All Exams >
MCAT >
Biochemistry for MCAT >
All Questions
All questions of Chromosomal Inheritance for MCAT Exam
Sickle-cell anemia is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder whose carriers have a genetic advantage in surviving malaria. If 42% of the population is malaria resistant, but not anemic, what is frequency of the sickle-cell allele?- a)49%
- b)9%
- c)21%
- d)30%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Sickle-cell anemia is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder whose carriers have a genetic advantage in surviving malaria. If 42% of the population is malaria resistant, but not anemic, what is frequency of the sickle-cell allele?
a)
49%
b)
9%
c)
21%
d)
30%

|
Orion Classes answered |
To determine the frequency of the sickle-cell allele, we can use the Hardy-Weinberg equation:
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
where:
p2 represents the frequency of individuals homozygous for the normal allele (not carrying the sickle-cell allele)
2pq represents the frequency of individuals heterozygous (carriers of the sickle-cell allele)
q2 represents the frequency of individuals homozygous for the sickle-cell allele
p2 represents the frequency of individuals homozygous for the normal allele (not carrying the sickle-cell allele)
2pq represents the frequency of individuals heterozygous (carriers of the sickle-cell allele)
q2 represents the frequency of individuals homozygous for the sickle-cell allele
Given that 42% of the population is malaria resistant but not anemic, which corresponds to the frequency of individuals homozygous for the normal allele (p2), we can calculate the frequency of the normal allele (p) using the square root:
p = √(0.42) ≈ 0.648
Since the sickle-cell allele is recessive, q = 1 - p:
q = 1 - 0.648 ≈ 0.352
The frequency of the sickle-cell allele is equal to 2pq:
2pq = 2(0.648)(0.352) ≈ 0.456
Therefore, the frequency of the sickle-cell allele is approximately 45.6%, which is closest to option D, 30%.
A gene, TALL, has recently been discovered that helps control the height that people will reach and results in taller than average height. Which of the following statements about this gene’s heritability are true?- a)If TALL has constant expressivity, every cell in the body will express the TALL protein
- b)If TALL has variable expressivity, everyone with the TALL gene will be tall
- c)If TALL has 50% penetrance, then only half the population has the TALL gene
- d)If TALL has 25% penetrance, it must be autosomal recessive
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A gene, TALL, has recently been discovered that helps control the height that people will reach and results in taller than average height. Which of the following statements about this gene’s heritability are true?
a)
If TALL has constant expressivity, every cell in the body will express the TALL protein
b)
If TALL has variable expressivity, everyone with the TALL gene will be tall
c)
If TALL has 50% penetrance, then only half the population has the TALL gene
d)
If TALL has 25% penetrance, it must be autosomal recessive

|
Orion Classes answered |
Variable expressivity refers to the phenomenon where individuals with the same genotype (in this case, carrying the TALL gene) can exhibit different phenotypes (in this case, different heights). It means that even though someone carries the TALL gene, other factors such as environmental influences or interactions with other genes can result in a range of heights among individuals.
Therefore, having the TALL gene does not guarantee that an individual will be tall, as the expression of the gene can vary and result in different heights.
A color-blind man marries a woman with no family history of color-blindness. What is the likelihood that they have a color-blind daughter?- a)0%
- b)25%
- c)50%
- d)100%
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A color-blind man marries a woman with no family history of color-blindness. What is the likelihood that they have a color-blind daughter?
a)
0%
b)
25%
c)
50%
d)
100%

|
Orion Classes answered |
The correct answer is A. 0%. Color blindness is a sex-linked recessive trait that is carried on the X chromosome. In this scenario, since the man is color-blind, he must have the recessive allele for color blindness (XcY) on his X chromosome. The woman, with no family history of color-blindness, is most likely homozygous for the dominant allele (XCXC) on her X chromosome.
When they have children, all the daughters will receive one X chromosome from the father (Xc) and one X chromosome from the mother (XC). Since the mother's X chromosome does not carry the color-blind allele, none of the daughters will be color-blind. The sons, on the other hand, have a 50% chance of inheriting the X chromosome with the color-blind allele from the father and being color-blind themselves.
The results of a linkage analysis of genes A, B, C, and D have just come in from the lab. In what order are the alleles found on the chromosome?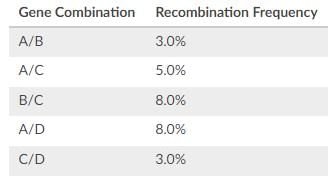
- a)ABCD
- b)DCAB
- c)CDAB
- d)ACDB
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The results of a linkage analysis of genes A, B, C, and D have just come in from the lab. In what order are the alleles found on the chromosome?

a)
ABCD
b)
DCAB
c)
CDAB
d)
ACDB

|
Orion Classes answered |
Based on the given recombination frequencies, we can determine the order of the alleles on the chromosome. The pairs with the lowest recombination frequencies are likely to be the closest together on the chromosome. Let's analyze the given recombination frequencies:
A/B: 3.0%
A/C: 5.0%
B/C: 8.0%
A/D: 8.0%
C/D: 3.0%
A/C: 5.0%
B/C: 8.0%
A/D: 8.0%
C/D: 3.0%
From these frequencies, we can conclude that the A and B alleles have the lowest recombination frequency, indicating that they are closest together. Similarly, the C and D alleles also have the lowest recombination frequency, suggesting that they are also closely linked.
Now let's consider the order of the alleles. Since A and B are closest together, they should be adjacent to each other on the chromosome. Similarly, C and D should be adjacent to each other.
Based on this information, the most likely order of the alleles on the chromosome is:
B - A - C - D
Therefore, option B (DCAB) is the most accurate representation of the order of alleles on the chromosome.
A researcher was doing test crosses on mice, but forgot which mice he had bred together. When the litter was born, every mouse had black eyes, and half had brown fur. What was the genotype of the parent mice?
R = red fur; r = brown fur
B = black eyes; b = brown eyes- a)RrBb x rrBB
- b)RrBB x Rrbb
- c)rrBb x RRBB
- d)RrBb x RrBb
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A researcher was doing test crosses on mice, but forgot which mice he had bred together. When the litter was born, every mouse had black eyes, and half had brown fur. What was the genotype of the parent mice?
R = red fur; r = brown fur
B = black eyes; b = brown eyes
R = red fur; r = brown fur
B = black eyes; b = brown eyes
a)
RrBb x rrBB
b)
RrBB x Rrbb
c)
rrBb x RRBB
d)
RrBb x RrBb

|
Orion Classes answered |
To determine the genotype of the parent mice, we can use the observed phenotypes of the offspring.
Given that all the offspring have black eyes, we can infer that the parent mice must have at least one dominant allele for eye color, which is B. This rules out options C and D.
Half of the offspring also have brown fur, which suggests that the parent mice must be heterozygous for fur color. This means that they must have one dominant allele (R) and one recessive allele (r) for fur color.
Considering these observations, the most likely genotype of the parent mice is:
RrBb x rrBB
Therefore, option A is the most probable genotype of the parent mice based on the given information.
Which of the following statements about synaptonemal complexes is not true?- a)They form between sister chromatids
- b)They are made up of functional RNA and protein
- c)They form during synapsis
- d)They act as a support structure
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements about synaptonemal complexes is not true?
a)
They form between sister chromatids
b)
They are made up of functional RNA and protein
c)
They form during synapsis
d)
They act as a support structure

|
Orion Classes answered |
Synaptonemal complexes are primarily composed of proteins and not functional RNA. The proteins in the synaptonemal complex play a crucial role in facilitating the pairing and alignment of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. RNA molecules are involved in other cellular processes but are not a major component of synaptonemal complexes.
A set of homologous chromosomes undergoes genetic recombination to create the following results: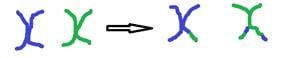 Q. Which of the following is the mostly likely recombination event?
Q. Which of the following is the mostly likely recombination event?- a)2 strand single crossover
- b)2 strand triple crossover
- c)3 strand single crossover
- d)
3 strand double crossover
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A set of homologous chromosomes undergoes genetic recombination to create the following results:

Q. Which of the following is the mostly likely recombination event?
a)
2 strand single crossover
b)
2 strand triple crossover
c)
3 strand single crossover
d)
3 strand double crossover

|
Orion Classes answered |
A single, double, or triple crossover refers to the number of crossover events.
Only two strands are involved in a crossover at a time.
As we can see in the figure, at least 3 strands are involved in the crossover events, meaning that most likely a 3 strand double crossover event took place.
Only two strands are involved in a crossover at a time.
As we can see in the figure, at least 3 strands are involved in the crossover events, meaning that most likely a 3 strand double crossover event took place.
Which of the following population’s coat/fur/feather color gene is most likely to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?- a)A pack of wolves in a zoo
- b)A flock of moths that must blend in with their environment to survive
- c)Lab rats being bred by scientists
- d)A flock of seagulls that feeds on one type of fish
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following population’s coat/fur/feather color gene is most likely to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium?
a)
A pack of wolves in a zoo
b)
A flock of moths that must blend in with their environment to survive
c)
Lab rats being bred by scientists
d)
A flock of seagulls that feeds on one type of fish

|
Orion Classes answered |
"A flock of seagulls that feeds on one type of fish," is the most likely population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, certain conditions must be met, including random mating, no migration, no mutations, no natural selection, and a large population size. In the given scenario, the flock of seagulls that feeds on one type of fish is more likely to meet these conditions.
When a population feeds on a single type of fish, it reduces the potential for genetic variations due to different food sources. This can contribute to a more stable gene pool and reduce the likelihood of natural selection affecting the coat/fur/feather color gene frequencies. As long as the population meets the other conditions of the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, such as random mating and no migration or mutations, the coat/fur/feather color gene in the seagull population is more likely to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
What of the following provides the best evidence that DNA is the genetic material?- a)Biomolecular composition of chromosomes
- b)Transformation using heat-inactivated bacteria
- c)Presence of DNA in all cells
- d)Mechanism of semi-conservative DNA replication
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
What of the following provides the best evidence that DNA is the genetic material?
a)
Biomolecular composition of chromosomes
b)
Transformation using heat-inactivated bacteria
c)
Presence of DNA in all cells
d)
Mechanism of semi-conservative DNA replication

|
Orion Classes answered |
The experiment conducted by Avery, MacLeod, and McCarty in 1944 demonstrated that when heat-inactivated bacteria containing DNA were mixed with live bacteria of a different strain, the live bacteria were transformed and acquired the genetic traits of the heat-inactivated bacteria. This transformation only occurred when DNA was present, indicating that DNA carries the genetic information.
This experiment provided strong evidence that DNA, rather than proteins or other molecules, is the genetic material responsible for transmitting hereditary information from one generation to the next. It showed that the genetic traits could be transferred through the transfer of DNA, supporting the idea that DNA is the carrier of genetic information.
Many people have DNA mutations that go unnoticed. What type of mutation is most likely to have no effect on phenotype?- a)Missense
- b)Deletion
- c)Frameshift
- d)Chromosomal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Many people have DNA mutations that go unnoticed. What type of mutation is most likely to have no effect on phenotype?
a)
Missense
b)
Deletion
c)
Frameshift
d)
Chromosomal

|
Orion Classes answered |
A missense mutation is a type of DNA mutation that results in a change in a single nucleotide, leading to the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein sequence. In some cases, this change may not significantly affect the structure or function of the protein. The resulting protein may still be able to carry out its normal role in the cell, and therefore, the mutation may have no noticeable effect on the phenotype of the individual.
It's important to note that the impact of a missense mutation on phenotype can vary depending on the specific mutation, the location of the amino acid change within the protein, and the function of the protein itself. In some cases, a missense mutation may lead to a mild or subtle change in phenotype, while in other cases, it may have more severe consequences. However, compared to other types of mutations such as deletions, frameshift mutations, or chromosomal abnormalities, missense mutations are generally more likely to have no effect on the phenotype.
Chapter doubts & questions for Chromosomal Inheritance - Biochemistry for MCAT 2025 is part of MCAT exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for MCAT 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chromosomal Inheritance - Biochemistry for MCAT in English & Hindi are available as part of MCAT exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Biochemistry for MCAT
138 videos|21 docs|26 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up within 7 days!
Access 1000+ FREE Docs, Videos and Tests
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup









