All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Physics for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Sound in Motion (Doppler Effect) for EmSAT Achieve Exam
A sound source of frequency 600 Hz is moving towards an observer with velocity 20m/s. The speed of sound is 340m/s. The frequency heard by observer will be- a)630.5hz
- b)30hz
- c)637.5hz
- d)63.5 Hz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A sound source of frequency 600 Hz is moving towards an observer with velocity 20m/s. The speed of sound is 340m/s. The frequency heard by observer will be
a)
630.5hz
b)
30hz
c)
637.5hz
d)
63.5 Hz
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
F(s)/F(l) = [V+V(s)]/[V+V(l)]
V = velocity of sound = 340m/s
V(l) = velocity of listener = 0
F(l) = frequency heard by listener = ?
V(s) = velocity of source = -20m/s (because, it's source to listener)
F(s) = frequency of source = 600hz
By putting these values in the above formula and solving we get,
F(l) = 637.5 Hz.
Hence C is correct.
V = velocity of sound = 340m/s
V(l) = velocity of listener = 0
F(l) = frequency heard by listener = ?
V(s) = velocity of source = -20m/s (because, it's source to listener)
F(s) = frequency of source = 600hz
By putting these values in the above formula and solving we get,
F(l) = 637.5 Hz.
Hence C is correct.
Phenomenon of beats is not used in- a)Tuning musical instruments
- b)Detecting the presence of dangerous gases in mines
- c)Designing low frequency oscillators
- d)Radars for detecting submarines
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Phenomenon of beats is not used in
a)
Tuning musical instruments
b)
Detecting the presence of dangerous gases in mines
c)
Designing low frequency oscillators
d)
Radars for detecting submarines

|
Top Rankers answered |
Radar uses electromagnetic energy pulses. The radio-frequency (rf) energy is transmitted to and reflected from the reflecting object. A small portion of the reflected energy returns to the radar set. This returned energy is called an ECHO. Radar sets use the echo to determine the direction and distance of the reflecting object.
It does not work on phenomena of beats.
It does not work on phenomena of beats.
Pure sound notes from two sources make the molecules of air at a location vibrate simple harmonically in accordance with the equations.
y1 = 0.008 sin (604 n t) and
y2 = 0.007 sin (610 n t) respectively.
The number of beast heard by a person at the location will be:- a)3
- b)1
- c)2
- d)4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Pure sound notes from two sources make the molecules of air at a location vibrate simple harmonically in accordance with the equations.
y1 = 0.008 sin (604 n t) and
y2 = 0.007 sin (610 n t) respectively.
The number of beast heard by a person at the location will be:
y1 = 0.008 sin (604 n t) and
y2 = 0.007 sin (610 n t) respectively.
The number of beast heard by a person at the location will be:
a)
3
b)
1
c)
2
d)
4

|
Tarun Kaushik answered |
Given that two sources produce pure sound notes as follows: y1= 0.008 sin (604 n t) y2= 0.007 sin (610 n t) To find the number of beats heard by a person at the location, we need to first understand the concept of beats.
Beats: When two sound waves of slightly different frequencies are superimposed, we hear a periodic variation in the loudness of sound. This variation is called beats.
The number of beats heard per second is given by the difference between the frequencies of the two sound waves.
Mathematically, the beat frequency is given by fbeat = |f1 - f2| where f1 and f2 are the frequencies of the two sound waves. In this problem, the frequencies of the two sound waves are 604 n and 610 n, respectively.
Therefore, the beat frequency is fbeat = |604 n - 610 n| = 6 n Since the beat frequency is 6 n, the number of beats heard per second is 6. Since each beat corresponds to two sound waves (one from each source), the total number of sound waves heard per second is twice the number of beats, which is 12.
However, the question asks for the number of distinct sounds heard, which is equal to the number of beats. Therefore, the answer is 3 (Option A).
When two tuning forks are sounded together 4 beats are heard per second. One tuning fork is of frequency 346 Hz. When its prong is loaded with a little wax, the number of beats is increased to 6 per second. The frequency of the other fork is:- a)352 Hz
- b)340 Hz
- c)350 Hz
- d)342 Hz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When two tuning forks are sounded together 4 beats are heard per second. One tuning fork is of frequency 346 Hz. When its prong is loaded with a little wax, the number of beats is increased to 6 per second. The frequency of the other fork is:
a)
352 Hz
b)
340 Hz
c)
350 Hz
d)
342 Hz
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Frequency of fork one is 346 Hz.
When the other fork is waxed, the beat is increased.
So, the frequency of other fork is less than the frequency of fork one.
So,
beat = frequency of fork one − frequency of second fork
4=346− Frequency of second fork
Frequency of second fork =350 Hz
When the other fork is waxed, the beat is increased.
So, the frequency of other fork is less than the frequency of fork one.
So,
beat = frequency of fork one − frequency of second fork
4=346− Frequency of second fork
Frequency of second fork =350 Hz
If a source of sound was moving toward a receiver at 1/3 the speed of sound, what would the resulting wavelength be?- a)6 times the emitted wavelength
- b)2/3 of the emitted wavelength
- c)1/3 of the emitted wavelength
- d)Can not be found
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a source of sound was moving toward a receiver at 1/3 the speed of sound, what would the resulting wavelength be?
a)
6 times the emitted wavelength
b)
2/3 of the emitted wavelength
c)
1/3 of the emitted wavelength
d)
Can not be found

|
Ambition Institute answered |
We need to find the resulting wavelength of the sound wave, which can be calculated using the formula: λ' = λ(v +/- vs) / (v + u) Since the source is moving towards the observer, we can use the negative sign for vs: λ' = λ(v - vs) / (v + u) λ' = λ(v - (-1/3)v) / (v + u) λ' = λ(4/3v) / (v + u) We can also use the formula for the speed of the sound wave: v = fλ which gives us: λ = v/f Substituting this value in the above equation, we get: λ' = (4/3)(v/f) / (v + u) λ' = (4/3)f / (3v + u) We know that the velocity of the observer (u) is zero since it is stationary. Thus, the equation simplifies to: λ' = (4/9)f/v This means that the resulting wavelength is 2/3 of the emitted wavelength since: λ' / λ = (4/9f/v) / (f/v) = 4/9 = 0.44 Therefore, the correct answer is option B, 2/3 of the emitted wavelength.
In Doppler effect change in frequency depends on- a)distance between source and listener
- b)speeds of source and listener
- c)density of air
- d)half of distance between source and listener
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In Doppler effect change in frequency depends on
a)
distance between source and listener
b)
speeds of source and listener
c)
density of air
d)
half of distance between source and listener
|
|
Om Desai answered |
The reason for the Doppler effect is that when the source of the waves is moving towards the observer, each successive wave crest is emitted from a position closer to the observer than the crest of the previous wave.
A radar sends a radio signal of frequency 9 x 109 Hz towards an aircraft approaching the radar. If the reflected wave shows a frequency shift of 3 X 103 Hz, the speed with which the aircraft is approaching the radar in m/s is (velocity of radio signal is 3 X 108 m/s).- a)100
- b)150
- c)50
- d)25
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A radar sends a radio signal of frequency 9 x 109 Hz towards an aircraft approaching the radar. If the reflected wave shows a frequency shift of 3 X 103 Hz, the speed with which the aircraft is approaching the radar in m/s is (velocity of radio signal is 3 X 108 m/s).
a)
100
b)
150
c)
50
d)
25
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
Given:
Frequency of radio signal n=9×10 9Hz
Frequency shift n0=3×103Hz
Velocity of radio signal v=3×108m/s
Frequency shift shown by reflected wave is Shift =n−n
=>n−n=(v+u/v−u)n−n
Shift=(2u/v−u)n
Now, putting the given values in Eq. (i), we get,
3×103=(2u/3×10-8−u)9×109
⇒3×108−u=2u×9×109/3×103
=6u×106
⇒6×106u+u=3×108
u(6×106+1)=3×108
u(6000001)=3×108
u=3×108/6000001=49.999≈50m/s
Frequency of radio signal n=9×10 9Hz
Frequency shift n0=3×103Hz
Velocity of radio signal v=3×108m/s
Frequency shift shown by reflected wave is Shift =n−n
=>n−n=(v+u/v−u)n−n
Shift=(2u/v−u)n
Now, putting the given values in Eq. (i), we get,
3×103=(2u/3×10-8−u)9×109
⇒3×108−u=2u×9×109/3×103
=6u×106
⇒6×106u+u=3×108
u(6×106+1)=3×108
u(6000001)=3×108
u=3×108/6000001=49.999≈50m/s
If the source of sound moves at the same speed or faster than speed of the wave then it results in- a)Doppler effect
- b)Beats
- c)Shock waves
- d)Refraction of sound
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If the source of sound moves at the same speed or faster than speed of the wave then it results in
a)
Doppler effect
b)
Beats
c)
Shock waves
d)
Refraction of sound
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The Doppler Effect is observed whenever the speed of the source is moving slower than the speed of waves. But if the source actually moves at the same speed as or faster than the waves, a different phenomenon is observed. This phenomenon is known as Shock waves or Sonic Booms.
Two sound sources fixed at a given distance apart are emitting sound each of wavelength λ. A Listener moves with a velocity v0 along the line joining the two sources , the number of beats heard by him per second is- a)4v0/λ
- b)v0/3λ
- c)v0/2λ
- d)2v0/λ
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two sound sources fixed at a given distance apart are emitting sound each of wavelength λ. A Listener moves with a velocity v0 along the line joining the two sources , the number of beats heard by him per second is
a)
4v0/λ
b)
v0/3λ
c)
v0/2λ
d)
2v0/λ

|
Jasvir Special answered |
A
Two trains A and B approach a station from opposite sides, sounding their whistles. A stationary observer on the platform hears no beats. If the velocities of A and B are 15 m/s and 30 m/s respectively and the real frequency of the whistle of B is 600 Hz, the real frequency of the whistle of A is (Velocity of sound = 330 m/s).- a)660 Hz
- b)600 Hz
- c)570 Hz
- d)630 Hz
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two trains A and B approach a station from opposite sides, sounding their whistles. A stationary observer on the platform hears no beats. If the velocities of A and B are 15 m/s and 30 m/s respectively and the real frequency of the whistle of B is 600 Hz, the real frequency of the whistle of A is (Velocity of sound = 330 m/s).
a)
660 Hz
b)
600 Hz
c)
570 Hz
d)
630 Hz
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
When no beats is listened at the station thus we get the relative frequencies of both the trains are the same.
Hence the relative frequency of the train B is 600 (330/300) = 660
similarly the relative frequency of train A is f(330/315) = 660
Hence we get f = 630Hz
Hence the relative frequency of the train B is 600 (330/300) = 660
similarly the relative frequency of train A is f(330/315) = 660
Hence we get f = 630Hz
Time interval between two successive maxima of sound waves with frequencies v1 and v2 is given by- a)v1/v2
- b)1/ (v1 - v2)
- c)v1 = v2 = 0
- d)v1 - v2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Time interval between two successive maxima of sound waves with frequencies v1 and v2 is given by
a)
v1/v2
b)
1/ (v1 - v2)
c)
v1 = v2 = 0
d)
v1 - v2
|
|
Nandini Iyer answered |
As we know time interval will have dimensions of time so check in option for dimension of time.
Dimensions of v is "per second" or [T-1]
Dimensions of v is "per second" or [T-1]
Doppler’s effect in sound is:- a)Superimposing
- b)Asymmetrical
- c)Infinite
- d)Symmetrical
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Doppler’s effect in sound is:
a)
Superimposing
b)
Asymmetrical
c)
Infinite
d)
Symmetrical

|
Ramesh Chand answered |
Sound wave require a material medium for their propagation. Therefore we say that the Doppler effect in sound is asymmetric. Hence option B is the right answer.
A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 Hz and above is approaching a stationary person with speed v ms-1. The velocity of sound in air is 300 ms-1. If the person can hear frequencies up to 10000 Hz, the maximum value of v upto which he can the whistle is- a)30√2 ms-1
- b)15 ms-1
- c)15/√2 ms-1
- d)30 ms-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 Hz and above is approaching a stationary person with speed v ms-1. The velocity of sound in air is 300 ms-1. If the person can hear frequencies up to 10000 Hz, the maximum value of v upto which he can the whistle is
a)
30√2 ms-1
b)
15 ms-1
c)
15/√2 ms-1
d)
30 ms-1
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
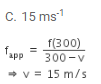
On adding two sine waves that are exactly the same, what would be the result?- a)an identical sine wave with half the amplitude
- b)an identical sine wave with double the frequency
- c)an identical sine wave
- d)an identical sine wave with double the amplitude
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
On adding two sine waves that are exactly the same, what would be the result?
a)
an identical sine wave with half the amplitude
b)
an identical sine wave with double the frequency
c)
an identical sine wave
d)
an identical sine wave with double the amplitude
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
According to the Principle of Superposition, if the particle of a medium is given an order (i.e. of oscillating sinusoidally) and then another order (similar or different), the particle simply adds the two orders vectorially (i.e. by vector method), and then oscillates by the amplitude of the resultant vector.
So if the particle of a medium is given two similar orders (i.e., both the sine waves having the same amplitude, say A) then the particle will oscillate with an amplitude, 2A, i.e., the amplitude will be doubled.
So if the particle of a medium is given two similar orders (i.e., both the sine waves having the same amplitude, say A) then the particle will oscillate with an amplitude, 2A, i.e., the amplitude will be doubled.
Two tuning forks are struck and the sounds from each reach your ears at the same time. One sound has a frequency of 256 Hz, and the second sound has a frequency of 258 Hz. The underlying beat frequency is:- a)257 Hz
- b)258 Hz
- c)2.0 Hz
- d)256 Hz
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Two tuning forks are struck and the sounds from each reach your ears at the same time. One sound has a frequency of 256 Hz, and the second sound has a frequency of 258 Hz. The underlying beat frequency is:
a)
257 Hz
b)
258 Hz
c)
2.0 Hz
d)
256 Hz
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
The beat frequency is always equal to the difference in frequency of the two notes that interfere to produce the beats. So if two sound waves with frequencies of 258 Hz and 256 Hz are played simultaneously, a beat frequency of 2 Hz will be detected.
For the formation of distinct beats, the frequencies of two sources of sound should be- a)Nearly equal say less than 10
- b)One frequency should be half of other
- c)Of greater variation say 100
- d)Double of each other
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the formation of distinct beats, the frequencies of two sources of sound should be
a)
Nearly equal say less than 10
b)
One frequency should be half of other
c)
Of greater variation say 100
d)
Double of each other
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
For the formation of distinct beats, frequencies of two sources of sound should be nearly equal, i.e., difference in frequencies of two sources must be small, say less than 10. The impression of sound heard by ow ears persists on our mind for 1 /10th of a second. If another sound is heard before (1 /10) second passes, the impressions of the two sounds mix up and our mind cannot distinguish between the two. In order to hear distinct beats, time interval between two successive beats must be greater than 1 /10 second. Therefore, frequency of beats must be less than 1 0,i.e., number of beats/sec, which is equal to difference in frequencies of two sources must be less than 10. Hence the two sources should be of nearly equal frequencies.
Which medical instrument uses doppler effect?- a)Echocardiography
- b)Ultrasound machine
- c)Stethoscope
- d)MRI machine
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which medical instrument uses doppler effect?
a)
Echocardiography
b)
Ultrasound machine
c)
Stethoscope
d)
MRI machine
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
In medicine, the Doppler Effect can be used to measure the direction and speed of blood flow in arteries and veins. This is used in echocardiograms and medical ultrasonography and is an effective tool in diagnosis of vascular problems.
Two guitar strings A and B are slightly out of tune and produce beats of frequency 6Hz.The tension of the string found to decrease to 4 Hz. What is the original frequency of B if the frequency of a is 430Hz?
- a)424 Hz
- b)438 Hz
- c)435 Hz
- d)420 Hz
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two guitar strings A and B are slightly out of tune and produce beats of frequency 6Hz.The tension of the string found to decrease to 4 Hz. What is the original frequency of B if the frequency of a is 430Hz?
a)
424 Hz
b)
438 Hz
c)
435 Hz
d)
420 Hz
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
To solve this problem, let's assume the original frequency of string B is x Hz.
When two slightly out-of-tune guitar strings produce beats, the beat frequency is equal to the difference in frequency between the two strings. In this case, the beat frequency is 6 Hz.
So, we can set up the following equation:
|430 Hz - x Hz| = 6 Hz
Now, we have two cases to consider:
-
If 430 Hz - x Hz = 6 Hz: In this case, the original frequency of string B would be 430 Hz - 6 Hz = 424 Hz.
What material is tuning fork made of and why?- a)Iron, ductile
- b)Aluminium, less tensile strength
- c)Elinvar, elasticity of elinvar does not change
- d)Steel, more tensile strength
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What material is tuning fork made of and why?
a)
Iron, ductile
b)
Aluminium, less tensile strength
c)
Elinvar, elasticity of elinvar does not change
d)
Steel, more tensile strength
|
|
Priya Patel answered |
A tuning fork is made of an alloy of steel, nickel and chromium, called elinvar, Le., the material for which the elasticity does not change.
A police car moving at 22 m/s, chases a motor cyclist. The police man sounds his horn at 176 Hz while both of them move towards a stationary siren of frequency 165 Hz. Calculate the speed of the motor cyclist, if it is given that he does not hear any beats. (Velocity of sound = 330 m/s).- a)zero
- b)33 m/s
- c)22 m/s
- d)11 m/s
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A police car moving at 22 m/s, chases a motor cyclist. The police man sounds his horn at 176 Hz while both of them move towards a stationary siren of frequency 165 Hz. Calculate the speed of the motor cyclist, if it is given that he does not hear any beats. (Velocity of sound = 330 m/s).
a)
zero
b)
33 m/s
c)
22 m/s
d)
11 m/s
|
|
Rajeev Saxena answered |

Chapter doubts & questions for Sound in Motion (Doppler Effect) - Physics for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Sound in Motion (Doppler Effect) - Physics for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for EmSAT Achieve
208 videos|329 docs|212 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









