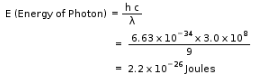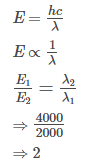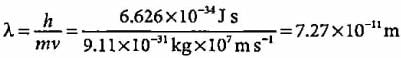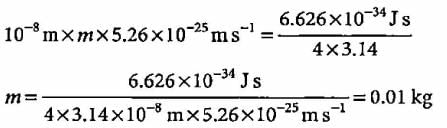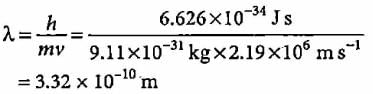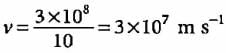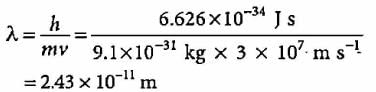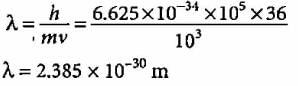All Exams >
EmSAT Achieve >
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve >
All Questions
All questions of Planck's Quantum Theory for EmSAT Achieve Exam
Which of the following radiation has the shortest wavelength.- a)Infra red
- b)ultraviolet
- c)microwave
- d)X-ray
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following radiation has the shortest wavelength.
a)
Infra red
b)
ultraviolet
c)
microwave
d)
X-ray
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Radio waves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet rays, X-rays, and gamma raysare all types of electromagnetic radiation. Radio waves have the longest wavelength, and gamma rays have the shortest wavelength.
The wavelength of light that has a frequency of 1.20 × 1013s-1 is __________ m.- a)2.50 × 10-5
- b)0.0400
- c)25.0
- d)12.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The wavelength of light that has a frequency of 1.20 × 1013s-1 is __________ m.
a)
2.50 × 10-5
b)
0.0400
c)
25.0
d)
12.0
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The speed of all form of electromagnetic wave is related by the equation c = λ.v, whereby, λ = 3.0 x 108 / 1.2 x 1013 = 2.5 x 10 -5 m.
The energy of a photon of light has what kind of proportionality to its frequency and its wavelength.- a)directly, inversely
- b)inversely, directly
- c)inversely, inversely
- d)directly, directly
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The energy of a photon of light has what kind of proportionality to its frequency and its wavelength.
a)
directly, inversely
b)
inversely, directly
c)
inversely, inversely
d)
directly, directly
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
As E=h(frequency) E is directly proportional to frequency and as frequency = speed of light / wavelength frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength.
If the value of azimuthal quantum number is 3, the possible values of magnetic quantum numbers would be:- a)0, 1, 2, 3
- b)3, -2, -1, +1, +2, +3
- c)0, -1, -2, -3
- d)3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the value of azimuthal quantum number is 3, the possible values of magnetic quantum numbers would be:
a)
0, 1, 2, 3
b)
3, -2, -1, +1, +2, +3
c)
0, -1, -2, -3
d)
3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The total possible values of m for l range from – through 0 to +.
As compared to 1s electron of H-atom in ground state, which of the following properties appear(s) in the radial probability density of 2s electron of H-atom in first excited state?- a)Spherical node appear
- b)Electron charge density is highest in the vicinity of the nucleus
- c)Electron density drops to zero after maximum probability is reache
- d)Electron density rises to second highest valu
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
As compared to 1s electron of H-atom in ground state, which of the following properties appear(s) in the radial probability density of 2s electron of H-atom in first excited state?
a)
Spherical node appear
b)
Electron charge density is highest in the vicinity of the nucleus
c)
Electron density drops to zero after maximum probability is reache
d)
Electron density rises to second highest valu

|
Jatin Dasgupta answered |
For2s-electron of H-atom (first excited state)
For 1s-electron of H-atom in ground state
At point Ar = a0 r at point Br > a0
(a) True (b) True (c) True (d) True
For 1s-electron of H-atom in ground state
At point Ar = a0 r at point Br > a0
(a) True (b) True (c) True (d) True
How many subshells and electrons are associated with n = 4?
- a)32, 64
- b)16, 32
- c)4, 16
- d)8, 16
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many subshells and electrons are associated with n = 4?
a)
32, 64
b)
16, 32
c)
4, 16
d)
8, 16
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
For nth orbital possible values of azimuthal quantum number (subshell), l are from 0 to (n-1). Total of 'n' values.
In n=4, l=0,1,2,3 thus there are 4 subshells i.e.s,p,d,f respectively.
Magnetic quantum number ml have values from -l to +l and total of 2l+1 values.
For n=4, possible values of l and ml are:
ml=0 for l=0; total ml values =1
ml=−1,0,1 for l=1; total ml values =3
ml=−2,−1,0,1,2 for l=2; total ml values =5
ml=−3,−2,−1,0,1,2,3 for l=3; total ml values =7
Total number of orbitals = total values of ml
for n=4,
∴1+3+5+7=16 orbitals
Each orbital can occupy maximum of two electron
Number of electrons =2×16=32
Therefore in n=4, number of subshells=4, orbitals=16 and number of electrons =32.
Describe the orbital with following quantum numbers:
(i) n = 3, l = 2
(ii) n = 4 , l = 3
- a)(i) 3p, (ii) 4f
- b)(i) 3d, (ii) 4d
- c)(i) 3f, (ii) 4f
- d)(i) 3d, (ii) 4f
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Describe the orbital with following quantum numbers:
(i) n = 3, l = 2
(ii) n = 4 , l = 3
(i) n = 3, l = 2
(ii) n = 4 , l = 3
a)
(i) 3p, (ii) 4f
b)
(i) 3d, (ii) 4d
c)
(i) 3f, (ii) 4f
d)
(i) 3d, (ii) 4f
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
(i) n = 3, l = 2 ⇒ 3 d
(ii) n = 4 , l = 3 ⇒ 4f
(ii) n = 4 , l = 3 ⇒ 4f
Quantum Numbers Description
i) n = 3, l = 2
- For the quantum numbers n = 3 and l = 2, the orbital is in the 3d subshell.
- The 3d orbital has a complex shape with two angular nodes and can hold a maximum of 10 electrons.
- Electrons in the 3d orbital have higher energy compared to those in the s and p orbitals.
ii) n = 4, l = 3
- For the quantum numbers n = 4 and l = 3, the orbital is in the 4f subshell.
- The 4f orbital has a more complex and intricate shape compared to lower energy orbitals.
- The 4f orbital can hold a maximum of 14 electrons and is located further from the nucleus due to higher energy levels.
i) n = 3, l = 2
- For the quantum numbers n = 3 and l = 2, the orbital is in the 3d subshell.
- The 3d orbital has a complex shape with two angular nodes and can hold a maximum of 10 electrons.
- Electrons in the 3d orbital have higher energy compared to those in the s and p orbitals.
ii) n = 4, l = 3
- For the quantum numbers n = 4 and l = 3, the orbital is in the 4f subshell.
- The 4f orbital has a more complex and intricate shape compared to lower energy orbitals.
- The 4f orbital can hold a maximum of 14 electrons and is located further from the nucleus due to higher energy levels.
How many orbitals in total are associated with 4th energy level?- a)4
- b)9
- c)16
- d)7
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many orbitals in total are associated with 4th energy level?
a)
4
b)
9
c)
16
d)
7
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
n = 4, l = 0,1, 2, 3
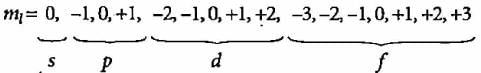
Total number of orbitals 1s + 3p + 5d + 7f = 16
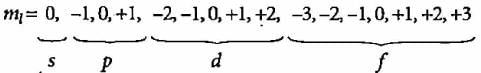
Total number of orbitals 1s + 3p + 5d + 7f = 16
Select the correct statement(s).- a)|
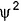 | measures the electron probability density at point in an atom
| measures the electron probability density at point in an atom - b)
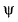 and |
and | 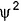 | vary as a function of the three coordinates r (radial), θ and (
| vary as a function of the three coordinates r (radial), θ and (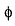 (angular part)
(angular part) - c)Angular wave function ‘θ
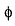 ’ depends an only l and m, and is independent of n
’ depends an only l and m, and is independent of n - d)All of the above are correct statements
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the correct statement(s).
a)
| 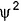 | measures the electron probability density at point in an atom
| measures the electron probability density at point in an atom
b)
c)
Angular wave function ‘θ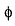 ’ depends an only l and m, and is independent of n
’ depends an only l and m, and is independent of n
d)
All of the above are correct statements

|
Telecom Tuners answered |
Thus, 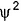 is d e pendent on r true
is d e pendent on r true
(b)
(c) Angular wave function is determined by /land m, and not by n: true
Which orbital gives an electron, a greater probability being found close to the nucleus?- a)3p
- b)3d
- c)3s
- d)equal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which orbital gives an electron, a greater probability being found close to the nucleus?
a)
3p
b)
3d
c)
3s
d)
equal

|
Atharva Pillai answered |
3s is spherically symmetrical and its electron density is maximum at the nucleus. It decreases with r.
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a frequency 4.62 ×1014s-1?- a)1.54 × 10-3
- b)649
- c)932
- d)1.07 × 106
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the wavelength of light (nm) that has a frequency 4.62 ×1014s-1?
a)
1.54 × 10-3
b)
649
c)
932
d)
1.07 × 106
|
|
Nandini Patel answered |
The wavelength (λ) and frequency (ν) of electromagnetic wave is related by the equation c = λ.ν, whereby, λ = 3.0 x108 / 4.62 x1014 = 0.649 x 10-6 m = 649nm
The ejected electrons from the surface of metal in photoelectric effect are called:- a)Photoelectrons
- b)Proton
- c)Electron
- d)Neutron
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The ejected electrons from the surface of metal in photoelectric effect are called:
a)
Photoelectrons
b)
Proton
c)
Electron
d)
Neutron
|
|
Jayant Mishra answered |
Photoelectric Effect: If light beyond a specific threshold frequency hits a metal surface, electrons are ejected from the surface of the metal. The minimum energy required to eject an electron from the surface is called the work function of the metal. These ejected electrons are called photoelectrons.
The 3d-orbitals having electron density in all the three axes is- a)3dxy
- b)3dz2
- c)3dyz
- d)3dzx
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The 3d-orbitals having electron density in all the three axes is
a)
3dxy
b)
3dz2
c)
3dyz
d)
3dzx
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
dz2 has electron density in all three axes.
Which of the following is not a correct statement regarding the energies of orbitals?- a)The lower the value of (n + 1) for an orbital, lower is its energy
- b)Electron in the same subshell have equal energy
- c)Energy of s-orbital is lower than the p-orbital and that of p-orbital is lower than the d-orbital
- d)If two orbitals have same value for (n + 1), the orbital with higher value of n will have lower energy
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a correct statement regarding the energies of orbitals?
a)
The lower the value of (n + 1) for an orbital, lower is its energy
b)
Electron in the same subshell have equal energy
c)
Energy of s-orbital is lower than the p-orbital and that of p-orbital is lower than the d-orbital
d)
If two orbitals have same value for (n + 1), the orbital with higher value of n will have lower energy
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
If two orbitals have same value for (n + l), the orbital with lower value of n will have lower energy.
What is correct about wave number?- a)It is defined as the number of waves which pass through a particular point in one second
- b)It is defined as the number of wavelengths per unit length
- c)It is defined as the distance between two neighbouring crests or troughs of wave
- d)It is the distance travelled by a wave in one second
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is correct about wave number?
a)
It is defined as the number of waves which pass through a particular point in one second
b)
It is defined as the number of wavelengths per unit length
c)
It is defined as the distance between two neighbouring crests or troughs of wave
d)
It is the distance travelled by a wave in one second
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Wave number, a unit of frequency in atomic, molecular, and nuclear spectroscopy equal to the true frequency divided by the speed of light and thus equal to the number of waves in a unit distance. The frequency, symbolized by the Greek letter nu (ν), of any wave equals the speed of light, c, divided by the wavelength λ: thus ν = c/λ. A typical spectral line in the visible region of the spectrum has a wavelength of 5.8 X 10-5 cm; this wavelength corresponds to a frequency (ν) of 5.17 X1014 Hz (hertz equals one cycle per second) obtained from the equation. Because this frequency and others like it are so extremely large, it is convenient to divide the number by the speed of light and hence reduce its size. Frequency divided by the speed of light is ν/c, which from the above equation is 1/λ. When wavelength is measured in metres, 1/λ represents the number of waves of the wave train to be found in a length of one metre or, if measured in centimetres, the number in one centimetre. This number is called the wave number of the spectrum line. Wave numbers are usually measured in units of reciprocal metres (1/m, or m-1) and reciprocal centimetres (1/cm, or cm-1).
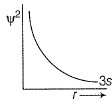
For 2s-orbital electron, radial probability density R2 as function of r (distance) is given by- a)
- b)

- c)

- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For 2s-orbital electron, radial probability density R2 as function of r (distance) is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)
all of these

|
Top Rankers answered |
Correct Answer : b
Explanation : (a) It represents R2 vs r for 1s
(b) It represents R2 vs r for2s
(c) It represents R2 vs r for 2p
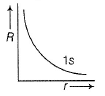
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Radial wave functio ns (R) of different orbitals are plotted. Which is/are correct graphs?- a)
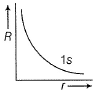
- b)
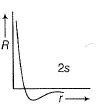
- c)
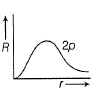
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-12) This section contains 12 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Radial wave functio ns (R) of different orbitals are plotted. Which is/are correct graphs?
a)
b)
c)
d)
All of these

|
Amrutha Chaudhary answered |
For 1s-orbital radial wave function (Ft) is maximum at r - 0, and falls rapidly as r increases thus, (a) correct.
For2s-orbital, radial wave function (R) is maximum at (r = 0), falls to zero and further decreases with r. There appears radial nodes. Thus (b) correct.
For2p-orbital, radial wave function is zero at r = 0, reaches maximum value (at r = a0) and then falls thus (c) is correct.
For2s-orbital, radial wave function (R) is maximum at (r = 0), falls to zero and further decreases with r. There appears radial nodes. Thus (b) correct.
For2p-orbital, radial wave function is zero at r = 0, reaches maximum value (at r = a0) and then falls thus (c) is correct.
How many electrons in an atom have the following quantum numbers?
n = 4, s = -1/2
- a)32
- b)18
- c)8
- d)16
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How many electrons in an atom have the following quantum numbers?
n = 4, s = -1/2
n = 4, s = -1/2
a)
32
b)
18
c)
8
d)
16
|
|
Anoushka Dasgupta answered |
Explanation:
Quantum numbers:
- The principal quantum number (n) determines the main energy level or shell of an electron.
- The spin quantum number (s) determines the spin of an electron, with values of +1/2 or -1/2.
Given quantum numbers:
- n = 4 (fourth energy level)
- s = -1/2 (spin of the electron)
Calculation:
- For a given energy level (n), the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated is given by 2n^2.
- For n = 4, the maximum number of electrons = 2 * 4^2 = 32.
Answer:
- The number of electrons with the given quantum numbers (n = 4, s = -1/2) is 16.
- Therefore, option 'D' (16) is the correct answer.
Quantum numbers:
- The principal quantum number (n) determines the main energy level or shell of an electron.
- The spin quantum number (s) determines the spin of an electron, with values of +1/2 or -1/2.
Given quantum numbers:
- n = 4 (fourth energy level)
- s = -1/2 (spin of the electron)
Calculation:
- For a given energy level (n), the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated is given by 2n^2.
- For n = 4, the maximum number of electrons = 2 * 4^2 = 32.
Answer:
- The number of electrons with the given quantum numbers (n = 4, s = -1/2) is 16.
- Therefore, option 'D' (16) is the correct answer.
For an electron in 2p-orbital, radial probability function 4πr2R2 as a function of r is given by- a)
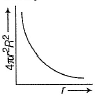
- b)
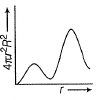
- c)
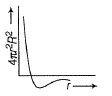
- d)
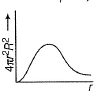
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
For an electron in 2p-orbital, radial probability function 4πr2R2 as a function of r is given by
a)
b)
c)
d)

|
Nikhil Sen answered |
(a) Describes radial wave function as a function of r for 1s
(b) Describes radial probability function as a function of r for 2s
(c) Describes radial wave function as a function r for 2s
(d) Describes radial probability function as a function of r for 2p
(b) Describes radial probability function as a function of r for 2s
(c) Describes radial wave function as a function r for 2s
(d) Describes radial probability function as a function of r for 2p
Few electrons have following quantum numbers,
(i) n = 4, l = 1
(ii) n = 4, l = 0
(iii) n = 3, l = 2
(iv) n = 3, l = 1
Arrange them in the order of increasing energy from lowest to highest.- a)(iv) < (ii) < (iii) < (i)
- b)(ii) < (iv) < (i) < (iii)
- c)(i) < (iii) < (ii) < (iv)
- d)(iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii)
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Few electrons have following quantum numbers,
(i) n = 4, l = 1
(ii) n = 4, l = 0
(iii) n = 3, l = 2
(iv) n = 3, l = 1
Arrange them in the order of increasing energy from lowest to highest.
(i) n = 4, l = 1
(ii) n = 4, l = 0
(iii) n = 3, l = 2
(iv) n = 3, l = 1
Arrange them in the order of increasing energy from lowest to highest.
a)
(iv) < (ii) < (iii) < (i)
b)
(ii) < (iv) < (i) < (iii)
c)
(i) < (iii) < (ii) < (iv)
d)
(iii) < (i) < (iv) < (ii)
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
(i) 4p, (ii) 4s, (iii) 3d, (iv) 3p
The order of increasing energy
(iv) < (ii) < (iii) < (i)
The order of increasing energy
(iv) < (ii) < (iii) < (i)
What will be the uncertainty in velocity of a bullet with a mass of 10 g whose position is known with ± 0.01 mm?- a)5.275 x 10-33 m s-1
- b)5.275 x 10-25 m s-1
- c)5.275 x 10-5 m s-1
- d)5.275 x 10-28 m s-1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the uncertainty in velocity of a bullet with a mass of 10 g whose position is known with ± 0.01 mm?
a)
5.275 x 10-33 m s-1
b)
5.275 x 10-25 m s-1
c)
5.275 x 10-5 m s-1
d)
5.275 x 10-28 m s-1
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
Δx = ± 0.01 mm = 1 x 10-5 m,
m = 10 g = 1 x 10-2kg
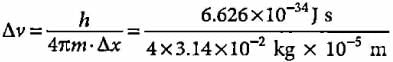
= 5.275 x 10-28m s-1.
m = 10 g = 1 x 10-2kg
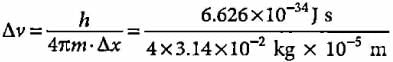
= 5.275 x 10-28m s-1.
Which of the following configurations does not follow Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity?- a)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
- b)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6
- c)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5
- d)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 4s2
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following configurations does not follow Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity?
a)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
b)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6
c)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5
d)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p4 4s2
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
The configuration does not follow Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity because 3p will be fully filled before the electrons go to 4s.
What is the electronic configuration of O2- ion?- a)1s2 2s2 2p6
- b)1s2 2s2 2p4
- c)1s2 2s2 2p5
- d)1s2 2s2 2p3
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the electronic configuration of O2- ion?
a)
1s2 2s2 2p6
b)
1s2 2s2 2p4
c)
1s2 2s2 2p5
d)
1s2 2s2 2p3
|
|
Anuj Singh answered |
Electronic configuration of O2- ion:
1. Explanation:
- The O2- ion is formed by gaining 2 electrons by oxygen atom.
- Oxygen atom has an electronic configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p4.
- When 2 electrons are gained, the electronic configuration changes as follows.
2. Electronic configuration of O2- ion:
- Adding 2 electrons to the oxygen atom configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p4 + 2e- = 1s2 2s2 2p6.
Therefore, the electronic configuration of O2- ion is 1s2 2s2 2p6.
1. Explanation:
- The O2- ion is formed by gaining 2 electrons by oxygen atom.
- Oxygen atom has an electronic configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p4.
- When 2 electrons are gained, the electronic configuration changes as follows.
2. Electronic configuration of O2- ion:
- Adding 2 electrons to the oxygen atom configuration: 1s2 2s2 2p4 + 2e- = 1s2 2s2 2p6.
Therefore, the electronic configuration of O2- ion is 1s2 2s2 2p6.
In how many elements the last electron will have the following set of quantum numbers, n = 3 and l = 1?- a)2
- b)8
- c)6
- d)10
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In how many elements the last electron will have the following set of quantum numbers, n = 3 and l = 1?
a)
2
b)
8
c)
6
d)
10
|
|
Ashwin Saini answered |
Explanation:
The set of quantum numbers given are n=3 and l=1.
The principal quantum number (n) determines the energy level of the electron, while the azimuthal quantum number (l) determines the subshell in which the electron resides.
For l=1, the subshell is the p subshell. In the third energy level (n=3), there are three subshells: s, p, and d.
The maximum number of electrons that can occupy a p subshell is 6, according to the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's Rule.
Therefore, the number of elements that can have the quantum numbers n=3 and l=1 (p subshell) is 6.
Option C is correct.
The set of quantum numbers given are n=3 and l=1.
The principal quantum number (n) determines the energy level of the electron, while the azimuthal quantum number (l) determines the subshell in which the electron resides.
For l=1, the subshell is the p subshell. In the third energy level (n=3), there are three subshells: s, p, and d.
The maximum number of electrons that can occupy a p subshell is 6, according to the Pauli Exclusion Principle and Hund's Rule.
Therefore, the number of elements that can have the quantum numbers n=3 and l=1 (p subshell) is 6.
Option C is correct.
Which of the following quantum numbers are correct for the outermost electron of sodium atom?- a)n = 4, l = 0, m = 0, s = +1/2
- b)n = 3, l = 0, m = 0, s = -1/2
- c)h = 3, l = 1, m = +1, s = +1/2
- d)n = 3, l = 2, m = -1, s = -1/2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following quantum numbers are correct for the outermost electron of sodium atom?
a)
n = 4, l = 0, m = 0, s = +1/2
b)
n = 3, l = 0, m = 0, s = -1/2
c)
h = 3, l = 1, m = +1, s = +1/2
d)
n = 3, l = 2, m = -1, s = -1/2
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
11Na = 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
For 3s1, n = 3, l = 0, ml = 0, s = -1/2
For 3s1, n = 3, l = 0, ml = 0, s = -1/2
A body of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 100 m s-1. The wavelength associated with it is- a)6.626 x 10-7 m
- b)6.626 x 10-34 m
- c)6.626 x 10-4 m
- d)6.626 x 10-35 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A body of mass 10 g is moving with a velocity of 100 m s-1. The wavelength associated with it is
a)
6.626 x 10-7 m
b)
6.626 x 10-34 m
c)
6.626 x 10-4 m
d)
6.626 x 10-35 m
|
|
Milan Nambiar answered |
Explanation:
The given problem involves calculating the de Broglie wavelength associated with a body of mass and velocity.
De Broglie Wavelength Formula:
The de Broglie wavelength (λ) of a particle is given by the formula:
λ = h / mv
Where:
λ = de Broglie wavelength
h = Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J s)
m = mass of the particle (10 g = 0.01 kg)
v = velocity of the particle (100 m/s)
Calculation:
Substitute the given values into the formula:
λ = (6.626 x 10^-34) / (0.01 x 100)
λ = 6.626 x 10^-34 / 1
λ = 6.626 x 10^-34 m
Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength associated with the body of mass 10 g moving at 100 m/s is 6.626 x 10^-34 m.
So, the correct answer is option B: 6.626 x 10^-34 m.
The given problem involves calculating the de Broglie wavelength associated with a body of mass and velocity.
De Broglie Wavelength Formula:
The de Broglie wavelength (λ) of a particle is given by the formula:
λ = h / mv
Where:
λ = de Broglie wavelength
h = Planck's constant (6.626 x 10^-34 J s)
m = mass of the particle (10 g = 0.01 kg)
v = velocity of the particle (100 m/s)
Calculation:
Substitute the given values into the formula:
λ = (6.626 x 10^-34) / (0.01 x 100)
λ = 6.626 x 10^-34 / 1
λ = 6.626 x 10^-34 m
Therefore, the de Broglie wavelength associated with the body of mass 10 g moving at 100 m/s is 6.626 x 10^-34 m.
So, the correct answer is option B: 6.626 x 10^-34 m.
What is the lowest value of n that allows g orbital to exist?- a)6
- b)7
- c)4
- d)5
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the lowest value of n that allows g orbital to exist?
a)
6
b)
7
c)
4
d)
5
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
For g orbital, value of l is 4.
(0 = s, 1 = p , 2 = d, 3 = f, 4 = g)
Since l = n - 1, n should be 5.
(0 = s, 1 = p , 2 = d, 3 = f, 4 = g)
Since l = n - 1, n should be 5.
An orbital is described with the help of a wave function. Since many wave functions are possible for an electron, there are many atomic orbitals. When atom is placed in a magnetic field the possible number of orientations for an orbital of azimuthal quantum number 3 is:- a)Three
- b)Two
- c)Five
- d)Seven
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An orbital is described with the help of a wave function. Since many wave functions are possible for an electron, there are many atomic orbitals. When atom is placed in a magnetic field the possible number of orientations for an orbital of azimuthal quantum number 3 is:
a)
Three
b)
Two
c)
Five
d)
Seven
|
|
Mira Joshi answered |
When l = 3, magnetic quantum number has 7 values ml = (2l + 1). These values are represented as -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
The probability of finding out an electron at a point within an atom is proportional to the- a)square of the orbital wave function i.e., ψ2
- b)orbital wave function i.e., ψ
- c)Hamiltonian operator i.e., H
- d)principal quantum number i.e., n
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The probability of finding out an electron at a point within an atom is proportional to the
a)
square of the orbital wave function i.e., ψ2
b)
orbital wave function i.e., ψ
c)
Hamiltonian operator i.e., H
d)
principal quantum number i.e., n
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
ψ2 is known as probability density and is always positive. From the value of ψ2 at different points with in an atom it is possible to predict the region around the nucleus where electron will most probably be found.
What is the frequency of light in s-1 that has a wavelength of 3.12 x 10-3 cm?- a)9.62 × 1012
- b)1.04 ×1013
- c)2.44 × 1016
- d)3.69
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the frequency of light in s-1 that has a wavelength of 3.12 x 10-3 cm?
a)
9.62 × 1012
b)
1.04 ×1013
c)
2.44 × 1016
d)
3.69
|
|
Mira Sharma answered |
The wavelength (λ) and frequency (ν) of electromagnetic wave is related by the equation c = λ.ν,
Where c is the speed of light = 3.00 x 108 m/s, λ is the wavelength in m and ν is the frequency is s^-1or Hz.
Substituting the values in the formula, we get,
c = λ.ν
ν = c/λ
ν = 3.0 x 10^8 / 3.12 x 10^-5
= 0.96 x 10^13 m = 9.62 X 10^12
What are the possible values of n, l and ml for an atomic orbital 4f?- a)n = 4, l = 0, 1, 2, 3, ml = -2, -1, 0, +1; +2
- b)n = 4, l = 3, ml = - 3, - 2, - 1, 0, +1, +2, +3
- c)n = 4, l = 2 , ml = - 2 , -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
- d)n = 4, l = 0,1, ml = - 1, 0, +1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What are the possible values of n, l and ml for an atomic orbital 4f?
a)
n = 4, l = 0, 1, 2, 3, ml = -2, -1, 0, +1; +2
b)
n = 4, l = 3, ml = - 3, - 2, - 1, 0, +1, +2, +3
c)
n = 4, l = 2 , ml = - 2 , -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
d)
n = 4, l = 0,1, ml = - 1, 0, +1
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
For 4f; n = 4, l = 3,
ml = 7 or -3 , -2, -1 , 0 , +1, +2, +3
ml = 7 or -3 , -2, -1 , 0 , +1, +2, +3
Electromagnetic radiation travels through vacuum at a speed of __________ m/s.- a)10,000
- b)It depends on wavelength.
- c)3.00 × 108
- d)186,000
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Electromagnetic radiation travels through vacuum at a speed of __________ m/s.
a)
10,000
b)
It depends on wavelength.
c)
3.00 × 108
d)
186,000

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
The speed of light (electromagnetic radiation) through vacuum has a constant value of 3.00 x 10^8 m/s and is independent of the wavelength in vacuum.
If uncertainty principle is applied to an object of mass 1 milligram, the uncertainty value of velocity and position will be- a)0.2 x 10-4 m2 s-1
- b)0.52 x 106 m2 s-1
- c)0.52 x 10-28 m2 s-1
- d)2 x 10-34 m2 s-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If uncertainty principle is applied to an object of mass 1 milligram, the uncertainty value of velocity and position will be
a)
0.2 x 10-4 m2 s-1
b)
0.52 x 106 m2 s-1
c)
0.52 x 10-28 m2 s-1
d)
2 x 10-34 m2 s-1
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
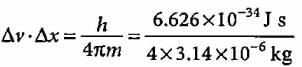
= 0.52 x 10-28 m2 s-1 (1 mg = 10-6 kg)
What will be the orbital angular momentum of an electron in 2s-orbital?- a)Zero
- b)One
- c)Two
- d)Three
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the orbital angular momentum of an electron in 2s-orbital?
a)
Zero
b)
One
c)
Two
d)
Three
|
|
Ameya Bose answered |
Introduction:
The orbital angular momentum of an electron is a property that arises from its motion around the nucleus in an atom. It quantifies the amount of rotational motion an electron has in its orbit. The orbital angular momentum is determined by the principal quantum number (n) and the azimuthal quantum number (l) of the orbital in which the electron resides.
Explanation:
- The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of an electron and determines the size of the orbital.
- The azimuthal quantum number, l, describes the shape of the orbital and can take on values from 0 to n-1.
- For an s-orbital, the azimuthal quantum number, l, is equal to 0. Therefore, the orbital angular momentum (L) of an electron in an s-orbital is given by the equation L = √(l(l+1))ħ, where ħ is the reduced Planck's constant.
- Plugging in the value l = 0 into the equation, we get L = √(0(0+1))ħ = √(0)ħ = 0.
- Hence, the orbital angular momentum of an electron in a 2s-orbital is zero.
Conclusion:
The orbital angular momentum of an electron in a 2s-orbital is zero. This is because the azimuthal quantum number, l, for an s-orbital is zero, resulting in a zero value for the orbital angular momentum.
The orbital angular momentum of an electron is a property that arises from its motion around the nucleus in an atom. It quantifies the amount of rotational motion an electron has in its orbit. The orbital angular momentum is determined by the principal quantum number (n) and the azimuthal quantum number (l) of the orbital in which the electron resides.
Explanation:
- The principal quantum number, n, describes the energy level of an electron and determines the size of the orbital.
- The azimuthal quantum number, l, describes the shape of the orbital and can take on values from 0 to n-1.
- For an s-orbital, the azimuthal quantum number, l, is equal to 0. Therefore, the orbital angular momentum (L) of an electron in an s-orbital is given by the equation L = √(l(l+1))ħ, where ħ is the reduced Planck's constant.
- Plugging in the value l = 0 into the equation, we get L = √(0(0+1))ħ = √(0)ħ = 0.
- Hence, the orbital angular momentum of an electron in a 2s-orbital is zero.
Conclusion:
The orbital angular momentum of an electron in a 2s-orbital is zero. This is because the azimuthal quantum number, l, for an s-orbital is zero, resulting in a zero value for the orbital angular momentum.
Who discovered and first used the constant h = 6.6 x 10-34 J.s?- a)De Broglie
- b)Einstein
- c)Bohr
- d)Planck
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Who discovered and first used the constant h = 6.6 x 10-34 J.s?
a)
De Broglie
b)
Einstein
c)
Bohr
d)
Planck

|
Sounak Chaudhary answered |
Max Planck gave the Planck’s quantum theory and was the first to determine the value of h which is the Planck’s constant.
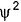 at any point is proportional to
at any point is proportional to- a)the probability of finding the particle at that point
- b)energy of the electron
- c)radius of the orbital
- d)(radius)-1 of the orbital
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
the probability of finding the particle at that point
b)
energy of the electron
c)
radius of the orbital
d)
(radius)-1 of the orbital

|
Tejas Chawla answered |
Radial probability density = 4πr2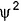 of find in g the electron within the volume of a very thin spherical shell at a distance r from nucleus.
of find in g the electron within the volume of a very thin spherical shell at a distance r from nucleus.
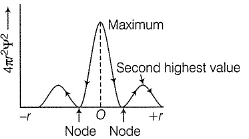
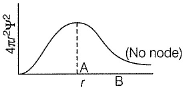
Can you explain the answer of this question below:C onsider the following figures A and B indicating distribution of charge density (electron probability 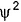 ) with distance r
) with distance r
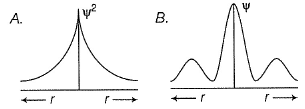
Select the correct statement(s).
- A:
Both A and B are for 1s
- B:
Both A and B are for 2s
- C:
A is for 2s and B is for 1s
- D:
A is for 1s and B is for 2s
The answer is d.
C onsider the following figures A and B indicating distribution of charge density (electron probability ) with distance r
Select the correct statement(s).
Both A and B are for 1s
Both A and B are for 2s
A is for 2s and B is for 1s
A is for 1s and B is for 2s

|
Nandini Nair answered |
in case of 1s, 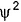 falls as r increases thus, (A) is for 1s.
falls as r increases thus, (A) is for 1s.
In case of 2s,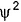 is maximum in the vicinity o f the nucleus, falls to zero giving spherical nodes and then rises to second highest value. Thus, (6) is for2s
is maximum in the vicinity o f the nucleus, falls to zero giving spherical nodes and then rises to second highest value. Thus, (6) is for2s
In case of 2s,
Two electrons present in M shell will differ in- a)Principal quantum number
- b)Azimuthal quantum number
- c)Magnetic quantum number
- d)Spin quantum number.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Two electrons present in M shell will differ in
a)
Principal quantum number
b)
Azimuthal quantum number
c)
Magnetic quantum number
d)
Spin quantum number.
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
For electrons present in M shell the value of other quantum numbers are same. But, the value of spin quantum number will be different.
Which of the following configurations represents a noble gas?- a)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2
- b)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4f14 5s2
- c)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6
- d)1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following configurations represents a noble gas?
a)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2
b)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4f14 5s2
c)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6
d)
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p3
|
|
Janhavi Patel answered |
Explanation:
Noble Gas Configuration:
- A noble gas configuration is when an atom has achieved a stable electron configuration similar to that of a noble gas.
- Noble gases have a completely filled outermost energy level, which makes them very stable and unreactive.
Identifying the Noble Gas Configuration:
- The electron configuration given in option 'C' is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2.
- This configuration represents the noble gas Krypton (Kr), which has the electron configuration of [Ar] 4s2 3d10 4p6.
- By comparing the given configuration with the electron configuration of Krypton, we can see that it matches, indicating a noble gas configuration.
Conclusion:
- Option 'C' (1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2) represents a noble gas configuration similar to that of Krypton, making it the correct answer.
Chapter doubts & questions for Planck's Quantum Theory - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve 2025 is part of EmSAT Achieve exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the EmSAT Achieve exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for EmSAT Achieve 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Planck's Quantum Theory - Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve in English & Hindi are available as part of EmSAT Achieve exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for EmSAT Achieve Exam by signing up for free.
Chemistry for EmSAT Achieve
191 videos|265 docs|160 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup