option C:
- Pseudocoel (false coelom) is not derived from the blastocoel of the embryo.
- It is actually derived from the blastocoel of the embryo in some animals.
- The pseudocoel is a fluid-filled body cavity that is not completely lined by mesoderm.
- It is found in organisms like roundworms (nematodes) and rotifers.
- The true coelom, on the other hand, is derived from mesoderm and is completely lined by mesoderm.
Therefore, option C is the incorrect statement as it misrepresents the origin and structure of the pseudocoel in certain organisms.
Explanation of Option C:
- Pseudocoel (false coelom) is not derived from the blastocoel of the embryo.
- It is actually derived from the blastocoel of the embryo in some animals.
- The pseudocoel is a fluid-filled body cavity that is not completely lined by mesoderm.
- It is found in organisms like roundworms (nematodes) and rotifers.
- The true coelom, on the other hand, is derived from mesoderm and is completely lined by mesoderm.
Therefore, option C is the incorrect statement as it misrepresents the origin and structure of the pseudocoel in certain organisms.
Which of the following are correct?
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
- a)(iv) and (v) are correct
- b)(i), (ii), (iii) ,(iv) and (v) are correct
- c)(i), (ii) and (v) are correct
- d)(iii) and (v) are correct
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are correct?
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
(i)Diploblastic:Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii)Triploblastic:Platyheliminthes to Chorodates
(iii)Acoelomate:Poriferans,Coelenterates,Platyhelminthes
(iv)Pseudocoelomate:Aschelminthes /Roundworms
(v)Eucoelomate:Annelids to Chordates
a)
(iv) and (v) are correct
b)
(i), (ii), (iii) ,(iv) and (v) are correct
c)
(i), (ii) and (v) are correct
d)
(iii) and (v) are correct
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
(i) Diploblastic - Poriferans, Coelenterates
(ii) Triploblastic - Platyhelminthes to Chordates
(iii) Acoelomate - Poriferans, Coelenterates, Platyhelminthes
(iv) Pseudocoelomate - Aschelminthes/Roundworms
(v) Eucoelomate - Annelids to Chordates
So, the correct answer is '(i), (ii), (iii), (iv) and (v)'.
Match the following columns and select the correct option:
Column I Column II
(a) Aptenodytes (i) Flying fox
(b) Pteropus (ii) Angel fish
(c) Pterophyllum (iii) Lamprey
(d) Petromyzon (iv) Penguin
- a)a-(iii), b-(iv),c-(ii), d-(i)
- b)a-(iii), b-(iv),c-(i),d-(ii)
- c)a-(iv), b-(i), c-(ii), d-(iii)
- d)a-(ii),b-(i), c-(iv), d-(iii)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the following columns and select the correct option:
Column I Column II
(a) Aptenodytes (i) Flying fox
(b) Pteropus (ii) Angel fish
(c) Pterophyllum (iii) Lamprey
(d) Petromyzon (iv) Penguin
Column I Column II
(a) Aptenodytes (i) Flying fox
(b) Pteropus (ii) Angel fish
(c) Pterophyllum (iii) Lamprey
(d) Petromyzon (iv) Penguin
a)
a-(iii), b-(iv),c-(ii), d-(i)
b)
a-(iii), b-(iv),c-(i),d-(ii)
c)
a-(iv), b-(i), c-(ii), d-(iii)
d)
a-(ii),b-(i), c-(iv), d-(iii)

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Aptenodytes is a genus of penguins, so it matches with (iv) Penguin.
Pteropus refers to a genus of flying foxes, so it matches with (i) Flying fox.
Pterophyllum is a genus of angelfish, so it matches with (ii) Angel fish.
Petromyzon is a genus of lampreys, so it matches with (iii) Lamprey.
Thus, the correct option is Option C: (iv), (i), (ii), (iii).
Pteropus refers to a genus of flying foxes, so it matches with (i) Flying fox.
Pterophyllum is a genus of angelfish, so it matches with (ii) Angel fish.
Petromyzon is a genus of lampreys, so it matches with (iii) Lamprey.
Thus, the correct option is Option C: (iv), (i), (ii), (iii).
Which phylum includes starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers?- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Mollusca
- c)Phylum Echinodermata
- d)Phylum Porifera
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum includes starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers?
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Mollusca
c)
Phylum Echinodermata
d)
Phylum Porifera
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Starfish, sea urchins, and sea cucumbers belong to Phylum Echinodermata. Echinoderms have a spiny skin and exhibit a radial symmetry in their body plan. They also possess a water vascular system, which aids in locomotion, gas exchange, and capturing food particles.
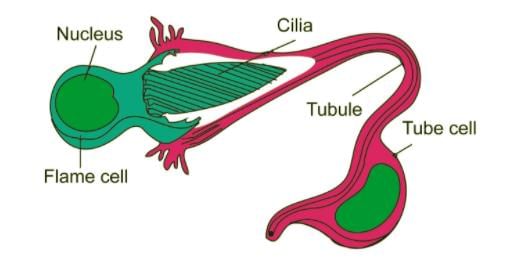
What is the term for specialized cells in flatworms that assist in osmoregulation and excretion?- a)Flame cells
- b)Cilia
- c)Glandular cells
- d)Nephrocytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the term for specialized cells in flatworms that assist in osmoregulation and excretion?
a)
Flame cells
b)
Cilia
c)
Glandular cells
d)
Nephrocytes

|
Stepway Academy answered |
Flame cells are specialized cells in flatworms that help in osmoregulation and excretion by regulating the balance of fluids and salts in their bodies.

Which phylum includes organisms with a foot, mantle, and radula?- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Mollusca
- c)Phylum Echinodermata
- d)Phylum Cnidaria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum includes organisms with a foot, mantle, and radula?
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Mollusca
c)
Phylum Echinodermata
d)
Phylum Cnidaria
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phylum Mollusca includes organisms with a foot, mantle, and radula. The foot is a muscular structure used for locomotion, the mantle is a fold of tissue that secretes the shell (if present), and the radula is a specialized feeding structure used for scraping or drilling food. Examples of mollusks include snails, clams, and squids.
Read the following statements:
(i) True coelom is a body cavity which arises as a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm.
(ii) Digestive cavity is found in acoelomates, pseudocoelomates as well as coelomates.
(iii) The body cavity of arthropods and non-cephalopod molluscs is called haemocoel.
(iv) Aschelminthes possess true body cavity.
(v) There is no cavity between the body wall and gut in Echinoderms.
Which of the statements are correct?- a)(i), (iii)
- b)(i), (ii), (iii)
- c)(iv), (v)
- d)(i), (iv), (v)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
(i) True coelom is a body cavity which arises as a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm.
(ii) Digestive cavity is found in acoelomates, pseudocoelomates as well as coelomates.
(iii) The body cavity of arthropods and non-cephalopod molluscs is called haemocoel.
(iv) Aschelminthes possess true body cavity.
(v) There is no cavity between the body wall and gut in Echinoderms.
Which of the statements are correct?
a)
(i), (iii)
b)
(i), (ii), (iii)
c)
(iv), (v)
d)
(i), (iv), (v)
|
|
Nandini Mukherjee answered |
Correct Statements:
- (i) True coelom is a body cavity which arises as a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm.
- (iii) The body cavity of arthropods and non-cephalopod molluscs is called haemocoel.
Explanation:
- Statement (i): True coelom is indeed a body cavity that develops from a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm. It is lined by mesoderm and provides space for organs to develop and move independently within the body.
- Statement (iii): Haemocoel is a body cavity found in arthropods and non-cephalopod molluscs. It is a spacious cavity that accommodates blood and surrounds the organs.
Incorrect Statements:
- (ii) Digestive cavity is found in acoelomates, pseudocoelomates as well as coelomates - This statement is incorrect as acoelomates lack a body cavity, pseudocoelomates have a pseudocoelom, and coelomates have a true coelom.
- (iv) Aschelminthes possess true body cavity - Aschelminthes are pseudocoelomates, not possessing a true coelom.
- (v) There is no cavity between the body wall and gut in Echinoderms - Echinoderms actually possess a water vascular system instead of a body cavity.
Therefore, the correct statements are (i) and (iii), making option (a) the correct choice.
- (i) True coelom is a body cavity which arises as a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm.
- (iii) The body cavity of arthropods and non-cephalopod molluscs is called haemocoel.
Explanation:
- Statement (i): True coelom is indeed a body cavity that develops from a cavity in the embryonic mesoderm. It is lined by mesoderm and provides space for organs to develop and move independently within the body.
- Statement (iii): Haemocoel is a body cavity found in arthropods and non-cephalopod molluscs. It is a spacious cavity that accommodates blood and surrounds the organs.
Incorrect Statements:
- (ii) Digestive cavity is found in acoelomates, pseudocoelomates as well as coelomates - This statement is incorrect as acoelomates lack a body cavity, pseudocoelomates have a pseudocoelom, and coelomates have a true coelom.
- (iv) Aschelminthes possess true body cavity - Aschelminthes are pseudocoelomates, not possessing a true coelom.
- (v) There is no cavity between the body wall and gut in Echinoderms - Echinoderms actually possess a water vascular system instead of a body cavity.
Therefore, the correct statements are (i) and (iii), making option (a) the correct choice.
Which class of vertebrates includes animals that are capable of flight?- a)Reptilia
- b)Aves
- c)Amphibia
- d)Mammalia
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which class of vertebrates includes animals that are capable of flight?
a)
Reptilia
b)
Aves
c)
Amphibia
d)
Mammalia
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The class Aves includes birds, which are the only vertebrates capable of true flight. Birds have adaptations such as wings, feathers, and lightweight skeletons that enable them to fly.
Which phylum exhibits a water vascular system used for locomotion and feeding?- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Mollusca
- c)Phylum Echinodermata
- d)Phylum Chordata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum exhibits a water vascular system used for locomotion and feeding?
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Mollusca
c)
Phylum Echinodermata
d)
Phylum Chordata
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phylum Echinodermata possesses a water vascular system, a network of fluid-filled canals and tube feet. This system enables echinoderms to move, capture prey, and exchange gases. The water vascular system is unique to echinoderms and is not found in other phyla like Arthropoda or Mollusca.
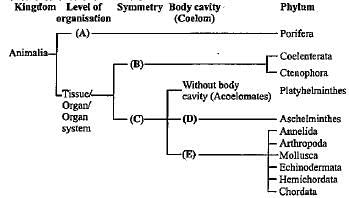
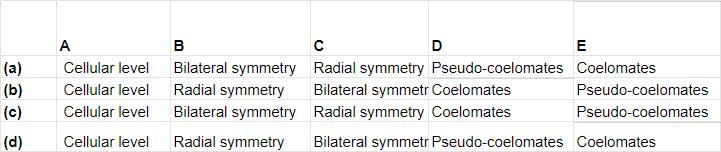
Study carefully the given flow chart and fill in the blanks (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Study carefully the given flow chart and fill in the blanks (A), (B), (C), (D) and (E).



a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
(A) Cellular level
(B) Radial symmetry
(C) Bilateral symmetry
(D) Pseudocoelomates
(E) Coelomates
(B) Radial symmetry
(C) Bilateral symmetry
(D) Pseudocoelomates
(E) Coelomates
Which class of vertebrates includes animals with a diaphragm for respiration?- a)Mammalia
- b)Aves
- c)Reptilia
- d)Amphibia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which class of vertebrates includes animals with a diaphragm for respiration?
a)
Mammalia
b)
Aves
c)
Reptilia
d)
Amphibia
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Mammalia is the class of vertebrates that possess a diaphragm for respiration. The diaphragm is a sheet of muscle that aids in breathing by expanding and contracting the chest cavity.
Which of the following phyla is known for their ability to regenerate lost body parts?- a)Phylum Cnidaria
- b)Phylum Ctenophora
- c)Phylum Platyhelminthes
- d)Phylum Mollusca
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following phyla is known for their ability to regenerate lost body parts?
a)
Phylum Cnidaria
b)
Phylum Ctenophora
c)
Phylum Platyhelminthes
d)
Phylum Mollusca
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phylum Platyhelminthes, or flatworms, have remarkable regenerative abilities and can regenerate lost body parts, such as their heads or tails.
Which subphylum of Chordata includes the largest number of species?- a)Urochordata
- b)Cephalochordata
- c)Vertebrata
- d)Hemichordata
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which subphylum of Chordata includes the largest number of species?
a)
Urochordata
b)
Cephalochordata
c)
Vertebrata
d)
Hemichordata
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The subphylum Vertebrata includes the largest number of species among the Chordates. It comprises all the vertebrate animals, including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals.
Which phylum includes segmented worms, such as earthworms and leeches?- a)Phylum Platyhelminthes
- b)Phylum Aschelminthes
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Mollusca
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum includes segmented worms, such as earthworms and leeches?
a)
Phylum Platyhelminthes
b)
Phylum Aschelminthes
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Mollusca
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Annelida is the phylum that includes segmented worms. Earthworms and leeches are examples of annelids.
The exoskeleton of arthropods is primarily made up of:- a)Chitin
- b)Calcium carbonate
- c)Collagen
- d)Silica
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The exoskeleton of arthropods is primarily made up of:
a)
Chitin
b)
Calcium carbonate
c)
Collagen
d)
Silica
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The exoskeleton of arthropods, such as insects and crustaceans, is primarily composed of a tough polysaccharide called chitin. Chitin provides rigidity and protection to the arthropod's body while allowing for flexibility at the joints.
Which class of vertebrates includes animals with a three-chambered heart?- a)Mammalia
- b)Aves
- c)Reptilia
- d)Amphibia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which class of vertebrates includes animals with a three-chambered heart?
a)
Mammalia
b)
Aves
c)
Reptilia
d)
Amphibia
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Amphibia is the class of vertebrates that possesses a three-chambered heart. This type of heart allows for a partial separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood but is less efficient than the four-chambered heart found in birds and mammals.
Which phylum includes organisms that have a pseudocoelom, a fluid-filled body cavity?- a)Phylum Platyhelminthes
- b)Phylum Aschelminthes
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Mollusca
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum includes organisms that have a pseudocoelom, a fluid-filled body cavity?
a)
Phylum Platyhelminthes
b)
Phylum Aschelminthes
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Mollusca
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Aschelminthes, or roundworms, have a pseudocoelom, which is a fluid-filled body cavity that partially surrounds the internal organs.
Which phylum is characterized by jointed appendages and a segmented body?- a)Phylum Arthropoda
- b)Phylum Mollusca
- c)Phylum Echinodermata
- d)Phylum Chordata
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum is characterized by jointed appendages and a segmented body?
a)
Phylum Arthropoda
b)
Phylum Mollusca
c)
Phylum Echinodermata
d)
Phylum Chordata
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phylum Arthropoda is characterized by jointed appendages and a segmented body. The jointed appendages allow for a wide range of movements, and the segmented body provides flexibility. Examples of arthropods include insects, spiders, and crustaceans.
Which phylum includes organisms that exhibit a high degree of cephalization and possess a centralized nervous system?- a)Phylum Platyhelminthes
- b)Phylum Aschelminthes
- c)Phylum Annelida
- d)Phylum Mollusca
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which phylum includes organisms that exhibit a high degree of cephalization and possess a centralized nervous system?
a)
Phylum Platyhelminthes
b)
Phylum Aschelminthes
c)
Phylum Annelida
d)
Phylum Mollusca
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Platyhelminthes, or flatworms, exhibit a high degree of cephalization and possess a centralized nervous system. This allows them to respond to stimuli and exhibit more complex behaviors.
Which class of vertebrates includes animals that are ectothermic?- a)Mammalia
- b)Aves
- c)Reptilia
- d)Amphibia
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which class of vertebrates includes animals that are ectothermic?
a)
Mammalia
b)
Aves
c)
Reptilia
d)
Amphibia
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Reptilia is the class of vertebrates that includes animals that are ectothermic, meaning their body temperature is primarily determined by the external environment. Mammals and birds, on the other hand, are endothermic and can regulate their body temperature internally.
Chapter doubts & questions for Animal Kingdom - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Animal Kingdom - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









