All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Electric Current for EmSAT Achieve Exam
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. Power consumed by it operated on 110 V is- a)90 W
- b)75 W
- c)25 W
- d)50 W
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. Power consumed by it operated on 110 V is
a)
90 W
b)
75 W
c)
25 W
d)
50 W
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
P = V^2/R
If V = 220 V we have
100 W = 220^2/R
R = 220^2/100 Ω = 484 Ω. This is the resistance of the bulb.
When V = 110 V, power consumed = V^2/R = 110^2 /484 = 25 W.
The Wheatstone bridge and its balance condition provides a practical method for the determination of- a)Unknown voltage
- b)Unknown current
- c)Unknown Resistance
- d)Unknown Resistivity
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
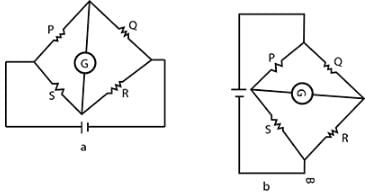
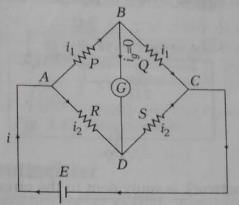
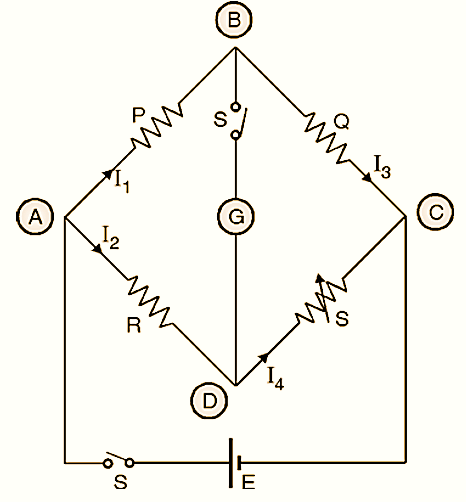
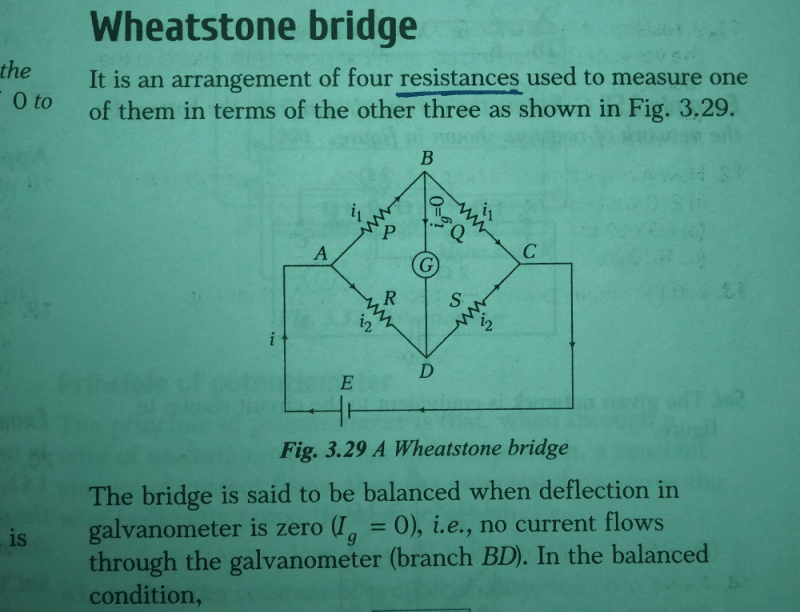
The Wheatstone bridge and its balance condition provides a practical method for the determination of
a)
Unknown voltage
b)
Unknown current
c)
Unknown Resistance
d)
Unknown Resistivity
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
A wheatstone bridge is an electrical bridge consisting of two branches of a parallel circuit joined by a galvanometer and used for determining the value of an unknown resistance in one of the branches.
Sensitivity of potentiometer can be increased by- a)Increasing voltage
- b)Decreasing length of potentiometer wire
- c)Increasing the length of potentiometer wire and reducing current.
- d)Increasing current in circuit
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sensitivity of potentiometer can be increased by
a)
Increasing voltage
b)
Decreasing length of potentiometer wire
c)
Increasing the length of potentiometer wire and reducing current.
d)
Increasing current in circuit
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Sensitivity of potentiometer can be increased by increasing the length of the potentiometer wire and by reducing the current in the circuit by using a rheostat. Both the methods help in decreasing the potential gradient, and thereby increasing the resistivity.
Two bulbs A and B are rated 100 W, 120 V and 10 W, 120 V respectively. They are connected across a 120 V source in series. Calculate the current through each bulb.- a)0.08 A
- b)0.0083 A
- c)0.083 A
- d)8 A
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two bulbs A and B are rated 100 W, 120 V and 10 W, 120 V respectively. They are connected across a 120 V source in series. Calculate the current through each bulb.
a)
0.08 A
b)
0.0083 A
c)
0.083 A
d)
8 A
|
|
Prateek Jain answered |
Bulb A,
PA=100w
VA=120v
We know that, P=VI
So, I=P/V=100w/120v=5/6A=0.83A
Bulb B,
PB=100w
VB=120v
We know that, P=VI
So, I=P/V=10w/120v=1/12A=0.083A
Bulb A will consume more energy than bulb B when they are connected in parallel.
PA=100w
VA=120v
We know that, P=VI
So, I=P/V=100w/120v=5/6A=0.83A
Bulb B,
PB=100w
VB=120v
We know that, P=VI
So, I=P/V=10w/120v=1/12A=0.083A
Bulb A will consume more energy than bulb B when they are connected in parallel.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electric Current - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electric Current - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|