All Exams >
MCAT >
Physics for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Electrostatics for MCAT Exam
The magnitude of electric field experienced by a charge at a certain distance from a source charge is equal to 64 N/C. What will be the magnitude of the electric field at four times that distance and with a source charge half as strong?- a)1 N/C
- b)2 N/C
- c)64 N/C
- d)128 N/C
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnitude of electric field experienced by a charge at a certain distance from a source charge is equal to 64 N/C. What will be the magnitude of the electric field at four times that distance and with a source charge half as strong?
a)
1 N/C
b)
2 N/C
c)
64 N/C
d)
128 N/C
|
|
Ava Brown answered |
The magnitude of the electric field is given by Coulomb's Law, which states that the electric field (E) is directly proportional to the source charge (Q) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between the source charge and the point where the electric field is being measured. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
E = k * (Q/r^2)
where k is the electrostatic constant.
In this question, we are given that the magnitude of the electric field at a certain distance (let's call it r1) is 64 N/C. Let's assume that the source charge at this distance is Q1.
So, we have:
64 = k * (Q1/r1^2) ...(1)
Now, we need to find the magnitude of the electric field at four times the distance (4r1) with a source charge half as strong (Q2 = Q1/2).
Using the same formula, we can write:
E' = k * (Q2/(4r1)^2) ...(2)
To find the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1, we can substitute 4r1 for r in equation (1):
64 = k * (Q1/(4r1)^2)
Simplifying this equation, we get:
64 = k * (Q1/16r1^2)
Multiplying both sides of the equation by 16, we get:
1024 = k * (Q1/r1^2)
This equation is equivalent to equation (1), which means that the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 is also 64 N/C.
Now, let's substitute the values into equation (2) to find the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 with a source charge half as strong:
E' = k * (Q2/(4r1)^2)
E' = k * ((Q1/2)/(4r1)^2)
E' = k * (Q1/8r1^2)
Since we know that the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 is 64 N/C, we can write:
64 = k * (Q1/8r1^2)
Simplifying this equation, we get:
512 = k * (Q1/r1^2)
Comparing this equation with equation (1), we can see that the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 with a source charge half as strong is 512 N/C.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B) 2 N/C.
E = k * (Q/r^2)
where k is the electrostatic constant.
In this question, we are given that the magnitude of the electric field at a certain distance (let's call it r1) is 64 N/C. Let's assume that the source charge at this distance is Q1.
So, we have:
64 = k * (Q1/r1^2) ...(1)
Now, we need to find the magnitude of the electric field at four times the distance (4r1) with a source charge half as strong (Q2 = Q1/2).
Using the same formula, we can write:
E' = k * (Q2/(4r1)^2) ...(2)
To find the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1, we can substitute 4r1 for r in equation (1):
64 = k * (Q1/(4r1)^2)
Simplifying this equation, we get:
64 = k * (Q1/16r1^2)
Multiplying both sides of the equation by 16, we get:
1024 = k * (Q1/r1^2)
This equation is equivalent to equation (1), which means that the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 is also 64 N/C.
Now, let's substitute the values into equation (2) to find the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 with a source charge half as strong:
E' = k * (Q2/(4r1)^2)
E' = k * ((Q1/2)/(4r1)^2)
E' = k * (Q1/8r1^2)
Since we know that the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 is 64 N/C, we can write:
64 = k * (Q1/8r1^2)
Simplifying this equation, we get:
512 = k * (Q1/r1^2)
Comparing this equation with equation (1), we can see that the magnitude of the electric field at 4r1 with a source charge half as strong is 512 N/C.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B) 2 N/C.
Sphere A and B have the same mass and charge magnitudes. They are placed a distance r away from each other so that gravitational forces and electrostatic forces allow both spheres to be in equilibrium. What would occur if sphere A doubled in charge?- a)Both spheres would move away from each other with the same force.
- b)Both spheres would move towards each other with increasing acceleration.
- c)Both spheres would move towards each other but sphere B will experience a greater force.
- d)Both spheres would move away from each other but sphere A will experience a greater force.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sphere A and B have the same mass and charge magnitudes. They are placed a distance r away from each other so that gravitational forces and electrostatic forces allow both spheres to be in equilibrium. What would occur if sphere A doubled in charge?
a)
Both spheres would move away from each other with the same force.
b)
Both spheres would move towards each other with increasing acceleration.
c)
Both spheres would move towards each other but sphere B will experience a greater force.
d)
Both spheres would move away from each other but sphere A will experience a greater force.
|
|
Chloe Turner answered |
Explanation:
Gravitational and Electrostatic Forces:
- In order for Sphere A and B to be in equilibrium, the gravitational force and electrostatic force between them should be equal and opposite.
Doubling Charge on Sphere A:
- When the charge on Sphere A is doubled, the electrostatic force between the two spheres will also double according to Coulomb's law.
Effect on Equilibrium:
- Since the mass and charge magnitudes of both spheres are the same, doubling the charge on Sphere A will not affect the gravitational force between them.
- As a result, both spheres will move away from each other with the same force to maintain equilibrium.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Both spheres would move away from each other with the same force.
Gravitational and Electrostatic Forces:
- In order for Sphere A and B to be in equilibrium, the gravitational force and electrostatic force between them should be equal and opposite.
Doubling Charge on Sphere A:
- When the charge on Sphere A is doubled, the electrostatic force between the two spheres will also double according to Coulomb's law.
Effect on Equilibrium:
- Since the mass and charge magnitudes of both spheres are the same, doubling the charge on Sphere A will not affect the gravitational force between them.
- As a result, both spheres will move away from each other with the same force to maintain equilibrium.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - Both spheres would move away from each other with the same force.
The figure below shows a source charge Q. Which of the following can best describe the electric potential difference as a positive point charge is moved from position A to position B through the indicated path?
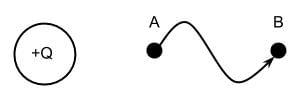
- a)The change in electric potential difference is zero
- b)The change in electric potential difference is positive
- c)The change in electric potential difference is positive then negative
- d)The change in electric potential difference is negative
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The figure below shows a source charge Q. Which of the following can best describe the electric potential difference as a positive point charge is moved from position A to position B through the indicated path?


a)
The change in electric potential difference is zero
b)
The change in electric potential difference is positive
c)
The change in electric potential difference is positive then negative
d)
The change in electric potential difference is negative

|
Orion Classes answered |
- The path does not matter when determining the change in electric potential difference of a point charge.
- The electric potential difference with respect to infinity of a charge Q, or voltage, at a point is determined by the formula
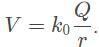 Where Q is the value of a source charge and r is the distance between the source charge and the point charge.
Where Q is the value of a source charge and r is the distance between the source charge and the point charge. - At both points, the k0 constant and value of source charge Q is the same. The only difference is the distance, r, between the test charge and the source charge.
- Since the distance r is larger at point B, the electric potential difference with respect to inifinity is smaller.
- The electric potential difference from A to B is this smaller V amount, at position B, subtracted by the original larger
- V at position A. The resulting electric potential difference is negative.
In the figure below, spheres q1 ,q2 , and q3 have the same positive charge magnitude. Which of the following is a possible direction for the net electric field vector on q4?
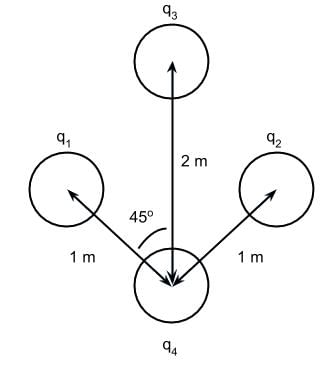
- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)

Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the figure below, spheres q1 ,q2 , and q3 have the same positive charge magnitude. Which of the following is a possible direction for the net electric field vector on q4?


a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- The superposition principle means that the net electric field vector is the sum of all individual electric field vector arrows made by each charge’s interaction with the charge being affected.
- If q1 and q2 have the same positive charge magnitude, then their electric field vector arrows should cancel out in the horizontal direction. This will occur whether q4 has a positive or negative charge.
- Since there is no other charge to influence the direction of the net electric field vector in the horizontal direction, the correct vector direction should not be angled toward the left or the right. An arrow that points straight up or straight down are possible directions for the net electric field vector.
A constant electric field moves a positive point charge from one position to another position so that the change in electric potential is −450 V. Which of the following must increase during this movement?- a)The charge’s potential energy
- b)The charge’s electric potential
- c)The charge’s acceleration
- d)The charge’s velocity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A constant electric field moves a positive point charge from one position to another position so that the change in electric potential is −450 V. Which of the following must increase during this movement?
a)
The charge’s potential energy
b)
The charge’s electric potential
c)
The charge’s acceleration
d)
The charge’s velocity
|
|
Chloe Turner answered |
Explanation:
Charge's potential energy:
- The potential energy of a charge in an electric field is given by the equation U = qV, where U is the potential energy, q is the charge, and V is the electric potential.
- Since the change in electric potential is -450V, the potential energy of the charge will decrease by 450V as it moves from one position to another.
Charge's electric potential:
- The electric potential of a charge is defined as the electric potential energy per unit charge. It is given by the equation V = U/q, where V is the electric potential, U is the potential energy, and q is the charge.
- Since the charge is moving in a constant electric field, the electric potential remains constant and does not increase or decrease.
Charge's acceleration:
- The acceleration of a charge in an electric field depends on the force acting on it, which in turn depends on the electric field strength and the charge of the particle.
- Since the electric field is constant, the acceleration of the charge will also remain constant and will not increase during the movement.
Charge's velocity:
- As the charge moves from one position to another against the electric field, its kinetic energy will increase, leading to an increase in velocity.
- Therefore, the charge's velocity must increase during this movement.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'D' - The charge's velocity must increase during the movement.
Charge's potential energy:
- The potential energy of a charge in an electric field is given by the equation U = qV, where U is the potential energy, q is the charge, and V is the electric potential.
- Since the change in electric potential is -450V, the potential energy of the charge will decrease by 450V as it moves from one position to another.
Charge's electric potential:
- The electric potential of a charge is defined as the electric potential energy per unit charge. It is given by the equation V = U/q, where V is the electric potential, U is the potential energy, and q is the charge.
- Since the charge is moving in a constant electric field, the electric potential remains constant and does not increase or decrease.
Charge's acceleration:
- The acceleration of a charge in an electric field depends on the force acting on it, which in turn depends on the electric field strength and the charge of the particle.
- Since the electric field is constant, the acceleration of the charge will also remain constant and will not increase during the movement.
Charge's velocity:
- As the charge moves from one position to another against the electric field, its kinetic energy will increase, leading to an increase in velocity.
- Therefore, the charge's velocity must increase during this movement.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'D' - The charge's velocity must increase during the movement.
In five seconds, a point charge moves from position A to position B as shown in the diagram below. Which one of the following two paths require the most energy?
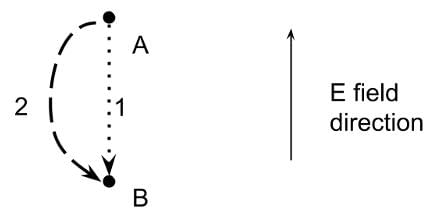
- a)Both paths require an equal amount of energy because work is independent of the path.
- b)Both paths require an equal amount of energy because they both complete the same displacement in position in the same amount of time.
- c)Path #1 requires more energy because it directly opposes the electric field.
- d)Path #2 requires more energy because it moves the point charge through a longer distance.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In five seconds, a point charge moves from position A to position B as shown in the diagram below. Which one of the following two paths require the most energy?


a)
Both paths require an equal amount of energy because work is independent of the path.
b)
Both paths require an equal amount of energy because they both complete the same displacement in position in the same amount of time.
c)
Path #1 requires more energy because it directly opposes the electric field.
d)
Path #2 requires more energy because it moves the point charge through a longer distance.

|
Orion Classes answered |
- The amount of time is not relevant to this problem.
- In electrostatics, energy is determined by product of the point charge magnitude, the displacement of the point charge, and the value of the electric field, for a constant field in the direction of displacement:
W = Fd
W = qEd - When the displacement is the same for both paths of a point charge along a constant electric field, the energy expended is equivalent.
The magnitude of the electric force experienced by a point charge a distance d away from a source charge is affected by which of the following?- a)The sign of the point charge.
- b)The sign of the source charge.
- c)The value of distance d.
- d)The mass of the source charge.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The magnitude of the electric force experienced by a point charge a distance d away from a source charge is affected by which of the following?
a)
The sign of the point charge.
b)
The sign of the source charge.
c)
The value of distance d.
d)
The mass of the source charge.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- The sign of the source charge affects only the direction of the electric force (either towards or away from a source charge), it does not affect the magnitude.
- Similarly, the sign of the point charge affects only the direction of the electric force and not its magnitude.
- The mass of an object is important for determining gravitational force, not electrostatic force. The electric force of a single point charge q at a distance d away from a source charge Q is given by the equation
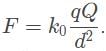 The signs of both charges will only affect the overall sign on the force value. The distance d is the only answer choice that affects the magnitude of the electric force.
The signs of both charges will only affect the overall sign on the force value. The distance d is the only answer choice that affects the magnitude of the electric force.
If one sphere has a mass of 2 kg and an electric charge of +4 μC while another sphere, 3 meters away, has a mass of 1 kg and an electric charge of +5 μC, what is the acceleration of the more massive sphere?- a)0.04 m/s2
- b)0.03 m/s2
- c)0.01 m/s2
- d)0.02 m/s2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
If one sphere has a mass of 2 kg and an electric charge of +4 μC while another sphere, 3 meters away, has a mass of 1 kg and an electric charge of +5 μC, what is the acceleration of the more massive sphere?
a)
0.04 m/s2
b)
0.03 m/s2
c)
0.01 m/s2
d)
0.02 m/s2
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- In order to determine the acceleration of an object, we must first determine the magnitude and direction of forces acting on the object.
- Since like charges repel, the more massive sphere experiences an electric force in the direction away from the less massive sphere. It also experiences a gravitational force attracting it to the less massive sphere.
- The gravitational force is much weaker than electric force by many orders of magnitude, thus it’s effect on the more massive sphere is negligible.
- The electric force felt by the massive sphere can be determined by Coulomb’s Law:
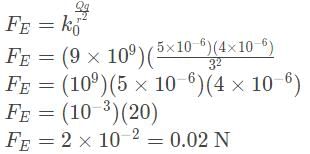
- In order to determine the acceleration, we must divide the net force by the mass of the object:
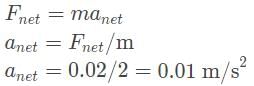
In the diagram below, which of the following statements is true about a point charge in position A, which is midway between two positive source charges of equal magnitude?
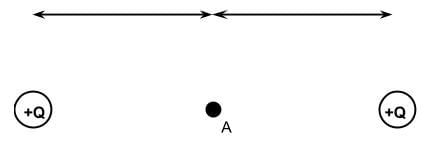
- a)The net electric potential difference with respect to infinity is 0
- b)The electric field is positive
- c)Work is currently being done on the point charge
- d)The net electrostatic force is 0
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the diagram below, which of the following statements is true about a point charge in position A, which is midway between two positive source charges of equal magnitude?


a)
The net electric potential difference with respect to infinity is 0
b)
The electric field is positive
c)
Work is currently being done on the point charge
d)
The net electrostatic force is 0
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- The electric potential at a point charge is the sum of each individual source charge’s contribution. Since both source charges are positive, they contribute a positive electric potential difference at point A.
- The electric field arrows of each source charge’s contribution to the point charge is in the direction away from the source charge. Since the two source charges are in opposing directions, are equidistant from the point charge, and are equal in magnitude, the electric field vectors cancel out, thus electric field at position A is 0.
- If the electric field is 0, then there is no electrostatic force moving the point charge. If an object is not displaced, no work is being done.
- Since the point charge is equally repelled by both source charges, the net electrostatic force experienced by the charge at that point must be 0.
After MgCl2 dissolves in a neutrally charged solvent, what is the net charge of the solution?- a)The solution becomes negatively charged due to the majority Cl- ions.
- b)The solution becomes positively charged due to the stronger Mg2+ ions.
- c)The solution remains neutrally charged.
- d)The solution becomes positive or negative, depending on the relative Mg2+ Cl− concentrations.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
After MgCl2 dissolves in a neutrally charged solvent, what is the net charge of the solution?
a)
The solution becomes negatively charged due to the majority Cl- ions.
b)
The solution becomes positively charged due to the stronger Mg2+ ions.
c)
The solution remains neutrally charged.
d)
The solution becomes positive or negative, depending on the relative Mg2+ Cl− concentrations.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- The law of conservation of charge states that the net charge of an isolated system remains constant.
- When the ions are added to a neutrally charged solvent like water, the overall solution remains the same.
- MgCl2 dissolves into one +2 cation and two -1 anions.
- The only way to change the net charge of a system is to introduce a charge from elsewhere, or to remove a charge from the system. In this closed system, the resulting Mg2+ cation and two Cl− anions will yield an overall neutral charge.
Chapter doubts & questions for Electrostatics - Physics for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Electrostatics - Physics for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Physics for MCAT
158 videos|21 docs|21 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









