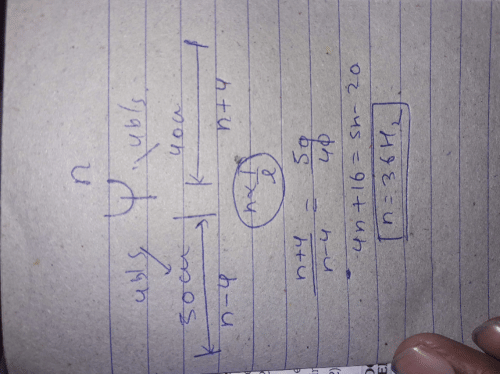All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Mechanical Waves Behavior for EmSAT Achieve Exam
As a wave propagates; which of the following is not satisfied?- a)the wave intensity remains constant for a plane wave
- b)total intensity of the spherical wave over the spherical surface centered at the source remains constant at all times
- c)the wave intensity decreases as the inverse of the square of the distance from the source for a spherical wave
- d)the wave intensity decreases as the inverse of the distance from the source for a spherical wave
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
As a wave propagates; which of the following is not satisfied?
a)
the wave intensity remains constant for a plane wave
b)
total intensity of the spherical wave over the spherical surface centered at the source remains constant at all times
c)
the wave intensity decreases as the inverse of the square of the distance from the source for a spherical wave
d)
the wave intensity decreases as the inverse of the distance from the source for a spherical wave
|
|
Shatabdi Malik answered |
I think it's ans is C.
An echo repeats two syllables. If the velocity of sound is 330 m/s, then the distance of reflecting surface is- a)16.5 m
- b)99 m
- c)66 m
- d)33.0 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An echo repeats two syllables. If the velocity of sound is 330 m/s, then the distance of reflecting surface is
a)
16.5 m
b)
99 m
c)
66 m
d)
33.0 m
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Let us say that we speak syllables at a rate of 2 to 9 per second. So let us say that a syllable takes a minimum of 0.1 sec for a fast speaker. Let us say that a sound pulse (syllable) is emitted starting at t = 0.
The effect of a syllable lasts on the ear for 0.1 sec. So if any echo reaches the year before t = 0.2 sec., then it is mixed with the direct sound present in the ear and so echo is not properly heard.
In this problem, two syllables are repeated in the echo. That is it took about 2 * 0.2 sec ie., 0.4 seconds for the sound to travel to the reflecting surface and come back to the ear.
The distance of the reflecting surface from the person
= 330 m/s * 0.4 sec / 2
= 66 meters.
The speed of propagation of a sinusoidal wave is given by V=νλ where- a)ν is the reciprocal of the period and λ is the dispersion
- b)ν is the reciprocal of the period and λ is the wave number
- c)ν is the angular frequency and λ is the wavelength
- d)ν is the reciprocal of the period and λ is the wavelength
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The speed of propagation of a sinusoidal wave is given by V=νλ where
a)
ν is the reciprocal of the period and λ is the dispersion
b)
ν is the reciprocal of the period and λ is the wave number
c)
ν is the angular frequency and λ is the wavelength
d)
ν is the reciprocal of the period and λ is the wavelength
|
|
Om Desai answered |
For a sinusoidal wave, V = v λ.
V = speed,
v = frequency,
λ = wavelength,
frequency (v) = reciprocal of the time period i.e. v =1/T
V = speed,
v = frequency,
λ = wavelength,
frequency (v) = reciprocal of the time period i.e. v =1/T
To the nearest order of magnitude, how many times greater than the speed of sound is the speed of light?- a)104
- b)1012
- c)108
- d)106
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
To the nearest order of magnitude, how many times greater than the speed of sound is the speed of light?
a)
104
b)
1012
c)
108
d)
106
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Speed of sound in air is 343 m/s or we can say approx 300m/s
And speed of light is approx 300,000,000 m/s
Clearly the ratio is 106
And speed of light is approx 300,000,000 m/s
Clearly the ratio is 106
Waves associated with moving protons, electrons, neutrons, atoms are known as- a)none of these
- b)Gamma rays
- c)Matter waves
- d)Electromagnetic waves
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Waves associated with moving protons, electrons, neutrons, atoms are known as
a)
none of these
b)
Gamma rays
c)
Matter waves
d)
Electromagnetic waves

|
Vik. Singh answered |
If they are associated with matter waves then what about electromagnetic waves..?
... I'm so confused now :(
Velocity of sound in air is 300 m/s. Then the distance between two successive nodes of a stationary wave of frequency 1000 Hz is.- a)20cm
- b)15 cm
- c)30cm
- d)10 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Velocity of sound in air is 300 m/s. Then the distance between two successive nodes of a stationary wave of frequency 1000 Hz is.
a)
20cm
b)
15 cm
c)
30cm
d)
10 cm
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Velocity of sound in air= 300m/s =300×100=30000 cm/s
And frequency = 1000 hz
So, wavelength = Velocity/frequency
= 30000/1000= 30
Distance = wavelength/2
=30/2 = 15
And frequency = 1000 hz
So, wavelength = Velocity/frequency
= 30000/1000= 30
Distance = wavelength/2
=30/2 = 15
A fork of unknown frequency when sounded with another fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats/sec. The first fork is loaded with wax. It again produces 4 beats/sec. When sounded together with the fork of 256 Hz frequency, then the frequency of first tuning fork is- a)252 Hz
- b)260Hz
- c)None of these
- d)252 or 260 Hz
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A fork of unknown frequency when sounded with another fork of frequency 256 Hz produces 4 beats/sec. The first fork is loaded with wax. It again produces 4 beats/sec. When sounded together with the fork of 256 Hz frequency, then the frequency of first tuning fork is
a)
252 Hz
b)
260Hz
c)
None of these
d)
252 or 260 Hz
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
After waxing the frequency of the tuning fork decreases and so the initial frequency must be higher so as to decrease it below 256 Hz in order to give 4 beats/sec.
Two harmonic waves traveling on a string in the same direction both have a frequency of 100 Hz, a wavelenqth of 2.0cm, and amplitude of 0.020 m. In addition, they overlap each other. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave if the original waves differ in phase by Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’./6?- a)3.5 cm
- b)4.2 cm
- c)3.7 cm
- d)3.9 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two harmonic waves traveling on a string in the same direction both have a frequency of 100 Hz, a wavelenqth of 2.0cm, and amplitude of 0.020 m. In addition, they overlap each other. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave if the original waves differ in phase by Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’./6?
a)
3.5 cm
b)
4.2 cm
c)
3.7 cm
d)
3.9 cm
|
|
Rajeev Nair answered |
Question:
Two harmonic waves traveling on a string in the same direction both have a frequency of 100 Hz, a wavelength of 2.0 cm, and amplitude of 0.020 m. In addition, they overlap each other. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave if the original waves differ in phase by 6π?
Solution:
Given parameters:
Frequency of each wave = 100 Hz
Wavelength of each wave = 2.0 cm
Amplitude of each wave = 0.020 m
Phase difference between the waves = 6π
To find: Amplitude of the resultant wave
We know that the displacement of a wave is given by the equation:
y = A sin(kx - ωt + φ)
where, A = amplitude of the wave, k = wave number, x = position, ω = angular frequency, t = time, and φ = phase constant.
For two waves with the same frequency and wavelength traveling in the same direction, the wave number and angular frequency are the same, and the displacement equation becomes:
y1 = A sin(kx - ωt + φ1)
y2 = A sin(kx - ωt + φ2)
where, φ1 and φ2 are the phase constants of the two waves.
The resultant wave is obtained by adding the two waves:
y = y1 + y2
= A sin(kx - ωt + φ1) + A sin(kx - ωt + φ2)
= 2A cos((φ1 - φ2)/2) sin(kx - ωt + (φ1 + φ2)/2)
where, cos((φ1 - φ2)/2) is the amplitude of the resultant wave.
Given that the phase difference between the waves is 6π, we have:
φ1 - φ2 = 6π
cos((φ1 - φ2)/2) = cos(3π) = -1
Substituting the given values, we get:
Amplitude of the resultant wave = 2(0.020) (-1) = -0.040 m
However, amplitude is always positive, so we take the absolute value:
Amplitude of the resultant wave = 0.040 m
Therefore, the amplitude of the resultant wave is 0.040 m.
Two harmonic waves traveling on a string in the same direction both have a frequency of 100 Hz, a wavelength of 2.0 cm, and amplitude of 0.020 m. In addition, they overlap each other. What is the amplitude of the resultant wave if the original waves differ in phase by 6π?
Solution:
Given parameters:
Frequency of each wave = 100 Hz
Wavelength of each wave = 2.0 cm
Amplitude of each wave = 0.020 m
Phase difference between the waves = 6π
To find: Amplitude of the resultant wave
We know that the displacement of a wave is given by the equation:
y = A sin(kx - ωt + φ)
where, A = amplitude of the wave, k = wave number, x = position, ω = angular frequency, t = time, and φ = phase constant.
For two waves with the same frequency and wavelength traveling in the same direction, the wave number and angular frequency are the same, and the displacement equation becomes:
y1 = A sin(kx - ωt + φ1)
y2 = A sin(kx - ωt + φ2)
where, φ1 and φ2 are the phase constants of the two waves.
The resultant wave is obtained by adding the two waves:
y = y1 + y2
= A sin(kx - ωt + φ1) + A sin(kx - ωt + φ2)
= 2A cos((φ1 - φ2)/2) sin(kx - ωt + (φ1 + φ2)/2)
where, cos((φ1 - φ2)/2) is the amplitude of the resultant wave.
Given that the phase difference between the waves is 6π, we have:
φ1 - φ2 = 6π
cos((φ1 - φ2)/2) = cos(3π) = -1
Substituting the given values, we get:
Amplitude of the resultant wave = 2(0.020) (-1) = -0.040 m
However, amplitude is always positive, so we take the absolute value:
Amplitude of the resultant wave = 0.040 m
Therefore, the amplitude of the resultant wave is 0.040 m.
In an interference arrangement similar to Young's double-slit experiment, the slits S1 & S2 are illuminated with coherent microwave sources, each of frequency 106 Hz. The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by a distance d = 150.0 m. The intensity I(q) is measured as a function of q, where q is defined as shown. If I0 is the maximum intensity then I(q) for 0 £ q £ 90° is given by 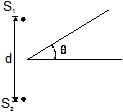
- a) I(q) =
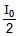 for q = 30º
for q = 30º - b)I(q) =
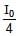 for q = 90º
for q = 90º - c) I(q) = I0 for q = 0º
- d)I(q) is constant for all values of q
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an interference arrangement similar to Young's double-slit experiment, the slits S1 & S2 are illuminated with coherent microwave sources, each of frequency 106 Hz. The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by a distance d = 150.0 m. The intensity I(q) is measured as a function of q, where q is defined as shown. If I0 is the maximum intensity then I(q) for 0 £ q £ 90° is given by
a)
I(q) = 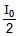 for q = 30º
for q = 30º
b)
I(q) = 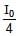 for q = 90º
for q = 90º
c)
I(q) = I0 for q = 0º
d)
I(q) is constant for all values of q

|
Lohit Matani answered |
I=I0cos2(πdtanθ/ λ)/
= I0cos2(πx150xtanθ/3x(108/106)
=I0cos2(πtanθ/2)
θ=30o
I= I0cos2 ((π/2√3)
I=I0/2
θ=0
I=I0cos2(0) [cos0=1]
I= I0
= I0cos2(πx150xtanθ/3x(108/106)
=I0cos2(πtanθ/2)
θ=30o
I= I0cos2 ((π/2√3)
I=I0/2
θ=0
I=I0cos2(0) [cos0=1]
I= I0
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 6500 Å and 5200 Å is used to obtain interference fringes in Young's double slit experiment. The distance between slits is 2mm and the distance of screen from slits is 120 cm. What is the least distance from central maximum where the bright due to both wavelength coincide ?- a)0.156 cm
- b)0.312 cm
- c)0.078 cm
- d)0.468 cm
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths 6500 Å and 5200 Å is used to obtain interference fringes in Young's double slit experiment. The distance between slits is 2mm and the distance of screen from slits is 120 cm. What is the least distance from central maximum where the bright due to both wavelength coincide ?
a)
0.156 cm
b)
0.312 cm
c)
0.078 cm
d)
0.468 cm
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
If n is least number of fringes of λ1(=6500A∘) which are coincident with (n+1) of smaller wavelength

also β=λD/d
substituting values for wavelength,D and d we get β = 0.039cm
So,
Hence b is the correct answer.

also β=λD/d
substituting values for wavelength,D and d we get β = 0.039cm
So,

Hence b is the correct answer.
In a standard YDSE appratus a thin film (m = 1.5, t = 2.1 mm) is placed in front of upper slit. How far above or below the centre point of the screen are two nearest maxima located ? Take D = 1 m, d = 1mm, l = 4500 Å. (Symbols have usual meaning)- a) 1.5 mm (
- b)0.6 mm
- c)0.15 mm
- d)0.3 mm
Correct answer is option 'C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a standard YDSE appratus a thin film (m = 1.5, t = 2.1 mm) is placed in front of upper slit. How far above or below the centre point of the screen are two nearest maxima located ? Take D = 1 m, d = 1mm, l = 4500 Å. (Symbols have usual meaning)
a)
1.5 mm (
b)
0.6 mm
c)
0.15 mm
d)
0.3 mm
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |

There are three sources of sound of equal intensities with frequencies 400, 401 and 402 Hz. The number of beats per seconds is- a)3
- b)1.0
- c)0
- d)2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
There are three sources of sound of equal intensities with frequencies 400, 401 and 402 Hz. The number of beats per seconds is
a)
3
b)
1.0
c)
0
d)
2
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Resultant displacement of the wave by these three wave is
y=asin2π400t+asin2π401t+asin2π402t
y=a(1+2cos2πt)sin2π401t
So the resultant magnitude a(1+2cos2πt) has a maximum when,
cos2πt=1
or, t=0,1,2...
The time interval between two successive maximum is 1 sec.
So beat frequency is 1sec.
y=asin2π400t+asin2π401t+asin2π402t
y=a(1+2cos2πt)sin2π401t
So the resultant magnitude a(1+2cos2πt) has a maximum when,
cos2πt=1
or, t=0,1,2...
The time interval between two successive maximum is 1 sec.
So beat frequency is 1sec.
Maximum destructive inference between two waves occurs when the waves are out of the phase by- a)π/2radians
- b)π radians
- c)π/3 radians
- d)π/4 radians
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Maximum destructive inference between two waves occurs when the waves are out of the phase by
a)
π/2radians
b)
π radians
c)
π/3 radians
d)
π/4 radians
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Destructive interference occurs when the maxima of two waves are 180 degrees out of phase: a positive displacement of one wave is cancelled exactly by a negative displacement of the other wave. The amplitude of the resulting wave is zero. ... The dark regions occur whenever the waves destructively interfere.
The waves on the surface of water are of two kinds:.- a)capillary waves and gravity waves
- b)capillary waves and sound waves
- c)sound waves and gravity waves
- d)seismic waves and cosmic waves
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The waves on the surface of water are of two kinds:.
a)
capillary waves and gravity waves
b)
capillary waves and sound waves
c)
sound waves and gravity waves
d)
seismic waves and cosmic waves

|
Srishti Roy answered |
Explanation:
As capillary & gravity waves are elastic waves or mechanical waves which require medium for their propagation.
Hence they are using the elastic behaviour of water.
Hence
The waves on the surface of water are of two kinds:
capillary waves and gravity waves
Longitudinal waves cannot be propagated through- a)a liquid
- b)a solid
- c)vacuum
- d)a gas
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Longitudinal waves cannot be propagated through
a)
a liquid
b)
a solid
c)
vacuum
d)
a gas
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Because longitudinal waves are the mechanical waves that need a medium to propagate such as air, gas, solid etc. but these are not available in vacuum, so this wave can't propagate in vacuum.
If a star emitting orange light moves away from the earth, its color will- a)appear yellow
- b)turns gradually blue
- c)remain the same
- d)appear red
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If a star emitting orange light moves away from the earth, its color will
a)
appear yellow
b)
turns gradually blue
c)
remain the same
d)
appear red
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
The faster a star moves towards the earth, the more its light is shifted to higher frequencies. In contrast, if a star is moving away from the earth, its light is shifted to lower frequencies on the color spectrum (towards the orange/red/infrared/microwave/radio end of the spectrum).
Y (x,t) = 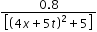 Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’. represents a moving pulse where X and y are n metres and t in second. Then which of the following dose not hold true?
Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’. represents a moving pulse where X and y are n metres and t in second. Then which of the following dose not hold true?- a)its maximum displacement is 0.16 m
- b)pulse is moving positive X-direction
- c)it is a symmetric pulse
- d)in 2 s it will travel a distance of 2.5 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Y (x,t) = 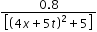 Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’. represents a moving pulse where X and y are n metres and t in second. Then which of the following dose not hold true?
Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’. represents a moving pulse where X and y are n metres and t in second. Then which of the following dose not hold true?
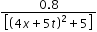 Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’. represents a moving pulse where X and y are n metres and t in second. Then which of the following dose not hold true?
Syntax error from line 1 column 49 to line 1 column 73. Unexpected ‘mathsize’. represents a moving pulse where X and y are n metres and t in second. Then which of the following dose not hold true?a)
its maximum displacement is 0.16 m
b)
pulse is moving positive X-direction
c)
it is a symmetric pulse
d)
in 2 s it will travel a distance of 2.5 m
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
t = 0 & x = 0
y = 0.16 m
ymax = 0.16 m
Pulse is symmetric because y (x) = y (-x)
t = 1s
x=-1.25m
y is again 0.16m
Therefore speed is 1.25m/s
So it travels 2.5 m in 2 sec
y = 0.16 m
ymax = 0.16 m
Pulse is symmetric because y (x) = y (-x)
t = 1s
x=-1.25m
y is again 0.16m
Therefore speed is 1.25m/s
So it travels 2.5 m in 2 sec
The quantity similar to extension or compression of the spring in sound wave propagation (air) is- a)the change in air density
- b)the change in air composition
- c)the change in air particles
- d)the change in air humidity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The quantity similar to extension or compression of the spring in sound wave propagation (air) is
a)
the change in air density
b)
the change in air composition
c)
the change in air particles
d)
the change in air humidity

|
Saumya Ahuja answered |
Explanation:As in air wave propagates in the form of compression (increase in density of air) and rarefaction (decrease in density of air).
When sound travels from air to water the quantity that remains unchanged is- a)wavelength
- b)frequency
- c)speed
- d)intensity
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When sound travels from air to water the quantity that remains unchanged is
a)
wavelength
b)
frequency
c)
speed
d)
intensity
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Because, frequency of a wave depend on source
V1/λ1 =V2/λ2 as frequency is constant
V1 - velocity of sound wave in air
V2 - velocity of sound wave in water
V1/λ1 =V2/λ2 as frequency is constant
V1 - velocity of sound wave in air
V2 - velocity of sound wave in water
When we make a mobile telephone call to a friend- a)the friend's mobile receives electromagnetic waves containing your audio
- b)the friend's mobile receives acoustic waves containing your audio
- c)the friend's mobile receives gravity waves containing your audio
- d)the friend's mobile generates possible electrical signals
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When we make a mobile telephone call to a friend
a)
the friend's mobile receives electromagnetic waves containing your audio
b)
the friend's mobile receives acoustic waves containing your audio
c)
the friend's mobile receives gravity waves containing your audio
d)
the friend's mobile generates possible electrical signals

|
Kritika Bajaj answered |
Explanation:Because mobile communication is a space communication and in space communication basically electromagnetic waves are used (as carrier waves as in case of radio communication) because of the modulation ( frequency, amplitude) operations which can be performed on EM waves. Thus when our friend receives the call, he also receives EM waves which is the carrier of our audio signals.
The velocity of sound in gas in which two waves of wavelength 1.0 m and 0.01 m produces 4 beats/sec. is- a)360 m/s
- b)1010 m/s
- c)404 m/s
- d)440 m/s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The velocity of sound in gas in which two waves of wavelength 1.0 m and 0.01 m produces 4 beats/sec. is
a)
360 m/s
b)
1010 m/s
c)
404 m/s
d)
440 m/s
|
|
Ruchi Dasgupta answered |
Beats = |f1 – f2| where f1 and f2 are the frequencies
Now, f1 = v/λ1 and f2 = v/λ2
So, 4 = |v (1/1- 1/0.01)|
v = 0.0404 m/s
Now, f1 = v/λ1 and f2 = v/λ2
So, 4 = |v (1/1- 1/0.01)|
v = 0.0404 m/s
The speed of transverse waves in a string depends on:- a)Pressure on the string
- b)tension in it and its linear mass density
- c)Shear modulus and linear mass density
- d)Young’s modulus and linear mass density
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The speed of transverse waves in a string depends on:
a)
Pressure on the string
b)
tension in it and its linear mass density
c)
Shear modulus and linear mass density
d)
Young’s modulus and linear mass density
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
For a string v = √(T/μ)
Speed of sound in air is 350 m/s. An engine blows a whistle of frequency of 1200 Hz, it is approaching the observer with velocity 50 m/s. The apparent frequency as heard by the observer is- a)300 Hz
- b)1400 Hz
- c)1600 Hz
- d)1050 Hz
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Speed of sound in air is 350 m/s. An engine blows a whistle of frequency of 1200 Hz, it is approaching the observer with velocity 50 m/s. The apparent frequency as heard by the observer is
a)
300 Hz
b)
1400 Hz
c)
1600 Hz
d)
1050 Hz

|
Anonymous answered |

The disc of a siren containing 60 holes rotates at a constant speed of 360 rpm. The emitted sound is in unison with a tuning fork of frequency. - a)10Hz
- b)216Hz
- c)60Hz
- d)360Hz
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The disc of a siren containing 60 holes rotates at a constant speed of 360 rpm. The emitted sound is in unison with a tuning fork of frequency.
a)
10Hz
b)
216Hz
c)
60Hz
d)
360Hz
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Frequency of revolution of disc = 360 rpm = 360 / 60rps = 60rps
Frequency of emitted sound = 6 × No.of holes
= 6 ×60 = 360Hz.
Frequency of emitted sound = 6 × No.of holes
= 6 ×60 = 360Hz.
Two waves of wavelength 1m & 1.01 m produce 10 beats in 3 sec. The velocity of sound in a gas is about- a)300 m/s
- b)337 m/sec
- c)33 m/s
- d)1120 m/sec
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Two waves of wavelength 1m & 1.01 m produce 10 beats in 3 sec. The velocity of sound in a gas is about
a)
300 m/s
b)
337 m/sec
c)
33 m/s
d)
1120 m/sec
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
As we know wavelength= spped/frequency
Wavelength 1= 1m
Wavelength 2= 1.01m
=> 1=v/f1
f1= v
1.01=v/f2
f2= v/1.01
Now beat is 19 beats /3 sec
f1 - f2= 10/3
Solving equations we get
v=336.6m/s
Two sinusoidal waves on the same string exhibit interference, adding or cancelling according to the principle of superposition. If the two are travelling in the same direction and have the same amplitude a and frequency but differ in phase by a phase constant φφ, the result is a single wave with the same frequency ω:If φ = 0 or an integral multiple of 2 π- a)the waves are exactly in phase and the interference is constructive.
- b)the waves are exactly out of phase and the interference is desstructive.
- c)the waves are exactly in phase and the interference is destructive.
- d)the waves are exactly out of phase and the interference is constructive.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two sinusoidal waves on the same string exhibit interference, adding or cancelling according to the principle of superposition. If the two are travelling in the same direction and have the same amplitude a and frequency but differ in phase by a phase constant φφ, the result is a single wave with the same frequency ω:If φ = 0 or an integral multiple of 2 π
a)
the waves are exactly in phase and the interference is constructive.
b)
the waves are exactly out of phase and the interference is desstructive.
c)
the waves are exactly in phase and the interference is destructive.
d)
the waves are exactly out of phase and the interference is constructive.
|
|
Jhanvi Chakraborty answered |
Let the waves be
y1 = Asin(wt)
y2 = Asin(wt + φ)
If φ = 0 or 2nπ then the waves are exactly in phase and the interference is constructive.
Hence A is the correct answer.
y1 = Asin(wt)
y2 = Asin(wt + φ)
If φ = 0 or 2nπ then the waves are exactly in phase and the interference is constructive.
Hence A is the correct answer.
Speed of the sound in a perfectly rigid rod would be- a)Oscillating
- b)Damp
- c)Infinite
- d)Dubbed
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Speed of the sound in a perfectly rigid rod would be
a)
Oscillating
b)
Damp
c)
Infinite
d)
Dubbed
|
|
Sonal Dey answered |
Speed of Sound in a Rigid Rod
Rigid rods are considered to be perfectly elastic and do not undergo any deformation when a force is applied to them. When a force is applied on one end of a rigid rod, the rod undergoes an instantaneous compression and the compression wave travels through the rod at a certain speed. This speed of sound in a rigid rod is given by the formula:
v = √(E/ρ)
where v is the speed of sound, E is Young's modulus of the material of the rod and ρ is the density of the material.
As the rod is perfectly rigid, its Young's modulus is infinite and its density is non-zero, hence the speed of sound in a perfectly rigid rod is infinite. This means that any compression wave applied to one end of the rod would travel instantaneously to the other end of the rod.
Option C is, therefore, the correct answer.
Rigid rods are considered to be perfectly elastic and do not undergo any deformation when a force is applied to them. When a force is applied on one end of a rigid rod, the rod undergoes an instantaneous compression and the compression wave travels through the rod at a certain speed. This speed of sound in a rigid rod is given by the formula:
v = √(E/ρ)
where v is the speed of sound, E is Young's modulus of the material of the rod and ρ is the density of the material.
As the rod is perfectly rigid, its Young's modulus is infinite and its density is non-zero, hence the speed of sound in a perfectly rigid rod is infinite. This means that any compression wave applied to one end of the rod would travel instantaneously to the other end of the rod.
Option C is, therefore, the correct answer.
In what types of waves can we find capillary waves and gravity waves?- a)Water waves
- b)Gases
- c)Sound waves
- d)x-rays
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In what types of waves can we find capillary waves and gravity waves?
a)
Water waves
b)
Gases
c)
Sound waves
d)
x-rays
|
|
Madhavan Chatterjee answered |
Types of Waves
Waves are disturbances that propagate through space and time, usually accompanied by the transfer of energy. There are different types of waves, such as mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves, and matter waves.
Capillary Waves
Capillary waves are a type of waves that occur at the interface of two fluids, such as air and water or water and oil. They are caused by the surface tension that exists between the fluids, which tends to minimize the surface area of the interface. Capillary waves have a short wavelength and a high frequency, and they are usually visible as ripples on the surface of a liquid.
Gravity Waves
Gravity waves are a type of waves that occur in a fluid or a medium under the influence of gravity. They are caused by the buoyancy force that exists between the fluid or medium and the surrounding environment, which tends to restore the equilibrium state. Gravity waves have a long wavelength and a low frequency, and they are usually visible as waves on the surface of a liquid, such as the ocean or a lake.
Water Waves
Water waves are a type of mechanical waves that propagate through water. They can be classified into two main types, namely surface waves and internal waves. Surface waves are waves that occur at the surface of the water, such as capillary waves and gravity waves. Internal waves are waves that occur within the water, such as waves that occur at the interface between layers of different densities.
Conclusion
Capillary waves and gravity waves can be found in water waves, which are a type of mechanical waves that propagate through water. Capillary waves occur at the interface of two fluids, such as air and water or water and oil, while gravity waves occur in a fluid or a medium under the influence of gravity. Water waves can be classified into two main types, namely surface waves and internal waves.
Waves are disturbances that propagate through space and time, usually accompanied by the transfer of energy. There are different types of waves, such as mechanical waves, electromagnetic waves, and matter waves.
Capillary Waves
Capillary waves are a type of waves that occur at the interface of two fluids, such as air and water or water and oil. They are caused by the surface tension that exists between the fluids, which tends to minimize the surface area of the interface. Capillary waves have a short wavelength and a high frequency, and they are usually visible as ripples on the surface of a liquid.
Gravity Waves
Gravity waves are a type of waves that occur in a fluid or a medium under the influence of gravity. They are caused by the buoyancy force that exists between the fluid or medium and the surrounding environment, which tends to restore the equilibrium state. Gravity waves have a long wavelength and a low frequency, and they are usually visible as waves on the surface of a liquid, such as the ocean or a lake.
Water Waves
Water waves are a type of mechanical waves that propagate through water. They can be classified into two main types, namely surface waves and internal waves. Surface waves are waves that occur at the surface of the water, such as capillary waves and gravity waves. Internal waves are waves that occur within the water, such as waves that occur at the interface between layers of different densities.
Conclusion
Capillary waves and gravity waves can be found in water waves, which are a type of mechanical waves that propagate through water. Capillary waves occur at the interface of two fluids, such as air and water or water and oil, while gravity waves occur in a fluid or a medium under the influence of gravity. Water waves can be classified into two main types, namely surface waves and internal waves.
What causes the rolling sound of thunder?- a)Reflection of waves
- b)Air currents
- c)Air currents
- d)Refraction of waves
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What causes the rolling sound of thunder?
a)
Reflection of waves
b)
Air currents
c)
Air currents
d)
Refraction of waves
|
|
Pranavi Kulkarni answered |
The air is not of uniform density as we go upwards. as we go upwards there is a gradual decrease in air density which results in refraction thereby leading to the rolling sound of thunder.
Properties of a kind of wave are given below. Identify the type of wavei. Wave can not be detected by human ear
ii. Velocity of wave in free space is 3x108m/s
iii. Velocity is not effected by temperature
iv. Waves can travel through vacuum- a)Radio waves
- b)Water waves
- c)Sound waves
- d)Tidal waves
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Properties of a kind of wave are given below. Identify the type of wave
i. Wave can not be detected by human ear
ii. Velocity of wave in free space is 3x108m/s
iii. Velocity is not effected by temperature
iv. Waves can travel through vacuum
ii. Velocity of wave in free space is 3x108m/s
iii. Velocity is not effected by temperature
iv. Waves can travel through vacuum
a)
Radio waves
b)
Water waves
c)
Sound waves
d)
Tidal waves
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
These are the properties of radio waves. No possible explanation.
In a transverse wave, the constituents of the medium oscillate ___________to the direction of wave propagation and in a longitudinal wave they oscillate ________to the direction of propagation.- a)perpendicular, parallel
- b)parallel, perpendicular
- c)parallel, parallel
- d)perpendicular, perpendicular
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a transverse wave, the constituents of the medium oscillate ___________to the direction of wave propagation and in a longitudinal wave they oscillate ________to the direction of propagation.
a)
perpendicular, parallel
b)
parallel, perpendicular
c)
parallel, parallel
d)
perpendicular, perpendicular

|
Seblewongel Girma answered |
Both transverse and longitudinal waves are mechanical waves where they need material medium to propagate. the motion of transverse wave is perpendicular to the direction of the wave motion , and parallel for longitudinal waves.
Which instrument work on the basis of reflection of sound waves?- a)Telescope
- b)Stethoscope
- c)Microscope
- d)Horoscope
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which instrument work on the basis of reflection of sound waves?
a)
Telescope
b)
Stethoscope
c)
Microscope
d)
Horoscope
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
Stethoscope works on the basis of reflection of sound waves.
In wave propagation- a)there is no flow of matter and there is no movement of disturbance
- b)there is flow of matter and there is no movement of disturbance
- c)there is flow of matter but there is movement of disturbance
- d)there is no flow of matter but there is movement of disturbance
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In wave propagation
a)
there is no flow of matter and there is no movement of disturbance
b)
there is flow of matter and there is no movement of disturbance
c)
there is flow of matter but there is movement of disturbance
d)
there is no flow of matter but there is movement of disturbance

|
Shanaya Tiwari answered |
Wave Propagation
Wave propagation refers to the transmission of energy through a medium via disturbances in the medium. Waves can be classified into mechanical waves (require a medium to propagate) and electromagnetic waves (can propagate through a vacuum).
Flow of Matter and Movement of Disturbance
- In wave propagation, there is no flow of matter. This means that the particles of the medium do not move along with the wave. Instead, they oscillate about their equilibrium positions.
- However, there is movement of disturbance. The disturbance created by the wave travels through the medium, causing the particles to oscillate but not to flow in the direction of the wave.
Characteristics of Wave Propagation
- Waves transfer energy from one point to another without the physical transfer of matter.
- The disturbance created by a wave propagates through the medium by causing particles in the medium to oscillate.
- Different types of waves (such as sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves) exhibit wave propagation characteristics.
In conclusion, in wave propagation, there is no flow of matter but there is movement of disturbance. This movement of disturbance allows energy to be transmitted through the medium without the physical displacement of matter.
Wave propagation refers to the transmission of energy through a medium via disturbances in the medium. Waves can be classified into mechanical waves (require a medium to propagate) and electromagnetic waves (can propagate through a vacuum).
Flow of Matter and Movement of Disturbance
- In wave propagation, there is no flow of matter. This means that the particles of the medium do not move along with the wave. Instead, they oscillate about their equilibrium positions.
- However, there is movement of disturbance. The disturbance created by the wave travels through the medium, causing the particles to oscillate but not to flow in the direction of the wave.
Characteristics of Wave Propagation
- Waves transfer energy from one point to another without the physical transfer of matter.
- The disturbance created by a wave propagates through the medium by causing particles in the medium to oscillate.
- Different types of waves (such as sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves) exhibit wave propagation characteristics.
In conclusion, in wave propagation, there is no flow of matter but there is movement of disturbance. This movement of disturbance allows energy to be transmitted through the medium without the physical displacement of matter.
Which one is not produced by sound waves in air?- a)Diffraction
- b)Reflection
- c)Refraction
- d)Polarization
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one is not produced by sound waves in air?
a)
Diffraction
b)
Reflection
c)
Refraction
d)
Polarization
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Polarisation is a phenomenon of converting unpolarized light to polarized. It is not done by sound waves.
Travelling or progressive wave- a)does not move from one point of the medium to all others
- b)does not move from one point of the medium to another
- c)does not move from one point of the medium to any other
- d)travels from one point of the medium to another
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Travelling or progressive wave
a)
does not move from one point of the medium to all others
b)
does not move from one point of the medium to another
c)
does not move from one point of the medium to any other
d)
travels from one point of the medium to another

|
Kritika Bajaj answered |
Explanation:As progressive wave means a wave propagating in some onward direction in the medium
Electromagnetic waves are different from sound waves in that- a)they need no medium and are transverse
- b)they need medium and are longitudinal
- c)they need medium and are transverse
- d)they need no medium and are longitudinal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Electromagnetic waves are different from sound waves in that
a)
they need no medium and are transverse
b)
they need medium and are longitudinal
c)
they need medium and are transverse
d)
they need no medium and are longitudinal

|
Rithika Khanna answered |
Explanation:Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, they move perpendicular to the direction of propagation of wave ( the direction in which energy is transferred) and EM waves( Electromagnetic waves) can travel in vacuum, thus doesn't require any medium also.
in the same medium transverse and longitudinal waves- a)travel changing longitudinal wave to transverse wave
- b)travel with different speeds
- c)travel changing transverse wave to longitudinal wave
- d)travel with same speeds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
in the same medium transverse and longitudinal waves
a)
travel changing longitudinal wave to transverse wave
b)
travel with different speeds
c)
travel changing transverse wave to longitudinal wave
d)
travel with same speeds

|
Rithika Khanna answered |
Explanation:
As speed of transverse & longitudinal waves depend on different modulus of elasticity (Young's modulus, Bulk modulus, Modulus of Rigidity) of the medium.
So in the same medium transverse and longitudinal waves
travel with different speeds
y(x,t) = 0.8/[(4x+5t)2+5] represents a moving pulse, where x and y are in meter and t in second. Then- a)pulse is moving in +x direction
- b)in 2s it will travel a distance of 2.5 m
- c)its maximum displacement is 0.16 m
- d)Both B and C.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
y(x,t) = 0.8/[(4x+5t)2+5] represents a moving pulse, where x and y are in meter and t in second. Then
a)
pulse is moving in +x direction
b)
in 2s it will travel a distance of 2.5 m
c)
its maximum displacement is 0.16 m
d)
Both B and C.
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |


In open end organ pipe- a)both odd and even harmonics are produced
- b)none of these
- c)only odd harmonics are produced
- d)only even harmonics are produced
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In open end organ pipe
a)
both odd and even harmonics are produced
b)
none of these
c)
only odd harmonics are produced
d)
only even harmonics are produced
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |
Organ pipes are musical instruments which are used to produce musical sound by blowing air into the pipe. Organ pipes are two types (a) closed organ pipes, closed at one end (b) open organ pipe, open at both ends.
If the distance d is varied, then identify the correct statement- a)The angular width does not change
- b)The fringe width changes in inverse proportion
- c)The positions of all maxima change
- d)The positions of all minima change
Correct answer is option 'B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the distance d is varied, then identify the correct statement
a)
The angular width does not change
b)
The fringe width changes in inverse proportion
c)
The positions of all maxima change
d)
The positions of all minima change
|
|
Shalini Ahuja answered |
Explanation:
When the distance between the slits and the screen is varied, the following changes occur in the interference pattern:
B. Fringe width changes in inverse proportion:
The fringe width is given by the equation:
w = λD/d
Where w is the fringe width, λ is the wavelength of the light, D is the distance between the slits and the screen, and d is the distance between the slits. As the distance D is varied, the fringe width changes in inverse proportion to D. This means that if D is increased, the fringe width will decrease and vice versa.
D. Positions of all minima change:
The positions of the minima in the interference pattern are given by the equation:
y = nλD/d
Where y is the distance from the central maximum to the nth minimum, n is the order of the minimum, and λ, D, and d are the same as before. As the distance D is varied, the positions of all the minima will change. If D is increased, the distance between the minima will increase and vice versa.
Therefore, the correct statements are B and D.
When the distance between the slits and the screen is varied, the following changes occur in the interference pattern:
B. Fringe width changes in inverse proportion:
The fringe width is given by the equation:
w = λD/d
Where w is the fringe width, λ is the wavelength of the light, D is the distance between the slits and the screen, and d is the distance between the slits. As the distance D is varied, the fringe width changes in inverse proportion to D. This means that if D is increased, the fringe width will decrease and vice versa.
D. Positions of all minima change:
The positions of the minima in the interference pattern are given by the equation:
y = nλD/d
Where y is the distance from the central maximum to the nth minimum, n is the order of the minimum, and λ, D, and d are the same as before. As the distance D is varied, the positions of all the minima will change. If D is increased, the distance between the minima will increase and vice versa.
Therefore, the correct statements are B and D.
Matter waves are useful in- a)explaining astronomical phenomenon
- b)explaining gravitational phenomenon
- c)explaining tidal wave phenomenon
- d)explaining quantum mechanical phenomenon
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Matter waves are useful in
a)
explaining astronomical phenomenon
b)
explaining gravitational phenomenon
c)
explaining tidal wave phenomenon
d)
explaining quantum mechanical phenomenon

|
Mrinalini Bose answered |
Explanation:Matter waves are also termed as De Broglie waves because they were initially introduced by him. All matters behave like a wave (during motion) and in there propagation there is action of forces due to collision between the particles, some time torque also exists, hence all the matters waves were consider to be a helpful part for understanding quantum.
A man is watching two trains one leaving and other approaching with equal velocities of 4 m/s. If they sound their whistles each of natural frequency 240 Hz, the number of beats heard per sec by the man will be (velocity of sound in air 320 m/s)- a)12
- b)None of these
- c)6.0
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A man is watching two trains one leaving and other approaching with equal velocities of 4 m/s. If they sound their whistles each of natural frequency 240 Hz, the number of beats heard per sec by the man will be (velocity of sound in air 320 m/s)
a)
12
b)
None of these
c)
6.0
d)
4
|
|
Kavita Joshi answered |
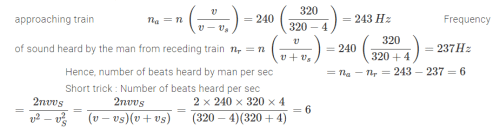
Chapter doubts & questions for Mechanical Waves Behavior - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Mechanical Waves Behavior - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily