All Exams >
MCAT >
Psychology and Sociology for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Normative and Non-normative Behavior for MCAT Exam
Which of the following is not a characteristic of social anomie?- a)Alienation from social groups
- b)Weakened social norms
- c)Social uncertainty
- d)Strengthened social norms
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not a characteristic of social anomie?
a)
Alienation from social groups
b)
Weakened social norms
c)
Social uncertainty
d)
Strengthened social norms
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Social anomie refers to a state of normlessness or a breakdown of social norms and values in a society. It is typically characterized by certain features. Alienation from social groups (A) is one of these characteristics, where individuals may feel disconnected or isolated from social relationships and communities. Weakened social norms (B) are another characteristic, indicating that the usual rules and expectations that guide behavior become unclear or ineffective. Social uncertainty (C) is also a key characteristic of social anomie, where individuals may experience a lack of predictability or stability in social interactions and societal structures.
On the other hand, strengthened social norms (D) would be contradictory to the concept of social anomie. Social anomie suggests a state of normlessness or a weakening of social norms, not an enhancement or strengthening of them. Therefore, D is the correct answer as it does not align with the characteristics typically associated with social anomie.
Josephine is an American college student who spends her sophomore year studying abroad in France. Her appreciation of French culture is heavily influenced by her experiences with French cuisine. She feels that the French believe it is important for families to take pride in the quality of their food and how it is prepared. She believes that the culture benefits from families eating and enjoying their food together. She ultimately decides French culture is superior to American culture. What term describes Josephine’s beliefs?- a)Xenocentrism
- b)Cultural relativism
- c)Ethnocentrism
- d)Cultural imperialism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Josephine is an American college student who spends her sophomore year studying abroad in France. Her appreciation of French culture is heavily influenced by her experiences with French cuisine. She feels that the French believe it is important for families to take pride in the quality of their food and how it is prepared. She believes that the culture benefits from families eating and enjoying their food together. She ultimately decides French culture is superior to American culture. What term describes Josephine’s beliefs?
a)
Xenocentrism
b)
Cultural relativism
c)
Ethnocentrism
d)
Cultural imperialism
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Xenocentrism refers to the belief or preference for the values, customs, or culture of another society or culture over one's own. In this scenario, Josephine's admiration and preference for French culture and considering it superior to American culture demonstrate xenocentrism. She values and appreciates the cultural practices of the French, particularly their emphasis on food and family meals, and perceives them as more desirable than her own American culture.
How would one describe the behaviors of an individual that enhance another individual’s or group’s fitness at a cost to that individual’s fitness?- a)Biological altruism
- b)Genetic altruism
- c)Psychological altruism
- d)Reciprocal altruism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
How would one describe the behaviors of an individual that enhance another individual’s or group’s fitness at a cost to that individual’s fitness?
a)
Biological altruism
b)
Genetic altruism
c)
Psychological altruism
d)
Reciprocal altruism
|
|
Lincoln Powell answered |
Understanding Biological Altruism
Biological altruism refers to behaviors performed by an individual that benefit another individual or group at a cost to the individual’s own fitness. This concept is pivotal in evolutionary biology, as it explains how cooperative behaviors can arise even when they seem to disadvantage the individual performing them.
Key Characteristics of Biological Altruism:
- Cost to Self: The altruistic individual incurs a fitness cost, which may include reduced reproductive opportunities or increased risk of predation.
- Benefit to Others: The behavior enhances the survival and reproduction of the recipient, thus increasing their overall fitness. This support may manifest in various forms, such as sharing resources, protecting others, or nurturing offspring.
- Evolutionary Perspective: Despite the cost to the altruist, these behaviors can be favored by natural selection if they contribute to the overall survival of a related group or kin. This is often explained through concepts like kin selection, where helping relatives can indirectly promote the altruist's genetic legacy.
Examples in Nature:
- Alarm Calls in Animals: Certain species make alarm calls to warn others of predators, risking their own safety to protect the group.
- Cooperative Breeding: In some bird species, non-breeding individuals assist in raising the offspring of others, which can increase the survival rate of the young.
