All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern >
All Questions
All questions of Biology: Topic-wise Test for NEET Exam
Haemoglobin has- a)Primary structure
- b)Secondary structure
- c)Tertiary structure
- d)Quaternary structure
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Haemoglobin has
a)
Primary structure
b)
Secondary structure
c)
Tertiary structure
d)
Quaternary structure
|
|
Anjali Iyer answered |
Hemoglobin is a tetramer that possesses a quaternary structure containing multiple folded polypeptide structures (tertiary structures). A tertiary protein will commonly contain a single polypeptide chain with one or more secondary structures.
Roots developed from parts of the plant other than radicle are called- a)Taproots
- b)Fibrous roots
- c)Adventitious roots
- d)Nodular roots
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Roots developed from parts of the plant other than radicle are called
a)
Taproots
b)
Fibrous roots
c)
Adventitious roots
d)
Nodular roots

|
Hearthacker answered |
Some roots, called adventitious roots, arise from an organ other than the root—usually a stem, sometimes a leaf. They are especially numerous on underground stems, such as rhizomes, corms, and tubers, and make it possible to vegetatively propagate many plants from stem or leaf cuttings.
Plasma membrane is made up of- a)Lipids and proteins
- b)Lipids, proteins and carbohydrates
- c)Nucleoproteins
- d)Mucopolysaccharides
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasma membrane is made up of
a)
Lipids and proteins
b)
Lipids, proteins and carbohydrates
c)
Nucleoproteins
d)
Mucopolysaccharides
|
|
Pooja Mehta answered |
All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer arranged back-to-back. The membrane is also covered in places with cholesterol molecules and proteins. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and regulates which molecules are allowed to enter and exit the cell.
Terminalisation occurs during- a)Diplotene
- b)Zygotene
- c)Diakinesis
- d)Leptotene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Terminalisation occurs during
a)
Diplotene
b)
Zygotene
c)
Diakinesis
d)
Leptotene
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
The two homologous chromosomes do not completely separate but remain attached together at one or more points as indicated by X arrangements known as Chiasmata.The displacement of Chiasmata is termed as terminalization.Terminalization is completed in Diakinesis stage.
What is the significance of the Golgi apparatus in a cell?
- a)It is the site of cellular respiration.
- b)It packages and modifies proteins.
- c)It captures light energy for photosynthesis.
- d)It packages and modifies proteins
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the significance of the Golgi apparatus in a cell?
a)
It is the site of cellular respiration.
b)
It packages and modifies proteins.
c)
It captures light energy for photosynthesis.
d)
It packages and modifies proteins

|
Madhavi Angel answered |
Gerl ---> golgi complexes, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes.....so your Ans is lysosomes ....
Water is absorbed by- a)Root hairs
- b)Root cap
- c)Root
- d)Root apex
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Water is absorbed by
a)
Root hairs
b)
Root cap
c)
Root
d)
Root apex
|
|
Priya Datta answered |
Water is absorbed by the roots of plants through a process called osmosis. The root system of a plant is responsible for absorbing water and nutrients from the soil, and distributing them throughout the plant. The process of water absorption by the roots is a complex one that involves several structures and mechanisms. Let us discuss them in detail.
Root Hairs:
Root hairs are elongated, thin-walled cells that are found on the surface of the root. They are responsible for the absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Root hairs greatly increase the surface area of the root, allowing for more efficient absorption of water and nutrients. They are constantly being replaced as they are sloughed off, and new ones are produced.
Root Cap:
The root cap is a structure located at the tip of the root. It is a protective layer that covers the delicate meristem cells at the apex of the root. The root cap releases a slimy substance that helps lubricate the soil around the root, making it easier for the root to penetrate the soil. The root cap also senses gravity and directs the root downward into the soil.
Root:
The root itself is an important structure for water absorption. The innermost layer of cells in the root, called the endodermis, is responsible for controlling the movement of water and nutrients into the plant. The endodermis acts as a barrier, allowing only certain molecules to pass through. This is important for preventing harmful substances from entering the plant.
Root Apex:
The root apex is the growing tip of the root. It is the site of cell division and growth in the root. As the root grows, it pushes through the soil, absorbing water and nutrients along the way. The root apex is constantly producing new cells, which eventually differentiate into the various types of cells that make up the root.
In conclusion, water is absorbed by the root hairs, root cap, root, and root apex of plants. Each of these structures plays an important role in the process of water absorption, allowing plants to grow and thrive in a variety of environments.
Root Hairs:
Root hairs are elongated, thin-walled cells that are found on the surface of the root. They are responsible for the absorption of water and minerals from the soil. Root hairs greatly increase the surface area of the root, allowing for more efficient absorption of water and nutrients. They are constantly being replaced as they are sloughed off, and new ones are produced.
Root Cap:
The root cap is a structure located at the tip of the root. It is a protective layer that covers the delicate meristem cells at the apex of the root. The root cap releases a slimy substance that helps lubricate the soil around the root, making it easier for the root to penetrate the soil. The root cap also senses gravity and directs the root downward into the soil.
Root:
The root itself is an important structure for water absorption. The innermost layer of cells in the root, called the endodermis, is responsible for controlling the movement of water and nutrients into the plant. The endodermis acts as a barrier, allowing only certain molecules to pass through. This is important for preventing harmful substances from entering the plant.
Root Apex:
The root apex is the growing tip of the root. It is the site of cell division and growth in the root. As the root grows, it pushes through the soil, absorbing water and nutrients along the way. The root apex is constantly producing new cells, which eventually differentiate into the various types of cells that make up the root.
In conclusion, water is absorbed by the root hairs, root cap, root, and root apex of plants. Each of these structures plays an important role in the process of water absorption, allowing plants to grow and thrive in a variety of environments.
Desmosomes are concerned with- a)Cell division
- b)Cellular excretion
- c)Cyclosis
- d)Cell adherence
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Desmosomes are concerned with
a)
Cell division
b)
Cellular excretion
c)
Cyclosis
d)
Cell adherence
|
|
Jyoti Sengupta answered |
Desmosomes (macula adherens) consists of intercellular thrckening matedals, disc-shaped intracellular thickening adjacent to each membrane with tonofibrils. These act as intercellular cementing material, adhere cells together at places like spot welding.
Mark theINCORRECT statement
- a)Counter-current flow of blood in vasa recta helps to retain the reabsorbed sodium in the renal medulla
- b)Glomerular filtrate is protein free plasma
- c)Vasa carry glomerula filtrate from distal convoluted tubule to the collecting duct
- d)Glomerular filterate in Bowman’s capsule is isotonic to the plasma
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mark theINCORRECT statement
a)
Counter-current flow of blood in vasa recta helps to retain the reabsorbed sodium in the renal medulla
b)
Glomerular filtrate is protein free plasma
c)
Vasa carry glomerula filtrate from distal convoluted tubule to the collecting duct
d)
Glomerular filterate in Bowman’s capsule is isotonic to the plasma
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
- The Henle’s loop and vasa recta play a significant role in this. The flow of filtrate in the two limbs of Henle’s loop is in opposite directions and thus forms a counter current. The flow of blood through the two limbs of vasa recta is also in a countercurrent pattern. The proximity between the Henle’s loop and vasa recta, as well as the countercurrent in them, help in maintaining an increasing osmolarity towards the inner medullary interstitium, i.e., from 300 mOsmolL–1 in the cortex to about 1200 mOsmolL–1 in the inner medulla. This gradient is mainly caused by NaCl and urea. NaCl is transported by the ascending limb of Henle’s loop which is exchanged with the descending limb of vasa recta. NaCl is returned to the interstitium by the ascending portion of vasa recta.
- The glomerular filtrate resembles the protein free plasma in composition and osmotic pressure.
- The glomerular filtrate contains all the materials present in the blood except blood cells and most proteins, which are too large to cross the basement membrane of the glomerulus.
- Hence, the filtrate is isotonic to blood plasma in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Which is correct?a) Argemone – axile,b) China rose – free central,c) Lemon – axile,d) mustard – parietal.- a)c & d.
- b)a, b,c.
- c) b, c, d.
- d) b & d.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is correct?
a) Argemone – axile,
b) China rose – free central,
c) Lemon – axile,
d) mustard – parietal.
a)
c & d.
b)
a, b,c.
c)
b, c, d.
d)
b & d.
|
|
Gayatri Bose answered |
It is not a complete question or statement. Please provide more information.
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is released in response to the increases in blood volume and blood pressure. Which of the following is not the function of ANF ?- a)Stimulates aldosterone secretion
- b)Inhibits the release of renin from JGA
- c)Stimulates salt loss in urine
- d)Inhibits sodium reabsorption from collecting duct
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is released in response
to the increases in blood volume and blood pressure.
Which of the following is not the function of ANF ?
a)
Stimulates aldosterone secretion
b)
Inhibits the release of renin from JGA
c)
Stimulates salt loss in urine
d)
Inhibits sodium reabsorption from collecting duct
|
|
Anuj Singh answered |
Function of Atrial Natriuretic Factor (ANF)
ANF is a hormone that is released from the heart in response to increases in blood volume and blood pressure. Its main function is to regulate fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. The functions of ANF include:
Inhibits the release of renin from JGA
ANF inhibits the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in the kidney. Renin is an enzyme that plays a role in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and fluid balance in the body. By inhibiting renin release, ANF reduces the activity of the RAAS and promotes salt and water excretion by the kidneys.
Stimulates salt loss in urine
ANF promotes salt and water excretion by the kidneys by increasing the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidney tubules. This leads to increased urine output and reduced blood volume and blood pressure.
Inhibits sodium reabsorption from collecting duct
ANF inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and water in the collecting duct of the kidney. This leads to increased urine output and reduced blood volume and blood pressure.
Does not stimulate aldosterone secretion
Aldosterone is a hormone that is produced by the adrenal gland and plays a role in the RAAS. It promotes the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidney tubules and increases blood volume and blood pressure. ANF does not stimulate aldosterone secretion; rather, it inhibits the activity of the RAAS and promotes salt and water excretion by the kidneys.
In conclusion, ANF is a hormone that plays an important role in regulating fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. It inhibits the release of renin from JGA, stimulates salt loss in urine, and inhibits sodium reabsorption from the collecting duct. However, it does not stimulate aldosterone secretion.
ANF is a hormone that is released from the heart in response to increases in blood volume and blood pressure. Its main function is to regulate fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. The functions of ANF include:
Inhibits the release of renin from JGA
ANF inhibits the release of renin from the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) in the kidney. Renin is an enzyme that plays a role in the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), which regulates blood pressure and fluid balance in the body. By inhibiting renin release, ANF reduces the activity of the RAAS and promotes salt and water excretion by the kidneys.
Stimulates salt loss in urine
ANF promotes salt and water excretion by the kidneys by increasing the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidney tubules. This leads to increased urine output and reduced blood volume and blood pressure.
Inhibits sodium reabsorption from collecting duct
ANF inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and water in the collecting duct of the kidney. This leads to increased urine output and reduced blood volume and blood pressure.
Does not stimulate aldosterone secretion
Aldosterone is a hormone that is produced by the adrenal gland and plays a role in the RAAS. It promotes the reabsorption of sodium and water in the kidney tubules and increases blood volume and blood pressure. ANF does not stimulate aldosterone secretion; rather, it inhibits the activity of the RAAS and promotes salt and water excretion by the kidneys.
In conclusion, ANF is a hormone that plays an important role in regulating fluid and electrolyte balance in the body. It inhibits the release of renin from JGA, stimulates salt loss in urine, and inhibits sodium reabsorption from the collecting duct. However, it does not stimulate aldosterone secretion.
First sound of heart beat is lower frequency and longer duration. It develops duringa)Opening of bicuspid and Tricuspid valveb)Closing of bicuspid and Tricuspid valvec)Opening of semi lunar valvesd)Closing of semi lunar valvesCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Deepika Iyer answered |
Explanation:
The sound of the heartbeat is produced by the closure of heart valves. The heart valves are responsible for ensuring that blood flows only in one direction. The sound of the heart is divided into two sounds. The first sound is a low-frequency, long-duration sound, and the second sound is a high-frequency, short-duration sound.
The first sound of the heartbeat is heard when the bicuspid and tricuspid valves close. These valves are located between the atria and ventricles. The closure of these valves causes the first sound of the heartbeat.
The second sound of the heartbeat is heard when the semilunar valves close. These valves are located between the ventricles and the great arteries. The closure of these valves causes the second sound of the heartbeat.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B - the first sound of the heartbeat is produced by the closing of the bicuspid and tricuspid valves.
The sound of the heartbeat is produced by the closure of heart valves. The heart valves are responsible for ensuring that blood flows only in one direction. The sound of the heart is divided into two sounds. The first sound is a low-frequency, long-duration sound, and the second sound is a high-frequency, short-duration sound.
The first sound of the heartbeat is heard when the bicuspid and tricuspid valves close. These valves are located between the atria and ventricles. The closure of these valves causes the first sound of the heartbeat.
The second sound of the heartbeat is heard when the semilunar valves close. These valves are located between the ventricles and the great arteries. The closure of these valves causes the second sound of the heartbeat.
Therefore, the correct answer is option B - the first sound of the heartbeat is produced by the closing of the bicuspid and tricuspid valves.
Which of the following pressure-change leads to an increased G.F.R.- a)
 Arterial plasma colloid osmotic pressure
Arterial plasma colloid osmotic pressure - b)
 Gomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
Gomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure - c)
 Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule - d)
 Net filtration pressure
Net filtration pressure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pressure-change leads to an
increased G.F.R.
a)
Arterial plasma colloid osmotic pressure
b)
Gomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
c)
Hydrostatic pressure in Bowman’s capsule
d)
Net filtration pressure

|
Abhinav Chowdhary answered |
Ans d also
The interphase between meiosis I and II, when present, is called- a)Diakinesis
- b)Cytokinesis
- c)Interkinesis
- d)Karyokinesis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The interphase between meiosis I and II, when
present, is called
a)
Diakinesis
b)
Cytokinesis
c)
Interkinesis
d)
Karyokinesis
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
Telophase I, is followed by an interphase, called interkinesis, similar to the mitotic interphase. During interkinesis the chromatin is partially uncoiled; however, there is no replication of the genetic material, because each chromosome already consists of two chromatids.
Chromosomes counting is best done during- a)Late anaphase
- b)Late prophase
- c)Telophase
- d)Metaphase
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Chromosomes counting is best done during
a)
Late anaphase
b)
Late prophase
c)
Telophase
d)
Metaphase

|
Aashika Packiaselvam answered |
The crt opt is D. Cuz during metaphase, all the chromosomes lined up on the metaphase plate and further proceeding anaphase. So it is easy to count them at that stage by counting the number of functional centromere. Bcoz the number of chromosomes = count the number of functional centromere.
Transformation of membrane is the function of- a)Ribosomes
- b)Golgi complex
- c)ER
- d)Plastids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Transformation of membrane is the function of
a)
Ribosomes
b)
Golgi complex
c)
ER
d)
Plastids

|
Sangita Mishra answered |
Transformation of membrane is the function of golgi complex.
Which muscle protein acts as ATPase ?- a)Actin
- b)Troponin
- c)Myosin
- d)Tropomyosin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which muscle protein acts as ATPase ?
a)
Actin
b)
Troponin
c)
Myosin
d)
Tropomyosin
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Because actin and tropomyosin is binding protein in muscle and myosin is a maximum active for independent calcium bind
In excitable cells, re-polarization is closely associated with one of the following events- a)
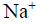 efflux
efflux - b)
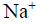 influx
influx - c)
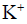 efflux
efflux - d)
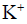 influx
influx
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In excitable cells, re-polarization is closely associated
with one of the following events
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Jatin Shah answered |
Re-polarization in Excitable Cells
In excitable cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, action potentials are generated and transmitted. These action potentials are caused by the movement of ions across the cell membrane.
During an action potential, the cell membrane becomes depolarized as sodium ions enter the cell. This depolarization causes the cell to become more positive, which then triggers the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels.
Re-polarization
Re-polarization is the process by which the cell membrane returns to its resting potential after an action potential has occurred. This process is closely associated with the efflux of potassium ions from the cell.
K Efflux
Efflux means the outward flow. During re-polarization, the voltage-gated potassium channels that opened during depolarization allow K+ ions to flow out of the cell, which causes the membrane potential to become more negative.
As more potassium ions leave the cell, the membrane potential becomes more negative, and the cell returns to its resting state. This process of re-polarization allows the cell to generate another action potential if needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, re-polarization in excitable cells is closely associated with the efflux of potassium ions from the cell. This process allows the cell to return to its resting potential and generate another action potential if needed.
In excitable cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, action potentials are generated and transmitted. These action potentials are caused by the movement of ions across the cell membrane.
During an action potential, the cell membrane becomes depolarized as sodium ions enter the cell. This depolarization causes the cell to become more positive, which then triggers the opening of voltage-gated potassium channels.
Re-polarization
Re-polarization is the process by which the cell membrane returns to its resting potential after an action potential has occurred. This process is closely associated with the efflux of potassium ions from the cell.
K Efflux
Efflux means the outward flow. During re-polarization, the voltage-gated potassium channels that opened during depolarization allow K+ ions to flow out of the cell, which causes the membrane potential to become more negative.
As more potassium ions leave the cell, the membrane potential becomes more negative, and the cell returns to its resting state. This process of re-polarization allows the cell to generate another action potential if needed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, re-polarization in excitable cells is closely associated with the efflux of potassium ions from the cell. This process allows the cell to return to its resting potential and generate another action potential if needed.
Which is the correct order of phases ?- a)Leptotene, diakinesis, pachytene, diplotene,zygotene
- b) Leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene,diakinesis
- c)Diakinesis, diplotene, pachytene, zygotene, leptotene
- d)Leptotene, pachytene, zygotene, diplotene,diakinesis
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is the correct order of phases ?
a)
Leptotene, diakinesis, pachytene, diplotene,
zygotene
b)
Leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene,
diakinesis
c)
Diakinesis, diplotene, pachytene, zygotene, leptotene
d)
Leptotene, pachytene, zygotene, diplotene,
diakinesis
|
|
Sreemoyee Saha answered |
Order of Phases in Meiosis
Leptotene
- This is the first stage of meiosis.
- During leptotene, chromosomes start to condense and become visible under a microscope.
- The chromosomes appear as thin threads, and homologous chromosomes start pairing up.
Zygotene
- In this stage, homologous chromosomes start to pair up completely.
- This process is called synapsis, and it results in the formation of bivalents or tetrads.
- The chromosomes continue to condense, and the paired chromosomes become visible as thicker threads.
Pachytene
- During pachytene, the chromosomes become even more condensed and shorten.
- Crossing over occurs between the paired homologous chromosomes and results in the exchange of genetic material between them.
- This exchange of genetic material increases genetic diversity.
Diplotene
- In this stage, the homologous chromosomes start to separate, but they are still linked at points called chiasmata where crossing over occurred.
- The chromosomes start to uncoil and become visible as thinner threads again.
- The nuclear envelope also starts to reform around each set of chromosomes.
Diakinesis
- This is the final stage of meiosis I.
- The chromosomes continue to condense and become visible as distinct structures.
- The nuclear envelope breaks down completely, and the spindle fibers start to attach to the chromosomes in preparation for their separation.
Correct Order of Phases in Meiosis
The correct order of phases in meiosis is:
Leptotene → Zygotene → Pachytene → Diplotene → Diakinesis
Option B is the correct answer as it presents the phases in the correct order.
Leptotene
- This is the first stage of meiosis.
- During leptotene, chromosomes start to condense and become visible under a microscope.
- The chromosomes appear as thin threads, and homologous chromosomes start pairing up.
Zygotene
- In this stage, homologous chromosomes start to pair up completely.
- This process is called synapsis, and it results in the formation of bivalents or tetrads.
- The chromosomes continue to condense, and the paired chromosomes become visible as thicker threads.
Pachytene
- During pachytene, the chromosomes become even more condensed and shorten.
- Crossing over occurs between the paired homologous chromosomes and results in the exchange of genetic material between them.
- This exchange of genetic material increases genetic diversity.
Diplotene
- In this stage, the homologous chromosomes start to separate, but they are still linked at points called chiasmata where crossing over occurred.
- The chromosomes start to uncoil and become visible as thinner threads again.
- The nuclear envelope also starts to reform around each set of chromosomes.
Diakinesis
- This is the final stage of meiosis I.
- The chromosomes continue to condense and become visible as distinct structures.
- The nuclear envelope breaks down completely, and the spindle fibers start to attach to the chromosomes in preparation for their separation.
Correct Order of Phases in Meiosis
The correct order of phases in meiosis is:
Leptotene → Zygotene → Pachytene → Diplotene → Diakinesis
Option B is the correct answer as it presents the phases in the correct order.
Which of the following serves as a second messenger for slowing contraction of the heart muscles in response to acetylcholine
- a)cGMP
- b)cAMP
- c)DG (Diacylglycerol)
- d)Inositol triphosphate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following serves as a second messenger for slowing contraction of the heart muscles in response to acetylcholine
a)
cGMP
b)
cAMP
c)
DG (Diacylglycerol)
d)
Inositol triphosphate
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Certain hormones such as peptide hormones or catecholamines have a large molecular size, or due to extreme polarity, they are unable to cross the plasma membrane.
These hormones bind to the protein receptors present on the plasma membrane of the target cell.
Secondary messengers are present within the target cell and produce the effect of the hormone inside the cell.
As soon as the hormone binds to the receptors on the membrane, the secondary messengers are activated and their concentration in the cell increases.
cAMP acts as a secondary messenger when epinephrine binds to protein receptors on the plasma membrane.
Ca2+ ions also act as secondary messengers and are usually secreted into the cytoplasm by the endoplasmic reticulum. The presence of calcium in the cytoplasm triggers the effect of the hormone in the cell.
cGMP also acts as a secondary messenger and mediates many cell and tissue responses. Especially in the heart, it slows muscle contraction in response to acetylcholine.
An apoenzyme is a- a)Vitamin
- b)Amino acid
- c)Carbohydrate
- d)Protein
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An apoenzyme is a
a)
Vitamin
b)
Amino acid
c)
Carbohydrate
d)
Protein
|
|
Rohan Singh answered |
A cofactor is a non-protein molecule that carries out chemical reactions that cannot be performed by the standard 20 amino acids. Cofactors can be either inorganic molecules (metals) or small organic molecules (coenzymes). .Holoenzyme- An apoenzyme together with its cofactor.
Which among the following is incorrect about the structure of plasma membrane?- a)Plasma membrane is made of lipids and proteins
- b)The proteins that are present on the surface of the plasma membrane are called integral proteins
- c)The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer membrane
- d)Lipids with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end are called amphipathic lipids
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is incorrect about the structure of plasma membrane?
a)
Plasma membrane is made of lipids and proteins
b)
The proteins that are present on the surface of the plasma membrane are called integral proteins
c)
The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer membrane
d)
Lipids with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end are called amphipathic lipids

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Plasma membrane is made of lipids and proteins. Lipids with hydrophobic and hydrophilic end are called amphipathic lipids. The plasma membrane is a lipid bilayer membrane. Integral proteins are not just present on the surface of the membrane but span along the entire width of the membrane.
Assertion (A): Osteoporosis results in increased bone density.Reason (R): Osteoporosis is characterized by the loss of bone mass and weakening of bone structure.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Osteoporosis results in increased bone density.
Reason (R): Osteoporosis is characterized by the loss of bone mass and weakening of bone structure.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
EduRev NEET answered |
Osteoporosis actually leads to a decrease in bone density, making the bones more fragile and prone to fractures. The assertion is false, but the reason is true, accurately describing the nature of osteoporosis.
Which of the following groups of protists resemble animals?- a)Chrysophytes and
- b)Protozoa
- c)Dinoflagellates
- d)Slime molds
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following groups of protists resemble animals?
a)
Chrysophytes and
b)
Protozoa
c)
Dinoflagellates
d)
Slime molds

|
Top Rankers answered |
Protozoans resemble animals because they can swallow food into their bodies and are mobile. Some protozoans consume food in a holozoic manner, just like mammals do. Protozoans are hence protists that resemble animals.
Which among the following statements is incorrect about plasma membrane?- a)Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane and allows only those particles that protect the cell
- b)Movement of air and water takes place through diffusion and osmosis respectively
- c)Active transport takes place through use of energy
- d)Osmosis and diffusion are examples of active transport
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following statements is incorrect about plasma membrane?
a)
Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane and allows only those particles that protect the cell
b)
Movement of air and water takes place through diffusion and osmosis respectively
c)
Active transport takes place through use of energy
d)
Osmosis and diffusion are examples of active transport

|
Lead Academy answered |
Plasma membrane is a selectively permeable membrane and allows only those particles that protect the cell. Movement of air and water takes place through diffusion and osmosis respectively. Osmosis and diffusion are examples of passive transport. Active transport takes place through use of energy.
Which among the following is incorrect about different types of cells?- a)Size and shape of the cells vary with the functions they perform
- b)Centrioles are present in plant cells but absent in animal cells
- c)The components in all eukaryotic cells are more/less the same
- d)In unicellular organism a single cell constitutes the entire organism
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which among the following is incorrect about different types of cells?
a)
Size and shape of the cells vary with the functions they perform
b)
Centrioles are present in plant cells but absent in animal cells
c)
The components in all eukaryotic cells are more/less the same
d)
In unicellular organism a single cell constitutes the entire organism
|
|
Sreemoyee Chopra answered |
Centrioles are present in plant cells but absent in animal cells:
Plant cells and animal cells have some distinct differences in their structures and organelles. One of the key differences is the presence of centrioles.
Centrioles in Animal Cells:
- Centrioles are cylindrical structures composed of microtubules that are found in animal cells.
- They are involved in organizing the microtubules during cell division, helping in the formation of the spindle fibers.
Absence of Centrioles in Plant Cells:
- Plant cells do not have centrioles in their cytoplasm. Instead, they have microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs) that perform similar functions to centrioles.
- The MTOCs help in organizing the microtubules during cell division in plant cells.
Function of Centrioles:
- Centrioles play a crucial role in cell division, especially in animal cells where they are involved in the formation of the mitotic spindle.
- The absence of centrioles in plant cells does not affect their ability to undergo cell division as they have alternative structures that serve a similar purpose.
Conclusion:
In summary, centrioles are present in animal cells but absent in plant cells. This difference is important in understanding the unique characteristics of these two types of cells.
Plant cells and animal cells have some distinct differences in their structures and organelles. One of the key differences is the presence of centrioles.
Centrioles in Animal Cells:
- Centrioles are cylindrical structures composed of microtubules that are found in animal cells.
- They are involved in organizing the microtubules during cell division, helping in the formation of the spindle fibers.
Absence of Centrioles in Plant Cells:
- Plant cells do not have centrioles in their cytoplasm. Instead, they have microtubule-organizing centers (MTOCs) that perform similar functions to centrioles.
- The MTOCs help in organizing the microtubules during cell division in plant cells.
Function of Centrioles:
- Centrioles play a crucial role in cell division, especially in animal cells where they are involved in the formation of the mitotic spindle.
- The absence of centrioles in plant cells does not affect their ability to undergo cell division as they have alternative structures that serve a similar purpose.
Conclusion:
In summary, centrioles are present in animal cells but absent in plant cells. This difference is important in understanding the unique characteristics of these two types of cells.
What is the effect of hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults?- a)Dwarfism
- b)Gigantism
- c)Acromegaly
- d)Cretinism
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the effect of hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults?
a)
Dwarfism
b)
Gigantism
c)
Acromegaly
d)
Cretinism

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
Hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults leads to acromegaly, characterized by abnormal growth of the hands, feet, and face, due to the enlargement of bones and tissues.
Assertion (A): Myosin and actin filaments slide past each other during muscle contraction.Reason (R): The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): Myosin and actin filaments slide past each other during muscle contraction.
Reason (R): The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The assertion and reason are both true, and the reason correctly explains the assertion. The sliding filament theory describes how the actin (thin) and myosin (thick) filaments slide past each other, shortening the sarcomere and causing muscle contraction.
Assertion (A): In monocotyledonous plants, the primary root is short-lived and is replaced by a large number of roots originating from the base of the stem.Reason (R): Monocotyledonous plants have a fibrous root system that helps in providing a more extensive network for water and nutrient absorption.- a)Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
- b)Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
- c)A is true, but R is false.
- d)A is false, but R is true.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Assertion (A): In monocotyledonous plants, the primary root is short-lived and is replaced by a large number of roots originating from the base of the stem.
Reason (R): Monocotyledonous plants have a fibrous root system that helps in providing a more extensive network for water and nutrient absorption.
a)
Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
b)
Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c)
A is true, but R is false.
d)
A is false, but R is true.
|
|
Nitya Kaur answered |
Assertion (A) Explained
Monocotyledonous plants, commonly known as monocots, exhibit a unique root system.
- The primary root in these plants is indeed short-lived.
- It is typically replaced by a fibrous root system that consists of numerous roots emerging from the base of the stem.
This characteristic is a fundamental aspect of monocot structure.
Reason (R) Explained
The fibrous root system is crucial for the survival and growth of monocots.
- This type of root system allows monocots to develop a vast network of roots.
- Such an extensive system enhances their ability to absorb water and nutrients effectively.
The fibrous roots spread out horizontally and are closer to the soil surface, making them efficient in capturing moisture and nutrients from the top layers of soil.
Relationship between A and R
- Both the assertion and reason are true statements.
- The reason (R) serves as an explanation for the assertion (A) since the fibrous root system is a direct consequence of the short-lived primary root in monocots.
In summary, the primary root of monocots is transient, and the subsequent development of a fibrous root system supports their adaptation and efficiency in resource acquisition. Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Monocotyledonous plants, commonly known as monocots, exhibit a unique root system.
- The primary root in these plants is indeed short-lived.
- It is typically replaced by a fibrous root system that consists of numerous roots emerging from the base of the stem.
This characteristic is a fundamental aspect of monocot structure.
Reason (R) Explained
The fibrous root system is crucial for the survival and growth of monocots.
- This type of root system allows monocots to develop a vast network of roots.
- Such an extensive system enhances their ability to absorb water and nutrients effectively.
The fibrous roots spread out horizontally and are closer to the soil surface, making them efficient in capturing moisture and nutrients from the top layers of soil.
Relationship between A and R
- Both the assertion and reason are true statements.
- The reason (R) serves as an explanation for the assertion (A) since the fibrous root system is a direct consequence of the short-lived primary root in monocots.
In summary, the primary root of monocots is transient, and the subsequent development of a fibrous root system supports their adaptation and efficiency in resource acquisition. Thus, the correct answer is option 'A': Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Smallest free living organism are- a)PPLOs
- b)Bacteria
- c)Viroids
- d)Virus
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Smallest free living organism are
a)
PPLOs
b)
Bacteria
c)
Viroids
d)
Virus
|
|
Ashutosh Rane answered |
- Smallest free-living organism
PPLOs, or pleuropneumonia-like organisms, are the smallest free-living organisms known. PPLOs are a type of bacteria that lack a cell wall and are classified as mycoplasmas. They are typically found in soil, water, and the respiratory tracts of animals.
- Bacteria, Viroids, and Viruses
Bacteria are larger and more complex than PPLOs, with a cell wall and organelles. Viroids are even smaller than bacteria and consist of only a short strand of RNA without a protein coat. Viruses are even smaller than viroids and can only replicate inside host cells.
- Comparison
When comparing the size of these organisms, PPLOs are considered the smallest free-living organisms due to their lack of a cell wall and minimal cellular structure. Bacteria, viroids, and viruses are all smaller than typical cells but are not considered free-living organisms in the same way that PPLOs are.
In conclusion, PPLOs are the smallest free-living organisms known, making them unique in their size and structure compared to bacteria, viroids, and viruses.
PPLOs, or pleuropneumonia-like organisms, are the smallest free-living organisms known. PPLOs are a type of bacteria that lack a cell wall and are classified as mycoplasmas. They are typically found in soil, water, and the respiratory tracts of animals.
- Bacteria, Viroids, and Viruses
Bacteria are larger and more complex than PPLOs, with a cell wall and organelles. Viroids are even smaller than bacteria and consist of only a short strand of RNA without a protein coat. Viruses are even smaller than viroids and can only replicate inside host cells.
- Comparison
When comparing the size of these organisms, PPLOs are considered the smallest free-living organisms due to their lack of a cell wall and minimal cellular structure. Bacteria, viroids, and viruses are all smaller than typical cells but are not considered free-living organisms in the same way that PPLOs are.
In conclusion, PPLOs are the smallest free-living organisms known, making them unique in their size and structure compared to bacteria, viroids, and viruses.
Which of the following statements regarding cyanobacteria is false?- a)Because the term “cyano” implies “greenish-blue,” cyanobacteria is sometimes known as “blue-green algae.”
- b)Cyanobacteria are chemosynthetic autotrophs.
- c)They produce chlorophyll, which gives them their color.
- d)They also contribute to the atmosphere’s oxygen enrichment.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements regarding cyanobacteria is false?
a)
Because the term “cyano” implies “greenish-blue,” cyanobacteria is sometimes known as “blue-green algae.”
b)
Cyanobacteria are chemosynthetic autotrophs.
c)
They produce chlorophyll, which gives them their color.
d)
They also contribute to the atmosphere’s oxygen enrichment.

|
Top Rankers answered |
Chlorophyll, which is found in cyanobacteria, aids in photosynthesis, which raises atmospheric oxygen levels. Blue-green algae are also known as cyanobacteria since “cyano” in cyanobacteria denotes blue-green algae. However, cyanobacteria do not appear green in color but rather blue-green due to the presence of other pigments along with chlorophyll.
What is the main function of the cerebellum?- a)Regulating heart rate
- b)Coordinating voluntary muscle movements
- c)Processing sensory input
- d)Controlling breathing rate
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is the main function of the cerebellum?
a)
Regulating heart rate
b)
Coordinating voluntary muscle movements
c)
Processing sensory input
d)
Controlling breathing rate

|
Lead Academy answered |
The cerebellum is primarily responsible for coordinating voluntary muscle movements and maintaining posture, balance, and equilibrium. It receives information from the sensory systems, the spinal cord, and other parts of the brain and then regulates motor movements. The cerebellum fine-tunes motor activity, making movements smooth and coordinated. An interesting fact about the cerebellum is that it contains more neurons than the rest of the brain combined, highlighting its complexity and importance in motor control.
Line in NCERT: "The cerebellum integrates information received from the semicircular canals of the ear and the auditory system."
Synaptonemal complex appears during- a)Amitosis
- b)Mitosis
- c)Meiosis – I
- d)Meiosis – II
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Synaptonemal complex appears during
a)
Amitosis
b)
Mitosis
c)
Meiosis – I
d)
Meiosis – II

|
Shruti Chauhan answered |
The synaptonemal complex (SC) is a protein structure that forms between homologous chromosomes (two pairs of sister chromatids) during meiosis and is thought to mediate chromosome pairing, synapsis, and recombination.
Why is the bilobed nature of an anther distinct in a transverse section?
- a)Because of the microsporangia
- b)Because of the tapetum layer
- c)Because of the epidermis
- d)Because of the longitudinal groove
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer??
Why is the bilobed nature of an anther distinct in a transverse section?
a)
Because of the microsporangia
b)
Because of the tapetum layer
c)
Because of the epidermis
d)
Because of the longitudinal groove
|
|
Aaditya Roy answered |
Understanding the Bilobed Nature of Anther
The bilobed structure of an anther is a significant feature in the reproductive system of flowering plants.
Key Factors Contributing to Bilobed Structure
- The distinct bilobed nature is primarily due to the microsporanguia, which are the pollen sacs located within the anther.
- Each lobe of the anther contains two microsporangia, which are responsible for producing pollen grains.
- The arrangement allows for efficient pollen production and distribution during the pollination process.
Microsporangia's Role
- Microsporangia develop within the lobes, leading to the characteristic shape of the anther.
- As these structures mature, they facilitate the release of pollen grains, which are crucial for fertilization.
Other Layers' Influence
- While the tapetum layer and epidermis play essential roles in supporting the anther's function, they do not directly contribute to its bilobed appearance.
- The tapetum assists in nourishing the developing pollen grains, and the epidermis provides protection, but the lobular structure is solely due to the arrangement of microsporangia.
Conclusion
In summary, the bilobed nature of an anther is distinctly observed in a transverse section because of the presence of microsporangia. This structural feature is essential for effective pollen development and dispersal, emphasizing the microsporangiua's critical role in the anther's anatomy and function.
The bilobed structure of an anther is a significant feature in the reproductive system of flowering plants.
Key Factors Contributing to Bilobed Structure
- The distinct bilobed nature is primarily due to the microsporanguia, which are the pollen sacs located within the anther.
- Each lobe of the anther contains two microsporangia, which are responsible for producing pollen grains.
- The arrangement allows for efficient pollen production and distribution during the pollination process.
Microsporangia's Role
- Microsporangia develop within the lobes, leading to the characteristic shape of the anther.
- As these structures mature, they facilitate the release of pollen grains, which are crucial for fertilization.
Other Layers' Influence
- While the tapetum layer and epidermis play essential roles in supporting the anther's function, they do not directly contribute to its bilobed appearance.
- The tapetum assists in nourishing the developing pollen grains, and the epidermis provides protection, but the lobular structure is solely due to the arrangement of microsporangia.
Conclusion
In summary, the bilobed nature of an anther is distinctly observed in a transverse section because of the presence of microsporangia. This structural feature is essential for effective pollen development and dispersal, emphasizing the microsporangiua's critical role in the anther's anatomy and function.
Which one of the following acts as a physiological barrier to the entry of microorganisms in human body?
- a)Monocytes
- b)Epithelium of Urogenital tract
- c)Tears
- d)Skin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer??
Which one of the following acts as a physiological barrier to the entry of microorganisms in human body?
a)
Monocytes
b)
Epithelium of Urogenital tract
c)
Tears
d)
Skin
|
|
Divyansh Joshi answered |
Understanding Physiological Barriers to Microorganisms
The human body has several mechanisms to prevent the entry of microorganisms, and the correct answer to the question is indeed "C) Tears." Here’s a detailed explanation:
Tears as a Physiological Barrier
- Role of Tears: Tears are not just for keeping the eyes moist; they play a crucial role in protecting the eyes from pathogens.
- Antimicrobial Properties: Tears contain lysozyme, an enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls, effectively killing bacteria.
- Flushing Effect: The act of tearing helps wash away debris and microorganisms from the surface of the eye.
- pH and Salt Content: The natural pH and saline content in tears create an inhospitable environment for many harmful microorganisms.
Why Other Options are Less Effective
- Monocytes:
- These are immune cells that respond to infections, but they act after a pathogen has entered the body. They are not a physical barrier.
- Epithelium of Urogenital Tract:
- While it does provide some level of protection, it is primarily a structural barrier rather than a physiological one. It does not actively neutralize pathogens like tears do.
- Skin:
- The skin is a significant physical barrier to microorganisms, but it does not have the same physiological properties as tears in actively combating pathogens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while all listed options contribute to the overall defense against pathogens, tears are uniquely effective due to their direct physiological role in safeguarding the eyes from microbial invasion.
The human body has several mechanisms to prevent the entry of microorganisms, and the correct answer to the question is indeed "C) Tears." Here’s a detailed explanation:
Tears as a Physiological Barrier
- Role of Tears: Tears are not just for keeping the eyes moist; they play a crucial role in protecting the eyes from pathogens.
- Antimicrobial Properties: Tears contain lysozyme, an enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls, effectively killing bacteria.
- Flushing Effect: The act of tearing helps wash away debris and microorganisms from the surface of the eye.
- pH and Salt Content: The natural pH and saline content in tears create an inhospitable environment for many harmful microorganisms.
Why Other Options are Less Effective
- Monocytes:
- These are immune cells that respond to infections, but they act after a pathogen has entered the body. They are not a physical barrier.
- Epithelium of Urogenital Tract:
- While it does provide some level of protection, it is primarily a structural barrier rather than a physiological one. It does not actively neutralize pathogens like tears do.
- Skin:
- The skin is a significant physical barrier to microorganisms, but it does not have the same physiological properties as tears in actively combating pathogens.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while all listed options contribute to the overall defense against pathogens, tears are uniquely effective due to their direct physiological role in safeguarding the eyes from microbial invasion.
Chapter doubts & questions for Biology: Topic-wise Test - NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Biology: Topic-wise Test - NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









