All Exams >
JAMB >
Biology for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Internal Structure of Flowering Plant for JAMB Exam
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
- a)Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
- b)Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
- c)Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
- d)Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements and select the correct option.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
Statement 1 : Anatomically, all the tissues present on the inner side of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele.
Statement 2 : Eustele is the stele in which vascular bundles are arranged in the form of a ring as present in dicot stems.
a)
Statement 1 is correct but statement 2 is incorrect
b)
Both statements 1 and 2 are correct
c)
Statement 1 is incorrect but statement 2 is correct
d)
Both statements 1 and 2 are incorrect
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
The term stele was coined by Van Tiegham and Dauliot (1886). It is the axial portion of plant axis. Anatomically, all the tissues on the innerside of endodermis such as pericyde, vascular bundles and pith constitute the stele. Eustele is the type of stele in which a ring of vascular bundles is present around the central pith and inner to the pericyde e.g., dicot stem. Stele containing irregularly scattered vascular bundles is called atactostele, e.g., monocot stem. Pteridophytes are the first plants possenssing stele.
Study the following statements regarding the anatomy of Isobllateral leal.
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?- a)(i) and (ii)
- b)(ii) and (iii)
- c)(ii) and (iv)
- d)All are correct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Study the following statements regarding the anatomy of Isobllateral leal.
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?
(i) Stomata are equally distributed on both the surfaces.
(ii) Certain adaxlal epidermal cells are modified Into bulllform cells in grasses.
(iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
(iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
Which of the above statements are correct?
a)
(i) and (ii)
b)
(ii) and (iii)
c)
(ii) and (iv)
d)
All are correct
|
|
Rohit Das answered |
Understanding Isobilateral Leaf Anatomy
Isobilateral leaves possess a symmetrical structure on both surfaces, leading to specific anatomical features. Let’s evaluate the statements provided about their anatomy:
Statement Analysis
- (i) Stomata are equally distributed on both surfaces.
This is correct. In isobilateral leaves, the stomata are typically found on both the adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) surfaces, promoting efficient gas exchange.
- (ii) Certain adaxial epidermal cells are modified into bulliform cells in grasses.
This statement is accurate. Bulliform cells are specialized cells in the adaxial epidermis of grasses that help in the regulation of leaf folding and unfolding, aiding in water conservation.
- (iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
This statement is incorrect. In isobilateral leaves, the vascular bundles are generally arranged in a collateral manner, not radial. Radial vascular bundles are more common in roots.
- (iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
This statement is also incorrect. In most leaves, including isobilateral types, the phloem is typically located abaxially, while xylem is adaxial.
Conclusion
Given the analysis above, the correct statements are (i) and (ii). Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (i and ii). This understanding is essential for NEET aspirants studying plant anatomy and physiology.
Isobilateral leaves possess a symmetrical structure on both surfaces, leading to specific anatomical features. Let’s evaluate the statements provided about their anatomy:
Statement Analysis
- (i) Stomata are equally distributed on both surfaces.
This is correct. In isobilateral leaves, the stomata are typically found on both the adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) surfaces, promoting efficient gas exchange.
- (ii) Certain adaxial epidermal cells are modified into bulliform cells in grasses.
This statement is accurate. Bulliform cells are specialized cells in the adaxial epidermis of grasses that help in the regulation of leaf folding and unfolding, aiding in water conservation.
- (iii) The vascular bundles are radial.
This statement is incorrect. In isobilateral leaves, the vascular bundles are generally arranged in a collateral manner, not radial. Radial vascular bundles are more common in roots.
- (iv) Phloem is adaxially placed.
This statement is also incorrect. In most leaves, including isobilateral types, the phloem is typically located abaxially, while xylem is adaxial.
Conclusion
Given the analysis above, the correct statements are (i) and (ii). Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' (i and ii). This understanding is essential for NEET aspirants studying plant anatomy and physiology.
Which of the following conditions of xylem is present in both monocot and dicot stems?- a)Endarch
- b)Polyarch
- c)Mesarch
- d)Exarch
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following conditions of xylem is present in both monocot and dicot stems?
a)
Endarch
b)
Polyarch
c)
Mesarch
d)
Exarch
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Based on position of protoxylem in relation to metaxylem, the xylem may be exarch/centripetal, endarch/centrifugal, mesarch and centerarch. In endarch condition, protoxylem lies on the inner side of metaxylem e.g., dicot and monocot stems.
Well develped pith is found in- a)monocot root and monocot stem
- b)monocot stem and dicot root
- c)monocot root and dicot stem
- d)dicot root and dicot stem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Well develped pith is found in
a)
monocot root and monocot stem
b)
monocot stem and dicot root
c)
monocot root and dicot stem
d)
dicot root and dicot stem
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
In a dicot stem, a well developed pith (made of parenchymatous or occasionally sclerenchymatous cells) is present whereas in a monocot stem, pith is absent. In a dicot root, pith is poorly developed whereas in a monocot root, a well developed pith is present.
Casparian strips are the bands of thickenings present on _____ walls of endodermis.- a)radial
- b)tangential
- c)central
- d)both (a) and (b)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Casparian strips are the bands of thickenings present on _____ walls of endodermis.
a)
radial
b)
tangential
c)
central
d)
both (a) and (b)
|
|
Priya Menon answered |
Endodermis is the innermost layer of cortex that consistws of tightly packed barrel shaped cells. It is called starch sheath in case of dicot stems. Radial and and tangential walls of endodermal cells possess thickenings of lignin, suberin and cutin in the form of strips or bands, which are known as casparian bands or casparian strips.
Select the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.- a)Phloem parenchyma is absent.
- b)Vascular bundles are scattered, conjoint, collateral and closed.
- c)Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath.
- d)Ground tissue is differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericyde and pith
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
a)
Phloem parenchyma is absent.
b)
Vascular bundles are scattered, conjoint, collateral and closed.
c)
Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath.
d)
Ground tissue is differentiated into cortex, endodermis, pericyde and pith
|
|
Meghana Datta answered |
Incorrect Statement Explanation
The anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem has distinct characteristics that differentiate it from dicotyledonous stems. The statement in option 'D' is incorrect because of the following reasons:
Ground Tissue Composition
- In monocots, the ground tissue does not differentiate into distinct regions like cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith.
- Instead, the ground tissue is generally homogeneous and lacks the specialized structures found in dicots.
Vascular Bundle Arrangement
- Monocots have scattered vascular bundles throughout the stem, which is a key feature.
- Each vascular bundle is composed of xylem and phloem, arranged in a conjoint, collateral, and closed manner.
Bundle Sheath Presence
- Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath, which is a layer of cells that can help in the transport and support of the vascular tissue.
Absence of Phloem Parenchyma
- In monocots, phloem parenchyma is typically absent, which is another distinguishing feature when compared to dicots.
In summary, the ground tissue in monocot stems lacks the differentiation into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith, making option 'D' the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
The anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem has distinct characteristics that differentiate it from dicotyledonous stems. The statement in option 'D' is incorrect because of the following reasons:
Ground Tissue Composition
- In monocots, the ground tissue does not differentiate into distinct regions like cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith.
- Instead, the ground tissue is generally homogeneous and lacks the specialized structures found in dicots.
Vascular Bundle Arrangement
- Monocots have scattered vascular bundles throughout the stem, which is a key feature.
- Each vascular bundle is composed of xylem and phloem, arranged in a conjoint, collateral, and closed manner.
Bundle Sheath Presence
- Each vascular bundle is surrounded by a bundle sheath, which is a layer of cells that can help in the transport and support of the vascular tissue.
Absence of Phloem Parenchyma
- In monocots, phloem parenchyma is typically absent, which is another distinguishing feature when compared to dicots.
In summary, the ground tissue in monocot stems lacks the differentiation into cortex, endodermis, pericycle, and pith, making option 'D' the incorrect statement regarding the anatomy of a typical monocotyledonous stem.
Which plant part possesses polyarch condition of vascular bundles with a well developed pith?- a)Dicot root
- b)Monocot root
- c)Dicot stem
- d)Monocot stem
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which plant part possesses polyarch condition of vascular bundles with a well developed pith?
a)
Dicot root
b)
Monocot root
c)
Dicot stem
d)
Monocot stem
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
vascular bundles in monocot roots are radial, polyarch and exarch. Large number (more than 6) of xylem and phloem groups alternate with each other. A well devloped pith is present in monocot root.
Hypodermis is _______ in sunflower stem and _______in maize stem.- a)parenchymatous, collenchymatous
- b)collenchymatous, sderenchymatous
- c)sderenchymatous, collenchymatous
- d)sderenchymatous, sderenchymatous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hypodermis is _______ in sunflower stem and _______in maize stem.
a)
parenchymatous, collenchymatous
b)
collenchymatous, sderenchymatous
c)
sderenchymatous, collenchymatous
d)
sderenchymatous, sderenchymatous
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
In a dicot stem (e.g., In sunflower), hypodermis is made up of collenchyma, which may be green. In monocot stem (e.g., maize), hypodermis is formed of non green sderenchyma tissue.
Bundle sheath extensions in a dicot leaf and in a monocot leaf are ________ and ________ respectively.- a)parenchymatous, collenchymatous
- b)parenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
- c)sclerechymatous, parenchymatous
- d)collenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bundle sheath extensions in a dicot leaf and in a monocot leaf are ________ and ________ respectively.
a)
parenchymatous, collenchymatous
b)
parenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
c)
sclerechymatous, parenchymatous
d)
collenchymatous, sclerenchymatous
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In dicot leaf, bundle sheath is generally single layered and formed of colourless cells. Bundle sheath extensions are parenchymatous. In monocot leaf, bundle sheath may be single or double layered and the cells generally possess chloroplasts. Bundle sheath extensions are sderenchymatous.
Read the following statements.
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eusteleAbove given features describe which of the following plant parts?- a)Monocot stem
- b)Monocot
- c)Dicot stem
- d)Dicot root
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Read the following statements.
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eustele
(i) Multicellular epidermal hair
(ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
(iii) Pith present
(iv) Vascular bundles present in a ring i.e. eustele
Above given features describe which of the following plant parts?
a)
Monocot stem
b)
Monocot
c)
Dicot stem
d)
Dicot root
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
The epidermis of dicot stem bears several unbranched multicellular hair or trichomes. The hypodermis is made of 3−4 layered sub-epidermal collenchyma tissue. Vascular strand is in the form of eustele or a ring of vascular bundles present around the central pith and inner to the pericycle.
Select the correct pair out of the follwing.- a)Hypostomatic leaf - Dicots
- b)Epistomatic leaf - Monocots
- c)Amphistomatic leaf - Free-floating hydrophytes
- d)Presence of sunken stomata in leaf - Submerged hydrophytes
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct pair out of the follwing.
a)
Hypostomatic leaf - Dicots
b)
Epistomatic leaf - Monocots
c)
Amphistomatic leaf - Free-floating hydrophytes
d)
Presence of sunken stomata in leaf - Submerged hydrophytes
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In dicot leaves, stomata are generally present on lower epiderm is (hypostomatic), whereas in monocot leaves, they are present on both the surfaces (amphistomatic). In free -floating hydrophytes, stomata are restricted to upper epidermis (epistomatic) whereas in submerged hydrophytes, stomata are either non-functional or ab sent. In algae and fungi, stomata are totally absent. Stomata are sunken (deepseated) in case of xerophytes.
In a dorsiventral leaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem is respectively on the______ surfaces.- a)adaxial and abaxial
- b)adaxial and adaxial
- c)abaxial and adaxial
- d)abaxial and abaxial
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a dorsiventral leaf, location of palisade tissue and phloem is respectively on the______ surfaces.
a)
adaxial and abaxial
b)
adaxial and adaxial
c)
abaxial and adaxial
d)
abaxial and abaxial
|
|
Roshni Basak answered |
Explanation:
Dorsiventral Leaf:
A dorsiventral leaf is a type of leaf that exhibits two distinct surfaces - adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) surfaces. This type of leaf is commonly found in dicotyledonous plants.
Location of Palisade Tissue:
- The palisade tissue is typically located on the adaxial surface of the leaf.
- Palisade tissue is responsible for photosynthesis and is composed of elongated cells arranged parallel to the leaf surface to maximize light absorption.
Location of Phloem:
- The phloem, which is involved in the transport of organic compounds such as sugars, is usually located on the abaxial surface of the leaf.
- The phloem is part of the vascular tissue system in plants, along with the xylem.
Therefore, in a dorsiventral leaf, the palisade tissue is located on the adaxial surface (upper surface), while the phloem is located on the abaxial surface (lower surface). This arrangement allows for efficient photosynthesis and transport of nutrients throughout the leaf.
Dorsiventral Leaf:
A dorsiventral leaf is a type of leaf that exhibits two distinct surfaces - adaxial (upper) and abaxial (lower) surfaces. This type of leaf is commonly found in dicotyledonous plants.
Location of Palisade Tissue:
- The palisade tissue is typically located on the adaxial surface of the leaf.
- Palisade tissue is responsible for photosynthesis and is composed of elongated cells arranged parallel to the leaf surface to maximize light absorption.
Location of Phloem:
- The phloem, which is involved in the transport of organic compounds such as sugars, is usually located on the abaxial surface of the leaf.
- The phloem is part of the vascular tissue system in plants, along with the xylem.
Therefore, in a dorsiventral leaf, the palisade tissue is located on the adaxial surface (upper surface), while the phloem is located on the abaxial surface (lower surface). This arrangement allows for efficient photosynthesis and transport of nutrients throughout the leaf.
Vascular bundle is enclosed with in a well developed sderenchymatous sheath in- a)monocot stem
- b)dicot stem
- c)monocot root
- d)dicot root
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Vascular bundle is enclosed with in a well developed sderenchymatous sheath in
a)
monocot stem
b)
dicot stem
c)
monocot root
d)
dicot root
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In most monocot stems, a sclerenchymatous bundle sheath is generally present on the outside of each vascular bundle.
Select the mismatched pair- a)Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles
- b)Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem
- c)Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns
- d)Radial vascular bundles - Maize root
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the mismatched pair
a)
Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles
b)
Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem
c)
Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns
d)
Radial vascular bundles - Maize root
|
|
Aditya Yadav answered |
Explanation:
Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem:
In maize stem, the vascular bundles are arranged in a bicollateral manner, meaning there are two separate vascular cambia present in the stem that produce xylem and phloem inwards and outwards. This arrangement is unique to maize stems and helps in the efficient transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles:
Sunflower stem bundles have collateral and open vascular bundles, where the xylem and phloem are located adjacent to each other in the same vascular bundle. The structure of these bundles allows for easy exchange of substances between xylem and phloem, aiding in the growth and development of the plant.
Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns:
Ferns have concentric vascular bundles, where xylem is surrounded by phloem in a circular arrangement. This type of vascular bundle arrangement is characteristic of ferns and helps in the efficient transport of water, minerals, and organic compounds throughout the plant.
Radial vascular bundles - Maize root:
In maize roots, the vascular bundles are arranged in a radial manner, with xylem and phloem alternating around the central core. This radial arrangement allows for efficient nutrient and water uptake from the soil and transport throughout the root system.
Therefore, the mismatched pair in the given options is "Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem" as maize stems indeed have bicollateral vascular bundles.
Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem:
In maize stem, the vascular bundles are arranged in a bicollateral manner, meaning there are two separate vascular cambia present in the stem that produce xylem and phloem inwards and outwards. This arrangement is unique to maize stems and helps in the efficient transport of water, nutrients, and sugars throughout the plant.
Collateral and open vascular - Sunflower stem bundles:
Sunflower stem bundles have collateral and open vascular bundles, where the xylem and phloem are located adjacent to each other in the same vascular bundle. The structure of these bundles allows for easy exchange of substances between xylem and phloem, aiding in the growth and development of the plant.
Concentric vascular bundles - Ferns:
Ferns have concentric vascular bundles, where xylem is surrounded by phloem in a circular arrangement. This type of vascular bundle arrangement is characteristic of ferns and helps in the efficient transport of water, minerals, and organic compounds throughout the plant.
Radial vascular bundles - Maize root:
In maize roots, the vascular bundles are arranged in a radial manner, with xylem and phloem alternating around the central core. This radial arrangement allows for efficient nutrient and water uptake from the soil and transport throughout the root system.
Therefore, the mismatched pair in the given options is "Bicollateral vascular bundles - Maize stem" as maize stems indeed have bicollateral vascular bundles.
Where is the phloem usually located in conjoint vascular bundles found in stems and leaves?- a)Along different radii
- b)Within cambium
- c)Inner side of xylem
- d)Outer side of xylem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Where is the phloem usually located in conjoint vascular bundles found in stems and leaves?
a)
Along different radii
b)
Within cambium
c)
Inner side of xylem
d)
Outer side of xylem

|
Ambition Institute answered |
In conjoint vascular bundles, which are common in stems and leaves, the phloem is typically located on the outer side of the xylem. This arrangement ensures efficient transport of food (sugars produced in the leaves) through the phloem, which is situated closer to the outer part of the stem or leaf where sugars are needed for growth or storage.
Which of the following complex tissues provides mechanical support to the plant?- a)Epidermis
- b)Parenchyma
- c)Collenchyma
- d)Phloem
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following complex tissues provides mechanical support to the plant?
a)
Epidermis
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Phloem
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Collenchyma is a complex tissue that provides mechanical support to the plant. Its cells have thickened cell walls, mainly at the corners, which allow flexibility and support in young and growing plant parts. Collenchyma cells are often found in leaf stalks, petioles, and young stems.
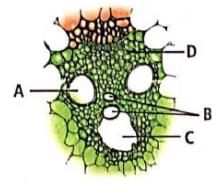
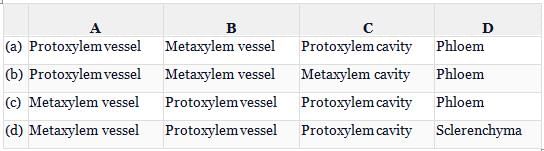
Refer the given figure which represents a section of vascular bundle as seen in T.S. of a monocot stem and select the option that correctly labels A, B, C and D.
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Refer the given figure which represents a section of vascular bundle as seen in T.S. of a monocot stem and select the option that correctly labels A, B, C and D.



a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
A monocot stem lacks secondary growth. The vascular bundles are oval or rounded in outline. They contain both phloem and xylem. Phloem lies towards the outside and the xylem on the inner side. Cambium is absent as the whole procambium is consumed in the formation of vascular tissues. Xylem is in the form of letter Y. It is endarch, i.e., protoxylem lies towards the centre of the stem. Xylem is made up of vessels, tracheids, xylem parenchyma and a few xylem fibres. Metandem generally consists of two large oval or rounded vessels lying at the upper two angles of xylem. Protoxylem cavity is present at the end of protoxylem vessels.
Stele includes- a)pericycle
- b)vascular bundles
- c)pith
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Stele includes
a)
pericycle
b)
vascular bundles
c)
pith
d)
all of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Word 'stele' is taken from Greek language, which means 'pillar'. Stele consists of pericycle, vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) and pith (if present).
The complex tissue responsible for the conduction of food in plants is:- a)Xylem
- b)Epidermis
- c)Phloem
- d)Collenchyma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The complex tissue responsible for the conduction of food in plants is:
a)
Xylem
b)
Epidermis
c)
Phloem
d)
Collenchyma
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phloem is the complex tissue responsible for the conduction of food in plants. It transports organic nutrients, such as sugars and amino acids, from the leaves (source) to other parts of the plant (sinks). The phloem consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells, which work together to facilitate the movement of food substances.
The cells in sclerenchyma tissue are characterized by:- a)Large intercellular spaces
- b)Thin cell walls
- c)Lignified cell walls
- d)Lack of chloroplasts
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cells in sclerenchyma tissue are characterized by:
a)
Large intercellular spaces
b)
Thin cell walls
c)
Lignified cell walls
d)
Lack of chloroplasts
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Cells in sclerenchyma tissue have lignified cell walls, which provide rigidity and strength to the plant. These walls contain a substance called lignin, which makes them hard and impermeable to water. Due to the presence of lignin, sclerenchyma cells are dead at maturity and cannot elongate.
Complex tissue in plants is made up of:- a)Only one type of cell
- b)Two or more types of cells
- c)Only parenchyma cells
- d)Only sclerenchyma cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Complex tissue in plants is made up of:
a)
Only one type of cell
b)
Two or more types of cells
c)
Only parenchyma cells
d)
Only sclerenchyma cells
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Complex tissue in plants is composed of two or more types of cells that work together to perform specific functions. Examples of complex tissues include xylem, phloem, and epidermis. These tissues have different cell types with specialized functions, allowing plants to transport substances, provide support, and protect against water loss.
Which of the following is an example of complex tissue in plants?- a)Xylem
- b)Parenchyma
- c)Epidermis
- d)Phloem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of complex tissue in plants?
a)
Xylem
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Epidermis
d)
Phloem
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Phloem is an example of complex tissue in plants. It is involved in the transport of food substances, such as sugars, from photosynthetic tissues to other parts of the plant. Phloem consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells, which work together to maintain the flow of organic nutrients throughout the plant.
Which of the following is a dead tissue in plants?- a)Parenchyma
- b)Collenchyma
- c)Phloem
- d)Xylem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is a dead tissue in plants?
a)
Parenchyma
b)
Collenchyma
c)
Phloem
d)
Xylem
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Xylem is a dead tissue in plants. The cells in xylem tissue, such as vessel elements and tracheids, are dead at maturity. Their main function is to transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. The cell walls of xylem cells are reinforced with lignin, providing strength and support.
A typical monocotyledonous root is characterized by- a)usually more than six xylem bundles
- b)large and well developed pith
- c)no secondary growth
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A typical monocotyledonous root is characterized by
a)
usually more than six xylem bundles
b)
large and well developed pith
c)
no secondary growth
d)
all of these
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
There is no such distinction between a young and an old root of monocotyledonous plant. This is due to the absence of secondary growth in the monocot roots. The centre of monocot root is occupied by the pith. It consists of parenchymatous cells which may be rounded or angular. Intercellular spaces are present amongst the pith cells. The pith cells store food. Xylem and phloem bundles are numerous and are 8 or more in number. Xylem vessels are oval or rounded.
In (i) protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem lies towards centre. Such an arrangement of primary xylem is called as (ii)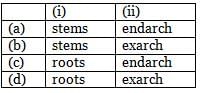
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In (i) protoxylem lies towards periphery and metaxylem lies towards centre. Such an arrangement of primary xylem is called as (ii)

a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
In exarch condition of xylem, protoxylem or the first formed xylem is present towards the periphery while metaxylem or later formed xylem is present towards the centre of the root. Such an arrangement can be seen in roots.
The supportive tissue responsible for providing mechanical strength and support to the plant is:- a)Phloem
- b)Epidermis
- c)Collenchyma
- d)Sclerenchyma
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The supportive tissue responsible for providing mechanical strength and support to the plant is:
a)
Phloem
b)
Epidermis
c)
Collenchyma
d)
Sclerenchyma
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Sclerenchyma is the supportive tissue in plants that provides mechanical strength and support. Its cells are characterized by thick, lignified secondary cell walls, which make them rigid and strong. Sclerenchyma cells are often found in mature plant parts like stems, branches, and the outer covering of seeds.
The cells in phloem tissue are responsible for:- a)Storage of food
- b)Conduction of water and minerals
- c)Conduction of food
- d)Mechanical support
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The cells in phloem tissue are responsible for:
a)
Storage of food
b)
Conduction of water and minerals
c)
Conduction of food
d)
Mechanical support
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The cells in phloem tissue are responsible for the conduction of food substances, such as sugars and amino acids, throughout the plant. The sieve tube elements form a continuous network of tubes for the efficient transport of these organic nutrients. Companion cells provide metabolic support to the sieve tube elements.
Which of the following is an example of supportive tissue in plants?- a)Xylem
- b)Parenchyma
- c)Phloem
- d)Epidermis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of supportive tissue in plants?
a)
Xylem
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Phloem
d)
Epidermis
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Xylem is a type of supportive tissue in plants. It is responsible for transporting water, minerals, and providing mechanical support to the plant. It is composed of several types of cells, including vessel elements and tracheids, which have thickened lignified cell walls that provide strength and rigidity.
What is the outermost layer of a root called?- a)Cortex
- b)Epiblema
- c)Endodermis
- d)Pericycle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the outermost layer of a root called?
a)
Cortex
b)
Epiblema
c)
Endodermis
d)
Pericycle

|
Bs Academy answered |
The outermost layer is epiblema (of dicotyledeons root). Many of the cells of epiblema protrude in the form of unicellular root hairs.
Which of the following tissues transports water and minerals in plants?- a)Collenchyma
- b)Parenchyma
- c)Phloem
- d)Xylem
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following tissues transports water and minerals in plants?
a)
Collenchyma
b)
Parenchyma
c)
Phloem
d)
Xylem
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Xylem is the tissue responsible for transporting water and minerals in plants. It consists of specialized cells called vessel elements and tracheids that are interconnected to form continuous tubes. These cells are dead at maturity and have thickened walls, providing structural support and allowing efficient water conduction.
Chapter doubts & questions for Internal Structure of Flowering Plant - Biology for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Internal Structure of Flowering Plant - Biology for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for JAMB
221 videos|172 docs|126 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