Conclusion:
Biological altruism highlights the complexities of social behaviors in the animal kingdom, showcasing how selfless acts can play a crucial role in the survival and evolution of species. Understanding this concept is essential for comprehending the dynamics of social interactions within species.
Biological altruism refers to behaviors performed by an individual that benefit another individual or group at a cost to the individual’s own fitness. This concept is pivotal in evolutionary biology, as it explains how cooperative behaviors can arise even when they seem to disadvantage the individual performing them.
Key Characteristics of Biological Altruism:
- Cost to Self: The altruistic individual incurs a fitness cost, which may include reduced reproductive opportunities or increased risk of predation.
- Benefit to Others: The behavior enhances the survival and reproduction of the recipient, thus increasing their overall fitness. This support may manifest in various forms, such as sharing resources, protecting others, or nurturing offspring.
- Evolutionary Perspective: Despite the cost to the altruist, these behaviors can be favored by natural selection if they contribute to the overall survival of a related group or kin. This is often explained through concepts like kin selection, where helping relatives can indirectly promote the altruist's genetic legacy.
Examples in Nature:
- Alarm Calls in Animals: Certain species make alarm calls to warn others of predators, risking their own safety to protect the group.
- Cooperative Breeding: In some bird species, non-breeding individuals assist in raising the offspring of others, which can increase the survival rate of the young.
Conclusion:
Biological altruism highlights the complexities of social behaviors in the animal kingdom, showcasing how selfless acts can play a crucial role in the survival and evolution of species. Understanding this concept is essential for comprehending the dynamics of social interactions within species.
A link between the color red and attraction has been suggested as representing a physiologically based association. All previous research regarding this association was conducted on Western university students. A researcher traveled to a remote village with little Western contact and negative associations regarding red. The village lacked specific associations between red and attraction. It also displayed extremely conservative societal norms regarding sex. A previous study’s methodology was replicated with villagers of this tribe. Why did the researcher choose to replicate this study with this tribe?- a)If the tribe showed an association, it would give weight to a universal human association.
- b)This tribe will likely be more truthful in responding to questions about sexual attitudes and norms.
- c)The researchers should have produced their own study, rather than replicating a previous study.
- d)The tribe would not have been exposed the color ‘red.’
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A link between the color red and attraction has been suggested as representing a physiologically based association. All previous research regarding this association was conducted on Western university students. A researcher traveled to a remote village with little Western contact and negative associations regarding red. The village lacked specific associations between red and attraction. It also displayed extremely conservative societal norms regarding sex. A previous study’s methodology was replicated with villagers of this tribe. Why did the researcher choose to replicate this study with this tribe?
a)
If the tribe showed an association, it would give weight to a universal human association.
b)
This tribe will likely be more truthful in responding to questions about sexual attitudes and norms.
c)
The researchers should have produced their own study, rather than replicating a previous study.
d)
The tribe would not have been exposed the color ‘red.’
|
|
Lincoln Powell answered |
Understanding the Research Context
The researcher’s decision to replicate the study in a remote village stems from the desire to examine the universality of the association between the color red and attraction, particularly in a cultural context that differs significantly from Western norms.
Significance of a Universal Association
- Cultural Diversity: Previous studies predominantly involved Western university students, raising concerns about cultural bias. Examining a different culture provides insights into whether the red-attraction link is a universal human phenomenon or culturally specific.
- Negative Associations: The village’s negative associations with red offer a unique opportunity to challenge or confirm existing theories. If the villagers show an attraction to red despite these associations, it would bolster the argument for a physiological basis for this connection.
Implications for Psychology
- Broader Understanding: Discovering a similar association in a culturally conservative environment could suggest that certain psychological responses to color are deeply ingrained in human biology, transcending cultural differences.
- Scientific Rigor: Replicating studies in diverse populations enhances the robustness of psychological theories. If findings are consistent across various cultural contexts, they gain greater credibility and relevance.
Conclusion
In summary, the researcher aimed to explore whether the color red holds a universal significance in attraction. Finding an association in this remote village would provide compelling evidence for an innate psychological link, regardless of cultural influences. This approach not only enriches the understanding of human attraction but also contributes to the broader field of psychology by highlighting the importance of diverse cultural perspectives in research.
The researcher’s decision to replicate the study in a remote village stems from the desire to examine the universality of the association between the color red and attraction, particularly in a cultural context that differs significantly from Western norms.
Significance of a Universal Association
- Cultural Diversity: Previous studies predominantly involved Western university students, raising concerns about cultural bias. Examining a different culture provides insights into whether the red-attraction link is a universal human phenomenon or culturally specific.
- Negative Associations: The village’s negative associations with red offer a unique opportunity to challenge or confirm existing theories. If the villagers show an attraction to red despite these associations, it would bolster the argument for a physiological basis for this connection.
Implications for Psychology
- Broader Understanding: Discovering a similar association in a culturally conservative environment could suggest that certain psychological responses to color are deeply ingrained in human biology, transcending cultural differences.
- Scientific Rigor: Replicating studies in diverse populations enhances the robustness of psychological theories. If findings are consistent across various cultural contexts, they gain greater credibility and relevance.
Conclusion
In summary, the researcher aimed to explore whether the color red holds a universal significance in attraction. Finding an association in this remote village would provide compelling evidence for an innate psychological link, regardless of cultural influences. This approach not only enriches the understanding of human attraction but also contributes to the broader field of psychology by highlighting the importance of diverse cultural perspectives in research.
“Sons of Anarchy” is an American television show that depicts the activities of a fictional motorcycle gang in California. The gang has their own specific rules and norms. They place high value on money, violence, and crime; they believe that they have the power to resolve conflicts with other groups and do not believe in the power of the law. Which type of culture would this group fit into?- a)Popular culture
- b)Normative culture
- c)Counterculture
- d)High culture
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
“Sons of Anarchy” is an American television show that depicts the activities of a fictional motorcycle gang in California. The gang has their own specific rules and norms. They place high value on money, violence, and crime; they believe that they have the power to resolve conflicts with other groups and do not believe in the power of the law. Which type of culture would this group fit into?
a)
Popular culture
b)
Normative culture
c)
Counterculture
d)
High culture
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Counterculture refers to a subculture or group within a society that holds values, beliefs, and norms that are in direct opposition or contrast to the dominant culture or mainstream society. These groups often challenge and reject the established norms, values, and practices of the larger society.
In the case of the fictional motorcycle gang depicted in the television show "Sons of Anarchy," their adherence to their own specific rules and norms, which prioritize money, violence, and crime over the power of the law, represents a counterculture. They operate outside the boundaries of conventional societal norms and engage in activities that are considered deviant or criminal by the larger society.
While the gang's values and behaviors may have elements of popular culture (A) due to the television show's portrayal and popularity, it is more accurately described as a counterculture given its opposition to dominant norms and its distinct subcultural identity. Normative culture (B) refers to the cultural norms and values that are widely accepted and practiced within a society, which the motorcycle gang in question opposes. High culture (D) refers to cultural products and activities that are considered to be of superior intellectual or artistic value, which is not the focus of the gang's activities.
Which of the following is an example of an informal negative sanction?- a)An individual is expelled from school after plagiarizing a research paper.
- b)An individual is patted on the back for helping an elderly resident carry groceries.
- c)An individual is scowled at after swearing loudly in a church.
- d)An individual is given a ticket for parking in a restricted zone.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of an informal negative sanction?
a)
An individual is expelled from school after plagiarizing a research paper.
b)
An individual is patted on the back for helping an elderly resident carry groceries.
c)
An individual is scowled at after swearing loudly in a church.
d)
An individual is given a ticket for parking in a restricted zone.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
An informal negative sanction refers to an unofficial form of punishment or disapproval for violating social norms or expectations. In this example, the individual's behavior of swearing loudly in a church goes against the expected norm of respectful behavior in a religious setting. The scowling reaction from others is a form of nonverbal disapproval, conveying the message that the individual's behavior is inappropriate or offensive. It is an informal negative sanction because it is not an official punishment imposed by an authority figure or institution but rather a social reaction from others.
Brian visits an ashram in India for a month. He returns with a deep appreciation of Indian food, art, and cultural customs. He begins taking cooking classes that emphasize the use of Indian spices, practices yoga with his friends, and has philosophical conversations about karma with his family. What term refers to this experience?- a)Cultural imperialism
- b)Globalization
- c)Diffusion
- d)Ethnocentrism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Brian visits an ashram in India for a month. He returns with a deep appreciation of Indian food, art, and cultural customs. He begins taking cooking classes that emphasize the use of Indian spices, practices yoga with his friends, and has philosophical conversations about karma with his family. What term refers to this experience?
a)
Cultural imperialism
b)
Globalization
c)
Diffusion
d)
Ethnocentrism
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Diffusion refers to the spread or transmission of cultural elements from one society or group to another. In the given scenario, Brian's experience at the ashram in India exposes him to various aspects of Indian culture, such as food, art, customs, cooking techniques, yoga, and philosophical concepts like karma. By immersing himself in the Indian culture and adopting these practices, Brian is engaging in cultural diffusion.
Cultural imperialism (A) refers to the dominance or imposition of one culture over others, often through political or economic means. Globalization (B) refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of societies worldwide, leading to the exchange of ideas, goods, and information. While Brian's experience may be influenced by globalization, the specific term that describes his engagement with Indian culture is diffusion.
Ethnocentrism (D) refers to the tendency to judge other cultures based on the standards and values of one's own culture. It is not applicable in this context as Brian's experience demonstrates an appreciation and adoption of aspects of Indian culture, rather than a judgment or comparison based on his own cultural perspective.
Which of these factors will cause aggressive behavior?- a)A person experiencing frustration, pain, or elevated temperature.
- b)A person with an increase in testosterone levels throughout the body.
- c)None of these choices alone is sufficient to cause aggressive behavior.
- d)A person who belongs to a culture of honor.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these factors will cause aggressive behavior?
a)
A person experiencing frustration, pain, or elevated temperature.
b)
A person with an increase in testosterone levels throughout the body.
c)
None of these choices alone is sufficient to cause aggressive behavior.
d)
A person who belongs to a culture of honor.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- An increase in testosterone can happen for many reasons. Although increased levels of testosterone increase the chances of aggressive behavior under certain circumstances, increased testosterone alone will not cause aggression.
- Psychological and sociocultural factors can inhibit or promote aggression.
- Aggression is caused by a combination of biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors.
- None of these choices alone is sufficient to cause aggressive behavior.
Which of these studies looked into attachment, comfort, and security as innate needs and the effects of maternal and social deprivation on development?- a)Schrodinger’s Cat Experiment
- b)Harlow monkey experiments
- c)Skinner’s studies with pigeons
- d)Bobo Doll experiments
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these studies looked into attachment, comfort, and security as innate needs and the effects of maternal and social deprivation on development?
a)
Schrodinger’s Cat Experiment
b)
Harlow monkey experiments
c)
Skinner’s studies with pigeons
d)
Bobo Doll experiments
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Schrodinger’s Cat Experiment was a thought experiment illustrating principles of quantum mechanics.
- The Bobo doll experiment studied the effects of observational and modeling learning.
- B. F. Skinner’s studies with pigeons were an analysis of operant conditioning.
- Harlow monkey experiments
Following the passing of a controversial law by a local leader, a crowd of individuals gathers and begins to act violently. The crowd destroys property, engages in theft, and sets fires in local business places. The crowd is fueled by a deep feeling that an injustice has occurred, but their behavior is unfocused, violent, and random. What collective behavior does this describe?- a)Riot
- b)Bystander effect
- c)Mass hysteria
- d)Mob
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Following the passing of a controversial law by a local leader, a crowd of individuals gathers and begins to act violently. The crowd destroys property, engages in theft, and sets fires in local business places. The crowd is fueled by a deep feeling that an injustice has occurred, but their behavior is unfocused, violent, and random. What collective behavior does this describe?
a)
Riot
b)
Bystander effect
c)
Mass hysteria
d)
Mob
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The described scenario fits the definition of a riot. A riot is a form of collective behavior characterized by a large group of people engaging in violent and destructive actions. Riots often occur in response to perceived grievances or injustices, and the actions of the crowd are typically unfocused, chaotic, and aimless. In this case, the crowd's destructive behavior, such as property destruction, theft, and arson, indicates a riotous situation. The collective anger and the sense of injustice contribute to the escalation of violence and chaos.
Inequality between the bourgeois and the proletariat is a key feature of which social deviance theory?- a)Social disorganization theory
- b)Conflict theory
- c)Labeling theory
- d)Strain theory
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Inequality between the bourgeois and the proletariat is a key feature of which social deviance theory?
a)
Social disorganization theory
b)
Conflict theory
c)
Labeling theory
d)
Strain theory
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Conflict theory emphasizes the role of social conflict and power differentials in shaping society. It suggests that social inequality, particularly the unequal distribution of resources and power, leads to conflict between different social groups. In the context of the bourgeoisie (owners of the means of production) and the proletariat (working class), conflict theory highlights the class struggle and the inherent inequality between these two groups. The bourgeoisie, who hold economic and social power, exploit the proletariat for their labor, leading to social tensions and deviance. Therefore, the inequality between the bourgeois and the proletariat is a key feature of conflict theory.
Which of the following is an example of an informal norm?- a)Customers line up to order their meal at a fast food restaurant.
- b)Employees read a staff manual outlining expectations for behavior.
- c)Children respond to a sign at the pool that tells them not to run around the pool deck.
- d)Students apply to medical school based on instructions outlined in entrance requirements.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of an informal norm?
a)
Customers line up to order their meal at a fast food restaurant.
b)
Employees read a staff manual outlining expectations for behavior.
c)
Children respond to a sign at the pool that tells them not to run around the pool deck.
d)
Students apply to medical school based on instructions outlined in entrance requirements.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Informal norms refer to unwritten, unofficial rules or expectations that guide behavior in a social group or society. In this case, the norm of lining up to order a meal at a fast food restaurant is an example of an informal norm. Although there may not be a specific rule or guideline explicitly stated, customers understand and follow the norm of forming a queue or line to maintain order and fairness in the process of ordering food. The other options listed involve more formal norms or rules that are explicitly communicated through manuals, signs, or instructions.
Which of these is NOT a form of social support?- a)Functional
- b)Tangible/Instrumental
- c)Emotional
- d)Esteem
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of these is NOT a form of social support?
a)
Functional
b)
Tangible/Instrumental
c)
Emotional
d)
Esteem
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Esteem support consists of expressions of encouragement, constructive feedback, and affirmation.
- Tangible/Instrumental support is often financial or consisting of material goods or services.
- Emotional support can be expressions such as affection (hugs), empathy, or sharing of experiences.
- Functional support is not regarded as a form of social support.
What is the primary difference between mores and folkways?- a)Deviance from mores is always punishable by law, whereas deviance from folkways is not
- b)Mores are based in ethics, whereas folkways are based in social approval
- c)Mores regulate material culture, whereas folkways regulate nonmaterial culture
- d)Mores regulate nonmaterial culture, whereas folkways regulate material culture
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the primary difference between mores and folkways?
a)
Deviance from mores is always punishable by law, whereas deviance from folkways is not
b)
Mores are based in ethics, whereas folkways are based in social approval
c)
Mores regulate material culture, whereas folkways regulate nonmaterial culture
d)
Mores regulate nonmaterial culture, whereas folkways regulate material culture
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
Mores and folkways are both types of norms, which are rules or expectations that guide behavior in a society. The primary difference between mores and folkways lies in their degree of social significance. Mores are norms that are based in ethics and are considered to be of great moral significance within a society. They reflect fundamental values and principles, and deviating from mores is often met with strong social disapproval and may even be punishable by law.
On the other hand, folkways are norms that govern everyday social interactions and are based on customary practices and social conventions. They are less morally significant compared to mores and violations of folkways are typically met with less severe social consequences. Deviating from folkways may result in mild disapproval or social sanctions, but they are not usually punishable by law.
In summary, mores are rooted in ethical values and carry a higher degree of social significance, while folkways are based on social approval and regulate more routine and customary behaviors.
How would a child that is described as having a secure attachment behave during the Strange Situation?- a)The child shows little interaction or desire for proximity with caregiver, even after the reunion episode.
- b)The child behaves erratic or runs away when the caregiver returns.
- c)The child shows moderate proximity and contact seeking, desires to maintain contact once engaged, and shows ambivalence toward caregiver after reunion episode.
- d)The child seeks proximity and contact or interaction with the caregiver both before and after the reunion episode.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How would a child that is described as having a secure attachment behave during the Strange Situation?
a)
The child shows little interaction or desire for proximity with caregiver, even after the reunion episode.
b)
The child behaves erratic or runs away when the caregiver returns.
c)
The child shows moderate proximity and contact seeking, desires to maintain contact once engaged, and shows ambivalence toward caregiver after reunion episode.
d)
The child seeks proximity and contact or interaction with the caregiver both before and after the reunion episode.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- A child that displays ambivalence to the caregiver and moderate seeking of proximity and contact is characterized as insecure resistant.
- A child that shows little interaction or desire for proximity with caregiver, even after the reunion episode is often characterized as insecure avoidant.
- A child that behaves erratically or runs away from the caregiver when she returns is described as having disorganized attachment.
- The child seeks proximity and contact or interaction with the caregiver both before and after the reunion episode.
To test the mere exposure effect on familiar brand recall, researchers asked participants to watch four movies (10 minutes each): two without visible product labels (masked) and two with product labels in the center of the screen. Without previous notification the participants were tested on brand recall and to ensure brand familiarity. Afterwards, the participants rated which brands were preferred. What is a possible confounder to this study?- a)When participants are not told they will be tested at the end, they often fail to pay attention.
- b)The masked labels did not allow the participants to see the product labels.
- c)Social priming effects from the actors interacting on the videos are highly reliable.
- d)The participants may have been unfamiliar with the brands used.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
To test the mere exposure effect on familiar brand recall, researchers asked participants to watch four movies (10 minutes each): two without visible product labels (masked) and two with product labels in the center of the screen. Without previous notification the participants were tested on brand recall and to ensure brand familiarity. Afterwards, the participants rated which brands were preferred. What is a possible confounder to this study?
a)
When participants are not told they will be tested at the end, they often fail to pay attention.
b)
The masked labels did not allow the participants to see the product labels.
c)
Social priming effects from the actors interacting on the videos are highly reliable.
d)
The participants may have been unfamiliar with the brands used.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- By asking the participants about brand familiarity after the test, the researchers were able to control for differences in brand familiarity.
- The two masked movies served as control conditions.
- Social priming effects depend on many variables and can vary widely between socioeconomic and cultural backgrounds.
- When participants are not told they will be tested at the end, they often fail to pay attention.
How does social support affect health?- a)Esteem support offers financial assistance to help pay costs after insurance.
- b)Children with strong tangible/instrumental support through encouragement and constructive feedback show increased interest in school activities.
- c)People with strong social support networks are more likely to use drugs.
- d)Emotional support, such as affirmation and affection, reduces the risk of mental and physical health problems.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
How does social support affect health?
a)
Esteem support offers financial assistance to help pay costs after insurance.
b)
Children with strong tangible/instrumental support through encouragement and constructive feedback show increased interest in school activities.
c)
People with strong social support networks are more likely to use drugs.
d)
Emotional support, such as affirmation and affection, reduces the risk of mental and physical health problems.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- People with strong social support networks are LESS likely to use drugs.
- Tangible/instrumental support is social support through goods, services, or financial aid, not encouragement and constructive feedback.
- Esteem support consists of expressions of encouragement, constructive feedback, and affirmation.
- Emotional support, such as affirmation and affection, reduces the risk of mental and physical health problems.
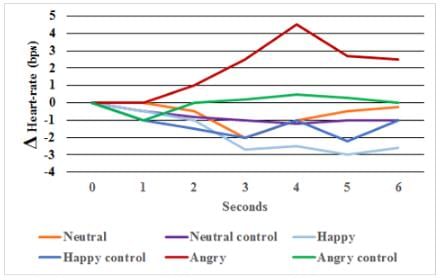
In the study shown in the figure above, subjects were injected with testosterone and then shown pictures of faces displaying different facial expressions. A control group was shown the same pictures but did not receive the injection. The heart-rate was recorded for six seconds after injection. Results across subjects are averaged. Neutral control, happy control, and angry control did not receive the injection. Which conclusion is supported by the figure above?- a)Testosterone decreases the ability to attribute emotion to happy and neutral faces.
- b)Testosterone increases the heart-rate when angry faces are shown.
- c)Testosterone increases anger when compared to the control.
- d)Testosterone decreases the ability to interpret happy and neutral faces.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?

In the study shown in the figure above, subjects were injected with testosterone and then shown pictures of faces displaying different facial expressions. A control group was shown the same pictures but did not receive the injection. The heart-rate was recorded for six seconds after injection. Results across subjects are averaged. Neutral control, happy control, and angry control did not receive the injection. Which conclusion is supported by the figure above?
a)
Testosterone decreases the ability to attribute emotion to happy and neutral faces.
b)
Testosterone increases the heart-rate when angry faces are shown.
c)
Testosterone increases anger when compared to the control.
d)
Testosterone decreases the ability to interpret happy and neutral faces.
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- There is no indication that anger was increased in subjects who received the injection, only changes in heart-rate are shown.
- It is not possible to draw a conclusion based on the given information regarding the subject’s interpretation or emotional understanding of the face pictures shown.
- Testosterone increases the heart-rate when angry faces are shown.
Altruistic punishment is the punishment of ‘someone’ for not punishing anti-social behavior. Why is this important for prosocial group functioning?- a)To enforce social norms
- b)To help allow people to maximize profits
- c)To discourage in-group cooperation
- d)To show that some people are above the law
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Altruistic punishment is the punishment of ‘someone’ for not punishing anti-social behavior. Why is this important for prosocial group functioning?
a)
To enforce social norms
b)
To help allow people to maximize profits
c)
To discourage in-group cooperation
d)
To show that some people are above the law
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
- Altruistic punishment encourages in-group cooperation.
- Altruistic punishment shows that there are checks on power.
- Pursuit of profits is often not viewed as altruistic behavior.
- Altruistic punishment aids in the enforcement of social norms.
A group of politicians is interested in determining how truancy laws influence academic performance in adolescents from a high crime urban area. If the politicians conducted a research study on the laws before implementing them officially, what would be the dependent variable?- a)Class attendance
- b)Crime rates
- c)Truancy laws
- d)Grade point average
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A group of politicians is interested in determining how truancy laws influence academic performance in adolescents from a high crime urban area. If the politicians conducted a research study on the laws before implementing them officially, what would be the dependent variable?
a)
Class attendance
b)
Crime rates
c)
Truancy laws
d)
Grade point average
|
|
Ayesha Joshi answered |
The dependent variable is the variable that is measured or observed in a research study and is expected to change as a result of the independent variable(s). In this case, the independent variable is the truancy laws, which are being investigated to determine their influence on academic performance. The researchers are interested in how the implementation of these laws affects the academic performance of the adolescents from a high crime urban area. The measure of academic performance that they are specifically interested in is the grade point average (GPA). Therefore, the GPA would be the dependent variable in this research study.
Chapter doubts & questions for Normative and Non-normative Behavior - Psychology and Sociology for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Normative and Non-normative Behavior - Psychology and Sociology for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Psychology and Sociology for MCAT
339 videos|20 docs|42 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily









