All Exams >
JAMB >
Economics for JAMB >
All Questions
All questions of Theory of Price Determination for JAMB Exam
Deficient demand
- a)Market price is same as the equilibrium price
- b)Market price is higher than the equilibrium price
- c)Market price is lower than the equilibrium price
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deficient demand
a)
Market price is same as the equilibrium price
b)
Market price is higher than the equilibrium price
c)
Market price is lower than the equilibrium price
d)
None of these

|
Vanshika Agrawal answered |
Crrct answer is B This is so because
During excess demand- a)Market price is lower than the equilibrium price
- b)Market price is higher than the equilibrium price
- c)Market price is same as the equilibrium price
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
During excess demand
a)
Market price is lower than the equilibrium price
b)
Market price is higher than the equilibrium price
c)
Market price is same as the equilibrium price
d)
None of these
|
|
Arun Khanna answered |
Excess Demand:
Excess demand refers to the situation when aggregate demand (AD) is more than the aggregate supply (AS) corresponding to full employment level of output in the economy. It is the excess of anticipated expenditure over the value of full employment output.
Excess demand occurs when- a)Market price fall below the equilibrium price
- b)Market price rise higher than the equilibrium price
- c)Market price remains the same
- d)none
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Excess demand occurs when
a)
Market price fall below the equilibrium price
b)
Market price rise higher than the equilibrium price
c)
Market price remains the same
d)
none
|
|
Arjun Singhania answered |
Excess Demand. When at the current price level, the quantity demanded is more than quantity supplied, a situation of excess demand is said to arise in the market. Excess demand occurs at a price less than the equilibrium price.
Ring deficient demand- a)Market price remains the same
- b)Market price rise
- c)Market price falls below the equilibrium price
- d)Market price fall
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Ring deficient demand
a)
Market price remains the same
b)
Market price rise
c)
Market price falls below the equilibrium price
d)
Market price fall
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
Deficient demand refers to the situation when aggregate demand (AD) is less than the aggregate supply (AS) corresponding to full employment level of output in the economy. ... The situation of deficient demand arises when planned aggregate expenditure falls short of aggregate supply at the full employment level.
A rise in the price of the complementary good leads to- a)Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
- b)Expansion of the supply curve of the given good only
- c)Contraction of the demand for the given good
- d)Shift of the demand and supply curves of the given good
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A rise in the price of the complementary good leads to
a)
Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
b)
Expansion of the supply curve of the given good only
c)
Contraction of the demand for the given good
d)
Shift of the demand and supply curves of the given good
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
Complementary good or complement is a good with a negative cross elasticity of demand, in contrast to a substitute good. This means a good's demand is increased when the price of another good is decreased. ... When two goods are complements, they experience joint demand.
A complementary good is a good whose use is related to the use of an associated or paired good. Two goods (A and B) are complementary if using more of good A requires the use of more of good B. For example, the demand for one good (printers) generates demand for the other (ink cartridges).
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Unfavorable change in the taste for a good leads to
- A:
Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
- B:
Movement of the demand and supply curves of the given good
- C:
Shift of the demand and supply curves of the given good
- D:
Contraction of the demand for the given good
The answer is D.
Unfavorable change in the taste for a good leads to
Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
Movement of the demand and supply curves of the given good
Shift of the demand and supply curves of the given good
Contraction of the demand for the given good

|
Kusum Chugh answered |
Ans :TASTE AND PREFERENCES --~The demand for a commodity is also affected by the taste and preference of the consumer. ~The demand for a commodity will increase if consumer’s taste changes in favour of the commodity and,~Any UNFAVORABLE CHANGE in taste or PREFERENCE will REDUCE the DEMAND for the COMMODITY.
Equilibrium price may or may not change with shifts in both demand and supply curve.- a)No
- b)Only may change
- c)Yes
- d)May not change only
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Equilibrium price may or may not change with shifts in both demand and supply curve.
a)
No
b)
Only may change
c)
Yes
d)
May not change only
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Factors that can shift the demand curve for goods and services, causing a different quantity to be demanded at any given price, include changes in tastes, population, income, prices of substitute or complement goods, and expectations about future conditions and prices.
An imposition of tax on a good leads to- a)Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
- b)Shift of the supply curve of the given good only
- c)Rightward shift of the supply curve of the given good only
- d)Movement of the demand and supply curves of the given good
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An imposition of tax on a good leads to
a)
Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
b)
Shift of the supply curve of the given good only
c)
Rightward shift of the supply curve of the given good only
d)
Movement of the demand and supply curves of the given good
|
|
Priyanshu Tiwari answered |
The imposition of either type of tax has an implication on the supply and demand framework. Specifically, it causes shifts in supply and demand, which in turn lead to new levels of quantity and prices in an economy.
The factor that causes a change in supply is- a)Price of the substitute good
- b)Price of the given good
- c)Price of the inputs
- d)Price of the complementary good
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The factor that causes a change in supply is
a)
Price of the substitute good
b)
Price of the given good
c)
Price of the inputs
d)
Price of the complementary good
|
|
Priyanshu Tiwari answered |
Supply is not constant over time. It constantly increases or decreases. Whenever a change in supply occurs, the supply curve shifts left or right. There are a number of factors that cause a shift in the supply curve: input prices, number of sellers, technology, natural and social factors, and expectations
After excess demand- a)Market price rise
- b)Market price fall
- c)Market price remains the same
- d)Market price falls below the equilibrium price
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
After excess demand
a)
Market price rise
b)
Market price fall
c)
Market price remains the same
d)
Market price falls below the equilibrium price
|
|
Rajat Patel answered |
A Market Surplus occurs when there is excess supply- that is quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. ... In this situation, excess supply has exerted downward pressure on the price of the product. A Market Shortage occurs when there is excess demand- that is quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 5 - Market Equilibrium of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinationsQ _____________ is the price at which demand for a commodity is equal to its supply?- a)Secular price
- b)Equilibrium price
- c)Short run price
- d)Normal price
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
This a MCQ (Multiple Choice Question) based practice test of Chapter 5 - Market Equilibrium of Economics of Class XII (12) for the quick revision/preparation of School Board examinations
Q _____________ is the price at which demand for a commodity is equal to its supply?
a)
Secular price
b)
Equilibrium price
c)
Short run price
d)
Normal price
|
|
Sanvi Kapoor answered |
At equilibrium price quantity demanded and quantity supplied of a commodity are equal. This quantity is called the equilibrium quantity of the commodity. In practical life, the price at which the seller/firm wants to sell a commodity, its quantity supplied may be greater or lesser than its quantity demanded.
If the demand for a product increases while the supply remains constant, what will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity?- a)Price increases, quantity increases
- b)Price decreases, quantity increases
- c)Price decreases, quantity decreases
- d)Price increases, quantity remains the same
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the demand for a product increases while the supply remains constant, what will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity?
a)
Price increases, quantity increases
b)
Price decreases, quantity increases
c)
Price decreases, quantity decreases
d)
Price increases, quantity remains the same
|
|
Ikechukwu Okoro answered |
Explanation:
Increased Demand and Constant Supply:
When the demand for a product increases while the supply remains constant, it creates a situation where more consumers are willing to buy the product at the existing price.
Impact on Equilibrium Price and Quantity:
- Price Increases: With an increase in demand and constant supply, there is now a shortage in the market as more consumers are trying to purchase the product. This increased competition among buyers leads to sellers increasing the price to capitalize on the higher demand.
- Quantity Increases: As the price increases, suppliers are willing to produce more of the product to take advantage of the higher prices. This results in an increase in the quantity supplied to meet the rising demand.
Therefore, in this scenario, the equilibrium price will increase due to the imbalance between demand and supply, and the equilibrium quantity will also increase as more of the product is being supplied to meet the higher demand. This adjustment in price and quantity helps to restore equilibrium in the market.
Increased Demand and Constant Supply:
When the demand for a product increases while the supply remains constant, it creates a situation where more consumers are willing to buy the product at the existing price.
Impact on Equilibrium Price and Quantity:
- Price Increases: With an increase in demand and constant supply, there is now a shortage in the market as more consumers are trying to purchase the product. This increased competition among buyers leads to sellers increasing the price to capitalize on the higher demand.
- Quantity Increases: As the price increases, suppliers are willing to produce more of the product to take advantage of the higher prices. This results in an increase in the quantity supplied to meet the rising demand.
Therefore, in this scenario, the equilibrium price will increase due to the imbalance between demand and supply, and the equilibrium quantity will also increase as more of the product is being supplied to meet the higher demand. This adjustment in price and quantity helps to restore equilibrium in the market.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in supply for the good will- a)Price is unaffected
- b)Only quantity exchanged is affected
- c)Lower the price
- d)Raise the price
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in supply for the good will
a)
Price is unaffected
b)
Only quantity exchanged is affected
c)
Lower the price
d)
Raise the price
|
|
Om Desai answered |
A decrease in demand and an increase in supply will cause a fall in equilibrium price, but the effect on equilibrium quantity cannot be determined. ... For any quantity, consumers now place a lower value on the good, and producers are willing to accept a lower price; therefore, price will fall.
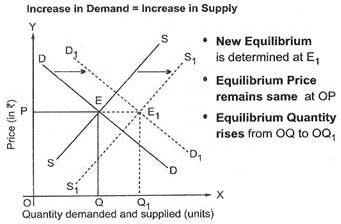
If the demand and supply for a product both increase, what will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity?- a)Price increases, quantity increases
- b)Price decreases, quantity increases
- c)Price increases, quantity remains the same
- d)Price decreases, quantity decreases
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the demand and supply for a product both increase, what will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity?
a)
Price increases, quantity increases
b)
Price decreases, quantity increases
c)
Price increases, quantity remains the same
d)
Price decreases, quantity decreases
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
If the demand and supply for a product both increase, the equilibrium price will increase, but the effect on the equilibrium quantity will depend on the relative magnitude of the changes in demand and supply. When both demand and supply increase, the equilibrium quantity will increase if the increase in demand is larger than the increase in supply. However, the equilibrium quantity may remain the same or even decrease if the increase in supply is larger than the increase in demand.
A fall in the price of the good for a seller leads to- a)Movement of the demand and supply curves of the given good
- b)Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
- c)Shift of the demand and supply curves of the given good
- d)Contraction of the supply curve of the given good only
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A fall in the price of the good for a seller leads to
a)
Movement of the demand and supply curves of the given good
b)
Shift of the demand curve of the given good only
c)
Shift of the demand and supply curves of the given good
d)
Contraction of the supply curve of the given good only
|
|
Ræjû Bhæï answered |
Garam money kal ko bataunga.
Excess demand is a situation when- a)Market demand is equal to market supply
- b)individual demand is greater than individual supply
- c)Market demand is greater than market supply
- d)Market demand is less than market supply
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Excess demand is a situation when
a)
Market demand is equal to market supply
b)
individual demand is greater than individual supply
c)
Market demand is greater than market supply
d)
Market demand is less than market supply
|
|
Poonam Reddy answered |
Explanation:
Excess demand is a situation that occurs when the market demand for a product or service exceeds the market supply. In this situation, there are more buyers willing and able to purchase a good or service than there are available units of that good or service.
Key Points:
- Excess demand occurs when the market demand exceeds the market supply.
- Market demand refers to the total quantity of a good or service that all buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
- Market supply refers to the total quantity of a good or service that all sellers are willing and able to produce and offer for sale at a given price.
- Excess demand can lead to a shortage of the product, as there are not enough units available to satisfy all the buyers.
- When there is excess demand, buyers may compete with each other to purchase the limited supply, which can drive up the price of the product.
- Excess demand is an indicator of a seller's market, where sellers have more bargaining power and can potentially increase prices.
- In order to eliminate excess demand and restore equilibrium, either the market supply needs to increase or the market demand needs to decrease.
- Excess demand can be temporary or long-term, depending on the factors influencing supply and demand for the product or service.
Excess demand is a situation that occurs when the market demand for a product or service exceeds the market supply. In this situation, there are more buyers willing and able to purchase a good or service than there are available units of that good or service.
Key Points:
- Excess demand occurs when the market demand exceeds the market supply.
- Market demand refers to the total quantity of a good or service that all buyers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
- Market supply refers to the total quantity of a good or service that all sellers are willing and able to produce and offer for sale at a given price.
- Excess demand can lead to a shortage of the product, as there are not enough units available to satisfy all the buyers.
- When there is excess demand, buyers may compete with each other to purchase the limited supply, which can drive up the price of the product.
- Excess demand is an indicator of a seller's market, where sellers have more bargaining power and can potentially increase prices.
- In order to eliminate excess demand and restore equilibrium, either the market supply needs to increase or the market demand needs to decrease.
- Excess demand can be temporary or long-term, depending on the factors influencing supply and demand for the product or service.
Deficient demand occurs when- a)Market price fall below the equilibrium price
- b)Market price rise higher than the equilibrium price
- c)Market price falls below the equilibrium price
- d)Market price remains the same
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deficient demand occurs when
a)
Market price fall below the equilibrium price
b)
Market price rise higher than the equilibrium price
c)
Market price falls below the equilibrium price
d)
Market price remains the same

|
Sai Kulkarni answered |
Deficient demand refers to the situation when aggregate demand (AD) is less than the aggregate supply (AS) corresponding to full employment level of output in the economy.
The factor that causes a change in demand is- a)Price of the inputs
- b)An improvement in technology
- c)Price of the substitute good
- d)Price of the given good
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The factor that causes a change in demand is
a)
Price of the inputs
b)
An improvement in technology
c)
Price of the substitute good
d)
Price of the given good
|
|
Rajdeep Rane answered |
Factors that cause a change in demand
The demand for a product or service refers to the quantity of that product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price during a specific period. Several factors can influence the demand for a good or service, including changes in consumer preferences, income levels, population, and prices of related goods. However, among these factors, the price of substitute goods has a significant impact on the demand for a particular good or service.
Explanation:
1. Price of substitute goods:
- A substitute good is a product or service that can be used as an alternative to another good or service.
- When the price of a substitute good increases, consumers are more likely to switch to the lower-priced good, resulting in an increase in demand for the lower-priced good.
- For example, if the price of coffee increases significantly, some consumers may switch to tea as a substitute. This shift in consumer behavior would lead to an increase in the demand for tea.
- On the other hand, if the price of a substitute good decreases, consumers may choose to switch from the given good to the substitute, causing a decrease in the demand for the given good.
- The price of substitute goods is an important factor in determining consumer choices and can have a significant impact on the overall demand for a particular product or service.
Other factors that influence demand:
2. Price of the given good:
- The price of the given good itself has a direct impact on demand. When the price of a good decreases, consumers may be more willing to purchase it, resulting in an increase in demand. Conversely, when the price of a good increases, demand is likely to decrease.
3. Price of inputs:
- The cost of inputs required to produce a good or service can impact its price, which in turn affects demand. If the price of inputs increases, the cost of production will increase, leading to a higher price for the final product and potentially lower demand.
4. An improvement in technology:
- Technological advancements can lead to the production of goods and services at lower costs, which can result in lower prices and an increase in demand. Improved technology can also lead to the development of new and innovative products, which can create new demand in the market.
Conclusion:
While several factors can influence the demand for a good or service, the price of substitute goods is a crucial factor that directly affects consumer choices and can significantly impact demand. As the price of substitute goods changes, consumers may switch their preferences, leading to changes in demand for the given good or service.
The demand for a product or service refers to the quantity of that product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price during a specific period. Several factors can influence the demand for a good or service, including changes in consumer preferences, income levels, population, and prices of related goods. However, among these factors, the price of substitute goods has a significant impact on the demand for a particular good or service.
Explanation:
1. Price of substitute goods:
- A substitute good is a product or service that can be used as an alternative to another good or service.
- When the price of a substitute good increases, consumers are more likely to switch to the lower-priced good, resulting in an increase in demand for the lower-priced good.
- For example, if the price of coffee increases significantly, some consumers may switch to tea as a substitute. This shift in consumer behavior would lead to an increase in the demand for tea.
- On the other hand, if the price of a substitute good decreases, consumers may choose to switch from the given good to the substitute, causing a decrease in the demand for the given good.
- The price of substitute goods is an important factor in determining consumer choices and can have a significant impact on the overall demand for a particular product or service.
Other factors that influence demand:
2. Price of the given good:
- The price of the given good itself has a direct impact on demand. When the price of a good decreases, consumers may be more willing to purchase it, resulting in an increase in demand. Conversely, when the price of a good increases, demand is likely to decrease.
3. Price of inputs:
- The cost of inputs required to produce a good or service can impact its price, which in turn affects demand. If the price of inputs increases, the cost of production will increase, leading to a higher price for the final product and potentially lower demand.
4. An improvement in technology:
- Technological advancements can lead to the production of goods and services at lower costs, which can result in lower prices and an increase in demand. Improved technology can also lead to the development of new and innovative products, which can create new demand in the market.
Conclusion:
While several factors can influence the demand for a good or service, the price of substitute goods is a crucial factor that directly affects consumer choices and can significantly impact demand. As the price of substitute goods changes, consumers may switch their preferences, leading to changes in demand for the given good or service.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will- a)Raise the price
- b)Lower the price
- c)Only quantity exchanged is affected
- d)Price is unaffected
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will
a)
Raise the price
b)
Lower the price
c)
Only quantity exchanged is affected
d)
Price is unaffected
|
|
Aryan Khanna answered |
According to basic economic theory, the supply of a good will increase when its price rises. Conversely, the supply of a good will decrease when its price decreases. There's also price elasticity of demand. This measures how responsive the quantity demanded is affected by a price change.
Which of the following is an example of a factor market?- a)Stock market
- b)Labor market
- c)Supermarket
- d)Real estate market
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of a factor market?
a)
Stock market
b)
Labor market
c)
Supermarket
d)
Real estate market
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The labor market is an example of a factor market. Factor markets are where factors of production, such as labor, capital, land, and entrepreneurship, are bought and sold. In the labor market, individuals supply their labor services, and businesses demand and hire workers. Factor markets are essential for the production of goods and services, as they provide the necessary resources for production.
What is the primary purpose of maximum price legislation?- a)To ensure the product quality
- b)To protect consumers from high prices
- c)To promote market competition
- d)To prevent shortages of essential goods
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary purpose of maximum price legislation?
a)
To ensure the product quality
b)
To protect consumers from high prices
c)
To promote market competition
d)
To prevent shortages of essential goods
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The primary purpose of maximum price legislation is to protect consumers from high prices. Maximum price legislation, also known as price ceilings, is implemented by the government to set a limit on the price that can be charged for a particular product or service. The aim is to ensure affordability and prevent price exploitation, especially for essential goods or during times of crisis. By capping prices, the government aims to make goods more accessible to consumers.
The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied is known as:- a)Equilibrium price
- b)Maximum price
- c)Minimum price
- d)Average price
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied is known as:
a)
Equilibrium price
b)
Maximum price
c)
Minimum price
d)
Average price
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The price at which quantity demanded equals quantity supplied is known as the equilibrium price. It is the point of balance in a market where the intentions of buyers and sellers align. At the equilibrium price, there is neither a shortage nor a surplus of the product. Buyers are willing to purchase the quantity supplied by sellers, and sellers are willing to supply the quantity demanded by buyers.
When the price is above the equilibrium price in a competitive market, what will happen?- a)Surplus
- b)Shortage
- c)No effect on quantity
- d)Equilibrium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When the price is above the equilibrium price in a competitive market, what will happen?
a)
Surplus
b)
Shortage
c)
No effect on quantity
d)
Equilibrium
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
When the price is above the equilibrium price in a competitive market, there will be a surplus. This means that the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at that price. As a result, sellers will have excess inventory, and they will need to lower the price to encourage buyers to purchase the product. This downward pressure on price continues until the market reaches a new equilibrium.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in price for the good will- a)Shift the demand curve
- b)Shift the supply curve
- c)Move the supply curve
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Market for a good is in equilibrium. A decrease in price for the good will
a)
Shift the demand curve
b)
Shift the supply curve
c)
Move the supply curve
d)
None of these

|
Sajid Hussain answered |
When only price will decrease or increase then moment will occur and other factors being constant.
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will- a)Shift the demand curve
- b)Move the demand curve
- c)Move the supply curve
- d)Shift the supply curve
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Market for a good is in equilibrium. An increase in supply for the good will
a)
Shift the demand curve
b)
Move the demand curve
c)
Move the supply curve
d)
Shift the supply curve

|
Shounak Malik answered |
Understanding Market Equilibrium
In a market, equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a certain price level. When there is a change in supply, it affects the equilibrium in specific ways.
Impact of Increased Supply
When the supply of a good increases, it means that producers are willing and able to sell more of the good at every price level. This situation can be represented graphically and conceptually as follows:
Why Not Shift or Move Demand Curve?
In this scenario, the demand curve remains unchanged because the increase in supply does not directly affect consumer preferences or desires for the product. Instead, it is the market's response to the new quantity available that adjusts the price and quantity demanded.
Conclusion
In summary, an increase in supply for a good will indeed shift the supply curve to the right, leading to new market dynamics that involve lower prices and potentially higher quantities demanded. This fundamental concept is crucial for understanding how supply and demand interact in economic markets.
In a market, equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a certain price level. When there is a change in supply, it affects the equilibrium in specific ways.
Impact of Increased Supply
When the supply of a good increases, it means that producers are willing and able to sell more of the good at every price level. This situation can be represented graphically and conceptually as follows:
- Shift in Supply Curve: An increase in supply is represented by a rightward shift of the supply curve. This indicates that at any given price, suppliers are offering more of the good than before.
- Price Adjustment: With more goods available in the market, the price typically decreases due to the higher quantity supplied. This price drop encourages more consumers to purchase the good, moving towards a new equilibrium.
- New Equilibrium: The market will eventually reach a new equilibrium point where the increased supply matches the new level of demand at the lower price.
Why Not Shift or Move Demand Curve?
In this scenario, the demand curve remains unchanged because the increase in supply does not directly affect consumer preferences or desires for the product. Instead, it is the market's response to the new quantity available that adjusts the price and quantity demanded.
Conclusion
In summary, an increase in supply for a good will indeed shift the supply curve to the right, leading to new market dynamics that involve lower prices and potentially higher quantities demanded. This fundamental concept is crucial for understanding how supply and demand interact in economic markets.
At the point of market equilibrium,- a)Quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
- b)Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
- c)Quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
- d)There is a surplus in the market
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
At the point of market equilibrium,
a)
Quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied
b)
Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded
c)
Quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
d)
There is a surplus in the market

|
Sai Kulkarni answered |
Answer: C) Quantity demanded equals quantity supplied
Explanation:
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in no surplus or shortage. This balance determines the equilibrium price and quantity in the market.
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers, resulting in no surplus or shortage. This balance determines the equilibrium price and quantity in the market.
Minimum price legislation is often enacted to protect the interests of:- a)Producers
- b)Consumers
- c)Government
- d)Exporters
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Minimum price legislation is often enacted to protect the interests of:
a)
Producers
b)
Consumers
c)
Government
d)
Exporters
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Minimum price legislation is often enacted to protect the interests of producers. A minimum price, also known as a price floor, is a price set by the government that is typically above the equilibrium price. By setting a minimum price, the government aims to ensure that producers receive a fair price for their goods or services. This protects the interests of producers by preventing prices from falling too low and potentially causing financial hardships.
What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity if there is an increase in supply and a decrease in demand?- a)Price decreases, quantity decreases
- b)Price decreases, quantity increases
- c)Price increases, quantity decreases
- d)Price increases, quantity remains the same
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity if there is an increase in supply and a decrease in demand?
a)
Price decreases, quantity decreases
b)
Price decreases, quantity increases
c)
Price increases, quantity decreases
d)
Price increases, quantity remains the same
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
If there is an increase in supply and a decrease in demand, the equilibrium price will decrease, but the effect on the equilibrium quantity will depend on the relative magnitude of the changes in supply and demand. When supply increases and demand decreases, the equilibrium quantity will decrease if the decrease in demand is larger than the increase in supply. However, the equilibrium quantity may remain the same or even increase if the increase in supply is larger than the decrease in demand.
Which of the following factors does not affect the demand for a product?- a)Price of related goods
- b)Consumer income
- c)Population size
- d)Technology advancements
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following factors does not affect the demand for a product?
a)
Price of related goods
b)
Consumer income
c)
Population size
d)
Technology advancements
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
Technology advancements do not directly affect the demand for a product. Factors such as the price of related goods (substitutes and complements), consumer income, and population size can impact the demand for a product. Technological advancements may indirectly influence demand by affecting production costs or creating new products, but they do not directly change consumers' desire for a specific product.
The imposition of a price ceiling by the government will result in:- a)An excess supply of the product
- b)An excess demand for the product
- c)No effect on the market
- d)The elimination of the product from the market
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The imposition of a price ceiling by the government will result in:
a)
An excess supply of the product
b)
An excess demand for the product
c)
No effect on the market
d)
The elimination of the product from the market
|
|
Deepak Iyer answered |
The imposition of a price ceiling by the government will result in an excess demand for the product. A price ceiling is a maximum price set by the government, which is typically below the equilibrium price. By setting the price ceiling below the equilibrium price, the government aims to protect consumers by making the product more affordable. However, this creates a situation where the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied, leading to a shortage or excess demand.
Market equilibrium is a situation when- a)Market demand is less than market supply
- b)Market demand is greater than market supply
- c)Market Demand equals market supply
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Market equilibrium is a situation when
a)
Market demand is less than market supply
b)
Market demand is greater than market supply
c)
Market Demand equals market supply
d)
None of these
|
|
Dhruba Ghoshal answered |
Market Equilibrium:
Market equilibrium is a state of balance in a market where the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers. In other words, it is the point at which the demand and supply curves intersect, and there is no excess demand or excess supply in the market. When a market is in equilibrium, there is no pressure for prices to change, and both buyers and sellers are satisfied.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the given question is option C, which states that market demand equals market supply. Let's understand why this is the correct answer:
Market Demand:
Market demand refers to the total quantity of a product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price during a specific period. It is determined by various factors such as price, income, tastes and preferences, and the availability of substitutes. The market demand curve is downward sloping, indicating that as the price of a product decreases, the quantity demanded increases, ceteris paribus.
Market Supply:
Market supply refers to the total quantity of a product or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price during a specific period. It is determined by factors such as the cost of production, technology, resource availability, and government policies. The market supply curve is upward sloping, indicating that as the price of a product increases, the quantity supplied also increases, ceteris paribus.
Market Equilibrium:
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers at a specific price. At this point, there is no excess demand or excess supply in the market. The equilibrium price, also known as the market clearing price, is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves.
Visual Representation:
To visually represent market equilibrium, we can draw a graph with price on the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis. The demand curve slopes downwards, while the supply curve slopes upwards. The point where these two curves intersect represents the equilibrium price and quantity.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, market equilibrium is a state of balance in a market where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is the point at which the demand and supply curves intersect, and there is no excess demand or excess supply. Market equilibrium is an important concept in economics as it helps to determine the market price and quantity of a product or service.
Market equilibrium is a state of balance in a market where the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers. In other words, it is the point at which the demand and supply curves intersect, and there is no excess demand or excess supply in the market. When a market is in equilibrium, there is no pressure for prices to change, and both buyers and sellers are satisfied.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the given question is option C, which states that market demand equals market supply. Let's understand why this is the correct answer:
Market Demand:
Market demand refers to the total quantity of a product or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price during a specific period. It is determined by various factors such as price, income, tastes and preferences, and the availability of substitutes. The market demand curve is downward sloping, indicating that as the price of a product decreases, the quantity demanded increases, ceteris paribus.
Market Supply:
Market supply refers to the total quantity of a product or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at a given price during a specific period. It is determined by factors such as the cost of production, technology, resource availability, and government policies. The market supply curve is upward sloping, indicating that as the price of a product increases, the quantity supplied also increases, ceteris paribus.
Market Equilibrium:
Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded by consumers is equal to the quantity supplied by producers at a specific price. At this point, there is no excess demand or excess supply in the market. The equilibrium price, also known as the market clearing price, is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves.
Visual Representation:
To visually represent market equilibrium, we can draw a graph with price on the y-axis and quantity on the x-axis. The demand curve slopes downwards, while the supply curve slopes upwards. The point where these two curves intersect represents the equilibrium price and quantity.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, market equilibrium is a state of balance in a market where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. It is the point at which the demand and supply curves intersect, and there is no excess demand or excess supply. Market equilibrium is an important concept in economics as it helps to determine the market price and quantity of a product or service.
Deficient demand is a situation when- a)individual demand is greater than individual supply
- b)Market demand is less than market supply
- c)Market demand is greater than market supply
- d)Market demand is equal to market supply
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Deficient demand is a situation when
a)
individual demand is greater than individual supply
b)
Market demand is less than market supply
c)
Market demand is greater than market supply
d)
Market demand is equal to market supply

|
Divey Sethi answered |
Deficient demand is a situation when:
- Market demand is less than market supply
- This means that the quantity of goods or services demanded by consumers is lower than the quantity supplied by producers.
- Market demand refers to the total demand for a product or service in the entire market, considering all consumers.
- Market supply refers to the total supply of a product or service in the entire market, considering all producers.
Explanation:
- Deficient demand occurs when there is an imbalance between the quantity of goods or services that consumers want and the quantity that producers are willing to supply.
- In this situation, there is an excess supply in the market. This can lead to several consequences:
- Lower prices: When there is deficient demand, producers may need to lower their prices to encourage consumers to purchase their products or services.
- Inventory buildup: Producers may end up with excess inventory if they cannot sell all their products. This can lead to additional costs for storage and maintenance.
- Decreased production: Producers may reduce their production levels to align with the lower demand. This can result in layoffs or reduced working hours for employees.
- Economic downturn: Deficient demand can be a sign of a weak economy, as it indicates that consumers are not spending as much as producers are producing.
Example:
- Let's consider the market for smartphones. If the market demand for smartphones is lower than the market supply, we have a deficient demand situation.
- This means that consumers are not buying as many smartphones as producers are producing. As a result, there will be excess inventory of smartphones, and producers may need to lower prices or reduce production levels to address the deficient demand.
Overall, deficient demand is a situation where market demand is less than market supply, indicating an imbalance in the market.
- Market demand is less than market supply
- This means that the quantity of goods or services demanded by consumers is lower than the quantity supplied by producers.
- Market demand refers to the total demand for a product or service in the entire market, considering all consumers.
- Market supply refers to the total supply of a product or service in the entire market, considering all producers.
Explanation:
- Deficient demand occurs when there is an imbalance between the quantity of goods or services that consumers want and the quantity that producers are willing to supply.
- In this situation, there is an excess supply in the market. This can lead to several consequences:
- Lower prices: When there is deficient demand, producers may need to lower their prices to encourage consumers to purchase their products or services.
- Inventory buildup: Producers may end up with excess inventory if they cannot sell all their products. This can lead to additional costs for storage and maintenance.
- Decreased production: Producers may reduce their production levels to align with the lower demand. This can result in layoffs or reduced working hours for employees.
- Economic downturn: Deficient demand can be a sign of a weak economy, as it indicates that consumers are not spending as much as producers are producing.
Example:
- Let's consider the market for smartphones. If the market demand for smartphones is lower than the market supply, we have a deficient demand situation.
- This means that consumers are not buying as many smartphones as producers are producing. As a result, there will be excess inventory of smartphones, and producers may need to lower prices or reduce production levels to address the deficient demand.
Overall, deficient demand is a situation where market demand is less than market supply, indicating an imbalance in the market.
Chapter doubts & questions for Theory of Price Determination - Economics for JAMB 2025 is part of JAMB exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JAMB exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JAMB 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Theory of Price Determination - Economics for JAMB in English & Hindi are available as part of JAMB exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JAMB Exam by signing up for free.
Economics for JAMB
162 videos|101 docs|66 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup