All Exams >
Grade 11 >
Biology for Grade 11 >
All Questions
All questions of Cell Membranes and Transport for Grade 11 Exam
Amphipathic molecule in plasma membrane is :-- a)Protein
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Phospholipids
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Amphipathic molecule in plasma membrane is :-
a)
Protein
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Phospholipids
d)
All the above
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer arranged back-to-back. The membrane is also covered in places with cholesterol molecules and proteins. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and regulates which molecules are allowed to enter and exit the cell.
Plasma membrane is :–- a)Selectively permeable
- b)Permeable
- c)Impermeable
- d)Semipermeable
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasma membrane is :–
a)
Selectively permeable
b)
Permeable
c)
Impermeable
d)
Semipermeable
|
|
Priya Mahale answered |
It allows hydrophobic molecules and small polar molecules diffuse through the lipid layer, but does not allow ions and large polar molecules cannot diffuse through the membrane.
Plasmodesmata are:-- a)Pores in cell wall
- b)Pores in cell membrane
- c)Protoplasmic connections
- d)1 and 2 both
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmodesmata are:-
a)
Pores in cell wall
b)
Pores in cell membrane
c)
Protoplasmic connections
d)
1 and 2 both

|
S. G. answered |
It's simple Plasmodesmata are protoplasmic connect... moreions between adjacent cells.These R threads like structure of protoplasms which travel from protoplasm of one cell to protoplasm of nearest adjacent cell crossing cell wall.These Plasmodesmata connects the protoplasm of adjacent cells.These are charastically found out only in plant cells and ABSENT IN ANIMAL CELLS ..
Plasma membrane is fluid structure due to presence of :–- a)Carbohydrate
- b)Lipid
- c)Glyco protein
- d)Poly saccharide
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasma membrane is fluid structure due to presence of :–
a)
Carbohydrate
b)
Lipid
c)
Glyco protein
d)
Poly saccharide
|
|
Sanjana Singh answered |
See-
composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded peoteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells. The plasma membrane is fluid structure due to composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded peoteins, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and regulates the movement of substances in and out of cells. The plasma membrane is fluid structure due to composed of a phospholipid bilayer.
Cell wall is :–- a)Dead and impermeable
- b)Dead and permeable
- c)Living and impermeable
- d)Living and selective
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall is :–
a)
Dead and impermeable
b)
Dead and permeable
c)
Living and impermeable
d)
Living and selective
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. ... In bacteria, the cell wall is composed of peptidoglycan.
Synthesis of cell wall material takes place in :–- a)Dictyosome
- b)Mitochondria
- c)Lysosome
- d)E.R.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Synthesis of cell wall material takes place in :–
a)
Dictyosome
b)
Mitochondria
c)
Lysosome
d)
E.R.
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
In plant cells, Golgi apparatus consists of a number of isolated units called as dictyosomes while in animal cells it occurs as single compact or loose complex. The dictyosomes are engaged in secretory activities (because secretory materials are produced in dictyosomes) and rapid divisions (because wall materials are synthesized in dictyosomes).
Which element mainly occurs in middle lamella:-- a)Ca
- b)Mg
- c)Na
- d)K
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which element mainly occurs in middle lamella:-
a)
Ca
b)
Mg
c)
Na
d)
K

|
Manvi Bansal answered |
Ca and mg pectate are present in middle lamella
Percentage of intrinsic proteins in the total proteins of plasma membrane :–- a)70%
- b)20%
- c)10%
- d)90%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Percentage of intrinsic proteins in the total proteins of plasma membrane :–
a)
70%
b)
20%
c)
10%
d)
90%
|
|
Lalit Yadav answered |
The plasma membrane or cell membrane is the outer covering of all cells but in a plant cell, it is present below the cell wall. It is mainly composed of phospholipid bilayer structure with the embedded proteins. The membrane proteins are extrinsic (on the surface of the membrane) and intrinsic (across the membrane i.e., cross the bilipid layer). About 70% of the proteins of the plasma membrane are intrinsic proteins. The intrinsic proteins, as their name implies, are firmly embedded in the phospholipid bilayer. Almost all intrinsic proteins contain special amino acid sequences.
Carbohydrates which present in the cell membrane take part in :–- a)Transport of substance
- b)Cell recognition
- c)Attachment to microfilament
- d)Attachment to microtubules
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates which present in the cell membrane take part in :–
a)
Transport of substance
b)
Cell recognition
c)
Attachment to microfilament
d)
Attachment to microtubules
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Carbohydrates which are present in the cell membrane take part in cell recognition. Cell recognition is defined as an active process giving rise to a specific response.
Cell adhesion is a good example of cell recognition when it can be demonstrated that the adhesion is mediated by molecules having specific binding properties. Such cell adhesion molecules have now been identified in several cellular systems. Carbohydrates, or sugars, are sometimes found attached to proteins or lipids on the outside of a cell membrane. That is, they are only found on the extracellular side of a cell membrane. Together these carbohydrates form the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx of a cell has many functions. It can provide cushioning and protection for the plasma membrane, and it is also important in cell recognition. Based on the structure and types of carbohydrates in the glycocalyx, your body can recognize cells and determine if they should be there or not.
Cell adhesion is a good example of cell recognition when it can be demonstrated that the adhesion is mediated by molecules having specific binding properties. Such cell adhesion molecules have now been identified in several cellular systems. Carbohydrates, or sugars, are sometimes found attached to proteins or lipids on the outside of a cell membrane. That is, they are only found on the extracellular side of a cell membrane. Together these carbohydrates form the glycocalyx. The glycocalyx of a cell has many functions. It can provide cushioning and protection for the plasma membrane, and it is also important in cell recognition. Based on the structure and types of carbohydrates in the glycocalyx, your body can recognize cells and determine if they should be there or not.
Carbohydrates are present in the plasmalemma in the form of :–- a)Hemicellulose
- b)Cellulose
- c)Starch
- d)Glycoprotein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbohydrates are present in the plasmalemma in the form of :–
a)
Hemicellulose
b)
Cellulose
c)
Starch
d)
Glycoprotein
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Chemically, cell membrane or plasma lemma is composed of proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and water. Carbohydrates of cell membrane are small unbranched or branched chains called as oligosaccharides. They are attached to both lipids and protein molecules found on outer surface of the membrane producing glycolipids and glycoproteins respectively.
Which of the following is main enzyme of plasma membrane :-- a)TPP ase
- b)ATP ase
- c)Peptidyl transferase
- d)Catalases
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is main enzyme of plasma membrane :-
a)
TPP ase
b)
ATP ase
c)
Peptidyl transferase
d)
Catalases
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Its name is due to short time attachment of inorganic phosphate at the aspartate residues at the time of activation. Function of P-ATPase is to transport a variety of different compounds, like ions and phospholipids, across a membrane using ATP hydrolysis for energy.
The chemical substance abundantly present in middle lamella is :–- a)Cutin
- b)Chitin
- c)Lignin
- d)Pectin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The chemical substance abundantly present in middle lamella is :–
a)
Cutin
b)
Chitin
c)
Lignin
d)
Pectin
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Middle lamella is the cementing material between two cells. It is mostly amorphous, thin and made up of calcium and magnesium pectate. The pectin present in this layer is a heteropolysaccharide which helps to bind the two cells together. It also helps in cell growth and cell wall extension. Thus, the correct answer is option D.
Cell wall of lignified cell is :–- a)Semipermeable and dead
- b)Permeable and living
- c)Impermeable and dead
- d)Impermeable and living
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall of lignified cell is :–
a)
Semipermeable and dead
b)
Permeable and living
c)
Impermeable and dead
d)
Impermeable and living
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
A plant cell is characterized by a well developed cellulosic cell wall which is dead at maturity and consists lignin. Since cell wall is dead at maturity it does not take part in any physiological or biochemical process and may not allow passing molecule across it. Therefore, the correct answer is option C.
Lignified cell wall is characteristic feature of:-- a)Vessels
- b)Sieve cells
- c)Sieve tubes
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Lignified cell wall is characteristic feature of:-
a)
Vessels
b)
Sieve cells
c)
Sieve tubes
d)
All the above
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Lignified cell wall is the characteristic of sclerenchymatous tissue... Where it is known to provide mechanical strength to the plants by plasticity... Cambium , thin layer of generative tissue lying between the bark and the wood of a stem, most active in woody plants.
The average thickness of plasma membrane is :-- a)70 Å
- b)75 — 100 Å
- c)100 — 150 Å
- d)200 Å
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The average thickness of plasma membrane is :-
a)
70 Å
b)
75 — 100 Å
c)
100 — 150 Å
d)
200 Å
|
|
Vishal Kumar answered |
The electron microscopic studies reveal that a typical cell/plasma membrane is 75-100 Ao (7.5-10.0 nm) in thickness.
Muramic acid is present in cell walls of :-- a)Bacteria and blue-green algae
- b)Green algae
- c)Yeast
- d)All fungi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Muramic acid is present in cell walls of :-
a)
Bacteria and blue-green algae
b)
Green algae
c)
Yeast
d)
All fungi
|
|
Akshay Akshu answered |
Outer layer of bacteria and blue green algae are made up of Miramichi acid.So,A is the answer
The outermost covering of the plant cell is constituted by:- a)Cellulose
- b)Lignin
- c)Chitin
- d)Glycocalyx
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The outermost covering of the plant cell is constituted by:
a)
Cellulose
b)
Lignin
c)
Chitin
d)
Glycocalyx

|
Lead Academy answered |
The correct answer is Cellulose.
- The epidermis is the protective outer layer of clonally related cells covering all plant organs.
- It is made up of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin.
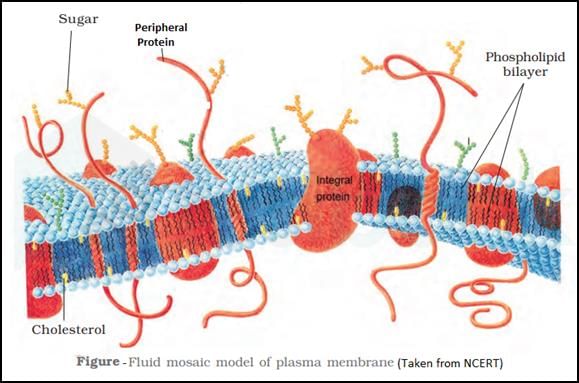
According to fluid mosaic model (proposed by Singer & Nicolson) plasma membrane is composed of :–- a)Cellulose, hemicellulose
- b)Phospholipid and integrated protein
- c)Phospholipid, extrinsic protein, intrinsic protein
- d)Phospholipid and hemicellulose
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
According to fluid mosaic model (proposed by Singer & Nicolson) plasma membrane is composed of :–
a)
Cellulose, hemicellulose
b)
Phospholipid and integrated protein
c)
Phospholipid, extrinsic protein, intrinsic protein
d)
Phospholipid and hemicellulose
|
|
Shalu answered |
The fluid mosaic model of the biomembrane or cell membrane was proposed by SJ Singer and GL Nicolson in the year 1972.
According to this model, the transmembrane proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer.
Transmembrane proteins are of two types-
Extrinsic membrane proteins- are present outside the membrane which bound to the lipid layer by weak molecular forces.
Intrinsic membrane proteins- are completely embedded in the membrane.
So, the correct answer is 'Phospholipids, extrinsic proteins and intrinsic proteins'. option C
According to this model, the transmembrane proteins are embedded within the phospholipid bilayer.
Transmembrane proteins are of two types-
Extrinsic membrane proteins- are present outside the membrane which bound to the lipid layer by weak molecular forces.
Intrinsic membrane proteins- are completely embedded in the membrane.
So, the correct answer is 'Phospholipids, extrinsic proteins and intrinsic proteins'. option C
Cell membrane have how many enzymes :-- a)20
- b)30
- c)40
- d)More than 50
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell membrane have how many enzymes :-
a)
20
b)
30
c)
40
d)
More than 50

|
Ved Patidar answered |
Around 30 enzymes are present in cell membrane, for example-ATPases, G-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Cholera affects millions of people around the world. It causes diarrhea, which can lead to dehydration and even death. Cholera toxin affects a chloride transporter that secretes chloride ion into the lumen of the small intestine. How does cholera toxin lead to dehydration?- a)The toxin turns off the transporter, so the negatively charged chloride pushes water into the lumen
- b)The toxin turns on the transporter, and water follows the ion due to osmosis
- c)The toxin turns on the transporter, and water is actively transported with the ion
- d)The toxin turns off the transporter, so water is no longer exchanged for chloride ion
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Cholera affects millions of people around the world. It causes diarrhea, which can lead to dehydration and even death. Cholera toxin affects a chloride transporter that secretes chloride ion into the lumen of the small intestine. How does cholera toxin lead to dehydration?
a)
The toxin turns off the transporter, so the negatively charged chloride pushes water into the lumen
b)
The toxin turns on the transporter, and water follows the ion due to osmosis
c)
The toxin turns on the transporter, and water is actively transported with the ion
d)
The toxin turns off the transporter, so water is no longer exchanged for chloride ion
|
|
Isaac Bailey answered |
Understanding Cholera Toxin and Dehydration
Cholera is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, which produces a potent toxin that disrupts normal intestinal function. This leads to severe dehydration, a life-threatening condition.
Mechanism of Cholera Toxin
- Cholera toxin binds to intestinal epithelial cells, leading to the activation of adenylate cyclase.
- This increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels in the cell, which in turn activates protein kinase A (PKA).
Effect on Chloride Transporter
- The activated PKA phosphorylates the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a chloride ion channel.
- This phosphorylation opens the CFTR channel, resulting in increased secretion of chloride ions (Cl-) into the intestinal lumen.
Role of Water and Osmosis
- As chloride ions are secreted into the lumen, water follows due to osmosis.
- Osmosis is the movement of water from areas of lower solute concentration (inside the cells) to areas of higher solute concentration (the intestinal lumen where chloride concentration is increased).
- Consequently, this leads to massive water loss from the body, resulting in severe diarrhea and dehydration.
Conclusion
- Thus, the correct answer is option 'B': "The toxin turns on the transporter, and water follows the ion due to osmosis."
- This critical mechanism underscores the importance of rapid rehydration and medical intervention in cholera cases to prevent death.
Cholera is caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae, which produces a potent toxin that disrupts normal intestinal function. This leads to severe dehydration, a life-threatening condition.
Mechanism of Cholera Toxin
- Cholera toxin binds to intestinal epithelial cells, leading to the activation of adenylate cyclase.
- This increases cyclic AMP (cAMP) levels in the cell, which in turn activates protein kinase A (PKA).
Effect on Chloride Transporter
- The activated PKA phosphorylates the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), a chloride ion channel.
- This phosphorylation opens the CFTR channel, resulting in increased secretion of chloride ions (Cl-) into the intestinal lumen.
Role of Water and Osmosis
- As chloride ions are secreted into the lumen, water follows due to osmosis.
- Osmosis is the movement of water from areas of lower solute concentration (inside the cells) to areas of higher solute concentration (the intestinal lumen where chloride concentration is increased).
- Consequently, this leads to massive water loss from the body, resulting in severe diarrhea and dehydration.
Conclusion
- Thus, the correct answer is option 'B': "The toxin turns on the transporter, and water follows the ion due to osmosis."
- This critical mechanism underscores the importance of rapid rehydration and medical intervention in cholera cases to prevent death.
Pit membrane of simple pit is formed by :-- a)Secondary cell wall
- b)Middle lamella
- c)Primary cell wall
- d)Plasma membrane
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Pit membrane of simple pit is formed by :-
a)
Secondary cell wall
b)
Middle lamella
c)
Primary cell wall
d)
Plasma membrane
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
Simple pit pairs occur in parenchyma cells, in medullary rays, in phloem fibres, companion cells, and in tracheids of several flowering plants. In the simple pits, the pit cavity remains of the same diameter and the pit or closing membrane also remains simple and uniform in its structure.
The cell wall of bacteria is made up of - a)Cellulose
- b)Hemicellulose
- c)Lignin
- d)Peptidoglycan
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The cell wall of bacteria is made up of
a)
Cellulose
b)
Hemicellulose
c)
Lignin
d)
Peptidoglycan
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Correct option is D.
Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan also called as murein, which is made from polysaccharide chains cross-linked by unusual peptides containing D-amino acids.
Bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan also called as murein, which is made from polysaccharide chains cross-linked by unusual peptides containing D-amino acids.
What is the cell wall of a plant made of ?- a)Cellulose
- b)Carbohydrates
- c)Lipids
- d)Lipoprotein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the cell wall of a plant made of ?
a)
Cellulose
b)
Carbohydrates
c)
Lipids
d)
Lipoprotein

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Cellulose is the most abundant macromolecule on Earth.
- Cellulose fibers are long, linear polymers of hundreds of glucose molecules.
- These fibres aggregate into bundles of about 40, which are called microfibrils.
Which transport process is responsible for the movement of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide across the cell membrane?- a)Diffusion
- b)Osmosis
- c)Facilitated diffusion
- d)Active transport
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which transport process is responsible for the movement of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide across the cell membrane?
a)
Diffusion
b)
Osmosis
c)
Facilitated diffusion
d)
Active transport

|
Orion Classes answered |
Diffusion is the process responsible for the movement of gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide across the cell membrane, as they passively move from areas of high concentration to low concentration.
How many layers are present in the bacterial cell envelope?- a)1
- b)2
- c)3
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many layers are present in the bacterial cell envelope?
a)
1
b)
2
c)
3
d)
4

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
- Bacterial have a tightly bound three – layered cell envelope.
- The uppermost layer is the glycocalyx, followed by the cell wall in the middle and the innermost plasma membrane.
- The cell envelope provides protection.
Plasma membrane is made up of which organic molecules?- a)Carbohydrates
- b)Lipids and protein
- c)Vitamin
- d)Roughage
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasma membrane is made up of which organic molecules?
a)
Carbohydrates
b)
Lipids and protein
c)
Vitamin
d)
Roughage

|
Lead Academy answered |
Plasma membrane, also called the cell membrane is mainly composed of lipids and proteins.
- The major lipids are arranged in a bilayer and called as phospholipids.
- Plasma membrane also contains cholesterol.
- Cell membranes also possess protein and carbohydrate as per Biochemical investigation.
- The ratio of lipid and protein varies in different cell types.
For example, in human beings, the membrane of the erythrocyte has approx 40 per cent lipids and 52 per cent protein.

Which of these bacteria lack a cell wall?- a)Escherichia
- b)Mycoplasma
- c)Pseudomonas
- d)Mycobacterium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these bacteria lack a cell wall?
a)
Escherichia
b)
Mycoplasma
c)
Pseudomonas
d)
Mycobacterium

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
- All bacteria have a cell wall covering the cell membrane, except in the genus mycoplasma.
- Since all bacteria are prokaryotic organisms, they do not have a well – defined nucleus.
- The genetic material is naked.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), used to treat depression, block a specific protein in the pre-synaptic neuron to keep the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft for a longer period of time. What sort of protein do they block?- a)A neurotransmitter ATP pump
- b)A phagocytosis-inducing protein
- c)A sodium-neurotransmitter symporter
- d)A neurotransmitter channel
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), used to treat depression, block a specific protein in the pre-synaptic neuron to keep the neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft for a longer period of time. What sort of protein do they block?
a)
A neurotransmitter ATP pump
b)
A phagocytosis-inducing protein
c)
A sodium-neurotransmitter symporter
d)
A neurotransmitter channel

|
Orion Classes answered |
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) work by blocking the reuptake of serotonin, a neurotransmitter, in the pre-synaptic neuron. They specifically target and block the serotonin transporter protein, which is a sodium-neurotransmitter symporter. This protein is responsible for the reabsorption of serotonin from the synaptic cleft back into the pre-synaptic neuron. By blocking this transporter, SSRIs increase the concentration of serotonin in the synaptic cleft, allowing it to interact with and stimulate the post-synaptic receptors for a longer period of time. This helps alleviate symptoms of depression and improve mood.
Pulmonary edema occurs when fluid builds up in the interstitium between the pulmonary capillaries and the alveoli, and eventually enters the alveoli. How do you decrease the risk of pulmonary edema?- a)Decrease hydrostatic pressure and increase osmotic pressure
- b)Increase hydrostatic pressure and decrease osmotic pressure
- c)Decrease hydrostatic pressure and decrease osmotic pressure
- d)Increase hydrostatic pressure and increase osmotic pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pulmonary edema occurs when fluid builds up in the interstitium between the pulmonary capillaries and the alveoli, and eventually enters the alveoli. How do you decrease the risk of pulmonary edema?
a)
Decrease hydrostatic pressure and increase osmotic pressure
b)
Increase hydrostatic pressure and decrease osmotic pressure
c)
Decrease hydrostatic pressure and decrease osmotic pressure
d)
Increase hydrostatic pressure and increase osmotic pressure

|
Orion Classes answered |
Pulmonary edema is the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, specifically in the interstitium and alveoli. To decrease the risk of pulmonary edema, it is necessary to address the factors that contribute to the movement of fluid into the interstitium and alveoli.
Hydrostatic pressure refers to the pressure exerted by fluid within blood vessels, and it tends to push fluid out of the vessels and into the surrounding tissues. To reduce the risk of pulmonary edema, it is important to decrease hydrostatic pressure, which can be achieved by improving heart function, reducing fluid volume, or relieving any obstructions or pressures on blood vessels in the lungs.
Osmotic pressure, on the other hand, is the pressure exerted by solutes (such as proteins) that draw water into the blood vessels. By increasing osmotic pressure, more fluid can be retained within the blood vessels, reducing the likelihood of it leaking into the interstitium and alveoli. This can be accomplished by maintaining adequate levels of proteins, particularly albumin, in the bloodstream.
The nephron reabsorbs glucose through a sodium / glucose transporter. What sort of transporter is it?- a)Protein channel
- b)Antiporter
- c)Sodium pump
- d)ymporter
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The nephron reabsorbs glucose through a sodium / glucose transporter. What sort of transporter is it?
a)
Protein channel
b)
Antiporter
c)
Sodium pump
d)
ymporter

|
Orion Classes answered |
The sodium/glucose transporter found in the nephron is a symporter. A symporter is a type of transporter protein that simultaneously moves two different molecules across a cell membrane in the same direction. In this case, the transporter moves both sodium ions and glucose molecules from the tubular fluid in the nephron into the cells of the renal tubules. This process is known as co-transport or secondary active transport, as it utilizes the energy stored in the electrochemical gradient of sodium ions to drive the uphill movement of glucose against its concentration gradient. The symporter binds both sodium and glucose on one side of the membrane and undergoes a conformational change to transport them together into the cell. This allows for the efficient reabsorption of glucose from the filtrate back into the bloodstream, helping to maintain glucose homeostasis in the body.
Which type of transport process involves the release of large particles or substances from the cell?- a)Facilitated diffusion
- b)Endocytosis
- c)Exocytosis
- d)Osmosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which type of transport process involves the release of large particles or substances from the cell?
a)
Facilitated diffusion
b)
Endocytosis
c)
Exocytosis
d)
Osmosis

|
Orion Classes answered |
Exocytosis is the process by which cells release large particles or substances from the cell by fusing vesicles containing the material with the cell membrane and expelling the contents outside the cell.
What cell membrane property in the nephron capillaries allows small molecules to pass through?- a)It has cholesterol rafts
- b)It has glycoprotein channels
- c)It has fenestrations
- d)It is amphipathic
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What cell membrane property in the nephron capillaries allows small molecules to pass through?
a)
It has cholesterol rafts
b)
It has glycoprotein channels
c)
It has fenestrations
d)
It is amphipathic

|
Orion Classes answered |
Fenestrations are small pores or openings in the endothelial cells lining the capillaries of the nephron. These fenestrations allow small molecules to pass through the capillary walls and enter the surrounding tissues. The presence of fenestrations increases the permeability of the capillaries, allowing for the filtration and exchange of small molecules, such as water, ions, and nutrients, between the blood and the surrounding tissues. This property is important in the function of the nephron, as it allows for the filtration of waste products and the reabsorption of essential substances during urine formation.
What sort of transporters would be required to move glucose from the blood to the lumen?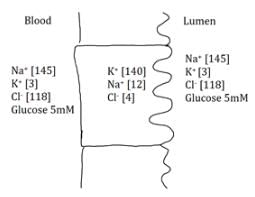
- a)Apical sodium/glucose symporter and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and glucose channel
- b)Apical glucose channel and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and sodium/glucose symporter
- c)Apical glucose channel and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and sodium/glucose antiporter
- d)Apical sodium/glucose antiporter and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and glucose channel
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What sort of transporters would be required to move glucose from the blood to the lumen?

a)
Apical sodium/glucose symporter and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and glucose channel
b)
Apical glucose channel and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and sodium/glucose symporter
c)
Apical glucose channel and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and sodium/glucose antiporter
d)
Apical sodium/glucose antiporter and basolateral sodium/potassium pump and glucose channel

|
Orion Classes answered |
- The apical side faces the lumen, while the basolateral side of the cell is the one closer to the capillary system.
- There is effectively no glucose inside the cell.
- To bring glucose into the cell requires some amount of energy.
- To bring glucose from the blood to the cell, a basolateral glucose channel will allow glucose to move down its gradient. An apical sodium/glucose antiporter will move glucose against its gradient by using the energy of sodium following its gradient. A sodium/potassium pump maintains sodium concentration.
The most abundant lipid in cell membrane is :–- a)Cutin
- b)Cholesterol
- c)Steroid
- d)Phospholipids
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most abundant lipid in cell membrane is :–
a)
Cutin
b)
Cholesterol
c)
Steroid
d)
Phospholipids

|
Neha Zanjurne answered |
Option D is right option coz they have polar head group and also have two hydrophobic tails. they are made of hydrocarbons. they form bi-layered membrane structure so, option D is right option.
Bacterial cell membrane is made up of- a)proteins and phospholipids
- b)Hemicellulose
- c)Cellulose
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Bacterial cell membrane is made up of
a)
proteins and phospholipids
b)
Hemicellulose
c)
Cellulose
d)
None of the above

|
Nipuns Institute answered |
The bacterial cell membrane is made up of proteins and phospholipids. The proteins are randomly distributed in the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane.
Cell wall is present in :-- a)Plant cells
- b)Procaryotic cell
- c)Algal cell
- d)All the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Cell wall is present in :-
a)
Plant cells
b)
Procaryotic cell
c)
Algal cell
d)
All the above
|
|
Mansi Awasthi answered |
Plant cell have cell wall made of cellulose
prokaryotes have cell wall made of peptidoglycan
algae cell wall is made of hemicellulose and pectin
so finally answer is all of these
prokaryotes have cell wall made of peptidoglycan
algae cell wall is made of hemicellulose and pectin
so finally answer is all of these
Immune system cells use damaging proteases and reactive oxygen species to destroy foreign invaders. The immune system cells are not harmed because the microbes are sequestered in vesicles. How did the invaders get to the vesicles?- a)Active transport
- b)Phagocytosis
- c)Exocytosis
- d)Pinocytosis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Immune system cells use damaging proteases and reactive oxygen species to destroy foreign invaders. The immune system cells are not harmed because the microbes are sequestered in vesicles. How did the invaders get to the vesicles?
a)
Active transport
b)
Phagocytosis
c)
Exocytosis
d)
Pinocytosis

|
Orion Classes answered |
In the context of the immune system, phagocytosis is the process by which immune cells engulf and internalize foreign invaders such as microbes. During phagocytosis, the immune cell surrounds the invader and forms a vesicle called a phagosome. The phagosome then fuses with lysosomes, forming a phagolysosome, where damaging proteases and reactive oxygen species are released to destroy the invaders.
So, the invaders reach the vesicles through phagocytosis. The immune cells recognize the presence of foreign substances and actively engulf them by extending pseudopods to surround the invaders and internalize them into vesicles for destruction. This sequestration in vesicles allows the immune system to isolate and neutralize the invaders while minimizing harm to the surrounding cells.
How do potassium ions travel as they move into the cell?- a)Down the concentration gradient and up the membrane potential
- b)Up the concentration gradient and down the membrane potential
- c)Down the concentration gradient and down the membrane potential
- d)Up the concentration gradient and up the membrane potential
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How do potassium ions travel as they move into the cell?
a)
Down the concentration gradient and up the membrane potential
b)
Up the concentration gradient and down the membrane potential
c)
Down the concentration gradient and down the membrane potential
d)
Up the concentration gradient and up the membrane potential

|
Orion Classes answered |
Potassium ions (K+) move into the cell by a process known as facilitated diffusion, which involves the movement of ions from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. In the case of potassium ions, they move from the extracellular fluid, where their concentration is higher, to the intracellular fluid, where their concentration is lower.
The movement of potassium ions is also influenced by the membrane potential, which is the difference in electrical charge across the cell membrane. The inside of the cell is negatively charged compared to the outside. This electrical gradient tends to attract positively charged potassium ions into the cell.
Therefore, the overall movement of potassium ions involves moving up the concentration gradient (from high to low concentration) and down the membrane potential (from a more positive to a less positive or negative potential) to enter the cell.
Chapter doubts & questions for Cell Membranes and Transport - Biology for Grade 11 2025 is part of Grade 11 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 11 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 11 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Cell Membranes and Transport - Biology for Grade 11 in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 11 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Biology for Grade 11
26 docs|12 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup











