All Exams >
MCAT >
General Chemistry for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Thermochemistry for MCAT Exam
Which of the following reactions is most likely to be spontaneous only at high temperatures?- a)
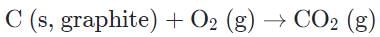
- b)
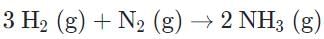
- c)
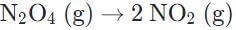
- d)
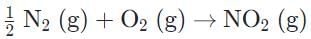
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reactions is most likely to be spontaneous only at high temperatures?
a)
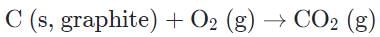
b)
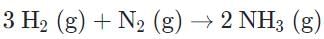
c)
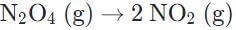
d)
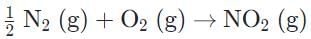
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
We are looking for a negative value of ∆G∘ to ascertain spontaneity. However, the condition of high temperatures would preclude some options.
When the sign for ∆H∘ and ∆S∘ are different, the system is either always spontaneous or non-spontaneous. When the signs are the same, there is the temperature-dependent spontaneity.
Only when both sign are positive is ∆G∘ spontaneous at high temperatures. We are looking for an endothermic reaction with a positive entropy.
Evaluating the change in entropy should allow us to more easily eliminate. The formation of ammonia and nitrogen dioxide both show a negative change in entropy, whereby moles of gases are reduced on the product side.
Of the remaining two reactions, one is a combustion reaction, which is strongly exothermic, and can be eliminated.
The decomposition of dinitrogen tetraoxide shows an increase in entropy.
The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) of an element in its most stable form is:- a)Always positive
- b)Always negative
- c)Zero
- d)Variable depending on the element
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) of an element in its most stable form is:
a)
Always positive
b)
Always negative
c)
Zero
d)
Variable depending on the element
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) of an element in its most stable form is defined as zero. This is because the formation of an element from its constituent elements does not involve any net energy change.
Which of the following statements best characterizes the data represented in the liquid-vapor phase diagram of carbon dioxide where the dotted line represents phase change?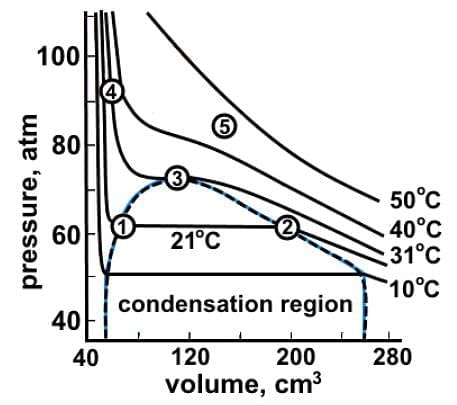
- a)Point 5 is the critical point of carbon dioxide.
- b)Moving from point 1 to 2, carbon dioxide is undergoing condensation.
- c)Moving left along the isotherm from point 1, the pressure increases drastically since carbon dioxide becomes an incompressible solid.
- d)Above the isotherm for 31∘C, carbon dioxide exists only as a supercritical fluid.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements best characterizes the data represented in the liquid-vapor phase diagram of carbon dioxide where the dotted line represents phase change?

a)
Point 5 is the critical point of carbon dioxide.
b)
Moving from point 1 to 2, carbon dioxide is undergoing condensation.
c)
Moving left along the isotherm from point 1, the pressure increases drastically since carbon dioxide becomes an incompressible solid.
d)
Above the isotherm for 31∘C, carbon dioxide exists only as a supercritical fluid.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
This is a P-V graph, so the plotted lines represent isotherms, whereby each line represents a different temperature. Normally, the plot is hyperbolic in shape, but as the temperature decreases, the plot flattens into a liquid-vapor equilibrium region or condensation region.
Moving from point 1 to 2, carbon dioxide is undergoing evaporation not condensation since the liquid region is to the left and the vapor region is to the right.
To the left of point 1, the pressure increases drastically because carbon dioxide has condensed into an incompressible liquid not solid.
Point 3 is the critical point of carbon dioxide, and the isotherm through point 3 is the critical isotherm.
Above the isotherm through point 3, carbon dioxide exists only as a supercritical fluid.
Which of the following statements can reasonably be deduced from the phase diagram of helium below?
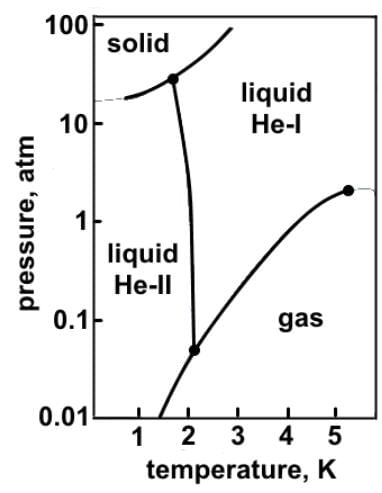
- a)At atmospheric pressure, helium can exist in all three phases, as well as a supercritical fluid phase near absolute zero.
- b)Solid and gaseous helium never exist in equilibrium with each other at any temperature or pressure.
- c)Helium does not exist as a solid below 25 atmospheres due to its low mass.
- d)At room temperature, helium exists as a gas, and as pressure increases eventually becomes a solid.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements can reasonably be deduced from the phase diagram of helium below?


a)
At atmospheric pressure, helium can exist in all three phases, as well as a supercritical fluid phase near absolute zero.
b)
Solid and gaseous helium never exist in equilibrium with each other at any temperature or pressure.
c)
Helium does not exist as a solid below 25 atmospheres due to its low mass.
d)
At room temperature, helium exists as a gas, and as pressure increases eventually becomes a solid.

|
Orion Classes answered |
Helium has some peculiar features in its phase diagram. A typical phase diagram looks like the following:
At room temperature, helium exists as a gas, and as pressure increases it eventually becomes a liquid. Looking at the line boundary between solid and the two liquid phases, the line curves up. Since the graph is using the logarithmic scale, the line curves more steeply than it would seem.
At atmospheric pressure, helium can exist as a supercritical fluid (He-II), normal liquid (He-I), and gas, but not as a solid.
Helium does not exist as a solid below 25 atmospheres due to the weak London dispersion forces that exist between noble gas atoms.
According to Hess's law, which of the following statements is true?- a)The enthalpy change of a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes of its individual steps.
- b)The entropy change of a reaction is inversely proportional to its enthalpy change.
- c)The enthalpy change of a reaction is dependent on the temperature at which it occurs.
- d)The entropy change of a reaction is always positive.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
According to Hess's law, which of the following statements is true?
a)
The enthalpy change of a reaction is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes of its individual steps.
b)
The entropy change of a reaction is inversely proportional to its enthalpy change.
c)
The enthalpy change of a reaction is dependent on the temperature at which it occurs.
d)
The entropy change of a reaction is always positive.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Hess's law states that the enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of the pathway taken and depends only on the initial and final states of the reaction. This means that the overall enthalpy change of a reaction can be calculated by summing up the enthalpy changes of the individual steps involved.
The heat capacity of a substance is defined as:- a)The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
- b)The heat energy released by a substance during a chemical reaction.
- c)The amount of heat required to convert a substance from a solid to a liquid.
- d)The enthalpy change of a substance during a phase transition.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The heat capacity of a substance is defined as:
a)
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
b)
The heat energy released by a substance during a chemical reaction.
c)
The amount of heat required to convert a substance from a solid to a liquid.
d)
The enthalpy change of a substance during a phase transition.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Heat capacity is a measure of the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. It is expressed in units of energy per degree Celsius (or Kelvin) and represents the ability of a substance to absorb heat.
Which of the following statements is true about the first law of thermodynamics?- a)Energy is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- b)The total entropy of a system and its surroundings always decreases.
- c)The enthalpy change of a reaction is directly proportional to the volume change.
- d)The heat energy released by a system is equal to the work done by the system.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is true about the first law of thermodynamics?
a)
Energy is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
b)
The total entropy of a system and its surroundings always decreases.
c)
The enthalpy change of a reaction is directly proportional to the volume change.
d)
The heat energy released by a system is equal to the work done by the system.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The first law of thermodynamics, also known as the law of conservation of energy, states that energy is conserved in a chemical reaction. It cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be converted from one form to another (e.g., from heat to work or vice versa).
Which of the following equations represents a formation reaction?- a)
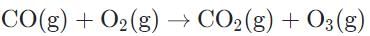
- b)
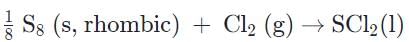
- c)
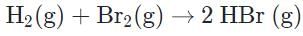
- d)
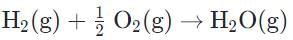
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following equations represents a formation reaction?
a)
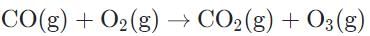
b)
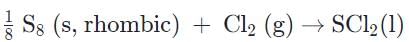
c)
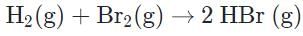
d)
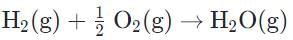
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The standard enthalpy of formation of a compound is defined as the heat associated with the formation of one mole of the compound from its elements in their standard states. Most formation reactions are exothermic, but some are endothermic.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is not an element, in its reaction with oxygen gas, so the reaction is not a formation reaction.
In the reaction with hydrogen and bromine gases reacting, bromine is not in its standard state, which is liquid not gas. Bromine and mercury are the only two elements that are liquid in its standard state. The formation reaction of HBr would look like this:
H2 (g) + Br2 (1) + 2BHr (g)
In the reaction with hydrogen and oxygen gases reacting, water on the product state is not in its standard state. The formation reaction of H2O would look like this:
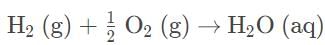
In the reaction with rhombic sulfur and chlorine gas, there are elements in their standard state on the reactant side and only one product in its standard state. Sulfur is peculiar in that sulfur is not monoatomic and additionally has two forms, rhombic and monoclinic, and rhombic is the more stable form. The formation reaction of is SC12 correct as stated.
Which of the following processes is associated with a positive entropy change?- a)Melting of ice
- b)Dissolution of a gas in water
- c)Combustion of a hydrocarbon
- d)Condensation of a vapor
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following processes is associated with a positive entropy change?
a)
Melting of ice
b)
Dissolution of a gas in water
c)
Combustion of a hydrocarbon
d)
Condensation of a vapor
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The dissolution of a gas in water is associated with a positive entropy change. When a gas dissolves, its particles become dispersed in the liquid, increasing the disorder or randomness of the system, which corresponds to an increase in entropy.
Which of the following statements accurately describes thermochemistry?- a)It studies the formation and properties of chemical bonds.
- b)It focuses on the behavior of gases under various conditions.
- c)It explores the relationships between heat and other forms of energy in chemical reactions.
- d)It investigates the rate at which chemical reactions occur.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements accurately describes thermochemistry?
a)
It studies the formation and properties of chemical bonds.
b)
It focuses on the behavior of gases under various conditions.
c)
It explores the relationships between heat and other forms of energy in chemical reactions.
d)
It investigates the rate at which chemical reactions occur.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Thermochemistry is a branch of chemistry that deals with the study of heat energy changes that occur during chemical reactions and phase transitions. It involves the measurement and calculation of quantities such as heat capacity, enthalpy, and entropy.
Chapter doubts & questions for Thermochemistry - General Chemistry for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Thermochemistry - General Chemistry for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
General Chemistry for MCAT
164 videos|11 docs|16 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









