All Exams >
MCAT >
General Chemistry for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Periodic Table for MCAT Exam
Which of the following statements accurately describes the first ionization energy data shown in the table?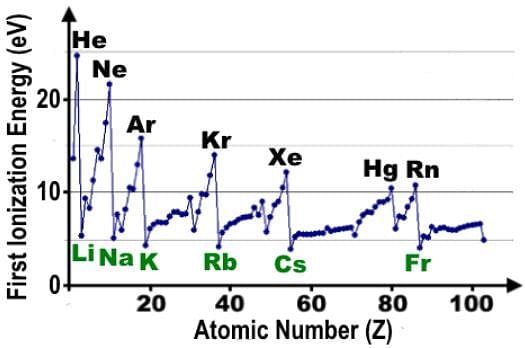
- a)Ionization energy increases as we move across a group on the periodic table.
- b)All the local peaks labelled in black correspond to the noble gases, and all the local minima or dips labelled in green correspond to the alkali metals.
- c)The exceptions to the ionization energy trend across a particular period correspond to the formation of half-filled and fully-filled orbitals.
- d)The plateaus in the data correspond to the actinide and lanthanide series, sometimes referred to as the “inner transition” metals.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the first ionization energy data shown in the table?

a)
Ionization energy increases as we move across a group on the periodic table.
b)
All the local peaks labelled in black correspond to the noble gases, and all the local minima or dips labelled in green correspond to the alkali metals.
c)
The exceptions to the ionization energy trend across a particular period correspond to the formation of half-filled and fully-filled orbitals.
d)
The plateaus in the data correspond to the actinide and lanthanide series, sometimes referred to as the “inner transition” metals.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Ionization energy is the energy needed to remove an electron from a neutral atom in the gaseous state and is considered endothermic.
As a general trend, ionization energy increases moving across a period on the periodic table, but the data seems to indicate there are dips along the way.
The local peaks labelled in black correspond to all the noble gases plus Hg or mercury, and the local minima correspond to the alkali metals.
The plateaus in the data correspond to the transition metals and the inner transition metals. Between K and Kr, there is one set of transition metals, and another between Rb and Xe.
The exceptions to the trend or the small dips correspond to half-filled and fully-filled orbitals. Between Li and Ne, there are two dips which correspond to B and O.
What comes prior to each is an element with half-filled or fully-filled orbitals. Be comes before B, and because of the stability of the fully-filled s orbital, it takes more energy to rip off an electron from the neutral atom. The same applies to N with half-filled p orbitals.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the electron affinity data in the chart below?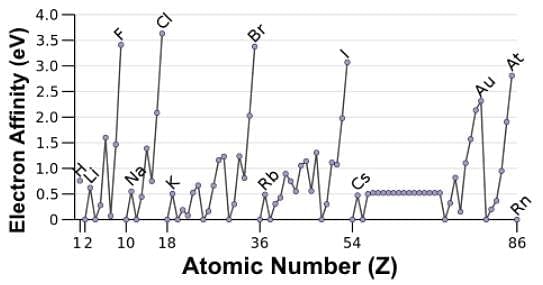
- a)The electron affinity values are smaller especially for the nonmetals in Period II because the repulsion between the electron being added and the electron already present is greatest for such atoms.
- b)The maxima correspond to the noble gas configurations because they have the greatest effective nuclear charge in a particular group.
- c)Electron affinity decreases as you move down the group due to increasing electron shells.
- d)Each of the minima correspond to elements with fully-filled orbitals since it would be energetically unfavorable to add an electron to such configurations.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the electron affinity data in the chart below?

a)
The electron affinity values are smaller especially for the nonmetals in Period II because the repulsion between the electron being added and the electron already present is greatest for such atoms.
b)
The maxima correspond to the noble gas configurations because they have the greatest effective nuclear charge in a particular group.
c)
Electron affinity decreases as you move down the group due to increasing electron shells.
d)
Each of the minima correspond to elements with fully-filled orbitals since it would be energetically unfavorable to add an electron to such configurations.

|
Orion Classes answered |
The minima correspond to the fully-filled s and p orbitals and some of the half-filled p and d orbitals. The stability of such configurations makes adding an electron energetically unfavorable where some elements have electron affinities (EA) that are endothermic.
There is no clear trend moving down a group due to increasing electron shells. Analyzing the data for the halides, for instance, which are the peaks, will reveal that fluorine has a lower EA than chlorine, which has the highest EA out of the group.
The maxima correspond to the halides since by acquiring one more electron they achieve a complete octet or the noble gas configuration.
The values are smaller for the nonmetals in Period II, i.e. O and F, because the repulsion between the electron being added and the electrons already present is greatest. Upon adding an electron to the neutral atom, the repulsion is more greatly felt due to their small size, and hence less energy is released.
Which of the following statements accurately describes the different classifications of elements?- a)Noble metals like gold, silver, and platinum are resistant to corrosion due to their fully-filled d-bands.
- b)The alkali earth metals react with water to form hydrogen gas as well as the metal oxides in aqueous solution.
- c)The alkali metals have distinctive flame colors because of their easily excited d electrons.
- d)All the halogens react with hydrogen to form hydrogen halides, which when mixed with water form strong acids.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements accurately describes the different classifications of elements?
a)
Noble metals like gold, silver, and platinum are resistant to corrosion due to their fully-filled d-bands.
b)
The alkali earth metals react with water to form hydrogen gas as well as the metal oxides in aqueous solution.
c)
The alkali metals have distinctive flame colors because of their easily excited d electrons.
d)
All the halogens react with hydrogen to form hydrogen halides, which when mixed with water form strong acids.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The common classifications of elements are the alkali metals (Group I), alkali earth metals (Group II), pnictogens (Group V), chalcogens (Group VI), halogens (Group VII), and noble gases (group VIII).
As for alkali metals, they have distinctive flame colors because of their easily excited electron in the s shell. Not all alkali metals even have d electrons.
As for alkali earth metals, they react with water to form hydrogen gas and the respective alkaline hydroxides in aqueous solution. Metal oxides became hydroxides in water.
All the halogens do react with hydrogen gas to form hydrogen halides, i.e. HF, HCl, HBr, HI, HAt. Not all of them form strong acids since HF is considered a weak acid because of the high electronegativity of fluorine. HAt would be the strongest acid but it readily decomposes back to hydrogen gas and astatine, and astatine has a short half-life.
The transition metals include the designation of noble metals, which comprises ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, silver, osmium, iridium, platinum, and gold. The noble metals resist corrosion because their d orbitals are fully-filled.
Which of the following inequalities accurately describes the relationship between the two ionic species in terms of size?- a)Se2- > p5-
- b)LI+ > At-
- c)As3- > Y3+
- d)l- < CA2+
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following inequalities accurately describes the relationship between the two ionic species in terms of size?
a)
Se2- > p5-
b)
LI+ > At-
c)
As3- > Y3+
d)
l- < CA2+
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
In comparing ionic radii, there are two guiding rules. First, in comparing isoelectronic species, anions are always bigger than the cations such that A3- > B2- > C- > noble gas > X+ > Y2 + > Z3
Secondly, in comparing elements in a group, the ionic radii always increase going down the group or with each extra energy level such that l- > Br- > Cl- > F-
For l- and Ca2+ using the isoelectronic trend, we know that the iodide ion is larger than the barium cation. Since calcium and barium are in the same group, it can be deduced that calcium is smaller than barium. I⁻ must be larger than Ca2+
For At- and Li+ start superscript, plus, end superscript, using the isoelectronic trend, we know that the astatine ion is larger than the cesium cation. Since cesium and lithium are in the same group, it can be deduced that lithium is smaller than cesium. At- must be larger than Li+
For Se2- and p3-, since they are neither isoelectronic or in the same group, it cannot be stated that Se2- > p3-. In fact Se2- < p3- with values of 198 pm and 212 pm.
As for As3- and Y3+, they are both isoelectronic. Anions are larger than corresponding isoelectronic cations, so it can be said with certainty that has As3- a larger ionic radius than Y3+.
Which of the following statements does NOT accurately describe the atomic trends?- a)Moving up, electronegativity increases due to the shortening distance between the nucleus and valence electron shell.
- b)Moving down, effective nuclear charge decreases due to increasing electron shells.
- c)Moving across from left to right, ionic radius decreases, increases, then decreases due to the switch from cationic to anionic species.
- d)Moving across from left to right, second ionization energy increases due to increasing nuclear charge.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements does NOT accurately describe the atomic trends?
a)
Moving up, electronegativity increases due to the shortening distance between the nucleus and valence electron shell.
b)
Moving down, effective nuclear charge decreases due to increasing electron shells.
c)
Moving across from left to right, ionic radius decreases, increases, then decreases due to the switch from cationic to anionic species.
d)
Moving across from left to right, second ionization energy increases due to increasing nuclear charge.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Effective nuclear charge increases moving across and decreases moving down.
Ionic radius decreases starting from the +1 to +3, sometimes +4, ion. Progressing to either the -4 or -3 ion, there is an increase in ionic radius since the anions are larger than the cations. Progressing from the -3 to the -1 ion, the radius decreases again.
Electronegativity increases moving across and decreases moving down.
The first ionization energy increases moving across and decreases moving down. For the second ionization energy, in period 2, lithium has the highest 2nd ionization energy because the electron is being removed from the noble gas configuration.
Which of the following statements describes a correct step in the formation of an ionic bond between sodium and chlorine?- a)Removing an electron from sodium (ionization energy) will provide energy for ionic bond formation.
- b)Adding an electron to chlorine (electron affinity) will require energy for ionic bond formation.
- c)The Coulombic potential between the ions (lattice energy) will release energy.
- d)Overcoming the Pauli repulsion from the overlap of wavefunctions of core electrons will release energy.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements describes a correct step in the formation of an ionic bond between sodium and chlorine?
a)
Removing an electron from sodium (ionization energy) will provide energy for ionic bond formation.
b)
Adding an electron to chlorine (electron affinity) will require energy for ionic bond formation.
c)
The Coulombic potential between the ions (lattice energy) will release energy.
d)
Overcoming the Pauli repulsion from the overlap of wavefunctions of core electrons will release energy.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
In order for the formation of an ionic bond to be favorable, the energy released must be greater than the energy consumed. Essentially, the cation and anion separately are formed and then brought together for bond formation.
Ionization energy is endothermic, so it would require energy. No energy is recovered from the ionization energy of sodium.
Electron affinity is exothermic, so it would release and provide energy for bond formation.
Once the ions are formed, they have to be brought together for bond formation. When the two charges are brought within picometers of each other, their electron shells which are both negatively charged will exert a certain repulsion on each other, and this repulsion will require energy to overcome.
However, the Pauli repulsion energy is small compared to the energy released in the loss in electrostatic or Coulombic potential when the opposite charges are brought together.
Based on the values for the first through fifth ionization energies in the table, what is the most likely identity of Element A and B?
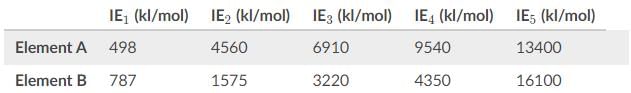
- a)Ca and S
- b)Na and Si
- c)K and P
- d)Ne and Al
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Based on the values for the first through fifth ionization energies in the table, what is the most likely identity of Element A and B?


a)
Ca and S
b)
Na and Si
c)
K and P
d)
Ne and Al

|
Orion Classes answered |
Ionization energies increase moving across a period, as a rule of thumb, since we are removing an electron first from a neutral atom then from a cation. To reiterate, second ionization energies are always larger than first ionization energies and are roughly double.
In analyzing the data for element A, look for the biggest gap. One way to approach this is to look at the factor between ionization energies.
The second ionization energy is almost 10 times as great as the first. As for the other ionization energies, the factor is only somewhere between 1 and 2.
The significance of the high amount of energy for IE2, is to due to the stability of the noble gas configuration. One electron was removed to reach IE2, so element A must be in group I.
As for element B, the doubling of IE1 to get IE2 is to be expected. The large gap does not occur until reaching IE5 whereby IE4 increases by a factor of almost 4.
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the characteristics of the transition metals?- a)The transition metals have little variability in their ionization energies and electronegativities due to their similar valence electron shells.
- b)Transition metals are characterized by the formation of many diamagnetic compounds due to the presence of unpaired d electrons.
- c)One difference between transition metals and main group metals is the latter’s ability to form coordination complexes.
- d)Transition metals are characterized by many oxidation states due to the high reactivity of the unpaired d electrons.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements most accurately describes the characteristics of the transition metals?
a)
The transition metals have little variability in their ionization energies and electronegativities due to their similar valence electron shells.
b)
Transition metals are characterized by the formation of many diamagnetic compounds due to the presence of unpaired d electrons.
c)
One difference between transition metals and main group metals is the latter’s ability to form coordination complexes.
d)
Transition metals are characterized by many oxidation states due to the high reactivity of the unpaired d electrons.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Transition metals are the ones which form one or more stable ions which have incompletely filled d orbitals. The filling of the d orbitals imparts particular properties to the transition metals.
Transition metals are characterized by the formation of many paramagnetic compounds due to the presence of unpaired
d electrons. Diamagnetic compounds have paired electrons and do not possess any magnetic capabilities.
d electrons. Diamagnetic compounds have paired electrons and do not possess any magnetic capabilities.
Transition metals also are characterized by many oxidation states due to the low reactivity of the unpaired d electrons. High reactivity would limit the number of oxidation states.
One difference between transition metals and main group metals is that transition metals can form coordination complexes, while main group metals tend to form binary compounds like CaCl₂.
The transition metals have little variability in their ionization energies and electronegativities due to their similar valence electron shells, which is the s shell. Even though, for instance, 3d fills after 4s, when forming ions, we remove from the highest energy orbital or the s orbital.
Which of the following statements about atomic radii accurately describes the data below?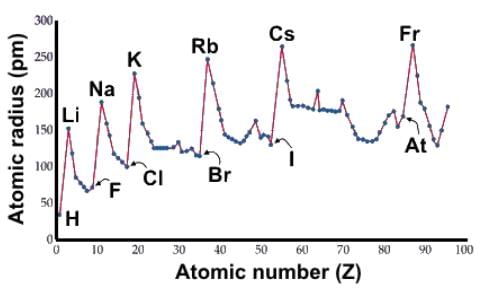
- a)The elements right after the d-block experience an expansion due to the repulsion created by the d electrons such that period 4 non metals are substantially larger than period 3 nonmetals.
- b)The minima of the graph correspond to the halides because they have the greatest effective nuclear charge.
- c)The transition metals have relatively the same atomic size moving across the group because their valence shell, which is the s orbital, essentially remains the same.
- d)The peaks of the graph correspond to the noble gas configurations because they have fully-filled orbitals.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about atomic radii accurately describes the data below?

a)
The elements right after the d-block experience an expansion due to the repulsion created by the d electrons such that period 4 non metals are substantially larger than period 3 nonmetals.
b)
The minima of the graph correspond to the halides because they have the greatest effective nuclear charge.
c)
The transition metals have relatively the same atomic size moving across the group because their valence shell, which is the s orbital, essentially remains the same.
d)
The peaks of the graph correspond to the noble gas configurations because they have fully-filled orbitals.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Solution:
- The atomic size of transition metals remains relatively consistent across a period.
- This consistency is because the valence shell primarily involves the s orbital, which does not change much.
- As a result, the atomic radii of transition metals do not significantly increase or decrease across the group.
Which of the following does NOT depend on the attraction of the bonding pair towards the nucleus?- a)The repulsion by the electrons in the same valence shell
- b)The amount of shielding by inner shell electrons
- c)The distance from the nucleus
- d)The number of protons in the nucleus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does NOT depend on the attraction of the bonding pair towards the nucleus?
a)
The repulsion by the electrons in the same valence shell
b)
The amount of shielding by inner shell electrons
c)
The distance from the nucleus
d)
The number of protons in the nucleus

|
Orion Classes answered |
The attraction of the bonding pair towards the nucleus is influenced by several factors:
- Repulsion by electrons in the same valence shell: This is due to electron-electron repulsion and does not depend on attraction to the nucleus.
- The amount of shielding by inner shell electrons: This affects how much of the nuclear charge is felt by the bonding pair.
- The distance from the nucleus: Greater distance generally weakens the attraction.
- The number of protons in the nucleus: More protons increase the nuclear charge, enhancing attraction.
Thus, option A, repulsion by electrons in the same valence shell, does not depend on the attraction to the nucleus.
Chapter doubts & questions for Periodic Table - General Chemistry for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Periodic Table - General Chemistry for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
General Chemistry for MCAT
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









