All Exams >
NEET >
NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern >
All Questions
All questions of NEET Minor Mock Test for NEET Exam
The distance covered by a body of mass 5g having linear momentum 0.3kgm∕s in 5s is:- a)0.3m
- b)300m
- c)30m
- d)3m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance covered by a body of mass 5g having linear momentum 0.3kgm∕s in 5s is:
a)
0.3m
b)
300m
c)
30m
d)
3m
|
|
Jyoti Shah answered |
Given:
Mass of body, m = 5g = 0.005 kg
Linear momentum of body, p = 0.3 kgm/s
Time, t = 5s
Formula:
Distance covered by the body, d = p*t/m
Calculation:
Substituting the given values in the formula, we get
d = (0.3*5)/0.005
d = 300m
Therefore, the distance covered by the body is 300m, which is option (b).
Mass of body, m = 5g = 0.005 kg
Linear momentum of body, p = 0.3 kgm/s
Time, t = 5s
Formula:
Distance covered by the body, d = p*t/m
Calculation:
Substituting the given values in the formula, we get
d = (0.3*5)/0.005
d = 300m
Therefore, the distance covered by the body is 300m, which is option (b).
Erythropoiesis starts in- a)spleen
- b)red bone marrow
- c)kidney
- d)liver
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Erythropoiesis starts in
a)
spleen
b)
red bone marrow
c)
kidney
d)
liver
|
|
M.l Gupta answered |
Erythropoiesis starts in red bone marrow and it is formating of red blood cells thats called erythrocyte also.
Name the plant growth regulator which upon spraying on sugarcane crop, increases the length of stem, thus increasing the yield of sugarcane crop.- a)Gibberellin
- b)Ethylene
- c)Abscisic acid
- d)Cytokinin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Name the plant growth regulator which upon spraying on sugarcane crop, increases the length of stem, thus increasing the yield of sugarcane crop.
a)
Gibberellin
b)
Ethylene
c)
Abscisic acid
d)
Cytokinin
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Spraying sugarcane crop with gibberellins increases the length of the stem, thus increasing the yield by as much as 20 tonnes per acre.
A student measures the distance traversed in free fall of a body, initially at rest, in a given time. He uses this data to estimate g, the acceleration due to gravity. If the maximum percentage errors in measurement of the distance and the time are e1 and e2 respectively, the percentage error in the estimation of g is- a)e2 − e1
- b)e1 + 2e2
- c)e1 + e2
- d)e1 − 2e2
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A student measures the distance traversed in free fall of a body, initially at rest, in a given time. He uses this data to estimate g, the acceleration due to gravity. If the maximum percentage errors in measurement of the distance and the time are e1 and e2 respectively, the percentage error in the estimation of g is
a)
e2 − e1
b)
e1 + 2e2
c)
e1 + e2
d)
e1 − 2e2
|
|
Pooja Kumar answered |
Percentage Error in Estimation of g
Given:
- Maximum percentage error in measurement of distance: e1
- Maximum percentage error in measurement of time: e2
Formula for Acceleration due to Gravity (g):
g = 2d/t^2
where d is the distance traversed and t is the time taken
Calculating the Percentage Error in g:
Percentage error in g = |(∂g/g) / (∂d/d) + (∂g/g) / (∂t/t)|
Calculating Partial Derivatives:
- ∂g/g = 1
- ∂d/d = e1
- ∂t/t = e2
Substitute the Values:
Percentage error in g = |1/e1 + 1/e2| = |(e1 + e2) / (e1 * e2)|
Therefore, the Percentage Error in Estimation of g is:
(e1 + e2) / (e1 * e2)
Correct Answer: Option B: e1 + 2e2
Given:
- Maximum percentage error in measurement of distance: e1
- Maximum percentage error in measurement of time: e2
Formula for Acceleration due to Gravity (g):
g = 2d/t^2
where d is the distance traversed and t is the time taken
Calculating the Percentage Error in g:
Percentage error in g = |(∂g/g) / (∂d/d) + (∂g/g) / (∂t/t)|
Calculating Partial Derivatives:
- ∂g/g = 1
- ∂d/d = e1
- ∂t/t = e2
Substitute the Values:
Percentage error in g = |1/e1 + 1/e2| = |(e1 + e2) / (e1 * e2)|
Therefore, the Percentage Error in Estimation of g is:
(e1 + e2) / (e1 * e2)
Correct Answer: Option B: e1 + 2e2
In a hierarchical system of plant classification, which one of the following taxonomic ranks generally ends in ‘-aceae’:- a)Family
- b)Genus
- c)Order
- d)Class
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a hierarchical system of plant classification, which one of the following taxonomic ranks generally ends in ‘-aceae’:
a)
Family
b)
Genus
c)
Order
d)
Class
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
There is no suffix for genus and species. Family is a taxonomic category between division and order. It includes one or more genera. Its suffix is 'aceae'. For example, Solanaceae. In the case of vascular plants order ends with the suffix 'ales'.
Thus, the correct answer is Family.
In the leaves of C4 plants, malic acid formation during CO2 fixation occurs in the cells of- a)bundle sheath
- b)phloem
- c)epidermis
- d)mesophyll
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In the leaves of C4 plants, malic acid formation during CO2 fixation occurs in the cells of
a)
bundle sheath
b)
phloem
c)
epidermis
d)
mesophyll
|
|
Sahana Datta answered |
Malic Acid Formation in C4 Plants
Mesophyll Cells
- In C4 plants, the initial step of CO2 fixation occurs in the mesophyll cells.
- Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPCase) enzyme catalyzes the fixation of CO2 to form oxaloacetic acid (OAA) in the mesophyll cells.
Malic Acid Formation
- OAA is then converted to malic acid in the mesophyll cells.
- Malic acid is transported to the bundle sheath cells where it undergoes decarboxylation to release CO2.
- This released CO2 is then utilized in the Calvin cycle for further photosynthesis.
Bundle Sheath Cells
- The bundle sheath cells surround the vascular tissue in C4 plants.
- The Calvin cycle, which involves the fixation of released CO2, takes place in the bundle sheath cells.
Epidermis and Phloem Cells
- The epidermis is the outermost layer of cells in plants, and the phloem cells are involved in the transport of sugars.
- These cells do not play a direct role in malic acid formation during CO2 fixation in C4 plants.
Therefore, malic acid formation during CO2 fixation occurs in the mesophyll cells of C4 plants, where the initial steps of the C4 pathway take place.
Blister copper is refined by stirring molten impure metal with green logs of wood because such a wood liberates hydrocarbon gases (like CH4 ). This process X is called ________ and it is used to purify the metal that initially contain impurities of Y. Y is _______.- a)X = poling, Y = CuO2
- b)X = cupellation, Y = CuO
- c)X = cupellation, Y = ZnO
- d)X = poling, Y = Cu2O
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Blister copper is refined by stirring molten impure metal with green logs of wood because such a wood liberates hydrocarbon gases (like CH4 ). This process X is called ________ and it is used to purify the metal that initially contain impurities of Y. Y is _______.
a)
X = poling, Y = CuO2
b)
X = cupellation, Y = CuO
c)
X = cupellation, Y = ZnO
d)
X = poling, Y = Cu2O
|
|
Sagarika Mehta answered |
Poling to Purify Blister Copper:
Poling is a refining process used to purify blister copper. It is a type of pyrometallurgical process that involves stirring molten impure metal with green logs of wood. The wood liberates hydrocarbon gases like CH4, which react with the impurities in the metal to form volatile compounds. These volatile compounds are then removed from the molten metal, leaving behind a purer form of the metal.
Steps involved in Poling:
1. Heating of the impure metal: The impure metal is heated to a molten state.
2. Addition of green logs of wood: Green logs of wood are added to the molten metal.
3. Formation of hydrocarbon gases: The wood liberates hydrocarbon gases like CH4.
4. Reaction with impurities: The hydrocarbon gases react with the impurities present in the metal to form volatile compounds.
5. Removal of volatile compounds: The volatile compounds are then removed from the molten metal using a vacuum or suction pump.
6. Purification of metal: The process of poling removes impurities from the metal, leaving behind a purer form of the metal.
Impurities in Blister Copper:
Blister Copper is an impure form of copper that contains impurities like Cu2O, Fe, S, and ZnO. These impurities can be removed using the poling process to obtain pure copper.
Poling is a refining process used to purify blister copper. It is a type of pyrometallurgical process that involves stirring molten impure metal with green logs of wood. The wood liberates hydrocarbon gases like CH4, which react with the impurities in the metal to form volatile compounds. These volatile compounds are then removed from the molten metal, leaving behind a purer form of the metal.
Steps involved in Poling:
1. Heating of the impure metal: The impure metal is heated to a molten state.
2. Addition of green logs of wood: Green logs of wood are added to the molten metal.
3. Formation of hydrocarbon gases: The wood liberates hydrocarbon gases like CH4.
4. Reaction with impurities: The hydrocarbon gases react with the impurities present in the metal to form volatile compounds.
5. Removal of volatile compounds: The volatile compounds are then removed from the molten metal using a vacuum or suction pump.
6. Purification of metal: The process of poling removes impurities from the metal, leaving behind a purer form of the metal.
Impurities in Blister Copper:
Blister Copper is an impure form of copper that contains impurities like Cu2O, Fe, S, and ZnO. These impurities can be removed using the poling process to obtain pure copper.
Plane angle and solid angle have- a)Units but no dimensions
- b)Dimensions but no units
- c)No units and no dimensions
- d)Both units and dimensions
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Plane angle and solid angle have
a)
Units but no dimensions
b)
Dimensions but no units
c)
No units and no dimensions
d)
Both units and dimensions
|
|
Manisha Basak answered |
Explanation:
Units and dimensions: In physics, every physical quantity has a unit and a dimension. The unit of a physical quantity is a standard quantity used to measure the physical quantity. For example, the unit of length is meter (m), and the unit of time is second (s). The dimension of a physical quantity is a kind of measurement that represents the physical nature of the quantity. For example, the dimension of length is [L], and the dimension of time is [T].
Plane angle: A plane angle is the angle between two planes that intersect each other. The unit of plane angle is degree (°) or radian (rad), and the dimension of plane angle is [1]. The dimension of plane angle is dimensionless because it is the ratio of two lengths.
Solid angle: A solid angle is the angle that an object subtends at a point. The unit of solid angle is steradian (sr), and the dimension of solid angle is [1]. The dimension of solid angle is also dimensionless because it is the ratio of two areas.
Units but no dimensions: Both plane angle and solid angle have units but no dimensions because they are dimensionless quantities. They are ratios of two lengths or two areas, respectively, and do not have any physical nature that can be represented by a dimension. Therefore, the answer is option 'A'.
Units and dimensions: In physics, every physical quantity has a unit and a dimension. The unit of a physical quantity is a standard quantity used to measure the physical quantity. For example, the unit of length is meter (m), and the unit of time is second (s). The dimension of a physical quantity is a kind of measurement that represents the physical nature of the quantity. For example, the dimension of length is [L], and the dimension of time is [T].
Plane angle: A plane angle is the angle between two planes that intersect each other. The unit of plane angle is degree (°) or radian (rad), and the dimension of plane angle is [1]. The dimension of plane angle is dimensionless because it is the ratio of two lengths.
Solid angle: A solid angle is the angle that an object subtends at a point. The unit of solid angle is steradian (sr), and the dimension of solid angle is [1]. The dimension of solid angle is also dimensionless because it is the ratio of two areas.
Units but no dimensions: Both plane angle and solid angle have units but no dimensions because they are dimensionless quantities. They are ratios of two lengths or two areas, respectively, and do not have any physical nature that can be represented by a dimension. Therefore, the answer is option 'A'.
The physical quantity that has the same dimensional formula as pressure is:- a)Coefficient of viscosity
- b)Force
- c)Momentum
- d)Young's modulus of elasticity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The physical quantity that has the same dimensional formula as pressure is:
a)
Coefficient of viscosity
b)
Force
c)
Momentum
d)
Young's modulus of elasticity
|
|
Sagarika Dasgupta answered |
Dimensional Formula of Pressure
Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit area. Its dimensional formula is given as:
[P] = [M L^-1 T^-2]
Dimensional Formula of Young's Modulus of Elasticity
Young's modulus of elasticity is defined as the ratio of stress to strain in a material when it is subjected to an external force. Its dimensional formula is given as:
[Y] = [M L^-1 T^-2]
Comparing the Dimensional Formulas
We can see that the dimensional formula of pressure and Young's modulus of elasticity are the same. Therefore, the physical quantity that has the same dimensional formula as pressure is Young's modulus of elasticity. This means that both pressure and Young's modulus of elasticity have the same units of measurement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pressure and Young's modulus of elasticity are two different physical quantities that have the same dimensional formula. This means that they have the same units of measurement and can be converted from one to the other using appropriate conversion factors.
Pressure is defined as the force exerted per unit area. Its dimensional formula is given as:
[P] = [M L^-1 T^-2]
Dimensional Formula of Young's Modulus of Elasticity
Young's modulus of elasticity is defined as the ratio of stress to strain in a material when it is subjected to an external force. Its dimensional formula is given as:
[Y] = [M L^-1 T^-2]
Comparing the Dimensional Formulas
We can see that the dimensional formula of pressure and Young's modulus of elasticity are the same. Therefore, the physical quantity that has the same dimensional formula as pressure is Young's modulus of elasticity. This means that both pressure and Young's modulus of elasticity have the same units of measurement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, pressure and Young's modulus of elasticity are two different physical quantities that have the same dimensional formula. This means that they have the same units of measurement and can be converted from one to the other using appropriate conversion factors.
If the error in the measurement of radius of a sphere is 2%, then the error in the determination of volume of the sphere will be- a)8%
- b)2%
- c)4%
- d)6%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If the error in the measurement of radius of a sphere is 2%, then the error in the determination of volume of the sphere will be
a)
8%
b)
2%
c)
4%
d)
6%
|
|
Swara Dey answered |
Explanation:
To understand the error in the determination of the volume of a sphere, let's first understand the formula for calculating the volume of a sphere and how it is affected by the measurement of the radius.
The formula for the volume of a sphere is given by:
V = (4/3)πr³
where V is the volume and r is the radius of the sphere.
Error in the Measurement of Radius:
The error in the measurement of the radius is given as 2%. This means that the measured value of the radius will have an error of 2%.
Propagation of Errors:
When errors are involved in multiple measurements and calculations, the concept of error propagation is used. In this case, we need to determine how the error in the radius affects the determination of the volume.
Formula for Error Propagation:
The formula for propagating errors through a mathematical function is given by:
Δf = |df/dr| * Δr
where Δf is the error in the function, |df/dr| is the derivative of the function with respect to the variable, and Δr is the error in the variable.
Error in the Determination of Volume:
To find the error in the determination of the volume, we need to calculate the derivative of the volume formula with respect to the radius.
dV/dr = 4πr²
Now, we can substitute the values into the error propagation formula:
ΔV = |dV/dr| * Δr
= 4πr² * Δr
Since the error in the radius is given as 2%, we can substitute this value into the equation:
ΔV = 4πr² * 0.02
Simplifying further:
ΔV = 0.08πr²
Percentage Error:
To express the error as a percentage, we can divide the error by the actual value of the volume:
Percentage Error = (ΔV / V) * 100
= (0.08πr²) / ((4/3)πr³) * 100
= 0.08 * (3/4) * 100
= 6%
Therefore, the error in the determination of the volume of the sphere is 6%, which corresponds to option D.
To understand the error in the determination of the volume of a sphere, let's first understand the formula for calculating the volume of a sphere and how it is affected by the measurement of the radius.
The formula for the volume of a sphere is given by:
V = (4/3)πr³
where V is the volume and r is the radius of the sphere.
Error in the Measurement of Radius:
The error in the measurement of the radius is given as 2%. This means that the measured value of the radius will have an error of 2%.
Propagation of Errors:
When errors are involved in multiple measurements and calculations, the concept of error propagation is used. In this case, we need to determine how the error in the radius affects the determination of the volume.
Formula for Error Propagation:
The formula for propagating errors through a mathematical function is given by:
Δf = |df/dr| * Δr
where Δf is the error in the function, |df/dr| is the derivative of the function with respect to the variable, and Δr is the error in the variable.
Error in the Determination of Volume:
To find the error in the determination of the volume, we need to calculate the derivative of the volume formula with respect to the radius.
dV/dr = 4πr²
Now, we can substitute the values into the error propagation formula:
ΔV = |dV/dr| * Δr
= 4πr² * Δr
Since the error in the radius is given as 2%, we can substitute this value into the equation:
ΔV = 4πr² * 0.02
Simplifying further:
ΔV = 0.08πr²
Percentage Error:
To express the error as a percentage, we can divide the error by the actual value of the volume:
Percentage Error = (ΔV / V) * 100
= (0.08πr²) / ((4/3)πr³) * 100
= 0.08 * (3/4) * 100
= 6%
Therefore, the error in the determination of the volume of the sphere is 6%, which corresponds to option D.
Mechanism of a hypothetical reaction X2 + Y2 → 2XY, is given below :(i) X2 ⇌ X + X (fast)(ii) X + Y2 → XY + Y (slow)(iii) X + Y → XY (fast)The overall order of the reaction will be- a)2
- b)0
- c)1.5
- d)1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mechanism of a hypothetical reaction X2 + Y2 → 2XY, is given below :
(i) X2 ⇌ X + X (fast)
(ii) X + Y2 → XY + Y (slow)
(iii) X + Y → XY (fast)
The overall order of the reaction will be
a)
2
b)
0
c)
1.5
d)
1
|
|
Devika Chavan answered |
The overall order of a reaction is determined by the sum of the orders of the reactants in the rate-determining step. In this hypothetical reaction X2 + Y2 → 2XY, the mechanism is given as:
(i) X2 ⇌ X + X (fast)
(ii) X + Y2 → XY + Y (slow)
(iii) X + Y → XY (fast)
Let's analyze each step to determine the overall order of the reaction.
(i) X2 ⇌ X + X (fast):
This step is a bimolecular reaction between two X molecules. Since the rate-determining step is slow, the order of this step is 2 (second order).
(ii) X + Y2 → XY + Y (slow):
This step is a bimolecular reaction between one X molecule and one Y2 molecule. Since the rate-determining step is slow, the order of this step is also 2 (second order).
(iii) X + Y → XY (fast):
This step is a bimolecular reaction between one X molecule and one Y molecule. However, since this step is fast, it does not contribute to the overall rate equation.
To determine the overall order of the reaction, we sum the orders of the reactants in the rate-determining step. In this case, the rate-determining step is step (ii), which has an order of 2. Therefore, the overall order of the reaction is 2 (second order).
Therefore, the correct answer is option (a) 2.
(i) X2 ⇌ X + X (fast)
(ii) X + Y2 → XY + Y (slow)
(iii) X + Y → XY (fast)
Let's analyze each step to determine the overall order of the reaction.
(i) X2 ⇌ X + X (fast):
This step is a bimolecular reaction between two X molecules. Since the rate-determining step is slow, the order of this step is 2 (second order).
(ii) X + Y2 → XY + Y (slow):
This step is a bimolecular reaction between one X molecule and one Y2 molecule. Since the rate-determining step is slow, the order of this step is also 2 (second order).
(iii) X + Y → XY (fast):
This step is a bimolecular reaction between one X molecule and one Y molecule. However, since this step is fast, it does not contribute to the overall rate equation.
To determine the overall order of the reaction, we sum the orders of the reactants in the rate-determining step. In this case, the rate-determining step is step (ii), which has an order of 2. Therefore, the overall order of the reaction is 2 (second order).
Therefore, the correct answer is option (a) 2.
Dimensions of resistance in an electrical circuit, in terms of dimension of mass M, of length L, of time T and of current I, would be- a)[M L2T−2]
- b)[M L2T−1I−1]
- c)[M L2T−3I−2]
- d)[M L2T−3I−1].
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Dimensions of resistance in an electrical circuit, in terms of dimension of mass M, of length L, of time T and of current I, would be
a)
[M L2T−2]
b)
[M L2T−1I−1]
c)
[M L2T−3I−2]
d)
[M L2T−3I−1].

|
Sushil Kumar answered |
According to Ohm's law,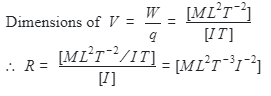
V = RI or R = V/I
Transgenic models can be used to investigate many human diseases such as:- a)Cancer
- b)Alzheimer’s disease
- c)Cystic fibrosis
- d)All of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Transgenic models can be used to investigate many human diseases such as:
a)
Cancer
b)
Alzheimer’s disease
c)
Cystic fibrosis
d)
All of these
|
|
Dev Patel answered |
Transgenic animals are used for testing the safety of vaccines, drugs, studying diseases, like cystic fibrosis, haemophilia, cancer and Alzheimer's disease and study of complex growth factors such as insulin-like growth factors and have provided new insights into the genetic origin of certain diseases and have improved our understanding of pathological processes on the cellular level.
Transgenic animals were used to study aspects of tumour growth, immune regulation, growth of the cardiovascular system and atherosclerosis. These studies provided new insights into the genetic roots of certain diseases and strengthened our understanding of cellular pathological processes.
Mutation theory couldn’t explain _______- a)variations
- b)saltation
- c)development of mimicry
- d)chromosomes of flowers
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Mutation theory couldn’t explain _______
a)
variations
b)
saltation
c)
development of mimicry
d)
chromosomes of flowers

|
Imk Pathsala answered |
One of the drawbacks of mutation theory was that it couldn’t explain the development of mimicry, the relationship between the position of nectars in flower and also length of proboscis in their insect pollinators. The problem was that these cannot be imagined to have developed all of a sudden.
Which one of the following statements is incorrect about enzyme catalysis?- a)Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
- b)Enzyme action is specific.
- c)Enzymes are denatured by ultraviolet rays and at high temperature.
- d)Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following statements is incorrect about enzyme catalysis?
a)
Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
b)
Enzyme action is specific.
c)
Enzymes are denatured by ultraviolet rays and at high temperature.
d)
Enzymes are least reactive at optimum temperature.
|
|
Ashish Chaudhary answered |
Incorrect Statement about Enzyme Catalysis:
The incorrect statement about enzyme catalysis is option 'D', which states that enzymes are least reactive at the optimum temperature.
Explanation:
Enzymes:
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They are mostly proteinous in nature and play a crucial role in various metabolic processes occurring in living organisms.
Specificity of Enzyme Action:
Enzyme action is highly specific, meaning that each enzyme catalyzes a particular reaction or a set of closely related reactions. This specificity is due to the unique three-dimensional structure of the enzyme's active site, which allows it to bind specifically to its substrate(s).
Denaturation of Enzymes:
Enzymes can be denatured by various factors such as high temperature, extreme pH, and exposure to certain chemicals. However, the denaturation of enzymes occurs primarily at high temperatures and extreme pH values, rather than by ultraviolet rays. Ultraviolet rays do not have sufficient energy to break the bonds holding the enzyme's tertiary structure together.
Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity:
Enzyme activity is highly influenced by temperature. At low temperatures, the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions is generally slow. As the temperature increases, the rate of reaction also increases due to the increased kinetic energy of the molecules involved. However, there is an optimal temperature at which enzymes exhibit maximum activity. This temperature is known as the optimum temperature.
Key Points:
- Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
- Enzyme action is specific, with each enzyme catalyzing a particular reaction or set of reactions.
- Enzymes can be denatured by high temperature and extreme pH, not by ultraviolet rays.
- Enzymes exhibit maximum activity at their optimum temperature.
Conclusion:
The incorrect statement in the given options is option 'D'. Enzymes are not least reactive at the optimum temperature. Instead, they exhibit maximum activity at their optimum temperature.
The incorrect statement about enzyme catalysis is option 'D', which states that enzymes are least reactive at the optimum temperature.
Explanation:
Enzymes:
Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being consumed in the process. They are mostly proteinous in nature and play a crucial role in various metabolic processes occurring in living organisms.
Specificity of Enzyme Action:
Enzyme action is highly specific, meaning that each enzyme catalyzes a particular reaction or a set of closely related reactions. This specificity is due to the unique three-dimensional structure of the enzyme's active site, which allows it to bind specifically to its substrate(s).
Denaturation of Enzymes:
Enzymes can be denatured by various factors such as high temperature, extreme pH, and exposure to certain chemicals. However, the denaturation of enzymes occurs primarily at high temperatures and extreme pH values, rather than by ultraviolet rays. Ultraviolet rays do not have sufficient energy to break the bonds holding the enzyme's tertiary structure together.
Effect of Temperature on Enzyme Activity:
Enzyme activity is highly influenced by temperature. At low temperatures, the rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions is generally slow. As the temperature increases, the rate of reaction also increases due to the increased kinetic energy of the molecules involved. However, there is an optimal temperature at which enzymes exhibit maximum activity. This temperature is known as the optimum temperature.
Key Points:
- Enzymes are mostly proteinous in nature.
- Enzyme action is specific, with each enzyme catalyzing a particular reaction or set of reactions.
- Enzymes can be denatured by high temperature and extreme pH, not by ultraviolet rays.
- Enzymes exhibit maximum activity at their optimum temperature.
Conclusion:
The incorrect statement in the given options is option 'D'. Enzymes are not least reactive at the optimum temperature. Instead, they exhibit maximum activity at their optimum temperature.
The oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is- a)-6
- b)+12
- c)+6
- d)+4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is
a)
-6
b)
+12
c)
+6
d)
+4
|
|
Isha Mishra answered |
Explanation:
To determine the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5, we need to assign oxidation numbers to each element in the compound.
Rules for assigning oxidation numbers:
1. The oxidation state of an element in its elemental form is always zero.
2. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is always zero.
3. The sum of oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
4. Oxygen generally has an oxidation state of -2, except in peroxides where it is -1.
5. The sum of oxidation numbers in a molecule is equal to zero.
Assigning oxidation numbers:
Let's assign the oxidation state of Cr as x.
The oxidation state of O in CrO5 is -2 (rule 4).
Since there are 5 oxygen atoms with a total oxidation state of -10, the oxidation state of Cr can be determined using rule 2:
x + (-10) = 0
x = +10
Therefore, the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is +10.
Converting the oxidation state to a whole number:
The oxidation state of an element is usually expressed as a whole number. To convert the oxidation state of Cr from +10 to a whole number, we need to divide it by the common factor: 2.
+10/2 = +5
Therefore, the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is +5.
Comparison with the given options:
a) -6: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is positive, not negative.
b) 12: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is not 12.
c) 6: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is not 6.
d) 4: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is not 4.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - 6.
To determine the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5, we need to assign oxidation numbers to each element in the compound.
Rules for assigning oxidation numbers:
1. The oxidation state of an element in its elemental form is always zero.
2. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is always zero.
3. The sum of oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
4. Oxygen generally has an oxidation state of -2, except in peroxides where it is -1.
5. The sum of oxidation numbers in a molecule is equal to zero.
Assigning oxidation numbers:
Let's assign the oxidation state of Cr as x.
The oxidation state of O in CrO5 is -2 (rule 4).
Since there are 5 oxygen atoms with a total oxidation state of -10, the oxidation state of Cr can be determined using rule 2:
x + (-10) = 0
x = +10
Therefore, the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is +10.
Converting the oxidation state to a whole number:
The oxidation state of an element is usually expressed as a whole number. To convert the oxidation state of Cr from +10 to a whole number, we need to divide it by the common factor: 2.
+10/2 = +5
Therefore, the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is +5.
Comparison with the given options:
a) -6: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is positive, not negative.
b) 12: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is not 12.
c) 6: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is not 6.
d) 4: This is not the correct answer as the oxidation state of Cr in CrO5 is not 4.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C' - 6.
In case of a couple where the male is having a very low sperm count, which of the following technique will be suitable for fertilization?- a)Intrauterine transfer
- b)Gamete intracytoplasmic fallopian transfer
- c)Artificial Insemination
- d)Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of a couple where the male is having a very low sperm count, which of the following technique will be suitable for fertilization?
a)
Intrauterine transfer
b)
Gamete intracytoplasmic fallopian transfer
c)
Artificial Insemination
d)
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION (AI): The introduction of seminal fluid directly into the uterus of female by artificial method is called artificial insemination. This technique is used in male who have low sperm count and inability to inseminate the female normally. It is of two types
a) Artificial insemination- homologous (AIH): In this method the semen is collected from husband and is introduced into the vagina or uterus of the female.
b) Artificial insemination- donor (AID): In this method the semen is collected from donor and is introduced into the vagina or uterus of the female.
Which one of the following pairs of codons in correctly matched with their function or the signal for the particular amino acid?- a)GUU, GCU - Alanine
- b)UAG, UGA - Stop
- c)AUG, ACG - Start/Methionine
- d)UUA, UCA - Leucine
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following pairs of codons in correctly matched with their function or the signal for the particular amino acid?
a)
GUU, GCU - Alanine
b)
UAG, UGA - Stop
c)
AUG, ACG - Start/Methionine
d)
UUA, UCA - Leucine
|
|
Rishabh Chavan answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option B: UAG, UGA - Stop.
Codons and their Functions:
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides on the mRNA that correspond to specific amino acids. They play a crucial role in protein synthesis by determining the order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Stop Codons:
Stop codons signal the termination of protein synthesis. They do not code for any amino acid but act as signals to release the polypeptide chain from the ribosome. There are three stop codons: UAA, UAG, and UGA.
Functions of the Given Codons:
a) GUU, GCU - Alanine: This pair of codons does not match the function or signal for the amino acid alanine. The codons for alanine are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG.
b) UAG, UGA - Stop: This pair of codons is correctly matched with their function. UAG and UGA are two of the three stop codons that signal the termination of protein synthesis.
c) AUG, ACG - Start/Methionine: This pair of codons does not match the function or signal for the start codon or methionine. The start codon is always AUG, which also codes for methionine.
d) UUA, UCA - Leucine: This pair of codons does not match the function or signal for the amino acid leucine. The codons for leucine are UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG.
Conclusion:
Among the given pairs of codons, only UAG and UGA are correctly matched with their function as stop codons. Stop codons signal the termination of protein synthesis.
The correct answer is option B: UAG, UGA - Stop.
Codons and their Functions:
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides on the mRNA that correspond to specific amino acids. They play a crucial role in protein synthesis by determining the order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Stop Codons:
Stop codons signal the termination of protein synthesis. They do not code for any amino acid but act as signals to release the polypeptide chain from the ribosome. There are three stop codons: UAA, UAG, and UGA.
Functions of the Given Codons:
a) GUU, GCU - Alanine: This pair of codons does not match the function or signal for the amino acid alanine. The codons for alanine are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG.
b) UAG, UGA - Stop: This pair of codons is correctly matched with their function. UAG and UGA are two of the three stop codons that signal the termination of protein synthesis.
c) AUG, ACG - Start/Methionine: This pair of codons does not match the function or signal for the start codon or methionine. The start codon is always AUG, which also codes for methionine.
d) UUA, UCA - Leucine: This pair of codons does not match the function or signal for the amino acid leucine. The codons for leucine are UUA, UUG, CUU, CUC, CUA, and CUG.
Conclusion:
Among the given pairs of codons, only UAG and UGA are correctly matched with their function as stop codons. Stop codons signal the termination of protein synthesis.
ELISA is used for:- a)DNA extraction
- b)DNA seperation
- c)Diagnostic purpose
- d)Genetic engineering
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
ELISA is used for:
a)
DNA extraction
b)
DNA seperation
c)
Diagnostic purpose
d)
Genetic engineering
|
|
Lakshmi Khanna answered |
ELISA stands for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is a diagnostic tool used to detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample.
Diagnostic Purposes
ELISA is extensively used for diagnostic purposes in the medical field. It can be used to diagnose infectious diseases such as HIV, hepatitis, and Lyme disease. It is also used to monitor autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. ELISA can detect the presence of specific antigens or antibodies in blood, urine, or other bodily fluids, allowing doctors to diagnose diseases quickly and accurately.
Principle of ELISA
ELISA works on the principle of antigen-antibody interactions. It involves the use of an enzyme-conjugated antibody to detect the presence of a specific antigen or antibody in a sample. The enzyme catalyzes a color-producing reaction, which can be measured using a spectrophotometer. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the concentration of the antigen or antibody in the sample.
Types of ELISA
There are different types of ELISA, including direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA, and competitive ELISA. The choice of ELISA type depends on the antigen or antibody being detected and the sample being tested.
Advantages of ELISA
ELISA is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tool. It can detect very low concentrations of antigens or antibodies in a sample. ELISA is also relatively easy to perform and can be used to test a large number of samples simultaneously.
Conclusion
ELISA is a widely used diagnostic tool in the medical field. It is used to diagnose infectious and autoimmune diseases quickly and accurately. ELISA works on the principle of antigen-antibody interactions and involves the use of an enzyme-conjugated antibody to detect the presence of a specific antigen or antibody in a sample. There are different types of ELISA, and the choice of ELISA type depends on the antigen or antibody being detected and the sample being tested. ELISA is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tool that can detect very low concentrations of antigens or antibodies in a sample.
Diagnostic Purposes
ELISA is extensively used for diagnostic purposes in the medical field. It can be used to diagnose infectious diseases such as HIV, hepatitis, and Lyme disease. It is also used to monitor autoimmune diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. ELISA can detect the presence of specific antigens or antibodies in blood, urine, or other bodily fluids, allowing doctors to diagnose diseases quickly and accurately.
Principle of ELISA
ELISA works on the principle of antigen-antibody interactions. It involves the use of an enzyme-conjugated antibody to detect the presence of a specific antigen or antibody in a sample. The enzyme catalyzes a color-producing reaction, which can be measured using a spectrophotometer. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the concentration of the antigen or antibody in the sample.
Types of ELISA
There are different types of ELISA, including direct ELISA, indirect ELISA, sandwich ELISA, and competitive ELISA. The choice of ELISA type depends on the antigen or antibody being detected and the sample being tested.
Advantages of ELISA
ELISA is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tool. It can detect very low concentrations of antigens or antibodies in a sample. ELISA is also relatively easy to perform and can be used to test a large number of samples simultaneously.
Conclusion
ELISA is a widely used diagnostic tool in the medical field. It is used to diagnose infectious and autoimmune diseases quickly and accurately. ELISA works on the principle of antigen-antibody interactions and involves the use of an enzyme-conjugated antibody to detect the presence of a specific antigen or antibody in a sample. There are different types of ELISA, and the choice of ELISA type depends on the antigen or antibody being detected and the sample being tested. ELISA is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic tool that can detect very low concentrations of antigens or antibodies in a sample.
Consider the statements given below regarding contraception and answer as directed thereafter:
Vasectomy involves cutting down vas deferens in females. Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months. Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives. Emergency contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception. Which of the following two statements are correct?- a)1 and 3
- b)1 and 2
- c)2 and 3
- d)3 and 4
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the statements given below regarding contraception and answer as directed thereafter:
Vasectomy involves cutting down vas deferens in females.
Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months.
Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
Emergency contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception.
Which of the following two statements are correct?
a)
1 and 3
b)
1 and 2
c)
2 and 3
d)
3 and 4
|
|
Sagarika Bajaj answered |
Vasectomy involves cutting down vas deferens in males.
Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months.
Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
Emergency contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception.
Correct Statements:
2) Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months.
3) Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
Explanation:
1) Vasectomy involves cutting down vas deferens in males: This statement is incorrect. Vasectomy is a surgical procedure performed on males to prevent the release of sperm during ejaculation. It involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra. It is a permanent method of contraception and does not involve females.
2) Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months: This statement is correct. Breastfeeding can act as a natural contraceptive method for a certain period of time. It is known as lactational amenorrhea method (LAM). When a woman breastfeeds her baby exclusively (no other food or drink) and frequently, it suppresses ovulation and prevents the release of eggs from the ovaries. This can provide effective contraception for up to six months after childbirth.
3) Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives: This statement is correct. Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are highly effective long-acting reversible contraceptives. Copper-T is a type of IUD that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It works by releasing copper ions that interfere with sperm function and prevent fertilization. Copper-T can provide contraception for up to 10 years and has a high success rate in preventing pregnancy.
4) Emergency contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception: This statement is incorrect. Emergency contraceptive pills, also known as "morning-after pills," are intended for use within a few days after unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure. The effectiveness of these pills decreases over time, and they are most effective when taken as soon as possible after unprotected sex. Generally, emergency contraceptive pills should be taken within 72 hours (3 days) after coitus for maximum effectiveness. There are also some types of emergency contraceptive pills that can be taken up to 120 hours (5 days) after coitus, but their effectiveness decreases with time.
Therefore, the correct statements are 2) Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months and 3) Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months.
Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
Emergency contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception.
Correct Statements:
2) Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months.
3) Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
Explanation:
1) Vasectomy involves cutting down vas deferens in males: This statement is incorrect. Vasectomy is a surgical procedure performed on males to prevent the release of sperm during ejaculation. It involves cutting or blocking the vas deferens, the tubes that carry sperm from the testicles to the urethra. It is a permanent method of contraception and does not involve females.
2) Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months: This statement is correct. Breastfeeding can act as a natural contraceptive method for a certain period of time. It is known as lactational amenorrhea method (LAM). When a woman breastfeeds her baby exclusively (no other food or drink) and frequently, it suppresses ovulation and prevents the release of eggs from the ovaries. This can provide effective contraception for up to six months after childbirth.
3) Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives: This statement is correct. Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are highly effective long-acting reversible contraceptives. Copper-T is a type of IUD that is inserted into the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It works by releasing copper ions that interfere with sperm function and prevent fertilization. Copper-T can provide contraception for up to 10 years and has a high success rate in preventing pregnancy.
4) Emergency contraceptive pills may be taken up to one week after coitus to prevent conception: This statement is incorrect. Emergency contraceptive pills, also known as "morning-after pills," are intended for use within a few days after unprotected intercourse or contraceptive failure. The effectiveness of these pills decreases over time, and they are most effective when taken as soon as possible after unprotected sex. Generally, emergency contraceptive pills should be taken within 72 hours (3 days) after coitus for maximum effectiveness. There are also some types of emergency contraceptive pills that can be taken up to 120 hours (5 days) after coitus, but their effectiveness decreases with time.
Therefore, the correct statements are 2) Generally, chances of conception are nil until the mother breast-feeds the infant for a period of a maximum of up to six months and 3) Intrauterine devices like copper-T are very effective contraceptives.
A diver is 10 m below the surface of water. The approximate pressure experienced by the diver is-- a)105 Pa
- b)2 × 105 Pa
- c)3 × 105 Pa
- d)4 × 105 Pa
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A diver is 10 m below the surface of water. The approximate pressure experienced by the diver is-
a)
105 Pa
b)
2 × 105 Pa
c)
3 × 105 Pa
d)
4 × 105 Pa
|
|
Nishtha Choudhary answered |
Explanation:
Pressure in a Fluid:
The pressure in a fluid (liquid or gas) increases with depth due to the weight of the fluid above. This is known as hydrostatic pressure. The pressure at any point in a fluid is equal in all directions and acts perpendicular to the surface. It can be calculated using the formula:
Pressure = Density × Acceleration due to gravity × Height
Where:
- Density is the density of the fluid
- Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration experienced by the fluid due to gravity
- Height is the depth or height from the surface
Pressure Calculation for the Diver:
In this case, the diver is 10 m below the surface of the water. The pressure experienced by the diver can be calculated using the above formula.
Given:
Density of water = 1000 kg/m³ (approximate value)
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s² (standard value)
Height = 10 m
Using the formula, we can calculate the pressure:
Pressure = Density × Acceleration due to gravity × Height
= 1000 kg/m³ × 9.8 m/s² × 10 m
= 98000 N/m² or 98000 Pa
Approximate Pressure:
The approximate pressure experienced by the diver is 98000 Pa. However, in the given options, none of them match this value exactly. We need to choose the closest option.
Among the given options, option 'B' is closest to the calculated pressure:
Option B: 2 × 10^5 Pa (200000 Pa)
While this value is not exact, it is the closest option to the calculated pressure of 98000 Pa. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' (2 × 10^5 Pa or 200000 Pa).
Pressure in a Fluid:
The pressure in a fluid (liquid or gas) increases with depth due to the weight of the fluid above. This is known as hydrostatic pressure. The pressure at any point in a fluid is equal in all directions and acts perpendicular to the surface. It can be calculated using the formula:
Pressure = Density × Acceleration due to gravity × Height
Where:
- Density is the density of the fluid
- Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration experienced by the fluid due to gravity
- Height is the depth or height from the surface
Pressure Calculation for the Diver:
In this case, the diver is 10 m below the surface of the water. The pressure experienced by the diver can be calculated using the above formula.
Given:
Density of water = 1000 kg/m³ (approximate value)
Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s² (standard value)
Height = 10 m
Using the formula, we can calculate the pressure:
Pressure = Density × Acceleration due to gravity × Height
= 1000 kg/m³ × 9.8 m/s² × 10 m
= 98000 N/m² or 98000 Pa
Approximate Pressure:
The approximate pressure experienced by the diver is 98000 Pa. However, in the given options, none of them match this value exactly. We need to choose the closest option.
Among the given options, option 'B' is closest to the calculated pressure:
Option B: 2 × 10^5 Pa (200000 Pa)
While this value is not exact, it is the closest option to the calculated pressure of 98000 Pa. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' (2 × 10^5 Pa or 200000 Pa).
The two antibiotic resistance genes on vector pBR322 are for- a)Tetracycline and Kanamycin
- b)Ampicillin and Tetracycline
- c)Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol
- d)Chloramphenicol and Tetracycline
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The two antibiotic resistance genes on vector pBR322 are for
a)
Tetracycline and Kanamycin
b)
Ampicillin and Tetracycline
c)
Ampicillin and Chloramphenicol
d)
Chloramphenicol and Tetracycline
|
|
Aman Sen answered |
Explanation:
The correct answer is option B, which states that the two antibiotic resistance genes on vector pBR322 are Ampicillin and Tetracycline.
Vector pBR322:
- Vector pBR322 is a commonly used plasmid vector in molecular biology. It was one of the first widely used cloning vectors and has been extensively studied and characterized.
- It is a circular double-stranded DNA molecule that can replicate independently of the chromosomal DNA in bacterial cells.
- pBR322 contains multiple restriction enzyme recognition sites, allowing the insertion of foreign DNA fragments for cloning purposes.
- It also carries two antibiotic resistance genes, which are essential for selection and maintenance of the vector in bacterial cells.
Antibiotic Resistance Genes on pBR322:
- Ampicillin Resistance Gene (AmpR): The pBR322 vector carries a gene that confers resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. This gene encodes an enzyme called β-lactamase, which inactivates the ampicillin by hydrolyzing its β-lactam ring. Bacteria that contain this gene can grow and survive in the presence of ampicillin.
- Tetracycline Resistance Gene (TetR): The pBR322 vector also carries a gene that provides resistance to the antibiotic tetracycline. This gene encodes a protein called TetR, which binds to tetracycline and prevents its inhibitory effects on bacterial protein synthesis. Bacteria that contain this gene can grow and survive in the presence of tetracycline.
Importance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes:
- The presence of antibiotic resistance genes in pBR322 allows for the selection and maintenance of the vector in bacterial cells.
- When the vector is introduced into bacterial cells, those cells that do not contain the resistance genes will be killed by the antibiotics, while those that have taken up the vector will survive and propagate.
- This selective pressure ensures that only the cells containing the desired vector and any inserted foreign DNA fragments will be able to grow and form colonies.
In summary, the two antibiotic resistance genes on vector pBR322 are Ampicillin and Tetracycline. These genes provide resistance to the antibiotics ampicillin and tetracycline, respectively, and allow for the selection and maintenance of the vector in bacterial cells.
The correct answer is option B, which states that the two antibiotic resistance genes on vector pBR322 are Ampicillin and Tetracycline.
Vector pBR322:
- Vector pBR322 is a commonly used plasmid vector in molecular biology. It was one of the first widely used cloning vectors and has been extensively studied and characterized.
- It is a circular double-stranded DNA molecule that can replicate independently of the chromosomal DNA in bacterial cells.
- pBR322 contains multiple restriction enzyme recognition sites, allowing the insertion of foreign DNA fragments for cloning purposes.
- It also carries two antibiotic resistance genes, which are essential for selection and maintenance of the vector in bacterial cells.
Antibiotic Resistance Genes on pBR322:
- Ampicillin Resistance Gene (AmpR): The pBR322 vector carries a gene that confers resistance to the antibiotic ampicillin. This gene encodes an enzyme called β-lactamase, which inactivates the ampicillin by hydrolyzing its β-lactam ring. Bacteria that contain this gene can grow and survive in the presence of ampicillin.
- Tetracycline Resistance Gene (TetR): The pBR322 vector also carries a gene that provides resistance to the antibiotic tetracycline. This gene encodes a protein called TetR, which binds to tetracycline and prevents its inhibitory effects on bacterial protein synthesis. Bacteria that contain this gene can grow and survive in the presence of tetracycline.
Importance of Antibiotic Resistance Genes:
- The presence of antibiotic resistance genes in pBR322 allows for the selection and maintenance of the vector in bacterial cells.
- When the vector is introduced into bacterial cells, those cells that do not contain the resistance genes will be killed by the antibiotics, while those that have taken up the vector will survive and propagate.
- This selective pressure ensures that only the cells containing the desired vector and any inserted foreign DNA fragments will be able to grow and form colonies.
In summary, the two antibiotic resistance genes on vector pBR322 are Ampicillin and Tetracycline. These genes provide resistance to the antibiotics ampicillin and tetracycline, respectively, and allow for the selection and maintenance of the vector in bacterial cells.
Endothecium and tapetum in anther are derived from- a)Primary sporogenous layer.
- b)Primary parietal layer.
- c)Both primary sporogenous layer and primary parietal layer.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Endothecium and tapetum in anther are derived from
a)
Primary sporogenous layer.
b)
Primary parietal layer.
c)
Both primary sporogenous layer and primary parietal layer.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Jhanvi Menon answered |
Endothecium and tapetum in anther are derived from primary parietal layer. Let's understand the formation of anther and the origin of its different layers.
Formation of Anther
Anther is a part of the stamen, which is the male reproductive organ of a flower. It consists of two lobes, each containing two microsporangia or pollen sacs. The anther is surrounded by four layers of cells, which are:
1. Epidermis
2. Endothecium
3. Middle layer
4. Tapetum
Origin of Different Layers
The four layers of cells in the anther are derived from two different layers of cells in the developing flower bud. They are:
1. Primary sporogenous layer: It is the innermost layer of cells in the developing flower bud. It gives rise to the microsporocytes or pollen mother cells, which undergo meiosis to form haploid microspores that develop into pollen grains.
2. Primary parietal layer: It is the outermost layer of cells in the developing flower bud. It gives rise to the different layers of cells in the anther, as described below:
- Epidermis: It is derived from the outermost layer of the primary parietal layer.
- Endothecium: It is derived from the innermost layer of the primary parietal layer. It forms the inner layer of the anther wall and helps in dehiscence (opening) of the anther to release the pollen grains.
- Middle layer: It is derived from the middle layers of the primary parietal layer.
- Tapetum: It is derived from the innermost layer of the primary parietal layer. It is the most important layer of the anther, as it provides nourishment to the developing microspores and helps in their maturation. It also produces the enzymes and proteins that form the pollen coat.
Conclusion
Thus, the endothecium and tapetum in anther are derived from the primary parietal layer, which is the outermost layer of cells in the developing flower bud.
Formation of Anther
Anther is a part of the stamen, which is the male reproductive organ of a flower. It consists of two lobes, each containing two microsporangia or pollen sacs. The anther is surrounded by four layers of cells, which are:
1. Epidermis
2. Endothecium
3. Middle layer
4. Tapetum
Origin of Different Layers
The four layers of cells in the anther are derived from two different layers of cells in the developing flower bud. They are:
1. Primary sporogenous layer: It is the innermost layer of cells in the developing flower bud. It gives rise to the microsporocytes or pollen mother cells, which undergo meiosis to form haploid microspores that develop into pollen grains.
2. Primary parietal layer: It is the outermost layer of cells in the developing flower bud. It gives rise to the different layers of cells in the anther, as described below:
- Epidermis: It is derived from the outermost layer of the primary parietal layer.
- Endothecium: It is derived from the innermost layer of the primary parietal layer. It forms the inner layer of the anther wall and helps in dehiscence (opening) of the anther to release the pollen grains.
- Middle layer: It is derived from the middle layers of the primary parietal layer.
- Tapetum: It is derived from the innermost layer of the primary parietal layer. It is the most important layer of the anther, as it provides nourishment to the developing microspores and helps in their maturation. It also produces the enzymes and proteins that form the pollen coat.
Conclusion
Thus, the endothecium and tapetum in anther are derived from the primary parietal layer, which is the outermost layer of cells in the developing flower bud.
The height at which the weight of a body becomes 1/16th its weight on the surface of earth (radius R), is- a)5 R
- b)15 R
- c)3 R
- d)4 R
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The height at which the weight of a body becomes 1/16th its weight on the surface of earth (radius R), is
a)
5 R
b)
15 R
c)
3 R
d)
4 R
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of earth is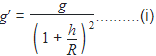
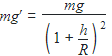
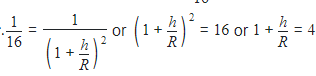
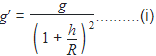
where g is the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of earth and R is the radius of earth.
Multiplying by m (mass of the body) on both sides in (i), we get
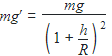
∴ Weight of body at height h ,W′ = mg′
Weight of body at surface of earth, W = mg
According to question,W′ = 1/16W
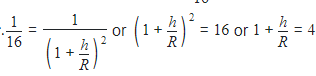
or h/R = 3 or h = 3R
The height of a mercury barometer is 75 cm at sea level and 50 cm at the top of a hill. The ratio of density of mercury to that of air is 104. The height of the hill is:- a)250 m
- b)2.5 km
- c)1.25 km
- d)750 m
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The height of a mercury barometer is 75 cm at sea level and 50 cm at the top of a hill. The ratio of density of mercury to that of air is 104. The height of the hill is:
a)
250 m
b)
2.5 km
c)
1.25 km
d)
750 m
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Difference of pressure between sea level and top of hill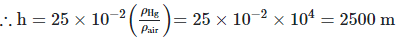
∆P = (h1 - h2) × ρHg × g = (75 - 50) × 10-2 × ρHg × g …(i)
and pressure difference due to h meter of air
∆P = h × ρair × g …(ii)
By equating (i) and (ii) we get
h × ρair × g = (75 − 50) × 10−2 × ρHg × g
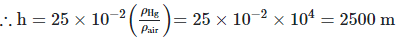
Height of the hill = 2.5 km.
In C4 plants, Calvin cycle operates in- a)stroma of bundle sheath chloroplasts
- b)grana of bundle sheath chloroplasts
- c)grana of mesophyll chloroplasts
- d)stroma of mesophyll chloroplasts
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In C4 plants, Calvin cycle operates in
a)
stroma of bundle sheath chloroplasts
b)
grana of bundle sheath chloroplasts
c)
grana of mesophyll chloroplasts
d)
stroma of mesophyll chloroplasts
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The C4 plants have a characteristic leaf anatomy called kranz anatomy. Here two types of chloroplasts are present - bundle sheath chloroplasts and mesophyll chloroplasts. In C4 plants, there are two carboxylation reactions which occur first in mesophyll chloroplasts and then in bundle sheath chloroplasts. CO2 acceptor molecule in mesophyll chloroplasts is PEP (Phospho-enol pyruvate) and not Ribulose 1 , 5-biphosphate. Further it has enzyme PEPcarboxylase for initial CO2 fixation. RuBP carboxylase is absent in mesophyll chloroplasts but is present in bundle sheath chloroplasts. The first product formed is oxaloacetic acid and hence it is known as C4 cycle. Bundle sheath cells fix CO2 through C3 cycle.
Respiration is _____.- a)anabolic and exergonic
- b)catabolic and exergonic
- c)anabolic and endergonic
- d)catabolic and endergonic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Respiration is _____.
a)
anabolic and exergonic
b)
catabolic and exergonic
c)
anabolic and endergonic
d)
catabolic and endergonic
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Respiration is a catabolic and exergonic cellular process. Respiration, which is also known as cellular respiration, is an enzymatic process of biological oxidation of food materials in a living cell, using molecular O2, producing CO2, H2O and releasing energy in small steps and then storing it in the form of ATP. When required, this ATP is utilised by the cell. Chemically it is a catabolic process and brings about the oxidation and decomposition of organic compounds like carbohydrate, fat, protein in the cells of plants and animals with the release of energy. But all the energy present in respiratory substrate is not released free into the cell.
The maximum current that can be measured by a galvanometer of resistance 40 Ω is 10 mA. It is converted into a voltmeter that can read upto 50 V. The resistance to be connected is series with the galvanometer (in ohm) is
- a)2010
- b)4050
- c)5040
- d)4960
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The maximum current that can be measured by a galvanometer of resistance 40 Ω is 10 mA. It is converted into a voltmeter that can read upto 50 V. The resistance to be connected is series with the galvanometer (in ohm) is
a)
2010
b)
4050
c)
5040
d)
4960
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
To convert galvanometer into voltmeter, the necessary value of resistance to be connected in series with the galvanometer is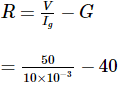
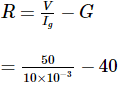
= 5000 − 40 = 4960Ω
Human body has, on an average, 10 L of blood and each cm3cm3 of this has 0.8 mg of dissolved CO2. What could be the volume of CO2 (at STP) that can be recovered from the human body on the average?- a)4.07 L
- b)22.4 L
- c)8 L
- d)5.5 L
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Human body has, on an average, 10 L of blood and each cm3cm3 of this has 0.8 mg of dissolved CO2. What could be the volume of CO2 (at STP) that can be recovered from the human body on the average?
a)
4.07 L
b)
22.4 L
c)
8 L
d)
5.5 L
|
|
Neha Sharma answered |
According to the question,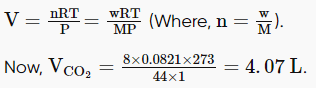
CO2 dissolved in 1 cm3 is 0.8 mg or 8 × 10−4 g.
So, CO2 dissolved in 10 L, i.e., 104 cm3 = 8 × 10−4 × 104 =8 g.
Then, using PV = nRT
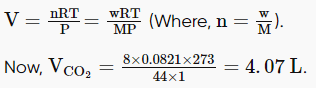
The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector, is termed- a)Ori site
- b)Palindromic sequence
- c)Recognition site
- d)Selectable marker
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The sequence that controls the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector, is termed
a)
Ori site
b)
Palindromic sequence
c)
Recognition site
d)
Selectable marker
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Because ori sequence is responsible for controlling the copy number of the linked DNA in the vector. Ori i.e. origin of replication is responsible for initiation of replication
A mass m is attached to a thin wire and whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break when- a)inclined at an angle of 60∘ from vertical
- b)the mass is at the highest point
- c)the wire is horizontal
- d)the mass is at the lowest point
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A mass m is attached to a thin wire and whirled in a vertical circle. The wire is most likely to break when
a)
inclined at an angle of 60∘ from vertical
b)
the mass is at the highest point
c)
the wire is horizontal
d)
the mass is at the lowest point
|
|
Mohit Nair answered |
Explanation:
Key Points:
- The tension in the wire is responsible for providing the centripetal force required to keep the mass moving in a circular path.
- At the lowest point of the vertical circle, the tension in the wire must be able to support the weight of the mass as well as provide the centripetal force needed for circular motion.
Analysis:
- At the lowest point of the vertical circle, the tension in the wire needs to be greater than at any other point in the circle because it must support the weight of the mass in addition to providing the centripetal force.
- If the tension in the wire is not sufficient at the lowest point, it will break due to the inability to support the weight of the mass and provide the necessary centripetal force simultaneously.
Therefore, the wire is most likely to break when the mass is at the lowest point in the vertical circle.
Twenty seven drops of same size are charged at 220 V each. They combine to form a bigger drop.Calculate the potential of the bigger drop.- a)660 V
- b)1320 V
- c)1520 V
- d)1980 V
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Twenty seven drops of same size are charged at 220 V each. They combine to form a bigger drop.
Calculate the potential of the bigger drop.
a)
660 V
b)
1320 V
c)
1520 V
d)
1980 V
|
|
Harshitha Reddy answered |
Calculation of Potential of Bigger Drop Formed by 27 Drops Charged at 220 V Each
Given:
Charge on each drop = q
Potential of each drop = V = 220 V
Number of drops = n = 27
To find:
Potential of bigger drop formed by 27 drops
Solution:
When two or more charged drops combine to form a bigger drop, their charges get added up while their potential remains the same.
Charge on each drop, q = CV where C is the capacitance of the drop and V is its potential.
The capacitance of a spherical drop of radius r is given by C = 4πεr, where ε is the permittivity of the surrounding medium.
Since all the drops are of the same size, their capacitances are the same.
Therefore, the total charge on the bigger drop formed by the 27 drops is Q = 27q.
The capacitance of the bigger drop is C' = 27C.
Thus, the potential of the bigger drop is given by V' = Q/C' = (27q)/(27C) = q/C.
Substituting the values of q and C, we get
V' = q/C = q/(4πεr) = (q^2)/(4πεqR)
where R is the radius of the bigger drop.
Since the drops are spherical, their radii are related by R = 3^(1/3)r.
Substituting this relation and the given values, we get
V' = (27q^2)/(4πεr^2)(3^(1/3)) = (27V^2)/(3^(4/3)) = 1980 V
Therefore, the potential of the bigger drop formed by the 27 drops is 1980 V.
Answer: option D (1980 V)
Given:
Charge on each drop = q
Potential of each drop = V = 220 V
Number of drops = n = 27
To find:
Potential of bigger drop formed by 27 drops
Solution:
When two or more charged drops combine to form a bigger drop, their charges get added up while their potential remains the same.
Charge on each drop, q = CV where C is the capacitance of the drop and V is its potential.
The capacitance of a spherical drop of radius r is given by C = 4πεr, where ε is the permittivity of the surrounding medium.
Since all the drops are of the same size, their capacitances are the same.
Therefore, the total charge on the bigger drop formed by the 27 drops is Q = 27q.
The capacitance of the bigger drop is C' = 27C.
Thus, the potential of the bigger drop is given by V' = Q/C' = (27q)/(27C) = q/C.
Substituting the values of q and C, we get
V' = q/C = q/(4πεr) = (q^2)/(4πεqR)
where R is the radius of the bigger drop.
Since the drops are spherical, their radii are related by R = 3^(1/3)r.
Substituting this relation and the given values, we get
V' = (27q^2)/(4πεr^2)(3^(1/3)) = (27V^2)/(3^(4/3)) = 1980 V
Therefore, the potential of the bigger drop formed by the 27 drops is 1980 V.
Answer: option D (1980 V)
Which of the following is an example of pleiotropy?- a)Haemophilia
- b)Thalassemia
- c)Sickle cell anaemia
- d)Colour blindness
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is an example of pleiotropy?
a)
Haemophilia
b)
Thalassemia
c)
Sickle cell anaemia
d)
Colour blindness
|
|
Rutuja Khanna answered |
Explanation:
Pleiotropy
- Pleiotropy is a phenomenon in genetics where a single gene has multiple effects on an individual's phenotype.
- This means that a mutation in one gene can result in multiple, seemingly unrelated traits or disorders.
Example of Pleiotropy
- Sickle cell anemia is an example of pleiotropy.
- Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, which codes for the beta-globin protein.
- This mutation not only leads to the characteristic sickle-shaped red blood cells but also has other effects on the body, such as increased susceptibility to infections, organ damage, and pain crises.
- These various effects of the HBB gene mutation demonstrate pleiotropy in action.
Other Options
- Haemophilia, thalassemia, and color blindness are genetic disorders caused by mutations in specific genes, but they do not exhibit the same level of pleiotropy as sickle cell anemia.
- These disorders primarily affect specific aspects of an individual's phenotype rather than multiple traits or systems in the body.
Therefore, the example of sickle cell anemia is a clear demonstration of pleiotropy in genetics.
Pleiotropy
- Pleiotropy is a phenomenon in genetics where a single gene has multiple effects on an individual's phenotype.
- This means that a mutation in one gene can result in multiple, seemingly unrelated traits or disorders.
Example of Pleiotropy
- Sickle cell anemia is an example of pleiotropy.
- Sickle cell anemia is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the HBB gene, which codes for the beta-globin protein.
- This mutation not only leads to the characteristic sickle-shaped red blood cells but also has other effects on the body, such as increased susceptibility to infections, organ damage, and pain crises.
- These various effects of the HBB gene mutation demonstrate pleiotropy in action.
Other Options
- Haemophilia, thalassemia, and color blindness are genetic disorders caused by mutations in specific genes, but they do not exhibit the same level of pleiotropy as sickle cell anemia.
- These disorders primarily affect specific aspects of an individual's phenotype rather than multiple traits or systems in the body.
Therefore, the example of sickle cell anemia is a clear demonstration of pleiotropy in genetics.
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of +2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order?(At. nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)- a)Mn > Fe > Cr > Co
- b)Fe > Mn > Co > Cr
- c)Co > Mn > Fe > Cr
- d)Cr > Mn > Co > Fe
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
For the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe and Co), the stability of +2 oxidation state will be there in which of the following order?
(At. nos. Cr = 24, Mn = 25, Fe = 26, Co = 27)
a)
Mn > Fe > Cr > Co
b)
Fe > Mn > Co > Cr
c)
Co > Mn > Fe > Cr
d)
Cr > Mn > Co > Fe
|
|
Mrinalini Kaur answered |
The stability of 2 oxidation state in the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co) can be explained based on the following factors:
1. Electronic configuration: The electronic configuration of these elements is as follows:
- Chromium (Cr): [Ar] 3d5 4s1
- Manganese (Mn): [Ar] 3d5 4s2
- Iron (Fe): [Ar] 3d6 4s2
- Cobalt (Co): [Ar] 3d7 4s2
2. Screening effect: The screening effect of the 3d electrons on the 4s electrons decreases as we move from left to right across the period. This is due to the increase in nuclear charge which attracts the 4s electrons more towards the nucleus.
3. Ionization energy: The ionization energy of the 4s electrons also increases as we move from left to right across the period. This is due to the increase in nuclear charge which makes it harder to remove an electron from the outermost shell.
Based on the above factors, the stability of 2 oxidation state in the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co) can be explained as follows:
- Chromium (Cr): In Cr, the 3d5 electrons have a strong screening effect on the 4s electron, making it easier to remove. Also, the ionization energy of the 4s electron is relatively low. Therefore, Cr has a stable 2 oxidation state.
- Manganese (Mn): In Mn, the 3d5 electrons still have a strong screening effect on the 4s electron, but the ionization energy of the 4s electron is higher than in Cr. Therefore, Mn has a less stable 2 oxidation state compared to Cr.
- Iron (Fe): In Fe, the 3d6 electrons have a weaker screening effect on the 4s electron, and the ionization energy of the 4s electron is higher than in Mn. Therefore, Fe has a less stable 2 oxidation state compared to Mn and Cr.
- Cobalt (Co): In Co, the 3d7 electrons have an even weaker screening effect on the 4s electron, and the ionization energy of the 4s electron is the highest among the four elements. Therefore, Co has the least stable 2 oxidation state among the four elements.
Therefore, the stability of 2 oxidation state in the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co) follows the order: Mn > Fe > Cr > Co.
1. Electronic configuration: The electronic configuration of these elements is as follows:
- Chromium (Cr): [Ar] 3d5 4s1
- Manganese (Mn): [Ar] 3d5 4s2
- Iron (Fe): [Ar] 3d6 4s2
- Cobalt (Co): [Ar] 3d7 4s2
2. Screening effect: The screening effect of the 3d electrons on the 4s electrons decreases as we move from left to right across the period. This is due to the increase in nuclear charge which attracts the 4s electrons more towards the nucleus.
3. Ionization energy: The ionization energy of the 4s electrons also increases as we move from left to right across the period. This is due to the increase in nuclear charge which makes it harder to remove an electron from the outermost shell.
Based on the above factors, the stability of 2 oxidation state in the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co) can be explained as follows:
- Chromium (Cr): In Cr, the 3d5 electrons have a strong screening effect on the 4s electron, making it easier to remove. Also, the ionization energy of the 4s electron is relatively low. Therefore, Cr has a stable 2 oxidation state.
- Manganese (Mn): In Mn, the 3d5 electrons still have a strong screening effect on the 4s electron, but the ionization energy of the 4s electron is higher than in Cr. Therefore, Mn has a less stable 2 oxidation state compared to Cr.
- Iron (Fe): In Fe, the 3d6 electrons have a weaker screening effect on the 4s electron, and the ionization energy of the 4s electron is higher than in Mn. Therefore, Fe has a less stable 2 oxidation state compared to Mn and Cr.
- Cobalt (Co): In Co, the 3d7 electrons have an even weaker screening effect on the 4s electron, and the ionization energy of the 4s electron is the highest among the four elements. Therefore, Co has the least stable 2 oxidation state among the four elements.
Therefore, the stability of 2 oxidation state in the four successive transition elements (Cr, Mn, Fe, and Co) follows the order: Mn > Fe > Cr > Co.
Alum helps in purifying water by- a)Forming Si complex with clay particles
- b)Sulphate part which combines with the dirt and removes it
- c)Aluminum which coagulates the mud particles
- d)Making mud water soluble
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Alum helps in purifying water by
a)
Forming Si complex with clay particles
b)
Sulphate part which combines with the dirt and removes it
c)
Aluminum which coagulates the mud particles
d)
Making mud water soluble
|
|
Sakshi Bajaj answered |
Alum's Role in Purifying Water:
Alum plays a crucial role in purifying water by coagulating the mud particles present in the water. This process helps in removing impurities and making the water clearer and safer for consumption.
Coagulation Process:
- When alum is added to water, it reacts to form aluminum hydroxide [Al(OH)3].
- The aluminum hydroxide then combines with the mud particles, causing them to clump together and settle at the bottom of the container.
- This process is known as coagulation, where the suspended particles get trapped in the floc formed by alum.
Removal of Impurities:
- As the mud particles coagulate and settle down, they take along with them various impurities present in the water, such as dirt, bacteria, and other contaminants.
- This helps in effectively removing impurities from the water and making it clearer and cleaner.
Benefits of Alum in Water Purification:
- Alum is an effective and affordable way to purify water on a large scale.
- It helps in removing suspended particles, turbidity, and impurities from water, improving its quality.
- The coagulation process with alum also aids in the removal of pathogens, making the water safer for drinking and other uses.
In conclusion, alum's ability to coagulate mud particles and remove impurities from water makes it a valuable tool in the purification process, ensuring access to clean and safe water for various applications.
Alum plays a crucial role in purifying water by coagulating the mud particles present in the water. This process helps in removing impurities and making the water clearer and safer for consumption.
Coagulation Process:
- When alum is added to water, it reacts to form aluminum hydroxide [Al(OH)3].
- The aluminum hydroxide then combines with the mud particles, causing them to clump together and settle at the bottom of the container.
- This process is known as coagulation, where the suspended particles get trapped in the floc formed by alum.
Removal of Impurities:
- As the mud particles coagulate and settle down, they take along with them various impurities present in the water, such as dirt, bacteria, and other contaminants.
- This helps in effectively removing impurities from the water and making it clearer and cleaner.
Benefits of Alum in Water Purification:
- Alum is an effective and affordable way to purify water on a large scale.
- It helps in removing suspended particles, turbidity, and impurities from water, improving its quality.
- The coagulation process with alum also aids in the removal of pathogens, making the water safer for drinking and other uses.
In conclusion, alum's ability to coagulate mud particles and remove impurities from water makes it a valuable tool in the purification process, ensuring access to clean and safe water for various applications.
For the reaction, 2Cl(g) ⟶ Cl2(g), the correct option is :- a)∆rH > 0 and ∆rS < />
- b)∆rH < 0="" and="" />rS > 0
- c)∆rH < 0="" and="" />rS < />
- d)∆rH > 0 and ∆rS > 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For the reaction, 2Cl(g) ⟶ Cl2(g), the correct option is :
a)
∆rH > 0 and ∆rS < />
b)
∆rH < 0="" and="" />rS > 0
c)
∆rH < 0="" and="" />rS < />
d)
∆rH > 0 and ∆rS > 0
|
|
Sonal Menon answered |
Explanation:
The reaction given is 2Cl(g) ⟶ Cl2(g).
∆rH: The enthalpy change of the reaction is the difference between the enthalpies of the products and reactants. Here, the reaction involves the breaking of a bond in Cl2 molecule and the formation of two Cl atoms. This requires energy, so the enthalpy change will be positive.
∆rS: The entropy change of the reaction is the difference between the entropy of the products and reactants. In this reaction, the number of moles of gas decreases from 2 to 1, so the entropy change will be negative.
Option (c) is correct because both enthalpy and entropy changes are positive and negative respectively. The Gibbs energy change (∆rG) of the reaction can be calculated using the equation:
∆rG = ∆rH - T∆rS
where T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Since both ∆rH and ∆rS have opposite signs, the sign of the Gibbs energy change will depend on the temperature. At low temperatures, the reaction will be spontaneous as ∆rG will be negative. At high temperatures, the reaction will be non-spontaneous as ∆rG will be positive.
Therefore, option (c) is correct because it takes into account both enthalpy and entropy changes in the reaction.
The reaction given is 2Cl(g) ⟶ Cl2(g).
∆rH: The enthalpy change of the reaction is the difference between the enthalpies of the products and reactants. Here, the reaction involves the breaking of a bond in Cl2 molecule and the formation of two Cl atoms. This requires energy, so the enthalpy change will be positive.
∆rS: The entropy change of the reaction is the difference between the entropy of the products and reactants. In this reaction, the number of moles of gas decreases from 2 to 1, so the entropy change will be negative.
Option (c) is correct because both enthalpy and entropy changes are positive and negative respectively. The Gibbs energy change (∆rG) of the reaction can be calculated using the equation:
∆rG = ∆rH - T∆rS
where T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Since both ∆rH and ∆rS have opposite signs, the sign of the Gibbs energy change will depend on the temperature. At low temperatures, the reaction will be spontaneous as ∆rG will be negative. At high temperatures, the reaction will be non-spontaneous as ∆rG will be positive.
Therefore, option (c) is correct because it takes into account both enthalpy and entropy changes in the reaction.
What is correct about self-incompatibility?- a)It is due to the non-synchronization of pollen release and stigma receptivity.
- b)It is a genetic mechanism.
- c)It is seen only in unisexual flowers.
- d)It is due to the anther and stigma are placed at different positions.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What is correct about self-incompatibility?
a)
It is due to the non-synchronization of pollen release and stigma receptivity.
b)
It is a genetic mechanism.
c)
It is seen only in unisexual flowers.
d)
It is due to the anther and stigma are placed at different positions.
|
|
Dishani Chavan answered |
Genetic Mechanism of Self-Incompatibility
Self-incompatibility is a genetic mechanism that prevents self-fertilization in plants. It involves the recognition and rejection of self-pollen to promote outcrossing, which increases genetic diversity within a population.
Recognition of Self-Pollen
Plants have a genetic system that allows them to distinguish between self and non-self pollen. This recognition process occurs at the molecular level, where specific proteins on the pollen grain interact with proteins on the stigma of the same plant. If the proteins are too similar, the pollen is rejected.
Mechanism of Action
When self-pollen lands on the stigma of a plant that exhibits self-incompatibility, a series of biochemical reactions are triggered, leading to the inhibition of pollen tube growth. This prevents fertilization from occurring, ensuring that only compatible pollen can successfully fertilize the ovule.
Benefits of Self-Incompatibility
Self-incompatibility promotes genetic diversity within a plant population by encouraging outcrossing. This genetic diversity increases the chances of survival and adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Self-incompatibility is a vital genetic mechanism in plants that plays a crucial role in promoting outcrossing and maintaining genetic diversity. By preventing self-fertilization, plants ensure the health and adaptability of their populations over time.
Self-incompatibility is a genetic mechanism that prevents self-fertilization in plants. It involves the recognition and rejection of self-pollen to promote outcrossing, which increases genetic diversity within a population.
Recognition of Self-Pollen
Plants have a genetic system that allows them to distinguish between self and non-self pollen. This recognition process occurs at the molecular level, where specific proteins on the pollen grain interact with proteins on the stigma of the same plant. If the proteins are too similar, the pollen is rejected.
Mechanism of Action
When self-pollen lands on the stigma of a plant that exhibits self-incompatibility, a series of biochemical reactions are triggered, leading to the inhibition of pollen tube growth. This prevents fertilization from occurring, ensuring that only compatible pollen can successfully fertilize the ovule.
Benefits of Self-Incompatibility
Self-incompatibility promotes genetic diversity within a plant population by encouraging outcrossing. This genetic diversity increases the chances of survival and adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Self-incompatibility is a vital genetic mechanism in plants that plays a crucial role in promoting outcrossing and maintaining genetic diversity. By preventing self-fertilization, plants ensure the health and adaptability of their populations over time.
Identify the wrong statement with regard to Restriction Enzymes.
- a)They cut the strand of DNA at palindromic sites.
- b)They are useful in genetic engineering.
- c)Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence.
- d)Sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Identify the wrong statement with regard to Restriction Enzymes.
a)
They cut the strand of DNA at palindromic sites.
b)
They are useful in genetic engineering.
c)
Each restriction enzyme functions by inspecting the length of a DNA sequence.
d)
Sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases.
|
|
Aarav Shah answered |
Restriction Enzymes
- Restriction enzymes are enzymes that cut the strand of DNA at specific recognition sites.
- These enzymes are useful in genetic engineering for cutting DNA into fragments that can be manipulated and studied.
- Sticky ends are the name given to the single-stranded overhangs that are created when a restriction enzyme cuts DNA at a palindromic site.
- These sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases to create recombinant DNA molecules.
- Each restriction enzyme recognizes and cuts a specific DNA sequence, usually one that is palindromic, meaning it reads the same backwards as forwards.
- Therefore, the statement that is wrong is option 'C', which states that sticky ends cannot be joined by using DNA ligases. This is incorrect, as DNA ligases can join these ends together to create recombinant DNA molecules.
- Restriction enzymes are enzymes that cut the strand of DNA at specific recognition sites.
- These enzymes are useful in genetic engineering for cutting DNA into fragments that can be manipulated and studied.
- Sticky ends are the name given to the single-stranded overhangs that are created when a restriction enzyme cuts DNA at a palindromic site.
- These sticky ends can be joined by using DNA ligases to create recombinant DNA molecules.
- Each restriction enzyme recognizes and cuts a specific DNA sequence, usually one that is palindromic, meaning it reads the same backwards as forwards.
- Therefore, the statement that is wrong is option 'C', which states that sticky ends cannot be joined by using DNA ligases. This is incorrect, as DNA ligases can join these ends together to create recombinant DNA molecules.
Sound waves travel at 350 m/s through a warm air and at 3500 m/s through brass. The wavelength of a 700 Hz acoustic wave as it enters brass from warm air- a)decrease by a factor 10
- b)increase by a factor 20
- c)increase by a factor 10
- d)decrease by a factor 20
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Sound waves travel at 350 m/s through a warm air and at 3500 m/s through brass. The wavelength of a 700 Hz acoustic wave as it enters brass from warm air
a)
decrease by a factor 10
b)
increase by a factor 20
c)
increase by a factor 10
d)
decrease by a factor 20
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Here,
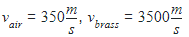
When a sound wave travels from one medium to another medium its frequency remains the same,∴ Frequency,υ = v/λ
Since υ remains the same in both the medium
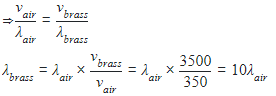
A unique vascular connection between the digestive tract and liver is called- a)Hepato-cystic system
- b)Hepato-pancreatic system
- c)Hepatic portal system
- d)Renal portal system
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A unique vascular connection between the digestive tract and liver is called
a)
Hepato-cystic system
b)
Hepato-pancreatic system
c)
Hepatic portal system
d)
Renal portal system
|
|
Janani Kaur answered |
Explanation:
The unique vascular connection between the digestive tract and liver is called the hepatic portal system.
Hepatic Portal System:
The hepatic portal system is a specialized part of the circulatory system that allows blood to flow from the digestive organs to the liver before returning to the heart. It is responsible for carrying nutrient-rich blood from the digestive tract to the liver for processing and detoxification.
Components of the Hepatic Portal System:
The hepatic portal system consists of the following components:
1. Hepatic Portal Vein: The hepatic portal vein is a large blood vessel that carries blood from the digestive organs, such as the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, to the liver. It collects blood rich in digested nutrients, toxins, and other substances absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
2. Liver Sinusoids: The hepatic portal vein branches out into smaller vessels called liver sinusoids. These sinusoids are a network of capillaries located within the liver. They allow the exchange of substances between the blood and liver cells.
3. Hepatic Veins: After passing through the liver sinusoids, the blood is collected by the hepatic veins. These veins carry the processed blood out of the liver and return it to the general circulation, ultimately reaching the heart.
Functions of the Hepatic Portal System:
The hepatic portal system performs several important functions, including:
1. Nutrient Processing: The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing and storing nutrients absorbed from the digestive tract. The hepatic portal system delivers these nutrients to the liver for processing and distribution to the rest of the body.
2. Detoxification: The liver filters and detoxifies substances absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, such as drugs, toxins, and metabolic waste products. The hepatic portal system allows these substances to be processed and eliminated efficiently.
3. Regulation of Blood Glucose Levels: The liver helps regulate blood glucose levels by storing excess glucose as glycogen or converting glycogen back into glucose when needed. The hepatic portal system ensures that the liver receives a constant supply of glucose from digested carbohydrates.
In conclusion, the hepatic portal system is a unique vascular connection between the digestive tract and liver that plays a crucial role in nutrient processing, detoxification, and regulation of blood glucose levels.
Calculate the energy in Joule corresponding to light of wave length 45nm (Planck's constant h = 6.63 × 10−34J s, speed of light, c = 3 × 108ms−1)- a)6.67 × 1015J
- b)6.67 × 1011J
- c)4.42 × 10−15J
- d)4.42 × 10−18J
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Calculate the energy in Joule corresponding to light of wave length 45nm (Planck's constant h = 6.63 × 10−34J s, speed of light, c = 3 × 108ms−1)
a)
6.67 × 1015J
b)
6.67 × 1011J
c)
4.42 × 10−15J
d)
4.42 × 10−18J
|
|
Anjali Sharma answered |
E = hc/λ [Given λ = 45nm = 45 × 10−9m]
On putting the given values in the equation, we get
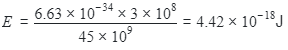
If Henle's loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which one of the following is to be expected?- a)There will be no urine formation
- b)There will be hardly any change in the quality of urine formation
- c)The urine will be more concentrated
- d)The urine will be more dilute
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
If Henle's loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which one of the following is to be expected?
a)
There will be no urine formation
b)
There will be hardly any change in the quality of urine formation
c)
The urine will be more concentrated
d)
The urine will be more dilute
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
In our nephron, the hairpin shaped Henle’s loop is the next part of the proximal convoluted tubule which has a descending and an ascending limb.
The main function of the Henle's loop is to absorb water from the tubular lumen, thus making the urine concentrated. If the loop of Henle becomes absent, then the urine becomes more dilute.
The descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water but almost impermeable to electrolytes, which is opposite to ascending limb. This concentrates the filtrate as it moves down. The ascending limb is impermeable to water but allows transport of electrolytes actively or passively.
The total mechanical energy of a spring-mass system in simple harmonic motion is E = 1/2mω2A2. Suppose the oscillating particle is replaced by another particle of double the mass while the amplitude A remains the same. The new mechanical energy will- a)become 2E
- b)become E/2
- c)become √2E
- d)remain E
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The total mechanical energy of a spring-mass system in simple harmonic motion is E = 1/2mω2A2. Suppose the oscillating particle is replaced by another particle of double the mass while the amplitude A remains the same. The new mechanical energy will
a)
become 2E
b)
become E/2
c)
become √2E
d)
remain E
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
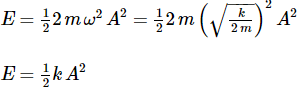
Total energy depends on k of spring and amplitude A. It is independent of mass.
Which of the following can replace zinc from ZnSO4 solution?- a)Copper
- b)Mercury
- c)Iron
- d)Aluminium
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following can replace zinc from ZnSO4 solution?
a)
Copper
b)
Mercury
c)
Iron
d)
Aluminium
|
|
Pankaj Singh answered |
Replacing Zinc from ZnSO4 Solution
Zinc in ZnSO4 solution can be replaced by other metals through a displacement reaction. Among the options provided, aluminum can replace zinc in ZnSO4 solution due to its higher reactivity.
Displacement Reaction
- Aluminum is more reactive than zinc, so it can displace zinc from its salt solution.
- The reaction can be represented as: 2Al(s) + 3ZnSO4(aq) -> 3Zn(s) + Al2(SO4)3(aq).
Explanation
- When aluminum is added to a solution of zinc sulfate, aluminum atoms donate electrons to zinc ions, forming zinc metal and aluminum sulfate.
- This displacement reaction occurs due to the reactivity series of metals, where more reactive metals displace less reactive metals from their compounds.
Why Other Options are Not Suitable
- Copper, mercury, and iron are less reactive than zinc in the reactivity series.
- Therefore, they cannot displace zinc from its sulfate solution.
In conclusion, aluminum is the suitable metal to replace zinc from ZnSO4 solution due to its higher reactivity.
One of the special characters of coelenterata only is the occurrence of- a)polymorphism
- b)flame cells
- c)hermaphroditism
- d)nematocysts
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the special characters of coelenterata only is the occurrence of
a)
polymorphism
b)
flame cells
c)
hermaphroditism
d)
nematocysts
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
The cells characteristic of the coelenterates include stinging cells (cnidocytes or cnidoblasts or nematoblasts) for offence and defence. The stinging cells, when discharged, give out from a sac, the cnide or cnidocyst or nematocyst, a long thread-tube that may coil around the prey, or attach to it, or inject a toxin, called hypnotoxin, into it to paralyse it.

How many factors shift the oxygen dissociation curve to the right shift?1. Low partial pressure of oxygen.2. High concentration of carbon dioxide.3. High number of hydrogen ions.4. Low body temperature.5. Daily exercise.6. Haemoglobin of babies or fetal haemoglobin.- a)6
- b)5
- c)4
- d)3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How many factors shift the oxygen dissociation curve to the right shift?
1. Low partial pressure of oxygen.
2. High concentration of carbon dioxide.
3. High number of hydrogen ions.
4. Low body temperature.
5. Daily exercise.
6. Haemoglobin of babies or fetal haemoglobin.
a)
6
b)
5
c)
4
d)
3
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Each haemoglobin molecule can carry a maximum of four molecules of O2. Binding of oxygen with haemoglobin is primarily related to partial pressure of O2. Partial pressure of CO2, hydrogen ion concentration and temperature are the other factors which can interfere with this binding. A sigmoid curve is obtained when percentage saturation of haemoglobin with O2 is plotted against the pO2. This curve is called the Oxygen dissociation curve and is highly useful in studying the effect of factors like pCO2, H+ concentration, etc., on binding of O2 with haemoglobin. In the alveoli, where there is high pO2, low pCO2, lesser H+ concentration and lower temperature, the factors are all favourable for the formation of oxyhaemoglobin, whereas in the tissues, where low pO2, high pCO2, high H+ concentration and higher temperature exist, the conditions are favourable for dissociation of oxygen from the oxyhaemoglobin.
A shift of the curve to the right indicates decreased affinity of the haemoglobin for oxygen and hence an increased tendency to give up oxygen to the tissues. A shift to the left indicates increased affinity and so an increased tendency for haemoglobin to take up and retain oxygen.
The effect of this rightward shift of the curve increases the partial pressure of oxygen in the tissues when it is most needed, such as during exercise, or hemorrhagic shock. In contrast, the curve is shifted to the left by the opposite of these conditions.
In which of the following forms is iron absorbed by plants?- a)Ferric
- b)Ferrous
- c)Both ferric and ferrous
- d)Free element
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following forms is iron absorbed by plants?
a)
Ferric
b)
Ferrous
c)
Both ferric and ferrous
d)
Free element
|
|
Ritu Singh answered |
Iron is absorbed by plants in the form of ferric ions.
Plants uptake iron in its oxidized forms, Fe2+ (ferrous form) or Fe3+ (ferric form). Another mechanism involves the release of protons (H+) and reductants by the plant roots, to lower pH levels in root zone. Iron is considered a micro-nutrient because only small amounts are required to aid in normal plant growth. Plants can suffer iron deficiency with symptoms of chlorosis and stunted growth, but plants can also take in too much iron, especially under certain growing conditions.
Two nonallelic genes produces the new phenotype when present together but fail to do so independently then it is called
- a)complementary gene.
- b)polygene
- c)non complementary gene
- d)epistasis
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Two nonallelic genes produces the new phenotype when present together but fail to do so independently then it is called
a)
complementary gene.
b)
polygene
c)
non complementary gene
d)
epistasis
|
|
Ajay Yadav answered |
Epistasis is the phenomenon of suppression of phenotypic expression of gene by a non-allelic gene which shows its own effect The gene which masks the effect of another is called epistatic gene while the one which is suppressed is termed hypostatic gene. Epistasis is of three types - dominant, recessive and dominant-recessive.
Carbonic anhydrase occurs in- a)Lymphocytes
- b)Blood plasma
- c)Leucocytes
- d)Leucocytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Carbonic anhydrase occurs in
a)
Lymphocytes
b)
Blood plasma
c)
Leucocytes
d)
Leucocytes
|
|
Nilesh Choudhury answered |
Carbonic Anhydrase in Leucocytes:
Leucocytes, also known as white blood cells, are a crucial part of the immune system and play a significant role in fighting off infections and diseases. Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide, which is essential for various physiological processes in the body.
Function of Carbonic Anhydrase:
Carbonic anhydrase is responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance in the body by catalyzing the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid, which then dissociates into bicarbonate ions and protons. This process is essential for regulating pH levels in tissues and organs.
Presence in Leucocytes:
Studies have shown that carbonic anhydrase is present in leucocytes, specifically in the cytoplasm of these white blood cells. The enzyme plays a crucial role in various functions of leucocytes, including cell adhesion, migration, and phagocytosis. Carbonic anhydrase helps leucocytes to maintain their pH balance, which is essential for their proper functioning in the immune response.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, carbonic anhydrase occurs in leucocytes, specifically in the cytoplasm of white blood cells. The enzyme plays a vital role in maintaining the pH balance of leucocytes and is essential for their proper functioning in the immune system.
Leucocytes, also known as white blood cells, are a crucial part of the immune system and play a significant role in fighting off infections and diseases. Carbonic anhydrase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide, which is essential for various physiological processes in the body.
Function of Carbonic Anhydrase:
Carbonic anhydrase is responsible for maintaining the acid-base balance in the body by catalyzing the conversion of carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid, which then dissociates into bicarbonate ions and protons. This process is essential for regulating pH levels in tissues and organs.
Presence in Leucocytes:
Studies have shown that carbonic anhydrase is present in leucocytes, specifically in the cytoplasm of these white blood cells. The enzyme plays a crucial role in various functions of leucocytes, including cell adhesion, migration, and phagocytosis. Carbonic anhydrase helps leucocytes to maintain their pH balance, which is essential for their proper functioning in the immune response.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, carbonic anhydrase occurs in leucocytes, specifically in the cytoplasm of white blood cells. The enzyme plays a vital role in maintaining the pH balance of leucocytes and is essential for their proper functioning in the immune system.
Chapter doubts & questions for NEET Minor Mock Test - NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of NEET Minor Mock Test - NEET Mock Test Series - Updated 2026 Pattern in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









