All Exams >
Class 10 >
Science Class 10 >
All Questions
All questions of The Human Eye and the Colourful World for Class 10 Exam
We use __________ lens to correct Hypermetropia- a)Biconvex
- b)Biconcave
- c)Concave
- d)Convex
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
We use __________ lens to correct Hypermetropia
a)
Biconvex
b)
Biconcave
c)
Concave
d)
Convex
|
|
Anjali Kapoor answered |
Concave lenses are used here. They spread the light out before it reaches the convex lens in the eye, therefore letting the image focus directly on the retina. Hyperopia is known to you probably as farsightedness.
The image formed on the retina of the human eye is- a)virtual and inverted
- b)real and inverted
- c)real and erect
- d)virtual and erect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The image formed on the retina of the human eye is
a)
virtual and inverted
b)
real and inverted
c)
real and erect
d)
virtual and erect
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Eye lens is convex, in nature. So, image formed by it on the retina is real and inverted.
Stars twinkle due to- a)atmospheric refraction
- b)atmospheric reflection
- c)scattering of light
- d)dispersion of light
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Stars twinkle due to
a)
atmospheric refraction
b)
atmospheric reflection
c)
scattering of light
d)
dispersion of light

|
Deepika Shah answered |
The twinkling of a star is due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight, on entering the earth’s atmosphere, undergoes refraction continuously before it reaches the earth. The atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually changing refractive index. Since the atmosphere bends starlight towards the normal, the apparent position of the star is slightly different from its actual position.
The near point of a human eye is at a distance of- a)10 cm
- b)20 cm
- c)40 cm
- d)25 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The near point of a human eye is at a distance of
a)
10 cm
b)
20 cm
c)
40 cm
d)
25 cm
|
|
Abhi Prajapati answered |
The near point of the eye is the minimum distance of the object from the eye, which can be seen distinctly without strain. For a normal human eye, this distance is 25 cm. The far point of the eye is the maximum distance to which the eye can see the objects clearly. The far point of the normal human eye is infinity.
The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the red light- a)is scattered the most by smoke or fog
- b)is scattered the least by smoke or fog
- c)is absorbed the most by smoke or fog
- d)moves fastest in air
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour. These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the red light
a)
is scattered the most by smoke or fog
b)
is scattered the least by smoke or fog
c)
is absorbed the most by smoke or fog
d)
moves fastest in air
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Red colour has longer wavelength so least scattered by smoke or fog.
A student sitting on last bench in a classroom cannot see clearly words written on the blackboard. He is suffering from- a)long sightedness
- b)short sightedness
- c)astigmatism
- d)long sightedness as well as short sightedness
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A student sitting on last bench in a classroom cannot see clearly words written on the blackboard. He is suffering from
a)
long sightedness
b)
short sightedness
c)
astigmatism
d)
long sightedness as well as short sightedness
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
A student, who cannot read words written on blackboard from the last bench of his class room, is suffering from the myopia or short-sightedness defect of vision of eye.
Cataract can be cured by- a)Bi-focal Lens
- b)Convex Lens
- c)Surgery
- d)Concave lens
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Cataract can be cured by
a)
Bi-focal Lens
b)
Convex Lens
c)
Surgery
d)
Concave lens
|
|
Rohan Kapoor answered |
Surgery to treat cataracts involves removing the clouded lens and replacing it with a synthetic new one. This procedure is safe and very effective.They're researching eye drops that may dissolve cataracts so patients don't have to go to surgery.
Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the formation of a rainbow ?- a)Reflection, refraction and dispersion
- b)Refraction, dispersion and scattering
- c)Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
- d)Dispersion, scattering and refraction
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the formation of a rainbow ?
a)
Reflection, refraction and dispersion
b)
Refraction, dispersion and scattering
c)
Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
d)
Dispersion, scattering and refraction
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Phenomena of refraction, dispersion and internal reflection are involved in the formation of rainbow.
When a beam of white light passes through a glass prism, it splits up into seven colours. This phenomenon is due to- a)refraction of light
- b)dispersion of light
- c)diffraction of light
- d)absorption of light
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When a beam of white light passes through a glass prism, it splits up into seven colours. This phenomenon is due to
a)
refraction of light
b)
dispersion of light
c)
diffraction of light
d)
absorption of light
|
|
Kajal verma answered |
Splitting of white light into its constituent seven colours, while passing through a prism, is on account of dispersion of fight.
On a clear day, the sky appears to be more blue towards the zenith (overhead) than it does toward the horizon. This occurs because:- a)the atmosphere is denser higher up than it is at the earth’s surface.
- b)the temperature of the upper atmosphere is higher than it is at the earth’s surface.
- c)the sunlight travels over a longer path at the horizon, resulting in more absorption.
- d)none of the above is true.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
On a clear day, the sky appears to be more blue towards the zenith (overhead) than it does toward the horizon. This occurs because:
a)
the atmosphere is denser higher up than it is at the earth’s surface.
b)
the temperature of the upper atmosphere is higher than it is at the earth’s surface.
c)
the sunlight travels over a longer path at the horizon, resulting in more absorption.
d)
none of the above is true.
|
|
Aditya Shah answered |
Because when the light of sun travel a long distance it meets with large amount of particles present in atmosphere. When they crush with small particles they got scattered due to which the blue color which have shorter wavelength, scatters most by which the sky seems blue.
A boy is wearing glasses and says that he cannot see the object kept at a distance without glasses. He is suffering from- a)Hypermetropia
- b)Cataract
- c)Presbyopia
- d)Myopia
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A boy is wearing glasses and says that he cannot see the object kept at a distance without glasses. He is suffering from
a)
Hypermetropia
b)
Cataract
c)
Presbyopia
d)
Myopia
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
As Myopia is a defect of vision in which a person cannot see the distant object clearly. This can be corrected by using the concave lens of appropriate focal length
The colour which deviates most in the formation of spectrum of white light by a prism is- a)Green
- b)Yellow
- c)Red
- d)Violet
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The colour which deviates most in the formation of spectrum of white light by a prism is
a)
Green
b)
Yellow
c)
Red
d)
Violet
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
When white light falls on a glass prism, each colour in it is refracted by a different angle, from which red colour is least deviated and violet most.
When light rays from stars enter into earth’s atmosphere, it travels from
- a)denser to rarer medium
- b)rarer medium to vacuum
- c)rarer to denser medium
- d)denser medium to vacuum
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
When light rays from stars enter into earth’s atmosphere, it travels from
a)
denser to rarer medium
b)
rarer medium to vacuum
c)
rarer to denser medium
d)
denser medium to vacuum
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Light travels from rarer to denser medium when it enters into earth's atmosphere
A person with defective eyesight is unable to see objects clearly nearer than 1.5 m. He wants to read a book placed at a distance of 30 cm from his eyes. The type of a required lens and its focal length is- a)Concave lens, f = 37.5 cm
- b)Convex lens, f = 30.5 cm
- c)Convex lens, f = 37.5 cm
- d)Concave lens, f = 30.5 cm
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A person with defective eyesight is unable to see objects clearly nearer than 1.5 m. He wants to read a book placed at a distance of 30 cm from his eyes. The type of a required lens and its focal length is
a)
Concave lens, f = 37.5 cm
b)
Convex lens, f = 30.5 cm
c)
Convex lens, f = 37.5 cm
d)
Concave lens, f = 30.5 cm
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
This person suffers from the defect of hypermetropia.
For him u = -30cm, v = -1.5 m = -150cm
Therefore, focal length of corrective lens to be used by him is
1/f = 1/v- 1/u = 1/-150 - 1/-30 = 4/150 = 37.5cm
The positive sign shows that the lens needed is a convex lens of focal length 37.5 cm.
Hence, power of lens needed
P =1/f = 100/37.5 = 2.67D
The clear sky appears blue because- a)blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere
- b)ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere
- c)violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere
- d)light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet and blue colour lights by the atmosphere
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The clear sky appears blue because
a)
blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere
b)
ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere
c)
violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere
d)
light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet and blue colour lights by the atmosphere
|
|
Kuldeep Kuldeep answered |
As the Sun is made up of all the colours, Sun scatters the colour having a shorter wavelength. Rather than other colours Violet and Blue having the shorter wavelength. So the Violet and Blue colour lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours by the atmosphere. So, option c is correct friend...
The air layer of atmosphere whose temperature is less than the hot layer behave as optically
- a)denser medium
- b)rarer medium
- c)inactive medium
- d)either denser or rarer medium
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The air layer of atmosphere whose temperature is less than the hot layer behave as optically
a)
denser medium
b)
rarer medium
c)
inactive medium
d)
either denser or rarer medium
|
|
Anita Menon answered |
The cold air layer of the atmosphere acts as a optically denser medium than hot air because the molecules are closely packed together.
When white light enters a prism, it gets split into its constituent colours. This is due to- a)different refractive index for different wavelength of each colour
- b)each colours has same velocity in the prism
- c)prism material have high density
- d)Scattering of light
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When white light enters a prism, it gets split into its constituent colours. This is due to
a)
different refractive index for different wavelength of each colour
b)
each colours has same velocity in the prism
c)
prism material have high density
d)
Scattering of light
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Dispersion takes place because refractive index of the material of prisra is different for different wavelength.
A prism splits a beam of white light into seven colours because different colours have different __________________ .
- a)Speed in prism
- b)phase in prism
- c)Amplitude in prism
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A prism splits a beam of white light into seven colours because different colours have different __________________ .
a)
Speed in prism
b)
phase in prism
c)
Amplitude in prism
d)
None of these
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
The phenomena due to which white light splits Into seven colours on passing through a prism is called dispersion. Upon passing through a medium, each of the colors travels at different speeds and hence has different angles of refraction leading to the splitting of the light.
What happens when white light is passed from air to glass prism?- a)Reflects back
- b)Bends towards normal
- c)Passes undeviated
- d)Bends away from normal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens when white light is passed from air to glass prism?
a)
Reflects back
b)
Bends towards normal
c)
Passes undeviated
d)
Bends away from normal

|
Harshu answered |
Light bends towards the normal as the light is passing from a rarer medium to denser medium.
Why does Sun appear slightly oval shaped at morning and evening ?- a)The rays of light from upper edge of the sun have to pass maximum thickness.
- b)Due to unequal bending of light.
- c)The rays of light from the lower edges of Sun are refracted more.
- d)All the above.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Why does Sun appear slightly oval shaped at morning and evening ?
a)
The rays of light from upper edge of the sun have to pass maximum thickness.
b)
Due to unequal bending of light.
c)
The rays of light from the lower edges of Sun are refracted more.
d)
All the above.
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The light rays pass through greater thickness of air because of which the light rays from the lower side of the sun are retracted more than those from the upper side. Because of unequal light bending, the sun looks oval and larger.
One cannot see through fog because :- a)light suffers total internal reflection at the droplets of fog.
- b)light is scattered by the droplets of fog.
- c)the refractive index of fog is infinity.
- d)fog absorbs light.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
One cannot see through fog because :
a)
light suffers total internal reflection at the droplets of fog.
b)
light is scattered by the droplets of fog.
c)
the refractive index of fog is infinity.
d)
fog absorbs light.
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
light is scattered by droplets.
This happens inherently because fog is composed of water or ice crystals that remain near the surface of the earth.
It can also be known as low-lying cloud which gets influenced by topography, water bodies and wind conditions of a place.
If the image was formed in front of the retina rather than behind the retina, then the person would need to correct the vision problem by using a:- a)converging lens
- b)diverging lens
- c)polar lens
- d)achromatic lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If the image was formed in front of the retina rather than behind the retina, then the person would need to correct the vision problem by using a:
a)
converging lens
b)
diverging lens
c)
polar lens
d)
achromatic lens
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Nearsighted individuals have image formed in front of the retina. They must correct the problem by wearing a lens which provides for some diverging of light prior to reaching the lens of the eye. This will move the image further from the lens of the eye and back towards the retina.
The cold air layers of the atmosphere behave as optically- a)Either inactive or rarer medium
- b)Denser medium
- c)Rarer medium
- d)Inactive medium
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The cold air layers of the atmosphere behave as optically
a)
Either inactive or rarer medium
b)
Denser medium
c)
Rarer medium
d)
Inactive medium
|
|
Nisha Choudhury answered |
Due to this change in speed light bends and travels when passing from one medium to other medium. When the light ray passes from rarer medium to denser medium it bends towards the normal.
Example: Light ray passing from air to glass (Air rarer medium, Glass - denser medium.
Example: Light ray passing from air to glass (Air rarer medium, Glass - denser medium.
What will be the colour of sky if there is no atmosphere on the earth?- a)Dark blue
- b)Black
- c)Red
- d)White
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What will be the colour of sky if there is no atmosphere on the earth?
a)
Dark blue
b)
Black
c)
Red
d)
White

|
Malavika Basu answered |
Raleigh Scattering of light by the atmosphere is what causes "the sky" to appear blue (and sunsets to appear red), but that "sky" is a colour of the atmosphere. If there is no atmosphere, what colour is it?
Without the atmosphere there is nothing local to act as a (secondary) source of light, so there is no light and we conventionally call objects that emit (little or) no light "black". So the non-object that is "the sky" could be called "black".
If we consider all light from "the heavens" to be the colour of "the sky" then it is clearly not "black". Even with the atmosphere and nasty light pollution from cities, the Milky Way appears rather off-white. With an even grander view of the Universe, we are told it's overall shade is Cosmic Latte, but I would take that with a pinch of salt or, perhaps, a tint of grey when it comes to human perception.
My preferred word for the apparent colour of "the sky" would be transparent rather than "black", but a pedant could argue that "transparent" is not a colour...
Which light is easily scattered ?- a)Long wavelength light
- b)Short wavelength light
- c)Sunlight
- d)Coherent light
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which light is easily scattered ?
a)
Long wavelength light
b)
Short wavelength light
c)
Sunlight
d)
Coherent light
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
The light having short wavelength can be scattered easily. For example, blue light shorter wavelength so it is scattered more easily.
The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?- a)diverging lens of power +1.25 D
- b)converging lens of power +1.25 D
- c)diverging lens of power -1.25 D
- d)converging lens of power -1.25 D
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The far point of a myopic person is 80 cm in front of the eye. What is the nature and power of the lens required to correct the problem?
a)
diverging lens of power +1.25 D
b)
converging lens of power +1.25 D
c)
diverging lens of power -1.25 D
d)
converging lens of power -1.25 D
|
|
Anjana Khatri answered |
Far point of the defective eye, v = -80 cm
Object distance, u = -∞ (-infinity)
To find :
Nature and power of the corrective lens.
Solution :
1/v - 1/u = 1/f
1/f = 1/(-80) - 1/(-∞)
1/f = - 1/80 + 0 [Since, 1/-∞ = 0]
1/f = - 1/80
f = -80 cm
Therefore, the corrective lens should be of the focal length 80 cm.
Power, P = 1 / focal length
As focal length is in centimetres, 1 m = 100 cm.
P = 100 / -80
P = -1.25 D
Therefore, the corrective lens is diverging or concave lens of power -1.5 D.
Image is formed for the shortsighted person:- a)Eye lens
- b)Before retina
- c)At retina
- d)Behind retina
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Image is formed for the shortsighted person:
a)
Eye lens
b)
Before retina
c)
At retina
d)
Behind retina

|
Naina Kaur answered |
Short-sightedness (myopia) usually occurs when the eyes grow slightly too long, which means they're unable to produce a clear image of objects in the distance.
When the light is very bright- a)the iris makes the pupil expand
- b)the iris makes the pupil contract
- c)ciliary muscles contract to make the eyelens thicker
- d)ciliary muscles expand to make the eyelens thinner
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When the light is very bright
a)
the iris makes the pupil expand
b)
the iris makes the pupil contract
c)
ciliary muscles contract to make the eyelens thicker
d)
ciliary muscles expand to make the eyelens thinner
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
When the light is very bright the iris makes the pupil contract so as to control the quantity of light entering the eye.
When white light passes through a glass prism- a)red coloured ray undergoes maximum deviation
- b)green coloured ray undergoes minimum deviation
- c)blue coloured ray undergoes minimum deviation
- d)violet coloured ray undergoes maximum deviation
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
When white light passes through a glass prism
a)
red coloured ray undergoes maximum deviation
b)
green coloured ray undergoes minimum deviation
c)
blue coloured ray undergoes minimum deviation
d)
violet coloured ray undergoes maximum deviation
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
When white light passes through a glass prism, the violet coloured ray undergoes maximum deviation. The red coloured ray undergoes minimum deviation.
A person has near point of his vision shifted to 50 cm. What lens must be used to see an object placed at 25 cm from the eye? What is the power of the lens?- a)A diverging lens of focal length 50 cm and power – 2 D
- b)A converging lens of focal length 50 cm and power + 2 D
- c)A converging lens of focal lens 50 cm and power – 2 D
- d)A diverging lens of focal length 50 cm and power + 2 D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person has near point of his vision shifted to 50 cm. What lens must be used to see an object placed at 25 cm from the eye? What is the power of the lens?
a)
A diverging lens of focal length 50 cm and power – 2 D
b)
A converging lens of focal length 50 cm and power + 2 D
c)
A converging lens of focal lens 50 cm and power – 2 D
d)
A diverging lens of focal length 50 cm and power + 2 D

|
Coachify answered |
When object is placed at 25 cm, then a virtual image should form at 50 cm.
So, u = -25 cm, v= -50 cm.
So, 1/f = 1/-50 - 1/-25
f = 50 cm = 0.5 m
Power, P = 1/f = 1/0.5 = +2D
Therefore , a convex lens is needed.
So, u = -25 cm, v= -50 cm.
So, 1/f = 1/-50 - 1/-25
f = 50 cm = 0.5 m
Power, P = 1/f = 1/0.5 = +2D
Therefore , a convex lens is needed.
A normal eye is not able to see objects closer than 25 cm because:- a)the focal length of the eye is 25 cm.
- b)the distance of the retina from the eye-lens is 25 cm.
- c)the eye is not able to decrease the distance between the eye-lens and the retina beyond limit.
- d)the eye is not able to decrease the focal length beyond a limit.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A normal eye is not able to see objects closer than 25 cm because:
a)
the focal length of the eye is 25 cm.
b)
the distance of the retina from the eye-lens is 25 cm.
c)
the eye is not able to decrease the distance between the eye-lens and the retina beyond limit.
d)
the eye is not able to decrease the focal length beyond a limit.

|
Sumit Singh answered |
The eye is not able to decrease the focal length beyond a limit
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles- a)are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
- b)contract and lens becomes thicker
- c)are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
- d)contract and lens becomes thinner
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
a)
are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
b)
contract and lens becomes thicker
c)
are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
d)
contract and lens becomes thinner
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Cilliary muscles modify the curvature of eye lens. When eye muscles are relaxed, eye lens becomes thinner thereby are relaxed, eye lens becomes thinner thereby increase in the focal length of eye lens.
When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the- a)crystalline lens
- b)outer surface of the cornea
- c)iris
- d)pupil
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
a)
crystalline lens
b)
outer surface of the cornea
c)
iris
d)
pupil

|
Harshad Majumdar answered |
When the light rays enters the eye through a thin membrane, forms the transparent bulge on the front surface of the eyeball, called the cornea. Most of the refraction for the light rays entering the eye occurs at this outer surface of the cornea.
The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particles is called- a)Dispersion of light
- b)Tyndall effect
- c)Atmospheric scattering
- d)Atmospheric refraction
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particles is called
a)
Dispersion of light
b)
Tyndall effect
c)
Atmospheric scattering
d)
Atmospheric refraction
|
|
Rahul Kapoor answered |
The phenomenon of scattering of light by the colloidal particles is called Tyndall effect. Due to this phenomenon the light rays are visible when light passes through a hole in a room or in a dense forest through the trees.
To an observer on Earth the stars appear to twinkle. This is due to- a)the fact that stars do not emit light continuously.
- b)frequent absorption of star light by earth’s atmosphere.
- c)the fluctuation of physical conditions in the earth’s atmosphere.
- d)frequent absorption of star light by their own atmosphere.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
To an observer on Earth the stars appear to twinkle. This is due to
a)
the fact that stars do not emit light continuously.
b)
frequent absorption of star light by earth’s atmosphere.
c)
the fluctuation of physical conditions in the earth’s atmosphere.
d)
frequent absorption of star light by their own atmosphere.
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
To an observer on Earth the stars appear to twinkle. This is due to the fluctuation of physical conditions in the earth’s atmosphere. Each single stream of starlight is refracted and is caused to change direction. This is because the light which passes the different layers of atmosphere differ in temperature and density. This causes the light from the star to twinkle when seen from the ground.
If a person with hypermetropia struggles to see objects placed closer than 50 cm, what is the power of the lens needed to correct this vision?- a)+2 D
- b)-2 D
- c)+1 D
- d)-1 D
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
a)
+2 D
b)
-2 D
c)
+1 D
d)
-1 D

|
Upsc Toppers answered |
For hypermetropia where the near point is significantly further than normal, a convex lens with a positive power, such as +2 D, is required to converge light rays correctly on the retina.
A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power- a)+ 0.5 D
- b)- 0.5 D
- c)+ 0.2 D
- d)- 0.2 D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be corrected by using a lens of power
a)
+ 0.5 D
b)
- 0.5 D
c)
+ 0.2 D
d)
- 0.2 D
|
|
Supriya dubey answered |
Person cannot see distant objects clearly. So he is suffering from myopia. The defect is corrected by using concave lens of power
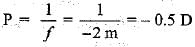
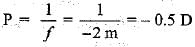
The danger signals are red in colour because it is- a)strongly scattered by fog or smoke
- b)least scattered by fog or smoke
- c)least absorbed by fog or smoke.
- d)strongly absorbed by fog or smoke
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The danger signals are red in colour because it is
a)
strongly scattered by fog or smoke
b)
least scattered by fog or smoke
c)
least absorbed by fog or smoke.
d)
strongly absorbed by fog or smoke
|
|
Amit Kumar answered |
The danger signals are red because among all other colours, red colour is scattered the least by smoke or fog. This is primarily because wavelength of red colour is the largest.
How much time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened because of atmospheric refraction?- a)4 hours
- b)2 minutes
- c)4 minutes
- d)2 hours
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
How much time from sunrise to sunset is lengthened because of atmospheric refraction?
a)
4 hours
b)
2 minutes
c)
4 minutes
d)
2 hours
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
We can see the sun 2 minutes before the actual sunrise and 2 minutes after the actual sunset due to atmospheric refraction. So, the total time lengthened is 2 + 2 = 4 minutes.
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his textbook. Which of the following statements is correct ?- a)The near point of his eyes has receded away
- b)The near point of his eyes has come closer to him
- c)The far point of his eyes has come closer to him
- d)The far point of his eyes has receded away
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his textbook. Which of the following statements is correct ?
a)
The near point of his eyes has receded away
b)
The near point of his eyes has come closer to him
c)
The far point of his eyes has come closer to him
d)
The far point of his eyes has receded away
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
A student sitting on the last bench of class can read the letters written on the blackboard. It means his farsight is normal. However, he cannot read the letters written in his textbook distinctly. It means he is suffering from long-sightedness (hypermetropia) and the near point of his eye has receded away
The range of vision of a normal human eye is from
- a)100 m to 25 cm
- b)infinity to 25 m
- c)1 km to 25 cm
- d)25 cm to infinity
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The range of vision of a normal human eye is from
a)
100 m to 25 cm
b)
infinity to 25 m
c)
1 km to 25 cm
d)
25 cm to infinity
|
|
Priyanshi Sharma answered |
Because the far point of the eye is infinity one explation can be that we can see sun and moon standing on earth .this distance is much much more than focal length of our eye therefore it is considered to be infinity. we know that crystalline lens in our eyes have a power to accommodate focal length but it can't reduce focal length below 25 cm therefore the near point of our eye is 25 cm
The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to- a)the presence of algae and other plants found in water
- b)reflection of sky in water
- c)scattering of light
- d)absorption of light by the sea
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
a)
the presence of algae and other plants found in water
b)
reflection of sky in water
c)
scattering of light
d)
absorption of light by the sea
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The fine water molecules mainly scatter blue light due to its shorter wavelength.
The deflection of light by minute particles and molecules of the atmosphere in all direction is called___________of light.- a)dispersion
- b)scattering
- c)interference
- d)tyndell effect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The deflection of light by minute particles and molecules of the atmosphere in all direction is called___________of light.
a)
dispersion
b)
scattering
c)
interference
d)
tyndell effect
|
|
Meha nambiar answered |
The said phenomenon is called scattering of light.
Which colour is strongly scattered by the molecules of air and other fine particles?- a)Green
- b)Red
- c)Red and Blue both
- d)Blue
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which colour is strongly scattered by the molecules of air and other fine particles?
a)
Green
b)
Red
c)
Red and Blue both
d)
Blue
|
|
Amit Sharma answered |
Sunlight reaches Earth's atmosphere and is scattered in all directions by all the gases and particles in the air. Blue light is scattered in all directions by the tiny molecules of air in Earth's atmosphere. Blue travels as shorter, smaller waves. So as shorter the wavelength, stronger will be the light scattered. Hence, blue light is strongly scattered.
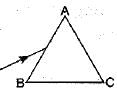
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in figure. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?- a)
- b)
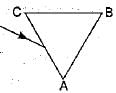
- c)
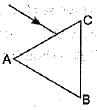
- d)
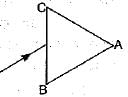
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in figure. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
In figure (a) base BC of the prism is at the bottom, then violet colour lies at the bottom but in figure (b), the base BC is at the top, then violet would be at the top after dispersion, and third colour would be blue.
By how much time is the sunset delayed due to atmospheric refraction ?- a)2 minutes
- b)5 minutes
- c)20 minutes
- d)2 hours
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
By how much time is the sunset delayed due to atmospheric refraction ?
a)
2 minutes
b)
5 minutes
c)
20 minutes
d)
2 hours

|
Anushka Chopra answered |
Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset : The sunrise is advanced due to atmospheric refraction of sunlight. An observer on the earth sees the sun two minutes before the sun reaches the horizon. A ray of sunlight entering the earth's atmosphere follows a curved path due to atmosphere refraction before reaching the earth.
The sun can be seen before the actual sunrise by about- a)2 minutes
- b)4 minutes
- c)20 minutes
- d)1 minute
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The sun can be seen before the actual sunrise by about
a)
2 minutes
b)
4 minutes
c)
20 minutes
d)
1 minute

|
Prasad Chavan answered |
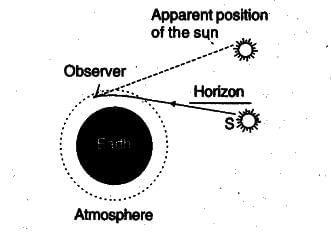
The Sun is visible to us about 2 minutes before the actual sunrise, and about 2 minutes after the actual sunset because of atmospheric refraction. By actual sunrise, we mean the actual crossing of the horizon by the Sun. Fig. shows the actual and apparent positions of the Sun with respect to the horizon. The time difference between actual sunset and the apparent sunset is about 2 minutes. The apparent flattening of the Sun’s disc at sunrise and sunset is also due to the same phenomenon.

Chapter doubts & questions for The Human Eye and the Colourful World - Science Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of The Human Eye and the Colourful World - Science Class 10 in English & Hindi are available as part of Class 10 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup












